How to recognize cystitis yourself
The prevalence of cystitis can be judged by statistics, which indicate that 35% of the adult female population and 1% of the male population have already experienced all the “delights” of the extensive symptoms of the disease. Perhaps because patients do not know how to recognize cystitis on their own, in 50% of patients who seek medical help, inflammatory processes in the bladder reservoir are diagnosed in the chronic stage.
How to treat cystitis and kidney stones. Urologist's advice for women
April 6, 2018
Urologist at Riga 1st Hospital Egita Deine provides outpatient consultations in the clinic, treats chronic urological diseases, and performs planned surgeries in the hospital. This time we'll talk about women's health problems.
“Girls have been told since childhood: don’t sit in the cold, dress warmly, otherwise you might catch a cold.” Is cystitis really a problem for those who don’t take care?
– According to statistics, up to 50% of women suffer from a urinary tract infection at least once in their lives. When the body experiences stress, diseases hit the so-called “weak spots”.
publicites
– Who gets urinary tract infections more often, young or older women?
– Cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), urethritis (inflammation or irritation of the urinary canal), pyelonephritis (inflammation of the upper urinary tract - kidneys and pelvis) most often affects two groups of women. The first are primarily young women who have an active sex life.
This is due to the physiological features of the structure of the female body: the urethra is short, and the proximity of the anal canal and vagina, from where bacteria very often enter the urinary tract, also affects.
Sexual activity, thongs and synthetic underwear can contribute to this.
The second group of women who are most likely to encounter these diseases are women after menopause: problems can arise under the influence of hormonal changes, due to dryness of the vaginal mucosa. Often other diseases, such as diabetes, lead to urinary tract infections.
Family doctors are good at treating cystitis. But if the diseases become complicated or affect the upper urinary tract, then patients need to consult a urologist. The diseases are treatable with properly selected antibacterial therapy.
– How can you check the health of your genitourinary system?
– First of all, if something worries you, you need to do a urine test. It is very important to do this correctly: wash and collect an average portion of urine into a container, as much as possible, so that the urine flows into the container directly from the canal.
Changes in the analysis may indicate not only urinary tract infections, but also other diseases - kidney stones or tumor processes. Depending on the urine test, the doctor may prescribe other examinations - ultrasound, x-ray, tomography, etc.
If repeated tests are normal and not changed, and irritation in the ureter persists, it would be wise to visit a gynecologist, since irritation can also be caused by some kind of inflammatory process in the vagina.
publicites
Urinary incontinence
– Often with age a problem such as urinary incontinence appears...
– Urinary incontinence can have several causes. Stress urinary incontinence, which is faced by both young women after childbirth and older women after menopause.
Risk factors arise after repeated births, excess weight or heavy physical work throughout life. Urinary incontinence results from weakening of the pelvic muscles.
This type of incontinence occurs when there is a sudden leakage of urine during sneezing, coughing, blowing your nose, laughing, or during intense physical activity.
The second type of disease is urge urinary incontinence, that is, urgent, sudden and urgent, which is associated with an overactive bladder urge. These are situations where you literally have to run to the toilet to make it in time.
In this case, the cause of the disease is a nerve impulse in the brain, which is sent even when the bladder is slightly full. The bladder is not very full, but it feels like you need to go to the toilet right now.
And sometimes this feeling is so strong that it ends with involuntary emptying of the bladder. In such situations, the patient goes to the toilet very often. Including at night, without delay.
publicites
Both types of urinary incontinence can be combined.
Sometimes urinary incontinence can be a symptom of another medical condition. For example, neurological - Parkinson's disease, age-related dementia, urinary tract infection, kidney stones or tumors.
– Should women resign themselves to using sanitary bags for the rest of their lives?
- No. One of the main methods of treating stress urinary incontinence is physiotherapy: performing special exercises under the guidance of a physiotherapist or independently at home that develop the pelvic muscles. These are the well-known Kegel exercises.
If the problem cannot be resolved with physical therapy, but persistent stress urinary incontinence persists, sling surgery may help.
A small incision is made in the vaginal area, and a small mesh - a tape - is sewn between the urethra and the anterior vaginal wall, which is designed to support the urethra and prevent urine from leaking out when straining.
After such an operation, you can safely go to the theater to see a comedy and no longer be afraid of your own laughter.
publicites
The operation is minimally invasive. But the mesh will not always cope with the task for the rest of your life: you need to train the pelvic muscles, especially if the woman continues to engage in physically difficult work or is going to become a mother again.
– What do you recommend for urge urinary incontinence?
– Treatment is mainly medicinal, which allows you to stretch the walls of the bladder, giving it the opportunity to increase the portion of urine retained, and therefore trips to the toilet will become less frequent. Sometimes sedatives also help.
Stones in the kidneys
– They say that pain during renal colic is one of the most unbearable. The reason for this is often stones formed in this excretory organ...
– Nowadays, kidney stones are treated more easily than before, using minimally invasive methods, through natural means and without large incisions on the abdomen. If a stone is stuck in the ureter or is in the kidney, but not too large, then using special equipment - an endoscope, the doctor gets to the stones and, depending on the size and location, evacuates them and, using a laser, crushes them.
publicites
If the stones are too large and occupy most of the renal pelvis or limpets, they can be removed using percutaneous (percutaneous) surgery or nephrolithotripsy.
The method allows you to remove kidney stones through lateral incisions of just a few centimeters.
This type of surgery is considered low-traumatic, so the patient can return to normal life after just a few days.
Both of these above-mentioned surgical treatment methods are available to patients of Riga 1st Hospital. Before and after surgery, we take care of patients in the newly renovated, double, modernly equipped wards of the Urology Department. There is also a ward with increased comfort and a ward for patients with special needs.
publicites
– How does a patient know that he has kidney stones?
– Usually a person experiences very severe pain in the side. He is hospitalized and upon examination (ultrasonography or computed tomography) it is discovered that the pain is caused by kidney stones. It happens that kidney stones are discovered by chance while being examined for other diseases.
In some cases, kidney stones are a chronic disease that people have been treating for years and undergo periodic examinations to understand the situation - whether the stones have become larger and whether the time has come for surgical treatment.
At Riga 1st Hospital, we suggest performing a planned operation in order to avoid exacerbation of the disease.
You can sign up for a consultation by calling the registration number +371 67366323 or online
Source: https://www.riga.lv/ru/news/kak-lechitj-cistit-i-kamni-v-pochkah-sovety-urologa-dlja-zhenshin?13363
How to identify cystitis yourself
Despite the fact that the signs of inflammatory reactions in the bladder organ have characteristic features, the symptoms of the disease are quite similar to the manifestations of other urological pathologies. Therefore, even if there is complete confidence that the patient has independently identified the manifestation of cystitis, it is not recommended to begin independent treatment.
In order to have 100% confidence in identification, we will consider the main signs of cystitis and its differences from the manifestations of other, most common diseases.
The clinical picture of cystitis is characterized by the manifestation of the classic triad of symptoms - dysuria (difficulty urinating), terminal hematuria (blood in urine) and pyuria (purulent inclusions in the urine). They can appear either individually or in combinations.
The acute process is characterized by the rapid development of bladder dysfunctions, manifested by:
- frequent mictions (urination) – pollakiuria;
- constant desire to urinate;
- sharp urges to perform mictions;
- pain, cutting and burning in the urethral canal during micturition;
- frequent night trips to the toilet - nocturia;
- fetid odor and turbidity of a fresh portion of urine.
Increased body temperature and chills with cystitis are not a mandatory sign of pathology, but can appear along with other symptoms. If signs of fever and chills appear, this may indicate the involvement of the renal tissue structure in the inflammatory process and the development of the acute stage of pyelonephritis.
In the first days of the disease, disorders in the urination process rapidly progress.
The intervals between movements are reduced (up to 5 – 15 minutes). Urine does not have time to accumulate in the cavity of the reservoir, so the mictions have a very small volume. The urge to urinate does not stop even at night. In most cases, they cannot be controlled, which causes urinary incontinence (patients do not have time to run to the toilet).
Pain syndrome accompanies movements at their beginning or end, or constantly. Sometimes the pain is not associated with urination. Pain in the pubic area or perineum can cause constipation due to cystitis, caused by compression of the inflamed urinary reservoir with feces.
The manifestation of the painful syndrome does not depend on the severity of the inflammatory process. Sometimes superficial inflammation of the structural tissues of the bladder causes acute unbearable pain, and with extensive inflammatory reactions, the pain is insignificant. Inflammatory processes in the bladder tissues can manifest themselves as an independent disease and be combined with other pathologies in the body.
This must be taken into account. For example, difficult bowel movements or diarrhea due to cystitis often appear simultaneously, especially in women during pregnancy. Once manifested, the disease may never occur again, but if signs of bladder inflammation appear repeatedly over the course of a year, this may mean a relapsing course of the disease.
As a result of research work, a new version has emerged, due to the fact that the manifestation of repeated inflammatory processes in the bladder is a newly emerging disease, and not a relapse of cystitis, which requires mandatory additional examination.
Professional diagnostics will help you understand that you have cystitis. Self-comparison of symptoms alone is not enough. Their differentiated analysis with similar signs of other pathologies is necessary. In addition, quite often, the clinical picture of the disease has a hidden course, and delay in treatment leads to chronicity of the inflammatory process and the development of undesirable consequences.
Features of cystitis in older women: symptoms and treatment
Women are much more likely than men to suffer from acute or chronic inflammation of the bladder. In old age, the risks of developing pathology increase due to the peculiarities of the physiological state of the body. After 50-55 years, ladies should pay increased attention to the prevention of an unpleasant disease, which is not so difficult to organize. If symptoms of the disease do appear, you must immediately consult a doctor who will draw up an optimal treatment regimen for the disease. You should not select therapeutic measures on your own; this can seriously complicate the situation.
Causes of cystitis in old age
In old age, a woman’s body is affected by all the same factors as in a young age, but there is one peculiarity. If at the age of 20-40 a strong immune system could cope with most negative aspects, then over time the natural defense weakens. After menopause, hormonal levels also change, which creates an additional risk factor.
Here are a few more things that increase the likelihood of developing bladder inflammation after age 50:
- The immune system not only weakens, but its reactivity also decreases. The body does not react so quickly to the fact that pathological changes occur in it, so the disease develops unhindered.
- By a certain age, many women have several foci of infection in their bodies, triggered by chronic diseases. Even without any special external influence, cystitis can develop in such an organism.
- A decrease in the elasticity of tissues leads to the fact that organs begin to sink and change their position. If a woman has also managed to gain excess weight, this scenario is guaranteed. Prolapse of the bladder leads to stagnation of urine in the cavity, which is fraught with inflammation.
- A decrease in the functionality of the excretory organs leads to an increase in the concentration of urine, its slower excretion by the body. In combination with a violation of the drinking regime, this leads to irritation of the bladder mucosa with an aggressive concentrate.
- The development of cystitis in older women is also facilitated by the fact that many of them are addicted to using medications. Most often, they take medications without consulting a doctor, which leads to negative consequences.
Despite this disappointing picture, potential risks can be significantly reduced.
It would also be a good idea to regularly visit a urologist, who will allow you to pay attention to risk factors in a timely manner and eliminate them.
Symptoms of the pathological process
The weakness of the immune system, characteristic of old age, leads to the fact that cystitis after 50 years does not manifest itself as clearly as in youth.
A blurred clinical picture often causes patients to delay seeking help. Some try to cure the disease by eliminating its symptoms, others wait until the disease goes away on its own. Here are the main signs of cystitis in an elderly woman:
- Urination becomes more frequent and occurs more than 10 times a day.
- There is a need to visit the toilet at night - at least 2-3 times.
- After finishing urination, 2-3 drops of blood may appear from the urethra.
- In the area above the womb, there is a nagging painful sensation that may not be associated with the act of urination. The process of urine excretion itself is often accompanied by a burning sensation in the urethra.
- On the underwear you can notice traces of discharge from the urethra, which have an unusual consistency and a more pronounced odor.
- Frequent trips to the toilet may alternate with urinary retention.
- There is often a slight increase in body temperature, which is due to the sluggish and latent course of the problem.
Even one of the symptoms characteristic of cystitis in old age is an indication to consult a doctor. The sooner the diagnosis is confirmed and treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of quickly getting rid of the problem. By delaying a visit to a urologist, women risk the condition moving into a protracted phase; in this case, therapy may take months rather than days.
Diagnostic methods and specifics
To make a diagnosis, you need to use all the usual methods: general urine and blood tests, ultrasound, urography. Additionally, bladder catheterization may be performed. Despite your age and regardless of sexual activity, a visit to a gynecologist is recommended. After confirming the diagnosis, the patient is recommended to undergo an MRI or CT scan to ensure that there are no tumors on the mucous membrane of the affected organ. In old age, the risk of developing cancer increases, so if polyps, cysts or other conglomerates are detected, their tissue can be taken for a biopsy.
Features of the course of pathology in elderly women
In old age, cystitis, regardless of its form and characteristics, is severe and often recurs even after proper therapy. This is explained not only by a decrease in the body’s defenses, but also by a deterioration in the tone of the urethral walls. The infection can penetrate through it into the bladder over and over again, causing inflammation. For this reason, taking antibiotics in the treatment of cystitis may not be enough, and antimicrobial therapy must be combined with local procedures.
Difficulties in treating inflammation may also arise due to the fact that older women are often diagnosed with urolithiasis, neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the excretory organs, as well as diverticula in the walls of the bladder. If these provoking factors are not addressed, therapy will not give the desired result, no matter how aggressive it is. An important point is the timely initiation of therapy, which can prevent the transition of an acute condition to a chronic one. Otherwise, complete recovery will take months or even years.
Treatment of cystitis in old age
Therapy begins with changing women's habits that contribute to the development of the pathological process. Refusal of taking medications uncontrolled by a doctor, introducing amendments to the diet and normalizing the drinking regime can work wonders and significantly strengthen the body.
Often in old age, drinking plenty of liquids may be prohibited due to hypertension, a tendency to edema, and heart problems. All these points must be agreed upon with your doctor.
Basics of drug therapy
Regardless of the form of cystitis, the symptoms and treatment of the disease in older women are closely related. But this does not mean that it is enough to react to the signs of the disease and try only to alleviate the patient’s condition. Therapy should be complex, versatile and massive.
When treating cystitis in old age, drugs from the following groups are used:
- Antibiotics. Depending on the type of pathogen, antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal agents are prescribed. Given the weakness of the immune system in old age, these aggressive products cannot be avoided. Even if the initial cause of the disease was a non-infectious factor, pathogens will quickly join the inflammation.
- Phytoproducts. Products based on herbal components facilitate the flow of urine, strengthen the immune system, eliminate inflammation and increase the functionality of the excretory organs.
- Antispasmodics. They help alleviate the condition by eliminating pain, stagnation of urine and other unpleasant manifestations of cystitis.
- NSAIDs. Their action is aimed at combating the inflammatory process and accelerating the restoration of the integrity of tissues damaged during cystitis.
- Immunostimulants. In old age, it is rarely possible to do without these funds. If you neglect the manipulations necessary to strengthen the body's defenses, the disease will return again and again.
- Probiotics. Their intake is necessary to prevent the development of side effects from the use of antibiotics.
- Antiseptics. These drugs are injected directly into the bladder to disinfect it. This is especially true in cases where taking antibiotics does not give the desired result. The procedure is performed in a hospital setting by medical personnel.
If signs of intoxication appear, other drugs may be additionally prescribed. These may include antipyretic products and analgesics. Some patients have to be prescribed medications with sedative properties.
Catheterization is a mandatory procedure for cystitis
This procedure is indicated not only for the further introduction of medicinal compounds into the cavity of the bladder, but also for normalizing the outflow of urine. The decision to conduct it is made by the doctor. Sessions must be carried out only under sterile conditions, otherwise a secondary infection can be introduced into the diseased organ, aggravating the situation.
Traditional medicine
The use of natural preparations prepared at home should be treated with increased attention. Even those products that are normally absolutely safe and give a quick positive effect can cause problems in old age. We need to consider how they affect blood pressure, heart function, sleep and sleep quality.
Prevention of cystitis in older women
It is very difficult to prevent bladder inflammation in old age in women. But there are several rules, compliance with which reduces potential risks to a minimum. Firstly, during menopause it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist who will monitor changes in hormonal levels and prescribe medications to maintain immunity. Secondly, personal hygiene will require special attention. For example, in case of urinary incontinence, you need to wash yourself more often than usual and promptly change your underwear to dry and clean ones.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
A properly composed diet will have a good effect, from which foods that contribute to fluid stagnation in the tissues will be excluded. You should not resort to low-calorie diets or generally abuse any restrictions that go to the extreme. The body must regularly receive sufficient amounts of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins. At least every other day you need to give your body physical activity in the form of exercises, special gymnastics or Kegel exercises. Systematic visits to a urologist or gynecologist will allow you to promptly identify problems in the genitourinary area and eliminate dangerous factors.
If conservative treatment methods do not help, or the condition is complicated by some factors, the patient may be shown surgical excision of parts of the organ or its complete removal. This is especially true when there is a high risk of tumors forming on the walls of the organ or prolonged intoxication, which affects the general condition of the woman. Despite the fact that after this special plastic surgery will be performed, the patient’s life will change, so all factors must be taken into account before making a decision.
Methods for diagnosing cystitis
The diagnostic examination begins with identifying the background of the disease (history) and assessing the present symptoms.
An integral part of diagnosis is laboratory monitoring of urine:
- General, bacterial.
- Microbiological – tank seeding for flora.
- Antibiotic resistance.
- Monitoring of non-centrifuged urine using a hematocytometer.
- A special rapid test for cystitis is carried out - leukocyte and esterase.
Possible instrumental methods include ultrasound, cytoscopic and x-ray examination, uroflowmetry and biopsy.
Women are advised to undergo examination by a gynecologist to rule out sexually transmitted infections.
Laboratory and instrumental examination indicators help doctors differentiate cystitis from other diseases (pyelonephritis, prostatitis, urethritis, urolithiasis and other urological problems). But based on a number of key points in the manifestation and localization of symptoms, it is possible to independently suspect the development of an undesirable pathology. Let's take a closer look at their differences.
Complications: what are the dangers?
Kidneys are natural filters that remove toxins, participate in the formation of urine and hematopoiesis, and perform an endocrine function. Kidney stones disrupt these processes, obstruct the outflow of urine, change the structure of the organ parenchyma, and provoke renal hypertension. In addition, stones damage the integrity of the internal membranes, which causes minor bleeding. With ICD, immunity decreases, and this threatens the addition of infections.
Prolonged and untreated presence of stones is dangerous for the development of kidney failure, which can result in kidney failure, coma or death.
What are the differences between cystitis and pyelonephritis?
Both diseases are characterized by damage to the genitourinary system. Their signs are quite similar. How to distinguish cystitis from pyelonephritis is helped by their severity and localization.
- With inflammatory damage to the urinary bladder, the severity of general symptoms, in most cases, is insignificant. The prevailing local symptoms are dysfunctions in the urinary system: dysuria, disturbances in mictions and detrusor functions, causing additional pain, a portion reduction in urine output per miction, the presence of false (imperative) urges, etc.
- Signs of the development of renal pathology - pyelonephritis are characterized by the severity of general symptoms - high temperatures, chills and the manifestation of hyperhidrosis (sweating), clear signs of intoxication (loss of strength, extreme tiredness and fatigue, insomnia, insomnia and poor appetite) due to the influence of pathogenic toxins. Painful symptoms of various types (paroxysmal, aching or dull) are localized in the lumbar area in the projection of the affected kidney. Acute pain syndrome, in the form of renal colic, can provoke stones that block the urethral lumen.
Dysuric signs appear only in the case of secondary development of inflammatory processes in the bladder.
Pregnancy with urolithiasis
Urolithiasis during pregnancy is not the most common pathology (no more than 1%), but it can affect any woman. If at the initial stage the disease is not able to disrupt the pregnancy of a child, then in complicated cases significant problems can arise.
This indicates the need to take health seriously. Only a doctor can assess the degree of danger and determine whether urolithiasis and pregnancy are compatible in each specific case.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day.
The essence of the problem
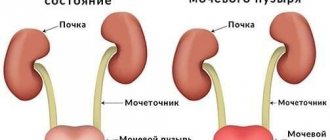
Urolithiasis, or urolithiasis, is a pathology associated with the formation of hard stones (stones) in organs related to the urinary system. As a rule, it involves damage to the ureter and bladder, but is also associated with nephrolithiasis, i.e. kidney stone disease. It is nephrolithiasis that often becomes a provocateur of the descent of kidney stones into underlying organs.
Stones in the urinary organs become the result of metabolic disorders. Insoluble salts (urates, phosphates, oxalates, etc.) precipitate, which become the crystallization nucleus around which solid formations are formed. The manifestation of this pathology is associated with the size and number of stones.
Under certain conditions, they can move and also block the urethra. Small stones can pass out along with urine, but large formations gradually accumulate in the organs.
A woman's pregnancy in itself cannot contribute to the onset of the disease. Urolithiasis begins long before conception, and the processes occurring in the female body only activate the growth of stones. The greatest danger during pregnancy is pyelonephritis, which usually accompanies urolithiasis in pregnant women. A certain pattern in the detection of this disease precisely after conception is due to the fact that the greatest prevalence of the disease occurs at the age of 20-35 years, i.e. the most active age for childbearing.
Etiology of pathology
Treatment of any disease first of all begins with eliminating the causes that give rise to it. That is why, despite the onset of urolithiasis even before the period under review, it is important to identify and exclude provoking factors. An important role in the etiological mechanism is played by the hereditary factor.
However, in addition to this, a number of other reasons should be highlighted:
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of spicy and sour foods that increase uric acidity, as well as excessive consumption of animal proteins and refined sugar;
- vitamin deficiency;
- diseases that disrupt metabolism;
- bone pathologies and injuries;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal system of a chronic nature (enteritis, pancreatitis);
- pathologies of the kidneys and genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis).
Symptomatic manifestations
The symptomatic manifestation of urolithiasis depends on the location of the lesion, the nature of the stones and their size. First of all, the disease is associated with a pain syndrome of a dull, aching nature in the chronic course of the pathology. Localization of the lesion in the upper part of the urinary tract causes paroxysmal pain in the lumbar region and in the area of the ureter.
Irradiation to the femoral and groin area and external genitalia is often observed. When stones form in the lower part of the ureter, the pain reaches the labia majora, and problems with urination arise - a sharp reduction in urination, up to its complete cessation.
Our readers successfully use CystoBlock to treat cystitis. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
An increase in the size of the stones leads to blocking the lumen of the ureter, which leads to the accumulation of urine in the kidneys and the manifestation of acute cramping pain in the lumbar region, spreading to the abdomen. These are so-called renal colics, which can last for hours. This complication is accompanied by chills, increased body temperature, nausea, vomiting, and flatulence.
Another characteristic sign is the appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria). This symptom results from mechanical damage to the canal walls when moving hard and sharp stones. Most often, hematuria is recorded at the final stage of renal colic and after physical exertion.
In addition, if an inflammatory reaction occurs, pyuria may occur. Small pebbles in the form of sand may come out along with urine.
When stones form in the bladder, in addition to blood impurities in the urine, pain appears in the lower abdomen, intensifying with movement and at the time of urination. There is an increased urge to urinate, especially acute when walking, shaking or physical activity.
Distinctive signs of bladder inflammation and prostatitis
The nature of the clinical state of both diseases will tell you how to distinguish cystitis from prostatitis. Often, especially in older men, these two pathologies provoke each other, since the organs (MP and prostate gland) are in close proximity. So, the symptoms may have identical manifestations. To make the most accurate diagnosis, you need to pay attention to special points.
- Dysuric signs of bladder damage are accompanied by frequent voiding with cutting symptoms at the beginning and end of urination. However, the volume of urine may not always decrease. Pain during movements intensifies, localizing in the area of the lower triangle of the abdomen. Body temperature occurs very rarely. It is possible for the infection to spread to the overlying parts of the urinary system.
- With prostatitis, dysuric problems are expressed by frequent false urges with a sharp reduction in the volume of urine output - a weak stream, urine output drop by drop. Soreness manifests itself in the rectum, groin or scrotum area. An increase in temperature indicators is not typical. The infectious process does not spread, but can cause the development of prostate cancer, adenoma, or the formation of stones. Therefore, it is very important to determine in time whether cystitis or prostatitis is the cause of the patient’s illness.
Thrush and its signs
How to distinguish thrush from cystitis? To do this, you need to consider the symptoms of candidiasis:
- specific smell,
- burning sensation and itching in the vaginal area,
- noticeable white discharge with an unpleasant odor and a cheesy consistency,
- unpleasant sensation during hygiene procedures.
This disease does not relate to the urinary system; it occurs as a result of suppression of the natural microflora of the vagina by a fungus of the genus Candida. When thinking about how to distinguish a burning sensation with thrush from cystitis, it is worth noting that in the first case, frequent urge to urinate and pain in the urinary canal are not characteristic.
Differences between the symptoms of cystitis and urethritis
Both diseases are characterized by the development of focal inflammatory reactions in the mucous membrane of organs - the reservoir cavity of the bladder and in the cavity walls of the urethra. In addition, the causes of the disease and symptoms are almost the same. But there is still a difference between cystitis and urethritis, and their timely identification will significantly reduce the duration of therapy.
The signs of one and the other pathology are largely identical. In both cases, similar dysfunctions in the processes of urination are noted.
Attention should be paid to the fact that with urethritis, urine does not have a specific odor, pain is local in nature, manifests itself mainly in the pubic area, mucous purulent discharge from the urethral canal is noted and inflammation can spread to the mucous membrane of the vaginal cavity, and the addition of bacterial flora often provokes the development of bacterial vaginosis.
It is difficult even for a specialist, let alone a patient, to independently identify a disease based on signs alone. The pathology is usually clarified using a diagnostic method.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of bladder inflammation and renal colic is similar. The same symptoms for them will be:
- Increased body temperature.
- Changes in the organoleptic properties of urine.
- Blood in the urine.
- Painful urination.
It is worth noting that with renal colic, which is accompanied by the release of particles (“sand”), the pain syndrome will be similar to an attack of cystitis.
This is due to the fact that the sensory receptors of the ureters respond only to strong stimuli. But the bladder and urethra are sensitive, and sand will cause burning and stinging.
The sign on which the differentiation of these two pathologies is based is Pasternatsky’s symptom.
It manifests itself as pain in the kidney area when lightly tapping this area of the lower back. It is characteristic of urolithiasis, but does not appear in uncomplicated cystitis.
Inflammation of the bladder is characterized by a pronounced intoxication syndrome. This is caused by the fact that bacteria at the site of inflammation produce toxins that enter the blood. This is not observed with renal colic.
Another feature of the onset of renal colic is the appearance of pain in the lumbar region. The pain is localized on one side, since simultaneous movement of stones from both kidneys is extremely rare.
Distinctive signs of urolithiasis (urolithiasis) and cystitis
These two diseases are closely related, as they develop as a result of inflammatory processes provoked by stone formation and spreading from the bladder reservoir to the kidney tissue. It is changes in the clinical picture that will tell you how to distinguish cystitis from urolithiasis.
- Inflammation of the parenchymal renal tissue causes failure of its functions, manifested by an increase in capillary capacity and the accumulation of minerals that form stones in the pelvic cavities of the kidneys. The opposite scenario is also possible - a traumatic one, when the removal of stones from the kidneys causes an irritating effect on the mucous tissue, its thinning and inflammatory reactions, manifested by signs of inflammation of the bladder.
- Clinical symptoms for both pathologies are very similar. It manifests itself with the same cutting and burning pains during mictions, caused by irritation from moving stones and sand, structural changes in the urine and blood impurities in it. The main distinctive symptoms of these pathologies are due to the manifestation of the symptom F.I. Pasternatsky. Light tapping in the lumbar area in the projection of the kidneys, with urolithiasis, is reflected by pain, which is not typical for cystitis.
- Concretions can also form in the reservoir cavity of the bladder, causing its inflammation. The same cutting pains occur, but they can radiate - in women to the groin area, in men to the groin and head of the phallus. Pain syndrome can occur in both pathologies, due to blockage of the urethral cavity by stones, abruptly interrupting the process of urination and a feeling of incomplete urine output.
- In case of urolithiasis, changing the position of the body can correct the situation by resuming acts of miction, which is impossible with inflammatory lesions of the bladder.
As you can see, distinctive signs of diseases exist. At first glance, differentiation is simple. But recognizing the disease in reality can be very difficult. Doubts and comparisons will take a lot of time. Self-diagnosis will lead to incorrect treatment, significantly worsen the condition and increase the risk of developing dangerous complications. Trust your health to a specialist.
Features of drug treatment
Most likely, if there are symptoms of cystitis in women and this diagnosis is made, the doctor will prescribe medication treatment.
The “medicinal basket” may include broad-spectrum antibiotics , since cystitis is an infectious disease.
Fluoroquinolones are the most effective against this disease. The second generation of these antibiotics includes the popular Ciprofloxacin.
Moxifloxacin, a fourth generation fluoroquinolone, will be much more effective. Narrower-spectrum antibiotics or combination drugs may be prescribed.
Depending on the symptoms, medications are prescribed to relieve spasms or improve blood circulation.
How to diagnose cystitis
This pathology is dangerous because with irrational self-treatment it can become chronic, leading to exacerbations. In addition, those who try to independently diagnose themselves often make mistakes, confusing cystitis with other pathological conditions, and begin self-medication, which only aggravates the situation.
Nonspecific signs of cystitis
Acute inflammation of the bladder mucosa begins with dysuric phenomena.
- There is an unbearable urge to urinate every 10, 20 or 30 minutes, but a small amount of urine is released - only 10 - 20 ml.
- The process of emptying the bladder is accompanied by a cutting pain in the urethra, which intensifies at the end of the act of urination. There is also pain above the pubis, which can radiate to the perineum and intensify with light pressure on the bladder.
- Patients often note that with the last drops of urine, several drops of blood are released.
It must be said that the frequency of urination, as well as the intensity of pain, directly depend on the severity of the inflammatory process. Chronic inflammation of the bladder is characterized by the same symptoms, but less pronounced.
Urine tests for cystitis usually reveal leukocyturia - the presence of “white” cells - leukocytes , which migrate into the tissue in response to inflammation. Red blood cells are also found in the urine in varying quantities ; bacteria that cause the disease are almost always inoculated.
Such symptoms and laboratory indicators are very nonspecific, because frequent urination can also be observed in other diseases, for example, in the case of urethritis or prostatitis in men, as well as pyelonephritis. And red blood cells in the urine can be detected in glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis or oncological processes. Therefore, you will not be able to diagnose yourself, and the symptoms must be considered together with the research results.
What does urinary retention mean?
- Sometimes inflammation of the bladder is accompanied by a reflex spasm of the smooth muscles of the sphincter of the urethra and pelvic floor, in which case urinary retention occurs (most often this symptom occurs in children), and at the same time aching pain appears in the perineum and anus. This condition can be confused with acute renal failure, when the kidneys simply stop producing urine, but a general blood test comes to the rescue. Normal levels of creatinine and urea will indicate that there are no problems with the kidneys.
- Also, urinary retention is characteristic of large stones in the renal pelvis or ureter, which obstruct the outflow of urine. This condition can be easily confirmed or refuted using x-ray or ultrasound.
- In addition, urinary retention is observed in men with prostatitis or adenoma, because the enlarged prostate gland compresses the urethra passing through it. But before anuria (lack of urine) occurs, the stream becomes thin and intermittent; straining is required to empty it, but even after this there is often a feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder. Palpation of the gland through the anus and ultrasound examination help to distinguish reflex urinary retention during cystitis from mechanical retention due to prostate enlargement.
Clear signs of cystitis
If a woman detects signs of cystitis, it is necessary to urgently consult a urologist for its treatment. If he does not accept without a referral from a therapist, you need to take this referral. You should not trust treatment to a therapist or gynecologist.
They most likely know what to do, but not being specialists in urology, they may overlook and not take something into account. Moreover, you cannot self-medicate. Indeed, in this case, the risk of complications increases significantly.
To “run” to a doctor with chronic cystitis, we can advise the following:
- Carry out hygiene procedures by adding chamomile decoction to the water or dissolving several furatsilin tablets in it;
- warm the bladder by placing a warm heating pad on the lower abdomen or wrapping the abdomen and lower back with a warm scarf (warming is contraindicated only if there is blood in the urine);
- take a tablet of one of the medications that are usually used in urology (they will be discussed below) and a tablet of no-shpa.
After visiting your doctor, follow his recommendations.
3. Clinical analysis of blood, urine, urine pH. Biochemical examination of blood and urine.
4. Culture of urine for microflora and determination of its sensitivity to antibiotics.
5. If necessary, stress tests with calcium (differential diagnosis of hypercalciuria) and ammonium chloride (diagnosis of renal tubular acidosis), and parathyroid hormone testing are performed.
6. Analysis of the stone (if any).
7. Biochemical and radioisotope studies of kidney function.
8. Retrograde ureteropyelography, ureteropyeloscopy, pneumopyelography.
9. Study of stones by tomographic density (used to predict the effectiveness of lithotripsy and prevent possible complications).
The main symptom of urolithiasis is pain in the lumbar region. However, there are other symptoms, or lack thereof, that help make the correct diagnosis.
We invite you to read: What is a vasectomy and who is it indicated for?
Sometimes the disease is confused with a manifestation of cystitis and they begin to take completely inappropriate medications to treat something that, in fact, does not exist.
In order not to subject your body to improper treatment, it is necessary to understand all the causes of urolithiasis and its symptoms.
Urolithiasis is characterized by the presence of stone formations in the kidneys, ureters or bladder. Stones, called calculi, appear due to various factors, including:
- increased calcium levels in urine;
- infection of the ureters;
- disturbance of phosphorus-calcium metabolism;
- sedimentation of magnesium and other substances that interact with oxalic acid;
- and others.
The above pathologies are not the norm, but symptoms of disturbances in the functioning of any processes in the human body.
The reasons can be very varied, for example:
- previous injuries, bone damage;
- lack of vitamins in the human diet;
- geographical and hereditary factors;
- disruption of the thyroid glands;
- infections and diseases leading to dehydration;
- excess salts and acids in the body as a result of poor nutrition;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary organs;
- Drinking water high in salts and calcium for a long time.
Frequent companions of urolithiasis, and sometimes its causes, are gout, pancreatitis, osteoporosis, cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Depending on the existing pathologies, the composition of the stones differs. This greatly facilitates the search for the cause of urolithiasis.
Genetic and geographical factors, in turn, are not a death sentence and do not mean that the disease will befall you if it is common among your relatives or close circle of friends. They only contribute to the development of kidney stone pathologies in the presence of any of the diseases listed above.
The number of stone formations can vary, and the size can vary from millimeters to several centimeters. Unpleasant symptoms make themselves felt when these stones begin to move from one organ to another.
Pediatric urolithiasis is extremely rare, mainly in underdeveloped regions of the world. The nature of stone formation indicates the presence of infectious diseases and the influence of dietary factors.
When it comes to adults, the disease is more often diagnosed in men than in women. For children, the statistics are approximately equal.
Urolithiasis can develop on either side, in the left and right kidneys, in one of the ureters or in the bladder - the location of the symptoms and their nature will depend on this.
The male half of the population seeks help much more often due to pain and other signs of urolithiasis. Among the manifestations specific to each gender, the following are distinguished:
- in women - pain spreading to the labia;
- in men - painful sensations are felt in the thigh, groin area and bladder.
Now let's look at how to find out the approximate location of stones in the body by characteristic symptoms.
Causes and mechanism of development
Urolithiasis and cystitis are common pathologies of the urinary system. The cause of cystitis is often infection of the bladder cavity.
Bacteria penetrate through the urethra (in case of domestic and sexual infection), through the blood or lymph flow (in the presence of foci of infection in the body), or penetrate through the wall of nearby organs.
In addition to bacteria, pathology is caused by injuries, surgical interventions, and autoimmune processes.
Urolithiasis has a different etiology. Kidney stones are formed due to metabolic disorders or excessive consumption of foods and water containing minerals.
These two pathologies are closely related. Thus, stone formation begins when the inflammatory process spreads from the bladder to the kidneys.
In the inflamed renal parenchyma, functional disorders occur, and the capillary capacity increases.
This leads to an increase in the amount of minerals that are excreted from the body. They accumulate in the renal pelvis, which leads to the formation of stones. And cystitis develops after an attack of renal colic.
The mechanical effect on the mucous membrane of stones or sand has an irritating effect.
This causes inflammation or thinning of the mucous membrane, which will lead to symptoms of bladder inflammation.
Inflammation of the bladder due to urolithiasis is traumatic in nature.
How to take Cyston correctly for cystitis and in what cases is the drug contraindicated?
We will describe another effective drug Cyston for cystitis, instructions for use, as well as prices and reviews of those people who, with its help, were able to get rid of pain and other symptoms. After all, this disease affects most of the female population, and sometimes the male population. Everyone needs to know what to do in this case and how to treat it.
Cystitis is considered not just an unpleasant pathology with severe pain. In the absence of competent and timely treatment, it can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of the body and even result in kidney failure. To avoid this, you should immediately see a doctor and take prescribed medications.
Composition and release form
This remedy is only available in tablet form. They are produced by the Indian company Himalaya Drug Co. For maximum effectiveness of the medicine, it is made from many plant components that have a complex effect on the body. This is a herbal medicine that contains many natural plants treated with steam:
- double-carp stem - has a diuretic effect;
- saxifrage reed - in addition to enhanced fluid removal, promotes the breakdown of silicon-colloidal compounds, and also destroys pathogenic microflora;
- madder cordifolia - helps reduce and remove stones, acts in a similar way to diuretics;
- roots of syta membranous – has an antibacterial effect;
- seeds of rough strawflower - reduces muscle spasms and accelerates the removal of fluid from the bladder;
- various parts of onosma bracts - protects the mucous membrane from irritating mechanical influences, relieves inflammatory symptoms, eliminates most pathogenic microorganisms;
- Vernonia ashy – promotes muscle relaxation.
As well as extracts of fragrant basil, fava beans, Tribulus creeping, mimosa pudica, fragrant ponytail, horsetail, teak wood. In addition to these plants, crushed mummy is also added here. It normalizes metabolic processes in the tissues and cells of all organs, the functioning of the digestive system and removes fluid from the body.
Small amounts of aerosil, magnesium stearate, lime silicate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose and crospovidone are also present as additional substances.
The tablets look convex on both sides, and their color is brown with different inclusions. The packaging is made in the form of a plastic jar containing 100 tablets. Since treatment most often takes a long course, such packaging is justified.
Does Cyston help with cystitis? Due to the above composition, it not only improves the functioning of the excretory system, but also actively fights the very cause of inflammation. But what sets it apart from other analogues is its complete safety for human health, because it is a herbal preparation made on a natural basis.
Operating principle
All components combine perfectly with each other and have a complex effect on the human body:
- antiseptic - destroys bacteria that lead to infection of the organ;
- anti-inflammatory – eliminates swelling and irritation of tissues, soothes them;
- diuretic – accelerates the excretion of salts and fluids;
- antispasmodic - relaxes smooth muscles, which greatly facilitates the patient’s well-being and even slightly relieves pain;
- antimicrobial – fights pathogenic microorganisms, thereby promoting rapid recovery;
- nephrolitholytic - dissolves and breaks down kidney stones into small parts, which are easier to remove naturally from the body, which cleanses the urinary system of excess formations;
- prevents the reappearance of salts, sand and stones by accumulating magnesium, sodium, potassium and reducing the concentration of calcium, oxalic acid and hydroxyproline.
Cyston stops infectious and inflammatory processes, eliminates congestion, accelerating all natural functions of the system. Due to muscle relaxation, not only fluid and salt are easily removed, but also purulent discharge, mucus, infectious bacteria and the results of their vital activity. Therefore, the body is quickly cleansed of pathogenic microflora and signs of intoxication.
What is especially appreciated when treating kidney diseases with Cyston is its ability to dissolve stones and salt crystals into small particles, making their removal safe and painless. As a result of taking this medicine, you can even avoid cases of surgical intervention.
If you use this remedy in combination with antibacterial therapy, the therapeutic effect is achieved much faster, and the risk of relapse is significantly reduced. Therefore, Cyston is often used in combination with other agents.
Indications and contraindications
Most often, this drug helps in the following situations:
- infectious lesions of the urinary system of all forms;
- signs of gout;
- with urolithiasis;
- to stop cases of urinary incontinence;
- with sylalolithiasis (stones in the salivary glands);
- to eliminate salt deposits;
- in order to prevent new diseases of this kind after surgical treatment.
Contraindications include only the age of children under 6 years of age and individual allergic reactions to any of the components of the drug, which happens quite rarely. Since the composition contains many different herbal ingredients, you need to make sure that the patient does not have an individual intolerance to at least one of them.
Treatment rules
The instructions for use of Cyston tell you how to drink it, in what quantities, and other nuances of therapy with its help are specified. We list the main ones:
- Only a doctor should prescribe the medication. Any independent treatment can lead to a lack of the expected effect and a deterioration in well-being. You should not stop therapy prematurely, reduce or increase the dose, or take extra pills.
- Don't expect instant results. Recovery with herbal remedies may take at least two weeks or even a month.
- The medicine should be taken immediately after meals and be sure to drink plenty of water.
- It is not advisable to chew the tablet, but if you are unable to swallow it whole, then you need to divide it into several parts.
- During treatment with Cyston, you should definitely drink a lot of water (at least 2-2.5 liters per day).
- In cases of large formations, this remedy is not prescribed, since its use can lead to the movement of large stones and unwanted blockage of the canals.
- If a painful reaction occurs, you should immediately stop taking the drug and consult a specialist.
- Sometimes long-term treatment may be required to completely remove all excess formations from the urinary tract. In some situations this takes a month or a month and a half, in others – up to six months.
For cystitis and other infectious diseases of the excretory system, the following dosage is recommended:
- children from 6 to 12 years old – 1 tablet three times a day;
- Children over 12 years of age and adults can take 2 pieces three times a day.
Treatment lasts about 7 days. But if a large number of stones or salt crystals are detected, then it continues until the organs are completely cleansed. At the same time, the daily dose remains at the same level.
For prevention, for example, after surgery, doctors prescribe 1 tablet three times a day for 4 or 5 months. This is done to prevent relapse of the disease.
Cyston during pregnancy
Very often, this drug is prescribed even for the treatment of pregnant women, because it is safe for the body as a whole, and also exhibits a mild and painless effect. This is very important during such a period, because cystitis and other diseases of the urinary system are often accompanying pregnancy.
Such women are prescribed this drug not only in cases of infectious or inflammatory diseases, but also simply to alleviate other conditions. For example, for problems with urination, spasms, the presence of salts or kidney stones, to relieve pain due to excessive pressure of the enlarged uterus on neighboring organs, etc.
How to take Cyston for cystitis in pregnant women? The number of tablets and duration of administration are similar to other cases - 2 tablets three times a day. It is very important during treatment to significantly increase the consumption of clean water to two liters per day.
The only case when taking Cyston during pregnancy is undesirable is urolithiasis. If there is no urgent need to get rid of stones right now, then there is no point in provoking their movement and splitting. After all, such a process can increase the tone of the uterus and lead to premature birth or miscarriage. Also, there is no need to prescribe this remedy to pregnant women only for the preventive purpose of new formations.
Analogs
In its composition, Cyston is completely different from any other drugs in this group. There are no exact analogues of this medicine. But you can find remedies that are similar in their action and have a similar therapeutic effect. Such drugs include:
- Urolesan;
- Rowatinex;
- Phytolysin;
- Canephron;
- Urokran;
- Bangshil;
- Trinephron;
- Pitemidine;
- Nephrophyte;
- Lespeflan;
- Afala;
- Prostanorm;
- Superlymph.
But you shouldn’t replace one remedy with another on your own. If for some reason Cyston is not suitable for you, then you should discuss with your doctor what exactly should be used instead.
Video: about the drug Cyston.
Price
The price for a package of the product is in the range of 370-415 rubles, depending on the pharmacy and the city. Since they are sold in 100 pieces per package, this is not such a large amount.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method that differentiates inflammation of the bladder from an attack of renal colic is ultrasound.
To conduct an ultrasound for cystitis, an inflammatory focus in the bladder will be identified. The size of the lesion can be large or spread over the entire surface of the mucous membrane.
But with urolithiasis, such inflammation will not be observed. Foreign bodies will be visible in the bladder, the size of which will not exceed a few millimeters. There may be inflammatory foci in the ureters and kidneys.
To diagnose cystitis, it is necessary to conduct an analysis such as bacteriological urine culture. It is carried out to determine the type of pathogen. With urolithiasis, the urine remains sterile and bacteria are not detected.
There are also differences in the general analysis of urine and blood. Cystitis is characterized by an increase in the number of leukocytes, which indicate the presence of bacteria and inflammation. But with urolithiasis there is no such change in indicators.
In a general urine test for cystitis, leukocytes, admixtures of pus, and dead cells of the mucous membrane appear. In urolithiasis, the predominant change is red blood cells in the urine.
How to treat: top 5 effective medications
| № | Name | What is it like? | Action, how to take | Contraindications |
| 1 | Nolicin (Normax, Norbactin) | Antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone group | Has an antimicrobial effect. It is usually taken 2 times a day before meals. | Childhood, pregnancy, cerebrovascular accident |
| 2 | Nitroxoline | Antibiotic of the hydroxyquinoline group | Effective against urinary tract infections, not suitable for treating chronic diseases. Prescribed 3-4 times a day for two weeks. | Pregnancy and lactation. Severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys. |
| 3 | Monural (fosfomycin) | Uroantiseptic based on fosfomycin trometamol, available in powder (granules) form. | Dilute in 1/3 glass of water, take 2 hours before meals. One sachet of the drug is enough for a course of treatment lasting one day. | Severe form of renal failure, children under 5 years of age. |
| 4 | Rulid | Semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic based on roxithromycin | Active against chlamydia, staphylococci and other microorganisms. Treatment lasts 1 day, during which 2 tablets of the medicine are taken before meals at a time or with a break of 12 hours. | Age up to 4 years, pregnancy and lactation, simultaneous use of drugs containing ergotamine. |
| 5 | Urolesan | Herbal medicine based on extracts of oregano and hop cones, fir and mint oils. | Antispasmodic and choleretic agent. Drink three times a day half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is from a week to a month. | Urolithiasis disease. During pregnancy it is prescribed as a last resort. |
Treatment
The differentiation lies in the fact that each of these pathologies requires specific treatment. If the diagnosis is incorrect, the treatment is incorrect, the patient’s condition worsens when using therapy.
The clinical picture of bladder inflammation and urolithiasis is similar, which requires qualified diagnosis.
Despite the presence of general symptoms, you can quickly distinguish, because there are specific manifestations.
Regardless of what pathology a person has, it is worth contacting medical professionals for examination and treatment.
Each of these pathologies causes complications that become a threat to health and life.
Folk remedies and methods
In folk medicine, decoctions of medicinal herbs that have anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects (chamomile, bearberry, plantain, parsley) are used to treat cystitis in women.
They are drunk several times a day before meals in small portions. Cranberry and lingonberry juice have diuretic properties. Fruit juice made from these berries has a pleasant taste and is useful for cystitis.
Decoctions of birch, spruce and pine cones can be used to prepare medicinal baths. They should be taken for a short time (no more than 15 minutes).