The kidneys are a paired organ that is one of the organs of the excretory system. They, along with the lungs and liver, remove all toxins, metabolic products and other harmful substances from the body. Is it worth talking about the powerful load that falls on the urinary organs throughout a person’s life. Therefore, if a patient has kidney pain and nausea, it is worth taking care of the healthy state of the excretory organ as quickly as possible, which means contacting a specialist urologist or nephrologist. Timely diagnosis of the pathological process will make it possible to restore diseased organs to health and fully restore their filtering capacity. Otherwise, the patient is at risk of developing renal failure.
Important: nausea with kidney pain can accompany any renal pathology. However, first of all, you should make sure that it is the kidneys that are hurting, and not nearby organs or the spine.
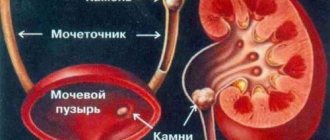
Urolithiasis disease
In urological practice, this condition is called urolithiasis. The formation of kidney stones occurs when calcium salts, uric acid crystals and other mineral salts accumulate in the renal pelvis.
The danger of this disease lies in the fact that full-fledged stones, when spontaneously moving, cause blockage of the ureter, which leads to the development of acute urinary retention. The advanced form of urolithiasis is characterized by renal intoxication, accompanied by acute pain, decreased daily diuresis or anuria, the appearance of a sallow skin color, nausea and vomiting.
Traditional recipes for pain
If pain develops in the kidneys and it is impossible to visit a doctor, you can try using folk remedies for pain.
These are herbal teas that are consumed instead of regular ones. Herbs such as motherwort, bearberry, cornflower petals, and licorice root have a good effect on the functioning of the organ.
The listed herbs are mixed in three tablespoons each and 300 ml of boiling water is poured. This tasty and healthy drink will significantly improve the patient’s health and well-being.
Pyelonephritis
Inflammatory damage to the renal pyelocaliceal apparatus occurs, as a rule, under the influence of an infectious factor. Other potential causes of this disease include traumatic kidney injuries, previous surgical interventions, as well as congenital or acquired abnormalities of the ureter structure.
Symptoms of renal intoxication with pyelonephritis do not have characteristic differences. Patients complain of severe nausea, vomiting, nagging pain in the lumbar region, discomfort and pain when urinating, general weakness and increased body temperature. Infectious pyelonephritis can be provoked by pathogens such as enterococci, staphylococci and E. coli.
Diagnostics
If the pain syndrome does not go away for a long time, then you need to consult a doctor.
If the pain syndrome does not go away for a long time, then you need to consult a doctor. In most cases, especially if the Pasternatsky test was negative, warming up the lower back is used, since in this case there is a high probability that the pain is associated with the spine or muscles. However, this should not be done if the kidneys are inflamed.
To diagnose the disease, the doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- UAC. In case of problems with the spine, no deviations from the norm will be found in the blood, but in case of problems with the kidneys, there is an increase in ESR, leukocytosis and anemia.
- The most informative test for kidney problems is a urine test. In this case, leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, and pathogenic microflora can be found in the urine. The density of urine changes.
- Using ultrasound, it is easy to assess the location of the kidneys, their shape, size, the presence of stones and other abnormalities.
- An X-ray is taken both for osteochondrosis and for kidney problems. In the latter case, contrast radiography will be more informative.
Important: for renal tumors and osteochondrosis, CT and MRI are especially informative.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are prescribed if the following additional symptoms are present:
- headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- pain radiating to the shoulder with simultaneous numbness of the fingers;
- if pain occurs in the buttocks and intensifies.
Nephroptosis
This condition is characterized by a change in the anatomical position of the kidney due to its descent downwards. As a rule, the paired organ extends beyond its bed with a sudden significant loss of body weight, with regular weight lifting, as well as under the influence of other internal factors.
Most often, nephroptosis is diagnosed in young and middle-aged women who tend to indulge in various diets and therapeutic fasting. Very often, nephroptosis is formed under the influence of such factors:
- Long-term chronic constipation;
- Traumatic damage to the ligamentous apparatus fixing the kidney in the anatomical bed;
- Previously suffered rickets;
- Complications caused by pregnancy;
- Injuries of the lumbar spinal column.
Why do my kidneys hurt and feel sick at the same time? How can I recognize the cause of the symptoms?
The kidneys are a paired organ; they are located on the back under the 6th rib.
The fact that a person has kidney pain and nausea is a common symptom of many pathologies. Pain may be felt on only one side or on both sides at once. As a rule, they are localized in the back area near the spine near the last thoracic and first lumbar vertebra. Basically, pain in the kidneys spreads in the direction of the ureters to the external genitalia.
The nature of the pain is pulling, stabbing, cutting. They appear spontaneously, by palpation, when walking or playing sports. Pain can be triggered by changes in body position, alcohol consumption, colds, mechanical damage, and in women - menstruation and pregnancy.
It is important! Pain can make itself felt due to impaired blood flow in the kidneys, mental trauma, and severe fatigue. Thanks to this, blood rushes to the kidneys, so the organ begins to swell, squeezing the capsules and causing renal colic.
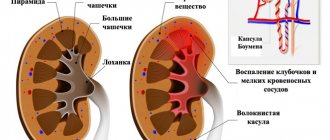
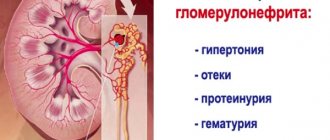
Glomerulonephritis
This pathological condition is of an autoimmune nature and is characterized by severe damage to the renal glomeruli. In addition to the autoimmune factor, the development of glomerulonephritis can be caused by pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the kidney through the ascending, hematogenous or lymphogenous route.
This severe pathological condition is accompanied by symptoms of renal intoxication, headache and dizziness, a decrease in the volume of daily diuresis or a complete absence of urine.
Along with the listed conditions, the causes of nausea and pain in the kidneys can be benign or malignant neoplasms in the area of the paired organ, as well as hydronephrosis, which is characterized by the accumulation of fluid inside the kidney, with its subsequent increase and the development of structural and functional failure.
Factors affecting kidney health
The urinary system, along with the liver, is the main factory for detoxifying waste, intermediate metabolites, drugs, and vitamins.
What can harm the urinary system?
- Unfavorable environment
- Air and drinking water pollution
- Toxins from food
- Excessive medication use
- Bad habits
- Unhealthy diet
- Frequent infections
- Chronic pathologies
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvis and glomeruli
- Toxic lesions or hypoxia (oxygen deficiency due to impaired blood flow)
For a long time, the kidneys may suffer silently; the person does not feel pain or other symptoms, although the functioning of the organs has already deteriorated significantly.
Kidney intoxication
The causes of nausea and pain in the kidneys are not only the above conditions, but also the entry of toxic substances and poisons into the human systemic bloodstream. Often this condition occurs when using certain groups of drugs, which with their metabolites damage the parenchyma of the paired organ.
If we say literally that this is kidney intoxication, then this is a pathological condition, as a result of which structural changes occur in the tissues of the organ, with the subsequent development of its failure. The so-called toxic nephropathy is characterized by rapid development and increased danger to human life and health.
In the initial period of structural and functional changes, intoxication is not accompanied by clinical symptoms or has a mild clinical picture. As structural and functional changes progress, the symptoms of renal intoxication take on the following form:
- Dyspeptic disorders, manifested by nausea and vomiting.
- Swelling in the face, neck, upper and lower extremities. This symptom complex indicates the development of functional renal failure.
- Pain syndrome localized in the lumbar spine. In some cases, patients complain of nagging pain in the lower back, which radiates to the perineum, left, and lower abdomen.
- Urinary disorders, which manifest themselves in the form of changes in the color of urine, the appearance of a characteristic sediment, a decrease in the volume of daily urine output or a complete absence of urine.
- Asthenovegetative syndrome. With the development of renal intoxication of various origins, a person experiences psychomotor retardation, general weakness, suppressed appetite, and decreased performance.
- Signs of hyperkalemia. When the filtration function of the kidneys is impaired, there is an increase in the concentration of potassium in the systemic circulation, resulting in changes affecting the functioning of the cardiovascular system and skeletal muscles.
This condition manifests itself in the form of depressed heartbeat, muscle weakness and a decrease in cardiac output.
Structure and functions of the urinary system
The kidneys are a key part of the urinary system.
Every healthy person has two of them, they are located deep in the abdominal cavity, on the back. They are located in the area of the border between the chest and abdominal cavity, on both sides of the spinal column, the upper third is covered by the ribs for additional protection in case of shocks or falls. The organs are shaped like beans; in adults they are the size of a human fist. If the kidneys are healthy, they filter about 200 ml of blood every minute, removing waste metabolic products, excess salts, and water in the urine.
The active work of organs maintains electrolyte balance - the correct ratio of minerals (sodium, magnesium, phosphorus).
They regulate protein metabolism, synthesize hormones that maintain stable blood pressure levels, and produce erythropoietin, a compound that stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells (erythrocytes).
Kidney health is important for maintaining skeletal strength - they regulate the metabolism of calcium and vitamin D.
Treatment
Therapy of renal intoxication of various origins requires an integrated approach, therefore such patients are usually treated in a specialized hospital. A comprehensive plan of therapeutic measures for this condition includes the following points:
- Detoxification measures. This set of measures is aimed at accelerating the elimination of toxic and metabolic substances, the accumulation of which served as a factor in the occurrence of intoxication. The components of infusion therapy are Ringer's solution, 5% glucose solution, and isotonic sodium chloride solution.
- The technique of forced diuresis, which consists of performing infusion therapy with one of the above solutions, followed by taking diuretics.
- Exchange transfusion of whole blood or plasma.
- In severe cases, patients are prescribed hemodialysis.
- Symptomatic therapy, including taking antiemetic, antiarrhythmic, analgesic and antihistamine (antiallergic) drugs.
If, against the background of severe renal intoxication, a person has developed exotoxic shock, glucocorticosteroids such as Prednisolone or Hydrocortisone are used to eliminate its manifestations. If a serious condition was provoked by the influence of poisonous and toxic components on the human body, then specific antidotes are administered to him.
Measures to help in case of organ damage as a result of poisoning
Since the kidneys are a vital organ, self-medication with traditional medicine should be avoided. Treatment and recovery should take place under the close supervision of the attending physician; the disease may have to be treated in a hospital.
The main emergency measure is first and foremost the removal of intoxication from the body. Drinking plenty of fluids is encouraged for several hours after poisoning. First aid also includes taking absorbent agents, for example, activated carbon. You should not take antibiotics if you are intoxicated.
If the symptoms of poisoning do not go away or a deterioration in the victim’s condition is noticed, then immediate hospitalization is necessary.
In a hospital setting, the patient undergoes measures: hemodialysis, diuresis, hemosorption. In some cases, a blood transfusion is required. The choice of treatment is determined by the doctor, based on studies showing the degree of organ damage.
Complications
Kidney intoxication of various origins is dangerous due to the complications it can cause. If a patient with a similar diagnosis is not provided with timely medical care, he may encounter the following complications:
- Development of DIC syndrome;
- Chronic renal failure;
- Exotoxic or septic shock;
- Renal failure;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Metabolic acidosis and hyperkalemia;
- Hypochloremic or uremic coma;
- Violation of cardiac conduction, which manifests itself in the form of arrhythmia and extrasystole.
What can a doctor do?
The doctor will first determine the cause of kidney failure and the stage of the disease. After which all necessary measures will be taken to treat and care for the patient.
Treatment of acute renal failure is aimed primarily at eliminating the cause that causes this condition. Measures are applicable to combat shock, dehydration, hemolysis, intoxication, etc. Patients with acute renal failure are transferred to the intensive care unit, where they receive the necessary assistance.
Treatment of chronic renal failure is inseparable from treatment of the kidney disease that led to kidney failure.