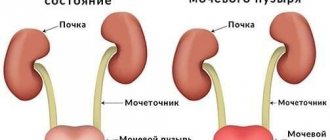
- frequent urge to empty the bladder, with a small amount of urine being released,
- severe pain in the lower abdomen radiating to the side,
- urination becomes painful, there is a feeling of cutting pain,
- men feel cutting pain in the penis,
- change in color and odor of discharge. Characterized by cloudy urine with a strong unpleasant odor, bloody impurities are possible,
- painful intercourse.
To the listed signs of the disease are added weakness, the patient complains of constant thirst, swelling of the extremities and noticeable changes in pressure.
The concept of non-infectious cystitis
Non-bacterial cystitis is not diagnosed very often, and, it must be said, it is more difficult to treat than a disease caused by bacteria. It is quite difficult to select drugs that will affect the source of the disease. Doctors have to analyze the patient's lifestyle to understand what exactly led to the problem.
In the case of the non-infectious nature of the disease, self-medication is very dangerous - it almost always leads to the fact that non-bacterial cystitis in women takes a chronic form.
The peculiarity of the disease is that there is no very bacterium that triggers the pathology. Inflammation in the bladder occurs due to a negative effect of a different type. A certain traumatic factor affects the walls of the organ and provokes their irritation. And if this influence becomes very strong, then non-infectious cystitis is diagnosed.
Causes
Medicine puts forward several causes of non-infectious cystitis. The sources of pathology are:
- Feminine hygiene products (pads, sprays, intimate hygiene wipes).
- Consequences of chemotherapy.
- Abortion.
- Consumption of foods that provoke allergies.
- The body's response to certain diseases in which bladder cells are destroyed.
- Congenital anomaly of the bladder.
- Disturbances in lymph circulation.
- Problems of psycho-emotional state.
Non-infectious cystitis is characterized by painful exacerbations and long-term remissions. The detonator of the acute manifestation of the disease is active sex life, eating foods that are irritants to the bladder.
Inflammation of this kind most often affects women of childbearing age, especially during pregnancy or after childbirth, when the body is defenseless against attacks from external and internal enemies. The development of the pathological process is often recorded during the menstrual cycle or during menopause.
Why does non-bacterial cystitis develop?
There may be several reasons for this. One of the most common is hypothermia. Many women are sure that this is, in principle, the most common cause of the disease, but in fact, the effect of cold is a provoking factor in the exacerbation of bacterial cystitis. It becomes much less common as an independent cause of bladder inflammation.
What injures the walls of the organ:
- Chemical components;
- Radiation exposure;
- Toxic influence;
- Exposure to medications;
- Neurogenic factor – stress;
- Nutritional features.
The neurogenic factor is quite insidious: due to the abundance of stressful situations, a general weakening of the body occurs, as well as a failure of brain control of the urinary system.
But it is not only the direct impact of negative factors that triggers the disease. By themselves, they can go unnoticed without having such a strong effect on the organ. But if the patient has a predisposition to developing cystitis, then the pathological effect takes on a different scale.
What is predisposition? This is, first of all, a weakening of the body. This often happens after severe illnesses, after long-term drug therapy, due to chronic diseases, as well as innate immune pathologies. The body does not have sufficient strength to cope with such factors, which causes inflammation.
Symptoms of the disease
The clinical picture of cystitis will vary somewhat, depending on the causative agent of the pathology and the degree of reactivity of the body. However, regardless of the cause of its appearance, the following symptoms are characteristic of cystitis of any etiology:
- pain in the suprapubic region;
- increased number of urinations (more than 7 times during the day);
- nocturia or the occurrence of more than 2 urinations at night;
The presence of pain above the pubis is characteristic of any form of cystitis
- the appearance of uncharacteristic discharge from the urinary canal;
- the appearance of pain during every trip to the toilet;
- the appearance of drops of blood after urination.
There are some differences in symptoms that suggest the presence of a particular pathogen in the body.
Does the disease manifest itself in the same way in all patients?
Signs and symptoms vary from person to person – this is what urologists believe. For example, patients with a high pain threshold may not listen to the first unpleasant symptoms. They will seem insignificant to them. That’s why they come to a specialist when the disease is already in an advanced state.
Doctors emphasize that today the statistics of obedient and frivolous patients are approximately equal: 50% rush to an appointment, the remaining 50% self-medicate. Many are simply afraid of diagnosis, perceiving a urologist and his diagnostic tools as something very scary. But there is nothing to be afraid of. The work of doctors begins with a routine examination and standard tests. Cystoscopy is usually required for chronic cystitis.
Prevention methods
It is quite difficult to accurately prevent the occurrence of non-bacterial cystitis, because it can occur for various reasons. But every patient can reduce the risk of pathology by following the following recommendations:
- You need to strengthen your immune system and harden yourself.
- It is very important to eat right.
- Every day you need to do exercises and lead an active lifestyle.
- You need to maintain hygiene, you cannot swim in dirty ponds, you need to wash yourself every day.
- Sexual intercourse with untested partners should only be carried out using a condom. It’s better to avoid casual sexual relationships in general.
- You cannot use medications uncontrollably; all medications must be prescribed by a doctor.
- When treating cancer with chemotherapy and radiation therapy, you need to strictly follow the dosage, and consult a doctor at the first unpleasant symptoms.
How to treat non-bacterial cystitis
Therapy is primarily intended to eliminate the cause of the disease. The goal of treatment is to remove the provocative factor. Sometimes a patient seriously needs to reconsider his menu, give up bad habits, and sometimes he needs to cure pathologies of the nervous system.
It is imperative to increase immune protection: fortified nutrition, hardening, physical education, etc. This part of the treatment of non-bacterial cystitis does not involve the use of pharmaceuticals, but it is very important.
If cystitis is caused by poor diet, you need:
- Avoid fried and fatty foods;
- Avoid spicy and smoked foods;
- Reduce the consumption of pickles and pickled foods to a minimum;
- Seriously limit your consumption of sweets;
- Introduce normal drinking regime;
- Avoid strong tea and coffee.
Cystitis often occurs after a feast, especially when accompanied by alcohol. If several factors coincide: weakened immunity, poor diet, exposure to cold, the likelihood of developing cystitis is very high.
The other part of treatment is symptomatic therapy. These can be painkillers, for example, Nimesulide and Nurofen, as well as antispasmodics (Papaverine and No-Shpa). Anti-inflammatory drugs can also be used to reduce the symptoms of cystitis. If the disease causes an allergic reaction (and this is possible), it is necessary to take antihistamines.
Traditional methods of treatment
For non-bacterial cystitis, you can use traditional medicine recipes, but after consulting a doctor. Folk remedies have a symptomatic effect, help relieve pain and normalize the process of urine excretion.
Traditional recipes for non-bacterial cystitis:
- Cranberry juice has a mild diuretic effect and saturates the body with vitamins.
- Urological fees from the pharmacy. Herbs relieve inflammation and pain and have a diuretic effect.
- Chamomile tea. Soothes, relieves inflammation and pain, improves sleep.
- A decoction of dill seeds relieves inflammation and pain.
Treatment with folk and traditional remedies involves drinking a lot of water, at least 3 liters of clean water without gas per day.
What if it’s not cystitis?
An important point that urologists are increasingly talking about. They often have to deal with the fact that a patient comes to an appointment and tells how she has been struggling with cystitis for many years, but she simply doesn’t have it! The patient’s tests are normal, the organ itself is not changed, and the patient is being treated for cystitis simply based on a number of signs. This usually happens if the patient goes not to a urologist, but to a therapist; the specialist herself assures that she has chronic cystitis. Therefore, it is simply dangerous to treat the disease without diagnosis.
Often a woman mistakes arthrosis of the symphysis pubis for cystitis. This is not such a rare pathology, but the treatment of this problem has nothing to do with the treatment of cystitis. Therefore, a competent urologist will never prescribe treatment simply during a consultation: only diagnosis makes sense. In addition, it will reveal the nature of cystitis, which will serve as the basis for choosing adequate therapy.
Relationship between infectious and non-infectious cystitis
The famous andrologist and urologist, scientist Yakov Makhmudov insists that the patient should not be treated exclusively by a gynecologist. You need to contact your general practitioner and take a referral for examination.
Another question is that such a doctor in domestic medicine is replaced by a local physician, and the line of subsequent actions does not always correspond to the norm.
The specialist also explains that the opinion that bacterial cystitis simply will not develop in a healthy organ is not unreasonable. This means that, in principle, cystitis, including infectious cystitis, is promoted by a certain pathology. Sometimes these are some anomalies in the development of the organ itself.
Sometimes these are concomitant diseases that cause the development of cystitis. For example, the external opening of the urethra is not located in its anatomical place, but very close to the entrance to the vagina or even displaced inside it.
If we talk about acquired diseases, then these are various pathologies of the urethra. Some muscle disorders and neurological problems can cause the development of the disease.
It turns out that as a result of almost any pathology, not only a certain part of the body will suffer, but also the body as a whole, as a system.
Therefore, every seemingly harmless viral disease can become a cause of inflammation. This means that it is not necessarily only the urogenital problem that can affect the occurrence of the disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms of non-infectious and infectious cystitis are almost identical, so it will not be possible to make a diagnosis after interviewing the patient. Some patients develop specific symptoms; some standard signs of the disease may be absent. The patient does not need to expect the full range of symptoms; a single sign of the disease is enough to seek medical help.
The most standard symptoms are as follows.
- Frequent and severe urge to urinate.
- After bowel movement, the urge repeats almost immediately.
- Nocturnal diuresis increases.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Discomfort when urinating.
- Inability to hold urine.
- Urine is cloudy, sometimes with bloody admixture.
- Pungent smell of urine.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Deterioration of condition due to intoxication.
- Chronic fatigue, drowsiness, lack of appetite, depression.