According to statistics, kidney tumors account for about 2% of all malignant neoplasms. Thanks to modern diagnostic tools: ultrasound, computed tomography, in 25-30% of cases, even asymptomatic cancer pathology can be detected at an early stage. Cancer accounts for up to 90% of all malignant neoplasms of the organ. Among benign ones, the most common are adenomas, oncocytomas, and angiomyolipomas. And if in the latter case the chances of saving the organ are higher, then if it is affected by cancer, this probability becomes much lower. The answer to the question: “How long do people live after kidney cancer” directly depends on the nature of the tumor?
About the disease
Initially, I would like to note that kidney cancer is an oncological disease that most often occurs after 40 years. If we talk about gender, it mainly affects middle-aged and older men. Doctors today cannot name the exact cause of the disease, but they identify factors that may contribute to its occurrence:
- Overweight.
- Drinking alcohol, especially beer, and smoking.
- Abuse of diuretics, that is, medicinal diuretics.
- Diseases such as hypertension, kidney cysts or diabetes may also contribute to tumor development.
- A kidney injury (from a fall or blow) can provoke the appearance of a tumor.
- And, of course, doctors do not rule out a hereditary factor.
There is no single forecast for this situation. It all depends on how early the disease is detected and whether treatment is started on time. Often in this case, surgical intervention is required.
Recurrence of kidney cancer
Is it possible for cancer to return if a kidney is removed? Unfortunately, such cases are still recorded. Kidney cancer may recur if
- the radicality of nephrectomy was insufficient;
- Metastases were not detected in distant organs and lymph nodes in time.
According to statistics, relapse occurs in 1.5 - 4% of cases after surgery to remove a kidney. Age category - from 50 years, the frequency of relapses does not depend on the gender of the patients. The localization of the repeated form of the disease is distributed in equal proportions according to the type of lesion: local, on the lymph nodes, on distant organs.
The danger of local relapses is their asymptomatic nature. The way to keep the situation under control is to be under the supervision of a specialist and promptly follow his recommendations for diagnosing and preventing the disease.
About deletion
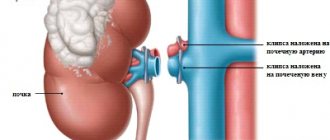
If a patient is diagnosed with kidney cancer, surgery is what is most effective in this case. No drug treatment will help completely cope with the problem. In this case, nonephrectomy is most effective. In this procedure, the renal vein and artery are ligated, after which a special part of the kidney is removed. This operation can be of two types:
- Partial nephrectomy, when the tumor itself is small and is located closer to the upper or lower part of the kidney, which makes it possible not to completely remove the organ, but to excise only the tumor.
- Radical nephrectomy, when only the tumor cannot be removed. This may be due to its large size or localization in the renal or inferior vena cava.
It is also worth distinguishing between two types of surgical intervention. Removal of a kidney for cancer happens:
- Traditionally, a small incision is made in the lumbar region.
- Laparoscopic, when the incision is very tiny, and a special technique is used for the intervention - a laparoscope.
Surgical treatment
This treatment can significantly increase life expectancy, even in cases where the cancer has produced regional metastases. There are three main types of surgical treatment: radical and extended nephrectomy and renal resection.
Radical nephrectomy - the tumor-affected kidney along with the perinephric tissues of its tissue, adrenal gland, adjacent lymph nodes and Gerota's fascia are removed. Removal is carried out simultaneously - in one block.
Extended nephrectomy is used in cases where the tumor has affected neighboring organs. In this case, additional removal of diseased areas is carried out.
Kidney resection is the least traumatic operation, but it is only possible if the tumor is small (less than 3 centimeters). Only the tumor and a small area of tissue adjacent to it must be removed.
Chemoemobilization is often used as preparation for surgery. Most often, this is the drug doxorubicin in combination with hyperthermia and hyperglycemia. Such measures make it possible to reduce the size of the tumor and suppress its activity, which simplifies the operation and increases its effectiveness.
Often, radiotherapy is introduced into the therapeutic treatment course - irradiation of tumor tissue with high-energy radioactive radiation, which destroys cancer cells, and in the most severe forms of the disease, palliative chemoembolization followed by immunotherapy shows good results. The latter is simply necessary to restore the body after the administration of chemotherapy drugs that cause severe intoxication.
Complications after nephrectomy
If a patient has been diagnosed with kidney cancer, the prognosis after removal can be very different. And everything depends on multiple factors, one of which is complications after surgery. What could happen in this case?
- Often there is damage to nearby organs or arteries and veins.
- During surgery, healthy kidney tissue may also be damaged.
- Bleeding in the postoperative period is a huge problem.
- Problems may include pneumothorax, that is, air entering the abdominal cavity, infection of the external wound, or postoperative hernia.
All these factors somewhat complicate the patient’s recovery process. However, doctors today cope with them skillfully.
Quality of life with one kidney
If the second kidney is functioning normally and certain rules are followed, the quality of life will actually not change in any way after a complete nephrectomy. A healthy organ will be able to remove excess fluid and toxins from the body. The patient should simply:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- avoid hypothermia;
- follow a diet;
- control drinking regime;
- do prescribed laboratory tests;
- avoid stressful situations.
As statistics show, modern medicine has made a huge breakthrough regarding the methods of surgical treatment of kidney cancer. Regardless of whether the patient is a child or an elderly person, survival after nephrectomy has increased significantly compared to the previous decade.
With surgical intervention in the first stages of the disease, about 90% of patients have a chance to continue living a full life for decades. In advanced forms of the disease (stages three or four), treatment does not end with surgery; it is necessary to use more aggressive techniques over a long period of time. The survival rate in such cases is significantly lower.
onkoexpert.ru
Artery embolization
When a patient is diagnosed with kidney cancer, the prognosis after removal depends on the treatment method. So, the method of surgical intervention is not always suitable for the patient, but it is necessary to excise the organ. In this case, they resort to artery embolization. This procedure is special in that the patient is made an incision in the groin area and, using a catheter, the lumen of the renal artery is blocked with a special liquid. As a result, the blood supply to the organ does not occur, and the kidney dies. Later, this organ can be removed from the patient's body through surgery. This is one of the forms of stopping the functioning of a diseased organ by killing it. The forecast in this case is very optimistic. The situation can be aggravated by metastases that appear even before the kidney is removed.
Considering how you can get rid of a diagnosis of kidney cancer, prognosis after removal of an organ using various methods - this is what is important to talk about. So, if surgery is contraindicated for a patient, organ removal can also be performed by cryoablation. In this case, special tubes are inserted into the organ, through which cold is supplied, and as a result, the diseased kidney is frozen. After this, the organ is thawed, and so on several times. As a result of such a temperature difference, the tumor dies, and the organ begins to function normally again. The risks of complications with this procedure are minimal, and the survival rate of patients is quite high.
Stages
The disease, according to international standards, is conventionally divided into 4 stages of development:
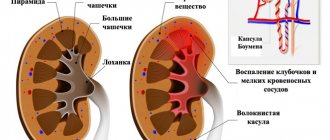
- Stage I. There are no symptoms at this time. The diameter of the tumor reaches a maximum of 2.5 cm. The tumor does not extend beyond the boundaries of the kidney, so diagnosis by palpation does not yield results.
- Stage II. The tumor grows, it can be diagnosed using hardware research methods and laboratory tests. But the neoplasm does not yet go beyond the boundaries of the organ. On palpation, a slight compaction may be felt at the site of the tumor.
- Stage III. The tumor has increased to a significant size, it spreads to the adrenal glands, lymph nodes and renal veins. The size of the formation is sometimes larger than the organ itself. Externally, it can be determined in the form of a swelling under the skin, multiple dense irregularities upon palpation.
- Stage IV. The growth of cancer cells continues. Metastases penetrate into neighboring and distant organs. They may be present in the intestines, lungs, liver, etc. If urgent surgery is not performed at this time, the outcome of the disease can be disastrous. Externally, it is easy to determine the location of the lesion, since the abdominal area changes its shape and size.
About patient survival
Patient survival depends on the stage of disease development:
- If treatment is started at the first stage, when the tumor has not left the capsule, the survival rate of patients is 80-100%.
- At the second stage, when the tumor extends beyond the capsule, survival rate drops by approximately 30%. The situation can be complicated by nodes and metastases. In this case, no more than 30% of patients live another 5 years, and only 5% of patients survive to 10 years.
- With tumor thrombosis of large veins, survival is reduced by approximately 40%.
We further consider such a problem as kidney cancer (prognosis after removal). Reviews from relatives of patients indicate that the following factors have a very negative impact on survival:
- Severe postoperative condition of the patient.
- It is most difficult to cope with kidney cancer when symptoms are already signaling the disease. It’s better if the tumor is detected by ultrasound, but there are no external manifestations yet.
- A dangerous fact is when the patient’s body weight decreases by more than 10%.
- Survival rate decreases if ESR in the blood increases.
Recovery period
Immediately after surgery, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where he is under constant supervision. During the first few days, a catheter is inserted into the patient to allow urine to be removed from the body.
In the first 1-2 days, the patient is prescribed painkillers in the form of injections. Gradually the pain subsides and completely disappears. There may be a slight increase in body temperature within 37 degrees. In the presence of high temperatures, there is suspicion of the development of an inflammatory process.
The operated patient can get out of bed 2-3 days after the end of the operation, which helps prevent adhesions. It is allowed to drink water, but eating food is allowed only on the second day. As a rule, if no complications are observed, then discharge occurs on 7-8 days.
As a rule, the main rehabilitation period begins at home, since all responsibility for health falls on the patient and his family. The complete recovery period for operated people lasts at least one and a half years. After this time, a healthy kidney begins to get used to increased loads and functions according to the principle of compensation.
Nutrition
The postoperative period for patients with one kidney should begin with a review of the diet. The main condition that must be observed is to eat easily digestible food. The diet should consist only of low-calorie foods that contain a minimum of protein.
On this topic
How long do they live after surgery for kidney cancer?
- Editorial board of Oncology.ru
- February 28, 2020
The daily diet must include:
- Rye bread;
- cereals and pasta;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- fermented milk products.
Meat is consumed with extreme caution. The daily norm should be about 100 grams of rabbit, veal or chicken. Low-fat fish, as well as chicken egg omelets, are not prohibited.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet such foods as:
- preservatives;
- smoked meats and sausages;
- cheese;
- marinades and pickles;
- salty, fatty and fried foods;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- strong tea and coffee;
- milk, as it contains a lot of calcium, which contributes to the development of kidney stones;
- legumes that promote increased gas formation in the intestines.
Meals should be taken up to 6 times a day with equal intervals between them. Only small portions are allowed. The daily rate of water consumption is strictly agreed with the attending physician.
In this case, the amount of liquid from soup, juice, fruits and vegetables must be taken into account. All dishes must be consumed boiled, baked or cooked in a steam bath. You must adhere to a special diet strictly in accordance with the recommendations of a specialist.
Prevention of complications
To restore a normal lifestyle after kidney removal surgery, you need to follow some recommendations given by a specialist. They are as follows:
- prevent the emergence and development of infectious processes;
- If inflammation is present, promptly carry out therapeutic measures to eliminate it.
You also need to regularly undergo examination of a healthy organ, which will allow you to monitor its condition and promptly identify any abnormalities.
Physical activity
For three months after surgery, it is necessary to limit physical activity. Daily walking in the morning and evening hours is allowed for no more than 30 minutes. If the treatment is successful, the duration increases.
In addition, lifting heavy objects weighing more than 3 kilograms and playing sports is prohibited. If there are no contraindications, the doctor may allow you to perform simple gymnastic exercises. During the rehabilitation period, they are an effective way to prevent diseases of the cardiovascular system, especially if the patient remains in bed all the time.
Organ removal and survival
The prognosis after removal of kidney cancer is in most cases positive. However, after such an operation the patient will have to be careful at all times. You will definitely have to regularly visit the doctor, go to an ultrasound, do an MRI or CT scan to examine the body for the presence of metastases. Sometimes it is also necessary to be constantly monitored by other specialists who will “guide” the patient on other diseases that significantly complicate the patient’s life. Often people also have to register with an endocrinologist, cardiologist or rheumatologist.
A special diet after kidney removal is also important. In this case, you will have to completely abandon salt and salted foods. Only in this case will the remaining kidney be able to easily work and perform the function of the second, excised part. You will also need to avoid animal protein.
If the patient has one kidney left after surgery, there is a possibility that it will be possible to do without dialysis. If all the doctor’s instructions are strictly followed and the rules are followed, the remaining organ will be able to function fully. However, in this case, you will also have to permanently abandon certain sports that place stress on the lumbar region. Also, when taking various medications, you need to carefully read the instructions so that the remaining organ does not create additional stress. Life will, of course, be a little more complicated. However, a person will be able to do a lot of good in this world, delighting relatives and friends with his presence.
Diagnostics
In most cases, kidney cancer is diagnosed at stages 3-4, when the patient’s pathological process is already very advanced. If you suspect kidney problems, you should immediately contact a urologist. He will conduct an initial examination, palpation, and collect a thorough medical history.
In order to confirm the diagnosis, various studies are prescribed:
- laboratory;
- ultrasonic;
- X-ray and others.
All patients need to undergo laboratory tests:
- general urine and blood;
- cytology;
- blood biochemistry.
If laboratory tests confirm the suspicion of the presence of a tumor in the kidneys, additional hardware tests are carried out:
- MRI;
- CT;
- renal angiography;
- excretory and radiopaque urography;
- radionuclide scanning;
- nephroscintigraphy.
Patients with suspected malignancy undergo a biopsy. The doctor makes a closed puncture to take biomaterial from the formation for analysis. The procedure is carried out under the control of an ultrasound machine. To determine whether there are metastases on other organs, an additional x-ray of the bronchi and lungs and an ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract are performed.