Discharge from the urethra during bowel movements can be observed for various reasons. Pathologies are also to blame for this, however, sometimes this condition does not indicate health problems. In men and women, different factors provoke discharge, since the anatomical structure of the urinary canal is very different. In the fairer sex, it is wider and shorter, which is why pathogenic bacteria penetrate there more easily.
Discharge from the urethra during urination is a very alarming signal, which may indicate the development of dangerous pathologies in the genitourinary system.
Basic therapy methods
Discharge from the urethra in women requires immediate treatment. Once the doctor has determined the exact cause of their appearance, he will be able to select an effective treatment method. The following means are used:
- Antibacterial drugs. Most often, medications that have a wide spectrum of action are used. You can start using them even before receiving the final results of bacteriological culture. When identifying a sexually transmitted infection, experts recommend using Amoxiclav, Clarithromycin, Ofloxacin, Azithromycin and some other drugs.
- Sulfonamide drugs effectively eliminate bacteria, the activity of which leads to the development of the inflammatory process. The most effective of them is Doxycycline.
- Antimicrobial drugs. Most often, doctors prescribe Metronidazole.
- Most often, the disease develops against the background of a decrease in the body’s protective functions. Therefore, experts recommend the use of immunocorrective agents, as well as vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Washing the genitals with decoctions of medicinal herbs is recommended. Chamomile, calendula and knotweed are effective in this situation. Antiseptic solutions can also be used for the same purpose. Potassium permanganate is good for preparing sitz baths.
- Discharge from the urethra can also be treated using physiotherapeutic techniques. Electrophoresis and heating applications are the most effective.
- Injecting uroseptics directly into the urinary canal. For these purposes, a solution of collargol, protargol or chlorhexidine is used.
In addition to basic treatment, women are advised to reconsider their lifestyle and especially their diet. It is necessary to completely avoid spicy, overly salted, smoked foods, marinades and canned food.
Give preference to light vegetable dishes, soups and cereals. focus on fermented milk products. They will help restore normal microflora in the intestines, which is greatly affected by taking antibacterial drugs.
During treatment, stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Try to lead a healthy lifestyle, walk more in the fresh air and do gymnastics, and do not get too cold. Avoid excessive physical and mental stress.
They significantly impair the body's protective functions. Avoid sexual contact with partners who may become carriers of infectious agents. When in contact with a regular partner, use a condom.
If, after bacteriological culture, it was discovered that the cause of the disease was the vital activity of pathogenic microflora, then treatment will be required not only for the woman, but also for her sexual partner. Otherwise, the infection will recur and the therapy will not bring the desired result.
Two weeks after the end of the course of treatment, a repeat laboratory test is performed. This is the only way a specialist can make sure that the pathogen is completely defeated.
Discharge from the urethra in women always becomes a symptom of a serious illness. Therefore, if they are detected, it is necessary to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible. Only competent diagnosis and competent treatment will help to completely cope with the problem.
Treatment
Many women who discover similar symptoms begin to be treated at home. This is wrong, since this kind of illness requires a competent, comprehensive approach.
Treatment of urethral discharge depends on the type of pathogen that caused the inflammation. Basically, therapy is based on antibiotics, which are selected individually for each case.
In combination with general medications, it is recommended to take sitz baths with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents. All kinds of decoctions and infusions of herbs are also suitable. Complex therapy includes local suppositories and tampons impregnated with medicinal substances.
Physiotherapy (electrophoresis) helps to get rid of the disease quickly and without harm to the body.
Discharge from the urethra during pregnancy
Expectant mothers often experience changes in secretion. In most cases, white discharge from the urethra during pregnancy, not accompanied by itching and burning in the vaginal area, appears due to physical fatigue.
Other reasons for their occurrence:
- improper fluid intake;
- non-infectious urethritis;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- the emergence of difficulties in the treatment of cystitis;
- psycho-emotional tension, stress;
- gynecological problems.
The presence of blood (brown impurities) in the discharge from the urethra is an alarming symptom indicating a pathological course of pregnancy. If it occurs, you should immediately go to a medical facility for examination.
Urolithiasis disease
Pain or burning during urination can also bother women with urolithiasis. This is especially often observed when stones leave the kidney and pass through the urinary tract.
During pregnancy, this develops somewhat more often, since an enlarged uterus creates an additional obstacle to normal excretion.
Depending on the level of stone retention, pain occurs both throughout urination and after it. They typically spread to the lower abdomen and lumbar region. You can often notice the appearance of streaks of blood in the urine, and sometimes the attack ends with the immediate passage of the stone.
Diagnosis of urethritis
In addition to discharge from the urinary canal, other signs of disease help the doctor diagnose the disease. Thus, chronic urethritis is manifested by periodic weak nagging pain in the lower abdomen, chlamydial urethritis gives practically no symptoms, and with bacterial urethritis a woman is bothered by:
- painful spasms, itching, pain in the urethra;
- frequent urge to urinate, as with cystitis;
- redness of the canal outlet, itching in the genital area, especially during menstruation.
A woman complaining of discharge will have general and clinical blood tests, smears from the urethra and vagina. In some cases, she will be asked to diagnose the infection using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
If a secretion comes out of the urinary canal, the color and consistency of which are suspicious, do not put off going to the hospital. Diagnosis and its implications are necessary to determine the optimal treatment strategy.
Basic diagnostic measures:
- determination of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics. This is required to prescribe an antibacterial drug that will cope with the infectious agent. Discharge from the urethra will stop after taking it;
- taking a smear from the urethra;
- general blood analysis;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- urethrocystoscopy;
- urethroscopy.
The course of treatment is prescribed after accurately determining the cause of this symptom.
A urologist carries out diagnostic measures and eliminates the causes of discharge from the urethra in women, if necessary, together with a gynecologist. The survey has the following scheme:
- Taking a smear of discharge from the urethra, followed by microscopic analysis using Gram staining or PCR.
- Blood tests for STIs using ELISA.
- Bacteriological studies to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics.
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system, urethroscopy.
Private clinics in Moscow offer to undergo a comprehensive examination of women with complaints of urethral discharge within the walls of one medical institution, or use the service of calling a urologist at home. When you call a urologist at home, the quality of service remains at the required high level. You can make an appointment with a doctor at one of the paid clinics through the “Your Doctor” Help Desk website.
Don't self-medicate!
Discharge from the urethra in women is not a disease, but a symptom of one of the diseases. Therefore, if you notice pathological manifestations in yourself, you should not independently determine from reference books what their cause is. Diagnosing yourself and self-medicating is very dangerous!
- Antibiotics chosen on the advice of friends or from reference books will relieve you of unpleasant sensations, but will not destroy, but will only muffle the infection. This means that if you catch a cold, everything will start again.
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics leads to pathogens developing resistance to them.
- The danger of self-medication is that trying to cope with the symptoms rather than the disease will “blur” its clinical picture, and it will become more difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis.
The same genitourinary disease can produce discharge of a different nature, and several diseases often have a similar course. In addition, discharge can also appear as a result of a combined infection:
If the appearance of urethral secretion is the result of physical fatigue or stress, then treatment is not required. After the normal functioning of the body is restored, this symptom will cease to appear.
Therapy will be required to restore normal secretion. Drug treatment of urethral discharge is aimed at combating the inflammatory process and pathogenic bacteria.
Drug groups:
- Antibacterial.
- Antimicrobial.
- Sulfanilamide.
- Immuno-strengthening.
- Uroseptic.
To treat urethritis in women, doctors prescribe antibacterial medications to get rid of pathogens that provoke the development of the disease.
During pregnancy
If a pathogenic infection enters the genitourinary system of a pregnant woman, she will experience symptoms such as severe vaginal itching, inflammation of the urethral canal, and frequent urge to urinate.
At a medical facility, she will take antibiotics to stop the development of this disease. Also, for pathological discharge in pregnant women, immunostimulating medications are prescribed.
Complications
The type of complication depends on gender and the origin of the disease. Most often, men are diagnosed with the following types of pathologies that appear due to untreated urethritis:
- Prostatitis.
- Balanitis.
- Orchitis.
- Narrowing of the ureters.
In women, the lack of qualified medical care leads to cystitis, the transition of urethritis to a chronic form, disruption of the vaginal microflora and chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
With severe lesions, infertility may develop in men and women. The disease greatly weakens the general immune system, which causes relapses of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections.
The immune system is able to stop the growth and development of Candida fungus. But at the same time it can remain in the seminal vesicles, testicles, and prostate gland. Against the background of hypothermia, with weakened immunity and exacerbation of chronic ailments, the fungus becomes active again, and the disease manifests itself again. In addition, the infection can affect other organs and cause the development of diseases such as pyelonephritis, prostatitis, and impotence.
Candida fungus
The greatest danger is candidiasis accompanied by high fever. A fungus can enter the bloodstream, which impairs the functioning of the entire body. As a result, the quality of life decreases, problems with ejaculation and erectile function begin, prostatitis and vesiculitis develop.
Features of discharge from the urethra in women
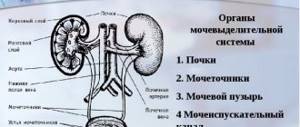
The urethra is an organ of the genitourinary system that performs the function of removing water-soluble waste products from the body.
Discharge of various shades from the urethra appears for various reasons. Since the female urethra is larger in size than the male urethra, it is more often attacked by pathogenic microorganisms.
As for bloody discharge, its exit from the urethra may indicate the onset of menstruation. When a follicle ruptures during ovulation, splashes of blood enter the urine, hence the release of a pinkish secretion from the vagina.
- Acute urethritis manifests itself with pain during urination, a feeling of burning or itching, and morning discharge from the urethra. Chronic urethritis may be asymptomatic.
- The color of discharge from the urethra in women takes on a green tint, often mixed with blood.
- White, cheesy discharge from the urethra in women is rare; usually such discharge accumulates under the skin covering the canal.
- The increase in body temperature does not reach high levels; it stays within 37 – 37.7. Latent inflammation does not lead to changes in body temperature.
Characteristic symptoms
During the incubation period (from the moment the infection hits the urethral mucosa until the onset of the disease), the pathology does not manifest itself in any way.
- Women are characterized by mild, mild symptoms (minor discomfort, burning and stinging when urinating, scanty discharge - in 65%), which most often are not even paid attention to (since they appear against the background of vulvovaginal candidiasis with more pronounced symptoms).
- In men, due to the anatomical features of the structure (small diameter of the urethra and inlet) and isolated course (only urethritis, without concomitant diseases), the symptoms appear brighter and more acute, causing noticeable discomfort when urinating.
- The chronic form of candidiasis in men and women is characterized by an almost asymptomatic course with frequent exacerbations (4 or more times a year) and increasing symptoms (with each exacerbation the manifestations become more pronounced).
- swelling, redness of the mucous membranes of the urethra and head of the penis (in men);
- pain, stinging, burning (less commonly, itching) when urinating;
- copious, moderate or scanty discharge (in the form of whitish, grayish or yellowish crusts around the entrance to the urethra, thread-like mucus during urination, cheesy clots from the urethra).
Discharge from candidiasis usually appears in the morning.
Click on photo to enlarge
| Complications in women | Complications in men |
| Candidiasis vulvitis and vaginitis (inflammation of the external labia and vagina) | Candidal balanitis and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the head of the penis and foreskin) |
| Fungal cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) | Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland) |
| Impaired renal filtration function | Fungal vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles) |
| Candidal orchitis (inflammation of the testicles) | |
| Cystitis |
Complications in womenComplications in men
| Candidiasis vulvitis and vaginitis (inflammation of the external labia and vagina) | Candidal balanitis and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the head of the penis and foreskin) |
| Fungal cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) | Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland) |
| Impaired renal filtration function | Fungal vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles) |
| Candidal orchitis (inflammation of the testicles) | |
| Cystitis |
Causes of urethral discharge in women
Urethritis is classified into specific infectious and nonspecific infectious, non-infectious urethritis.
- Specific urethritis develops after the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into the mucous membrane that cause infections of the genital apparatus (gonococci, ureaplasma, chlamydia, trichomonas). Discharge from the urethra in women increases after sexual intercourse. In this case, inflammation of the urethra is not isolated, but is combined with damage to the urinary system and reproductive system.
- Nonspecific urethritis occurs when local immune defense is reduced due to hypothermia, abuse of strong alcoholic drinks, and spicy seasonings. A favorable background is diseases of the endocrine glands, urolithiasis, pathologies of the structure of the urethra (curvature). The cause of discharge from the urethra in women in such cases is opportunistic bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, fungi, E. coli).
- Non-infectious urethritis is characterized by itching or burning during periods of little need. The smear contains no bacteria, but a large number of formed elements that appear during inflammation or allergic conditions. The cause of such urethritis is trauma to the mucous membrane after catheterization or an allergy to the use of cosmetics in the intimate area, intimate lubricants, or medications.
Useful information on the topic:
Discharge from the genital tract and urinary canal also occurs for reasons not related to sexually transmitted infections. The inflammatory process in this case is caused by so-called opportunistic microorganisms. These include streptococci, intestinal flora, and Candida fungi.
In a healthy person, the number and activity of these microorganisms is controlled by the immune system, and they do not cause harm. When the immune system weakens, microbes begin to multiply rapidly and cause inflammation.
Urethral discharge in women can occur for many reasons. Among them we can particularly highlight:
- Venereal diseases. Most often, the causes of urethritis lie in the activity of chlamydia, gardella, gonococci, trichomonas and other microorganisms. Depending on the causative agent of the infection, discharge in women may have different shades.
- Urolithiasis disease. The resulting stones move along the urethra and injure it, which provokes the development of inflammation.
- Decreased protective functions of the body.
- Prolonged exposure to the cold. This factor contributes to the active proliferation of bacteria in the female body.
- Mechanical injuries of the urinary canal. This can happen during accidents or improper medical procedures.
- Wrong lifestyle. Eating large amounts of fatty, sour and bitter foods.
- Malignant neoplasms in the urethra, which provoke inflammatory processes.
Discharge from the urethra in women is often the result of sexually transmitted diseases. Infection occurs during contact with a carrier of the infection. The rapid progression of the disease is facilitated by non-compliance with the rules of contraception and personal hygiene, weakened immunity, emotional stress, hypothermia and other factors.
The quality of therapy will largely depend on the correct identification of the cause of the disease. You can't make a diagnosis yourself. At the first sign of a problem, consult a doctor.
The reasons why cystitis may occur are varied.
1. Colds in women who do not take care of themselves at all, dress lightly. 2. Infections that were transmitted to a girl after sexual intercourse. They can make themselves felt from time to time, manifesting themselves in the form of cystitis. 3. A weak bladder that can instantly respond to hypothermia.
The category of women who have encountered this disease probably knows the symptoms indicating the presence of cystitis.
The nature of secretion depends on the functioning of the body. If for some reason there is a malfunction in its operation, this will affect the cyclicity.
Let's consider the main reasons for the appearance of such discharge:
- urolithiasis. It is characterized by the movement of stones along the urethra, which injure it. As a result, the walls of the urethra become inflamed and painful;
- inflammatory diseases, such as cystitis. With such ailments, the bladder becomes inflamed. This leads to a frequent urge to urinate;
- decreased immunity;
- venereal diseases. They are provoked by pathogenic bacteria, such as chlamydia or trichomonas;
- hypothermia, leading to active reproduction of pathogenic bacteria in the body;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms in the urethral canal;
- injury to the urinary canal.
Also, urethral secretion can be caused by an unhealthy lifestyle. For example, its appearance is provoked by eating large amounts of fatty foods.
When the urinary canal is injured, the urethra also becomes inflamed. For example, this often happens when a catheter is inserted into the vagina.
Urinary incontinence and discharge of clear mucus from the vagina are symptoms of inflammation of the urethra. They also appear with non-infectious urethritis, which is accompanied by severe itching in the perineal area.
Other causes of non-infectious etymology:
- non-compliance with healthy eating rules;
- radiation exposure;
- intoxication of the body;
- active sexual intercourse leading to injury to the urethra;
- venereal pathology.
What is the danger of pathology?
The complications that arise and a number of consequences depend on the form of the disease. The infectious type is considered more dangerous. With it, there is a high probability of bacteria entering the uterus, where they will continue to multiply in the waters surrounding the fetus. All this will affect the normal development of the unborn child and will begin to threaten his life. Urethritis caused by chlamydia poses a great danger. It causes significant harm to the fetus. Pathology can cause a number of problems:
- Pregnancy will be difficult.
- The birth may be premature.
- There is a possibility of a stillborn baby.
- Placental insufficiency occurs.
- There have been cases of spontaneous miscarriages and abnormal fetal development.
Non-infectious urethritis is not so dangerous with complications, but when the pathology is not treated, then the likelihood of infectious lesions appears. To prevent this kind of problem and avoid complications, it is necessary to contact a specialist with the first signs of the disease. Identified pathology at an early stage gives hope for a quick and safe recovery from such a nuisance.
Prevention of discharge
The chronic stage of a gynecological disease should be a reason for regular adherence to the rules for the prevention of urethral discharge. In this case, urethrography and urethroscopy are necessary.
By regularly observing personal hygiene rules, you can reduce the risk of urethral secretion to a minimum. Also, do not forget to warm yourself in winter and autumn. It must be remembered that many gynecological diseases, for example, urethritis, are provoked not only by infection, but also by simple hypothermia.
Types of discharge
Depending on the cause of the problem, discharge of varying shades and consistency may be observed. The following options are possible:
- White discharge. This symptom does not indicate the factors causing the disease. It only indicates the development of the inflammatory process. Therefore, in such a situation, careful diagnosis will be required.
- Brown discharge. This shade indicates the presence of blood in the secretion. Most often, this symptom accompanies the formation of tumors in the urinary system. Brown discharge can also be caused by mechanical damage to the urethra.
- Purulent bleeding indicates the progression of a sexually transmitted disease. They may have whitish streaks or a greenish tint.
- Yellow discharge from the urethra is observed with gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and some other sexually transmitted diseases.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is not enough to determine the type of discharge. It is necessary to analyze the entire complex of symptoms.
Sexually transmitted infections
Infectious urethritis develops as a complication of sexually transmitted diseases: gonorrhea, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma. They are transmitted sexually through unprotected sex, and if left untreated, the infection spreads to the urinary canal. The nature of the discharge partly tells the gynecologist or urologist what infection caused the disease:
- foamy, whitish - ;
- purulent or mucopurulent - bacterial;
- yellowish-gray purulent - gonorrheal;
- resemble a curdled mass - fungal.
However, identifying the pathogen and determining its sensitivity to drugs can only be done using laboratory diagnostics.