The dosage of drugs and the duration of treatment depend on the complexity of the disorder and the characteristics of the patient’s body, so they determined by the doctor individually.
Urinary incontinence is a common complication after stroke. It may go away on its own or with medical intervention. The main thing is to properly care for the patient and choose effective treatment.
Sources used: kardiobit.ru
Urinary incontinence after stroke in women and men: treatment
A fairly common phenomenon in the human body that occurs in men and women is urinary incontinence after a stroke.
This delicate problem develops as a result of motor and sensory deficits, and the severity of the disease and the areas of the brain that were affected by the disease determine the degree of complication of involuntary urination.
With properly selected and timely treatment, the patient can quickly return to a normal rhythm of life.
Why does the symptom appear in women and men?
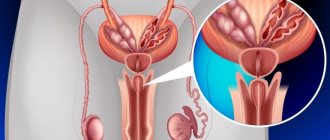
In medicine, an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, which leads to damage and death of nerve cells, is called a stroke. Often, after an illness, urinary retention, blood in the urine, and urinary incontinence may occur.
The cause of the latter pathology is loss of consciousness, psycho-emotional problems and the formation of diseases that affect the intellectual abilities of the patient.
Urinary disorders occur when the lower extremities and muscle system, which is responsible for the functioning of organs within a person, are paralyzed. Older people are more likely to experience uncontrolled urination.
The primary cause of urinary incontinence after a stroke in females is menopause or previous surgical intervention on the pelvic organs. Men are susceptible to this pathological phenomenon after a stroke and have had prostate disease.
Treatment of the problem
B vitamins are used in treatment.
The occurrence of urinary incontinence depends on the age of the patient and the severity of the stroke. However, it is believed that this phenomenon can be observed more often in women.
What to do in this case and how to normalize urination? Specialists strongly recommend not to be ashamed, but to contact a medical facility in a timely manner to receive proper and effective treatment.
It should be borne in mind that in men, treatment for urinary incontinence that occurs after a stroke differs from the therapeutic course required for women. This is due to the different anatomical structure. Urinary incontinence is treated with the following pharmaceuticals:
To eliminate uncontrolled urination, nootropic drugs are used, the action of which is aimed at restoring the activity and functioning of nerve cells.
It is recommended that patients with urinary incontinence after a stroke take vascular and metabolic medications. During treatment, the patient is recommended to use absorbent pads or panties. Comfortable to wear and diapers for adults.
When choosing absorbent products, you should pay attention to the quality of the materials and the presence of protective sides that prevent liquid from leaking out.
It is extremely important to take care of your skin to prevent dermatitis, which often appears due to bedsores or contact of urine with the skin. Today, there are many dermal care products that can be purchased at pharmacy chains.
Devices for urinary incontinence after stroke
If after a stroke a patient experiences urinary retention or incontinence, it is advisable to use various devices. The following types are used in medical practice:
- Ducks. Used for patients who are unable to move independently.
Bedside chairs. Relevant use for patients who do not have time to get to the toilet.
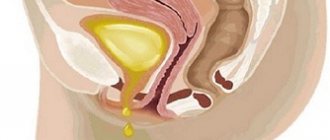
For convenience, women can use special pads.
A comfortable catheter has not yet been developed for women, but there are special pads and panties.
They should be selected depending on the amount of liquid released; it is important that they are soft and absorb moisture well.
Women note that with prolonged use a specific odor appears, but to prevent it, it is recommended to change pads more often and clean the external genitalia throughout the day.
Today, new external catheters are being produced, which need to be changed once every 3 weeks. It is important that the urine bag and catheter are always clean, otherwise the patient is at risk of bladder infection.
The catheter should be placed so that it does not put pressure and does not provoke ulcerative lesions in the urethral area.
It is necessary to ensure that the device is not clogged or pinched, and that urine can flow freely into the urinal.
Prevention of stroke
To prevent the development of circulatory disorders, which entails damage and death of nerve cells, you must first reconsider your lifestyle and, if necessary, change it.
You can prevent a stroke if you always monitor your blood pressure and, if necessary, try to normalize it in a timely manner.
If you have previously suffered an ischemic stroke, the patient should take antithrombotic medications and statins.
In case of violations of speech and motor function, they carry out therapeutic exercises and sessions with a speech therapist, and to improve higher brain functions they take anti-dementia drugs.
To prevent stroke, they take antidepressants and attend psychotherapy sessions. The best way to prevent various diseases is to immediately consult a doctor.
Self-medication of the first symptoms of the disease can worsen the condition and provoke serious complications.
Sources used: 1lustiness.ru
Questions and answers on: urinary incontinence after stroke
Source: https://poligon23.ru/nederzhanie-mochi-v-preklonnom-vozraste/posle-insulta-nederzhanie-mochi-mozhno-li-vylechit
Why does enuresis occur?
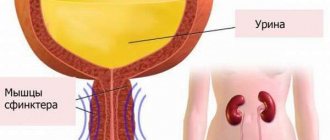
A stroke occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. After hemorrhage, extensive damage to the brain occurs, especially to the frontotemporal lobe, which is responsible for the functioning of the sphincters. Enuresis occurs due to deterioration of conductivity between parts of the central nervous system and the nerve pathways that conduct impulses. As a result, the bladder loses its ability to contract, but the sphincter is still able to hold urine. Once it becomes overfilled and urinary retention occurs, the sphincter is unable to perform its function. Urinary incontinence develops. Typically, such enuresis goes away within a month; drug therapy helps solve this problem faster.
According to statistics, enuresis occurs 2-3 times more often in men than in women.
Diagnostics
Just like with any other disease, urinary incontinence after a stroke requires diagnosis - a full physical examination of the patient, as well as a medical history. The most important aspects to pay attention to first are fluid intake and toilet habits.
In addition, when carrying out diagnostics, specialists study a person’s heredity. An equally important factor is the presence of a history of previous operations on the pelvic organs.
In order to obtain an initial assessment, a urine test is performed and a urination diary is kept. Additionally, the patient is examined to detect urination during straining or coughing - a special stress test is used for this.
If surgical intervention is required to treat this consequence of a stroke, a urodynamic study is necessary to obtain the clearest possible clinical picture. To date, it is considered the only technique that can be used to thoroughly check the functional state of the lower urinary tract. This procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. It lasts approximately thirty minutes and does not cause discomfort or pain.
Other bladder problems
Urinary incontinence is not the only urological complication of stroke. Stroke patients experience the following problems:
- Urinary retention. In this condition, the patient is unable to completely empty the bladder. The delay is dangerous because its prolonged presence in the body leads to acute intoxication.
- Neurogenic bladder is a complete loss of the organ’s ability to empty itself.
- Difficulty in the flow of urine. Occurs due to disruption of the sphincter.
- Hematuria is blood in the urine. The amount of blood varies from little to completely red discharge. The reason for this is infection, which is also a common complication of stroke.
Treatment and what to do?
Many patients who have suffered a stroke complain of urinary incontinence. However, doctors claim that this problem is treatable. Therefore, it is necessary to make efforts and choose the right treatment. As for the duration of the course of therapy, it is different for each person: for one it may last several days, while for another it will take several weeks, or even months, to completely get rid of the consequences of a stroke.
The main factors of urinary incontinence directly depend not only on the severity of the attack, but also on the person’s age. It should be noted that women suffer from this problem much more often. If urinary retention occurs after a stroke, a special catheter is inserted into the body, otherwise doctors use anticholinergic medications.
Most people are embarrassed by such consequences, so they are in no hurry to seek help from highly qualified specialists. Because of this, they are deprived of the necessary treatment, which will be effective and will contribute to the rapid establishment of the urination process.
According to medical information, many patients after a stroke are not helped by medications, as well as traditional medicine.
While the course of treatment is being carried out, it is recommended to use adult diapers, pads or special absorbent panties.
The following medications are usually prescribed for therapy:
The dosage of drugs and the duration of treatment depend on the complexity of the disorder and the characteristics of the patient’s body, so they are determined by the doctor individually.
Urinary incontinence is a common complication after stroke. It may go away on its own or with medical intervention. The main thing is to properly care for the patient and choose effective treatment.
Urinary incontinence, and even more so fecal incontinence, is perhaps the most catastrophic consequence of a stroke. This problem can be overwhelming for people caring for someone who has had a stroke. It is the most common reason that patients are sent to specialized institutions. At the same time, urinary and fecal incontinence is not a hopeless situation. Below you will find out how to make it easier.
Urinary and fecal incontinence after a stroke: learn how to cope
The good news is that for many patients, within a few weeks after a stroke, the incidence of urinary and fecal incontinence is significantly reduced, or even this problem disappears completely. It is important that the patient feels free to discuss incontinence with their doctor. He can suggest many effective ways to restore control over the intestines and bladder. In fact, urinary and fecal incontinence turns into a disaster mainly in cases where doctors do not know about it and, accordingly, do not treat it.
Treatment of urinary incontinence after stroke in women and men
Often, post-stroke enuresis is treated with physiotherapy.
After conducting laboratory and clinical studies and establishing the exact cause of enuresis, the next stage of treatment is the selection of an individual treatment regimen, and it often happens that they differ in women and men. In the treatment of urinary incontinence, pills, traditional recipes, physiotherapy, and less commonly, surgery are used.
Medicines
Treatment for urinary incontinence is based on medication. Patients are prescribed drugs from the following groups:
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - enhance the transmission of nerve impulses from the brain to the bladder. Among the products in this group, Prozerin and Aksamon are most often used.
- Drugs to improve cerebral circulation: Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, Hopantenic acid.
- Nootropic drugs that restore brain cells: Piracetam, Phenibut and their analogues.
ethnoscience
As an auxiliary method for urinary incontinence after a stroke, you can take herbal decoctions.
Specific urinary disorders can be successfully treated with alternative medicine. They are used as an independent remedy or as an auxiliary therapy to speed up the rehabilitation process and get rid of an unpleasant problem. Patients who are concerned about frequent urination or incontinence are advised to take the following decoctions:
- From a plantain leaf. 1 tbsp. l. plants in 1 cup of boiling water, leave this mixture for an hour, and then, after straining, take 1 tablespoon 4 times a day half an hour before meals.
- An infusion of 40 g of sage, poured into 1 liter of boiling water, is allowed to brew for 4 hours. Drink three times a day.
- An infusion of a mixture of herbs is useful: a teaspoon of yarrow and St. John's wort per glass of liquid. Drink 2 glasses every day for 1.5-3 weeks.
- Decoctions of berries are often used: blueberries, lingonberries, blackberries.
- Much attention is paid to various fresh or canned natural juices. If you have incontinence, it will be helpful to drink 1-2 glasses of carrot juice every day.
The overwhelming number of doctors do not approve of taking folk remedies without their consultation.
Other methods
Surgical treatment, which is considered effective, is less commonly used. In women, TVT surgery is common, which involves placing a special loop made of synthetic material in a certain place in the urethra. It is performed under local anesthesia and does not require tissue dissection, which is certainly a big plus. For men, a device is implanted that performs the function of a sphincter, which in 90% of cases eliminates the problem. It is placed inside the scrotum and has a special pump: if the patient wants to go to the toilet, he presses on it and the bladder is emptied. The sphincter then closes and prevents urine from flowing out. Physiotherapy procedures include galvanic currents, electrophoresis and electromyostimulation.
How to get fecal incontinence under control
At least 30% of people who have had a stroke suffer from fecal incontinence in the first 7-10 days after the accident. By 6-12 months, 2/3 of these patients manage to regain control of their bowels. Over the next 2 years, the prevalence of fecal incontinence in patients who have had an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke increases from 10% to 15%. This problem is seen among people in whom a stroke has caused overt dementia.
You need to choose your diet so that it does not cause constipation or a laxative effect. Try to consume plenty of fiber, especially if you have problems swallowing food. Drink enough fluids - stay hydrated. The norm for healthy people is 30 ml of water and herbal teas per 1 kg of body weight per day. Discuss with your doctor whether this rate is appropriate for a patient who has had a stroke. In heart failure, it should be significantly reduced.
Take steps to avoid constipation, although this recommendation may seem counterintuitive. Antidepressants and diuretics can cause constipation. Discuss this with your doctor. Magnesium-B6 tablets normalize blood pressure, improve heart function, and also stimulate the movement of food through the intestines. Talk to your doctor about whether a stroke patient should take them. In addition to these, you can also try vitamin C, probiotics, and fructooligosaccharides—nutrients for beneficial bacteria in your gut—for constipation.
A patient who has suffered a stroke needs to restore his ability to move in space. If it is difficult for him to get to the toilet or potty on time, then incontinence is inevitable. Take measures to ensure that furniture does not interfere with the disabled person’s movement around the room. Do regular muscle and joint exercises recommended by your physical therapist. The higher the physical activity, the better the intestines will work. You may need a special toilet seat.
Treatment in Moscow and abroad
Children's Hospital in Moscow Treatment in Germany Clinics in Germany Orthopedic Clinic KASSEL Treatment in Israel Medicine in Israel - MC IMedical Clinics in Israel Treatment in Switzerland Dentists in Israel University Clinic Zurich Treatment in Austria Minimally invasive spine surgery University Clinic Tübingen Ichilov Clinic in Israel Sources used:
- https://s.spadys.ru/glossary/158
- https://sochi-mebel.ru/lechenie/nederzhanie-mochi-posle-insulta
- https://prourinu.ru/nedugi/enurez/nederzhanie-mochi-posle-insulta.html
- https://id-direct.ru/articles/problema-neproizvolnogo-mocheispuskaniya-/
- https://www.rusmedserv.com/neurologycenter/stroke/retentionurineafterstroke/
Why is bladder rehabilitation necessary after ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke?
Urological problems after cerebrovascular accident are observed in approximately 50-70% of patients. Rehabilitation allows you to get rid of the unpleasant consequences of a stroke and gradually return to normal life. The duration of the recovery period directly depends on the disease and the condition of the patient’s body. The list of restoration measures includes:
- diuresis control;
- hygiene (change of bed linen and diapers as needed, water procedures, etc.);
- drinking regime;
- catheterization;
- treatment prescribed by a specialist.
Conclusion
Why does a patient experience abnormalities in bladder function after a stroke?
Problems with bladder control after ischemic and hemorrhoidal strokes occur for certain reasons, including:
- Damage to areas of the brain that control the bladder, causing the patient to not realize that they need to go to the bathroom;
- the need to endure for a long time if the patient cannot get to the toilet on his own, and also call someone for help due to speech problems;
- taking medications that may negatively affect bladder control.
DRUGS USED TO REDUCE BLADDER CONTRACTILITY
Tricyclic antidepressants: imipramine triptyline nortriptyline Other drugs: flavoxate hydrochloride oxybutynine hydrochloride propantheline bromide Common side effects: dry mouth “blurred vision” nausea or vomiting constipation or diarrhea confusion in the elderly urinary retention in case of compression of the bladder neck accelerated development of acute glaucoma
the reason for this must be carefully explained and reassured to reduce their anxiety. Caregivers may also benefit from this information. Since urinary urgency is a very common cause of incontinence, simple measures such as regular toileting, using techniques to get the nurse's attention in patients with aphasia, improving mobility, or having a toilet seat at the bedside can be quite effective.
Of course, the underlying cause (eg, infection, urinary obstruction) must be treated and, if possible, factors contributing to incontinence (eg, excess fluid, uncontrolled hyperglycemia, or diuretics) must be addressed. Urodynamic study helps to identify patients with detrusor hyper- or hyporeflexia.
There is no need to use a permanent catheter, since it is impossible to detect the restoration of urination, which can lead to a number of complications (HERE IS A LINK FOR PROBLEMS WITH A CATHETER). To avoid unwanted catheterization, you can use other aids and items.
However, if the patient is at high risk of developing bedsores or for some other reason needs to be dry at all times, a catheter may be the optimal solution. Catheterization may also be needed to treat urinary retention (HERE LINK URINary Retention AFTER STROKE) until the cause or trigger (eg, enlarged prostate, urinary tract infection, severe constipation, anticholinergic medications) is treated.
If urinary incontinence is a barrier to discharge, then long-term catheterization is indicated. In many areas of the UK, the dry cleaning system, overseen by health and social services, provides significant support to families with incontinence patients.
Restoring urination after a stroke
A stroke occurs as a consequence of an acute disruption of the blood supply to the brain. After hemorrhagic or ischemic damage, the basic functions of the body are disrupted. Problems with urination after a stroke are observed in 30% of cases. The situation is significantly complicated by the patient’s partial or complete paralysis and the need to remain in bed.
- The most common causes of incontinence
- Problems urinating after a bladder infection
- Clinical signs and symptoms
- Diagnosis and recommended tests
- Differential diagnosis
- How to cure urinary incontinence in older people?
Incontinence problems are usually a consequence of another disease, which is characterized by the involuntary process of urination without clear reasons for this.
There are several groups of factors that cause this problem.
For reasons that caused this problem:
- after a woman has undergone surgical intervention in the pelvic organs, which led to the occurrence of adhesions and fistulas;
- the most “popular” reason for uncontrolled urination is not completing the course of treatment or not following all instructions in the process of eliminating cystitis in young years;
- after an illness that affects the nervous system;
- as a result of physical influences.
Urinary incontinence in women over 50 can be divided into the following types:
- changes as stress urinary incontinence in women as a consequence of nervous stress or heavy loads, and;
- if you have a problem with an “overactive bladder”, which is often in a state of urge to urinate;
- due to incomplete bowel movements of the bladder;
- due to the emergence of special externally manifested mechanisms that provoke the process of emptying, ending at the moment when the external stimulus disappears;
- when mixing the two above factors.
The likelihood of a recurrent stroke is greatest in the first days of the disease, so secondary prevention should begin as early as possible after the development of the first stroke [1-4]. It is based on the correction of risk factors for its development, the combination of which varies significantly among patients.
Prevention of recurrent stroke includes lifestyle modification, medications and, in some patients, surgical treatment. A patient who has suffered a stroke is recommended to give up smoking and alcohol abuse, normalize weight, maintain sufficient physical activity and, in the case of an ischemic stroke, a cholesterol-restricted diet.
Reducing high blood pressure through antihypertensive therapy is one of the most effective ways to prevent recurrent stroke; it can prevent approximately one third of strokes [2-4]. In patients who have suffered a cerebral hemorrhage due to arterial hypertension, normalization of blood pressure is the only effective method for preventing a recurrent stroke [1].
Swallowing disorders also provoke digestive problems, which leads to constipation and diarrhea, which, in turn, is fraught with severe dehydration.
Speech disorders
A person who has suffered a cerebral infarction can be recognized by his manner of speaking. A common consequence of a brain stroke is speech impairment. And if there are also motor disorders, then it is difficult for the patient not only to pronounce, but also to reproduce speech in writing.
Often people have to relearn how to speak and write - it all depends on the degree of brain damage, namely changes in the left hemisphere.
Vision problems
In Russia, on average, about 100 thousand recurrent strokes are registered annually. Six months after a stroke, disability occurs in 40% of surviving patients.
During the first 5 years, up to 85% of patients die or remain disabled and only the remaining 15% of patients manage to recover.
Massage should be used exclusively as prescribed by the attending physician and performed only by a specialist! Self-indulgence in this matter can lead to a deterioration in the patient’s condition and cause a recurrent stroke.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures may include electrophoresis, electrical myostimulation of muscles, darsonvalization, magnetic therapy for paralysis of the limbs, heat and cold therapy, various types of baths and applications. As a result of a full course of physiotherapy, blood circulation in the brain improves and the intensity of vascular manifestations of the disease decreases.
A patient after a stroke may begin to feel less pain, which is an alarm signal about problems in the body. Therefore, it is important to teach the patient to recognize and recognize other signals from the bladder and intestines that indicate disturbances in their functioning. The following symptoms may provide important information.
1) Increased sweating of the face and non-paralyzed parts of the body, redness of the face, nasal congestion, increased headache. These symptoms may accompany the occurrence of acute urinary retention. If such a delay does occur, call a doctor or immediately go to the nearest hospital.
If you want to remove the Foley tube and the balloon does not deflate, do not waste time trying to deflate it. 2) Change in urine color. Greenish urine may appear after light bleeding from the kidneys or bladder. Dark red urine occurs when there is heavy bleeding due to stones (although some laxatives can color the urine).
It may be a consequence of hemorrhoids (dilation of the veins of the anus and rectum) or rectal fissure (tear of the tissue of the rectal wall as a result of injury). Invite a doctor to clarify the cause. Treatment with medications and injections is possible. Surgery is necessary in rare cases. 5) Blood and pus in the stool.
The cause may be a fistula or anal cavity - a small depression in the wall of the rectum caused by injury or infection. There is a danger of pockets of pus accumulating in the area of the fistula. Consult your doctor. Most often, minor surgery is necessary. 6) Tar-black stool.
May be a signal of bleeding caused by a stomach or intestinal ulcer. The patient must be hospitalized.7) In men - swelling, hardening and possible redness of the testicles. Such symptoms can appear with hydrocoelia - a small bubble of water in the testicle. This condition is not dangerous, although it sometimes requires surgery.
Prevention measures
A stroke is a local disturbance of blood circulation in the brain, leading to damage to nerve tissue and death of nerve cells.
The chances of recovery after a vascular accident depend on age, health status, and the location and size of the affected area.
The consequences of strokes range from speech and mobility problems to problems with urinary and bowel control.
With age, the risk of cerebral hemorrhage increases. This happens because the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels and the influence of various chronic diseases (arterial hypertension, etc.) increase the susceptibility of blood vessels to damage.
But in recent years, the problem has become “younger” and more and more people under 40 years of age suffer strokes. Young people experience the consequences of the disease especially hard, since they have to radically change their usual lifestyle and limit themselves in choosing work and hobbies. The recovery period can last for years - its duration depends on the location and size of the brain damage.
Damage to the frontal cortex as a result of a major stroke leads to loss of urinary control.
Incontinence of varying degrees of severity occurs: from dripping urine when laughing, coughing and sneezing, to the release of large volumes of liquid or complete uncontrolled emptying of the bladder.
Urinary incontinence can continue for several weeks after a stroke, or for a longer period, and even become chronic. If during the recovery period the problem with urinary control persists without improvement, you should inform your doctor about this and undergo additional examination, if necessary.
- • if a person is unconscious after extensive brain damage;
- • in case of mobility impairment, when a person cannot move independently in order to pick up a duck or get to the bathroom in time;
- • with speech impairments and cognitive problems, a person cannot make it clear in time that he wants to go to the toilet;
- • if, as a result of damage to certain brain structures, the ability to inhibit bladder contractions is impaired;
- • due to a urinary tract infection, which can quickly develop as a result of the patient being forced to lie down, the use of urinary catheters, or simply against the background of a general decrease in immunity;
- • against the background of overfilling and overstretching of the bladder due to urolithiasis or prostatitis. Long-term constipation can also provoke incontinence, which resolves after taking a laxative or performing a cleansing enema. Therefore, those caring for the patient should pay attention to this issue and, if necessary, consult a doctor to eliminate the cause of constipation and bladder fullness;
- • when being treated with certain medications, for example, antidepressants, etc. Therefore, you need to inform your doctor about the medications you are taking. In some cases, replacing the drug can correct the situation and restore control over urination.
How to treat difficulty urinating
Therapy for difficulties with urine outflow is selected taking into account the diagnosis. If the disease is caused by a urinary tract infection, it is often possible to get by with antibiotics. Anticholinergic drugs are prescribed for men with an enlarged prostate gland. Alpha blockers, finesterides, steroids and others are prescribed. A catheter inserted into the urethra helps to completely empty the bladder. Manual manipulation in the pelvic area, namely stroking and palpation, also helps. If stones are present in the bladder or urethra, surgery may be required. Surgery is also necessary if treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia does not produce the desired results or the patient is diagnosed with prostate cancer.
Basic methods of restoring normal functioning of the urinary system after a stroke
Problems with urination are one of the consequences of poor blood circulation in the brain. Patients with incontinence, obstructed urine outflow and other disruptions in the functioning of the urinary system require diagnosis and treatment, which should be prescribed by a specialist. Therapy is selected depending on the characteristics of the disease and may include the following restorative methods:
- taking medications (cholinesterase inhibitors, nootropics, metabolic and vascular drugs, diuretics, sedatives and others);
- using a catheter to divert urine;
- phytotherapy;
- treatment of diseases of the urinary system using traditional methods;
- surgical intervention.