home >>>
Gynecological diseases
>>> Urethral caruncle.
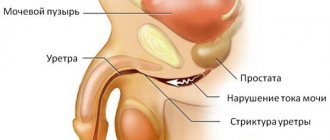
Treatment of urethral caruncle Urethral caruncle (urethral urethra) - occurs in postmenopausal women, due to prolapse of the urethral mucosa with subsequent inflammation (ectropion of the posterior wall of the urethra). Urethral caruncle develops secondary to atrophy of vulvovaginal tissue. The external opening of the urethra becomes red, its diameter increases from a few millimeters to 1 cm. In most cases it is asymptomatic, but can cause postmenopausal bleeding (“spotting”).
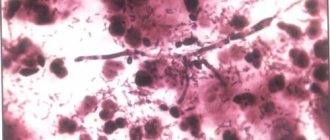
Microscopic examination of the urethral caruncle
: the caruncle is covered with stratified squamous or transitional epithelium. There is loss of connective tissue, numerous dilated capillaries and inflammatory cells.
Treatment for urethral caruncle in the absence of symptoms is not required. If necessary, systemic or local estrogen replacement therapy (estrogen cream, etc.) is prescribed. If estrogen replacement therapy is ineffective, local excision of the caruncle or cryocauterization is possible.
Description
The main component of a benign neoplasm is the tissue of the organ mucosa. The formation is characterized by small dimensions, has a round shape, and a small leg is used as fastening. The caruncle in the urethra is quite soft in consistency, and its surface is velvety.
View of the urethral caruncle on the wall of the organ. Source: fb.ru
In addition, there are a large number of vessels inside the tumor body. It is due to this feature that blood is often present in urine when urinating. Since the formation is constantly in contact with biological fluid and is also subject to injury, there is a risk of its transformation into a malignant tumor.
In some situations, doctors use the term ectropion in relation to this polyp. Its formation always occurs during the period when the initial stage of menopause is completed and menopause occurs. A urethral polyp provokes not only bleeding, but also increased swelling and soreness of the organ.
Preventive measures
As a preventative measure, the following preventive measures can be taken to reduce the risk of polyp formation:
- avoid promiscuity and use personal protective equipment;
- be examined by a gynecologist every 6 months;
- do not cause inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genitourinary and digestive systems;
- during menopause, use medications to normalize hormonal levels;
- give up alcohol and nicotine addiction, adhere to proper nutrition and take vitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system.
You need to take your health seriously and, if you notice the first alarming symptoms of the disease, seek medical help.
Treatment of the formation, begun in the early stages of the development of pathology, will prevent complications and restore health in a short time.
Causes
A urethral polyp in women, which must be treated after its discovery, looks like a red ring or circle. It is slightly raised above the surface of the mucous membrane. In medicine, formations are also distinguished that have a leg and are “sessile”. If the scarlet tint changes to brownish, black or blue, it is possible that the tumor has been pinched.
Experts call the main reason for the appearance of caruncle atrophic processes that occur in the body during its natural aging. Accordingly, such a neoplasm is more often detected in patients who suffer from insufficient estrogen production.
Changes in the amount of sex hormones produced by a woman’s age. Source: sertimed.ru
In addition to this, there are other provoking factors that can result in the formation of urethral ulceration in women:
- Immune system dysfunction;
- Presence of concomitant viral diseases;
- Inflammatory-proliferative processes;
- Various hormonal imbalances;
- Early puberty and adolescence;
- Frequent relapses of inflammation of the urethra;
- Insufficient blood supply to the organ;
- The presence of chlamydia, condylomas, papillomas;
- Difficulty with bowel movements;
- Injuries during labor.
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical case, the patient’s age, the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies, as well as the main reason for the formation of the tumor, the doctor may carry out drug treatment or indicate removal of the polyp on the urethra.
General information
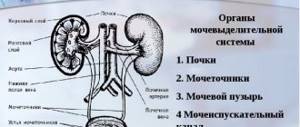
Urethral caruncle is currently considered a type of urethral polyp. This neoplasm is registered only in women, most often in postmenopausal age (over 45-50 years). The exact occurrence of the pathology is unknown, since the disease is sometimes not accompanied by obvious symptoms and does not cause complaints from the patient. The favorite location is the posterior wall of the distal canal. Often the caruncle is combined with prolapse or prolapse of the urethra, which indicates a possible common etiology of these diseases. Sometimes malignancy of the polyp occurs with the development of squamous cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
The caruncle is a neoplasm with a fairly soft consistency. Inside it there are a large number of blood vessels. That is why one of the main symptoms of the pathological formation is the appearance of pain when urinating, as well as the presence of blood in the urine.
If the tumor is very small in size, you may not even be aware of its presence, since it does not cause any discomfort or unpleasant sensations. Often, urethral caruncle is detected by chance, during a routine gynecological examination, which was carried out as planned or prescribed to identify another disease.
In certain cases, symptoms may be present. Moreover, it is expressed in a painful syndrome that does not allow intimate intimacy, and sometimes even wearing underwear.
In addition, tumors are characterized by the following clinical manifestations:
- Redness of the urethral opening;
- Increased urethral diameter;
- Presence of blood in urine (hematuria);
- Frequent urge to defecate;
- Painful process of urination;
- Inability to control urges;
- Leakage of biological fluid of a chronic type;
- The presence of itching and burning sensations in the genitals;
- Slight increase in body temperature.
Removal of a polyp from the urethra is urgently required for those patients who experience a rapid increase in tumor size. This is due to the fact that in such a state it is almost impossible to perform the act of urination.
Complications
How dangerous is urethral caruncle? Without treatment, a polyp in the urethra can lead to serious complications:
- Anemia. If the polyp is accompanied by frequent bleeding, the patient’s hemoglobin level drops. In this case, weakness, fatigue and frequent dizziness are noted. This condition develops over a long period of illness.
- Purulent cystitis and urethritis. Polypous formations in the urethra and chronic delay in the outflow of urine create a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, inflammatory processes in the urinary tract are often accompanied by suppuration.
- Malignant degeneration of tumor cells (malignancy). This is the most dangerous complication of caruncle. In advanced cases, the polyp can develop into urethral cancer. A sign of such a terrible disease is increased bleeding from the urethra. Subsequently, the patient's pain increases, the urethra becomes swollen, and nearby lymph nodes enlarge.
Diagnostics
If specialists accidentally find a polyp on the urethra in women, treatment can be prescribed only after a thorough diagnosis. If there is a suspicion of a tumor, the patient should go to an appointment with a urologist or gynecologist. During the consultation, you should carefully describe your condition and complaints.
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor prescribes the following diagnostic measures:
- General blood type examination;
- General urine examination;
- Blood chemistry;
- Carrying out a biopsy of the urethra;
- Sending a small piece of the tumor (caruncle) for histological examination;
- Ultrasound screening of the pelvic organs.
It is also worth noting that the primary diagnosis is often made by a gynecologist during a standard examination on the chair. Subsequently, only clarifying measures are carried out. Some women, having learned about their disease, try to cope with it using traditional methods, so as not to resort to the help of doctors.
This approach can result in the development of serious complications, for example: the formation of malignant melanoma and urethral cancer, the development of tuberculosis or lymphoma, intestinal ectopy, periurethral abscess, urethral leiomyoma. Each disease described is very serious, so all treatment measures must be agreed upon with a leading specialist.
Methods for removing urethral polyp
Removal of polypous tissue does not require special preparation. Therefore, the operation is often performed on the day the patient visits the doctor. If the patient is taking drugs that interfere with blood clotting, this should be reported to the specialist.
In women, if the growth is close, the procedure can be performed under the influence of local anesthetics. In men, the operation is almost always performed under general anesthesia, due to difficult access to the lumen of the urethra. In this case, the procedure is monitored using an endoscope (urethroscope).
Treatment
After the doctor confirms that the urethral polyp in women, the photo of which was presented earlier, has been diagnosed, the selection of the most appropriate therapeutic tactics will begin. In this situation, there are two ways to solve the problem: conservative drug therapy and surgical intervention.
Conservative
A urethral caruncle in a woman of small size, which does not cause discomfort or pain, is initially only subject to observation. Not one doctor will immediately suggest removing the formation. It will be necessary to come for regular checkups.
In situations where the cause of the appearance of a neoplasm is the natural aging of the body, that is, there is already an established menopause, during which insufficient estrogen production occurs, then the basis of therapy will be taking medications from the hormonal group.
Most often, complex therapy is practiced, in which the patient jointly takes anti-inflammatory drugs and medications containing estrogens. Thanks to this, it will be possible to stop the process of pathological growth of neoplasm tissue.
If, when a caruncle is identified, it gradually becomes the cause of the development of an acute inflammatory process, or the body becomes infected, then specialists select a completely different therapeutic regimen. That is why it is not allowed to solve the problem on your own.
Operational
When, for a long time, polyps in the urethra in women become the cause of persistent unpleasant symptoms that cannot be corrected in a conservative way, the specialist decides on the need for surgical intervention.
In each clinical case, the surgical method will be selected individually. It is also worth noting that surgery is required for patients who have heavy bleeding. The most common surgical techniques are:
- Catheterization or reflow method;
- Vaporization or laser treatment of the affected area;
- Classical scalpel excision of the tumor;
- Ligation of the polyp stalk, if any;
- Cryodestruction or cauterization with liquid nitrogen.
If you carry out timely treatment and strictly follow medical recommendations, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Correctly performed surgical or conservative therapy provides a real opportunity to get rid of tumor formation in the urethral canal.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of urethral caruncle, it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations by a gynecologist. This is especially important for women aged 45-50 years, since such patients are at risk. A specialist will be able to diagnose a polyp at an early stage and provide timely treatment.
If a doctor recommends that a woman undergo hormone replacement therapy during menopause, she must take the prescribed medications regularly. This will help normalize estrogen levels and prevent the formation of polyps in the urethra.
Without a medical education, it is unlikely that you will be able to find out what a urethral caruncle is from the name alone. This term hides a benign neoplasm localized in the urethra. In particular, experts also say that urethral caruncle is a type of polyp.
If we turn to the data of urological statistics, we can find out that pathology, in most clinical cases, is detected in representatives of the fairer sex who are already in old age. Often the formation is located on the posterior wall of the urethral canal.