Complications after a sore throat in adults and children occur very often, especially in cases where the course of antibiotics was interrupted. The main causative agent of purulent tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis) is group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (pyogenic streptococcus). These are gram-positive bacteria that are very dangerous to the body because they can destroy red blood cells. During their life, these microorganisms secrete a number of poisons and toxins, which cause the development of unpleasant symptoms.
Tonsils are lymphoid organs with a large number of blood and lymphatic vessels, therefore, if there is an inflammatory process in them, pathogenic microbes through the blood and lymph flow very quickly spread throughout the body and cause the development of complications in both adults and children.
Treatment for bacterial sore throat should include the use of antibiotics. But if you do not start taking them on time or stop therapy ahead of schedule, the disease becomes chronic. Along with the blood flow, streptococcus moves, causing inflammatory processes in other organs and tissues.
Possible complications of sore throat
Peritonsillar abscess
Refers to early complications of acute tonsillitis. With a peritonsillar abscess, the inflammatory process affects the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the pharynx.
This is a fairly serious disease in which the patient experiences symptoms such as:
- severe pain in the throat, during which it is impossible not only to eat, but also to open your mouth;
- spasms of the masticatory muscles;
- change in the relief of the neck (the patient always tilts his head towards the inflammatory process);
- increased salivation;
- weakness, headache;
- elevated body temperature.
In 30% of cases, despite treatment, endocarditis leads to death because the heart valves are damaged.
To treat peritonsillar abscess, antibiotics, corticosteroids, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used; in addition, local therapy can be prescribed. In severe cases, surgery is necessary.
Otitis
Otitis media is also one of the earliest and most common complications of tonsillitis in children and adults. In this case, the infection enters the middle ear, causing an acute inflammatory process that can spread to the salivary gland or outer ear. In this case, in addition to the symptoms of acute tonsillitis, the patient experiences:
- severe shooting pain in the ear (most often in one), radiating to the temple, teeth or throat;
- ear congestion;
- purulent discharge from the ear.
As the disease progresses, the eardrum ruptures.
Treatment of otitis media is carried out using antibiotics in the form of tablets, suspensions, injections and ear drops. They also take painkillers and antipyretics.
Lymphadenitis
With lymphadenitis, inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs. The infection, penetrating from the primary focus, affects the lymph nodes, resulting in symptoms such as:
- enlargement and pain of the lymph node;
- general weakness and malaise.
The disease is treated with antibiotics; for a purulent abscess, surgical intervention is necessary.
Sepsis
This complication is quite rare, but requires immediate medical intervention as it can be fatal. Why is it developing? With this pathology, pathogenic microorganisms enter the patient’s blood, causing inflammation not in any individual organ, but throughout the entire body.
To treat peritonsillar abscess, antibiotics, corticosteroids, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used; in addition, local therapy can be prescribed.
This disrupts the functioning of the heart, kidneys and respiratory system. The patient may be unconscious. Treatment is carried out in the intensive care unit.
Complications on the kidneys after a sore throat
The first signs of kidney disease appear a few days after a sore throat. This is a fairly common complication of the disease, the causative agent of which is streptococcus.
Pyelonephritis
With pyelonephritis, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the lower back;
- increase in body temperature to 38–40 °C;
- dry mouth, nausea and vomiting;
- general weakness and sweating;
- cloudy urine and difficulty urinating;
- blood in the urine (in some cases).
Treatment is carried out in a hospital. In complex therapy of the disease, antibiotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is classified as an autoimmune disease, the trigger of which is infection. In this case, the body's immune cells begin an attack on the kidney parenchyma. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- intense pain in the kidney area;
- change in urine color (it becomes brown);
- increased blood pressure (in some cases to critical levels);
- increase in body temperature to 38–39 °C;
- an increase in the daily amount of urine.
In the treatment of glomerulonephritis, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and antispasmodics are used.
Joint damage
This complication of tonsillitis can appear 2-4 weeks after tonsillitis. It is less common than damage to the heart and kidneys, but is quite difficult to treat. In some cases, a person becomes disabled.
Rheumatoid arthritis
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks healthy tissue and causes many unpleasant symptoms. This is an autoimmune disease that is almost impossible to get rid of.
The following symptoms are typical for rheumatoid arthritis:
- shooting pain in the joints of the leg or arm;
- the affected joint is limited in movement;
- body temperature rises;
- joints become deformed (in later stages of the disease).
Treatment of rheumatism is very long and includes the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids and chondroprotectors. Cardiac complications are among the most dangerous; their development usually requires hospitalization
This is a fairly serious disease that requires treatment by qualified specialists in a hospital setting.
Endocarditis
It is one of the dangerous late complications of tonsillitis. In 30% of cases, despite treatment, endocarditis leads to death because the heart valves are damaged. The patient has symptoms resembling myocarditis:
- dyspnea;
- disruption of normal breathing as a result of stagnant processes, it manifests itself as suffocation and can be complicated by pneumonia;
- increased body temperature (this symptom is a specific sign of endocarditis and distinguishes it from myocarditis);
- weakness;
- pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left arm;
- rapid loss of body weight.
Glomerulonephritis is classified as an autoimmune disease, the trigger of which is infection. In this case, the body's immune cells begin an attack on the kidney parenchyma.
Treatment of the disease is carried out in a hospital. In addition to antibiotics, hormonal drugs, diuretics, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Sore throat is a very serious disease, the improper treatment of which can lead to serious consequences. But this can be avoided if, if you experience a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or an increase in body temperature, consult a doctor in time and strictly follow all his recommendations.
Complications after tonsillitis - pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis
Sore throat is considered by many to be almost an analogue of any respiratory viral disease - the familiar sore throat, high temperature and other symptoms. This often results in a mild, irresponsible attitude towards angina: the disease is tolerated on the legs without appropriate treatment, they do not complete the course, they self-medicate and resort to folk methods.
This approach to the disease can be dangerous, and is fraught not only with chronic tonsillitis, but also with many complications. And first of all, this affects the kidneys.
Kidney damage is the second most common complication of all types of tonsillitis, and this organ is especially at risk. Most often, kidney disease following a sore throat results in pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
Why do complications occur?
Pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis after tonsillitis
During the course of a sore throat, the protective functions of the human body are significantly reduced. The damage to the tonsils that occurs with angina negatively affects the general state of the immune system, so infections that cause inflammation can easily migrate throughout the body.
The main cause of kidney problems after a sore throat is the consequences of its treatment. A course of antibiotics, without which it is impossible to destroy the source of the disease, provokes the body to produce special antibodies, which then fight the disease.
By neutralizing bacteria and viruses, the antibodies produced are beneficial. But as they spread throughout the body, they also cause harm to it: their interaction with kidney tissue leads to the appearance of protein formations. The latter cause a malfunction in the normal functioning of the kidneys.
Also read: Treatment and prevention of purulent tonsillitis, advice from an ENT doctor!
How to determine the presence of a disease?
As a rule, the first symptoms of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis appear no less than 2-3 weeks after the final stage of tonsillitis and are manifested by a lot of symptoms. But the main sign is, of course, the test results.
When and what tests should I take to detect the disease in time? The first signs of glomerulonephritis appear in the urine 10-14 days after the end of a sore throat, pyelonephritis is detected a little later. The only test that needs to be taken to determine the risk of consequences for the kidneys is a urine test, which is prescribed between the second and third weeks after the end of the sore throat. If the unfavorable prognosis is confirmed, this is followed by a doctor’s examination and repeated tests.
Other symptoms common to pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis are:
- Increased body temperature;
- Weakness and dizziness;
- Headache due to intoxication of the body;
- High blood pressure;
- Severe lower back pain;
- In cases of serious exacerbations, swelling in the lumbar region is also observed;
- Frequent painful urination;
- Change in urine color to deep red-yellow, reddish, or the presence of bloody inclusions in the urine.
Success in the treatment of any of these diseases depends mainly on their timely detection, which is facilitated by a good knowledge of their symptoms.
Nature of the disease
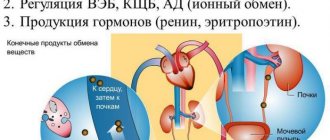
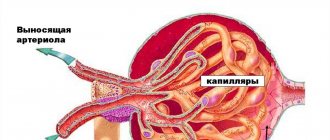
The consequences of angina can be expressed in unilateral or bilateral inflammation of the kidneys. In the case of glomerulonephritis, we are talking about fundamental violations of kidney function. The glomeruli serve to “squeeze” and filter the blood, taking all the useful components from it and turning the remainder into urine. After an attack, the body’s immune system becomes “blind” due to the action of an antibiotic in the glomeruli, diffuse inflammation begins. The “glomeruli” stop functioning, do not pump blood well, and cause discomfort.
With pyelonephritis, not only the urine processing system becomes inflamed, but also the parenchyma, which is responsible for the entry of fluid into the ureter. Therefore, pain with pyelonephritis is stronger.
Also read:
Consequences of kidney complications
In addition to the transition of both diseases to a chronic form, poor treatment or late detection of the disease can lead to their progression and serious consequences for the entire genitourinary system.
The result of glomerulonephritis can be the failure of one or both kidneys, the inability to restore their full functioning (then you have to resort to hemodialysis - an artificial kidney technology) and even the need for an organ transplant. Pyelonephritis has similar consequences.
A side effect of any of these diseases is also an increase in blood pressure, which can lead to a stroke or heart attack. The intoxication of the body that accompanies glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis, including the accumulation of waste, can also be dangerous if left untreated.
Main aspects of treatment
What does a kidney look like with pyelonephritis?
Due to the connection of kidney complications with tonsillitis and the presence of chronic tonsillitis, the question often arises: is there a need to remove tonsils, as is often done for related diseases? The answer to this is decided individually after examination by a doctor, evaluation of tests, assessment of the condition of the tonsils. Both pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis are diseases for which angina only gives impetus to the development, and does not serve as the main reason for their onset. In any case, at a minimum, a course of conservative treatment of the tonsils is required in the form of rinsing, physical therapy. procedures, etc.
How to treat pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis that affects the body after a sore throat? The recovery system should be developed by a doctor; in most cases it is implemented in a hospital setting. Treatment and prevention of these kidney diseases comes down to several areas of action.
- Compliance with the daily routine recommended by the doctor. The purpose of this or that routine depends on what kind of disease the patient is suffering from, what stage he is at, and many other nuances.
- The diet, usually designated number 7 in diet books, is followed in critical situations. In general, the patient’s diet should contain a lot of protein foods and be rich in vitamins and microelements. Too spicy, salty and fatty foods should be excluded from the diet for a while.
- Drug therapy aimed at eliminating the source of infection. She fights the cause of the disease. With the help of special drugs, the mechanism of processing and emission of urine is established.
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs helps anti-infective drugs achieve their goal, works with the consequences of diseases and treats symptoms, making life much easier for the patient.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to help restore blood circulation in the kidneys.
- Passive gymnastics and kidney massage.
- Herbal medicine is treatment using herbal teas and infusions.
In addition to the above measures, patients are often recommended sanatorium-resort treatment, preferably in latitudes with a warm climate.
With timely detection and, most importantly, proper treatment of kidney diseases caused by sore throat, the acute phase passes in one and a half to two weeks and does not become chronic. Subsequent physiotherapeutic and sanatorium treatment, as well as measures to prevent chronic diseases, will help you avoid kidney problems in the future.
lor-online.com.ua
Video
We offer you to watch a video on the topic of the article.
Complications on the kidneys after a sore throat rank second in frequency of occurrence after rheumatic lesions of the cardiovascular system. The leading role among them is occupied by pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
According to studies, after tonsillitis, complications of the kidneys and urinary tract occur in 5.8% of all patients who have suffered from the disease. Of these, pyelonephritis accounted for 78.9%, glomerulonephritis – 5.3%. The remaining 15.8% are due to other urinary tract diseases. As a rule, due to complications, the kidneys hurt after the end of the sore throat, but it happens that the pain begins even during the course of the disease.
When the kidneys are damaged, the patient develops characteristic pain in the lower back.
Both diseases - pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis - are life-threatening and require hospitalization. However, glomerulonephritis is the most dangerous renal complication, since it affects the “holy of holies” - the glomeruli, or glomeruli, which perform the main function - glomerular filtration. And if acute pyelonephritis can still be cured, then with glomerulonephritis, the changes that occur in the kidneys are irreversible, completely incurable and require constant medical support throughout the patient’s life. When neglected, both diseases can lead to acute renal failure with a fatal outcome.
Symptoms of complications
The first symptoms of complications are determined by the following signs:
- after a sore throat, the temperature persists, which, if it goes down, does not last long;
- the patient complains that something is bothering his throat;
- constant headache;
- my ears are blocked, and this feeling does not go away;
- frequent cough after a sore throat.
A rash after a sore throat is not such a common occurrence, but when it appears, rule out chickenpox.
It is much more complicated, and in itself is fraught with serious complications - damage to intracranial nerves or meningitis.
Pediatrician Irina Leonova talks about the nature of complications:
The mechanism of development of kidney complications
Complications after tonsillitis on the kidneys are caused by the action of toxins produced by pathogens of tonsillitis. Streptococcus is the most dangerous in this regard. Its toxins both directly affect the kidneys even during illness, and after the end of the sore throat, they cause an autoimmune response of the body, causing the incurability of glomerulonephritis.
Microphotograph of an accumulation of hemolytic streptococcus, the main causative agent of sore throat and its complications.
Due to direct damage, the kidneys sometimes hurt even with a sore throat, and both kidneys, or only the right or left kidney, can hurt. The more active the infection and the worse the patient feels, the more toxins enter the bloodstream, spread throughout the body and reach the kidneys. They directly affect the cells and tissues of the kidneys, causing various lesions. Because of them, pain and disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys may develop.
However, this action is less dangerous because when taking effective antibiotics, the infection is quickly suppressed, the amount of toxins in the blood is sharply reduced and the effect on the kidneys stops.
Long-term complications are much more dangerous, usually developing 2-3 weeks after the end of a sore throat, and in some cases - after several months or even years if the sore throat has not been successfully treated. Their development is based on an autoimmune mechanism. The immune system in humans works in such a way that, as a result of the introduction of foreign proteins (antigens) into the body, the production of antibodies begins - its own proteins, the task of which is to destroy bacterial antigens, not only toxins, but also the proteins that make up the bacterial cell membrane.
Streptococcus antigens are similar to those in the tissues of the kidneys, heart and joints. As a result, the resulting antibodies do not distinguish between streptococcal antigens and the body’s own proteins, which are similar in structure, and therefore attack both bacterial cells and cells in the tissues of the kidneys, heart and joints with equal activity. In many cases, after the development of such an autoimmune mechanism and after the infection has been completely eliminated from the body, the immune system continues to attack its own tissues. This is how autoimmune diseases develop, including pyelonephritis. Their main danger is that they are incurable and require constant therapy throughout the patient’s life.
A prototype of a portable artificial kidney device, with which patients suffering from severe renal failure after glomerulonephritis have to live.
It is important to understand that such incurable complications develop no earlier than the 9th day of sore throat.
Even if the kidneys hurt with the sore throat itself, but taking effective antibiotics that suppress the infection begins earlier than 9 days, the infection is suppressed and incurable complications do not develop in the patient.
Pain and complications in the kidneys after a sore throat - causes and what to do
Sore throat or acute tonsillitis is an acute infectious inflammation of the body, localized in the nasopharynx and tonsils. It is caused by microorganisms that often live on human mucous membranes.
Some circumstances, against the background of reduced immunity, can activate them and cause inflammation. For example, wet feet, large portions of ice cream, cold drinks and others. However, the causative agent of the disease can enter the body from the outside, that is, a person can simply become infected.
Complications after a sore throat are divided into local and general. Local ones are primarily abscesses of the soft tissues of the larynx, swelling and bleeding. General complications are more dangerous. Among them:
- Rheumatism.
- Heart failure
- Streptococcal infection
- Nephritis
- Sepsis
For what reasons do complications develop?
In general, factors contributing to the development of complications with angina are:
- Refusal to take antibiotics when ill;
- Antibiotic therapy started too late;
- Taking ineffective antibiotics and refusing to replace them;
- Interruption of the course of antibiotic therapy, when the patient stops taking medications after his own condition has normalized, but before the entire infection is eliminated. Even individual streptococcal cells that persist in tissues and do not cause symptoms of the disease will form an immune response, which will lead to complications in the future.
Sumamed is a drug based on the antibiotic azithromycin, used on a 3- and 5-day dosage regimen. Practice shows that when taken for 3 days, it often does not completely eliminate the infection, which is why complications develop.
Also, the likelihood of developing complications is influenced by the immune status of the body, but a clear connection between the strength of the immune system and the frequency of complications has not been established. There is a reasonable hypothesis that the stronger the immune system, the greater the likelihood of complications, since such a strong immune system forms antibodies to streptococcal antigens more quickly and efficiently. In such conditions, the autoimmune response develops faster and more reliably than in a person with a weak immune system.
Kidney pain, causes
One of the most common complications after tonsillitis is kidney pathology. Acute tonsillitis is caused by strains of streptococcal and staphylococcal infections that produce antigens similar to the tissue of the heart muscles and kidneys. Therefore, the immune system, while fighting pathogenic bacteria, can damage antigens contained in the tissues of internal organs. In addition, during the course of illness, the body’s protective functions are significantly reduced, which allows the infection to spread freely.
Symptoms of complications of tonsillitis on the kidneys
The two main complications of tonsillitis on the kidneys manifest themselves with different symptoms and clinical pictures.
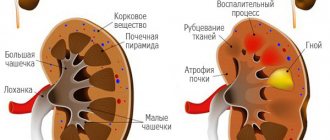
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of an infectious nature, which affects the renal pelvis, parenchyma and calyces.
The disease may affect one kidney, sometimes both. The first signs of the disease can be observed 2-4 weeks after a sore throat. In this case, the following are observed:
- Pain in the lumbar region and increased muscle tone on the affected side;
- Increase in body temperature to high values - 39-40°C;
- Chills followed by profuse sweating;
- Muscle and joint pain;
- Painful, frequent and copious urination.
At the first such symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to seek medical help, undergo an examination and begin treatment on time. The sooner therapy is started, the greater the chance of cure and prevention of irreversible consequences.
With glomerulonephritis, as a result of damage to the capillary glomeruli, the filtration process in the renal system is disrupted. This leads to a deterioration in the general condition, the development of edema, a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, and the appearance in it of a large amount of protein and red blood cells (blood). In the last stages of the disease, urine has a characteristic rusty tint, the color of “meat slop.” These symptoms are accompanied by complaints of nagging pain in the lumbar region, general weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
Often the disease begins with few symptoms, which makes diagnosis difficult. In the initial stages, sometimes only increased urination is present. Then more clear signs of glomerulonephritis develop:
- Weakness, headache;
- Severe swelling of the limbs and the whole body, up to anasarca, sometimes with the development of ascites and exudative pleurisy (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal and pleural cavities);
- Development of arterial hypertension;
- The appearance of shortness of breath, an increase in heart size;
- Weight loss;
- Development of heart failure.
Swelling, characteristic of complications with angina.
At the final stages of the disease, chronic renal failure and uremia occur. The patient often smells ammonia from his mouth. Kidney failure is fatal and requires urgent hospitalization of the patient, sometimes placing him in intensive care.
Children are also susceptible to complications after a sore throat. The symptoms are similar in many ways, but in children the symptoms of the disease are much stronger than in adults. Moreover, the smaller the child, the more pronounced the following symptoms and clinical manifestations of intoxication are:
- Febrile body temperature, up to seizures;
- Vomiting, regurgitation;
- Pale skin, cyanosis of the face or nasolabial triangle;
- Refusal to eat;
- A sharp decrease in body weight;
- Stool disorders;
- Symptoms of dehydration, sagging skin.
Due to the fact that these symptoms are similar to those of poisoning or intestinal infection, professional diagnosis is required to reliably determine the disease.
Types of kidney pathologies, their symptoms and treatment
The kidneys are paired organs of the genitourinary system responsible for urine formation and excretion. Failures in their work can lead to very serious problems for the body. Among the consequences of acute infectious tonsillitis, there are several types of pathology:
Pyelonephritis
This is an inflammatory process of the renal pyelocaliceal system, as well as the renal parenchyma, which responds to urine excretion. The disease manifests itself as follows:
- High, up to 40 degrees, body temperature.
- Chills and profuse sweating.
- Muscle pain.
- Nagging pain in the lumbar region.
- Weakness, headache.
- Pain when urinating.
With improper or insufficient treatment, the acute form of pyelonephritis can become chronic.
Glomerulonephritis
An infectious disease in which inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidney glomeruli occurs. Glomeruli serve to filter blood and, when inflamed, cease to cope with their functions. Most often, this complication occurs with streptococcal sore throat. Characteristic symptoms:
- Increased body temperature.
- High blood pressure.
- Headache and lower back pain.
- Edema.
- Oliguria (decreased urine output)
- Hematuria (blood in the urine)
- Enlargement of the liver.
There are acute and chronic forms of the disease. Moreover, the latter does not necessarily appear as a consequence of the first and may arise primarily.
Kidney failure
The most dangerous form of kidney pathology is renal failure. It develops due to improper or insufficient treatment. This is a complete or partial disruption of the functions of these organs.
In the worst cases, this can lead to complete failure of one or both kidneys. There are acute or chronic forms of pathology.
Symptoms of chronic renal failure depend on the stage of the disease. If in the initial (latent) stage patients may not complain of anything except weakness, dry mouth and increased fatigue, then at the last (terminal) stage swelling, lethargy, drowsiness, inappropriate behavior, the smell of ammonia from the mouth, and diarrhea are observed. The skin takes on a grayish-yellowish color.
The acute form of failure is characterized by: a decrease in the amount of urine or a complete absence of urination, swelling of the extremities, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, lethargy or, conversely, increased excitability of the patient.
Risk of kidney complications
Of the complications of tonsillitis on the kidneys, the most dangerous is glomerulonephritis. As a disease of an autoimmune nature, it is incurable and the patient will suffer from it for the rest of his life. During the disease, kidney function is impaired and specific syndromes develop. Often, glomerulonephritis, even with high-quality therapy, becomes a cause of disability for the patient.
In the later stages, advanced disease results in acute renal failure and uremia. With them, uremic coma and death of the patient can occur.
Uremic coma is one of the consequences of advanced glomerulonephritis.
Diagnosis of diseases
When diagnosing, first of all, a thorough examination of the patient, collection of complaints and anamnesis are carried out. The very presence of a sore throat in the previous period is one of the reasons to suspect kidney damage as a complication of this disease.
A number of laboratory and instrumental studies are also carried out, which include:
- General blood and urine tests;
- Urinalysis using the Nechiporenko method;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys;
- Rehberg's test;
- X-ray of the chest organs;
- Excretory urography.
Photo of an x-ray taken to diagnose glomerulonephritis.
An additional indication of the development of complications of tonsillitis on the kidneys is the symptoms of other complications of this disease: acute rheumatic fever, chronic tonsillitis, abscess. If a doctor sees that a patient has developed one of the complications of a sore throat, he has reason to believe that the characteristic kidney symptoms also indicate typical complications of a sore throat.
Diagnostics
If you suspect complications of angina affecting kidney tissue, you should consult a specialist in the field of nephrology. The doctor, after listening to the patient’s complaints, will prescribe a number of examinations:
- clinical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
The results of instrumental and laboratory diagnostics will help to create a complete picture of the disease, make the correct diagnosis, and select the necessary therapy.
Treatment of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis
Therapy for pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis is prescribed by the attending physician. In the vast majority of cases, patients are treated in hospitals. Glomerulonephritis requires mandatory treatment in a clinic; outpatient therapy is possible only with a sluggish chronic course.
During therapy, the following principles must be followed:
- Strictly observe bed rest;
- Adhere to a low-calorie diet with a limited amount of protein (table No. 7 according to Pevzner);
- Limit the amount of fluid consumed during glomerulonephritis, and vice versa, drink as much as possible during pyelonephritis;
- Take antibacterial agents prescribed by your doctor;
- Take medications that reduce intoxication, including detoxification solutions for intravenous infusion.
In general, symptomatic therapy is prescribed according to indications, and may include antispasmodics (no-spa, papaverine), anti-inflammatory drugs (paracetamol, nimesil), and blood pressure lowering agents.
From the group of antibacterial agents, cephalosporins (ceftriaxone), drugs from the macrolide group (erythromycin, azithromycin), nitrofurans (furadonin), nalidixic acid derivatives (5-NOC) and others are used. In acute glomerulonephritis, penicillins are mainly prescribed, avoiding the use of nephrotoxic drugs (nitrofurans and aminoglycosides are excluded).
The use of heavy antibacterial drugs for glomerulonephritis can worsen the disease due to side effects on the kidneys.
When acute heart failure develops, pathogenetic therapy is used, and when edema appears, diuretics are used. In some cases, hemodialysis (artificial kidney machine) is indicated.
Treatment methods
In order to avoid the development of complications, you need instructions that clearly explain the sequence of actions.
To avoid unwanted consequences you should:
- Maintain bed rest for at least 5 days, even if you feel like you are feeling better.
- Take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor, follow the duration of the course of treatment and dosage.
- Drink plenty of fluids to reduce symptoms of intoxication. Herbal teas, black or green tea, juices and fruit drinks, and warm milk are suitable for this.
- In addition, you can use folk recipes. DIY inhalations and rinses. For rinsing, you can use iodine and soda, hydrogen peroxide, chlorophyllipt, miramistin, and herbal decoctions. The price of these products is low, but after using them you are guaranteed to feel better.
If a complication does occur to the kidneys, then adhere to the following treatment regimen:
- Maintaining bed rest;
- Specialized diet;
- Fluid restriction with glomerulonephritis;
- Drinking plenty of fluids during pyelonephritis;
- Antibiotic therapy;
- Antihypertensive drugs;
- Diathermy.
Other medications are prescribed depending on the course of the disease and the severity of clinical symptoms.
Differences and characteristic signs of kidney diseases:
Source: gorlor.com
How to avoid the development of complications of tonsillitis on the kidneys?
The main and most reliable way to prevent the development of complications of tonsillitis on the kidneys is to carry out intensive antibiotic therapy for the disease with effective drugs. In most cases, inexpensive and relatively safe antibiotics of the penicillin (ampicillin, amoxicillin) and macrolide (erythromycin, azithromycin, josamycin) series are suitable for this. In some cases, cephalosporins may be indicated. Be that as it may, the decision on the choice of antibiotic is made by the doctor, since certain antibiotics for a particular patient may be either ineffective or dangerous.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner for a sore throat, it is enough to take antibiotics in tablets or capsules - they are no less (and sometimes even more) effective.
It is important to start antibiotic therapy as early as possible, immediately after the symptoms of a sore throat appear, without waiting for the right, left or both kidneys to hurt or other complications to appear. In this case, it is possible to replace the antibiotic if it turns out to be ineffective. In addition, early use of antibacterial agents shortens the duration of the disease and contributes to the rapid normalization of the patient’s condition.
Finally, an antibiotic for a sore throat should be taken for as long as indicated by the doctor. It is unacceptable to stop taking it immediately after the condition has normalized, if the prescribed period of use has not yet been completed.
In some cases, long-term prevention of complications of angina is carried out with bicillins. In many situations, it is required when any of the previous rules are violated and increases the risk of complications. Such bicillin prophylaxis is sometimes carried out for several weeks, months and even years on an outpatient basis.
Among diseases affecting the ENT organs, tonsillitis is considered the most common. In 90% of cases, the cause of the disease is a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection, less often viral or fungal pathogens. Sore throat as an independent disease is not dangerous to human health, but when the patient does not adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations, the disease is fraught with its own complications. Many patients after an acute period complain that their kidneys hurt after a sore throat. Such complaints should not remain unattended by a competent specialist.
Any complications that occur with tonsillitis can cause the development of chronic diseases. Complications on the kidneys after a sore throat can occur for several reasons:
- lack of proper treatment;
- incorrect diagnosis;
- failure to comply with doctor's instructions;
- presence in the person’s medical history of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
Those at risk for developing complications are people with reduced immunity, children, as well as those who lead an unhealthy lifestyle, abuse alcohol, and do not watch their diet. The child’s body is in the stage of growth and development and is not always able to resist pathogenic bacteria, so the risks of complications after a sore throat are quite high. Competent treatment under the supervision of a doctor will significantly reduce the possible consequences of the disease.
Normally, the human kidneys perform a kind of “laboratory” function for the body. They remove toxins and harmful substances. When their work is disrupted, toxins begin to accumulate in the body, causing symptoms of intoxication. If kidney function is impaired, the recovery period will take much longer. Complications of sore throat often appear when the patient refuses to treat the disease with antibiotics, prefers traditional medicine, or completely ignores the symptoms of the disease.
The causative agents of sore throat (streptococci, staphylococci) contain antigens that are similar to kidney and cardiac tissues. During the development of angina, human immune antibodies begin to resist infection and destroy foreign antigens, affecting those contained in the kidney tissues. As a result, the kidneys cannot cope with their functions, which increases the risk of complications.
Why do complications occur?
Sore throat is an inflammatory process that is characterized by a sharp rise in temperature and a white coating on the tonsils. In addition, the person has a very sore and sore throat. At the same time, the patient’s immune system begins to actively produce antibodies to the infection. Antibodies are proteins whose job is to destroy foreign antigens. But streptococci, the causative agents of sore throat, contain antigens similar to kidney, heart and other tissues of the body. Therefore, when the immune system begins to attack foreign microorganisms, it can accidentally destroy organ tissue. As a result, this leads to complications. The consequences of sore throat are especially severe for children. Thus, the child’s kidneys are in the stage of growth and development, and their damage slows down this process. Therefore, it is especially important to diagnose sore throat in children in time and subsequently treat it correctly.
Kidney disease due to sore throat
Complications of tonsillitis can be early or late. The consequences of the disease can be noticed on the 4-5th day of illness. Late ones appear 1-2 or more weeks after the acute period. Among the consequences of angina that affect the functioning of the kidneys and urinary system are:
- pyelonephritis;
- nephritis;
- poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis;
- glomeluronephritis.
Severe complications include renal failure, which is characterized by a complete or partial decrease in kidney function.
Attention! Nephrologists assure that in 75% of cases the cause of acute nephritis and pyelonephritis is a previous sore throat, the treatment of which was carried out incorrectly.
Sore throat in children and its complications
Complications of angina in children can manifest themselves in the form of a retropharyngeal abscess, which is characterized by the development of pustular formations in the back of the pharynx and spine. This is where the lymph nodes are located in children.
6 years after birth, the lymph nodes disappear, and therefore complications of this kind cannot appear in an adult. But in children, this disease negatively affects the respiratory process, which can result in suffocation. To prevent such an outcome, surgical intervention by a surgeon will be required, who during the operation will open a purulent abscess located in the larynx.
Signs of complications
According to medical observations, kidney damage after tonsillitis ranks second after the heart. Complications can be recognized by severe symptoms, which may appear 1-4 weeks after tonsillitis:
- discomfort, pain in the lumbar region, lower abdomen;
- increased body temperature;
- problems with urination;
- urine becomes cloudy;
- blood in the urine;
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling of the limbs;
- deterioration in general health;
- signs of intoxication.
The symptoms that appear should be a reason for immediate contact with a urologist or nephrologist. Self-medication for such symptoms is unacceptable.
Treatment
If pain in the kidneys occurs, along with other characteristic symptoms, you should immediately consult a urologist or nephrologist. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. The doctor will prescribe a series of examinations. It usually includes a general and clinical blood and urine test and an ultrasound examination.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe adequate drug therapy, including antibiotics and symptomatic treatment with anti-inflammatory and herbal medicines. Clearly expressed signs of glomerulonephritis are indications for hospitalization.
In addition to drug treatment, it is important to maintain bed rest and adhere to a diet. Also, with pyelonephritis, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, while with glomerulonephritis, the amount of fluid should, on the contrary, be limited.
Prevention of complications
Sore throat is a bacterial disease, so taking antibiotics is mandatory. In addition to antibacterial therapy, the patient must take other medications prescribed by the doctor for oral or topical use.
Even minor viral colds have a severe impact on the kidneys. Decreased immunity forces the heart and kidneys to work to the limit, so if a patient experiences lower back pain with the flu or sore throat, they should see a doctor.
Why do complications occur?
The causative agents of sore throat are streptococci and staphylococci, as well as more than 80 strains of viruses. These microorganisms can cause complications on the kidneys after a sore throat. In addition, there are a number of other reasons due to which negative consequences may develop.
- Failure to comply with bed rest, neglect of sanitary standards, unbalanced diet.
- Incorrect treatment of sore throat - advanced disease, incorrectly selected course duration, dosage or group of antibiotics (see Which antibiotics to choose for sore throat) can also cause complications. In this case, the infection that was in the tonsils does not die completely, but circulates throughout the body with the flow of blood and lymph. In such cases, the infection needs time to settle in the new organ, so after a sore throat, the kidneys usually hurt for 7-14 days.
- About 10 viruses that cause tonsillitis are classified as “rheumatogenic” - the structure of these viruses is very similar to the structure of the tissues of the heart, kidneys and joint membranes. Once they enter the body, the immune defense is activated not only against these viruses, but also against one’s own tissues. As a result, autoimmune processes develop that cause inflammation of the kidneys of various natures.
Symptoms of complications
As a rule, at the initial stage the disease does not have pronounced symptoms: slight pain, you want to go to the toilet a little more often. But with the development of pathology, the following signs appear:
- persistent, persistent pain in the lower back of a stabbing or aching nature;
- pain in the lower abdomen, groin;
- febrile state, aggravated by temperature fluctuations;
- change in the color or smell of urine;
- all signs of intoxication: fatigue, headache, nausea, less often vomiting;
- swelling of the eyelids and face, especially noticeable in the morning;
- frequent urination, sometimes painful;
- blood pressure surges due to excessive hormone production.
Symptoms can be simultaneous or appear separately. The degree of manifestation of symptoms depends on the dynamics of the disease, the prevalence and intensity of infection.
What else you need to know about complications
In this video, Dr. Phil will talk about complications after a sore throat:
- The degree of damage to organs by bacteria will help determine a blood test for ESR after a sore throat (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). If the blood on a special scale shows a high level of inflammation (in women more than 20, in men more than 15), then in this case only an antibiotic is needed. In pregnant women it can even be 33, the same in women after IVF. For them, this figure does not exceed the norm.
- Problems arise for a person if he needs to have his gastrointestinal tract examined, and his pharynx is affected by tonsillitis or other complications after a sore throat. After gastroscopy with a probe, such a patient will have a laceration in the throat.
- If you decide to undergo in vitro fertilization, be sure to prepare your body for the procedure and bearing a child so that any residual effects from a recent sore throat do not harm the plan, since complications can lead to fetal rejection.
Diagnosis, treatment
To make a correct diagnosis, a specialist needs to collect tests and anamnesis. The patient will have to undergo examination. The presence of infection will be shown by the following test results:
- the presence of protein in urine – normally it should not be there;
- high red blood cell count;
- leukocyturia;
- ESR – increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- a high level of creatinine is a clear indicator of the presence of inflammation in the genitourinary tract.
In addition to laboratory tests, it is a good idea to undergo an ultrasound to identify the location and extent of the disease.
After collecting data, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment. Conservative therapy is limited to antibiotics, the course of which is drunk in the specified volume. It is imperative to maintain a diet avoiding too salty, fatty, heavy foods and alcohol, as well as maintaining a drinking regime to facilitate kidney function.
Herbal renal infusions help very well, helping to eliminate infection, reducing pain symptoms and serving as a good preventive measure for the development of renal pathologies.
Important! The main thing is to prevent the disease from developing into a chronic form, as this can lead to long and expensive treatment and the need to maintain a diet throughout your life. Otherwise, complications on the kidneys, after the usual sore throat or flu suffered on the legs, can end fatally
What to do when your kidneys hurt after a sore throat
If, after suffering from a sore throat, symptoms appear indicating disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Based on the collected complaints, the results of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, the doctor will be able to determine the cause, the degree of damage to the kidney tissue, make the correct diagnosis, and then prescribe the necessary therapy.
Treatment for diseases affecting the kidneys depends on the diagnosis. Complex therapy for any disease of the urinary system and kidneys consists of taking medications, following a diet, and a healthy lifestyle. The doctor can also recommend traditional medicine recipes that will complement the basic treatment and speed up the recovery period.
Drug therapy may include symptomatic and systemic medications to manage the cause and symptoms of the disease. This:
- antibiotics;
- uroseptics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- herbal preparations;
- hormonal immunosuppressants.
The choice of medication always remains with the attending physician. Often, after tonsillitis and the risk of complications, Bicillin is prescribed, the administration of which will minimize the negative consequences. After administration, the active component of the drug retains its effect for a week.
Taking medications will eliminate the source of infection, improve kidney function, and prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
Treatment of kidneys after tonsillitis in addition to taking medications:
- bed rest in the first days of illness;
- take all medications prescribed by your doctor;
- drink plenty of fluids;
- follow diet number 7.
Important! If glomerulonephritis develops against the background of a previous sore throat, the amount of daily fluid should be reduced. For pyelonephritis - increase to two liters per day. Fruit drinks, herbal teas, and compotes are allowed as drinks. Coffee and any alcohol should be completely avoided.
After treatment, the patient may be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, therapeutic exercises, and kidney massage. All these techniques will help improve blood supply to the kidney tissues and improve their functionality. Sanatorium-resort treatment in latitudes with a warm climate, healing waters and mud will bring benefits.
If you detect kidney pathology that appears against the background of a sore throat in time and carry out the correct treatment, you can prevent the disease from becoming chronic, thereby avoiding problems in the future.
Infectious kidney diseases
The paired filtration organ is the body’s weak point. Due to the fact that the kidneys process all the blood and fluid, they are susceptible to the slightest infections. The most common complications are:
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the renal glomeruli (glomeruli), characterized by a violation of the filtration process. Destruction of the functioning of organs is expressed in a change in the color of urine, its accumulation, less excretion and, as a result, intoxication of the body up to kidney failure. The disease is extremely dangerous, difficult to treat and occurs regardless of the patient’s age or gender.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys that does not have pronounced symptoms and is often painless. The danger of pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney tissue, blood vessels, and tubules. The infection affects absolutely all organ systems and at any time can provoke a purulent abscess, damage to the cortex and, as a result, renal failure.
Important! Both pathologies can be acute or chronic. The disease must be treated regardless of the stage of diagnosis. If therapy is insufficient, the body will receive a huge dose of toxins, which will further disrupt kidney function. Infections of internal organs are the number one cause of infertility in men and women
What diseases cause complications?
The kidneys are paired organs involved in urine formation and excretion. In addition, they have a lot of vital functions, failures of which can cause serious health problems.
The kidneys hurt after a sore throat with the following diseases:
- Glomerulonephritis is a disease that is manifested by inflammation of the capillary glomeruli (glomeruli). Most often, after a sore throat, a complication on the kidneys occurs if its causative agent was streptococcus. After a couple of weeks, a headache, increased body temperature and blood pressure appear. Further, due to disturbances in the kidney filtration system, edema, oliguria (decreased amount of urine excreted), proteinuria and gross hematuria develop (urine takes on the color of meat slop). In addition, there are complaints of lower back pain, loss of appetite, weakness and nausea.
Quite often, the clinical picture is mild or only urinary syndrome is present; this condition is called the monosymptomatic variant and makes diagnosis extremely difficult.
Characteristic manifestations of the disease:
- Clear signs indicating the presence of glomerulonephritis are severe edema and arterial hypertension.
- Edema, in most cases, is so pronounced that it leads to the development of anasarca (swelling of the subcutaneous tissue), and in some cases to ascites or hydrothorax.
- Arterial hypertension is manifested by a sharp increase in blood pressure up to 160-180/90-100 mm Hg, with possible symptoms of shortness of breath and an increase in heart size.
- A complication of the kidneys after a sore throat can be caused by pyelonephritis , an infectious-inflammatory nonspecific disease that affects the renal parenchyma, renal pelvis and calyces.
The disease manifests itself as high body temperature, chills, which are replaced by heavy sweat, pain in muscles and joints, nausea and vomiting, and headache. In addition, there is pain and muscle tension in the lower back, urination is copious, frequent and painful.
After a sore throat, a complication on the kidneys is manifested by a characteristic feature - asymmetric kidney damage - either one kidney or both are involved in the pathological process, but the damage to one of them is more pronounced.
Important! If treatment for kidney diseases is not started in time, serious complications may develop - acute renal failure, eclampsia, acute left ventricular heart failure.
Prevention
The most terrible diseases can be avoided if you lead a reasonable and correct lifestyle. Simple tips will help both patients who already have kidney complications, and those who want to protect themselves from pathologies:
- Dress for the weather. This means that the kidneys should be covered, the feet should be dry and warm.
- Avoid frequent drinking, smoking, and eating large quantities of very fatty foods.
- Monitor your weight – excess obesity increases the risk of kidney infection with all the ensuing consequences.
- Do not tolerate sore throat, flu, or other colds and infectious diseases on the legs. Even if it is not possible to take full sick leave, the patient can spend a day in bed.
- Treat infectious diseases to the end, do not end the course of treatment as soon as the first bright symptoms have passed.
- Try to constantly improve your immunity: walks, vitamins, water - these three components will help support the body during the off-season.
And, of course, try to be less nervous. It’s not for nothing that they say that “all diseases come from nerves” - this statement is most relevant to today. During periods of stress, the body spends huge reserves of vitality and resources, but the patient does not pay attention to recovery. Depletion of immunity is the surest path to all diseases. Take care of yourself, get treatment on time, don’t be nervous, even if your boss demands it, and be healthy!