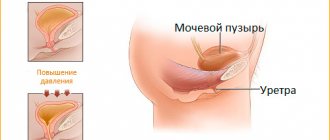
A paraurethral cyst is a closed cystic formation filled with secretion, localized in the area of the mouth of the urethra, less often in the canal itself.
Skene's glands (small vestibular glands, paraurethral glands) are glands located in the area of the external opening of the urethra on the anterior wall of the vagina, throughout the spongy body of the urethra. These glands produce a secretion that moisturizes the urethral mucosa. In some cases, the mouths of the Skene glands narrow, close, become clogged, and the internal cavity of the gland is filled with secretion, stretching its walls and forming a paraurethral cyst.
Paraurethral cysts in most cases are diagnosed in women of childbearing age, which is associated with the susceptibility of the glands to significant changes during different periods of a woman’s life. During pregnancy, women experience hypertrophy of the glands; in the postpartum period, involution is observed; the menopausal period is characterized by atrophy of the paraurethral glands.
A paraurethral cyst is a small tumor-like formation of a round shape, located mainly at the external opening of the urethra, less often in the depths of the superficial tissues, which significantly complicates the diagnosis of the neoplasm. The paraurethral cyst is palpable from the vagina; when pressed, mucous fluid may be released. If the cystic formation is complicated by an infectious-inflammatory process, the discharge may be purulent. An uncomplicated paraurethral cyst is characterized by an elastic consistency and the absence of inflamed tissue in the area of the cystic formation.
There are two types of paraurethral cysts:
- Skinian paraurethral cysts are cystic formations that occur when small glands located around the urethra are blocked;
- Gartner's duct cysts are cysts that arise as a result of abnormal development of the female genitourinary system. In rare cases, the germinal ducts between the vaginal wall and the urethra do not close, which leads to the accumulation of fluid in them and the formation of a cyst.
A paraurethral cyst of any type does not regress or resolve on its own. The longer a cyst exists in the urethra or in its vestibule, the greater the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process and suppuration. Paraurethral cysts provide a favorable environment for the accumulation of stagnant urine and the proliferation of bacteria. Inflammation of a paraurethral cyst can lead to the development of an abscess, which opens into the urethra with subsequent development of a diverticulum.
Description of the disease and its varieties
The area around the urethral opening and the female urethra itself is abundantly covered with small Skene glands. Their function is to moisturize the mucous membrane. At different periods of life they can be subject to serious changes:
- increase during pregnancy;
- deterioration in the functioning of the glands (involution) after labor;
- atrophy during the climatic period.
Sometimes the processes described above provoke narrowing or clogging of the mouths of the glands. The secretion secreted by the glands remains inside the formed cavity, thereby stretching it, and a paraurethral cyst develops.
Mostly, neoplasms appear at the mouth of the urinary canal, much less often they form in the urethra itself. There are cases of congenital pathologies that lead to the formation of a paraurethral tumor - non-closure of the duct located between the woman’s vagina and the genitourinary system.
Regardless of the cause of the disease, it must be eliminated correctly and in a timely manner. The tumor itself does not resolve, but only progresses over time.
In advanced cases, severe inflammation develops, since urine accumulates in the area of the cystic formation and is a favorable environment for the proliferation of painful microorganisms.
In medical practice, there are 2 forms of paraurethral neoplasm:
- Tabernacle cysts . They occur due to blockage of the small glands around the urethral canal.
- Gartner's cyst . They are formed due to the abnormal development of the woman’s genitourinary system.
Each of the forms can be in varying degrees of progression:
- The initial stage is characterized by infection of the gland and is mostly asymptomatic. Typically, cystic formations at the initial stage are detected during a routine examination. When the infection begins to spread, the woman experiences discomfort while emptying the bladder, as well as uncharacteristic discharge.
- The second stage is characterized by the growth of the tumor and a feeling of pain, especially during intimacy.
In 20% of cases, a paraurethral cyst does not manifest itself in any way for a long time, so it is necessary to regularly visit a doctor and undergo examinations.
Development of the disease
In the formation of pathology, two stages can be distinguished:
- Inflammation in the urethra leads to tissue swelling. As a result, the duct of the paraurethral gland narrows or is completely blocked. The mucus produced accumulates in the cavity, forming a cyst. Invaded pathogenic microorganisms multiply inside the formation. The first discomfort appears.
- The secretion continues to accumulate, the cyst grows not only due to it, but also due to the progressive growth of microorganisms. Suppuration occurs. Symptoms of the pathology become more varied and intense.
.gif' data-lazy-type='image' data-src='https://parnas42.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/1f1lz4lb.jpg' alt='01' width='506′ height ='327′ » data-'https://parnas42.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/kista_uretri.jpg 862w, https://parnas42.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/kista_uretri -300×194.jpg 300w, https://parnas42.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/kista_uretri-768×496.jpg 768w' sizes='(max-width: 506px) 100vw, 506px'>
Next, the infected fluid gradually leaks into the urethra, or the formation ruptures. Then a cyst forms in the cavity again.
Reasons for the development of cystic formation
The reasons that provoke the appearance of formation are varied and are closely related to failures in the drainage of the glands. The main ones are:
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- injuries of the urinary system;
- microtrauma of the urethra during hard sexual intercourse;
- various processes occurring during pregnancy;
- injuries that occurred after childbirth, such as ruptures;
- diabetes mellitus;
- use of low-quality intimate hygiene products;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- diseases that suppress the body's immunity.
If you discover the reasons described above, you must carefully monitor your health and do not delay consulting a doctor if you detect even the slightest discomfort in the urinary system.
Why does men urinate frequently at night?
Frequent urination at night in men is the most common reason for visiting a urologist; This pathological condition is called nocturia. Not all patients pay attention to this problem, however, this is an alarming signal that something is wrong in the body.
Symptoms of nocturia
Urination with nocturia occurs more often at night than during the day. This is due to the production of excess urine during sleep. Due to the need to frequently visit the toilet, the patient's sleep is disturbed. The man feels tired during the day and cannot sleep at night.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Constant urges contribute to memory deterioration, the development of aggression and depressive disorders.
Number of urinations and quality of urine
A healthy person excretes about 1.5 liters of urine per day. Increased urination when you are nervous, have a cold, or take a large amount of liquid is normal.
The volume of urine normally excreted at night is 20% of the daily volume for young men, and 30% for older men. In middle-aged people, this indicator is between the indicated values. Since with nocturia the daily amount of urine does not change, its abundant excretion at night is accompanied by a decrease in daytime volume. The quality of urine remains virtually unchanged; sometimes sugar or protein is found in it.
Causes of frequent night urination in men
There are many factors that contribute to the development of nocturia. First of all, these are diseases of the excretory system, diabetes and prostatitis. Rare causes are: acute heart failure, decreased tone of the pelvic floor muscles, use of diuretics, obstructive apnea, overactive bladder.
Diseases of the urinary system
The cause of nocturia can be some diseases of the urinary system: cystitis, urolithiasis.
Cystitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the bladder, which has unpleasant symptoms. Frequent urination is accompanied by pain and burning in the lower abdomen. The urine becomes cloudy, purulent and bloody inclusions appear in it. Body temperature often rises and a febrile syndrome develops.
Urolithiasis is a pathology in which stones appear in the kidneys, bladder and ureters. Nocturia is the first sign of this disease. Pain occurs when a stone passes through the urethra or ureter. Renal colic is observed.
In addition, frequent urination is a sign of diseases such as nephritis and pyelonephritis. However, when making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account typical manifestations: dull pain in the lower back, fever, general weakness, chills. Frequent night urination develops in the later stages of nephritis. The amount of urine decreases, and bloody inclusions appear in it. Inflammation of the urethra may also be accompanied by nocturia.
Diseases of the genital organs
Diseases of the genital organs such as prostatitis and prostate adenoma can lead to nocturia.
Prostatitis has an acute or chronic form. In addition to frequent urination, he has other pronounced symptoms. The urge occurs suddenly, and urine is released in drops. The problem gets worse, there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, pain and burning in the perineum, and general weakness.
Prostate adenoma and cyst are benign neoplasms that form from glandular tissue. The organ suddenly increases in size and puts pressure on the bladder. The disease is diagnosed mainly in older men. The patient frequently visits the toilet, and urine is excreted in small quantities; the stream is weak and intermittent. Incontinence develops.
Other factors
Nocturia often occurs during alcohol intoxication, which is associated with decreased muscle tone and intoxication of the body. Other causes of frequent urination include diabetes. Nocturia has long been the only symptom of this disease. It is discovered during a routine inspection. Frequent urination is accompanied by thirst, itchy skin, erectile dysfunction and infertility.
Diagnostics
If you experience frequent urination without pain, you should consult a urologist. The examination begins with collecting anamnesis and examining the patient. Be sure to donate blood for sugar. To confirm the diagnosis, urine culture, general examination and Zimnitsky's test are performed. A man should keep a urination diary for at least 3 days. Ultrasound of the bladder helps determine the residual amount of urine. Additionally, a general and biochemical blood test is prescribed.
Treatment for frequent urination at night
Treatment for frequent urination begins with lifestyle changes.
It is not recommended to drink a lot of water in the evening. Dinner should be completed no later than 3 hours before bedtime. If a man still drinks a lot of liquid, it is recommended to go to bed later.
Drug treatment
The selection of drugs is based on the cause of nocturia. For prostatitis, adrenoreceptor and 5a-reductase inhibitors are prescribed. Sometimes these drugs are taken at the same time. The drug Darifenacin normalizes the process of urination. The medicine relaxes the muscles, causing the urethra to open and urine to flow freely. If infections are detected, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Folk remedies
For prostatitis and adenoma, it is recommended to drink pumpkin juice (200 ml per day for 3 weeks) or eat the seeds of this vegetable. A decoction of birch leaves normalizes urination. 2 tbsp. l. raw materials, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, cool, filter and take 100 ml in the morning and evening.
Blackcurrant leaves are useful for cystitis. 150 g of raw materials are poured into 2 glasses of hot water, infused in a thermos and drunk instead of tea. For inflammatory diseases, take parsley-based remedies. 50 g of greens are poured into 0.5 liters of milk, heated in a water bath for 20 minutes and taken 100 ml every hour. For overactive bladder, drink plantain decoction. 1 tbsp. l. dry leaves, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 2 hours and take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day.
Prevention
Observing a special drinking regimen and avoiding coffee and alcohol in the evening helps prevent the development of nocturia.
You need to regularly visit a urologist and treat diseases of the genitourinary system.
Clinical picture of the pathology
The main complaints from patients when visiting a doctor:
- swelling in the area of the urethra, some discomfort;
- difficulty urinating and feeling pain during the process, weak urine pressure - these complaints indicate that the cyst has increased (up to 4 cm);
- discomfort when moving;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of a paraurethral cyst in the presence of infection in women:
- obvious increase in tumor, accompanied by pain;
- feeling of burning and itching;
- feeling of fullness in the groin;
- difficulty urinating and cutting pain;
- in rare cases, discharge of pus is observed.
Sometimes the inflammation process subsides on its own or is blunted by taking antibiotics when treating another disease. However, the neoplasm with the pus it contains does not regress, and its walls become denser.
If this condition is neglected and treatment is ignored, small stones will form inside the formation.
Symptoms
If the paraurethral cyst is small in size, the pathological process will occur without the manifestation of characteristic symptoms. As the disease progresses, corresponding signs and discomfort will appear.
On this topic
- urinary system
How to improve urination with prostate adenoma
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- November 29, 2020
The most common symptoms include:
- swelling of the soft tissues surrounding the cyst;
- difficulty urinating;
- discomfort during movement or sexual intercourse;
- feeling of squeezing from inside;
- purulent discharge from the urethra;
- hematuria;
- burning sensation and pain in the urethra;
- low rate of urine output;
- pain;
- feeling of the presence of a foreign object;
- urethral diverticulum.
A paraurethral cyst does not have a predisposition to self-resorption. If one or more symptoms occur, immediate assistance from a specialist is required.
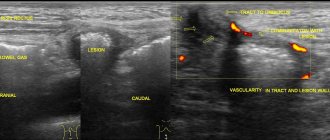
Diagnostics
If during a gynecological examination the patient talks about characteristic complaints, the doctor may assume the presence of a formation in the urethra and refer her to an appointment with a urologist. During diagnosis, the doctor first examines the urethra. To make a diagnosis, you will need to undergo the following tests:
- collect urine for general analysis and culture it;
- undergo an ultrasound examination of the uterus, appendages, and all organs of the urinary system;
- cytological examination of urine;
- in some cases, undergoing an MRI;
- taking a smear from the urethra;
- uroflowmetry (measurement of urinary flow rate);
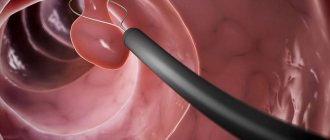
- endoscopic examination of the urethra and bladder (urethrocystoscopy).
Based on the results obtained during the diagnosis, the doctor will confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Prognosis and possible complications
If the treatment course is not started in a timely manner, the disease develops into complex forms. For them, the hardness of the abdomen and an increase in its size are considered inherent. Attacks of pain begin. In this case, the person is subject to immediate hospitalization, he is diagnosed and surgery is prescribed.
Many people simply do not think about a cyst, although the risk of its appearance is present in everyone without exception. The initial stages of the appearance of a cyst do not bring any discomfort, but it is not recommended to ignore the problem. Pus can accumulate in the resulting cavity and the cyst ruptures.
It must be remembered that if a cyst is found in the bladder and it does not manifest itself in any way, you cannot avoid surgery. The formation must be removed unambiguously to avoid life-threatening consequences.
Traditional treatment
Despite the degree of progression of paraurethral urethritis in a woman, drug treatment is a temporary measure and is used before surgery or in the postoperative period. Taking medications is indicated only if there is inflammation in women, which does not allow surgery. If conservative therapy is delayed, it is possible to open the cyst to alleviate the patient’s condition and rupture the tumor.
The opening of the formation is carried out in the doctor’s office, observing all sterility measures, or in the clinic. A small puncture is made on the wall of the cyst and the purulent contents are removed from there, after which antibacterial medications are prescribed.
Soon the cystic cavity fills again, this takes about 1 month. During this period, it is advisable to have time to eliminate the inflammatory process in order to eliminate the cyst without consequences and difficulties, since repeated opening weakens the tumor tissue and increases the chance of sudden rupture.
Medication and folk treatment
It is impossible to completely get rid of a urethral cyst without removal surgery. But the treatment in any case will be complex, since as long as there is an inflammatory process in the urethra, surgical intervention is not performed. Opening a paraurethral cyst without removing it gives only a temporary effect, since the membrane of the neoplasm remains in place. Doctors perform emergency surgical intervention only in cases of severe suppuration and suspected rupture of the capsule of the formation.
Removal of tumors in the urethra
Surgical removal of a paraurethral cyst is the only method to eliminate the pathology. The operation involves excision of the tumor walls and is performed under any type of anesthesia (local, general anesthesia). Typically, laparoscopy is used for these purposes.
The surgeon performs manipulations through small punctures in the peritoneum, monitoring his actions on a computer screen. Since the cyst is located in a place that is not so hard to reach, it is impossible to get serious injuries during the operation.
After removal of the paraurethral cyst, the patient is under the supervision of medical workers in the hospital, as a catheter is inserted into the urethral canal for several days. After discharge from the hospital, the patient must take a course of prescribed antibiotics and exclude sexual activity for a period of 2 months.
Depending on the complexity of the cyst, complications may occur after surgery:
- narrowing of the urethra and relapse of the disease;
- increase in regular pain;
- purulent fistulas in the vagina;
- hematomas;
- development of infection;
- bleeding.
The postoperative result depends on the experience of the operating doctor, so this procedure should be taken with full responsibility and carefully select the clinic for the operation.
What is the disease?
A urethral cyst in women is a round formation filled with secretory fluid and located at the mouth of the urethra or in it.
Paraurethral cysts are formed from the vestibular glands of the urinary tract (Skeene's glands), localized outside the urethral opening on the anterior wall of the vagina, throughout the corpus spongiosum. Skene's glands secrete a secretion, the purpose of which is to moisturize the mucous walls of the canal. In some cases, the urethral glands become inflamed, the excretory duct becomes blocked due to swelling with mucus, bacteria, and epithelium. Then, due to the obliteration of the duct, the secret fluid does not come out, and therefore a urethral cyst is formed, which has a tendency to grow slowly.
Stagnation of secretory fluid in the gland is not always associated with inflammation - often the disease occurs as a result of hormonal changes that occur in the human body throughout his life.
A urethral cyst in women is palpated from the vaginal side as a round, hard-plastic formation, which can sometimes release fluid when pressed; If there is an infection in the cyst, pus is often released.
What are the dangers of not seeking help in a timely manner?
Paraurethral tumor is not able to go away on its own. The disease requires therapeutic measures. If treatment is ignored, there is a risk of developing an inflammatory process in the urethra or its vestibule, as well as the appearance of pus inside the cyst cavity.
Pathology provides a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacterial infections and the accumulation of stagnant urine, as a result of which a woman may experience parallel inflammation in the genital tract area. Such complications lead to the accumulation of pus in the tissues and the formation of diverticula.
Lack of therapy increases the chance of the cyst degenerating into a malignant tumor, so you need to monitor for uncharacteristic sensations in the urethra and be regularly examined by a specialist.
What is a paraurethral cyst?
Neoplasms of this localization are a female pathology, according to statistics, detected in 1–3% of patients. More than 80% of cysts occur in women aged 20 to 50 years .
The urethra (urethra) in women is a tubular organ 3–5 cm long, located in front of the vagina and opening into its vestibule. In the soft tissues surrounding the canal at a distance of 5–30 mm, Skene’s glands (paraurethral) are located.
The main part of the glands are concentrated along the lateral surfaces of the middle part of the urethra, and the mouths of the glands are located on the lower wall of the canal, near the external opening. In addition, there are from 6 to 31 glands and their mouths (epithelial pockets) in the lower third of the urethra - these ducts surround the “tube” on all sides.
The tabernacle glands in women are similar in structure to the male prostate gland and develop from similar embryonic rudiments. Their function is to secrete mucus to moisturize the urethra and create a protective barrier that prevents pathogenic flora from the vagina from entering the urethra.
The urethral cyst has a code according to ICD 10 - D 30.7. – “benign neoplasm of other urinary organs.”
Among the cavities there are:
- Congenital - usually refers to cysts of the Gartner's duct (canal, cord), located parallel to the fallopian tube and continuing along the cervix and vagina. If fusion of the canal does not occur (in 25% of patients), a cyst of the duct from the cervix along the lateral wall of the vagina may develop. It can reach significant sizes, protrude towards the urethra and be mistakenly identified as a diverticulum.
- Acquired – developing in adulthood due to narrowing/blockage of the gland duct. These are retention-type cavities filled with a mixture of mucus and inflammatory discharge.
Acquired urethral cysts are often located at the external opening, less often - deeper, on the walls of the urethra.
According to some experts, paraurethral cystosis is a condition that precedes diverticulosis (the formation of “pockets” on the walls of a tubular organ) of the urethral mucosa.
Disease prevention
Every woman who cares about her health needs to know measures to prevent the occurrence of the disease. After all, it is more expedient to prevent the development of a cyst than to treat it in the future. The doctors' recommendations are as follows:
- Timely sanitation and proper treatment of foci of acute (chronic) infection of the genitourinary system.
- Avoid promiscuity.
- Have sex with a condom.
- Use high-quality intimate hygiene products, preferably based on natural ingredients.
- Wearing underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Regular examinations by a gynecologist and urologist.
Following simple rules of prevention will help prevent the occurrence of a pathological condition. And if you discover alarming symptoms, you should definitely seek help from a doctor and under no circumstances self-medicate.
Prevention of pathologies of the urethral canal
You can avoid the appearance of formation in the paraurethral organs if you follow the following precautions:
- Treat any inflammatory diseases,
- Prevent infection. Use condoms, avoid casual relationships,
- Keep your body and genitals clean,
- Wear panties only from natural fabrics,
- Change sanitary pads every 3-4 hours,
- Choose hypoallergenic mild cleansers for the intimate area,
- Conduct regular examinations 1-2 times a year.
- Such preventive measures are effective for any pathology of the genitourinary system.
An important role is played by hormonal levels and immune status, which largely depend on a person’s diet and lifestyle. The presence of harmful addictions in the form of alcohol and smoking, as well as an unbalanced diet, leads to breakdowns of the body at all levels. As a result, infections flourish, neoplasms grow, and pathologies are layered on top of each other. That's why it's so important to eat healthy foods and lead an active, healthy lifestyle.
Urethral cyst in women
Paraurethral cysts in women are not as common as other types of tumors. Surgical methods are almost always suitable for its treatment. Severe symptoms appear if the formation grows to a large size, before which the woman may not even suspect its existence.
Typically, 8% of women experience this disease. At a young age, the risk of its occurrence is much higher than at an older age. There are a number of factors that influence the development of this pathology.
What it is
A paraurethral cyst is a pathological formation in the mouth and other places of the urethra. It has a round shape and contains liquid inside.
The source of fluid accumulation is the paraurethral and Skene glands, located on the anterior wall of the vagina. These glands are necessary for secreting moisturizing secretions.
Under certain factors, the mouth of the glands becomes blocked and a cyst appears.
Only the female half of the population faces this disease. An increase in the size of the glands can be observed during pregnancy, and after childbirth they become the same. Hormonal imbalance also affects the size of the tumor. During menopause, the moisturizing glands atrophy, so after 50 years the disease is less common.
Classification
There are two types of cysts on the urethra in women:
- Gartner's duct cysts are usually congenital, resulting from fusion of the vaginal wall with the urethra.
- Tabernacle cysts. They form around the urethra and develop due to impaired outflow of secretions produced by the glands.
Causes
Congenital neoplasms appear extremely rarely. More often, these cysts occur due to injury to the urethra or inflammation due to:
- acute form of chronic urethritis;
- excessive use of intimate hygiene products;
- weakened immune system;
- STI;
- childbirth accompanied by trauma to the perineum;
- rough sexual intercourse;
- blows, falls that led to injury.
The formation of paraurethral cysts is characterized by staged development.
The first stage is often asymptomatic. Damage or inflammation of the gland occurs, and the orifice becomes blocked. This cyst can be detected during examination. The second stage is accompanied by active growth, the first clinical signs appear, due to which the woman is forced to consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Detection of a formation occurs, as a rule, when it reaches a large size. A woman complains to a gynecologist or urologist. Small cysts are rarely diagnosed.
Detection can also occur during a routine examination, and the woman does not have any alarming symptoms. The cyst is located at the entrance to the urethra. In rare cases, it develops deeper.
Here the doctor requires instrumental techniques to accurately confirm the diagnosis.
After the initial examination, the specialist prescribes:
- Ultrasound using a transvaginal probe;
- urethroscopy.
The formation is differentiated as a vaginal cyst. Additionally, the woman undergoes a general blood test to exclude the possibility of developing an inflammatory process. Additionally, urine is examined for bacterial culture. This way the doctor will see the overall picture of the body’s condition.
Signs
A small, non-decaying cyst does not bother a woman. During this period there are no phenomena that worsen your health. The first ailment appears when the formation begins to actively grow. Pain and discomfort appear during sex. Many people complain of a feeling of fullness and discomfort that occurs even while walking.
A number of other signs characteristic of this condition have also been identified:
- It is already possible to visualize the swelling at the entrance to the urethra.
- The woman notices that urine comes out in just a few drops. This brings significant discomfort.
- The process of urination is accompanied by a burning sensation, pain, and stinging. These are similar to the symptoms of urethritis.
- Small amounts of purulent discharge and blood may appear from the urethra.
- There is urinary incontinence.
If the cyst suppurates, symptoms of general inflammation appear. There is an increase in body temperature, headache attacks, weakening of the body, malaise, and a feeling of severe fatigue.
If any alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately visit a doctor, get tested, and undergo the necessary diagnostics to make an accurate diagnosis. Ignoring the situation can worsen the body's condition.
Treatment methods
Treatment of a paraureal cyst involves surgery. This problem cannot be completely overcome using conservative methods. The doctor selects the most appropriate complex therapy methods that prevent the development of inflammatory processes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=57mZ-u62zeQ
Without surgery by opening the tumor, the effect will be short-lived. Therefore, the patient is recommended to have it removed. An exception is possible if severe suppuration develops. First, the formation is pierced with a needle and the pus is pumped out. Then a course of antibacterial therapy is required to stabilize the person’s condition.
Drug therapy
Conservative therapy, chosen at the very beginning of treatment, involves puncturing and pumping out the internal contents of the cystic formation. The next stage is treatment of the developing infection. For this, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. The duration of treatment is from 7 to 14 days.
The prescription of antibacterial drugs is fully justified before surgery. This prevents possible complications. The operation is usually scheduled 25-30 days after the contents of the tumor have been pumped out.
A patient who refuses surgery should understand that conservative treatment increases the risk of rupture of the formation.
Removal operation
Removal of a parauteral cyst is performed using general anesthesia. This is the only method that increases the chances of no relapse in the future. Laparoscopy is used if the formation is located in the distant parts of the urethra.
The first 5-7 days after surgery, the woman is in the inpatient department under the supervision of a doctor. The catheter is in the urethra for two days after the procedure. The recovery period includes sexual rest for a period of 1.5 to 2 months. Physical activity should also be excluded for the same period, this is provided for by the operation performed.
Possible complications
If a woman’s urethral cyst is not removed, suppuration occurs in it, since it does not resolve on its own. In addition to suppuration, there is a possibility of developing infections in a chronic form, for example, cystitis, urethritis. Removal of the formation has a favorable prognosis.
Lack of treatment contributes to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the accumulation of stagnant urine, which causes diseases of the genital tract. This often causes the accumulation of pus in the tissues and the development of diverticula.
After the operation, there is also a risk of some complications:
- due to the formation of adhesions, the urethra narrows;
- pain;
- re-formation of the tumor;
- bleeding;
- inflammation.
With timely medical care, a paraurethral cyst can be treated quickly and effectively. If you ignore this pathology, it will cause the development of various negative symptoms.
Source: https://kistaoff.ru/drugie-organy/parauretralnaya-kista-u-zhenshhin
Urethral cyst in women: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, surgery
A cavity called a cyst may form in the urethra. Based on the time of formation, these formations are divided into congenital and acquired. Most often they form in the thickness of the tissue in women, located between the urethra and vagina.
Urethral cyst
The cyst is quite rare to form and is very difficult to diagnose.
This paraurethral pathology of the urethra in most cases develops unnoticed by the patient, but the sooner its treatment is started, the better the outcome of the situation, since the glands necessary for the normal functioning of the genitourinary system are blocked. The disease is quite rare; women aged 20-50 years suffer from it more often.
The female urinary system is structured differently than that of men, so representatives of the stronger sex do not develop a cyst in the urethra. In women, there are many glands in the urethra that look like grapes.
Under the influence of many factors, they undergo significant changes: they can increase in size or atrophy (during menopause). This is why the cyst develops during reproductive age.
In the international classification of diseases ICD-10, the disease is assigned code D 30.7.
The photo shows a urethral cyst in women
Varieties
In medicine, there are several classifications of neoplasms of the urethra. They can be formed in the skinev or gartner course. In the first case, the fluid is clogged in the gland near the urinary tract, in the second, a cyst is formed when the ducts and the wall of the urethra grow together with the vagina.
By origin, cysts can be:
The first are caused by pathologies of intrauterine development and are diagnosed in women quite rarely. Acquired ones can appear at any stage throughout life. The contributing factors in this case may be injuries, inflammation and other abnormalities in the functioning of the genitourinary system.
Reasons for the appearance of formations
The formation is formed during the inflammatory process occurring in the glands. They swell and become clogged with epithelial cells and bacteria.
The mucus produced to moisturize the canal does not find a way out, accumulates and forms a cyst. Hormonal imbalance can also cause such a disorder. The formation density is high, the shape is round.
Its infection is accompanied by purulent discharge.
The causes of congenital cyst formation are pathologies of the development of the urethra and vagina. It is between these organs that it is formed.
Acquired seals arise due to:
- Inflammatory processes of the reproductive and urinary system;
- Injuries during labor;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Decreased immunity;
- Bruises of the genital organs;
- Wrong choice of intimate hygiene products.
It is impossible to exclude the influence of all factors at once. Therefore, women should be attentive to their health and regularly see a doctor. Especially if there are prerequisites for the development of a cyst.
In the initial stages, the disease proceeds almost unnoticed. Discomfort appears only in case of complications caused by an infectious-inflammatory process.
As the formation grows, the patient begins to experience the following symptoms:
- Inconvenience when walking;
- Pain when having sexual intercourse;
- Sensation of a foreign object in the urethra;
- Increased body temperature;
- Painful urination;
- Going to the toilet is frequent, intermittent and difficult.
Some women only learn about the presence of a cyst in the urethra at an appointment with a urologist or gynecologist. With severe inflammation, purulent discharge is added to the listed signs of a cyst.
Treatment
Prescriptions directly depend on the cause that caused the development of the cyst.
There are two main directions in treatment:
- Medication.
- Surgical.
An integrated approach is the most effective. When prescribing an operation, the size of the cyst, its location, the existing connection with the urethra and the presence of an inflammatory process are important.
Removal of the formation can be performed under general or local anesthesia, depending on the severity of the case. Removal involves excision of the cyst wall. The wound heals within a few days.
After treatment of the formation, women should abstain from intimacy for at least 2 months.
Reproductive function is preserved after removal of the cyst. Medicines are prescribed when an inflammatory process occurs. The course consists of taking antibiotics.
Surgical intervention sometimes has complications during the rehabilitation period. They manifest themselves in bleeding, blood accumulation in tissues, and narrowing of the urethra. The risk of relapse cannot be ruled out.
Traditional methods
Treatment of cysts with folk remedies is not used as the main treatment method. It can be an auxiliary step on the path to recovery after surgical removal of the formation.
The most effective are:
- Herbal infusion made from equal proportions of wormwood, yarrow, string, sweet clover and sage. Herbs poured with boiling water should infuse for about 10 hours.
- Celandine. The juice from it is mixed with alcohol in equal proportions. The resulting composition is added to water (just a few drops) and consumed internally.
- Burdock. The juice from the young leaves of the plant is taken orally. It can also be inserted into the vagina using a tampon.
When choosing a component of traditional medicine recipes, you should avoid those to which you are allergic. Herbs in treatment must be combined with drug therapy.
Complications and consequences
Without treatment, the cyst in women does not go away. If the pathology is not treated in a timely manner, suppuration or severe inflammation may appear in the urethra. In such conditions, pathogenic bacteria multiply very well, and stagnant urine accumulates. The result of this is inflammation of the genital tract. In the future, this will cause suppuration.
After the operation the following are possible:
- Hematomas;
- Development of urethral syndrome;
- Bleeding;
- Recurrence of infection.
There is a possibility of a fistula forming between the bladder and vagina. In the area of the urethra there is aching, pulling pain. If you have any ailments or health problems, you should seek medical help. In the video about the causes, symptoms and treatment of urethral cysts:
Source: https://gidmed.com/urologiya/zabolevaniya-urolog/uretry/kista-mocheispuskatelnogo.html