Natalya June 10 at 0:00 —> 4739
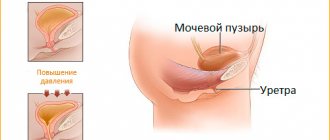
Kidney bleeding and bleeding from the urinary tract are called hematuria
(presence of blood in urine). Sometimes they are significant. Hematuria can be caused by various reasons: kidney injury, kidney infarction, kidney tumor, and can be observed with hemorrhagic diathesis. A small amount of blood in the urine, as a rule, is present in acute and chronic nephritis, arteriosclerosis of the kidney vessels, and sometimes in congestive kidneys. However, this does not require emergency measures to control bleeding and is therefore not described in this section. In cases of severe injuries, patients develop a number of general signs caused by both the severity of the injury and the degree of bleeding: severe general weakness, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, a drop in cardiovascular activity (pulse increases, blood pressure decreases), and copious discharge of bloody urine. .
Treatment
Delay in hospitalization in such cases can lead to the death of the patient from blood loss.
In a hospital setting, the patient should be consulted by a urologist and, if necessary, undergo urgent surgery (up to and including removal of the affected kidney). If he is in a state of shock, then before transporting to the hospital measures should be taken against shock: injections of adrenaline, cardiazol (or cordiamine), camphor, morphine. These measures, carried out urgently, can be limited and then quickly transport the patient to the hospital. If transportation is delayed, more extensive measures to combat shock must be considered and implemented. In addition to those listed, this may include: blood transfusion, injection of large doses of saline solution under the skin, intravenous infusion of glucose, etc. However, these measures should not delay the transportation of the patient, who may be continuing to lose blood, to a surgical hospital. Kidney infarction is characterized by sudden pain in the lumbar region in a patient suffering from circulatory failure. After a few hours, the pain may be followed by hematuria. Kidney infarction in its manifestations often resembles an attack of renal colic. The diagnosis of renal infarction can be facilitated by taking into account the underlying disease (septic endocarditis, heart disease). Such a patient should be sent to the therapeutic department of the hospital, taking into account both the manifestation of renal infarction and the underlying disease. In the presence of symptoms of circulatory failure, the patient must be administered intravenously 0.5 ml of a 0.05% solution of strophanthin. If intravenous infusion is not possible, this amount of strophanthin can be injected intramuscularly into 5-10 ml of saline solution. Cardiazol, cordiamine or camphor are injected under the skin. To calm the pain caused by renal infarction, it is necessary to inject morphine (0.5-1 ml of 1% solution). The patient must be transported in an ambulance accompanied by medical personnel. Hematuria, which seems causeless, can be caused by a malignant kidney tumor. The absence of pain and rapid cessation of bleeding sometimes serves as a reason for complacency for the patient and the doctor. Hematuria may recur many months later. If “unreasonable” hematuria is established, the patient must be urgently referred to a urologist. Detection of a tumor at the first bleeding will make it possible to perform surgery in a timely manner. Acute hematuria may be a manifestation of hemorrhagic diathesis (especially hemorrhagic vasculitis - Henoch-Schönlein disease). Such a patient should be urgently hospitalized, although the initial symptoms of diseases included in the group of hemorrhagic diathesis may not be severe. Hematuria is sometimes caused by a tumor of the bladder or diseases of the urethra. Frequent, painful passage of blood-stained urine may indicate disease in these organs. But if the diagnosis remains unclear, hematuria itself should serve as a serious warning. In these cases, the patient seeking advice should be referred to a urologist. M. G. Abramov Similar articles
- June 10 at 00:00 1739—>
Providing first aid for intestinal bleeding
Bleeding from the small intestine, like bleeding from the stomach and duodenum, is characterized by the appearance of tarry stools, but without bloody vomiting. When bleeding from the sigmoid and rectum, scarlet blood is released with feces.
Cuts and bleeding
- June 10 at 00:00 3064—>
First aid for bleeding from the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
Bleeding from the esophagus is possible when dilated veins of the esophagus rupture, which is observed in atrophic cirrhosis of the liver. The clinical manifestation of such bleeding is profuse bloody vomiting and tarry stools, caused by a large admixture of blood in the stool.
Cuts and bleeding
Last news
Photo gallery
—>
Additional facts
Pulmonary hemorrhage is one of the most dangerous conditions that complicate the course of a wide range of diseases of the bronchopulmonary and cardiovascular systems, diseases of the blood system and hemostasis. Therefore, the problem of providing emergency care for pulmonary hemorrhage is relevant for specialists in the field of pulmonology, phthisiology, oncology, cardiology, hematology, and rheumatology. Delay in carrying out emergency hemostatic measures can cause rapid death of patients. Depending on the severity of blood loss and the condition that caused it, mortality from pulmonary hemorrhage varies from 5-15% to 60-80%. Among patients with pulmonary hemorrhage, elderly people (50-55 years old) with aggravated somatic pathologies predominate.
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Hematuria during pregnancy
During gestation, hematuria may occur, which can occur without significant reasons. The expectant mother is at risk of detecting changes in urine due to: Increased pressure in the abdominal cavity. After the appearance of hormonal imbalance. Child development, which leads to flattening of internal organs. Pathologies inside the renal cavities. Oxygen starvation of the fetus. Placental dysfunction. Weakening of labor forces or premature birth. Postpartum bleeding.
Symptoms of blood in the kidneys
suspect blood in the kidneys by blood in the urine, since blood from the kidneys passes through the ureter into the bladder, and then into the urethra, after which it can already be detected.
Pain and bleeding can also be caused by a stone lodged in the ducts or moving towards the bladder. By irritating the walls of the ducts, it initiates bleeding and unpleasant pain.
Irritation and bleeding can be caused by infection, or if your blood doesn't clot properly because you're taking anticoagulants, for example, bleeding can occur anywhere in the body, including the kidneys.
However, red urine may not always mean blood is leaving the kidneys.
Description
Pulmonary hemorrhage.
A dangerous complication of various respiratory diseases, accompanied by the leakage of blood from the bronchial or pulmonary vessels and its release through the airways. Pulmonary hemorrhage is manifested by a cough with the release of liquid scarlet blood or clots, weakness, dizziness, hypotension, and fainting. For diagnostic purposes in case of pulmonary hemorrhage, pulmonary radiography, tomography, bronchoscopy, bronchography, angiopulmonography, and selective angiography of the bronchial arteries are performed. Stopping pulmonary hemorrhage may include conservative hemostatic therapy, endoscopic hemostasis, and endovascular embolization of the bronchial arteries. In the future, to eliminate the source of pulmonary bleeding, surgical treatment is indicated, taking into account etiological and pathogenetic factors.
Why the blood appeared - the doctor will give you the exact answer
Only a doctor can identify the reasons for the appearance of blood spots. An examination, clinical tests, and only at the end of the diagnosis will an accurate diagnosis be made. The main laboratory test for the manifestation of hematuria is a general urinalysis with sediment microscopy.
This laboratory diagnosis makes it possible to establish indicators that will ultimately reveal why blood appears when a woman urinates: The color of the urine is determined. If the patient is in normal health, it is yellow, transparent, and has no sediment. The density of urine is determined. Increased density indicates a high sugar content. Decreased - may indicate progressive renal failure. The existing protein is a sign of inflammatory processes in the female body. Infection is indicated by the number of leukocytes and red blood cells exceeding the norm.
What is blood in urine
Hematuria is the presence of red blood cells - erythrocytes - in the urine. They are present due to inflammatory processes of tissues, organs, mechanical damage, and internal bleeding. The condition is a marker of chronic infections in the genitourinary system. Hematuria is divided into macrohematuria and microhematuria (occult blood) based on the number of red blood cells. Microscopic hematuria cannot be detected without the help of a microscope. Large blood clots are found with injuries to the urethra.
Forecast
Even a one-time and spontaneously stopped pulmonary hemorrhage is always potentially dangerous in terms of recurrence. Excessive pulmonary hemorrhage threatens the patient's life. In severe cases, death occurs as a result of asphyxia caused by blockage of the airways with blood clots and simultaneous spastic contraction of the bronchi. The percentage of postoperative complications and mortality during operations performed at the height of pulmonary hemorrhage is more than 10 times higher than similar indicators during planned operations.
Causes of blood in urine
The release of blood into the urine can come from any part: both from the kidneys and down to the urethra itself. There are a great many reasons that cause blood to enter the urine, but the most common causes include stones in the urinary tract, various internal injuries, tumors, infectious and inflammatory processes.
In mature people, the release of blood clots into the urine can be painless, but in this case this is the first sign to sound the alarm, because the most common cause of such abundant discharge is cancer, in particular of the bladder and urinary tract.
If we look at cancer diseases separately, there are several types that are found in the bladder. This is mainly cancer of the bladder mucosa, as well as the drainage system and ureters, otherwise called transitional cell carcinoma. Cancers are named in medicine based on the type of cells that are damaged.
- Blood in urine during pregnancy: causes, treatment, tips and reviews
And finally, the third type of cancer, which is the rarest, is adenocarcinoma. bladder is rare. The tumor of this disease contains glandular elements, which determines the name of this type of bladder cancer.
Reasons for the release of blood into the urine from the urinary tract:
- Blunt trauma
- Deep wound with penetration.
- Serious internal injury - rupture of the kidney leads to the appearance of blood in the urine
- Presence of urolithiasis.
One of the main reasons for the release of blood into the urine is urolithiasis, due to which salts are deposited in the kidneys and cause the formation of stones. Urolithiasis, as a rule, occurs with the formation of internal infections, which do not bother you at first. But in addition to infections, stones can form due to the presence of bacteria. Bacteria break down urine and release ammonia.
A minimum of symptoms manifests itself in the presence of kidney stones in the body. They cause internal inflammatory processes that are difficult to recognize with the naked eye, but urine tests show the release of blood into it. An increase in the size of kidney stones results in severe cutting pain in the lower abdomen, which occurs due to the stones blocking the urinary tract.
To confirm a particular diagnosis associated with the formation of stones, it is necessary to do excretory (intravenous) urography. Treatment of kidney stones is a rather complex and lengthy process. In this case, extracorporeal shock lithotripsy is used. If the number of stones and their size in some cases is too large, then this technique is powerless; only surgical intervention will help.
Pathogenesis
The morphological basis for pulmonary hemorrhage is made up of thinned and aneurysmically dilated branches of the pulmonary artery or bronchial arteries, as well as pulmonary veins. Rupture or erosion of altered vessels may be accompanied by pulmonary hemorrhage of varying severity. In this case, the amount of pulmonary hemorrhage is largely determined by the caliber of the damaged vessel, and the severity of disorders occurring in the body is determined by the rate and intensity of blood loss. Developing further disorders are associated with obstruction of the respiratory tract by shed blood and the actual amount of blood loss. Getting into the bronchi even in small quantities, blood causes the development of obstructive atelectasis and aspiration pneumonia. In turn, this leads to a decrease in the volume of functioning lung tissue, gas exchange disorders, a progressive increase in respiratory failure, and hypoxemia. Hypovolemia and anemia accompanying acute and chronic (with recurrent pulmonary hemorrhages) blood loss lead to a general disruption of homeostasis. This, first of all, is expressed in the activation of fibrinolytic and anticoagulant mechanisms, which causes an increased tendency to hypocoagulation and increased permeability of vascular walls. The cumulative result of such changes determines the pathological readiness of the body to resume pulmonary hemorrhage at any time.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of hematuria
In addition to blood and urine tests, you may need to undergo additional procedures such as:
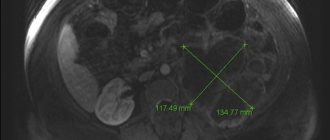
- CT scan.
It can help detect kidney or bladder stones, tumors, and other urinary abnormalities. - Ultrasound of the kidneys.
It allows you to see the structure of the kidneys. - Intravenous X-ray pyelogram.
This is an x-ray examination of the urinary tract, which requires the injection of a special substance. - Cystoscopy.
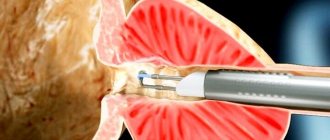
This is a procedure in which a camera is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. It can be used to perform a biopsy and check for cancer cells. - Renal biopsy.
In this procedure, a sample of kidney tissue is taken, which is then examined under a microscope to determine if there is any disease.
Treatment of hematuria
To get rid of blood in urine, you need to cure the cause of its appearance.
. After treatment of hematuria, additional blood and urine tests will be required. If the blood from the urine has not disappeared, then additional procedures may be required to find out the root cause of the hematuria.
If after the initial medical examination the cause of blood in the urine is not found, then you may be prescribed regular examinations every 3-6 months. This is especially important for those who are at risk of cancer.
Detected blood during urination in women may indicate the development of life-threatening complications in the body, which are important to promptly identify and begin treatment. However, the release of blood after urination is often observed due to physiological processes occurring in the body of a girl or woman that are in no way related to the pathological condition. But if urination with blood is of an unknown nature, accompanied by pain, the presence of mucus and pus in the urine, you must immediately visit a urologist and find out what caused this disorder.
- Changed and unchanged red blood cells in the urine of men: what do they mean?
High kidney pressure
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
High renal pressure is a disease that develops due to a narrowing of the lumens of the kidney vessels and manifests itself as an increase in blood pressure. Renal hypertension is associated with pathological processes within the kidneys. Elevated blood pressure enhances these processes and affects kidney health in the opposite order. Blood pressure increases under the influence of higher than normal amounts of renin. This substance produces angiotensin, which is responsible for the production of aldosterone. Aldosterone is a hormone responsible for increasing blood pressure.
Kidney pressure symptoms
The symptomatic picture is divided into 2 parts: symptoms of arterial hypertension and symptoms of kidney disease. In addition, there are 2 types of progression of this disease.
Clinical picture:
Slow development of pathology:
- Constant increase in blood pressure (systolic and diastolic).
- Headache.
- Noise in the head, dizziness.
- Weakness.
- Tachycardia, chest tightness.
The dynamic development of pathology is characterized by:
- Very high blood pressure levels.
- Partial loss of vision.
- Headaches in the back of the head.
- Feeling of nausea, vomiting.
- Dizziness.
Symptoms allow us to determine the main directions of treatment.
In the presence of certain chronic diseases of internal organs in adults, some of the symptoms are masked by taking medications. For example, headaches and dizziness do not occur in patients who take pills for increased intracranial pressure. The appearance of decreased muscle tone and rapid fatigue is not typical for all patients. There is a category of people who practically do not feel that their blood pressure is elevated. Only by the indicators of the tonometer can one judge the presence of pathology.
In addition to the main symptoms of renal pressure, the following are also observed:
- Increase in body temperature.
- Increased sweating.
With significant damaging changes in the kidney tissue, loss of consciousness and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract may occur.
Only a specialist can diagnose renal hypertension. The final diagnosis is made after a combination of studies: biochemical, instrumental. In many cases, patients independently make decisions about the presence of the disease without taking into account the similarity of symptoms with simple arterial hypertension.
Clinical signs of renal pressure from the kidneys:
- Swelling of the legs, bags under the eyes. Usually this symptom appears in the morning and goes away in the evening.
- Lumbodynia.
- Dysuria: pain when urinating.
- Increased diuresis.
- Decreased diuresis.
Treatment
Treatment of renal pressure is based on treatment of the causes and symptomatic relief of the conditions that they provoke. First of all, the attention of the attending physician is drawn to the specific type of disease:
- Vasorenal hypertension.
- Parenchymal hypertension.
- Mixed form
The causes of each of these types lie in chronic diseases. The first stage of therapy eliminates exactly the causes of pathologies.
How to reduce kidney pressure? Drug treatment is based on drugs that reduce blood pressure.
- ACE inhibitors. Reducing the amount of angiotensin, which entails vasoconstriction. This group of drugs has some side effects: cough, general allergic reactions. The main drugs are enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril, perindopril. This medication is taken as prescribed by a doctor. For urgent relief of high blood pressure, Captopril is used in various dosages. The tablet is placed under the tongue until completely dissolved.
- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists. The main representatives are the drugs losartan, valsartan, telmisartan. A group of these drugs is prescribed to be taken at night, or twice a day - in the morning and in the evening.
- Slow calcium channel blockers. The main active ingredients are amlodipine, nifedipine, nitrendipine. This group of drugs is also produced in the form of slow-release tablets, which makes it easier to take.
A side effect of taking these medications is that your blood pressure is too low.
All of the above drugs are prescribed in combination with each other for complicated course of the disease. Statins are also prescribed in combination with drug therapy - drugs that can lower cholesterol levels in the blood, which prevents the formation of cholesterol plaques in the blood vessels.
Combinations of drugs that improve heart function are also used. Beta blockers belong to this group.
Important! Before lowering blood pressure at home, you need to check the contraindications to taking the above medications, since a ban on the use of a particular medication is based on the danger to the patient’s life.
Surgical intervention
For proper therapy for renal pressure, symptoms and treatment are considered individually. The attending physician analyzes each individual case, complex of symptoms, chronic diseases and makes a prognosis for the success of a particular treatment method.
Unfortunately, drug therapy does not always provide significant results other than symptomatic relief. With this situation of the patient, the prognosis is disappointing. The prognosis is also disappointing if the causes of the pathology are eliminated, but improvement still does not occur.
What to do? To restore blood supply to the kidneys and microcirculation at the level of its functional components, surgical methods are used.
Modern medicine can significantly improve the patient’s condition with the help of:
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
- Angioplasty.
- Walling.
- Bypass surgery.
All 3 methods lead to restoration of blood supply to the kidney.
Before treating a patient with surgery, a thorough examination of his vital signs is carried out.
Angioplasty
In advanced cases of the disease, when severe vascular damage occurs, the vessel is dilated mechanically. A special catheter is inserted into the vessel. At its end there is a small can of air. The air stream from the cylinder physically affects the walls of the vessel. As a result, the vein or artery takes on its normal shape.
Angioplasty can lower renal pressure without complications. The effect is observed immediately after the end of the procedure.
Stanning
If high renal pressure appears due to atherosclerotic plaques that close the lumen of blood vessels, then a stenotic procedure is indicated.
The surgical procedure is similar to angioplasty. But it is not a catheter that is used, but a special probe. There is a stent inside it. The material from which it is made can be metal or organic fabric.
Through a small incision in the groin, under local anesthesia, the probe is inserted into the vessel, where expansion is carried out using a stent and an air stream. Organic stents may subsequently be resorbed. Metal elastic stents - meshes are left inside.
Along with a stream of air, which straightens the vessel, antithrombotic drugs are also introduced. The pressure decreases even during the operation.
Bypass surgery
What it is? This operation is performed only in cases where stenting and angioplasty are contraindicated due to the presumed ineffectiveness of such therapy. Unfortunately, in many cases, patients are admitted with already severely damaged vessels, the restoration of which is impossible.
A vessel that cannot be healed is excluded from the general blood flow using a shunt. Typically, the femoral vessel is used as a branch of the bloodstream. A shunt is placed on it, and the damaged vessel is cut out.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The blood pressure returns to normal within 24 hours after surgery.
Surgical interventions are not always permitted. There are certain contraindications to them:
- Age. People over 70 years of age do not tolerate such interventions well due to weakened cardiac activity.
- High degree of atherosclerotic lesions in old age.
- High level of damage to arteries and veins.
- Contraindications to anesthesia.
- Impossibility of treating chronic inflammatory diseases.
Based on symptoms and treatment, renal pressure is considered a completely curable pathology.
Diet for high kidney pressure
Diet is an important component of the answer to the question: “How to reduce blood pressure at home and in a hospital setting?”
The diet for kidney inflammation is based on the need to consume certain foods. Their composition saturates the body with minerals and vitamins.
- Mineral compounds are found in seaweed, the consumption of which will restore their balance.
- Berries containing natural antiseptics and large amounts of vitamin C, for example, lingonberries, cranberries, currants, juniper, must be eaten several times a week.
- Consume semiunsaturated fatty acids, which are found in natural oils and fish oil. They lower blood cholesterol levels and have a positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
- You can eat onions and garlic. This helps reduce blood pressure and strengthen the body's immune functions.
For kidney inflammation, diet No. 7 is preferable. It assumes:
- Low content of table salt in food.
- Low daily calorie intake.
- Multiple meals.
- The daily volume of liquid is up to 1 liter.
Excludes or allows low levels of the following products:
- Fatty meat and fish broths.
- Fried and stewed meat, sausages, smoked products
- Canned fish, smoked fish.
- Radish, radish, spinach, sorrel.
- Fatty and spicy snacks.
- Coffee, cocoa, mineral water with high sodium content.
These products can increase kidney pressure, so their intake is limited.
Diets can partially reduce kidney pressure at home. In order for the disease to be successfully treated with the chosen method, you need to understand what renal pressure is, what symptoms it presents, and what kind of diagnosis is carried out. Independent choice of medicine and treatment procedures can cause harm and complicate the situation. To avoid such situations, use the above information.
Treatment methods
To get rid of bladder hematuria, you need to identify and treat the underlying disease, which is the cause of such manifestations. Medicines are used to stop bleeding. If the blood loss is large, special infusion treatment is required to replenish the blood volume.
For chronic hematuria of the bladder, B vitamins and preparations containing iron are prescribed. If there is a stone in the urethra or ureter, thermal procedures and antispasmodics are prescribed to facilitate its release. If the stone cannot pass on its own, it is removed cystoscopically or surgically.
Only emergency surgical intervention will help eliminate renal injuries, which are caused by hematomas and rupture of renal tissue. High proteinuria along with hematuria is treated with corticosteroids. If hematuria is not a consequence of severe renal damage, conservative treatment is prescribed, including bed rest and hemostatic drugs, and in the presence of inflammation, antibiotics. If hematuria occurs, the symptoms of anemia increase and blood pressure decreases, this is a reason for urgent surgery.
Possible reasons
To determine what caused the presence of blood in a man’s urine, a specialist prescribes a number of necessary examinations
. In addition, the process of urination and urine itself is usually monitored. Based on this, you can also understand a lot:
- blood without pain can be considered the cause of the appearance of tumors in the urinary organs;
- if the color of the urine is reddish or brownish, we can talk about kidney disease
; - if the shade of urine is rich scarlet, perhaps we are talking about problems in the lower urinary tract;
- pain and effort when urinating often indicate problems with the bladder - the presence of stones or negatively affecting bacteria and viruses in it;
- if there is a constant urge to urinate, however, there is no feeling of complete emptying, there is probably a connection with prostatitis
.
The first signs in colored urine are to see blood discharge
Very often, confusion occurs in tests when the urine turns red from the blood of menstrual flow, and not from the blood released due to more complex problematic diseases. It should also be noted that a number of food dyes affect the color of urine. For example, if on the eve of a urine test the patient consumed drinks with dyes, beets, and other foods that can cause a change in the color of urine, then this will be clearly noticeable.
Medicines can also cause changes in the color of urine without the side effects of bleeding into the urine. Such examples include rifampicin, a drug used to treat tuberculosis patients. It may appear as a reddish-orange hue in the urine, which is often mistaken for blood in the urine.
In the process of destruction of red blood cells, hemoglobin is formed, which can affect urine analysis performed using special strips. In this case, the strips will show a positive result, but during laboratory tests, when examining the drop under a microscope, no red blood cells are found.