Nephrectomy and its consequences
Patients with kidney failure, cysts or malformations of the organ are often prescribed its removal. Many of those who are about to undergo a complex surgical operation think about the possible serious consequences for their health. It is difficult to predict what the state of the body will be, since everything depends on the outcome of the intervention itself and the complications that inevitably arise after it.
Most often, patients in the late period develop the following conditions:
- pneumonia;
- stroke;
- thrombophlebitis;
- heart failure;
- myocardial infarction.
Some people experience disturbances in the functioning of the spleen and adrenal glands. In addition, during the first time of the adaptation period, a healthy kidney begins to increase in size, since it performs the functions of both organs. Therefore, in order to reduce the load, the patient is forced to adhere to a special lifestyle and restore his own health. In this regard, it is considered reasonable to ask: does removal of a kidney provide disability, and what documents must be provided for this.
Rehabilitation
Nephrectomy is a very complex and dangerous operation. To fully recover, the patient must undergo a rehabilitation course that lasts at least 1 year. The speed of adaptation of the body to new living conditions depends on the technique of the surgical procedure, the presence of any negative consequences, the age and health of the patient.
You should also take into account the fact that the only kidney will now have to experience a double load, because of this it gradually grows and becomes more voluminous. To make the work of the organ as easy as possible, the patient is recommended to adhere to a special diet. The course of recovery after nephrectomy includes:
- Careful hygiene of the genital organs;
- Active walking in the fresh air;
- Hardening and protection from hypothermia;
- Prevention of infectious diseases;
- Following a strict diet.
Intense sports involving heavy lifting are prohibited. Simple gymnastics with minor weights is enough. To evaluate the effect of surgical treatment, it is important to regularly visit a medical specialist and conduct follow-up examinations. All results are recorded officially, in special medical documents.
Obtaining disability after kidney removal
According to the laws of the Russian Federation, the absence of one kidney is not a compelling argument for disability. However, there are a number of amendments that allow you to make an exception and resolve the issue positively for the patient, adult or child.
Grounds for assignment of disability
Many people believe that a complex operation and a diagnosis gives the patient some advantages, because he can no longer perform his functions, engage in work, and lead his previous lifestyle as before.
But you should know that a disability group is assigned in the presence of three circumstances:
- impairment of the patient’s health due to complex disorders in the functioning of the body;
- inability to self-care, need for help and services of another person;
- the need for rehabilitation measures and social protection.
If a person has one or more of these conditions, he is sent to the ITU commission, providing a complete package of documents. She, in turn, is obliged to consider the situation - whether to grant disability or not and make an appropriate decision.
Required list of documents
In order for the expert commission to consider an application for assignment of disability, regardless of degree, for the first time, it is necessary to provide a complete package of documents, the list of which is established at the legislative level.
- application according to the established form;
- identification documents - birth certificate, passport, TIN;
- a referral issued by the attending physician for examination;
- a complete extract from the patient’s medical record;
- documents that can complement the picture of health status;
- results of completed studies (ultrasound, MRI, ECG, laboratory tests);
- a copy of the work book certified by a notary office and the original for comparison;
- a certificate characterizing the availability of work activity and its conditions;
- characteristics provided by the educational institution (for students);
- pension certificate, insurance policy.
If the re-examination procedure is carried out, an IPR and a certificate of disability should be added to the existing package. If the decision is made in favor of the pensioner, then he is obliged to apply for paperwork to the Pension Fund and the Social Security Administration, where he is assigned payments in the amount due under his new status. In addition, he receives benefits for utility bills, as well as the purchase of medicines at discounts or free of charge. The serviceman must contact management, who will apply for benefits. Having received a refusal, a person can appeal the commission’s decision in a district court or at the regional level.
Examination for passing the ITU
To receive a medical referral for submission to the commission for medical and social protection, the patient is required to undergo a comprehensive examination of the whole body. This diagnosis includes the following list of procedures:
- general clinical blood and urine tests;
- determination of the dynamics of urea and creatinine levels in the blood before and after therapy;
- excretory urography and x-ray of the preserved kidney to assess its functionality;
- large-frame fluorogram;
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- plain X-ray of the lungs.
Disability groups and main criteria for their appointment
Today, there are three groups of disability, each of which can be assigned to a patient only if certain conditions are met. In any specific case, the disease itself and the prognosis provided by the attending physician are studied. Documents and diagnostic results are also subject to study. Only after this a decision is made on the possibility of assigning a certain category of disability.
III group. Involves partial limitation of the patient’s functionality and normal life activities. Assigned to persons working in heavy industries, after undergoing an intervention and in the presence of a wound that is in the healing stage. It is assigned to people whose qualification category is temporarily reduced due to a decrease in the volume of work responsibilities.
Group II. Assigned to persons who have significant limitations in their ability to live. This is due to the questionable prognosis after radical surgery, in the presence of chronic renal failure in the remaining organ, which requires long-term therapy, as well as cancer above stage IIB, when the outcome of treatment is predicted as unfavorable.
Group I. It is prescribed for serious functional limitations, as well as in cases of inability to independently support life and the need for regular assistance from another person. As a rule, such conditions are considered characteristic of the treatment of stage IV cancer tumors.
Group assigned after kidney removal
Patients who have undergone a complex operation often look on forums for an answer to the question: if one kidney has been removed, is it entitled to disability. Despite clear rules and guidelines, most often disability is assigned after kidney removal.
Modern criteria for assigning disability are quite strict, so the patient must provide really serious reasons to confirm his limited legal capacity. As a result, commission members can assign group II or III.
These categories are considered limited, and depending on what specific disability group is given to a person after removal of a kidney, he will have to undergo a re-examination procedure after a year or two. At the same time, he must undergo the examination again and provide the results to the commission.
How to remove a cyst from a kidney?
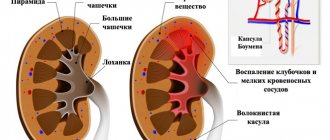
If a cyst is found on the kidney, you should consult a doctor to monitor the danger of this pathological condition. The cyst looks like a cavity - a benign neoplasm, filled with a serous liquid substance, arising from the parenchyma and having thin walls containing connective tissue. The size of the cyst can be more than 10 cm. Neoplasm occurs quite often.
Usually, congenital pathology is not dangerous for humans, since it does not increase, but remains within the same limits as it was initially. A kidney cyst that occurs as a result of previous kidney disease or injury can pose a health threat:
- during the growth process, the formation puts pressure on the parenchyma and blood vessels;
- an infectious focus appears;
- the neoplasm can become malignant.
Pain in the lumbar region or hypochondrium, as well as the detection of a lump on palpation and the appearance of blood in the urine are symptoms that require immediate consultation with a doctor.
For what reasons does the disease appear?
A cyst is a cavity in the overgrown epithelium of the kidney tubules. Formed for the following reasons:
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
- long-term inflammatory process of the kidneys;
- if you have kidney infections;
- the presence of stones in the urinary system;
- difficulty excreting urine;
- renal failure;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- prostate hyperplasia;
- high blood pressure;
- weak immunity;
- aging of the body.
Cavities tend to grow. Chronic diseases of the urinary system, kidney injuries, hypothermia are the causes of the development of neoplasms.
Congenital abnormalities in the kidneys are possible, arising at the genetic level due to a malfunction in chromosomes and under the influence of external factors during intrauterine development of the fetus:
- pregnancy during which alcohol was consumed;
- cigarette addiction;
- untreated intrauterine infections.
There is a possibility that a small cyst will begin to resolve on its own.
A neoplasm up to 5 cm does not manifest itself and is detected only on ultrasound, but it is possible to get by with conservative treatment and monitoring the size and condition of the cavity by a nephrologist. For cysts from 5 cm to 10 cm or more, pain will occur.
Cysts differ in shape and location of origin and are divided into:
- parenchymal;
- sinus;
- solitary.
And also cavities filled with different types of liquid will be treated individually in each case:
- serous fluid does not pose a threat to the patient;
- hemorrhagic, containing blood, subject to immediate treatment;
- purulent requires removal of the infection.
Symptoms of pathology
In most cases, the presence of a cyst is detected during an ultrasound and resolves on its own. Since there are often no symptoms, the patient may not even be aware of the presence of a cyst. Symptoms occur if the tumor grows and puts pressure on neighboring organs, such as:
- enlarged kidney;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- increased pain due to physical labor and stress;
- urine is excreted abnormally;
- blood impurities in urine;
- difficulty in renal circulation;
- overestimation of diastolic pressure.
Complications from neoplasms in the kidneys
Usually, the cyst is not dangerous, but in 5% of cases complications occur:
- suppuration;
- bleeding;
- gap
In this situation, immediate surgical intervention is required.
Cysts smaller than 5 cm are constantly monitored by a nephrologist. Elective surgical removal is suggested if:
- the cyst is large and puts pressure on neighboring tissues and organs;
- suffer from constant severe pain;
- arterial hypertension occurs;
- hemorrhage from the kidney occurs;
- the outflow of urine is disrupted;
- infectious infection occurs;
- there is a risk of cavity rupture.
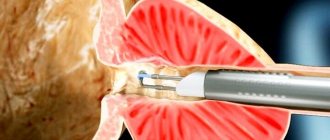
Open surgery is performed:
- with suppuration in the kidneys;
- if the cyst has ruptured;
- when the tumor degenerates into kidney cancer;
- if there are concomitant urological diseases.
In all other situations, cyst removal is performed endoscopically or laparoscopically. However, operations can lead to kidney injuries and do not exclude recurrence of the disease. Therefore, it is worth trying to be treated with medications or folk remedies. Can a cyst resolve if treated without surgery? Yes, it's possible. Benign neoplasms respond well to treatment, although this is a long process.
Diagnosis of the disease
To identify a cyst, an examination by a urologist or nephrologist is necessary. And also you need:
- take blood and urine tests;
- do an ultrasound;
- conduct contrast radiography;
- urography;
- in case of complicated cystosis, tomography is prescribed.
These studies will determine the type, shape and size of the pathology, show the condition of the neoplasm and help the specialist determine how to treat the kidney cyst.
If the tumor size is more than 6 cm, a puncture of the cavity contents is performed.
Treatment of the disease
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor determines the method by which it is possible to cure the cyst. In 95%, this is drug treatment of kidney cysts and the use of traditional methods. If the cystosis does not pose a threat to the patient’s life, we can limit ourselves to treating the symptoms:
- relieve inflammation;
- relieve pain;
- resume urine output.
The subsequent condition must be constantly monitored and controlled.
Treatment lasts approximately 1 month. Medicines are prescribed to stop the growth of the cavity and remove the causes of its occurrence:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics and antispasmodics;
- drugs that normalize blood pressure;
- complexes containing vitamins and minerals;
- immunomodulators.
Use of folk remedies
How to cure a kidney cyst at home, what to do to make it resolve? It is necessary to use traditional medicine after consulting a doctor in order to exclude side effects and not to start the course of the disease. The greatest result is achieved when treatment with folk remedies and medications is carried out mutually.
Taking folk remedies for kidney cysts is allowed after a full examination and checking for allergic reactions, as well as individual tolerance of the components. At the same time, every six months a kidney cyst is diagnosed so as not to aggravate the patient’s condition and not to miss complications. If there are any contraindications, then this therapy is strictly prohibited.
Recipes
The available treatment is ordinary green tea using milk and honey, you need to drink 2 cups a day, morning and evening.
The most popular plant for treating cysts is burdock; leaves and roots are used. The leaves are ground into a paste and taken 1 tsp. 2 times a day. Or make a tincture from burdock rhizome.
And also, in order to make the kidney cyst smaller, use elecampane root. To do this you need up to 30 gr. chopped rhizome, pour 3 liters of water and add 30 g. yeast, infuse for two days, drink 120 ml after meals, when the entire infusion is used, take a break for 21 days and repeat the course again.
Dandelion root is crushed and 200 g is poured. boiling water, leave for 15 minutes. and drink a third of a glass twice a day for 5 days. Or make an infusion of 2 tbsp. l. dandelion root and 5 tbsp. l. kidney tea, leave for 5 hours and drink 100 ml every 3 hours. If treated regularly, the cyst will shrink.
Good results will come from using herbal tinctures:
- Chamomile;
- Calendula;
- St. John's wort;
- Yarrow;
- hog uterus;
- red brush;
- winterweed;
- lingonberry leaves.
One teaspoon of any herb is infused, poured with 1 glass of boiling water and drunk 70 grams. 3 times a day for 7 days.
An alcohol tincture made from the golden mustache herb will be effective. For this purpose 50 gr. 500 grams of flowers are poured. vodka and leave to infuse for 10 days. Then they use it according to the following scheme: first use 10 drops, drinking one drop more every day, for 25 days, and then continue taking it, on the contrary, decreasing it by a drop every day.
Treat with birch tar: drink 3 drops with 1 glass of milk 3 times a day, 3 days, then the next 3 days, 15 drops, and the next 4 days, 7 drops. Then take a break for 10 days and repeat the intake in the reverse manner.
Diet for cystosis
If a cyst forms in the kidney, you must follow a special diet to prevent complications and reduce the load on the urinary system. You need to reduce or completely remove salt from your diet. And also exclude consumption:
- smoked meats;
- fried food;
- fat sour cream;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- hot and spicy foods;
- alcohol.
There are useful:
- dairy products;
- dill;
- cinnamon;
- caraway.
Meals should be divided, in small portions.
Disease prevention
How to cure a kidney cyst depends entirely on the patient. Strict adherence to doctor’s orders, timely treatment, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, following a diet and caring for your body will significantly simplify the task. However, a recurrence of the disease cannot be ruled out; the tendency to develop neoplasms may persist. Pay close attention to your kidney health. Patients with a cyst larger than 6 cm should limit:
- overheat;
- visiting saunas and baths;
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- hypothermia;
The main thing is not to self-medicate.
Video: Kidney cyst
Guidelines for living with a disability
To maintain a long and comfortable life after nephrectomy, a person must change his habits, eliminating harmful ones, adhere to certain dietary rules, and not feel disabled, that is, maintain a positive attitude and presence of mind under any circumstances.
Diet
Nutritional therapy plays an important role in the lives of people with one kidney. It allows you to minimize the load on the urinary system and its main organ. Excluded from the diet: fatty, fried, spicy foods, smoked foods, preserved foods. Limit consumption of foods high in protein and salt. Dishes should be light and quickly digestible. Cooking should be done by boiling, stewing or steaming. At the same time, you need to control the amount of liquid consumed. Coffee, strong tea, alcohol, and carbonated drinks are prohibited.
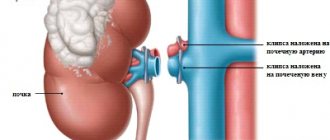
General information about nephrectomy
Nephrectomy is the removal of a kidney through surgery, which is performed for appropriate medical reasons, for example:
- with severe anomalies in the development of the organ, leading to irreversible consequences, sometimes incompatible with life;
- in case of severe damage to the kidney (as a result of a car accident, fall from a great height, etc.);
- for diseases causing organ dysfunction;
- for kidney cancer;
- with polycystic disease (a congenital pathology characterized by the presence of cysts in the kidneys).
Note! A kidney can be removed not only for medical reasons, but also for the purpose of obtaining a donor organ (with subsequent transplantation to the recipient). In most cases, this is done with the consent of the kidney owner. Exceptions are severe, incompatible with life, injuries to a person (donor) resulting from accidents and other incidents.
Rehabilitation period
The rehabilitation period after nephrectomy lasts from a year to a year and a half and directly depends on the type of surgical intervention (laparoscopy or open surgery). Other indicators that affect the rehabilitation period include possible complications, the general condition of the body (including the functioning of other organs) and the activity of the remaining kidney, because it will need to work twice as hard.
To reduce the load on the organ, experts recommend that patients lead a certain lifestyle, which involves observing the following rules:
- Daily hygiene of the external genitalia.
- Regular walks in the fresh air and light exercise.
- Proper nutrition. Food should not be fatty; during the recovery period, it is advisable to eat steamed, plant-based foods.
- Moderate physical activity. It is strictly prohibited to lift objects weighing more than 3-5 kg.
- No hypothermia or overheating of the body in the postoperative period, because The immune system is still too weak.
- Quitting bad habits, especially drinking alcohol.
Among other things, after the operation it is necessary to be observed by the attending physician (including tests, ultrasound, etc.).
What prognosis should patients expect?
The likelihood of a successful and complete cure for a cancer depends on the stage of the cancer process and the effectiveness of therapy. An indicator of the effectiveness of treatment is five-year survival.
At the first stage, the tumor is small, and the patient has a good chance of recovery and a long life. Prognosis - 90% of surviving patients in a 5-year period;
In the second stage, the chance of recovery is... Forecast - 70%;
In the third forecast - 50%;
At the last stage, the five-year survival rate decreases to 10%.
For successful treatment, all factors are taken into account: age, lifestyle, smoking, alcohol abuse, eating habits, method of treatment and how well the patient’s body tolerated the treatment method. During rehabilitation and research, if a relapse occurs, other more effective treatment methods can be used. In this case, survival rate at 5 years will increase by 75%.
Oncologists and scientists around the world have been conducting research for many decades that improves cancer treatment methods and helps cure malignant neoplasms. Thanks to this, the percentage of patients with a 5-year survival prognosis increases every year.
Using modern diagnostic methods, it is possible to accurately determine the type of cancer and reduce the risk of errors in treatment. Thanks to the methods used, the chance of recovery and prolongation of the patient’s life expectancy increases by 71%.
The real threat of kidney cancer lies in the absence of symptoms in the first stages, because of this, patients notice their symptoms too late and turn to oncologists. In addition, even a successfully performed surgical intervention does not guarantee the patient a long life.
The reason for this is metastases, which can appear after a few years. The appearance of metastases in most cases does not provide a chance for recovery.
Important! During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to regularly visit the oncologist and undergo relevant studies, follow the recommendations in order to immediately identify metastases and other complications.
It is impossible to say exactly how long a person will live after surgery. But statistics suggest that with a tumor of one kidney, five-year survival is achieved in 90% of cases, and with a bilateral process - 85%. To make an accurate determination, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the disease and the patient, since many interrelated factors influence the chance of survival.
Relapses are observed in 30% of cases. At the same time, in the last stages of cancer, metastases begin to spread to other organs: lungs, bone structures, spleen, liver. The numbers confirm that metastasis is common.
Relapses are detected 1.5–2 years after medical intervention, so during this period doctors monitor the patient’s condition and conduct regular examinations. If cancer does not appear within 3-4 years, then the cancer is unlikely to return again. In the absence of metastases and in the early stages of the disease, a successful treatment outcome is very likely.
It is important to note that comorbidities also affect life expectancy after surgery: tuberculosis, HIV, hypertension and diabetes. The patient needs to undergo a histological analysis so that the doctor can prescribe the correct therapy.
How to prolong life after kidney resection
In general, in most cases the prognosis for patients is positive. But to return life to normal, you need to be careful in your activities and diet. The patient should also consult a doctor, undergo tests, ultrasound and MRI to check for metastases. In some cases, the patient needs to see other doctors, for example, an endocrinologist or a psychotherapist.
What to do if the condition does not improve
If after 1-1.5 years the patient’s condition does not improve, you need to contact your doctor and take a referral to a medical commission, which, based on diagnostic examinations, will decide whether to assign the person a disability.
Important! Removing a kidney in itself is not a reason for disability. A person can be recognized as disabled only in the case of certain diseases (for example, oncology, chronic renal failure, etc.) leading to limitation of vital functions (based on the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled” of 2006 No. 95 , latest version of the document dated June 21, 2018).
Patient examination
To receive a medical referral for MTU, the patient will have to undergo a comprehensive examination of the body. Such diagnostics will necessarily include the following standard procedures:
- Laboratory examination of urine and blood;
- Comparative analysis of creatine content in the blood before and after surgery;
- Urography and x-ray of the kidney to clarify the level of functioning of the organ;
- X-ray of the spine (if oncology is present);
- Ultrasound of the lungs, liver, fluorography (in rare cases).
There are several disability groups, each of which corresponds to the severity of the disease and the severity of disability. After surgery to remove one kidney, you can consult with your doctor about all your questions. Assigning a disability is an individual matter. It all depends on your state of health and the effectiveness of the rehabilitation course.
Features of registering disability for a child with one kidney from birth
If a child was born with one working kidney and the body functions normally (i.e. the kidney is healthy), disability in this case is not allowed. If there is a serious threat to the health condition with limited life activity, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician or nephrologist and request a referral for an MSE (medical and social examination). And ITU workers, based on medical documents and studies conducted, will decide whether to assign a disability to the child.
For this you will need the following documents:
- Child's birth certificate (original and copy).
- Passport of one of the parents.
- Extract from the medical record about the state of health.
- Application from one of the parents to the ITU office.
- Medical results examinations (tests, ultrasound, etc.).
For the medical and social examination, you need to take with you a diaper for examination and a change of shoes for the parent and child. The examination is carried out by 4 experts with pediatric specialization (including the presence of the child’s attending physician).
After receiving a certificate of disability, parents must contact the Pension Fund at their place of residence to apply for a pension (according to the assigned group) and benefits (including a discount on housing and communal services, free medications, etc.).
Let's now find out whether disability is granted when one kidney is removed.
List of documents
In order for the expert commission to consider your application for disability after kidney removal, you need to provide the specialists with a complete package of documents, which must include:
- Life with one kidney: is it possible to fully feel like a healthy person?
- Identity documents (passport, TIN, birth certificate);
- A written application drawn up according to a special template;
- Medical referral for a commission;
- Complete extract from the medical record;
- Documents on the results of the examination (tests, instrumental diagnostics, etc.);
- Original or notarized photocopy of the work book;
- Certificates from the place of work or study;
- Pension certificate, insurance.
If you are planning to pass the commission for assignment of disability again, you should add an IPR and a certificate of disability to the documents listed above. If the result is positive, the patient receives certain benefits - an increase in pension, a discount on medicines, and benefits on utility bills. If the commission refuses you, this decision can be challenged in court or at the regional level.
Conditions for assigning disability
One kidney does not always mean a disability. It can be assigned only if certain conditions are met, for example:
- If there are health problems in which the patient cannot perform usual actions without outside help (emptying the bladder, leaving the house, etc.) and most of the time remains in a serious condition.
- If a person is disabled and needs social protection (i.e. he needs rehabilitation).
- Pathologies of the remaining kidney (polycystic disease, cancer, developmental abnormalities, etc.).
Thus, in the presence of the above points and medical documents confirming the serious condition of the patient, the ITU can assign a disability to the person (usually group 2 or 3 for a period of 1-2 years). At the end of the period (1-2 years), re-examination will be required.
Disability
A kidney has been removed - do you qualify for disability? After surgery, doctors monitor the patient's condition. If no improvement in health status is observed, the patient can undergo a medical examination and apply for disability. After the removal of one kidney, disability is usually not assigned. However, in the presence of oncology and other dangerous concomitant pathologies, such a status is possible.
A patient can be recognized as disabled if he has been diagnosed with diseases that lead to limitations in life, learning or performance. If these conditions are not met, disability is not assigned. To receive benefits, the following criteria must be met:
- The patient suffered a serious illness or injury, which led to permanent impairment of the body’s vital functions.
- The patient suffers from certain limitations in his life - he cannot take care of himself, work, study, or move independently.
- The patient needs social protection and rehabilitation.
If all of the above conditions are present, the person is assigned a disability. Patients with one kidney are usually given disability for 1 year until the period of rehabilitation and complete restoration of normal functioning is completed. When this period of time comes to an end, you must undergo a medical examination again to renew your status.
Package of documents for assignment of disability
The following documents must be submitted to the ITU Bureau:
- application for the need to obtain disability;
- identification document;
- a copy of the work book;
- insurance pension certificate;
- referral to medical examination from the attending physician;
- an extract from an outpatient card about the person’s health status;
- test results (blood, urine, ultrasound, urography - x-ray of the kidneys);
- certificate of working conditions at the workplace;
- characteristics from the place of study (for students).
If ITU has assigned a person a disability, you must contact the Pension Fund and the Social Security Administration with the list of required documents (see above).
Attention! In case of refusal to assign a disability, the decision can be challenged in a higher authority (in the regional commission or in court).
Kidney removal and disability: when and who is included in the group
Having been left with one kidney after removal, people wonder whether this condition is a basis for assigning disability, because they underwent a rather difficult surgical intervention that requires serious, long-term rehabilitation. Patients who have undergone surgery are interested in whether disability is granted after removal of a kidney; it is important for them to find out what conditions and documents are necessary for this, and what group will be assigned.
Documents for obtaining disability
For the examination you need:
- write a statement about the need to obtain disability;
- provide a referral for a medical and social examination, certified by a doctor and signed by the chief physician of the medical institution;
- provide an extract from the patient’s outpatient card, test results and other documents about the patient’s health status;
- have an identification document (passport), a work record book, a reference from the place of study (for students) and an insurance card.
Analyzes required for examination:
- blood (detailed clinical analysis);
- urine (clinical analysis, creatine and urea);
- X-ray or urography to determine the functionality of the kidney.
Additional examinations may be needed. If there has been contact with poisons that are toxic to the kidneys, you need to take a Rehberg test (glomerular filtration). If the last stage of cancer is detected, patients should have an x-ray of the spine, fluorography, ultrasound examination of the liver, blood biochemistry (bilirubin and aminotransferases).
After becoming disabled, a person is assigned a pension from the Pension Fund (its size depends on the group) and benefits are established from the Social Security Administration (for example, to pay for utilities or medicine).
But not everything is so simple - in practice, it will take time and patience to prove the need to assign disability. ITU takes into account such factors as the frequency of seeking medical help, the number of sick days, and the time spent in hospital treatment. If the patient does not like the decision of the ITU, he can file a complaint with the Main Bureau of the ITU or the court.
Criteria for determining disability groups
A particular group can be assigned in accordance with certain criteria, for example:
- The third disability group is indicated for moderate restrictions on the vital functions of the body, as well as for persons engaged in heavy types of work (where great physical activity is required). This also includes patients with a postoperative wound that requires healing. The period for determining disability in this case is 1-2 years.
- The second group is if the prognosis for recovery is questionable and there is a persistent limitation of life activity (with acute pyelonephritis in the remaining kidney, chronic renal failure, cancer, etc.).
- The first group is assigned when there is a sharp limitation of vital functions, when the patient needs constant care and cannot care for himself (for example, disability due to stage 4 kidney cancer).
If, after the expiration of the period of disability, the patient has not improved, it is necessary to undergo re-examination (i.e., the person must undergo the examination again and provide the results to the members of the commission).
Standard examination for ITU
When referred to ITU, you must undergo an examination.
When referred to ITU, you must undergo the following types of examination:
Recommended reading:
What hormones do the kidneys produce?
- Clinical general blood and urine tests;
- Dynamics of the level of creatine and urea in the blood before and after treatment;
- Nuclide renography or excretory urography, which clarify the functionality of the remaining kidney;
- For persons working in contact (including temporary) with nephrotoxic poisons, it is necessary to have data on the glomerular filtration test of Roberge.
Also, for differential diagnosis of stage IVB cancer, it is necessary to have on hand the results of an X-ray of the spine. In addition, determination of aminotransferases and bilirubin, ultrasound of the liver, plain X-ray of the lungs, and large-frame fluorogram may be necessary.
Group assigned after kidney removal
Is there a disability category if a kidney is removed? Because the designation criteria are quite strict, the person must provide a truly compelling reason to demonstrate his or her disability (or limitation thereof). And based on medical data on the patient’s health status, they are assigned to group 2 or 3. The first is given extremely rarely, when there is a serious threat to life.
But the mere fact of not having a kidney does not provide a guaranteed right to receive one or another group. After all, if the functions of the remaining kidney are not lost, a person can fully work and live in the usual way. Among other things, the decisive role in assigning disability is played by how many times a person has recently (six months, a year) sought medical help, as well as the number of hospital stays and critical conditions during the rehabilitation period (from the moment of nephrectomy).
Groups
If the commission approves the patient’s application, then one of three groups is assigned:
1st disability group
It is prescribed if there is a sharp deterioration in vital functions or if regular assistance is needed in caring for a person with stage 3 cancer.
2nd group
Assigned when there is a slight loss of the ability to lead normal life activities, with an unknown prognosis for life.
If complications arise during kidney removal and acute renal failure occurs, long-term therapy is required, as a result of which the person becomes unable to work. With stage 2 oncology, an unfavorable outcome of the disease is predicted, as a result of which the person becomes a group 2 disabled person.
3 group
Prescribed for minor disabilities; participation in contraindicated areas of work; if stage 2 or 1 cancer; There are restrictions on getting a job.
To obtain the status of a disabled person, you need to undergo a series of examinations, visit a medical institution more than once, and collect a package of documents. It will take care and patience, but it is possible to achieve group assignment.