Hypothermia or hypothermia can cause a lot of negative consequences for the human body. One of the most dangerous complications is kidney problems. In most cases, renal hypothermia creates the preconditions for the formation of serious diseases of this organ, the most famous of which are considered to be pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
Why do my kidneys hurt after hypothermia? What are the symptoms of this problem? How to detect it in time? How effective is home treatment for pathology? You will read about this and much more in our article.
Causes and conditions of kidney hypothermia
Hypothermia of the kidneys cannot occur just like that - it requires certain prerequisites, which together predetermine both hypothermia of the body as a whole and negative consequences for this organ in particular.
The main factors that increase heat loss in people:
- Environment. The predetermining cause of most diagnosed hypothermia. The main role here is played by low temperatures - the stronger the cold, the more intense the heat exchange between the environment and the body, as a result of which the latter cannot compensate for heat loss and begins to cool significantly. Additional factors include wind and humidity. The first one directly “blows away” from the surface of the skin a layer of relatively still air heated by the body, while the second one predetermines the speed of this process, acting as a kind of “conductor”. In some cases, additional weather conditions may play a dominant role in the mechanism of formation of pathology: cases of hypothermia are often diagnosed even at positive air temperatures, but strong wind and humidity, especially in early spring and late autumn;
- Wardrobe . Properly selected clothing and shoes significantly slow down the body's heat loss, allowing you to be outdoors even in very severe frosts without harm to your health. Wardrobe requirements include high-quality natural materials, a comfortable fit, sufficient length and functional style, the presence of several layers of clothing, as well as separate shoes - the latter should not be tight or have thin soles. If your wardrobe is poorly chosen and out of season, then the chances of catching a cold in your kidneys increase tenfold;
- Diseases, syndromes and pathologies . Internal problems with the body - diseases, pathologies and syndromes - can play a certain negative role in the mechanism of formation of kidney hypothermia. This process is facilitated by bleeding, cardiovascular problems, skin diseases, alcohol intoxication, trauma, cachexia, hypothyroidism, diabetes, Addison's disease and much more.
Basics of Ayurveda
The concept of “Ayurveda” is defined as a combination of sciences with the philosophy of Indian dualism - Samkhya. Ayurvedic treatment is practiced by Buddhists, Hindus, Jains and Sikhs. Proponents of this method claim the following: “A person accumulates toxic and poisonous substances in the body throughout his entire life. They accumulate even in the body and mind, leading to negative emotions that negatively affect the organs inside a person. For example, severe fear experienced is reflected in renal functioning; the organ stops fully performing its job. Anger worsens the performance of the liver and digestive system. This leads to the fact that incompletely processed food appears in the body, which pollutes the body, gradually leading to its destruction.
An unconventional method of treatment - Ayurveda divides human ailments into the following types:
- occurring seasonally;
- inherited;
- resulting from acquired injuries;
- natural;
- natural;
- formed as a result of an infectious lesion;
- differing in the individual morphological and functional characteristics of the organism.
- laboratory research;
- visual examination of the patient;
- general examination.
Laboratory tests in Ayurveda help to correctly diagnose the disease.
Ayurvedic medicine considers the most important diagnostic process, during which the true cause of the disease is determined. Only with correct diagnosis is it possible to heal and prevent the appearance of other ailments that may appear in the future. Ayurvedic diagnostics include:
Return to contents
Symptoms and degrees of hypothermia
Hypothermia of the kidneys does not have any clear specific symptoms, since it directly depends on the degree of hypothermia and the presence of additional negative factors that predetermine the development of side complications.
Manifestations of kidney hypothermia can be diagnosed only during the reactive period after the body has warmed up.
In the vast majority of cases, hypothermia of the organ leads to the start of an inflammatory process associated with the localization of the pathology.
Degrees of kidney hypothermia:
- Mild degree . Minor risks of kidney inflammation. In most cases, conventional home treatment, active warming procedures, and bed rest are sufficient for the basic symptoms (pulling pain, discomfort in the kidney area) to disappear 3-4 days after the start of the measures;
- Average degree . High risks of the formation of pyelonephritis - an inflammatory process affecting the tubular system of the organ, its parenchyma, pelvis, and calyces. With timely, qualified therapy, the prognosis for recovery is conditionally favorable;
- Severe degree . In most cases, it is accompanied by glomerulonephritis - inflammation of the glomeruli with a parallel increase in negative autoimmune processes. In this case, the pathology can cause both morphological disorders and act as a secondary manifestation of infectious lesions against the background of a significant drop in the level of general and local immunity. The prognosis for recovery is conditionally unfavorable;
- Extremely severe . With extremely severe cold of the kidneys, it is not inflammatory and autoimmune processes that come to the fore, but direct necrosis of soft tissues caused by concomitant contact frostbite of stages 3-4. In this situation, with direct cold damage to the organ, there is practically no chance of complete recovery, regardless of the therapy performed.
Typical nonspecific symptoms of organ hypothermia include the following manifestations:
- Drawing and aching pain in the kidneys in the lumbar region;
- Intoxication of the body, on the 2-3rd day of the reactive period of hypothermia, manifested in the form of chills, fever, nausea, increased sweating, vomiting;
- Persistent urination disorders - frequent urge to urinate, changes in the color of urine (including the appearance of bloody or purulent discharge), discomfort during the procedure, swelling.
Cold diseases
When it is an internal pathogenic factor, cold can cause deterioration in the functions of the spleen, stomach and kidneys
Wind cold: When combined with pathogenic wind, cold attacks the body and lungs, causing chills, lack of sweating, occipital headache (pain at the base of the skull), pain in the upper body, including the shoulders and neck, and a stuffy nose. The influence of wind causes symptoms to appear suddenly and affect the upper body, while cold causes muscles to contract, causing stiffness and pain. A runny nose is another sign of cold. The treatment principle is to repel the wind and dispel the cold with warm diaphoretic herbs, acupuncture and moxibustion.
Obstruction due to cold: Traditionally known as cold obstructions. This is usually body pain or joint pain that goes away after exposure to heat. The most common example of this syndrome is arthritis. Because the syndrome is caused by cold, the affected parts are usually cold to the touch, and the pain is usually worse in cold weather. The principle of Chinese treatment is to apply heat to the acupuncture meridians through which Qi and blood circulate. Moxibustion, acupuncture and herbs are effective.
Cold spleen and stomach. The disorder is caused by external cold causing digestive symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting and watery diarrhea. Although it is usually accompanied by cold-induced or stomach-borne bacteria or viruses (stomach flu), this syndrome can also be caused by eating cold foods such as ice cream.
Treatment first displaces the cold pathogenic factor. It then tonifies the yang aspect of the spleen and kidneys to produce a long-term increase in the body's basal metabolism, or its ability to retain heat necessary for proper digestion, which is known in traditional Chinese medicine as the gateway of life (metabolic) fire. Spleen yang deficiency is treated by cauterization and taking warming herbs that tonify the spleen yang.
Diagnostics
In case of hypothermia of the kidneys, it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis of the body, which is prescribed by a nephrologist, urologist and other specialized specialists to accurately determine the complication that has arisen and identify the formed pathology.
Procedures for diagnosing kidney diseases:
- General urine analysis . Allows you to detect general problems in the functioning of the kidneys based on the indicators of leukocytes, the presence of bacteria in the sample, deterioration in the density of the liquid, its alkaline balance, as well as the presence of foreign impurities in the form of proteins or glucose;
- Analysis according to Nechiporenko . A clarifying laboratory test that evaluates the quantitative indicators of leukocytes, red blood cells and casts;
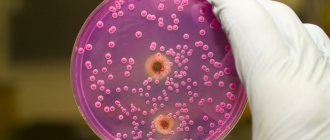
- Bacteriological study of biomaterial . Urine culture to identify pathogens of the inflammatory process;
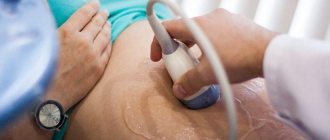
- Ultrasound examination of the organ . Provides comprehensive data on the condition of the organ and is the most reliable way to diagnose kidney problems after hypothermia;
- Excretory urography . An additional technique that visualizes the urinary tract and other related systems;
- CT scan . It is used to identify additional complications after cold of the kidneys and assess the degree of damage to organ tissue.
First aid
If hypothermia of the kidneys is suspected, the victim of hypothermia must be provided with appropriate first aid.
Basic first aid steps for kidney hypothermia:
- Stopping contact with external environmental factors. The person must be transported to a warm and dry room, cold clothes must be removed from him, and warm, clean clothes must be given in return;
- Warming. If the patient feels relatively normal, consciousness and swallowing reflex are preserved, the victim can be given warm drinks and food (with a temperature of no more than 45 degrees). After this, you should perform a warming back massage or lower the person into a bath with water at room temperature, and then gradually increase the water temperature to 40 degrees over the course of 1 hour;
- Thermal insulation. The person must be completely wrapped in a heat-insulating cotton blanket and be provided with bed rest;
- Call a doctor. It is advisable to call a therapist at home for further consultation. In severe forms of cold, you should not wait for a visit from a general specialist - the victim should be taken by ambulance to the nearest multidisciplinary hospital with intensive care, nephrology, and urology departments.
Treatment of kidney hypothermia
Hypothermia of the kidneys with the presence of pronounced negative symptoms and complications is prohibited from being treated at home due to the high risks to the health and life of the patient.
A specific therapeutic regimen for the treatment of kidney inflammation is developed by a nephrologist, urologist and other specialized specialists based on the diagnosis, the presence of additional pathologies and other factors.
Possible treatment methods include taking a number of medications, herbal medicine, and in some cases, surgery.
Classic drugs:
- Antibiotics . Prescribed in the case of a bacterial nature of the inflammatory process after hypothermia, based on the results of laboratory tests that make it possible to identify the causative agent of the infection. Typical representatives are penicillins (Augmentin), cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone), aminoglycosides (Gentamicin), chloramphenicol (Chloramphenicol), tetracyclines (Doxycycline), sulfonamides (Urosulfan), quinolones (Nitroxoline), nitrofurans (Furagin);
- Diuretics . They fight swelling and remove excess fluid from the body. A typical representative is Furosemide;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs . Used to counteract systemic inflammation. Typical representatives are Voltaren, Dexamethasone, Prednisolone;
- Catalysts of renal blood flow . Improves blood circulation in the vascular periphery of the organ. A typical representative is Kurantil;
- Antispasmodics . Relieves spasms of muscle structures and renal colic. Typical representatives are Drotaverine, Spazmalgon, Papaverine;
- Analgesics . Used for severe pain, depending on the intensity of the pain. Typical representatives are Analgin, Ketorolac;
- Immune modulators . Necessary for restoring the immune system, preventing the transition of pathologies to the chronic phase. Typical representatives are Timalin, T-activin;
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
Herbal medicine is not a separate method for treating pathologies that occur when an organ is overcooled, but it can act as an addition to basic conservative therapy, providing a restorative, antiseptic, and antimicrobial effect on the body.
It is recommended to use decoctions, tinctures, compresses based on oats, bearberry, cranberries, birch, calendula, chamomile, and lingonberries.
The use of any folk remedies must be coordinated with your doctor!
Surgical intervention is usually prescribed for severe and extremely severe degrees of renal cold, combined with various complications.
Complications and consequences
Hypothermia of the kidneys can cause a huge number of complications that significantly worsen human health.
Consequences and complications of kidney hypothermia:
- Cystitis . Cystitis;
- Pyelonephritis - inflammation of individual elements of the organ, in particular the pelvis, calyces, parenchyma;
- Apostematous nephritis . Formation of an organ carbuncle and the formation of purulent foci of pathology;
- Glomerulonephritis . Inflammatory damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys;
- Uremia . Systemic autointoxication of the whole body;
- Nephrosclerosis . Replacement of healthy organ structures with connective tissue with impaired kidney function;
- Kidney failure . Acute or chronic condition of an organ in the stage of decompensation;
- Exacerbation of other chronic diseases . Malfunctions of the kidneys entail a significant exacerbation of any third-party chronic diseases present in the body;
- Failure of kidney function . In the absence of qualified and timely treatment, after severe stages of over-coldization of an organ, its transplantation may be required.
Functions of the organ
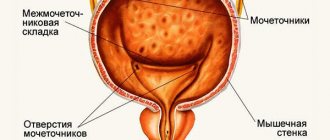
Two small organs, similar in appearance to beans and about the size of a fist, are the initial part of the urinary tract. They are located under the ribs, on either side of the spine.
Blood purification
The kidneys filter about 200 liters of blood every day, removing toxins, acids, chemicals and excess fluid. Waste in the form of urine is sent down the ureters to the bladder, where it is stored until it leaves the body through the urethra.
Blood Pressure Regulation
Kidney tissue, by filtering plasma, controls fluid levels in the body and produces hormones that constrict blood vessels.
Maintaining Bone Health
Organs produce the active form of vitamin D and balance calcium and phosphorus in the body, which makes bones strong.
Stimulation of red blood cell production
The kidneys produce hormones that stimulate the bone marrow to produce red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.