Burning and cramping when urinating in men occurs suddenly if the provocateur is an infection. Discomfort increases gradually if the cause is changes in the structure of the lower urinary tract. Pain in the urethra and pain during urination can be either a temporary self-limiting phenomenon due to the abuse of foods or alcohol that irritate the mucous membranes of the urinary tract and bladder walls, or a sign of serious pathologies.
Burning and cramping when urinating in men occurs suddenly if the provocateur is an infection
Burning in the urethra as a symptom of urethritis
A constant companion of urethritis is a burning sensation during urination. The occurrence is triggered by unprotected sexual contact, inflammation, increased physical activity, and prolonged exposure to the cold.
The causative agents are staphylococci, streptococci, ureaplasma, E. coli, gonococcus.
Our readers recommend
Our regular reader got rid of PROSTATITIS using an effective method. He tested it on himself - the result was 100% - complete relief from prostatitis. This is a natural remedy based on honey. We tested the method and decided to recommend it to you. The result is fast. EFFECTIVE METHOD.
In addition to discomfort and pain, the following symptoms occur with each urination:
- pain in the urethra, itching;
- the head of the penis itches and hurts;
- mucus with pus is secreted from the urethra, periodically interspersed with blood;
- the head and foreskin become inflamed.
A timely visit to a specialized doctor will relieve not only pain when urinating, but also complications such as orchitis, calliculitis, epididymitis, and prevent the spread of inflammation. Therapy is carried out with antibacterial drugs and washing with antiseptic solutions. The burning sensation with each urination usually disappears within 2-3 days.
When chlamydia is active in the body, clear discharge may be observed.
It is possible to restore erectile function! Proven FOLK CARE ... Reviews My story spotenciey.ru
Treatment of PROSTATITIS using a new method To restore the functions of the prostate, you need every day... Website Interview with a doctor bezprostatita.ru
The problem of the small size of the dignity has been solved. The mechanism of erection has been revealed... Official website Recovery bigbigrazmer.ru
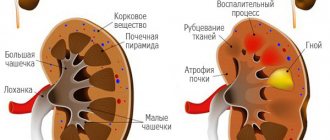
Causes, symptoms, treatment of hemorrhagic cystitis
One of the forms of inflammation of the bladder is hemorrhagic cystitis; its dangerous and severe course requires mandatory and prompt access to a medical institution. Hemorrhagic cystitis can be acute or chronic.
Causes of hemorrhagic cystitis
Against the background of a viral infection and the effects of chemicals on the walls of the bladder, hemorrhagic cystitis most often occurs; the reasons may be different, but adenoviral infection ranks first among them.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Hemorrhagic cystitis can occur in children, boys are most susceptible, in women and men. The cause of hemorrhagic cystitis in women is a bacterial infection, and in older men it is prostate adenoma.
Hemorrhagic cystitis with blood in the urine is observed, caused by the presence of foreign bodies (sand, stones in urolithiasis) in the lumen of the urinary tract.
In all other respects, hemorrhagic cystitis occurs under the influence of similar provoking factors that cause many other forms of the disease:
- hypothermia,
- decreased immune system function during illness, pregnancy, the elderly and children,
- proximity of the source of infection to the urethra,
- the presence of metastases in cancer.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease is classified as severe. Acute hemorrhagic cystitis begins with the appearance of frequent and painful urination, fever and chills. There is a constant desire to urinate - the urinary mucosa is inflamed, and this is where the nerve endings pass, so even a small amount of liquid irritates them.
After a few hours, blood can be found in the urine, which in large quantities forms blood clots that can clog the narrow urethra - urinary retention occurs.
Symptoms of the acute period disappear in a week or a little more (and in cases where no treatment is carried out), a day or two before this, the blood in the urine disappears. The disease progresses to the next stage, chronic hemorrhagic cystitis.
What are the distinctive symptoms of hemorrhagic cystitis: the presence of red blood cells and blood fragments in the urine.
Under the influence of bacteria, viruses and chemical irritants, not only the mucous, but also the submucosal layer is destroyed, and partial rejection of the inner surface of the bladder occurs. Platelets, blood clotting factors and an acidic environment contribute to the formation of clots that can partially or completely block the flow of urine in the urethra and cause acute urinary retention. This dangerous condition most often develops in children and men due to a narrow urethra.
The urge to urinate with hemorrhagic cystitis is felt more sharply and stronger, since the nerve endings located in the walls of the bladder become more accessible due to the destruction of the mucous layer.
Symptoms may also include increased body temperature, fever and weakness.
The consequence of hemorrhagic cystitis can be iron deficiency anemia due to blood loss, which manifests itself more quickly in men and children. The course of the chronic form of the disease is characterized by a less vivid picture of symptoms and the presence of periods of “quiet”.
Basic treatment
If hemorrhagic cystitis is diagnosed, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Based on the tests, basic therapy with antiviral or antimicrobial drugs, withdrawal or removal of aggressive chemicals from the body is prescribed, aimed at eliminating the main cause of the disease. If you seek help in a timely manner, acute hemorrhagic cystitis and its treatment will be effective, and the risk of becoming chronic is minimal.
Antiviral drugs effective in this case:
- proteflazid,
- neovir,
- cycloferon,
- Lavomax,
- groprinosin,
- laferon,
- Viferon.
Antimicrobial drugs for treatment:
- ciprofloxacin,
- ofloxacin,
- co-trimaxazole,
- lomefloxacin,
- pipemidine,
- nitroxoline.
In addition to specific drugs, additional treatment is prescribed in the form of hemostatic agents (vicasol, etamsylate, tranexam, aminocaproic acid) and agents that strengthen the walls of blood vessels (ascorutin, ascorbic acid, ascocin).
To improve hemoglobin levels, iron deficiency anemia is treated.
In addition to the basic treatment, plant-based folk remedies can also be used:
- two tablespoons of a mixture of equal parts of yarrow, shepherd's purse, horsetail, groundsel, white damselfish, and bedstraw are brewed in one liter of boiling water and taken up to five times a day, 2/3 cup;
- It will be effective to use an infusion of rose hips;
- It is useful to include cabbage, lettuce and spinach leaves, and fresh cucumber in the menu.
Pain when urinating due to chlamydia
Pain and itching in the urethra in men sometimes indicate the activity of chlamydia in the body. In this case, transparent discharge (not always), pain in the lower back, scrotum, and groin are observed. Urine may contain purulent threads and blood. Sometimes the body temperature rises.
Chlamydia quickly adapts to antibiotics, so self-medication is unacceptable, since then the course prescribed by the doctor may be ineffective. If you contact a specialist in a timely manner, treatment takes about 2 weeks if the medications are selected correctly. Not only pain and burning when urinating go away, but also discomfort in the digestive system and joints, since chlamydia can develop active activity in all organs.
Diagnostic methods
Many provoking factors influence the appearance of itching in the genital area. Therefore, it will not be possible to turn to a specific specialist for recommendations. A urologist, andrologist, venereologist, oncologist and nephrologist help eliminate problems affecting the urethra. When the examination is carried out, the patient is prescribed certain diagnostic measures:
- urethral smear for bacterial culture;
- microscopic diagnosis of discharge;
- General and biochemical analysis of blood and urine;
- detection of the presence of antibodies inside the body.
After conducting a comprehensive diagnosis, it is possible to eliminate the original cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Pain in the urethra with trichomoniasis
Trichomonas are protozoan parasites. In the male body, the favorite habitat is the prostate gland and seminal vesicles. Trichomonas are transmitted through unprotected sexual contact.
Main symptoms:
- burning in the urethra;
- discharge appears in men, periodically mixed with pus;
- sudden need to urinate after waking up;
- hematuria.
The burning starts to get stronger after drinking alcohol. With trichomoniasis, not only pain during urination is characteristic. Men periodically experience nagging pain in the head of the penis; ulcers and abrasions may appear. In severe forms of the disease, the penis increases in size, takes on a pear-shaped shape, and the head is completely hidden by swelling. Pain when urinating in men is of a burning nature. In 15% of cases, the course of the disease is complicated by epididymitis.
Trichomonas in the male body settle in the prostate gland and are transmitted through unprotected sexual contact
Trichomonas poison the host's body with their metabolic products, attracting additional pathogens. Characterized by high mobility, parasites are able to transfer the bacterial pathogen to the kidneys and even the abdominal cavity. Constant burning and itching in the urethra in men are associated with the active activity of these microorganisms. Without treatment, trichomoniasis can lead to infertility by affecting sperm motility.
The disease sometimes occurs latently, then there is no pain when urinating, and in the morning a small transparent clot in the form of a drop appears from the urethra. A man may not notice the symptoms for a long time, meanwhile, against the background of trichomoniasis, prostatitis occurs, vision decreases, premature ejaculations become more frequent (after which there is pain in the urethra for a short time).
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female genital tract.
PID occurs when a bacterial infection that starts in the vagina or cervix spreads up into the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries.
- Unpleasant sensations in the urethra in women: causes and what to do
Sometimes the bacteria responsible enters the urethra, which can cause urethral pain.
Other possible symptoms include:
- painful urination
- abnormal vaginal or urethral discharge
- irregular menstrual bleeding
- aching pain in the lower abdomen
- pain during sex
- fever and chills
- nausea and vomiting
PID can cause scarring of the reproductive organs. Left untreated, it can lead to long-term problems including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain.
A doctor will usually prescribe antibiotics for PID. In some cases, a person may need surgery to remove abscesses that result from an infection.
Pain when urinating as a symptom of inflammatory processes in the prostate
A burning sensation when urinating in men often occurs against the background of prostatitis, mainly during the acute phase of the disease. Exacerbation is provoked by infections, hypothermia, weakened immunity.
In addition to pain when urinating, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- discomfort in the testicles, rectum, pain in the penis;
- “pulls” the lower abdomen;
- frequent urge to urinate, little urine is released, hematuria may occur;
- the urethra hurts after sexual intercourse;
- there may be delays in the beginning of urination;
- decreased rate of urination.
Acute prostatitis is often accompanied by fever and weakness. The pain may be paroxysmal, cutting in nature. The pain when urinating radiates to the scrotum, groin, and there is a burning sensation in the rectum area.
Infectious prostatitis is treated with antibiotics. The neglected process will lead to kidney diseases, impotence, cystitis, as well as inflammation of the testicles and their appendages.
Painful urination, as well as severe lower back pain in men, can occur in the presence of stones in the kidneys and lower urinary tract
Urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra. This usually occurs as a result of a bacterial or viral infection.
Symptoms of urethritis include:
- painful or difficult urination
- itching
- discharge containing mucus or pus
There are two types of urethritis, called gonococcal urethritis (GU) and nongonococcal urethritis (NGU).
The same bacteria that cause gonorrhea are responsible for GU, while NGU is usually due to chlamydia. Other causes of NGU:
- other bacterial infections
- viral infections
- penile injury
- urethral stricture, which is a narrowing of the urethra
Antibiotics are the standard treatment for bacterial causes of urethritis. If the underlying cause is a sexually transmitted infection, people should avoid sexual contact until they and any affected partners have completed antibiotic treatment.
Pain when urinating with urolithiasis and nephrolithiasis
Painful urination in men occurs due to the presence of stones in the kidneys and lower urinary tract. Stones are formed due to changes in blood composition, due to metabolic disorders due to diseases such as osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, and thyroid pathologies.
Symptoms:
- severe pain in the lower back, radiating to the ureter, groin area and even legs;
- frequent urination and burning, blood appears;
- blood pressure rises.
Frequent urination in men against the background of urolithiasis leads to severe irritation of the mucous membranes of the urinary tract with stones.
Depending on the condition, treatment can be carried out conservatively - dissolving stones using drugs and special equipment. In case of critical development of the situation, surgical intervention is used.
Additional causes of pain when emptying the bladder
Pain in the groin area
Pain syndrome can be provoked by pathologies of a non-infectious nature. Such pathologies include diseases of gout, tumors, urolithiasis, and lice pubis. The main causes of pathologies are the use of alkaline detergent, soap, condoms with a lubricant, and powders. The painful syndrome is similar to allergic reactions. Sometimes patients experience renal colic, with sharp, acute symptoms radiating to the groin area and genitals. With urolithiasis, renal colic is the most common manifestation.
Sensations of pain are provoked by stones in the bladder or urethral canal. When the bladder is emptied, sand and pebbles are expelled through the urethral canal. This phenomenon injures the mucous layer of the urethra.
Urolithiasis is caused by metabolic disorders.
However, there are also predisposing factors:
- poor nutrition;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary and reproductive system;
- injury;
- gout;
- harmful work.
When a third of the urea at the bottom of the organ is blocked, the symptoms resemble acute cystitis and urethritis.
Burning in the urethra due to cystitis
Pain during urination, as well as a burning sensation in the urethra in men, is observed with the development of cystitis - inflammation of the walls and neck of the bladder. The male body is less susceptible to this disease, and the treatment process is simpler and faster than in women.
The disease can be triggered by hypothermia, stagnation of residual urine due to adenoma or prostatitis, and the spread of infection due to urethritis.
In addition to pain and cutting in the urethra, with cystitis, men often have a fever, discomfort in the lower abdomen, and a frequent urge to urinate. Urine is excreted in small portions, cloudy, and may contain pus or blood. The outside of the urethra becomes red and swollen, and mucous discharge is possible. After urination, the head may hurt and itch, but the symptom of pain persists.
Cystitis is treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor based on test results. Drinking large amounts of herbal teas and fruit drinks helps remove infection from the bladder and urethra, dulling pain in the head and urethra. To relieve pain in the urethra, antispasmodics and analgesics are prescribed.
Pain and discomfort when urinating in men is sometimes a sign of oncological processes in the prostate gland
Anatomy of the male urinary system
The urinary system plays an important role in the body and is responsible for filtering the blood, concentrating urine and removing it to the outside. The overall health of a person depends on the functional ability of the organs included in the urinary system.
These include:
- kidneys,
- pelvis,
- ureters,
- bladder,
- urethra.
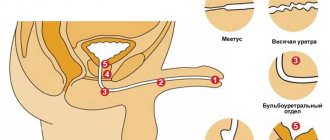
The urethra is a tubular organ through which urine is excreted from the body. The inside of the urethra is covered with mucous membrane, and the outside is supplied with muscle tissue. In men, the urethra is much longer than the female (18-22 cm), this is due to the structure of the genital organs.
The male urethra is divided into three parts:
- prostatic – passes through the prostate, has an internal sphincter and seminal tubercle, which prevents sperm from being thrown into the bladder during ejaculation,
- membranous - the narrowest and shortest part of the urethra, equipped with an external sphincter, responsible for the ability to hold urine,
- spongy - the longest part of the organ, located inside the male penis, has an external opening on the surface of the head, it is in this part of the urethra that all inflammatory processes develop.
Therefore, if a man has pain in the urinary canal, it is necessary to visit a doctor and find out the reason on the basis of which treatment is prescribed.
Pain when urinating due to bladder tuberculosis
Tuberculosis develops in the human body due to mycobacterium Koch bacillus. It penetrates by airborne droplets and spreads through the circulatory system, including the kidneys and urinary tract.
Pain in the urethra in men during urine excretion is one of the main signs of bladder tuberculosis. The urge to urinate becomes frequent, the urine is cloudy, and blood often comes out with the last portion.
Therapy is carried out using anti-tuberculosis drugs, special chemotherapy, and possibly surgery.
Urethral syndrome
Urethral syndrome is inflammation and irritation of the urethra that is not associated with infection.
This type of urethral pain may occur due to irritation or sensitivity to:
- bubble baths and soap
- perfume
- scented sanitary napkins
- sexual intercourse
- condoms
- spermicides
- contraceptive gels
- showers
- chemotherapy
- radiation therapy or radiation
- damage to the urethra
Doctors will advise people with urethral syndrome to avoid suspected irritants. Treatment options may include pain medications and antispasmodics to reduce bladder spasms.
Pain in the urethra is one of the symptoms of prostate cancer
Pain and discomfort when urinating in men is sometimes a sign of oncological processes in the prostate gland. According to statistics, the disease affects men over 60 years of age. As the disease progresses, the urge to urinate becomes more frequent, especially at night, and urinary retention occurs. Cuts and pains in the urethra initially occur only during urination in men, but as the tumor progresses they become constant.
The prostate itself does not hurt, but the nerve pathways extending from it cover the entire pelvic area, so pain may occur in the lower back, sacrum, hips, and scrotum.
If you experience any discomfort, you should consult a specialist without waiting for the symptoms to worsen. The end in such cases is sad.
A burning sensation in the urethra in young and older men can be a harmless symptom caused by irritation of the mucous membranes by spicy food or alcohol. Painful and impaired urination in men can occur after prostate and bladder surgery. But for such reasons, symptoms tend to decrease. Currently, diagnosis is carried out quickly, so you should not neglect a visit to the doctor.
Diseases of the urinary system
Pain in the urethra in men occurs for various reasons. This phenomenon is only a symptom of some pathology in the genitourinary system. Only a specialist can determine the causes of the disease. Timely treatment of the disease will help eliminate pain and maintain sexual function. If the symptom is ignored for a long time, the pathology can become chronic.
Structure of the urinary system
To understand the sources of pain, you need to know the structure of the urinary system. It includes the following organs:
- Bladder;
- Output channels;
- Sphincters;
- Urethral canal.
The urinary system consists of organs and tissues. The genital organs are directly connected to the urinary organs. The reproductive system includes organs such as: testicles, prostate gland, vas deferens. The urethra has an outlet into the urethra, just like the vas deferens. Any pathology in these organs causes inflammation, the symptom of which is pain.
Causes of the unpleasant symptom
Inflammatory processes of various etiologies very often occur in the pelvic organs. Inflammation can occur due to infection with a pathogenic microorganism. There is a specific microflora in the urethra.
Under the influence of various factors, atypical microorganisms appear in it. They destroy beneficial bacteria and take their place. Prolonged presence of pathogenic flora causes necrosis of the tissues of the urethra.
The decomposition process causes pain.
The most dangerous are microbes that cause sexually transmitted pathologies. These bacteria include:
- Chlamydia;
- Gordenellas;
- Staphylococcus;
- Mycoplasmas;
- Ureoplasma.
Sexually transmitted diseases affect the appearance of many unpleasant symptoms. A man experiences pain in the urethra, impurities are found in the urine, and various tumors may appear. All pathogenic bacilli can be detected in the laboratory by culture of a smear from the urethra. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor.
Injuries to the internal and external genitalia are also the cause of pain in the urethra. Compression of the soft tissues of the penis causes severe pain and discomfort for the man. Various wounds can become a source of infection of the genitourinary system. In case of any injury to the genital organs, the patient should immediately contact a urologist to exclude pathologies.
Inflammatory processes in the urethra also occur due to a decline in immunity. The general condition of the body at this moment is weakened. The body is easily susceptible to pathogenic microorganisms. For any type of pain, the cause must be determined by a urologist. Self-treatment leads to worsening of the problem.
Signs of pathology
A patient experiencing pain pays attention to the appearance of other symptoms. These symptoms include the following:
- Difficulty urinating;
- Decreased potency;
- Irritability;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Frequent trips to the toilet;
- Sometimes itching occurs;
- Allergic rashes on the genitals.
When collecting anamnesis, the doctor determines what additional symptoms arose along with pain in the urethra. A combination of several may indicate that a man has pathologies such as chlamydia, cystitis, urethritis or prostatitis. Next, the patient is sent for a full examination and tests.
Diagnosis of pathology
A man suffering from severe pain must undergo a complete hardware examination. Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to examine the pelvic organs and determine the cause of pain. On the screen, a specialist can note the presence of compactions in tissues, changes in the shape of an organ, or the presence of stones in the bladder.
If no cause is identified, the patient is sent for magnetic resonance imaging. The device allows you to view internal organs in a three-dimensional image. The MRI method reveals pathology.
A man needs to undergo an unpleasant procedure - taking a smear from the urethral canal. Patients experiencing pain are usually afraid of this procedure, but it is necessary. The collected smear is sent to the laboratory for testing.
Specialists isolate microorganisms from the sample. The bacteria are placed in a special cup, where they actively multiply. The grown bacteria are exposed to antibiotic substances.
This method allows you to determine the type of microbe that caused the pain and the drug that can destroy it.
To make a diagnosis, you need to take a detailed blood test. The qualitative and quantitative content of red blood cells, leukocytes and unusual cells is determined in the patient’s blood.
If the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased and a large number of red blood cells are detected, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in a man. Some patients have pathogenic cells in their blood.
Such cells cause viral diseases in the human body. The AIDS and HIV viruses are very dangerous.
After a complete examination, the results are transferred to the attending physician. Using them, he makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Cystitis
Cystitis is often the cause of pain in the urethra. The disease occurs due to various colds. The process of inflammation begins to develop in the bladder and moves into the urethral canal.
With cystitis, urination becomes difficult. The person begins to go to the toilet frequently. Urine is released in droplets, the bladder does not empty completely.
If the patient is diagnosed with cystitis, then treatment is carried out with the help of medications.
Medicines for the treatment of cystitis include three pharmacological groups:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Antibiotic drugs;
- Diuretics.
Cystitis can have two main forms. The disease occurs in chronic or acute form. Chronic cystitis occurs unnoticed by the patient; the symptom is a rare cutting pain in the urethral canal. The treatment is long-term.
In the first stages, painkillers are added to therapy. The acute form of cystitis is accompanied by constant cutting pain and fever. Some men experience a rise in body temperature.
Treatment of acute pathology must be carried out in a hospital setting under medical supervision.
Urethritis
Pathology occurs due to bacteria unusual for the urethra. It is often possible to detect the presence of staphylococcus in the microflora. The bacterium causes inflammation along the entire length of the urinary tract. Treatment includes antibiotic and antimicrobial drugs.
The usual treatment regimen is carried out for 5–7 days. The patient is prescribed an antimicrobial drug, metronidazole, and antibiotics. Antibiotic drugs are selected based on the sensitivity of microorganisms. Staphylococcus is not immediately treatable.
In this case, levofloxacin is more effective. The drug has high absorption and rapid action. The action of the substance is to disrupt the integrity of the membranes of pathogenic cells. A destroyed cell wall leads to its death.
Urethritis causes nagging pain in the groin and penis. The pain is concentrated in the urethral ring and the sphincter of the bladder.
Prostatitis
Prostate adenoma appears for various reasons. Prostatitis can be infectious or non-infectious. Inflammation occurs in the prostate gland.
The walls and soft tissues of the prostate enlarge and thicken. Complex forms of pathology lead to changes in the shape of the prostate gland. The prostate has a connection with the urethra.
If pathology occurs in it, the patient experiences pain when urinating.
Treatment of pathology depends on the type and type of disease. The treatment is complex. There are three methods of therapy:
- Medication;
- Operating;
- Massage.
Surgery is prescribed for patients with severe forms of the disease. The pain spreads to all organs of the genitourinary system. The most famous surgical procedure is resection. Pathogenic tissues are removed through the urethral canal without an incision in the abdominal area.
Drug therapy is selected by a specialist. Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis. Chronic nonbacterial forms can be treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Other types of prostatitis require treatment with antibiotics.
Pain in the urethra may disappear under the influence of analgesics. Long-term use of painkillers blurs the picture of the disease. The patient's sensitivity to the active substance decreases and a stronger drug has to be selected.
The genitourinary system requires special attention from men. Pain and difficulty urinating are reasons to consult a doctor.
Source: https://DoktorSos.com/zabolevaniya/urologiya/bol-v-mocheispuskatelnom-kanale-u-muzhchin.html
Diagnostic measures
An alarming symptom is an increase in the urge and pain when urinating. This phenomenon requires research to identify the causes. A complicated manifestation is considered to be the phenomenon when urine is released after urination or its spontaneous release occurs in a sitting position. Depending on the nature of the disease, accompanying symptoms are identified. The pathology can develop without pain or with a painful symptom. Body temperature indicates the presence of inflammatory reactions.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out. General urine and blood tests and their biochemical examination are considered mandatory. Urethral swabs provide important information. The most common instrumental method is ultrasound of the kidneys, bladder, and urinary canals. Urethroscopy is performed. The presence of stones and tumors is detected by radiography. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, computed tomography is provided.
Traditional medicine recipes
Although medications are effective in treating burning sensation, it is important to remember about traditional medicine. One of the well-known remedies is parsley. You need to take 150 g of crushed plant roots, pour 1 liter of boiling water and put on low heat for half an hour. After time, strain, drink 50 g up to 5 times a day.
It is quite popular to treat chronic prostatitis with pumpkin seeds. To do this, grind them in a coffee grinder, consume 100 g of powder per day, washed down with water, to which you can add 2 teaspoons of honey. It is recommended to take it for a year to achieve the desired result.
It is useful to use garlic to treat prostatitis. You need to take 5 cloves, pour 2 cups of boiling water over them, leave for 12 hours, strain and drink 1 tbsp. l. 2 times a day before meals. The course is 30 days.
Propolis is often used in the treatment of prostatitis. It has anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic properties. To prepare the extract, you need to evaporate 40 g of propolis in 200 g of medical alcohol. Then take 0.1 extract and mix with 2 g of cocoa butter. From the resulting mixture you need to form a candle. It must be carefully inserted into the rectum overnight. The course of treatment with propolis suppositories is 30 days. Then you need to take a break for 1 month and then repeat the treatment.
Onions have a healing effect for prostatitis. It is necessary to grind the onion seeds, then mix them in equal proportions with honey. Use the resulting product 1 tsp. 3 times a day.
It is useful to combine honey with white wine. To prepare a miracle remedy, you need to take 1 glass of grated onion and half a liter of white wine, mix, then add 1 tbsp. l. natural honey. Infuse the mixture for 1 week. Take 3 tsp. before eating.
If a man has kidney stones, the disease should be treated with oat tincture. To prepare it you will need 250 g of green oat grass and half a liter of vodka, mix both components and leave for 3 weeks in a dark place. The product must be consumed 3 times a day before meals, 30 drops, diluted in 50 g of water.
If in men it is caused by a large number of uric acid salt crystals, then it is necessary to adjust your diet. From the diet you should exclude fried and smoked foods, salted and pickled dishes, alcoholic drinks, meat and fish soups, coffee and tea, replace them with natural fruit drinks, compotes and freshly squeezed juices.
Treating kidney stones can be not only beneficial, but also delicious. For example, it is useful to use strawberry jam. It is important to remember that you cannot add sugar to it. You need to take the treat half an hour before meals, 1 tsp. It is recommended to gradually increase the dose. The course lasts 8 days. Then you need to undergo an ultrasound examination.
Quite often, a burning sensation when urinating occurs due to urethritis. It is an infectious-inflammatory pathology in men. For this disease, it is necessary to include berries, parsley, onions, and vegetable oils in the diet. It is useful to eat cranberry juice and black currants.
Pain associated with the digestive organs
Pain in the lower abdomen in men can cause not only the loops of the small and large intestines located here, but also neighboring organs by spreading.
Crohn's disease
The cause is unknown, but the granulomatous nature of the inflammation has been studied. Pathology develops in any part of the intestine, in the stomach. It affects the wall through and through, causing ulcers, cracks, scars, fistulous tracts between organs, and suppurative abscesses. Has a relapsing course.
- burdened heredity;
- smoking and alcoholism;
- infectious diseases;
- decline in immunity.
Characteristics of the pain syndrome: constant distension in the lower abdomen when the lower intestinal loops are affected, intensified after eating or excitement. In addition, there are: loose stools ten or more times a day, flatulence, loss of appetite and weight loss, nausea and vomiting, moderate fever, weakness.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Considered a functional disorder. The reason is associated with the body’s special reaction to stress. Predisposing factors are: non-compliance with food intake, frequent long breaks, lack of fiber in foods, low physical activity, hormonal changes, dysbacteriosis.
The main symptom is severe spasmodic pain along the intestines, stool disorder is manifested by diarrhea or prolonged constipation. The stomach is constantly bloated. Patients are concerned about the feeling of a full intestine.
Appendicitis
A paroxysmal disease associated with inflammation of the appendix. It may be caused by:
- prolonged constipation;
- chronic diseases of the abdominal organs with cicatricial adhesions and the formation of appendicular adhesions;
- some infectious diseases (typhoid fever, tuberculosis);
- abdominal trauma;
- abnormal structure of the process;
- blockage of the outlet with rough food (seeds, nuts).
Pain occurs first in the stomach area, accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting. After 2–3 hours, the pain moves to the right iliac region and intensifies. There is irradiation to the back, anus, and upward. The patient experiences diarrhea or constipation. The abdominal muscles are locally tense.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis
An unclear disease of the large intestine, accompanied by damage to the mucous membrane. Predisposing factors are considered: heredity, nicotine intoxication, exposure to antibacterial agents, low immunity. The pain is cramping in nature and intensifies after eating.
- frequent loose stools mixed with pus, mucus and blood;
- intestinal bleeding;
- temperature rises;
- appetite and weight decrease;
- weakness is growing.
Diverticulosis
The pathology is characterized by the formation of saccular protrusions from the intestinal wall. Risk factors: lack of water and fiber in the diet, low physical activity, excess weight, tendency to constipation, developmental abnormalities, impaired intestinal circulation, loss of wall tone in old age. Spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen on the left occurs due to inflammation of the diverticula. The clinical picture of intestinal obstruction develops.
Inguinal hernia
Forms in a weak area of the tendon of the muscle wall. Here, intestinal loops protrude into the hernial orifice. The disease is provoked by heavy lifting, obesity, constipation, and ascites.
First, the patient experiences a tingling sensation at the site of the hernial orifice. Then he learns to adjust the fallen “bag” on his own. The most serious complication is strangulation: a section of the intestine falls out, but the hernial ring contracts and does not allow it to return to its place. There is a sharp pain in the groin area at the site of the hernia, vomiting, and constipation.
Colon cancer
The formation most often affects the sigmoid and rectum. The causes can be considered any of the above diseases and nutritional disorders. The important thing is that cancer does not appear at an early stage. As the tumor grows, the following are observed:
- constant dull pain in the left iliac region and side;
- constipation;
- flatulence;
- elevated temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- paleness of the patient.
How is diagnostics carried out?
If the patient suffers from acute pain, he is completely examined using machines. Using ultrasound diagnostics, the area in the pelvis is examined. The screen will show whether there are stones in the urinary tract, the formation of tissue compactions, or various changes.
If such examination is insufficient, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed. In this case, the internal organs are examined and determined using the MRI method.
The existence of an unpleasant but necessary procedure always causes protest among the male population because of the painful procedure, this is a smear taken from the urethral tube. Microbes are separated from it and placed in a container for active reproduction.
Then they are experimentally destroyed with antibiotic substances to determine the type of bacteria obtained and which of the drugs affects it.
Men and women become infertile. The area in the woman’s genital organ to which the embryo is attached is affected. In men, chlamydia affects sperm, they are not able to fertilize an egg, they become too slow, with an altered structure.
The bacterium is very secretive and detection of the disease as an independent one is impossible; it proceeds in a hidden mode, masquerading in other diseases that arose due to the penetration of chlamydia into the body.
Beginning pain in the ureters forces you to consult a doctor. Even in this case, it is difficult to detect such bacteria; they reliably protect themselves by hiding. They cannot be detected using conventional tests.
Because of these microbes, cystitis, prostatitis, burning and itching of the genitals are provoked, and it is painful to empty the bladder.
Therefore, it is important, as soon as you feel the listed symptoms, go to a urology office, where they will prescribe the necessary examination. Since the cunning of chlamydia lies in their ability to settle in an epithelial cell and camouflage with their own, therefore, an analysis cannot determine it and promptly begin treatment for this particular disease, and not in combination with newly acquired ones.
Improvements in technology have made it possible to identify them as follows:
- take smears from the uterus, vagina, urethra
- extract a drop of secretion from the male prostate glands
- anti-chlamydial antibodies are looked for in the blood using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- carry out polymerase chain reaction
Since at the initial stage of penetration of microbes, there is usually no need to see a doctor, chlamydia quickly invades the walls of many organs, so the disease is treated in a complex and long-term manner. Only the strongest antibiotics are used, in an attempt to destroy the pathogenic microorganism along with the complications resulting from it.
Why is regular preventive examination necessary?
To identify each of these diseases, not only an examination is required, but also tests, laboratory tests and other procedures.
Regular examination of the urinary canal is required even when there are no visible signs of any disease. This must be done for the reason that most genitourinary infections do not manifest themselves at all at the very beginning, but as the disease progresses, the patient’s condition may subsequently worsen sharply. Preventive examinations make it possible to prevent many diseases even before they become complex. Waiting time for artificial sphincter placement. Unfortunately, patients must wait long enough to ensure that the urethra is completely healed. This is approximately three months after the catheters are removed from urethral surgery. Then another operation is performed to install an artificial sphincter around the urethra.
Your surgeon can talk with you about using hyperbaric oxygen. These treatments last about one to two hours and are usually performed once a day. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment can improve damage around scar tissue and may make surgery more successful.
If you ignore pain in the urinary canal in men, sooner or later the disease will become chronic and may lead to other disorders of the genitourinary system. Without treatment, even minor painful symptoms can turn into serious health problems, and even lead to erectile dysfunction, prostatitis or infertility.
Treatment with folk remedies
Unfortunately, hyperbaric oxygen treatment will not cure the stricture.
Not all locations have a hyperbaric oxygen treatment center, and in patients where this is not possible, surgery may be successful. Another thing your surgeon may recommend is to place a piece of muscle from your inner thigh under the surgical area. This can result in increased blood supply to the surgical area and protect the area from the complications of very slow healing. Will this operation really work? The results of this type of surgery are not as good as urethral surgery, which is done without radiation damage, but we have gotten this surgery to work well for many patients. Many patients come to us believing that nothing can be done because of the information they have been given about radiation damage. We can usually find some plan that will improve the patient's quality of life, even if the radiation damage is severe.
Treatment regimens
The main types of urethral diseases and their treatment. A common disease that affects the urethra is chlamydia, which is considered a sexually transmitted disease. Chlamydia begins to affect the genitals and the canal through which the urethra is excreted. Chlamydia needs to be treated urgently to prevent complications from developing. Sometimes infertility may develop.
Treatment is complex, so medications are prescribed for both men and women. After completing the course, tests are required and repeated after a month.
Gonorrhea is an infection that is caused by gonococci and is sexually transmitted. Organs affected are:
- urethra;
- epithelium;
- genitourinary organs;
- lower part of the rectum.
Treated with antibiotics to block the spread of infection. For simple forms and initial stages, etiotropic treatment will be sufficient. It is much more difficult and problematic to deal with more advanced forms, so therapy is complex and includes etiological and pathogenetic drugs. It often hurts during urination, which is typical for urolithiasis and urethritis.
The occurrence of stones in the genitourinary system is provoked by a complex of factors and affects all age groups. With this pathology, pain occurs in the following areas:
- underbelly;
- crotch;
- genitals.
Often the pain becomes intense when a person begins to walk, especially quickly. Other symptoms of stones in the urethra include a constant urge to go to the toilet and the need to empty the urethra. Such urges can appear when a man walks or engages in physical labor. A characteristic sign of the disease is a sudden interruption of the stream, although the bladder has not yet been completely emptied.
Urination occurs again if you change your body position. If the stones are large, then you can only go to the toilet while lying down. There are three types of treatment:
- surgical;
- conservative;
- instrumental.
Urethritis refers to inflammatory diseases when pain appears at the end of urination. The pain is constant or periodic. If an acute form of urethritis is diagnosed, the pain will be sharp, sometimes very painful, and in case of chronic urethritis, a burning sensation appears, and other symptoms are not so intense.
The most common symptoms of urethritis are infection and discharge. The presence of such signs should be a reason to consult a urologist for advice, since prostatitis may develop. Treatment is not general for all patients, but is exclusively individual.
Cystitis
A burning sensation during urination is characteristic of cystitis, an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the bladder. Although this disease is more familiar to the female population, it also occurs among the stronger sex. Cystitis is suspected if a person complains of frequent painful urination, pain in the lower abdomen and dark urine.
With the development of STDs (gonorrhea, herpes, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis), painful urination is combined with signs of sexually transmitted diseases. Gonorrhea is characterized by mucous or mucopurulent copious discharge, in men - from the urethra, in women - from the urethra and vagina; with herpes and trichomoniasis, severe itching and swelling of the genital organs is felt, but the discharge is scanty, in men it is in the form of a drop. The diagnosis is confirmed by PCR.
Oncological neoplasms
Pain in the urethra in men may indicate the appearance of malignant neoplasms. A cancerous tumor can have different locations in the urinary system. The most common are such severe pathologies as kidney adenocarcinoma and renal cell carcinoma, cancer of the ureters and bladder. The most common causes of the disease are smoking, urolithiasis, parasitic infections (especially schistosomiasis).
The tumor blocks the urinary tract, which causes pain. Specific oncological symptoms appear - sudden weight loss, general weakness, nausea, persistently elevated body temperature.
Diseases of the genital organs
Pain during urination occurs with the development of diseases of the male reproductive system, most often the prostate gland:
- BPH . It is a benign formation that can block the urethral canal at the entrance to the bladder.
- Prostatitis . This very common disease in men over 45-50 years old causes swelling of the prostate gland, and an increase in its size contributes to blocking the urinary canal. Most often, the pathology is bacterial in nature and develops as an inflammatory process.
- Prostate cancer . Lack of treatment for prostatic pathologies leads to malignancy of the process. The appearance of a tumor leads to blockage of the urinary canal, resulting in pain when urinating.
- Inflammation of the epididymis is also characterized by signs of difficulty urinating. Epididymitis and orchitis are particularly prominent. No less pronounced symptoms are observed in other specific male inflammatory pathologies: balanitis, balanoposthitis.
- Sexually transmitted diseases . Cramps are observed with candidiasis, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
When should you contact a urologist?
Why a urologist? This doctor specializes in pathologies of the genitourinary system. He treats not only the stronger half of humanity. He is consulted regarding sexually transmitted diseases and ailments related to the prostate gland. It helps to diagnose pathologies of adjacent organs when it is unclear why the lower abdomen hurts.
A urologist is consulted for:
- Getting advice.
- Preventive examination.
- Confirming or eliminating doubts about a urological disease.
- Treatment of intimate pathologies.
A visit to a urologist is necessary if:
- Pain, bloody discharge, pus and burning sensation when urinating.
- Urine incontinence.
- Frequent visits to the toilet.
Timely assistance from a specialist guarantees the patient’s complete recovery. Inflammation is much easier to treat at an early stage. In extreme cases, surgery is performed.
Urolithiasis disease
Mechanical problems for the passage of urine are created when salt formations (stones) of different compositions are deposited on the walls of the canals. Urolithiasis can be provoked by metabolic disorders, certain infectious lesions, excess cholesterol, poor diet, and vascular pathologies.
The most characteristic signs of the disease:
- pain syndrome (sharp - in the acute form of the disease, aching - in the chronic form);
- a noticeable decrease in the volume of urine excreted against the background of an increase in the unproductive urge to urinate;
- the appearance of sand in the urine;
- possible blood impurities.
The pain is most often localized in the area of the ureter (lumbar region), but can radiate to the thigh, groin, and genitals.
The most dangerous option is when large stones completely block the urinary canal. Urination stops completely, which is manifested by attacks of severe pain and can lead to serious consequences. In such cases, surgical intervention is necessary.