A healthy bladder does not cause any unpleasant symptoms in humans. But if there is a feeling of a full bladder, this is a sign of serious pathologies of the urinary system. Such sensations interfere with the normal flow of a person’s life, because they can be accompanied by more unpleasant manifestations, such as incontinence or acute pain. Therefore, it is important to know what the feeling of a full bladder indicates.
The feeling of bladder discomfort, such as false filling, should not be left without due attention.
The process of urination
The human bladder is capable of holding 300 ml of urine for 5 hours. The walls of the organ are covered with receptors, from which signals are sent to the center, which is responsible for urination. It is located in the sacral region of the spinal cord. This area controls bladder activity through stimulation through parasympathetic nerve fibers. Under the influence of signals from the nerves, the walls gradually tense up, and the sphincters of the organ, on the contrary, relax, this is how the bladder is emptied, that is, at this moment urine comes out of the bladder.
Common causes of residual urine
There can be many reasons for this condition:
p, blockquote 5,0,1,0,0 —>
- Benign hyperplastic changes in the tissues of the prostate gland, in other words, prostate adenoma;
- Neurogenic bladder;
- Urolithiasis, especially when the stones are localized in the bladder cavity;
- Urethritis or inflammation of the urethra, narrowing or stricture of the urethra and other pathologies leading to difficulty passing urine through the urethra;
- Cystitis of any origin and form;
- Tumor processes in the bladder of a malignant or benign nature such as polyps, cancer, leukoplakia, etc.;
- Innervation disorders of the pelvic organs;
- Pathologies of the pelvic organs of an inflammatory nature, which are characterized by the presence of side effects such as bladder irritation.
In general, various types of urinary outflow difficulties and neurogenic functional disorders lead to such a pathological condition. Since residual urine is regarded by specialists only as a pathological symptom, in the absence of therapeutic measures, such a phenomenon can provoke the development of many complications such as renal failure, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, vesicoureteral reflux, etc. Therefore, the causes of incomplete urination should be identified in time and eliminated, then dangerous complications can be avoided.
p, blockquote 6,0,0,0,0 —>
Adenoma is to blame
Benign prostatic hyperplastic processes are usually found in men over 45 and are manifested not only by impaired urinary outflow, but also by complete urinary stagnation. Pathology is the uncontrolled growth of the gland, caused by age-related changes in tissue with the formation of nodes, growths or compactions, etc. Gradually, the formed formation increases in size, however, metastasis is not observed, because hyperplasia is benign in nature.
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 —>
The main provoking factor, according to experts, is age, which increases the likelihood of adenoma. When overgrown tissues compress the urination channel, the patient begins to worry about the first manifestations of the disease - difficulty urinating and a feeling of incomplete emptying when relieving himself.
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
In addition, the patient complains of longer urination, frequent urges (especially at night), a thin and sluggish stream with interruptions towards the end of the urination process. When the pathology is neglected, painful sensations appear in the lower abdomen, drip urination, painful ejaculation, difficulty holding urine when urinating, etc.
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
Neurogenic bladder
Often the cause of residual urine is a neurogenic bladder - these are urinary disorders caused by disorders in the nervous system, which is responsible for urinary functions. The causes of a neurogenic bladder can be spinal lesions (hernia or vertebral pathologies, etc.), brain pathologies (stroke, hemorrhage or tumor processes, Parkinson's syndrome, etc.), HIV, peripheral nervous system lesions (for example, diabetes or intoxication, etc.) .
p, blockquote 10,0,0,0,0 —>
Symptoms of a neurogenic (hyperactive) bladder usually include:
p, blockquote 11,1,0,0,0 —>
- Frequent urge;
- Incontinence;
- Night urges;
- Urine leakage;
- Feeling of incomplete emptying, etc.
Typically, the phenomenon of residual urine indicates the presence of spinal lesions in the area just above the sacrum. As a result, the urethral sphincter becomes tense, making urinary flow significantly more difficult. Treatment of a neurogenic bladder is based on a set of measures such as taking medications that correct nervous system activity, physiotherapeutic sessions, forced urination using tension in the abdominal muscle tissue, physical therapy exercises, and surgical actions.
p, blockquote 12,0,0,0,0 —>
Urolithiasis disease
One of the common causes of residual urine is cystolithiasis (or the formation of stones in the bladder), which is found much more often in men. Such a pathology can develop for a number of internal or external reasons. Internal causes are caused by chronic infectious foci, metabolic pathologies such as gout, traumatic factors or heredity. External factors that provoke cystolithiasis include poor diet, physical inactivity, occupational hazards, or drinking regimen.
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>
Among the most characteristic manifestations of urolithiasis, pain in the half of the abdomen below the navel, radiating to the groin, perineum, or penis and scrotum, is especially noticeable. During the process of urination, a sudden interruption of the stream may occur, after which the release of urine stops, however, the man feels that the emptying of the bladder has not yet been completed. In other words, there is a pronounced residual urine syndrome. If a man changes his body position, urination may suddenly resume.
p, blockquote 14,0,0,0,0 —>
Treatment is based on the elimination of stones, for which the patient can be prescribed stone-dissolving drugs that break down stones into small particles, which are then naturally excreted along with urine. The technique of lithotripsy or stone crushing is also popular. It is necessary to adhere to a specific diet, drinking regimen, rest and sanatorium treatment.
Reasons why you feel like your bladder is full
As noted above, the bladder can normally hold 300 ml of urine. If such an amount accumulates in it, a person has a feeling of a full bladder, as the pressure on the walls increases. At the same time, you will really want to relieve yourself. But there are a number of factors that interfere with the normal excretion of urine, and, accordingly, cause discomfort in the bladder:
- diseases associated with inflammatory processes in the tissues of the urinary system: cystitis, urethritis;
- diseases associated with inflammatory processes of neighboring organs that spread to the bladder (there may not be urine in it, but it feels like this is not the case): pyelonephritis, enterocolitis, pelvioperitonitis, inflammation of the appendix;
- prostatitis and prostate adenoma (in this condition it puts pressure on the urethra);
- diseases of the genitourinary system in women: adnexitis, fibroids, endometritis, ovarian tumors;
- urolithiasis, due to which the walls of the bladder are affected - the presence of stones does not allow it to completely empty;
- neoplasms of any nature;
- problems with the spinal cord: multiple sclerosis, radiculitis, spina bifida;
- congenital impaired conduction of the nerves of the bladder, causing increased urinary function;
- excessive reduction in the lumen of the urethra;
- decreased contractile function of the walls and muscles of the bladder, which makes it impossible to fully contract it during urination;
- problems with stool, constipation, during which an overcrowded intestine puts unnecessary pressure on the bladder.
Gynecological diseases
Painful sensations in the anus and itching after defecation are symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. When hypothermia or pathogenic bacteria penetrate the ovaries, inflammation occurs. Because of this, pain and other unpleasant symptoms are noted.
Treatment of such diseases is carried out with medication. The basis of therapy is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. NSAIDs relieve pain. Antibiotics prevent reproduction and thus destroy harmful microbes. The duration of therapy and dosage of drugs is determined only by the attending physician.
Feelings of incomplete emptying of the bladder and associated symptoms
Attention to uncomfortable symptoms when urinating is the key to timely treatment of emerging diseases.
The feeling of a full bladder after urinating is complemented by other unpleasant sensations:
- constant pain that intensifies when palpating the abdomen, active movements, or lifting something heavy;
- attacks of acute pain in the lumbar region, characteristic of urolithiasis;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the lower abdomen;
- pain during the emission of urine;
- elevated temperature, fever;
- changed composition of urine;
- involuntary frequent urination or trouble urinating;
- the appearance of blood in urine.
Violation of personal hygiene rules
Insufficient anal hygiene can lead to unpleasant symptoms. When washing the anus, you must use a special product for the intimate area. This soap contains various antiseptics that kill pathogenic microbes that cause itching and burning after defecation.
In addition, too frequent washing is also dangerous for the intestines. Constant friction can damage soft tissue and cause irritation. To prevent this from happening, you must not abuse hygiene.
Possible complications due to incomplete emptying
When the bladder is not completely emptied, stagnation of urine forms in its cavity. Very often this residue provokes a constant pressing sensation and the feeling that the bladder is full. In addition, the development of bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms that affect the bladder and urethra begins in stagnant urine. This means that cystitis occurs as a result. If the inflammation rises along the urinary tract and reaches the kidneys, the person will also develop pyelonephritis. No matter what sensations a person has, it is important to seek medical help in a timely manner, otherwise there is a chance of starting an already progressive disease.
Urethritis
This disease can be infectious or non-infectious in nature, so it should be given special attention. In the first case, the disease is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that enter the urethra. In the second, the cause is non-infectious factors: narrowing and neoplasms in the urethra, urolithiasis, allergic reactions, etc.
Urethritis occurs in both sexes with equal frequency, but in men it is more often complicated. This occurs due to the structural features of the urethra: the male urethra is much longer than the female urethra, so the infection lingers here and causes inflammation.
Symptoms of an acute condition:
- urination is accompanied by itching and other unpleasant sensations;
- hematuria;
- purulent discharge;
- feeling of sticking of the external opening of the urethra;
- disturbance of urine outflow.
In the chronic form of the disease, symptoms periodically appear and then subside.
What are the characteristic signs to use to diagnose the disease?
Since a large number of diseases can provoke a feeling as if the organ is full, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis before prescribing treatment. When making a diagnosis, not only the patient’s symptoms are taken into account, but also diseases of any nature that he had previously suffered from, gender and age. According to statistics, women are more often susceptible to diseases of the genitourinary system.
Inflammation of the urinary system
With the development of the inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system, the most common diseases are cystitis and urethritis. If you do not pay attention to the felt filling of the bladder and other manifestations, the disease will develop into pyelonephritis. Most often it is women who get sick due to physiological characteristics. Characteristic manifestations of the inflammatory process: In men, sensations of incomplete emptying may occur due to problems with the prostate
outward and there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The main signs indicating prostatitis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- a weak, intermittent stream when a man relieves himself;
- involuntary leakage of a certain amount of urine.
Also, swelling and similar symptoms are characteristic of the development of impotence. If the patient has prostate adenoma, in addition to the previously listed signs, weight loss and prolonged elevated temperature will be added. In addition to prostate tumors, neoplasms can also occur in other organs of the genitourinary system. The appearance of blood in urine is a signal of the onset of bladder cancer.
The process of urine excretion for each person is purely individual. Some people visit the restroom five times a day, while others go to the toilet after every cup of liquid they drink. Normally, it is believed that if a person visits the toilet no more than 10-12 times a day, then his urinary system functions normally. A change in this frequency may indicate progression of the pathology. Also, patients often complain that after urination there is a feeling that they want more. The causes of this condition can be both pathological and physiological.
This suggests that you should not immediately panic and run to the doctor. But if such a feeling occurs systematically, then this is a serious reason to consult a urologist.
This specific sensation can occur in people of different age categories. It is worth noting that the pathology is more often diagnosed in the fair sex. This is due, for the most part, to the structural features of their urinary system. The urethra in women is much shorter than in men, so various pathogenic microorganisms can easily penetrate it and provoke the progression of the inflammatory process (this reason is one of the main reasons that provoke the feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder).
Urethritis and its varieties
The inflammatory process in the urethra, expressed by pain, burning during urination, false urges and copious discharge, is urethritis. It can manifest itself in an acute form, occurring abruptly and causing severe discomfort. Most often, its occurrence is caused by microorganisms such as gonococcus and Trichomonas. Sometimes the cause of inflammation is injury or some kind of chemical irritant.
Treatment of acute urethritis requires anti-inflammatory therapy with antibiotics, sulfonamides, warm baths, and drinking plenty of fluids.
Candidal urethritis occurs as a result of yeast-like fungi entering the body and damaging the urethra. Treatment is carried out with etiotropic and pathogenetic drugs (Levorin, Nystatin, Fluconazole).
Neglected treatment, causing even greater complications, in most cases leads to chronic urethritis. It is characterized by pain in the urethra, in the groin, and frequent urge to empty the bladder, which often turns out to be false. In some cases, urinary incontinence may occur, for example, when sneezing or straining. Treatment of chronic urethritis begins, first of all, with determining the root cause of the inflammatory process to eliminate the source of endemic disease. After that, only an experienced doctor selects the appropriate antibiotics and necessary chemotherapy.
In medicine, there are such concepts as primary and secondary urethritis. Primary is a disruption of the normal course of the life process in the body when exposed to pathogenic factors in the urethra. And secondary urethritis occurs as a result of complications due to the presence of other diseases in the body. This could be urolithiasis, prostatitis, diabetes and others.
There are some other types of urethritis:
- Granular. It got its name because of the formations in the form of granules in the proximal urethra. Treatment is carried out by shading the urethral mucosa using a solution of silver nitrate. Another treatment option is electrocoagulation. This disease is prone to periodic relapses, so the body needs regular medical examinations.
- Senile. Occurs in women during menopause. The symptoms are similar to chronic urethritis. In this case, necrosis of the vaginal mucosa occurs, an inflammatory process occurs, and sometimes bleeding appears. Treatment is selected individually in the form of various vaginal suppositories and chemotherapy drugs.
- Allergic. May be caused by medications or food. Swelling, tightness and itching appear in the urethra. It can be eliminated with the help of bougienage (insertion of thin tubes into the urethra - bougies) or electrocoagulation. To eliminate an allergic reaction, antiallergic drugs (Tavegil, Suprastin) are often prescribed.
- Premenstrual. May occur before the start of the menstrual cycle. It goes away in a few days.
- Post-traumatic. It is an inflammation of the urethra due to injury.
Etiological factors
If after urination you want to pee more, then this is an alarming sign, which usually signals disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the urinary system. The following pathological conditions can provoke the occurrence of this sensation in a person:
- . The presence of formed conglomerates of various sizes in the bladder significantly reduces the volume of this organ. All this leads to the fact that a person, after visiting the restroom, wants to pee again. Simultaneously with this symptom, a picture of this particular illness appears - pain in the lumbar region, the presence of pathological impurities in the urine, and hyperthermia may also be noted;
- Diabetes. Diabetics often experience this symptom;
- Cystitis. If after urination you want more, then in most cases it is cystitis that causes such an unpleasant sensation. With this infectious process, not only the urethral mucosa is affected, but also the bladder mucosa, which leads to disruption of its functioning. Therefore, a person has a regular urge to evacuate, after which there is an uncomfortable feeling that he has not emptied completely;
- Often the cause of the feeling that you want to urinate again is progressive renal failure. This is due to the fact that the patient experiences a constant feeling of thirst and consumes a lot of fluid. Accordingly, a fairly large volume of urine is excreted naturally. Due to the irritation of the bladder, there is a feeling of incomplete emptying (I want to write more);
- In men, such a discomfort may occur due to damage to the prostate;
- Various sexually transmitted infections can also provoke the feeling that after passing urine you want to visit the toilet again. This group includes gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.
Physiological factors:
- period of bearing a child. At this time, the bladder is under pressure from the ever-expanding uterus. Therefore, pregnant women often have the feeling that after emptying their bladder they want to visit the toilet again;
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- consuming too much liquid per day (the norm is no more than 2.2 liters).
Video
: Signs of prostatitis
Chlamydia in men: routes of infection and treatment
Have you been trying to cure PROSTATITIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Chlamydia is an infectious disease diagnosed in both men and women. The most common cause of its occurrence is sexual contact with an infected partner.
- Causes
- Classification of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic measures
- Treatment methods for chlamydia
- Possible complications
- Prevention
- Conclusion
Before treatment for this disease, a man must be diagnosed by a urologist. In the future, antibacterial drugs and accompanying agents are prescribed to eliminate the pathology.
Causes
The main reasons contributing to the occurrence of chlamydia:
- sexual intercourse with an infected partner;
- household contact - the use of common hygiene items, food, infection through the seat of the toilet, bathhouse and sauna - the likelihood of infection with chlamydia in men and women is significantly lower than during intimate intimacy;
- vertical method - infection of a child during childbirth from the mother.
Important: the incubation period of the disease is several weeks, after which the first symptoms of chlamydia appear in a man.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology:
- a large number of sexual partners;
- refusal to use barrier contraceptives;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene, including intimate hygiene;
- decreased immunity;
- past infectious or viral diseases.
With a high level of immunity, the likelihood of a man becoming infected with chlamydia is significantly reduced. The risk of any infectious diseases increases against the background of a weakened state of the body.
Classification of the disease
Chlamydia is divided into several types. Depending on the time of infection:
- primary – the first manifestations of the disease, often occurs in an acute form;
- chronic – repeated and subsequent occurrence of symptoms of the disease.
By localization of infection:
- infection of the lower parts of the urethra – urethritis;
- infection of organs in the pelvis, inflammatory processes in the scrotum or prostate gland - an ascending type of chlamydia;
- damage to the anorectal area;
- infection of the mucous membrane of the eyes, joints - chlamydial pharyngitis.
According to the severity of chlamydia:
- acute – a vivid manifestation of symptoms with a deterioration in general well-being;
- subacute – rapid development of signs of the disease, but less intense than in the acute form;
- chronic – periodic manifestation of pathological symptoms that practically do not bother the man;
- chlamydia carriage – complete absence of signs of the disease, infection detected only during laboratory tests.
Fact: most men do not pay attention to the manifestation of chronic chlamydia, the symptoms of which can disappear within a few days - this can lead to a more widespread spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
Symptoms
After the incubation period, the first symptoms of the disease appear. Often chlamydia is not accompanied by any characteristic signs, especially if the infected person has a high level of immunity.
The first signs of chlamydia in men:
- pain and stinging of varying intensity when urinating;
- discharge from the head of the penis with an unpleasant odor;
- swelling of the scrotum;
- itching of the head of the penis;
- cloudiness of urine, the appearance of pus in it.
In the acute form of the disease or with the further development of other forms of chlamydia, a man experiences the following signs of infection:
- increased pain when urinating;
- pain in the scrotum, lower back;
- an increase in the amount of discharge from the head of the penis in a man, which, with the progression of chlamydia, can acquire a yellowish tint;
- increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees;
- increased fatigue, weakness;
- impurities of pus and blood in the urine.
Important: the symptoms of chlamydia in men are similar to other sexually transmitted infectious diseases - they can only be distinguished through diagnosis.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
Diagnostic measures
To identify an infectious infection, a comprehensive study is required. It is necessary to conduct several types of tests for chlamydia to determine the localization of the infection in a man, the degree of its spread, type, and the presence of possible accompanying pathogenic microorganisms. Treatment is prescribed strictly based on research results.
Types of diagnostics for identifying chlamydia in men:
- cytological smear from the urethra - determination of the state of the local microflora, the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and their activity, leukocytes, the presence of which signals an inflammatory process;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – examination of biomaterial for the presence of a pathogen; this type of analysis is highly accurate;
- enzyme immunoassay blood test - detecting the presence of antibodies to infection, allows you to differentiate the primary lesion from chronic pathology;
- immunofluorescence method - examination of a smear for the presence of chlamydia using a microscope, based on a specific immunological reaction;
- bacterial culture of urine or semen - identifying the presence of a pathogen in the body.
Important: the sexual partner of a man who has been diagnosed with chlamydia should be diagnosed for the presence of infections in the body, followed by treatment.
All research results may turn out to be false if you have sexual intercourse less than 2-3 days before the study, or if you take antibacterial drugs on your own. In the latter case, diagnosis should be carried out no earlier than 2 weeks after the last dose of the medicine.
Treatment methods for chlamydia
Antibiotics are considered the main type of drugs needed to eliminate chlamydia in men. They are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora to the individual components of the drug, the location of the infection and possible side effects and contraindications.
Drugs for the treatment of chlamydia in men:
- Antibiotics. The most effective are tetracyclines, macrolides and fluoroquinolines. To eliminate chlamydia in men, Azithromycin, Zithromax, Spiramycin, Ciprofloxacin are prescribed. Some antibiotics are additionally used in the form of gels and creams, which must be used to treat the head of the penis.
- Immunostimulants. Strengthen the immune system, speed up the healing process - Amiksin, Cycloferon, Polyoxidonium.
- Enzymatic. They increase the effectiveness of antibiotics and speed up the process of eliminating infection - Wobenzym, Flogenzyme.
- Antiseptics. Used to treat the mucous surfaces of the genital organs, reduce itching and burning - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
- Vitamins. Participate in restoring the body's defenses - ascorbic and glutamic acids, Alphabet for men, Complivit.
- Probiotics. They are used after the end of treatment with antibacterial drugs, they are necessary to restore the local microflora - Bifiform, Lactobacterin, Linex.
Important: a man is allowed to resume sexual activity only after a complete course of treatment for chlamydia and a diagnosed recovery.
After completion of therapy, a re-examination is necessary in a few weeks. This is required to confirm the elimination of the disease. If it is detected again, the man is prescribed a new treatment regimen for chlamydia, consisting of more powerful antibacterial drugs.
To relieve symptoms, it is allowed to use some traditional methods of therapy. To do this, a man at home can make special herbal baths that treat chlamydia - decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and yarrow are suitable for this purpose. If it is impossible to use this method, herbal decoctions and infusions are used to regularly treat the surface of the glans penis.
Possible complications
Complications most often develop in the absence of treatment for chlamydia or in the incorrect selection of medications. In both cases, the acute manifestation of the disease often contributes to the development of its chronic form, which is much more difficult to treat.
Possible consequences of chlamydia in men:
- urethritis - an inflammatory process in the urethra, accompanied by difficulty urinating, pain and purulent discharge;
- acute or chronic pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys, considered one of the most dangerous complications;
- narrowing of the urethra as a result of a long-term inflammatory process, eliminated surgically;
- chronic prostatitis is a disease of the prostate gland, characterized by narrowing of its ducts, deterioration of sperm quality, disruption of the urination process, weakening of erection;
- Reiter's syndrome - a combination of urethritis, arthritis and conjunctivitis;
- vesiculitis – a disease of the seminal vesicles, accompanied by impaired potency, general weakness, and increased body temperature;
- cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder, often a consequence of urethritis and a harbinger of pyelonephritis.
Fact: The likelihood of complications increases with repeated infection with chlamydia.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of an infectious disease, it is necessary to follow some recommendations from specialists:
- regular visits to the urologist;
- refusal of promiscuity;
- use of barrier methods of contraception;
- careful personal hygiene - washing hands before eating, daily hygiene of the genitals;
- refusal to use other people's personal household items - towels, spoons, etc.;
- caution when visiting baths and saunas - do not go to unverified establishments or sit on dirty surfaces;
- getting tested for infections once a year prevents the latent form of the disease.
Conclusion
Chlamydia in men is a disease that requires immediate treatment. Otherwise, it can become chronic, which is difficult to treat. To prevent pathology, personal hygiene should be carefully observed and barrier methods of contraception should be used.
- Causes of pain when urinating in women
- Cystitis
- Urethritis
- Urolithiasis disease
- Pyelonephritis
- Candidiasis
- Vaginitis
- Urogenital tuberculosis
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- After childbirth
- Which doctor should I contact?
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
Pain when urinating in women indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. The symptom is nonspecific, so to make an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to analyze your health status and conduct examinations.
Causes of pain when urinating in women
Painful urination in women can be associated with both pathologies of the bladder and kidney damage. Sometimes a burning sensation occurs after surgery, such as a caesarean section. There are several reasons for pain during and after urination.
Cystitis
Inflammation of the mucous membranes is caused by the presence of infection, reduced immunity or hypothermia. Urine is released frequently, but in small portions, sometimes with blood. Pain worries women during bowel movements or only at the end of urination; a pulling sensation appears in the lower abdomen at rest. The course of the disease is accompanied by incontinence and nausea. The urine becomes cloudy and has an unpleasant odor. If cystitis becomes chronic, there may be no pain.
Urethritis
Pathology of the genitourinary system develops due to hypothermia, immune deficiency, infectious infection and mechanical damage, including loss of virginity. Symptoms of urethritis include frequent and painful urination, itching, burning and irritation of the external genitalia. Manifestations intensify during menstruation.
Urolithiasis disease
Unpleasant sensations during urolithiasis are caused by the passage of stones through the ducts. There may be partial or complete blockage of the pathways, which makes it difficult to remove urine. The movement of stones and sand causes acute pain less often in women than in men due to the width of the ducts. With pathology, vomiting and a change in urine color from yellow-red to dark brown also occur.
Pyelonephritis
An acute infectious lesion that most often appears against the background of other bacterial pathologies. The causative agent of kidney disease first enters the vagina and then rises through the urethra, bladder and ureters. With pyelonephritis, blood and pus are found in the discharge, the temperature rises, and the urine acquires an unpleasant odor. Pain is felt not only during bowel movements, but also at rest in the kidney area.
Candidiasis
A fungal disease in which a cheesy secretion is released from the vagina. The first symptom is frequent painful urges. After sexual intercourse, discomfort occurs. A woman constantly feels burning and itching in the external genitalia.
Vaginitis
Vaginitis occurs due to disruption of the natural microflora, mechanical damage, hormonal fluctuations and unprotected sexual intercourse. Common symptoms include: irritation, itching, a feeling of fullness, pain during sex and when urinating, unusual discharge and slight bleeding on contact.
Urogenital tuberculosis
Most often, genital tuberculosis is a secondary lesion. Infectious agents enter the genitourinary system from the intestines or lungs. The main symptom of the pathology is infertility associated with damage to the fallopian tubes and endometrium. There is severe pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies with urination. The menstrual cycle is disrupted. The woman suffers either from incontinence or difficulty in bowel movements.
Sexually transmitted diseases
The most common pathologies that can appear after sex are syphilis, herpes, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis and trichomoniasis.
Each disease has specific symptoms, but common symptoms include burning and pain at the beginning or end of urination, and frequent urge.
After childbirth
When a child passes through the birth canal, the bladder, nerve endings and mucous membranes are compressed and injured. As a result, the woman does not feel when it is necessary to have a bowel movement, and feels pain in the process. Normally, the discomfort goes away after 3 days.
Pain after cesarean section is normal. It disappears after 1 week, but sometimes the recovery process takes a month. Doctor intervention is only required if the temperature remains at 37.5°C or higher, discomfort persists for a long period of time, or abnormal discharge occurs.
Diagnosis of the causes of painful urination in women
The results of ultrasound, smears for sexually transmitted infections and urine and blood tests are of decisive importance in identifying a disease that causes nagging pain.
Ultrasound is most informative for nonspecific abdominal pain. Before examining the bladder and kidneys, you must drink at least 0.5 liters of plain water. To obtain reliable results, it is necessary to reduce fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract to a minimum. To do this, you should temporarily remove foods containing a lot of fast carbohydrates from your diet, and take a carminative or sorbent the day before the procedure.
If cutting pain and itching are present, a urine test will indicate the cause. For the study you will need a morning portion. The woman must first perform hygiene procedures and then collect the sample in a sterile container. The first and last servings should be skipped. Before taking the test, it is important to adhere to a normal drinking regime, remove coloring foods from the menu (carrots, rhubarb, etc.) and reduce the amount of protein in the menu.
Most often, sharp pain after urination is accompanied by an increase in the number of leukocytes. This indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. Red blood cells are found in glomerulonephritis and urolithiasis. Mucus and bacteria are present in infections.
If pain in the lower abdomen is associated with kidney pathologies, a blood test will help detect the cause. Before the procedure, you should not eat food 8 hours before the test. It is advisable not to drink water from the moment you wake up.
When visiting a doctor, it is necessary to describe in as much detail as possible the nature of the sensations and their intensity, depending on the conditions and time of day. For example, if pain when urinating appears only in the morning, most often the cause lies in the ureter or bladder.
Treatment of painful urination in women
It is important to seek help in a timely manner, because in the absence of therapy, most of the above diseases lead to complications. Advanced cystitis causes pyelonephritis, vaginitis does not allow you to bear a child, and genital tuberculosis can be fatal.
Which doctor should I contact?
The choice of doctor and treatment for frequent and painful urination depend on the pathology. For example, a nephrologist deals with the correction of pyelonephritis. For sexually transmitted infections, you should consult a venereologist.
In general cases and for bladder diseases, you can make an appointment with a gynecologist or urologist.
Medicines
Doctors prescribe different medications depending on the cause of the burning sensation. The most commonly used medications are:
- Penicillin antibiotics (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Azithromycin).
- Antiviral drugs (Anaferon, Viferon).
- NSAIDs (Nimesil, Diclofenac).
- Immunostimulants (Echinacea, Polyoxidonium).
- Homeopathic remedies (Canephron, Phytolysin).
- Antispasmodics (Baralgin, Papaverine).
- Antifungal drugs (Nystatin, Diflucan, Pimafucin).
The duration of the course and dosage are determined by the attending physician.
Folk remedies
The choice of traditional method depends on the disease. The following recipes are used:
- For urethritis. Linden is a powerful antiseptic. To prepare the medicine, pour 2 tbsp. l. flowers 0.5 liters of boiling water and place on low heat for 10 minutes. After straining, bring the volume back to the previous level. Take 250 ml of the decoction once a day before bed. Course duration is 10-14 days.
- For urolithiasis. Dried watermelon seeds help cleanse the kidneys and improve fluid circulation. Pour 250 g of raw material into 1 glass of hot water, place on low heat for half an hour and strain. You need to take the decoction before meals, 1 glass 3 times a day. The course will take 7 days.
- For cystitis. Dill seeds promote fluid circulation, help remove toxins and germs from the body, relieve inflammation and destroy pathogens. Take 1 tbsp. l. powder and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Place the container in a water bath for 15 minutes. Strain. Take 100 ml up to 5 times a day. Course duration is 7-10 days.
Before using folk remedies, you must obtain a doctor's permission, since medicinal herbs have contraindications and side effects. The above methods should not be used in place of traditional treatment.
Prevention of pain when urinating in women
To avoid pain when urinating, just follow these recommendations:
- Maintain drinking regime. To prevent inflammation and congestion, you need to drink 2-3 liters of water per day. In the hot season and when playing sports, the norm should be increased, since some of the liquid leaves the body through the skin.
- Don't hold back. Prolonged suppression of urges leads to stagnation of urine and irritation of the bladder walls.
- Buy underwear only from natural materials. Synthetics impair air exchange, which creates a favorable environment for the development of bacteria and can cause irritation. It is not recommended to use bleaching chemicals when washing.
- Maintain good hygiene. After each urination, you should rinse with water. It is also necessary to empty the bladder and carry out hygiene procedures after sexual intercourse. At the end, you need to dry the external genitalia using a disposable napkin or cotton towel.
- Avoid hypothermia. This is especially true for the legs. Low temperature weakens the body, causes exacerbations of chronic diseases and does not allow the immune system to actively fight pathogens.
Painful urination can be caused by both natural birth injuries and pathologies. In any case, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner for a diagnosis and prescription. To prevent infection, it is important to follow preventative measures.
Symptoms
The feeling that after passing urine you want to pee again is already a symptom, but a symptom of another ailment that is progressing in the human body. Therefore, the clinical picture can be supplemented by signs characteristic of the underlying pathology. For example, a sick person may exhibit the following symptoms:
- pain syndrome in the lumbar region;
- discharge of urine containing pathological impurities - blood, pus, mucus, sand;
- burning during urine output;
- hyperthermia;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- disruption of urine outflow, etc.
If one or several of these symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a medical facility for a comprehensive diagnosis.
Preventive measures
To prevent discomfort when urinating, a person needs:
- do not neglect generally accepted rules of hygiene.
- have a regular partner and use contraceptives that protect against STDs;
- wear underwear made from high-quality natural fabrics;
- use hypoallergenic personal hygiene products;
- don't get too cold.
Video: Burning sensation when urinating, painful urination
Diagnostics
If a person, after passing urine, has the feeling that he wants more, then first of all he will need to go to an appointment with a urologist. At the initial appointment, the doctor will interview the patient and examine him. Based on the information received, a pathology diagnostic plan is developed, which may include the following activities:
- blood analysis;
- urine test (the most informative in this case);
- urine culture. It is carried out if the doctor suspects the progression of the infectious process in the patient’s urinary system;
- blood biochemistry;
- daily urine;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, kidneys, and abdominal organs;
Inflammation of the cervix
This is the most common cause among genital diseases, which provokes a burning sensation in the urethra in women.
Causes of cervical inflammation:
- Hypothermia.
- Sitting for a long time on a cold surface.
- Low general and local immunity.
- Inflammatory process in neighboring organs.
If you start therapy at the first stage of the disease, the inflammation goes away quite easily. Antibiotic or anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as immunomodulators, may be prescribed for treatment.
Therapeutic measures
It is important to understand that therapy will not be aimed at eliminating this particular discomfort. Treatment will be carried out for the pathology that provoked the appearance of this symptom. Therapy is selected for each patient strictly individually, taking into account the severity of his underlying pathology, as well as the characteristics of his body.
The patient may be prescribed the following medications:
- drugs that have a destructive effect on formed conglomerates in the lobes and bladder;
- antispasmodics to reduce pain (if present);
- muscle relaxants;
- diuretics;
- antibiotics are prescribed if an infectious process is detected;
- anti-inflammatory and so on.
Video:
Frequent urination? Signs of prostatitis in men
Table of contents
Dribbling
is the term used for the symptom when men experience unintentional loss of urine immediately after completing urination, usually after leaving the toilet. These symptoms are present in 17% of healthy adult men and in 67% of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Urine leakage after urination does not threaten the life of patients, but leads to a sharp deterioration in its quality.
Why do women feel burning and stinging during and after urination?
A strong burning sensation at the end of urination in women is an alarming symptom indicating an inflammatory process taking place in the pelvis. Unpleasant sensations, which also include pain and pain, cause a lot of trouble because they do not allow you to relax, forcing the girl to constantly think about the problem.
The female genital organs are located in such a way that, unwillingly, they can be exposed to many infections. Therefore, inflammatory processes are something that almost every representative of the fairer sex faces.
Women's urethra
The urethra is a hollow tube with flexible walls. The female canal (urethra feminine) is small, short, 2.5-4.5 cm long, 1.5 cm wide and 7-13 mm in diameter. The beginning of the female urethra is located at the bladder, it has a wide opening.
The canal passes through the urogenital diaphragm and has a narrow external opening. The end of the urethra is hidden in the genital slit. The canal runs parallel to the vagina and resembles a funnel.
The canal walls are formed from shells:
- mucous membrane (tunica mucosa);
- submucosa (tela submucosa);
- muscular (tunica muscularis).
Under the stratified epithelium there is a plate of the mucous layer, rich in elastic tissues that form longitudinal folds.
When dissected, you can find that its shape is star-shaped. On its back wall there is the highest fold, which is called the crest of the canal.
The submucosal layer is filled with venous microvessels. They pass into muscle tissue. This shell is formed by loose fibrous connective tissue.
The muscularis propria makes up a circular layer of smooth muscle fibers:
- External longitudinal.
- Internal circular.
The urethra has a voluntary sphincter (compressor), it is located where the urethra muscles pass.
Candidiasis
Damage to the mucous membranes of organs by colonies of fungi of the genus Candida is called candidiasis or thrush.
The disease causes the appearance of a whitish coating, under which an ulcerated surface forms. The affected epithelium appears swollen and reddened. Candidiasis of the vagina and head of the penis very often causes damage to the inner lining of the urethra - candidal urethritis.
The disease is characterized by the presence of:
- constant feeling of itching;
- burning in the urethra during and after urination;
- redness of the labia, vaginal surface, glans penis and external urethral opening;
- In men, whitish discharge from the urethra is noticeable.
Candidiasis is treated with the use of antibacterial drugs with antifungal action in the form of topical dosage forms (vaginal suppositories, ointments) and general use (tablets and capsules for oral use).
Burning sensation in the urethra in women
If unpleasant symptoms of burning in the urethra appear, then we can certainly assume the presence of some pathology, or an infectious and inflammatory etiology. The female channel is quite short, wide and open. These anatomical features facilitate easy entry of infectious microorganisms into the canal.
Often, the causes of burning in the urethral area are inflammations of either the mucous membrane or the bladder. Infectious microorganisms can enter and spread through both ascending and descending routes.
Factors provoking the occurrence of symptoms
These factors are:
- the need for long-term patience when it is impossible to go to the toilet. As a result, vigorous division of microbes in the bladder occurs, which leads to infection;
- absence of an organ that disinfects the urinary tract (prostate);
- undergoing operations in which a catheter was used;
- diabetes;
- an allergic reaction to medications that the patient is forced to take for a long time;
- openness to bacteria and close proximity to the vagina;
- incontinence in sex.
A little anatomy and physiology
Urine is formed in the kidneys, then enters the ureters and accumulates in the bladder.
When its walls are stretched, a urge to urinate occurs, which can be consciously restrained for some time thanks to the orbicularis muscle, the sphincter of the bladder.
During deurination, the sphincter relaxes and urine enters the urethra, urethra. The intensity of urination is regulated by the abdominal muscles, whose contractions increase pressure on the bladder.
In women, the urethra is short and quite wide, so inflammation from the genitals easily spreads to the urethra and higher to the bladder, ureters and kidneys.
In men, the urethra is narrow and long; the ducts of the prostate gland open into it, secreting a fluid with an antimicrobial effect.
Inflammation of the urethra in the stronger sex is observed less frequently than in women, but urethritis is often complicated by a narrowing of the lumen of the urethra.
The infection is primarily transmitted to the prostate and epididymis (prostatitis and epididymitis), and to the seminal vesicles (vesiculitis).
Causes of burning when urinating
The reasons why burning and severe pain occur can vary from simple lack of personal hygiene to serious illnesses. The main reasons for the development of symptoms:
- inflammatory process in the urinary system;
- infectious disease;
- intestinal inflammation;
- prolonged stress and periodic nervous overload.
If the burning does not stop after urination, then the reasons change somewhat.
Doctors often encounter patients who complain of a burning sensation, but no other additional symptoms have been detected. Then specialists conduct additional examinations, as a result of which it turns out that the person suffers from prolonged depression or chronic neuroses.
The causes of a false burning sensation are constant fears, anxieties and other disorders.
What does pain at the end of urination indicate?
In contrast to itching and discomfort, burning and frequent urination in women indicate the development of inflammatory processes in the bladder.
Irritation and inflammation appear in the area of Lieto's triangle, as well as the urethra, which leads to a narrowing of the urethra. During straining, discomfort is felt, and later a burning sensation occurs when urinating in women.
In order to determine exactly which infections caused the discomfort: infectious or non-infectious, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Only after this will it be possible to begin treatment at home.
Without this, burning when urinating in women may indicate various problems, which should be eliminated in different ways.
Painful urination with blood in the urine
Burning during urination in women is not so bad; it’s another matter when a small amount of blood is released during the process. This indicates more complex diseases, which could be caused by infections, injuries, tumors, or the presence of foreign bodies in the urethral canal.
Source: https://gb4miass74.ru/bolezni/zhzhenie-pri-mocheispuskanii.html
Etiology
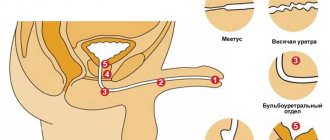
Urine leakage after urination is caused by insufficiency of the bulbocavernosus muscle, which surrounds the middle and proximal parts of the urethra (urethra). Normally, after urination, the m.bulbocavernosus reflexively contracts and promotes the “evacuation” of urine from the urethra. Urine leakage is associated with retention of urine in the bulbar urethra with subsequent release of the latter during movement or under the influence of gravity.
In the urologist's office, there are often cases when patients complain that urine does not completely come out. Moreover, both women and men can suffer from such a problem. Doctors call this phenomenon residual urine - liquid that remains in the organ, despite a person’s efforts to completely empty himself. In this case, 50 ml is already considered a significant volume, although in especially severe cases the “unnecessary weight” reaches a limit of several liters.
Prevention measures
To avoid diseases that lead to painful urination, you must adhere to the following rules:
- maintain personal hygiene and do not forget about personal hygiene products,
- avoid hypothermia and contact with possible allergens,
- wear comfortable cotton underwear,
- give up promiscuity,
- Visit a gynecologist at least once a year and consult a doctor at the slightest suspicion of a disease.
Simple rules for preventing urogenital infections will help avoid many women's troubles.
The appearance of discomfort in the urethra (urethra) is not uncommon. Urologists note that almost a third of patients who seek help in city and regional clinics present this complaint as their main one. Moreover, in women of childbearing age, the frequency of unpleasant sensations in the urethra is slightly higher than in men, which is associated with the anatomical features of the structure of the small pelvis.
Similar article - Teflon coated frying pans
Symptoms
It is not surprising that the main complaint of people with this disorder is incomplete emptying of the bladder. There may be several reasons for concern: a weak “signal” to go to the toilet, a process that extends over several stages, as well as muscle tension and effort to ensure that the desired act takes place. In this case, patients may not feel any other discomfort. But doctors are confident that even these seemingly minor problems should be a reason for a visit to the clinic. After all, they lead to a number of severe and serious complications.
Chronic causes impaired renal function - this is easy to detect thanks to isotope renography. As a result, pyelonephritis, diverticula, cystitis or any other disease develop. If a person experiences chills, high fever and severe lower back pain, then doctors may suspect urosepsis. In the body, it can occur in a malignant form, as evidenced by toxic changes in the blood - high leukocytosis, for example.
Urine standards
To find out when a woman needs to go to the doctor, you should determine how many urges are normal per day.
Experts advise contacting a clinic if the urge to go to the toilet during the day exceeds the number of times you went to the toilet in the previous week. A woman will immediately notice a change in the process of urine excretion, especially if it occurs with painful sensations. The average rate of urination per day is noted:
- no more than 10 times during the day;
- no more than 3 times a night.
Various factors can affect the frequency of urination:
- elderly age;
- the presence of chronic genitourinary diseases;
- amount of fluid consumed;
- emotional condition;
- taking specific medications.
If increased urine production was observed in a woman only for 1-2 days and was not accompanied by symptoms such as pain and burning, then there is no reason to worry. But for preventive purposes, it is recommended to undergo an examination by a doctor.
If a violation of the normal process of urination is observed constantly, even without additional symptoms, it is necessary to undergo a full examination. You should make an appointment with two doctors at once: a gynecologist and a urologist. Typically, the causes of frequent urges to go to the toilet are diseases that fall within the scope of competence of these doctors.
Most common reasons
Based on the above facts, we can draw an absolutely logical conclusion: urine does not completely leave the bladder when the body “eats” a disease - chronic or acute. There are many factors leading to the problem:
- Mechanical causes are diseases of the genitourinary system and kidney infections. For example, trauma to these organs, the presence of tumor formations on them, as well as prostate cancer, adenoma, phimosis, and the presence of stones.
- Diseases of the nervous system: spinal cord or brain injuries, tumors, myelitis, and so on.
- Drug intoxication. It is diagnosed when the patient takes narcotic drugs or sleeping pills for a long time.
The most common cause of urinary retention in men is adenoma. The problem occurs when blood rushes too much to this organ. The acute form is caused by severe hypothermia, alcohol abuse, a sedentary lifestyle and digestive tract disorders.
Causes of burning in the urethra
Many factors can easily affect the organs of the genitourinary system, since the microflora in their area is very sensitive. Women especially suffer in this regard, since they do not have a prostate that could secrete a protective substance.
Despite the different structure of the urethra in women and men, the causes of burning are similar
The behavior of women and men when feeling sick is of no small importance. Some people immediately try to purchase sedatives in the form of ointments and creams, while others wait until the burning sensation stops. You absolutely cannot do any of this. Initially, you need to understand the reason, and only then take measures, but not on your own, but according to the instructions of doctors.
Discomfort after urination in women
- Penetration of infection. The fact is that it can easily get into the urinary tract. Occurs as a result of urolithiasis or is transmitted sexually. It is important to remember that infection entails inflammatory processes that may be irreversible.
- If a person has taken any medications, this may be a side effect. For example, after Miramistin, many feel discomfort. Remember that such a manifestation is still acceptable within normal limits, but it can also provoke serious deviations.
- Allergic reaction to certain hygiene products, use of contraceptives. It also happens that purchased personal hygiene products turn out to be of poor quality, and they contain unwanted and harmful chemicals. It may also depend directly on the girl herself and her women’s health.
- Failure to maintain intimate hygiene. When a woman neglects basic steps to take care of herself and her body, a burning sensation begins in her urethra. If the situation does not improve within a few days, then we have to draw a conclusion about the possible progression of the disease and its transition to a chronic form. The same applies to men.
- People suffering from diabetes also tend to experience a slight burning sensation in the urethra as the endocrine system ceases to function normally.
- Constant stress, physical activity and poor nutrition create a perfect atmosphere for the invasion of infections and the proliferation of all kinds of bacteria. Poor working conditions also provoke urolithiasis, a symptom of which may be a constant burning sensation.
- Many workers have to wait a long time before going to the toilet. This lifestyle negatively affects the human excretory system as a whole, so doctors strongly recommend not to endure it and to take care, first of all, of your health.
In order not to experience unpleasant sensations, sometimes it is enough to carefully monitor your hygiene.
All these prerequisites allow us to conclude that the genital organs are very sensitive to the external environment. Even careless sexual intercourse can cause injuries, after which partners feel a burning sensation in the urethra. But the problem is rather that people do not attach importance to such a manifestation, which is why, of course, they suffer in the future.
Advice: practice basic personal hygiene and don’t try to suppress the urge to go to the toilet. This adversely affects, firstly, the microflora of the genital organs and urethra, and, secondly, the general condition of your urinary system.
Expectant mothers often experience all kinds of discomfort in their bodies. The fact is that all his forces are aimed at maintaining and developing a new organism. Hormonal imbalance most affects the genitals, since they are subject to double stress. Therefore, it is during this period that a burning sensation appears in the urethra in women.
Pregnancy greatly weakens a woman's immune system
Pregnant women receive the greatest attention in this regard, since any infection can have an adverse effect on the baby. The fruit develops moderately and nothing should interfere with it. But the frequent urge to urinate and constant discomfort in a woman’s urethra affect her general condition.
Pathologies and infections can easily affect the fetus, so a woman should often visit a gynecologist during pregnancy. To avoid diseases of the genitourinary system, it is necessary to observe special preventive measures, which include a simple diet and complete freedom from various stresses. Female urethritis or cystitis can cause irreparable harm to the child’s health.
The urethra in women is shorter and thinner than in men. The inside walls are covered with mucous membrane, followed by a layer of muscle tissue and connective fibers. The length of the urethra in women is from three to five centimeters, and the diameter is no more than one and a half centimeters.
The function of the organ in women is to excrete urine, and in men it also excretes seminal fluid.
Microflora is becoming a common cause of discomfort in the urethra in women. The number of pathological microorganisms depends on the age of the patient and the state of her immunity. In a healthy adult woman, the vast majority of microorganisms are lactobacilli. Saprophytic staphylococci and epidermal staphylococci on the mucous membrane are also acceptable. The presence of up to 10% of bifidobacteria is also considered normal for women from thirty to sixty years old.
To accurately diagnose the causes of discomfort in the urethra, women most often take a smear. Such a study is carried out in the direction of a nephrologist, gynecologist or urologist. The purpose of taking a smear is to determine the presence of infection, type of pathogens, pathogenic microflora, erosions or ulcers.
Indications for taking a smear from the urethra are the following conditions:
- Pain and burning when urinating.
- Unpleasant sensations in the urethral area.
- Suspicion of an inflammatory process.
- Suspicion of the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
A smear can be taken directly in the office of a gynecologist or urologist if it is a preventive examination. This procedure is quite painful if the urethral mucosa is irritated.
Before taking a smear to determine the cause of discomfort in the urethra in women, you need to follow some rules:
- Seven days before the test, do not take antibiotics.
- Seven to ten days before taking a smear, do not drink alcoholic beverages.
- Do not have sexual intercourse for twelve hours.
- An hour or two before the test, do not urinate.
To accurately diagnose the cause of the problem, the following tests are performed:
- Urine according to Nechiporenko.
- Bacteriological culture.
- Blood chemistry.
- Blood test for glucose levels.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
Some more factors...
But these are not all the reasons that people complain about when they notice residual urine and pain when emptying the bladder. It happens that the problem arises against the background of a fracture of the pelvic bones and trauma to the urethra - in most cases in representatives of the stronger sex. Less commonly, such discomfort is a consequence of a disorder of the nervous regulation of the muscular membrane of the bladder or inadequate functioning of the sphincters of this organ. It can be caused by hemorrhages in the spinal cord, compression of the vertebrae, etc.
Often has a reflex character. That is, it is observed in a person in the first few days after he has undergone surgery on the pelvic organs or has suffered from severe stress. Sometimes the disease is diagnosed in completely healthy people who regularly drink alcohol. Alcoholics develop atony of the bladder muscle - weakening of the walls of the bladder, as a result of which the patient cannot fully control the act of emptying.
How to get rid of discomfort in the urethra
Depending on the root cause of this discomfort, the urologist outlines a treatment regimen. In case of urolithiasis, the very first step is to remove stones and sand from the urinary system. If the cause of discomfort in the urethra is prostatitis or prostate adenoma in men, then treatment of these pathologies becomes a priority.
Whatever the urethritis, primary or secondary (against the background of other diseases), the therapeutic regimen consists of three areas:
- Impact on the causative agent of inflammation.
- Elimination of unpleasant and painful sensations in the urethra, relief of intoxication syndrome.
- Prevention of the spread of the infectious process to other parts of the urinary system and neighboring organs.
The main direction - fighting infection - is carried out through antibacterial drugs. It is advisable to culture urine for microflora in order to accurately determine the type of pathogen. But even without this research, the choice of antibiotics is in favor of the latest generation of drugs that have a wide spectrum of action. Thus, Amoxiclav, Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Monural are effective for nonspecific urethritis. They are taken either orally (by mouth) or by insertion into the urethra or vein.
For specific urethritis, antibiotics are also prescribed, but according to a certain scheme, and the partners must be treated at the same time. If the disease is caused by gonococcus, then Cefixime or Ceftriaxone or other drugs from the group of macrolides and floxacins are prescribed. Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Levofloxacin are effective for chlamydia. Fungal urethritis is an indication for treatment with Ketoconazole and Miconazole.
Another direction of therapy is symptomatic. To get rid of severe pain, you need painkillers. If the pain syndrome is insignificant, then it can be relieved, as well as burning or cramping, by means of sanitation of the urethra (baths with decoctions of chamomile, sage, mint, which have an anti-inflammatory effect). If the patient has a body temperature above 38 degrees, then you need to take an antipyretic tablet (Aspirin, Paracetamol).
If you seek help late, self-medicate, or have concomitant diseases, it happens that the acute form of inflammation cannot be eliminated after 6 weeks of taking antibiotics. In these cases, a chronic form of the disease develops, which will require even longer and more persistent therapy.
The appearance of unpleasant sensations in the urethra is a reason to urgently consult a doctor. Otherwise, the disease can permanently worsen a person’s health and quality of life.
Discomfort when urinating is a complex of unpleasant sensations that occur when emptying the bladder. In clinical medicine, this pathological condition is called dysuria. A healthy person should not feel any negative effects during the act of urination. Therefore, if discomfort occurs, this indicates the presence of a disease that can be diagnosed with a more detailed study of the nature of the sensations that arise when passing urine. Let's take a closer look at the causes and features of the treatment of discomfort in the urethra in women.
Types of urinary retention
This disorder can be of two types. When urine does not completely exit the bladder, doctors diagnose complete or incomplete retention. The first involves the patient’s desire to go to the toilet, in which the body cannot release even a drop of liquid. For such people, urine has been released from the organ artificially for years - through a catheter. When the liquid comes out partially, they say that the act began, but for some reason was never completed. Usually, trouble occurs against the background of the diseases described above. As soon as the problem is resolved, the process will be restored. If the necessary measures are not taken in time, the delay can become chronic.
Frequent emptying of the bladder without its final emptying leads to stretching of the walls of the organ. This, in turn, provokes another problem - the inability to retain fluid in the middle of the body. At first, a person loses a few drops at a time, but after some time he is not able to fully control the process - urination occurs anywhere under different conditions. This phenomenon is called paradoxical ischuria.
Discussions: discomfort after using the toilet in general
- Good afternoon I am 27 years old, since childhood I have suffered from intestinal problems (constipation, bloating, abdominal pain). But the biggest problem that worries me is that I don’t seem to know how to push. Don't know…
In the first half of 2010 we opened a breathing exercises group on one of the sites for women losing weight. Three users from different cities of Russia persuaded us to give them EXPERIMENTAL samples to try...
After I go to the toilet, there is generally an unpleasant sensation there. And sometimes I feel some kind of compaction in the anus from the outside, which makes it impossible to sit, and after using the toilet it remains...
Hello! I have the following problem: I am constantly blown by the air conditioner, if it blows under my clothes, in the wind, also after swimming in a pond, or if my feet are a little cold. After…
Hello! Alina is 22 years old. Please tell me what it could be! I can’t see a doctor at the moment, I want to find out if this could be serious! I have a lump in my vagina on the left side...
Other forms
A disorder called “residual urine” is sometimes associated with rather unusual factors. For example, there is a peculiar form of delay, which is characterized by a sudden interruption of the process with the opportunity to continue it. The patient begins to have bowel movements normally, but the act suddenly stops. Often the cause is a stone located in the ureter. When the body position changes, the manipulation is resumed. Doctors say that some patients with urolithiasis can only go to the toilet in one position - sitting, squatting, or sideways.
Delayed emptying may be accompanied by hematuria - the presence of blood in the fluid. Sometimes it can be seen with the naked eye: the urine takes on a pinkish or brown tint. If the presence of blood is too small to be noticed, the fluid is taken for analysis, where it is analyzed under a microscope and conclusions are drawn. By the way, experienced urologists can detect urinary retention even during a routine examination. In such patients, swelling is felt in the lower abdomen, caused by the presence of an incompletely emptied bladder.
How to help the patient?
If urine does not completely exit the bladder, a person needs urgent medical advice. An acute form of organ dysfunction requires emergency care. Typically, such people have a catheter inserted for normal emptying. For these purposes, the outer opening of the canal is treated and disinfected, after which a rubber tube generously moistened with Vaseline or glycerin is carefully inserted into it. Tweezers regulate the movement of the catheter, securing it in the urethra. The procedure is carried out progressively - 2 centimeters at a time, without haste or sudden movements.
If the cause of the patient’s problem is urolithiasis or prostatitis, then the manipulation is not performed. In these cases, the presence of a rubber tube in the organ can lead to serious complications. The catheter may be placed permanently. In this case, the procedure is performed by a urologist, prescribing antibiotics after it to avoid the development of inflammatory processes. The patient himself can insert a temporary rubber tube immediately before bowel movement. But before that, he must consult a doctor.
Gonorrhea and trichomoniasis
Among sexually transmitted diseases, the most common causes of discomfort in the urethra in women are gonorrhea and trichomoniasis. The manifestations of these ailments are very similar. However, treatment will vary dramatically.
Trichomoniasis is caused by urogenital Trichomonas. This is a single-celled microbe that multiplies very quickly in the human body, gaining a foothold in the organs of the urinary system. After a few days, urogenital Trichomonas multiplies to such an amount that can provoke an inflammatory process.
In relatively rare cases, trichomoniasis can be transmitted through household means, for example, through a toilet seat or a shared towel. In conditions of high humidity and heat, Trichomonas can continue its life activity outside the human body for some time.
A feeling of discomfort in the urethra is also characteristic of gonorrhea. Gonococcus is the causative agent of this disease. After entering the body, it does not manifest itself in any way for two weeks, and then becomes the cause of the inflammatory process.
You can become infected with gonorrhea in the following ways:
- Sexual intercourse.
- By everyday means (probability is low).
- Transmission from mother to baby (through the birth canal).
Treatment
The feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder is quite unpleasant. To get rid of it forever, you must first remove the cause that caused the problem. Get a full examination from a qualified urologist. Having consulted, if necessary, with a nephrologist, gynecologist and oncologist, he will diagnose the disease and take measures to treat it. Oddly enough, reflex delays are the hardest to heal, since they are psychological in nature. Psychotherapy sessions help here, as well as simple manipulations such as irrigating the genitals with warm water or running a water tap during urination.
Remember that incomplete bowel movements can be a lifelong problem. In this case they talk about a relapse. Moreover, it occurs in cases where the patient catches a urinary tract infection. That’s why it’s so important to take care of your health and sound the alarm at the slightest sign of discomfort. Self-medication is extremely dangerous and often leads to serious consequences and serious complications.
Normal urination in humans is characterized by the fact that no sensations are noted before, during or after the process. The number of urinations per day is about 4-6
. A change in urges can be observed under the influence of various conditions:
- The amount of fluid you drink during the day;
- Climatic conditions, ambient temperature;
- Food that a person consumed per day;
Most often, in a healthy person, the feeling that after urinating you want more is noted after taking a large amount of liquid or food that has a diuretic effect (watermelon). A person with general illnesses may experience a repeated urge to urinate after taking diuretics and other medications, the side effect of which is increased urination.
In all other cases, the urge to urinate repeatedly is a deviation from the norm, and requires consultation with a specialist, determining the cause and prescribing appropriate treatment.
In the first place among the diseases that cause the feeling that after urination you want to pee, there are infectious and inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system:
- Inflammation of the bladder (typical mainly for women);
- Inflammation of the urethra (more common in men);
- Pyelonephritis is an infectious process in the kidneys;
- Inflammation of the prostate gland in men;
- Inflammation of the uterus and appendages in women.
These diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms or opportunistic microflora of the reproductive system, which, under the influence of unfavorable factors, begins to grow and develop excessively.
Pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation are: Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus, gonococcus, Klebsiella, Proteus, enterobacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Some of these microorganisms can be transmitted to humans through sexual contact.
Opportunistic microorganisms are fungi of the genus Candida, lactobacilli and clostridia. They begin to grow uncontrollably under the influence of unfavorable factors.
Predisposing factors to the development of the inflammatory process are:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Decreased immunity, hypothermia;
- Bad habits;
- Chronic diseases of the body.
Also, these diseases can be caused by traumatic agents (trauma, exposure to high or low temperature, electric current). In this case, inflammation occurs due to medical procedures in which the technique was violated.
In addition to infectious and inflammatory diseases, an unpleasant sensation after urination can occur due to the following reasons:
- Diabetes. Polyuria () is one of three characteristic symptoms that indicate the development of the disease.
- Diabetes insipidus. The feeling that after urinating you want to urinate again is accompanied by the release of a large amount of urine. In this case, thirst may not be observed.
- Neurogenic bladder. Observed when the nervous system is damaged.
Malignant or benign neoplasms in the bladder can lead to the fact that after urination a person wants to go to the toilet again. This sensation occurs due to the constant irritating effect of the tumor on the wall of the bladder. Urolithiasis has the same effect when the stone is localized in the bladder.
Predisposing factors to the formation of a tumor in the bladder are long-term smoking and work in chemical production, which are combined with frequent urine retention in the body (if a person constantly holds back urine and does not go to the toilet).
Urolithiasis occurs due to poor diet or diseases associated with metabolic disorders. Also, drinking alcohol or salty foods can lead to stone formation. Men are at risk for this disease.
Infections
Unpleasant sensations can occur due to an inflammatory process caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Nonspecific pathogens of infectious diseases are Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus, etc.
STIs that can cause discomfort:
- The first place in terms of incidence is occupied by trichomoniasis, the causative agents are Trichomonas. The area affected in women is the vagina; in men, the seminal vesicles and prostate. At the initial stage, an inflammatory process develops in the urethra, which leads to pain and discomfort.
- Chlamydia is an infectious disease caused by chlamydia, an intracellular microorganism. They affect the urinary and reproductive systems.
- Gonorrhea, caused by gonococcus. Affects the genitourinary system and part of the rectum.
- Ureaplasmosis (caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum) can occur without symptoms. Possible signs of the disease: burning sensation, discomfort in the groin area, pain in the urethra.
Diagnosis of patients with this problem
Diagnosis begins with clarifying complaints by which a doctor can suspect a person has a disease and make a preliminary diagnosis. A patient with an infectious-inflammatory process, in addition to the feeling of wanting more after urinating, may complain:
- The pain that accompanies the urge occurs during the act of urination or after the release of urine;
- Itching, burning in the urethra;
- Change in the amount of urine released (with each urge, little urine is released, it comes out drop by drop, or, conversely, with frequent urges, a large amount of liquid is released);
- Change in color (white, red, brown or green) and clarity of urine, appearance of foam;
- Violation of general condition, weakness, fatigue, increased body temperature, headache, decreased ability to work;
- Decreased sexual function, lack of libido, erectile dysfunction in men.
For patients with suspected malignancy or urolithiasis, the appearance of blood in the urine is typical. The patient may notice both streaks of blood and a change in the color of the urine to red, brown or pink, depending on the degree of hematuria.
A mandatory diagnostic measure is passing a clinical test of blood and urine. In the blood you can detect leukocytosis, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, increased ESR (characteristic of an infectious process), anemia (with hematuria). The level of protein, leukocytes, and red blood cells increases in the urine. The organoleptic properties of urine change. With urolithiasis, salts appear, which can indicate the structure of the stone.
It is also necessary to culture the urine and determine the sensitivity of the microflora to antibiotics. If a sexually transmitted disease is suspected, PCR is performed to identify the pathogen.
Ultrasound is used to detect changes in the genitourinary organs. Helps determine the location of a tumor or stone (if present), determine the size of the prostate gland or uterus during the inflammatory process.
If a malignant neoplasm is suspected, the following is carried out:
- MRI or CT, which will help determine the location and size of the tumor;
- Cystoscopy to visualize the tumor;
- Biopsy to determine the nature of the process.
If you feel like you want to go to the toilet again after urinating, you should not engage in self-diagnosis. Diseases that cause such sensations can lead to serious complications if you do not seek help from a specialist in time.
Treatment of urinary discomfort in women
Depending on the disease that provoked the appearance of pain and cramping, the treatment provided differs. It is worth noting that the earlier treatment is started, the lower the risk of complications.
Medicines are selected individually, and the doctor must take into account:
- course of the disease (acute or chronic);
- age of the patient;
- condition at the time of application;
- allergy to drug components.
The attending physician prescribes a course of treatment for both partners in order to prevent the woman from becoming reinfected in the future after recovery.
For therapy, the doctor uses the following groups of drugs:
- Antibacterial agents - Ampicillin, Azithromycin and Doxycycline.
- Antifungal agents - Nystatin, Fluconazole.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Nimesil, Diclofenac.
- Antispasmodics - Papaverine, Baralgin, No-shpa.
- Herbal tea - horsetail, knotweed, lingonberry leaves.
- Plant-based uroantiseptics - Cyston, Canephron.
- Immunomodulators - echinacea tincture.
The course of drug treatment lasts at least 10 days, which is supplemented by physical therapy after the acute inflammation has subsided.