What causes discomfort
Cutting pain in the male urethra, as well as in the female one, has the same causes. Gender variety has virtually no effect on differences in the factors causing symptoms.
Usually this:
Pain in the urethra
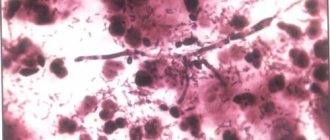
- The inflammatory process of the urinary tract is urethritis of a nonspecific nature. The disease can be caused by enterococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, staphylococcus, Klebsiella, and pathogenic fungi.
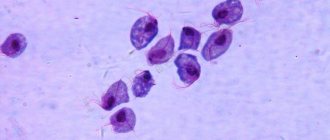
- Infected specific flora - mycoplasmosis, trichomonas, gonococcus, chlamydia.
- Injury during a medical examination (instrumental examination of the urethra).
- Radiation or toxic intoxication.
- Weakened immunity.
All these reasons provoke pathologies in the urethral tissues with the occurrence of focal inflammation.
The female urethra is an order of magnitude shorter, but wider than the male urethral canal. In women, this pathology is more common.
Cutting pain in the urethra in men occurs due to the presence of several causes. For example, when catheterization was performed on a patient with a weakened immune system.
The urethral canal may hurt after stone formations pass through it.
Preventive recommendations
To reduce the risk of developing diseases, a symptom of which may be pain when urinating, men need to follow some recommendations.
Helpful Tips:
- eat right, exclude “heavy” foods and alcohol;
- avoid hypothermia;
- do not be stressed;
- exercise moderately;
- drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day;
- avoid promiscuity, use condoms;
- Conduct a preventive examination of the genitourinary area several times a year.
The etiology of pain when urinating can be varied. If an unpleasant phenomenon occurs, a man should immediately contact a specialized specialist and carry out a diagnosis. A disease, the symptom of which is pain or pain during urination, will not go away on its own. A neglected pathological process will ultimately lead to serious consequences, which can be very difficult to eliminate.
Find out more about the probable causes of pain when urinating in men after watching the following video:
Etiology of the disease urethritis
Reasons for this symptomatology
Often, pain in the urethra occurs during an inflammatory process. There are infectious and non-infectious pathologies. Infectious urethritis can be caused by cocci, fungus, gonococcus, Escherichia coli, mycoplasmosis, and chlamydia.
The disease can be secondary or primary. Secondary pathology can be provoked by other diseases (cystitis, prostatitis, vesiculitis). Since the female urethral canal is shorter and wider, microorganisms multiply there less easily.
Female pathology has a number of causes:
- catheterization;
- infection through unprotected sexual contact;
- poor quality hygiene procedures;
- irritation of the mucous membrane after gels, soaps;
- microbes that have penetrated from neighboring organs.
Symptoms of acute urethritis include:
- pain in the urinary duct when excreting urine;
- inflammation;
- redness;
- traces of pus in the urine;
- itching;
- burning sensations;
- Sometimes there is a discharge of secretion with pus.
Inflammatory process of the bladder
When the urethra hurts in females and males, this indicates inflammation of the bladder. Harmful bacteria penetrate the urethra, blood, and lymph. Most often this agent is Escherichia coli.
The urinary tract can become inflamed for several reasons:
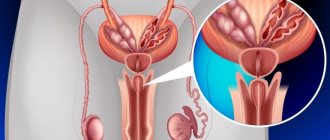
Anatomy of the genitourinary system
- hypothermia;
- chronic infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- pathologies of the urinary mucosa;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pathological failure of the central nervous system;
- medical procedures (catheterization, cystoscopy);
- chemical intoxication of the body;
- frequent colds, respiratory diseases;
- impaired microcirculation;
- physical inactivity;
Acute cystitis at a young age can be triggered by neglect of the rules of intimate and hygienic procedures. In acute cystitis, pain occurs when urinating, frequent urge to go to the toilet (25-30 times), and a painful sensation in the pubic area. Unpleasant symptoms most often appear after sexual intercourse. A spasmodic sphincter and severe pain reflexively stop urination.
Treatment
Treatment methods are chosen depending on test results. If an infection is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. The causative agent is often a nonspecific infection, which is detected during bacterial culture, and this analysis can take more than a week. If the prescribed antibiotic does not relieve the symptoms, then after obtaining the culture result, the drugs are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the identified pathogen to them.
Medicinal and minimally invasive surgical techniques are used to remove stones from the kidneys and bladder.
Pudendal neuropathy is treated with muscle relaxants, vitamins, physical therapy, and anticonvulsants.
In some cases, idiopathic (according to test results) burning sensation, which torments for months, can be eliminated by taking a uroantiseptic called Furagin (a tablet three times a day for a week) plus Lomexin cream 2 times a day for 10 days.
Furagin is an antibacterial drug used for acute and chronic urinary tract infections: pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis. Price in pharmacies from 136 rubles.
How to relieve pain
The burning sensation when urinating can be dulled with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Ketorol. These products are more effective in the form of suppositories (the active substances will enter the pelvic bloodstream faster).
If it is not possible to see a doctor, and the pain is very severe, then you can buy Fitolysin paste at the pharmacy. This is a herbal medicine that effectively relieves inflammation in the genitourinary organs. As a last resort, you can purchase Monural. This is a fairly strong antibiotic, active against a wide range of nonspecific infections that cause burning in the urethra. It can help with infection with E. coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus. The drug is powerless against fungus. Flucostat and Fluconazole may help. As a last resort, douching with a weak soda solution.
Phytolysin is a combined herbal preparation that has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effect. Price in pharmacies from 398 rubles.
If there is no pharmacy nearby, then you can use available antiseptics: Miramistin, chlorhexidine, a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Among the folk remedies, you can try douching the urethra with a decoction of chamomile, sage, diluted aloe juice, and strong green tea. To do this, you can use a syringe without a needle.
The above methods, except for painkillers, are used only in extreme cases before taking tests. If you have a burning sensation in the urethra, you should immediately go to a urologist or a private laboratory. After independent manipulations, the test results will be blurry.
Diet
A diet will help prevent increased burning during treatment. Basic principles:
- Avoid alcohol, strong tea, coffee, spicy foods;
- Minimum marinade, smoked meats, pickles;
- More water, compotes, fruit drinks, herbal teas.
Alcohol itself can provoke a burning sensation, since its consumption reduces immunity and activates hidden infections.
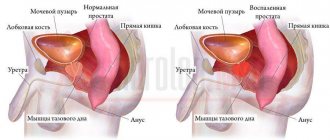
Pain due to inflammation of the prostate
A painful syndrome in the urethral canal warns of prostatitis. This is the most common disease among the male population. Most often, the pathology haunts men aged 28-47 years. Often, due to untimely treatment, the disease changes from an acute form to a chronic one.
Acute catarrhal process has a milder course. It causes painful urination, frequent urges, especially at night, and a feeling of heaviness in the perineum.
Follicular prostatitis is caused by difficulty urinating, pain during defecation, elevated body temperature, pain in the perineum, radiating to the genitals and anus.
In a difficult situation, acute urine retention occurs and the general condition worsens. In acute prostatitis, pain appears in the urethral canal. An outbreak of prostatitis in men is possible against the background of the impossibility of regular sexual intercourse for various reasons, unprotected sexual intercourse and intimacy with partners in whom he is not sure, physical inactivity, the use of a catheter, and the presence of cracks in the anal canal.
Diagnostics
If the symptoms described above are detected, you should urgently contact a urologist, he will prescribe tests and diagnostic procedures. To make a correct diagnosis, you should undergo a general analysis and bacterial culture of urine, and perform an ultrasound of all organs of the excretory system, including the prostate gland. A urogenital urethral swab may be needed to identify hidden infections.
To find out why the bladder hurts in men, sometimes the inner lining of the organ is examined using cystoscopy. The examination is carried out using a flexible, long optical device, which is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. A system of optical fibers and lenses on the device transmits the image to a computer.
Through a cystoscope, if necessary, medications are administered, a biopsy is performed, polyps are removed, and various therapeutic and diagnostic procedures are performed.
Additional causes of pain when emptying the bladder
Pain in the groin area
Pain syndrome can be provoked by pathologies of a non-infectious nature. Such pathologies include diseases of gout, tumors, urolithiasis, and lice pubis. The main causes of pathologies are the use of alkaline detergent, soap, condoms with a lubricant, and powders. The painful syndrome is similar to allergic reactions. Sometimes patients experience renal colic, with sharp, acute symptoms radiating to the groin area and genitals. With urolithiasis, renal colic is the most common manifestation.
Sensations of pain are provoked by stones in the bladder or urethral canal. When the bladder is emptied, sand and pebbles are expelled through the urethral canal. This phenomenon injures the mucous layer of the urethra.
Urolithiasis is caused by metabolic disorders.
However, there are also predisposing factors:
- poor nutrition;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary and reproductive system;
- injury;
- gout;
- harmful work.
When a third of the urea at the bottom of the organ is blocked, the symptoms resemble acute cystitis and urethritis.
Inflammation of the bladder mucosa
Cystitis, i.e. inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder, usually causes problems with urination of the second type, since it is most often caused by an infectious lesion. The disease can develop in acute or chronic form. The following symptoms are characteristic of the exacerbation period:
- frequent urination;
- pain localized in the lower abdomen;
- pain and burning when urinating;
- turbidity of urine and the appearance of blood impurities in it;
- general weakness;
- sometimes - an increase in temperature.