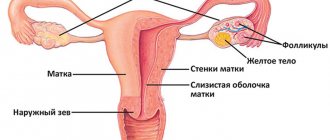
Factors
The appearance of mucus discharge and its characteristics are determined by the following factors:
- infectious agents that are sexually transmitted (gonococcus, chlamydia, etc.);
- nonspecific flora (Proteus, fungi, E. coli);
- infectious diseases (measles, diphtheria, tuberculosis);
- neoplasms;
- disturbances in the blood supply to the mucous membranes of the genital organs and bladder due to digestive failure;
- fluctuations in hormonal levels due to diabetes mellitus or thyroid disorders;
- condition after cancer and use
- drugs that suppress the immune system;
- constant irritation of the mucous membranes due to kidney stones;
- taking medications that cause allergic irritation.
Bladder pathologies, aggravated by urethritis and inflammation of the reproductive organs, require the combined efforts of a therapist and gynecologist for diagnosis and therapy.
The appearance of this phenomenon in women often accompanies inflammatory diseases of the urinary system. This is caused by physiological characteristics. The pathologies are caused by a single pathogen, which requires complex treatment.
- Milky color - close to normal, if the patient does not complain of itching and discomfort in the labia.
- Abundant purulent greenish discharge is caused by STIs.
- Brown discharge due to cystitis is caused by injuries and destruction of the cervix, pathologies of the ovaries, and hormonal imbalance.
In some cases, tumors of the reproductive organs cause acute cystitis due to mechanical compression, and treatment will consist of eliminating the underlying cause.
When diagnosing, the smell indicates a pathogen:
- fish. characteristic of vaginal dysbiosis and the growth of pathogenic microflora;
- sour. caused by fungal infection, due to medication, incorrect use of antibiotics, fluctuations in acid-base balance;
- A completely unpleasant odor indicates sexually transmitted infections.
For a correct diagnosis, the doctor must ask the patient about the nature of the discharge:
- how abundant they are;
- their consistency;
- duration in time. Constant or periodically recurring.
If there is simultaneous discharge from the urethra and vagina, pain when urinating, the patient should absolutely not self-medicate. Advanced sexually transmitted infections can lead to loss of reproductive function.
Causes
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder, mainly of an infectious nature. There are two types of flow:
- viruses;
- fungi;
- microorganisms (Proteus, chlamydia);
- bacteria (coliform, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Trichomonas,
- gonococci, streptococci, staphylococci, Treponema pallidum).
Routes of entry of the pathogen into the urinary tract:
- viruses, bacteria and protozoa enter from the outside;
- The natural flora begins to multiply uncontrollably.
When a number of conditions arise, the immune system cannot suppress the growth of opportunistic microbes and they, multiplying uncontrollably, cause this problem.
The following factors can provoke it:
- traumatic injuries;
- severe hypothermia;
- kidney disease;
- habit of holding back urination;
- inflammation of the urethra;
- incorrectly performed medical interventions;
- stones in the bladder;
- severe hormonal imbalance;
- decreased immunity;
- rough sex;
- failure to comply with specific hygiene;
- frequent urination;
- severe pain at the beginning and end of intercourse;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- blood in urine.
To understand the issue, we will fully analyze the signs (causes) of discharge due to inflammation of the bladder.
What is cystitis?
This pathology is an inflammatory process in the bladder in representatives of both sexes at any age. In most cases, it is caused by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. The short urethra and the proximity of the vagina, as a source of infection, make a woman vulnerable to cystitis. Therefore, the fair half of humanity more often suffers from this disease.
Symptoms of pathology:
- The urine becomes cloudy, the color may change due to the secretions present in it;
- Emptying the bladder occurs with pain and stinging, leaving a feeling of incompleteness of the process;
- Often and sharply there is a desire to “go small”;
- A state of general intoxication, which is characterized by body aches, nausea, weakness, fever;
- A person cannot normally engage in everyday activities, the disease exhausts him;
- At night the condition does not improve, which leads to sleep disturbance;
- Men have problems with potency.
Causes of cystitis:
- Non-infectious inflammation can occur due to injury, hypothermia, urolithiasis, hormonal disorders, poor immunity, kidney pathologies, untimely emptying of the bladder;
- The infection develops due to the penetration of bacteria into the organ cavity. This can happen through unprotected sexual intercourse, germs from the vagina, poor hygiene, or general infection with viruses and bacteria.
Each woman may secrete 1-2 ml of uncolored secretion from the vagina during the day. This condition corresponds to its healthy microflora. If we exclude diseases, then the first sexual intercourse, frequent change of sexual partners, abortion or pregnancy can also upset its balance.
Then the type and composition of the discharge changes, its quantity increases, itching and a strange smell appear. Bacterial vaginosis develops, which is characterized by white or green discharge.
Ascendingly, from the affected reproductive system, the infection enters the urinary system. This is facilitated by the short and wide female urethra.
Cystitis is more often diagnosed in the fair sex. This can be explained by the physiological characteristics of the structure of the urinary tract. These include:
- the urethra is shorter and wider than in men;
- a smaller distance between the urethra and anus, which creates a favorable environment for the entry of pathogenic microorganisms from feces (if cleansing of the skin after bowel movements occurs in the wrong direction - from the anus to the vagina);
- the development of hormonal disorders (during pregnancy, the postpartum period, during menopause), which reduce local immunity and weaken the body’s protective function, creating conditions for the development of infectious processes;
- during menopause, the level of production of some hormones decreases, in particular estrogen, which is involved in the activity of the bladder (atrophy of the organ lining develops, it becomes thinner);
Each reproductive organ is interconnected, and the development of an infectious disease in one of them can spread to others, including the bladder.
During pregnancy
Every 10 pregnant women are diagnosed with bladder disease. Pathology occurs due to:
- reducing the protective function of the body, which creates excellent conditions for the penetration and activity of various pathogens;
- changes in hormonal levels, and this interferes with the production of natural microflora and contributes to the development of pathogenic ones;
- an increase in the size of the uterus, which compresses blood vessels and impairs blood circulation in the bladder and urinary tract;
- reducing the tone of the organ membrane due to the influence of progesterone, which causes stagnation and the proliferation of pathogens.
Diagnosis of cystitis
A doctor diagnoses cystitis during a visual examination of the genital organs. In order to clarify the diagnosis, additional studies are prescribed: general analysis of urine, blood, smears from the vaginal environment, ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys and pelvic organs, cystoscopy, urine sample according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko. If you have cystitis, it is necessary to culture your urine for sensitivity to antibiotics. A complete blood count reveals an elevated level of white blood cells and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which indicates inflammation within the body.
A bacterioscopic smear from the vagina allows you to determine the condition of the genitourinary organs. It is made by taking a small amount of liquid and applying it to painted glass. Under the influence of a chemical reaction, harmful bacteria that cause the inflammatory process become visible under a microscope. To conduct this type of analysis, you need to stop sexual intercourse for two days, use vaginal medications, and not have bowel movements for two hours. A smear is taken on the fifth day of the menstrual phase. Compliance with these simple conditions will ensure an accurate diagnosis of inflammation.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and kidneys allows you to determine the parameters and condition of the urinary system, identify abnormalities in the early stages, and diagnose changes in the tissues of the genital organs (density and echogenicity of organs). You need to prepare for this type of verification. Two days before the ultrasound, do not consume foods that contribute to flatulence. Do not conduct an X-ray examination on the eve of the procedure. Before diagnosis, have a bowel movement.
Ultrasound is performed in several ways: transabdominal, transvaginal, obstetric method. There are also certain preparation rules here. During a transabdominal examination, the bladder is filled with a large amount of fluid (1-2 liters). During a transvaginal examination, the bladder should be properly emptied. Obstetric ultrasound diagnostics does not require special preparatory measures.
Important! It is forbidden to perform an ultrasound during menstrual blood loss due to low information content, since the uterus is enlarged in size. After the end of menstruation, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound in the first week.
Carrying out a cystoscopic examination is a painful procedure; under anesthesia, a special device is inserted into the urethra. A cystoscope consists of a metal tube and a camera. With its help, a tissue biopsy is taken with a syringe for analysis. Cystoscopy allows you to diagnose not only inflammation, but also tissue compaction. It is strictly forbidden to carry out this examination in case of acute inflammation of the genitourinary system or obstruction of the urethral canal.
Using urine diagnostics according to Zimnitsky, the functioning of the kidneys is determined by the formation and removal of fluid from the body. Normally, one and a half to two liters of urine are released. Accordingly, with a large amount of water, the kidneys work at full capacity, urine is excreted in large quantities with low concentration. With water deficiency, the volume of urea decreases. If kidney function is impaired, all body processes are affected, including urine production. A urine sample according to Zimnitsky determines the amount of urine and its concentration. Urine is collected throughout the day, a total of eight samples every three hours. During this time, the person records the time and volume of water he drinks. The collected analysis is stored in a cool place. Before emptying, maintain hygiene; if there is discharge, cover the urethral area with a napkin.
During the analysis, the following indicators are taken into account: the volume of urine over three hours, the density of urea in one portion, the total amount of urine, as well as daytime and nighttime fluid excretion.
Diagnosis of urine according to Nechiporenko evaluates the level of functioning of the kidneys and urinary system. In this way, a hidden inflammatory process can be recognized. The test is prescribed after poor results of a general urine test are obtained. This method calculates the level of leukocytes, red blood cells and casts per millimeter of urine. To do this, an early morning portion of urine is taken, but the first portion is poured out, and the second amount is taken for analysis.
Before taking the test, you must adhere to some recommendations: do not drink alcohol, do not eat foods that color your urine (beets, carrots, carbonated drinks), avoid excessive physical activity. It is forbidden to take a urine test according to Nechiporenko during menstrual bleeding, a week after a bladder biopsy, or while taking diuretics. All of these types of studies make it possible to determine abnormalities in the functioning of the urinary system so that appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
If there is a smell
Normally, leucorrhoea does not smell, and if it does, it will have a characteristic sour-milk odor.
If cystitis has developed, it is extremely important to identify the smell that accompanies it
When there are manifestations of cystitis and discharge, normally there will be a whitish and transparent secretion that has no odor. If it does appear, doctors may suspect the development of additional infections. Moreover, each of them has its own variant:
- A putrid odor, similar to the smell of rotten cabbage, or other variants, will indicate a genital tract infection;
- If the discharge from cystitis smells sour, you need to check for fungi;
- The smell of fish will indicate vaginal dysbiosis.
It is difficult to distinguish infectious diseases from cystitis, because In both cases, itching and burning may occur, as well as pain during urination. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. If there is discharge due to cystitis in women, it is not worth delaying, because... with improper treatment or even self-therapy, it can easily develop into kidney disease.
Prevention
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v >
Bloody and brown discharge is a frequent accompaniment of urinary tract inflammation. Discharge from cystitis in women can be of a different nature, differ in consistency and smell, and indicate danger.
Cystitis is not always accompanied by any discharge. But if there are any, it is necessary to inform the doctor about their color, volume, and intended origin (urethra, vagina). This may be due to the presence of additional diseases (urethritis, vaginitis, etc.).
What kind of discharge occurs with cystitis: color
You can tell a lot about a disease by color:
- A small amount of white and mucous discharge is normal. Most likely, the woman had such discharge before, with the only condition that it did not cause trouble for the owner in the form of irritation and itching. If a woman has been diagnosed with cystitis, and white discharge appears simultaneously with other signs of inflammation, then you should definitely inform your doctor about it. White discharge, accompanied by severe itching, usually indicates a fungal infection of the genitourinary organs. For example, the familiar thrush manifests itself this way.
- If the nature of the discharge is purulent, and the color is green-yellow, then we can most likely talk about a sexually transmitted infection. The type of pathogen can be determined more accurately only after testing. Cystitis in this case is only a consequence of the infection itself.
- A woman may have brown discharge, which indicates local damage to the cervix. The brown color of the discharge is given by small particles of blood, which, due to the permeability of the vessels of the cervix and their trauma, easily entered the vagina. Blood impurities in the discharge can also appear as a result of bacteria entering the kidneys, where they disrupt their function and contribute to the reduction of organ walls.
Why cystitis with bleeding?
A woman suffering from cystitis may experience a small amount of clear or whitish discharge from the urethra. They have a mucous consistency, do not have a specific odor and are explained by damage to the urinary canal - urethritis.
With this inflammation, blood is detected in urine tests, so its inclusions can be found in traces on underwear or a pad.
If there is vaginal discharge during cystitis, this indicates a pathology of the genital organs, which has caused inflammation of the bladder.
Examples could be:
- Purulent, unpleasant-smelling discharge due to lesions of Trichomonas, Chlamydia, Treponema pallidum.
- A pink or brown tint indicates ulcerative processes in the lower urinary tract.
- The yellow, greenish color of a moderate amount of discharge with an unpleasant odor characterizes trichomoniasis.
- White, scanty or copious discharge that may smell like fish indicates a fungal infection, bacterial vaginosis, or mycotic cystitis.
The bloody nature of the discharge accompanies purulent cystitis. This pathology is caused by infection with E. coli, which enters the urethra due to poor hygiene.
Streptococcal infection also leaves a bloody trail. It affects women and men suffering from blood diseases.
When considering the signs of cystitis, blood deserves special attention. Inflammation of the urinary system can be accompanied by bloody discharge, and this is associated with a violation of the integrity of the walls of the bladder and rupture of capillaries. They may come out in separate clots or mix with urine, giving it a pink tint. The appearance of blood during cystitis is typical for the acute stage and exacerbation of the chronic form.
It is important to consider that blood is not always the cause of cystitis. It may be a sign of other pathologies:
- malignant tumors;
- urolithiasis disease;
- bladder injuries;
- glomerulonephritis.
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after conducting an examination and studying test results. In any case, discharge with blood in women with cystitis should not be ignored.
The mucous surface is so called because the lining layer of the epidermis is capable of producing a thick viscous secretion. This mucus is needed in order to envelop and remove dangerous substances, bacteria, allergens, etc. from the organ. With the development of inflammation, this secretion begins to be produced in large quantities in order to remove from the bladder not only the pathogens themselves, but also the products of their vital activity, the results of the body’s fight against them.
Inflammation of the bladder can be both a consequence of problems of the genital organs and their cause. That is, pathogens of vaginosis, thrush, colpitis, and STDs can enter the urethra and penetrate the bladder cavity along the ascending path. And at the same time, pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and allergens from the urethra can enter the vagina and cause inflammation in the genital tract.
In the presence of other symptoms of cystitis, such as pain, frequent urges, general malaise, a woman may not pay due attention to the presence and nature of the discharge. It is even more difficult to understand where exactly they come from. However, it is worth being careful, since the secretion can vary in color, consistency, smell, and each variety signals a particular inflammatory agent.
From the urethra
It is logical to assume that most of the secretions leave the bladder during urination and noticing them, much less assessing the consistency and color, is an almost impossible task. All that remains is to record the presence of suspensions in the urine, changes in its color and odor. However, a small amount of secretion is released from the urethra in the intervals between trips to the toilet, and then characteristic marks remain on the underwear, as well as immediately after the end of the emptying process.
So, what are urethral discharge and what does it mean:
- Abundant transparent mucous. A small amount of colorless mucus is normal. If it is present in large quantities, this indicates irritation of the inner layer of the bladder and urethra, and incipient inflammation.
- White thick. Secretion that resembles cottage cheese in consistency and color indicates the proliferation of a fungal infection.
- Yellow or green. A change in the color of the discharge towards yellow or green indicates the presence of pus, and, accordingly, a strong inflammatory process.
- Bloody. Red or brown discharge with cystitis occurs when the capillaries of the mucous layer are damaged. Usually, in this case, the urine also changes color, acquiring different shades of red or brown. The reason for this may be ulcerative, necrotic processes in the bladder, as well as the appearance of cracks in the epidermis due to severe inflammation.
From the vagina
Due to the very close location of the urinary canal and genital organs, cystitis is often accompanied by vaginal discharge. They remain in sufficient quantities on underwear and for an attentive woman it will not be difficult to determine their consistency, color and smell.
Vaginal discharge may be:
- white curdled ones. This secretion has a sour odor and indicates the development of a fungal infection. The most common pathogens are fungi of the genus Candida;
- red or brown. A change in the color of leucorrhoea occurs as a result of blood entering it from the cervix, uterus, ovaries, or when the inner layer of the vagina is damaged. The cause may be the development of a severe inflammatory process with deep damage to the tissues of the genital organs;
- yellow-green. The coloring of leucorrhoea in various shades of yellow and green indicates the presence of sexually transmitted infections: trichomonas, chlamydia, and other STDs. Itching and burning appear in the labia and vagina;
- white or grayish with a fishy smell. This secretion occurs as a result of vaginosis, that is, an imbalance of microflora in the vagina;
- purulent. Leucorrhoea containing pus, causing severe itching, and having an unpleasant putrid odor is a symptom of bacterial colpitis.
Cystitis can also be a complication of tuberculosis
Infectious cystitis caused by Trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasmas, gonococci, Koch bacilli is called specific. Nonspecific cystitis is a disease caused by opportunistic bacteria that constantly inhabit the body.
Infrequent types of cystitis are those caused by purpura, actinomycosis and schistosomiasis.
The route by which pathogens enter the bladder may vary. Depending on it, cystitis is divided into descending, ascending, lymphogenous and hematogenous. Ascending infection (from the urethra) in male patients is quite rare. Cystitis in men is most often descending (in the case of a kidney infection), as well as hematogenous and lymphogenous.
There are also cystitis of a non-infectious nature. They can be caused by:
- surgeries or diagnostic procedures on the bladder;
- radiation exposure to the body, for example, during radiation therapy of the prostate gland;
- bladder injuries caused by foreign bodies, such as stones;
- chemicals that are excreted in the urine and cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
Cystitis is also divided into primary and secondary. In the first case, the disease begins on its own, directly in the bladder. In the second, cystitis is caused by some other pathological processes in the body.
Secondary cystitis, in turn, is divided into cystitis of intravesical and extravesical origin. For example, stones in the bladder and neoplasms of this organ are intravesical causes, and diseases of other organs (prostate adenoma, pyelonephritis) are extravesical.
If the area of inflammation is the bladder triangle, then such cystitis is called trigonitis. Also, depending on the location of inflammation, cervical and diffuse cystitis are distinguished. With cervical cystitis, only inflammation is observed at the neck of the bladder. The diffuse form of the disease manifests itself in inflammation of the entire wall of the organ.
Depending on how severely the bladder wall is affected, the following forms of cystitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal,
- hemorrhagic,
- cystic,
- ulcerative,
- phlegmonous,
- gangrenous.
The mildest form, affecting only the superficial layers of the walls, is catarrhal. In the gangrenous form, the pathological process leads to necrotization of the walls. To determine the extent of the disease, cystoscopy followed by a biopsy is used.
Factors contributing to the appearance of cystitis in men:
- hypothermia of the body;
- decreased immunity;
- stress;
- conscious urinary retention, rare emptying of the bladder;
- kidney and prostate diseases;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- diseases accompanied by the occurrence of foci of infection (tonsillitis, sinusitis, furunculosis, dental diseases, etc.);
- spinal injuries;
- diabetes;
- alcohol abuse.
Complications of cystitis may include paracystitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the bladder), pyelonephritis, sclerosis of the bladder walls, perforation of the bladder walls, inflammation of the kidneys (as a result of vesicoureteral reflux).
How to get rid of a symptom
Whether there is discharge with cystitis depends on many factors. In the acute form of the disease, these are usually absent if the infection was not caused by an STD.
Treatment is based on medications, in most cases antibiotics.
Therapy is prescribed taking into account the etiology of the exudate. If it has a mucous consistency and white color, and is present in a small volume, no specific treatment is carried out. It is enough to use methods to cure the main pathology – cystitis.
For brown and bloody exudate that occurs against the background of damage to the cervix, one of the following treatment procedures is performed, such as chemical coagulation, laser coagulation, cryodestruction, radical surgery using a scalpel, or radio wave therapy.
If the infection has spread to the kidneys, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, multivitamin complexes to increase the body's protective function, and painkillers are prescribed
It is important to adhere to proper nutrition in case of any kidney disease
Medicines
You can alleviate the general condition during the development of the disease by using drugs such as:
- Cyston, Monural to reduce the intensity of unpleasant symptoms;
- Chlorhexidine for douching, which has an anti-inflammatory and disinfecting effect.
It is important to regulate your drinking regime. Drinking a sufficient volume of water helps to “wash” the organ and remove pathogens from it with urine
You can improve your immune system by eating vegetables and fruits rich in ascorbic acid. Taking warm baths with infusions or decoctions of medicinal herbs: chamomile, calendula, rosemary will help reduce the intensity of pain.
Drug treatment of cystitis is carried out for 1-3 weeks.
What causes the symptom to appear?
Against the background of severe pain symptoms and cramps in the lower abdomen, discharge due to cystitis in women is not such a pronounced manifestation, which is often not paid attention to. Since the pathology occurs due to the influence of a bacterial infection, its reproduction causes a change in the vaginal microflora, which is the source of discharge.
With cystitis, there may also be pathological discharge: purulent, bloody, brown in color, and having an unpleasant odor. The hue, volume and smell depend on the pathogen that caused the disease.
An infection that affects the development of pathology can be present in the body for a long time, but not cause characteristic symptoms until exposure to a provoking factor.
Discharge after cystitis is associated with the following conditions:
- weakened immune system after illness;
- impaired blood circulation in the pelvis;
- internal disorders due to a failure in the production of certain hormones;
- promiscuous sex life;
- the development of pathology that causes disruption of the vaginal microflora;
- therapy with drugs that have a destructive effect on the mucous membrane of the organ;
- tumor neoplasm present;
- venereal disease occurring in a woman;
- endocrine disease;
- chronic constipation;
- history of surgical therapy in the urinary or genital area.
The doctor will be able to determine the source, after exposure to which there may be discharge due to cystitis, based on the results of the studies.
What does discharge with cystitis mean?
From the vagina
When discharge appears, you should pay attention not only to the color, but also to the smell. He can tell you about the cause of formations from the genital tract
Please note if there is:
- The smell of sour milk, unpleasant, intrusive. Appears with candidiasis (thrush). Accompanied by a white coating on the mucous membranes, pain, burning and itching. Fungal infection is a frequent companion to cystitis, due to decreased immunity and the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
- Fishy smell. It speaks of changes in the vaginal microflora and the development of gardnerellosis. Against the background of this pathology, thrush and infectious diseases appear.
- Pungent odor, fetid, persisting after hygiene. Discharge accompanied by a strong odor is the cause of a purulent process, which is caused by various sexually transmitted infections.
Women suffering from cystitis may notice discharge of different colors. You should definitely inform your doctor about this. This sign sometimes plays a decisive role in diagnosis.
For example, white discharge (usually with a cheesy consistency) is characteristic of infections caused by fungi.
The secret for thrush
Purulent - a sign of a serious inflammatory process in the bladder or urinary canal. Often accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Purulent
Brown discharge with cystitis appears as a result of damage to the urinary tract or due to erosion of the cervix. In these cases, pink or bloody discharge is observed. Any damage to the mucous membrane can lead to the presence of drops of blood in the sexual secretion, which is what gives the characteristic shade.
Spotting
Abundant transparent mucus is another evidence of an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs.
LeucorrhoeaYellow
The most dangerous to a woman’s health is bloody discharge due to cystitis.
With blood stains
Traces of blood in the urine indicate some complications during the course of the disease (infection entering the kidneys, damage to the bladder, etc.)
If you do not pay attention to this symptom and do not treat it in time, the situation may worsen until the appearance of pyelonephritis
Another sign that will help the doctor in correctly diagnosing your condition is the smell of female sexual secretion. Bacteria, which often cause several ailments at once, tend to create pathogenic microflora in the affected organs, which has a characteristic odor.
- For example, a fishy aroma often indicates the development of dysbiosis in the vagina (gardnerellosis). Gardnerella itself is present on the mucous membrane of every woman in a normal amount, not dangerous to health. In some cases (hormonal imbalances, sudden changes in the acid-base balance, etc.), these microorganisms begin to multiply rapidly, which causes damage.
- An acidic smell is a particular symptom of an infection caused by fungal pathogens (candidiasis). A similar illness usually occurs while taking a number of medications (antibiotics, hormonal agents), which seriously affect the vaginal microflora.
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge with cystitis is considered a sign of a purulent process. The reason for this is most often sexually transmitted infections.
Urethra and vagina
- clear mucus is a normal phenomenon, but may indicate a slight inflammation in the urethra;
- emissions in the form of pus indicate quite severe inflammation that occurs in the urinary tract and urethra;
- If the color of the substance is brown or pink, damage to blood vessels or the formation of ulcers can be detected. The color will be affected by the blood that gets into them;
- if the color is white, then the presence of the symptom is caused by the presence of fungi.
The color and characteristics of the discharge determine the nature of its appearance. Their appearance in men is quite rare with cystitis.
With the development of inflammation of the bladder, discharge from the urethra may be observed. After laboratory tests and examination of the vagina, their cause can be determined.
What types of vaginal discharge are there?
- White mucus may not be caused by a complex disease. Unless there is any itching involved.
- Yellow-green pus indicates the development of an infection in the genitals. Therefore, in parallel with cystitis, this disease will also need to be treated.
- A brown tint indicates the appearance of erosions on the cervix, an inflammatory process or ovarian diseases.
If such symptoms are present, inflammation of the bladder may be a separate or concomitant disease. But most often it is still a consequence of another disease. It is usually provoked by inflammation in the internal genital organs or the formation of tumors.
The stage of cystitis can be judged by the discharge from the urethra in men and women:
- clear discharge with a light colorless coating indicates minor inflammation or the initial stage of cystitis;
- pus from the urethra signals the development of a purulent-infectious process affecting the urinary system;
- brown discharge during cystitis indicates rupture of the blood capillaries of the mucous membrane or the development of an ulcerative process in the urinary tract;
- bloody discharge indicates damage to the upper part of the urinary system;
- white discharge is the cause of a fungal infection.
Blood and purulent discharge are especially dangerous. They occur in situations where cystitis is in an advanced form and complications are already developing. The formations are accompanied by severe cutting pain. When pus is released, the body temperature rises to 39 degrees or more.
Cystitis has different symptoms, but the onset of the disease is always scanty, manifested by slight cloudiness of the urine. If the unusual color persists for 2-3 days, then you should consult a nephrologist. In most cases, cloudy urine indicates the onset of an inflammatory process.
Causes of discharge due to cystitis
Increased secretion formation during cystitis indicates the development of an inflammatory process and damage to neighboring organs. Most often, uncharacteristic leucorrhoea is observed when cystitis is accompanied by urethritis - inflammation of the urinary canal. In addition, such a phenomenon may indicate the transition of inflammation to the vaginal area. This creates a risk of damage to the uterus and appendages. Discharge may occur in the form of bleeding or be spotting.
Most often, the symptom is provoked by the following possible causes:
- endocrine disorders;
- severe irritation of the bladder, urethra or genitals;
- the presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- long-term use of medications, etc.
Discharge after cystitis indicates that the disease was not completely cured. It is worth noting that in men, a similar problem with urethral discharge is much less common.
Treatment of discharge
Since cystitis is often caused by bacteria, treatment with antibiotics is required to eliminate the problem first. Drugs that have a wide range of actions are best suited for these purposes. In this case, oral medications are not suitable.
In addition to antibiotics, patients with this diagnosis are indicated for symptomatic therapy. It is aimed at eliminating all signs of cystitis. In addition, the use of other means is required:
- Anti-inflammatory. They reduce the intensity of inflammation, while discomfort during urination, as well as the characteristic burning sensation, decreases.
- Antipyretic. It is not uncommon for cystitis and concurrent diseases to be characterized by an increase in temperature.
- Antipyretics. To normalize body temperature, you should carefully monitor the dosage.
- Painkillers. Excellent when dealing with severe pain syndrome, before using painkillers, analgesics are recommended.
If discharge appears during cystitis, this is a sign of serious pathological disorders. First of all, this indicates damage to the genital area. In any case, an urgent request for help from specialists is required.
Treatment of cystitis consists of eliminating the cause, relieving symptoms and restoring damaged bladder walls. There is no single drug for all types of cystitis.
Only complex therapy can be effective:
- The bacterial flora is affected by cephalosporin antibiotics.
- For viral etiology, Viferon and Gelon are used.
- Fungal infections are suppressed with Nystatin and Fucis.
- Painful symptoms are relieved with Papaverine and No-shpa.
- The bladder is strengthened with uroseptics “Furagin”, “Palin”, “Nitroxoline”.
- Rinse the bladder cavity regularly with plenty of water and berry juices.
- Herbal medicine with kidney tea, bearberry and horsetail extracts, chamomile, and calendula is useful.
If inflammation occurs due to sexually transmitted diseases, the pathogen must first be eliminated.
Cystitis requires complex treatment, consisting of taking medications:
- broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum antibiotics when identifying a specific pathogen;
- antiviral drugs;
- immunomodulators;
- anti-bleeding drugs;
- anti-inflammatory medications.
At the same time, gynecological discharge therapy should be carried out. The list of medications depends on the pathogen. If it is an STI (sexually transmitted infection), then antibiotics are prescribed; for thrush, antifungal drugs are prescribed. You cannot prescribe treatment on your own, without consulting a doctor and conducting a diagnostic examination.
One of the signs of cystitis is pathological discharge from the urethra and vagina. They can be of a different nature, allowing one to determine the cause of the disease. A woman with inflammation of the bladder should be more attentive to possible diseases of the genital organs, so as not to miss a serious infection that can cause complications.
Treatment options
Cystitis is treated using conservative methods. However, in the presence of such a complication as tamponade of the bladder with blood clots in hemorrhagic cystitis, surgical intervention is required.
| Symptoms | Treatment tactics |
| Frequent and painful urination, false urges | Thermal effects on the lower abdomen, painkillers, antispasmodics |
| Purulent discharge | Antibacterial therapy |
| Brown discharge | Hemostatic agents |
| Acute urinary retention | Removing a blood clot |
First aid
To alleviate the condition, you need:
- Maintain bed rest.
- Warmth on the lower abdomen.
- Drink plenty of fluids (fruit drinks, weak tea, non-concentrated compotes).
- Analgesics and antispasmodics.
Use of medications
Cystitis of bacterial origin, as evidenced by purulent discharge, requires antibiotics. The doctor selects an antibacterial drug based on microbiological research methods, determines the dose of the drug and the course of treatment.
As a result of the use of herbal medicine (treatment with medicinal plants), a uroseptic effect is achieved. In urology, the properties of lingonberries, cranberries and rose hips are used.
Drugs such as aminocaproic and tranexamic acid, sodium etamsylate and Dicinone stop bleeding. However, they are used when there is significant bleeding. Minor damage to blood vessels (brown discharge) resolves on its own.
NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Ketorolac, Ibuprofen, etc.) help eliminate pain. The middle layer of the bladder contains smooth muscle that contracts involuntarily. With cystitis, smooth muscle cells are in a spasmodic state, which causes frequent urination and a feeling of discomfort. Drugs that eliminate spasms include: Papaverine, No-shpa, Drotaverine.
Surgery
When the bladder is tamponade by a blood clot, acute urinary retention occurs, which requires emergency care. The clot is removed using endoscopy (cystoscopy).
Cystoscopy is a minimally invasive intervention that provides the opportunity to examine the bladder mucosa and stop bleeding by cauterizing individual vessels.
Discharge in men
The symptoms of cystitis in men are similar to bladder inflammation in women. The patient is concerned about frequent urination, pain and cramps, and deterioration in general well-being. Less common symptoms include:
- temperature increase;
- decreased potency;
- headache;
- stomach ache.
Discharges do not always appear. They are typical for the advanced stage, when there is no treatment for 3-4 weeks. They are characterized by a cloudy substance released during urination, droplets of blood on the underwear, and pieces of the mucous membrane. Discharge in men may increase during and after sexual intercourse.
The meaning of the color of the discharge
- Color.
- Smell.
With cystitis, discharge is not the most characteristic symptom. If a bladder disease is accompanied by discharge, it is recommended to inform the doctor about the abundance, color and intended area of discharge of this secretion (vagina, urethra).
Due to the fact that in women infectious cystitis is often associated with urethritis (the process of inflammation of the urinary tract) and damage to the genital structures inside, discharge from the urethra is a reason to conduct a smear analysis at three points, as well as urethrocystoscopy.
It is worth mentioning separately the discharge of blood during urination. A similar symptom is observed in hemorrhagic cystitis and requires special attention. In addition to the typical signs of bladder inflammation, the following are also noted:
- fever;
- general weakness;
- chills;
- unpleasant odor of urine;
- heat.
Blood in the urine indicates bleeding in the body. Its localization can be set as follows:
- if one or several drops after urination is a sign of bladder pathology; such a symptom indicates a complicated type of cystitis, and urolithiasis cannot be ruled out;
- blood is released during the entire time of urination - the kidneys are affected, there may be a tumor or stones; additionally, the likelihood of renal tuberculosis or injury (after a fall or strong blow) is assumed;
- if the urethra is damaged, traces of blood will appear in the first portion of urine immediately at the beginning of urination, sometimes such discharge occurs outside of this process; Often the blood appears as a result of stones moving through the canal or trauma caused by medical procedures.
Since cystitis in almost all cases is accompanied by other inflammatory processes in the body, blood can be a symptom of many diseases. Only a doctor can adequately assess the patient’s condition after all the necessary studies.
Do women have discharge due to cystitis? We have answered this question. A woman’s body reacts very sensitively to all changes and quickly signals pathologies. Discharge is not just a discomforting phenomenon, but a reason to be more attentive to your condition.
Vaginal leucorrhoea
Vaginal discharge with cystitis is not uncommon, since the urethra is located close and the pathologies are both concomitant and mutually caused. That is, cystitis can cause colpitis or vaginosis or vice versa. Therefore, symptoms in women expand, including vaginal leucorrhoea.
Brown
Such vaginal discharge may be a symptom of cervical erosion, endometriosis, or polycystic ovary syndrome. The color indicates the presence of blood cells, so the shade ranges from pink and red to brown. Black clots are a sign of severe endometriosis or cancer. Here we mean discharge outside of menstruation.
Yellow
With a green tint and a putrid odor, they are a sign of various STDs: chlamydia, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea and others. The consistency can be liquid or thick, and foamy discharge is often noted. With a cheesy yellow or greenish structure, a combination with candidiasis can be assumed.
White
A small amount of light discharge without an unpleasant odor or other symptoms is a variant of the norm, and with cystitis it is only a consequence of increased work of the glands. However, a significant volume, sour odor, cheesy structure of white discharge, severe itching, redness and swelling of the genitals are the clinical picture of thrush. In the future, Candida fungi eat away the mucous membranes, which can lead to the appearance of blood impurities in the leucorrhoea.
Transparent
Abundant colorless discharge indicates inflammation or uterine polyps. A small amount is a sign of normality. A lot here depends on the smell, which we’ll talk about later.
Main causes of the disease
What pathologies and infections provoke the appearance of discharge during cystitis? Let's list them:
- bacteria that are transmitted through sexual contact: mycoplasma, gardnerella, chlamydia, gonococcus;
- infections of a nonspecific nature: fungi, E. coli, streptococci, staphylococci, Proteus;
- severe infections: septic diseases, diphtheria, measles, tuberculosis;
- tumor pathologies;
- defects in the nutrition of the tissues of the external surfaces of the bladder and genital organs, caused by chronic constipation and the inability to empty the bladder frequently;
- endocrine system disorders that reduce local protective factors and regenerative stages (thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus);
- the use of immunosuppressants, as well as conditions after radiotherapy and chemotherapy;
- long-term use of medications that chemically irritate mucous tissues;
- local irritation by salts of the bladder mucosa in case of urolithiasis and insufficient fluid intake.
How often does discharge appear during cystitis in women? Various infections can provoke the appearance of discharge during cystitis.
- chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonococci and all bacteria that are sexually transmitted;
- intestinal infections;
- development of tuberculosis, diphtheria or measles;
- postpartum illnesses;
- tumor development;
- severe and prolonged constipation;
- poor bladder function and incomplete urine output;
- high blood sugar;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- the use of chemotherapy or radiological treatment;
- small amount of fluid consumed;
- irritation of the mucous membranes when taking medications for a long time.
Discharges have their own characteristics:
- Color.
- Smell.
But in the case of cystitis, these characteristics are not of great importance. But if such a symptom appears, you need to tell a specialist about it. To establish a developing infection, laboratory tests are carried out. You need to take a swab and analyze it.
Very often, along with the development of cystitis, urethritis is also detected. Therefore, discharge can come from the urethra itself. To conduct such an analysis, you need to do a urethrocystoscopy.
- Sometimes clear mucus is released.
- Purulent discharge with a greenish tint.
- Brown shade.
- White.
Based on the characteristic color, an experienced doctor will be able to guess the cause of the leakage. But still, you can’t do without an examination. After this, a treatment method is selected.
Gynecological causes include vaginal dysbacteriosis or infectious inflammation (colpitis). When the vagina is normal, it contains lactobacilli, which closely interact with a certain number of bifidobacteria and a number of other microorganisms. When a woman is healthy, the bacteria in her vagina are controlled by each other, this prevents the entry of foreign, harmful microbes. As a result of disorders in the vagina, thrush, vaginosis, and colpitis can develop.
With bacterial vaginosis, symptoms such as profuse mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor appear. A symptom of bacterial vaginosis is an unpleasant sensation during sexual intercourse. As for the nature of the symptoms, they can be pronounced or milder. If colpitis appears, itching occurs in the vagina, and a burning sensation appears. Discharge from cystitis and colpitis comes in the form of pus. If these diseases are not treated promptly, the symptoms worsen.
An infection that is located in the bladder can penetrate the kidneys, then pyelonephritis occurs, characterized by inflammation of the kidney tissue. With this disease, the functioning of the kidneys is significantly impaired. After treatment of pyelonephritis, measures should be taken to restore the normal microflora of the vagina and intestines. Thus, it will be possible to reduce the occurrence of cystitis and pyelonephritis in the future.
Many women are interested in whether there is vaginal discharge during cystitis and what its nature is. Inflammation of the urinary system can be accompanied by the release of a substance of varying consistency, color and odor. This indicates the addition of a secondary infection and the rapid development of pathogenic flora.
With cystitis there may be discharge:
- transparent or with a white tint in small quantities, not accompanied by an unpleasant odor and itching are the norm;
- purulent, greenish, gray indicate the presence of a sexually transmitted infection. In this case, the cause of cystitis is also an STI;
- Bloody and brown discharge with cystitis indicates damage to the cervix.
If there is a pathological process in the genitals, then it becomes the main cause of cystitis. And treatment should consist of eliminating the factor that provoked inflammation of the bladder.
Discharge due to cystitis is more common in women than in the male half of the population. This is due, first of all, to the fact that pathological formations are associated with exacerbation of existing pathologies of the genital area. Inflammation of the bladder worsens the situation, causing the rapid development of diseases (for example, erosion, bacteria).
The main causes of discharge include:
- A fungal infection that develops against the background of inflammation.
- Decreased immunity, which provokes herpes, thrush and other pathologies.
- Poor hygiene associated with poor health and soreness of the genital organs.
- Taking antibiotics to treat cystitis, leading to vaginal dysbiosis.
Inflammation in the body often causes pathologies in the female genital area. Against the background of cystitis, hormonal levels are disrupted and the microflora of the mucous membranes changes. All this provokes vaginal discharge due to cystitis.
Causes
The reasons why cystitis may occur are varied.
1. Colds in women who do not take care of themselves at all, dress lightly. 2. Infections that were transmitted to a girl after sexual intercourse. They can make themselves felt from time to time, manifesting themselves in the form of cystitis. 3. A weak bladder that can instantly respond to hypothermia.
The category of women who have encountered this disease probably knows the symptoms indicating the presence of cystitis.
- Frequent urination, and sometimes there is nothing to go to the toilet with, but the urge is constant.
- It hurts in the very bottom of the abdomen when a girl walks small.
- Aching pain in the abdomen.
- Burning of the genitals after urination.
- Brown discharge or blood in the urine.
Symptoms!
You can identify the onset of cystitis by the characteristic symptoms:
- cloudy urine or change in color;
- the appearance of pain and discomfort when going to the toilet;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- symptoms of body intoxication (pain, fever, weakness);
- decreased performance;
- deterioration of sleep.
Cystitis reduces the quality of life, leads to neuroses and psychological disorders. Patients have to give up their usual activities; due to frequent urges to go to the toilet, they are forced to stay at home.
The listed symptoms are characteristic of the acute stage, during which discharge of different colors and smells may appear. They require separate treatment if the cause is pathology of the genital tract.
Clinical picture
Pathogenic microorganisms, multiplying, infect the urethra and cause inflammation of the walls of the bladder. Changes gradually occur in the structure of its mucous membrane. It begins to become inflamed, the vessels swell. Their walls can burst from tension, and multifocal hemorrhages occur on the mucous membrane of the organ.
Due to the presence of infection, the damaged surface of the mucous membrane becomes abundantly covered with mucus, and gradual suppuration of the tissue begins. A purulent or fibrous-purulent plaque is observed on the walls of the organ. An acute purulent process begins.
With serous catarrh, a gradual clouding of the exudate occurs due to the accumulation of epithelial cells in it and an increase in the proportion of leukocytes. Next, the inflammatory process degenerates into a mucous one.
This stage of catarrh is characterized by the release of exudate mixed with thick mucus. The longer time passes, the more mucus is released. At the last stage there is purulent discharge due to cystitis. The patient emits a characteristic pungent odor of rot.
Gradually, pathological processes spread to the tissues surrounding the bladder. Pericystitis begins to develop, that is, the serous membrane of the bladder becomes inflamed. Then the tissues surrounding the organ suffer. A paracyst develops, which is characterized by the presence of severe pathologies. At this stage, inflammatory processes are accompanied by ulceration of the bladder itself. Later, ulcers perforate and fistulas form.
In parallel, atrophic or hyperotrophic catarrh develops.
The lining of the bladder begins to thin and gradually atrophy. The organ itself shrinks and decreases in size.
Diagnostic measures
The nature of the discharge can be determined based on the results of the diagnostic measures performed. Laboratory tests are carried out, including urine analysis (with cystitis, leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, and uric acids increase).
To identify other diseases that are accompanied by symptoms, additional studies are prescribed:
- gynecological examination and laboratory tests of a taken smear (bacteriological, microscopic, PCR) to detect STDs;
- cytoscopy to identify tumor-like neoplasms and other growths on the organ (ulcers, fistulas);
- ultrasound diagnostics, which allows a detailed examination of the condition of the bladder and, if necessary, other organs.
Taking into account the diagnostic results, further treatment is prescribed.
The diagnosis of “cystitis” is made based on the patient’s complaints (of frequent urination accompanied by pain and cramps, the presence of false urges, discharge), survey data (unprotected sexual intercourse, hypothermia, the presence of inflammatory pathology in the kidneys), laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Discharge from the urethra in men
Cystitis is a disease more common in women. Despite this, in some cases it is diagnosed in the male half of the population, more often after 45 years.
Often, men who have been diagnosed with this question arise whether there is discharge from the urethra due to cystitis. Since this is a disease of the urinary system, the answer is, of course, affirmative. And if in women it is not always possible to understand exactly where this unusual mucus came from (the vagina and urethra are too close), then in men everything is simpler.
The norm may be discharge that has a transparent color, mucous consistency and a small amount.
You should consult a doctor when the discharge:
- become abundant - this is a sign of inflammation of the urethra;
- are purulent in nature and are accompanied by elevated body temperature - this is a symptom of an inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- become thick and white – fungal infection;
- have acquired a bloody or brown tint - this indicates dangerous damage to the tissues of the urinary canal or bladder.
Each of the described cases carries the risk of certain complications. This should be reported to your doctor immediately so that he can prescribe appropriate tests and, if necessary, additional therapy.
How to treat discharge
Therapy must be comprehensive, and only then its effectiveness will be high and long-lasting. After the doctor identifies the pathogen, treatment will be prescribed. What it includes:
Taking medications
If there is an infection, then you need to get rid of it, and the easiest way to do this is with the help of medications. The active components of the drugs enter the bloodstream and enter all organs of the female body. This effect on the pathogen lasts several days, usually up to two weeks.
Restoration of the natural microflora of the vagina
Some doctors combine two points and try to restore a woman’s flora while taking antibacterial agents.
In all other situations, it is better to pay special attention to restoring the balance of microorganisms natural to the female flora, immediately after antibacterial treatment.
Physiotherapy
Unfortunately, very little attention is paid to this point in complex therapy today. But it is physiotherapeutic procedures that can restore and improve blood flow in the affected organs. Here you can recommend that the patient undergo a course of treatment with mud baths and electrophoresis. By the way, the latter method is especially useful for those women who are planning and do not exclude pregnancy in the near future. Electrophoresis will increase the tone of organs and improve local immunity.
Maintaining personal hygiene rules
This is not a preventive measure, as many believe, but an independent point of therapeutic treatment. Without observing the rules of body hygiene, a woman will not be able to recover from cystitis and get rid of discharge, even if she takes antibacterial drugs.
As additional measures during therapy, it can be advised to wash and douche not with water, but with medicinal compounds that not only have an anti-inflammatory effect, but also restore the damaged mucous membrane of the genitourinary organs.
Diagnostic measures
The nature of the discharge can be determined based on the results of the diagnostic measures performed. Laboratory tests are carried out, including urine analysis (with cystitis, leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, and uric acids increase).
To identify other diseases that are accompanied by symptoms, additional studies are prescribed:
- gynecological examination and laboratory tests of a taken smear (bacteriological, microscopic, PCR) to detect STDs;
- cytoscopy to identify tumor-like neoplasms and other growths on the organ (ulcers, fistulas);
- ultrasound diagnostics, which allows a detailed examination of the condition of the bladder and, if necessary, other organs.
Taking into account the diagnostic results, further treatment is prescribed.
How to get rid of discharge and whether it is worth contacting a gynecologist
If the symptoms of cystitis are accompanied by the appearance of atypical vaginal secretions, a trip to a gynecologist is inevitable. After all, any change in the nature of vaginal secretion, be it quantity, consistency, color or smell, indicates penetration of the causative agent of cystitis into the genitals. Based on microbiological studies aimed at identifying pathogens and establishing their sensitivity to drugs, the doctor will be able to prescribe effective therapy.
Discharge after cystitis, with properly selected treatment, very quickly returns to normal and ceases to bother the woman. However, you should not stop taking medications after the main symptoms disappear. Otherwise, bacteria will develop resistance to the active substance of the drug, and inflammation may become chronic.
The main point
The urethra and vagina are physiologically very close. Therefore, migration of pathogenic microflora to neighboring organs occurs quite often. Accordingly, with cystitis, discharge can be not only from the urethra, but also from the vagina. Bloody inclusions tell us about deep damage to the inflamed tissues, and in some cases, the development of pyelonephritis. Leucorrhoea with a sour smell is a sign of a fungal infection. Yellow or green color indicates the presence of sexually transmitted infections. The smell of fish is a symptom of colpitis. If there is any change in the quantity, consistency, color or smell of the discharge, you should contact a specialist to prescribe effective treatment.
How to prevent disease
Frequent relapses of cystitis, against the background of which discharge may be observed, are a signal of problems in the body, including chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, poor immunity, hormonal disorders, anatomically abnormal structure of the urethra, etc.
To minimize relapses of cystitis, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid hypothermia by excluding sitting on the cold ground, on a stone, swimming in cold water, and wearing short skirts in the winter.
- Normalize your drinking regimen. The average daily volume of liquid consumed should be at least 2 liters. You can drink pure water, mineral water, berry juice, rosehip broth, and non-concentrated juice.
- Timely treatment of a chronic inflammatory process caused by infectious pathogens.
- Control examination of the body by a gynecologist, conducting research to identify pathologies whose transmission route is sexual.
- If a person leads a sedentary lifestyle, it is recommended to do a warm-up every 60 minutes.
- Maintaining proper nutrition with the exception of foods that burden the gastrointestinal tract;
- Proper drying of the skin after defecation is from front to back. If possible, it is better to wash yourself.
- Timely emptying of the urinary tract when there is an urge to micturate.
You should tell your doctor about any, even minor, discharge due to cystitis. Changes require diagnostic measures and timely therapy. This is the only way to eliminate complications and hope for a favorable prognosis.
Prevention Tips
After a course of treatment of the pathology, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- To improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs, you need to move more. Particular attention should be paid to those women who have sedentary work. In this case, you need to do a short warm-up or walk at least once every hour and a half.
- To maintain pH levels and microflora in general, doctors do not recommend using various shower gels and bath foams. They adversely affect the mucous membrane, drying it out. During menstruation, you should change sanitary pads more often. As for tampons, you need to change them every two hours.
- It is worth paying attention to the fact that holding back urine inevitably leads to stagnation and increased activity of microorganisms in the microflora. In this regard, it is necessary to empty the bladder on time.
- It is necessary to monitor the hygiene of intimate organs after defecation.
- You should also take into account the fact that foreign flora has a significant influence on the occurrence of cystitis. Therefore, before and after sexual intercourse, it is recommended to take a shower, concentrating on the hygiene of intimate places.
- Pay special attention to the choice of underwear. Lace and satin, which are directly made from synthetic materials, impair air entry and cause severe irritation. It is this kind of underwear that is considered unsuitable for daily wear; it is better to leave it for special occasions. Women need to pay attention to cotton fabrics.
- You should avoid tight-fitting clothes, these include tights and corsets, tight and tight jeans.
- Women need to visit a gynecologist once a year, even if there are no complaints.
- Diet will also be an integral part of prevention. It should include healthy foods that will strengthen and support the immune system. Spicy and too salty foods have a detrimental effect on people who have chronic cystitis. Such products provoke irritation of the bladder and lead to exacerbation of inflammation.
The surest approach to preventing bladder inflammation is timely treatment of gynecological diseases.
It is possible to prevent the occurrence of cystitis or the development of a chronic form of the disease. To do this, there are certain recommendations that are not difficult to follow:
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Treat inflammation of the genitourinary system in a timely manner.
- Maintain intimate hygiene.
- If you frequently change sexual partners, visit a gynecologist regularly.
- Flush the urinary system by drinking at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day.
- Strengthen immunity.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z_JHuRJCDgo
If a girl who has begun sexual activity feels discomfort in the urethral area, she should consult a doctor.