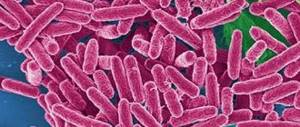
Escherichia coli, which has the Latin name Escherichia coli, is a representative of a species of bacteria that combines various species, both pathogenic and beneficial. A pathogenic type of E. coli causes infectious and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract system (E. coli in the bladder is quite common), as well as the male and female reproductive systems.
Beneficial species of this genus of bacteria colonize the intestinal tract of a healthy person and are representatives of the standard microflora of the human body.
What should the norm be?
Normally, bacteria in urine culture during flora testing should contain no more than 105 bacteria per 1 cm3 of liquid. An increase in numbers inevitably leads to a clear deterioration in well-being and the development of inflammation. When bacteria, chlamydia or gonococci spread deep into the urinary tract, damage to the bladder, ureter and kidneys as a whole can occur. Inflammation caused by E. coli will lead to intestinal upset with all the accompanying unpleasant symptoms and a number of serious diseases. When staphylococcus, gonococcus, streptococcus are added, it leads to severe suppression of the immune system and dangerous diseases: gonorrhea, syphilis.
Therapy methods
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CvmYdm7rv5M
Treatment of E. coli that has settled in the bladder should be comprehensive. Therapy includes improving the body's protective functions, fighting inflammation, restoring the affected mucosa, eliminating pain and intoxication.
The attending physician prescribes the following medications:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antipyretics;
- uroseptics;
- anesthetics, painkillers;
- drugs that strengthen the immune system.
The latter are prescribed if the bacterium is found in the urine and there are no symptoms. It is necessary to maintain a drinking regime, monitor your diet and cleanliness of your body.
Any infection, including rod-shaped bacteria in the bladder, can be treated with antibiotics. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor and can range from 3 days to 2 weeks. The following drugs are most often prescribed: Amikacin, Cefotaxime, Ofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Ceftazidime, Imipenem.
Repeated tests will help ensure complete recovery. They must be taken one month after therapy.
ethnoscience
The folk method of combating E. coli that has settled in the urinary system involves the use of decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs (plantain, cinquefoil). You can wash yourself with string, calendula or chamomile. These plants have an antimicrobial effect.
It is recommended to drink more fluids and fermented milk products (fruit drinks, teas, yogurt, whey). Shilajit will help get rid of the infection. The product is taken three times a day before meals, no more than 0.5 grams at a time.
How to treat such cystitis
If the disease is not treated, then cystitis will be advanced, and the chronic disease will become a “faithful companion” of the careless patient. Moreover, there is a very high probability that E. coli will then cause pyelonephritis. Therefore, at the first symptoms, go to a urologist or at least a local physician.
What treatment will the specialist prescribe:
- Antibiotics – since cystitis is bacterial in nature, this will be the main drug treatment;
- Uroseptics have proven themselves well as adjuvant therapy;
- Vitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system.
Dietary nutrition is an essential component of treatment. The physician must select an individual nutrition plan for the patient, which is based on a dietary menu. Be sure to drink plenty of water throughout your treatment.
Prevention
To prevent relapses, it is necessary to carefully observe the rules of intimate hygiene, wear comfortable underwear made of high-quality fabrics (preferably cotton), and also be regularly examined by a doctor. The patient should change his diet, making a choice in favor of healthy, balanced foods (an individual diet is prescribed by the doctor), and eliminate bad habits.
Doctors recommend separating sexual contacts, observing sterility measures. You should also regularly take vitamin complexes and medications prescribed by your doctor that help strengthen your immune system.
Possible reasons
Intestinal rod-shaped bacteria easily penetrate and settle in the intestines due to:
- development of dysbacteriosis,
- eating low-quality stale foods,
- taking a number of medications, in particular long-term courses of antibiotics.
When bacteria appear in the urine, it means that they have migrated and spread to the genitourinary system from the gastrointestinal tract and intestines. Reasons for this:
- non-sterility of the urinary canal,
- promiscuity,
- lack of compliance with basic standards of personal hygiene.
Penetration of E. coli into the blood may well occur and lead to the development of an infectious-inflammatory process in the bloodstream due to:
- lack of timely implementation of hygiene measures,
- improper collection of urine to study the composition of urine.
When E. coli gets into the urinary ducts, a fairly thorough attachment to the walls occurs, which is impossible to wash off. As bacteria pass up the urethra, damage to the bladder and kidneys is possible, with all the ensuing consequences. Bacteria quickly begin to multiply in the bladder against a background of weakened immunity.
Reasons for appearance
Escherichia coli invades the bladder from parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
The most common routes of transmission of infection are:
- Oral-fecal, when dirty hands accidentally transfer Escherichia from the anus to the mucous membrane of the vagina or head of the penis, from where the microorganisms enter the urethra and rise to the overlying organ.
- Medical procedures - cystoscopy and catheterization, if the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are not followed.
- Poor quality products, due to which the balance between beneficial and opportunistic microflora in the intestines is disrupted, and therefore E. coli actively multiplies and, spreading beyond the organ, enters the bladder.
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse with sexual experiments, a combination of vaginal and anal sex.
Sometimes E. coli is detected in urine due to improper collection of biomaterial for culture: failure to maintain genital hygiene before analysis, dirty container, unsterile instruments.
Normal in urine
The norm is the absence of E. Coli in the urine.
If the E. coli content is 105 CFU/ml and the disease is asymptomatic, the patient is asked to retake the tests: incorrect collection of biological material is allowed.
But this indicator is considered critical. If a repeat test shows the same value, then a diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis is made and treatment is started. Bacteriuria with an indicator of 102 CFU/ml is a sign of cystitis.
Is bacteria in the bladder dangerous?
Once in the urinary environment, this bacterium very quickly provokes inflammation. It is dangerous because it definitely does not come out in urine. The bacterium is able to go deep into the body, negatively affecting the patient’s immunity. Other bacteria can also join it, so the disease can become truly dangerous, requiring immediate treatment.
- E. coli in urine treatment with antibiotics
How does E. coli get into the bladder? This has already been mentioned above, but some points are worth dwelling on in more detail.
Routes of infection:
- Hematogenous. Pathological agents can enter the bloodstream through the transfusion of biological fluid, through cuts;
- Contact. Everything is simple here - failure to comply with basic sanitary measures can lead you not only to the urologist’s office, but even to a hospital bed;
- Lymphogenic. The bacterium is able to pass through lymph;
- Descending. The infection enters the bladder from other, “upper” organs, and simply attaches to its wall;
- Rising. Microorganisms enter the organ through the urethra through clothes and other infected objects.
And then follows a comprehensive treatment of E. coli in the bladder. It is extremely important not to delay in starting therapy.
general characteristics
The occurrence of this disease occurs under the influence of bacteria such as E. coli. This bacterium is a completely normal and natural component of the human body, contributing to the proper functioning of the human intestine. But when it gets into the urine or urinary tract, it becomes the causative agent of all kinds of inflammatory processes, and with them diseases.
But not only E. coli can cause cystitis. There are also a number of harmful bacteria, such as:
- Chlamydia.
- Staphylococci.
- Streptococci.
- Ureaplasma microbes.
How to recognize?
If a person’s immune system is quite stable, then the wand is unlikely to make itself known in any way, and may remain unnoticed for a long time. Only during a urine test do doctors often recognize its pathogenic effect on the urinary tract, when patients begin to experience unpleasant symptoms in full:
- frequent urination,
- pain in the lower abdomen,
- discharge of urine mixed with blood and pus,
- apathy, loss of strength,
- increased temperature due to the inflammatory process,
- suppression of the immune system,
- development of the inflammatory process in the urinary system,
- pain when urinating.
When such symptoms appear, E. coli no longer goes unnoticed and, of course, requires elimination, stopping its development, which can lead to more severe and difficult-to-treat diseases.
How is the infection transmitted?
The main route of transmission is oral-fecal, in rare cases it is transmitted through household contact. When transmitted through the oral-fecal route, the pathogen, together with feces, penetrates into the soil or water, as well as onto plants grown in garden plots. The routes of entry in the future are predetermined, through unwashed hands with which a person touched the soil or plants. In addition, cases of ingestion of contaminated water are not uncommon.
Another type of pathogen transmission is much less common than the first. Typically, infection occurs in places where there are large numbers of people who come into contact with each other in one way or another. These are kindergartens, schools, hospitals, maternity hospitals. Pathogenic microorganisms can be transmitted to a child from a woman in labor during the birth process.
The role of E. coli in the male genitourinary system
Like the female half of the population, Escherichia can cause an intestinal infection. But diseases caused by this pathogen in the genitourinary system are of much greater importance.
Penetrating into the urethral canal of the male body causes inflammation of the urethra; after a few days of the disease, it enters the chronic stage. In addition, the infection will continue to develop and affect other organs of the genitourinary system.
A characteristic feature of the occurrence of inflammatory processes in men is that the reproductive system is most often affected rather than the urinary system. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure.
A man who is a carrier of the infection causes frequent cystitis, pyelonephritis and colpitis in his sexual partners.
Pathogenic species
Nowadays, scientists have identified the main groups of pathogenic Escherichia:
- Enteropathogenic
- Enterotoxigenic
- Enteroinvasive
- Enterohemorrhagic
The most common causes of infectious processes occurring in the small intestine in children under 1 year of age, and traveler's diarrhea in children over one year of age and adults, are enteropathogenic bacilli.
The cause is enterocolitis. The routes of transmission are different - in children's institutions and maternity hospitals, through unsterile instruments, the hands of women in labor and medical personnel.
In adults, the manifestation of “traveler's diarrhea” does not require special drug treatment. It manifests itself as a disorder of defecation, loose and watery stools. It develops in people who travel to hot countries in the summer in the absence of sanitary standards for food storage and preparation.
A different situation arises if this type of pathogen enters the baby’s body. Manifestations occur in the form of vomiting, loose stools, and abdominal pain. In children, immediate treatment is required, since the immune defense system in children is not developed and it is not possible to destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
The entry of enterotoxigenic E. coli into the body causes general stool upset, with continuous liquid diarrhea. Usually no treatment is prescribed, and the pathogenic microflora is destroyed by the internal forces of the body.
Manifestations can very often resemble the course of cholera. These types of E. coli are very widespread in countries with insufficient sanitary conditions. Infection occurs through consumption of contaminated water and food.
The enteroinvasive form causes an acute course of foodborne toxic infections in adults and children. The symptoms and course of the disease are very similar to those of dysentery.
Hemolytic Escherichia coli causes hemorrhagic colitis and the development of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. In these cases, properly selected treatment is necessary.
In addition to severe poisoning, the hemolytic bacillus has the ability to lead to the formation of neuritis and kidney disease in children if it enters the urinary system or bloodstream. Infection mainly occurs through water and food.
In addition to causing intestinal disorders, pathogenic types of microorganisms can cause various diseases of the genitourinary system of both the female and male half of the population. A common reason for pathogenic microflora entering the genitourinary system is simply not following the rules of hygiene, wearing incorrect underwear or anal sex.
When a pathogenic bacillus enters the urinary system, inflammation may develop in the urethra, bladder, and kidneys.
How is the treatment carried out?
Like any other inflammation, the spread of pathogenic microflora in the urine is treated with antibiotics. This is the first thing the doctor will prescribe with the goal of suppressing E. coli and restoring microflora in the intestines.
- E. coli in urine during pregnancy - causes and treatment
If treatment is not carried out, E. coli will eventually lead to settlement not only in the bladder and ureter, but will provoke the development of pyelonephritis and cystitis. In addition to antibiotics, the doctor will prescribe uroseptics to suppress the inflammatory process and antimicrobial drugs. In order to expel the stick from the urinary tract, patients are advised to drink more fluids, teas, and fruit drinks.
Self-medication is unacceptable. If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should urgently consult a urologist, since in advanced cases it is often impossible to do without surgical intervention on the pelvic organs. Pregnant women in case of urine infection require the most gentle and special treatment.
Features of treatment
The main therapy should be aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, as well as alleviating clinical manifestations and improving the general condition of the patient. Initially, doctors prescribe antibacterial medications. The treatment process, aimed at blocking the mechanisms of development of the disease, involves the use of the following medications:
- Antispasmodic drugs that relieve muscle spasms.
- Medicines aimed at dilating blood vessels. They have a beneficial effect on the condition of vascular walls and improve blood flow.
- Medications that eliminate tissue hypoxia.
Drugs that help strengthen the immune system and anti-inflammatory (non-steroidal) drugs used to reduce foci of the inflammatory process may also be prescribed. The duration of the course of antibiotics usually does not exceed five days in the acute form. In chronic cases, it can last up to ten days.
Non-drug treatment includes following a prescribed diet, which is aimed at improving intestinal functions. The patient is also required to maintain an optimal work schedule and leave time for proper rest. It is recommended to drink more fluid, as bacteria leave the body faster along with urine.
Bacterial cystitis must be treated promptly. Otherwise, the patient may develop serious complications: hemorrhagic bladder inflammation (often due to infection with the herpes virus), pyelonephritis, paracystitis, urinary incontinence, vesicoureteral reflux.
Treatment
The treatment regimen for eliminating the inflammatory process caused by pathogenic Escherichia is standard for the male and female half of the population, including children.
After bacterial culture, sensitivity to certain groups of antibiotics is determined. The course of antibiotic therapy usually ranges from several days to two weeks. 30 days after the end of treatment, repeat tests must be taken to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
Nowadays, the following drugs have been identified that successfully combat pathogenic microflora that infects the mucous membranes of the genital organs and urinary tract:
- Cefataxime
- Ceftazidime
- Imipenem
- Amikacin
- Oflaxacin
- Moxifloxacin.
In order to eliminate the rise in temperature that is possible with the development of the inflammatory process, antipyretics are used: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide.
Therapy during pregnancy
Treatment during pregnancy is strictly selected by the doctor. The drugs cause side effects and negatively affect the development of the fetus. Therefore, it is important that medications are selected by a urologist, taking into account the condition of the female body and the degree of development of pathological processes.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Antibiotics | Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin | The adult dosage is 1 tablet every 12 hours. The course of therapy lasts 14 days. |
| Immunostimulants | Imunofan, Polyoxidonium | Suppositories during pregnancy are used with caution, strictly as prescribed by the doctor. The recommended dosage is 1 suppository per day. The course of treatment lasts 8-10 days. |
| Probiotics | Bactisubtil, Bificol | The medicine is taken 1 hour before meals, 3-6 capsules per day for 7-10 days. |
| Diuretics | Cyston, Urolesan | The drug is prescribed 2 capsules 2 times a day. The course of therapy lasts 4-6 months. |
The expectant mother is also advised to drink more clean water, stick to a diet and follow simple rules of personal hygiene. Avoid wearing tight underwear. Use exclusively personal hygiene products (towel, pads, napkins).
New drugs for the treatment of cystitis
For adults, when E. coli is detected in the urine and unpleasant symptoms appear, new generation antibacterial drugs with antimicrobial effects are prescribed:
- nitrofurans,
- fluoroquinolones (Fosfomycin, Ampicillin, Nitroxoline, 5 NOC, Biseptol), Amoxicillin, applicable to children and pregnant women,
- cephalosparins for oral administration,
- Fosfomycin for children over 5 years old and nursing mothers, as a harmless drug to suppress E. coli, create bactericidal flora in the urine, eliminate negative symptoms,
- bifidobacteria for children and pregnant women, which contribute to the rupture of bacterial cell walls, provide a bactericidal effect and are completely harmless to the body,
- antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, Tsiprolet, Tsifran, Ecotsifol, Tsiprinol, Levofloxacin) are applicable for uncomplicated cystitis,
- Norfloxacin, Norbactin in the event of a high concentration of bacteria in the urine,
- Ofloxacin taken 200 mg per day to alleviate the condition, reduce unpleasant symptoms,
- anti-inflammatory antispasmodics.
The development of therapeutic actions is carried out exclusively by the doctor. The main thing is not to harm the body, to have the maximum impact on bacteria and to help remove infection from the urinary system naturally, without resorting to surgical intervention. It is possible to prescribe stepwise therapy, starting with safer antibiotics and gradually moving to reserve ones.
If accompanying symptoms appear, you should consult a urologist as soon as possible. For example, cystitis has a recurrent course, leading to complications when hospital treatment and even surgery can no longer be avoided.
- How does E. coli manifest itself in the urethra in men: symptoms and treatment
At home, patients are advised to drink more fluids, stop taking salt, adjust their diet, and include fermented milk products with lactobacilli in their diet: yogurt, curd whey, sour milk, since it is the acidic environment that has a detrimental effect on E. coli, killing it.
Indicated for the treatment of E. coli, taking mumiyo 3 times a day, 0.5 g before meals, as an excellent means for removing bacteria. The course of treatment is 5 days. You can douche by dissolving 1 g of mumiyo in 1 glass of warm water. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. After a 5-day break, the course can be repeated 2-3 more times.
Treatment of pathology with folk remedies
Shilajit can be used as therapy for cystitis; it is available to anyone. The course of treatment should be 30 days, during which the patient takes 0.5 grams three times a day before meals. Folk remedies that help cope with bacterial cystitis:
- dairy products. Lactic acid destroys bacteria and stops the proliferation of E. coli. It is recommended to drink yogurt, whey, kefir;
- herbal infusions based on chamomile, St. John's wort, mint and plantain;
- goose cinquefoil. To prepare the decoction, you need to take 1 tablespoon of the substance and pour 250 ml of boiled water, then boil for 30 minutes. Leave the broth to brew overnight, then drink it three times a day;
- Jerusalem artichoke.
It is necessary to drink as much fluid as possible and follow a diet that consists of excluding from the diet foods that irritate the bladder: salty, fried, spicy. You should maintain genital hygiene and avoid hypothermia.
Complications
If you have started treatment for bacterial cystitis, or perhaps not treated it at all, then the risk of complications in the form of other diseases is too great. Most often, pyelonephritis, chronic cystitis, trigonitis may occur, and urinary incontinence may develop.
It is quite simple to prevent the occurrence of such complications - at the first symptoms, contact a urologist and undergo the necessary course of treatment.
E. coli can also cause other diseases. Therefore, it is very important to maintain hygiene, strengthen the immune system, and if unpleasant symptoms appear, immediately seek qualified help.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
To begin treatment for bacterial cystitis caused by E. coli, an accurate diagnosis must first be made. To do this, first of all, the doctor interviews and examines the patient, and then prescribes diagnostic tests:
- urine and blood analysis;
- urethral smear;
- Ultrasound and X-ray;
- cystoscopy.
Urine cultures may be tested several times; test results may be incorrect due to improper collection of urine. An increased number of leukocytes and a specific pungent odor will indicate the presence of inflammatory processes.
When cystitis caused by E. coli has been discovered, the doctor selects a suitable comprehensive treatment, which consists of taking medications, folk remedies, as well as following a diet and drinking regime.
Predisposing factors for the presence of bacteria
Once in the urinary tract, the bacterium does not necessarily gain a foothold there. It is washed off with a stream of urine (which has some bactericidal properties). But in the presence of predisposing factors, the bacterium can settle in the mucous membrane of the urethra and ascend into the
bladder. Such factors may be:
- stagnation of urine associated with urolithiasis;
- stagnation of urine caused by prostate adenoma (in men);
- rare emptying of the bladder, when a person is unable to go to the toilet on time;
- compression of the bladder in pregnant women;
- changes in the chemical composition and acid-base balance of urine in kidney diseases and diabetes mellitus;
- infection of the urinary tract by other microorganisms (including sexually transmitted ones), which reduces the natural protective properties of the mucous membrane;
- damage to the cells of the mucous membrane of the urethra and bladder during chemotherapy for cancer (cytostatics suppress the renewal of the epithelium of all mucous membranes of the body);
- degenerative changes in the mucous membrane of the bladder as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation during radiation therapy for cancer of nearby organs;
- immunodeficiency conditions caused by other diseases, malnutrition, vitamin deficiency;
- decreased local immunity due to local hypothermia.
It should be noted that with good immunity, E. coli can live in the urinary system for some time without causing symptoms of inflammation. The E.Coli bacterium is often found in urine when analyzed (although normally it should not be there).
If there are no symptoms of inflammation and if the number of rods does not exceed 10 5 in 1 ml of urine, no special treatment is carried out. In this case, it is also impossible to exclude incorrect collection of urine for analysis.
But if the patient seeks medical help due to symptoms of cystitis (frequent urge to urinate, pain during and after urination, constant nagging pain in the suprapubic region, the appearance of blood or mucus in the urine), the E.Coli concentration is more than 10 2 per ml urine most likely suggests that the inflammation is caused by Escherichia coli.
Traditional treatment
E. coli is well eliminated by Jerusalem artichoke, which is taken raw. You can prepare the following mixture:
- soak kefir in a water bath;
- separate the curd mass from the whey;
- take 2-3 times a day, 1/3 cup.
For the treatment and removal of E. coli in children, infusions of cinquefoil with antibacterial properties, chamomile, plantain, peppermint, St. John's wort, and agrimony are indicated. It is recommended to drink as tea in case of chronic inflammation to cleanse the urethra when pain occurs and urine with blood and pus is discharged.
To treat E. coli in urine, traditional medicine will come to the rescue.
The main thing is to neutralize the harmful effects of E. coli, choose the right medicine to remove gram-positive bacteria from the bladder. A diet that excludes salt from the diet plays a significant role in treatment. It is imperative to drink more clean water to flush out the bacterial flora from the urethra, when urine with a putrid odor and greenish-yellow mucus begins to pass, and the proliferation of bacteria becomes uncontrollable.
When a bacterial infection occurs and the temperature rises, it is impossible to do without taking penicillin antibiotics, and for pregnant women while carrying a baby - more gentle means, for example, Furagin, Nitrofuran, also to normalize the microflora in the digestive tract - dietary supplements: Bifidumobacterin, Linex, bio-yogurt .
It is important to maintain a healthy diet in order to correct the level of E. coli in the urine. In severe cases of the inflammatory process, patients are advised to take a urine test for bacterial culture again and undergo hospital treatment.
Often, women are diagnosed with pyelonephritis or cystitis when the stick, when it enters the urinary tract, becomes firmly attached to the walls. Correct collection of urine for its analysis is of considerable importance, since incorrect collection can result in completely different results and, accordingly, a different diagnosis.
Symptoms of manifestation
Frequent manifestations of inflammatory processes that occur due to the presence of pathogenic microflora in adults are characterized by the following types of diseases:
- Cystitis
- colpitis
- pyelonephritis
- urethritis
- prostatitis
When colpitis occurs, the following manifestations are typical: pain during sexual intercourse, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, discomfort during urination.
With cystitis, discomfort and frequent urge to urinate occur, and blood may be present in small portions of urine.
Pyelonephritis is manifested by pain in the lumbar back, characterized by a pulling nature and discomfort when urinating
Urethritis in the male and female half of the population has practically no pronounced symptoms - burning and itching in the urethral canal, the skin around it may be hyperemic.
Prostatitis is typical only for men, and is manifested by pain in the prostate gland, as well as sexual dysfunction.
Why is it dangerous?
Escherichia coli in the bladder leads to the development of an inflammatory process - cystitis. The disease is accompanied by pain when urinating and frequent urge to urinate, burning, itching. The bacterium is able to attach to the mucous membranes, so the inflammation does not go away on its own. Sometimes the symptoms of the acute phase disappear after 3-5 days without outside intervention. This occurs when the pathology becomes chronic.
The next stage is accompanied by the introduction of the pathogen into the mucous membranes. Blood clots appear in urine. This indicates that cystitis has acquired a hemorrhagic form. In such cases, hospitalization may be necessary. If the patient is not helped, the walls of the bladder will begin to die and the cavity will fill with purulent exudate. As a result, a rupture will occur, which will lead to the progression of peritonitis. This can cause death.
In the absence of therapy, microorganisms cause infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system: pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), urethritis (damage to the urethra), etc.
Live healthy! Cystitis. Inflammation of the bladder.(04/13/2017)
Escherichia coli
For women
In women, bacteria can enter the vagina and reproductive organs. This is fraught with the development of adnexitis and endometritis. Complications that can cause Escherichia include infertility. Pregnant women need to be especially careful, as pathogens can multiply rapidly due to hormonal fluctuations. The infection weakens the body and can cause abnormalities in the development of the fetus. It is also possible for a child to become infected when passing through the birth canal.
In women, bacteria can enter the vagina and reproductive organs.
For men
In men, the pathogen most often penetrates the reproductive system. Escherichia can provoke the development of inflammation of the prostate gland, testicles and appendages. Often infection leads to prostatitis.
For children
Since the immune system in children is not fully formed, the mucous walls are less likely to destroy the pathogen. Diagnosis and treatment are complicated by the lack of complaints. In childhood, inflammation occurs more rapidly, but is also suppressed more quickly. It is important to consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease to prevent complications from developing.
It is important to consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease to prevent complications from developing.
Escherichia coli in the bladder causes a disease called bacteriuria. This is the most common cause of cystitis in patients of all ages.
For women
Bacteriuria in women often develops against the background of bacterial vaginosis, an inflammatory process of the vagina. The urethra is short and wide; if the rules of intimate hygiene are violated, Escherichia from the anus fall onto the surface of the vulva, and then rise into the bladder.
Bacteriuria in women often develops against the background of bacterial vaginosis, an inflammatory process of the vagina; the symptoms of the disease resemble cystitis.
Symptoms of the disease resemble cystitis: frequent urination accompanied by pain, the presence of pus and blood in the urine, increased temperature. With chronic bacteriuria in women, the functioning of the bladder is impaired, the risk of developing incontinence increases, and chronic pyelonephritis occurs, which reduces the ability to bear and give birth to a healthy child.
For men
Bacteriuria in men is often asymptomatic. Exacerbations occur with a pronounced decrease in immunity. The disease is dangerous for the elderly, those with diabetes mellitus and upcoming operations on the urinary system.
Bacteriuria in men is often asymptomatic, exacerbations occur with a pronounced decrease in immunity, the acute process causes the same symptoms as cystitis.
The acute process causes the same symptoms as cystitis. With frequent relapses, the infection spreads throughout the body, causing inflammation of the kidneys and prostate. When Escherichia penetrates the prostate tissue, reproductive functions are disrupted.
For children
The introduction of Escherichia into the bladder in children rarely occurs without severe symptoms. Signs of cystitis appear - pain, burning when urinating, blood spots and white purulent flakes in the urine. Children have accelerated metabolic processes, due to which the infection spreads to the kidneys and can cause inflammatory processes in the body - sepsis, meningoencephalic syndrome.
With Escherichia in the bladder in children, signs of cystitis appear - pain, burning when urinating, blood spots and white purulent flakes in the urine.
Even if the symptoms are erased, the children’s behavior changes. They are often capricious and irritated. Insomnia develops, appetite decreases, and itching occurs in the genitals. In boys, the head of the penis turns red, in girls, the mucous membrane of the vulva turns red.
Escherichia coli
Bacteria usually enter the human body in a variety of ways. This is either lack of personal hygiene, frequent wearing of thongs, poor diet, as well as the bad habit of having to endure the urge to go to the toilet.
Based on the name of this virus, we can conclude that E. coli affects the human intestines. It is responsible for the normal intestinal microflora, participates in the process of food digestion, and produces vitamin K.
The stick prevents the development of various bacteria harmful to the human body. The bacterium is constantly present in the intestinal flora, it is harmless and brings some benefits. E. coli inhibits the proliferation of harmful microorganisms and synthesizes vitamins.
However, it is very bad if it is found in a person’s urine during testing. When intestinal bacteria enter the urinary environment, they lead to inflammation. It is also dangerous because it is not excreted in the urine. The bacterium moves deeper into the body and negatively affects the human immune system. The patient becomes open to dangerous illnesses. E. coli is joined by other microbes and infectious agents, which then provokes a whole range of diseases that require urgent treatment.
If a person is healthy, his internal organs are normal, E. coli may not linger in the bladder mucosa. But with any deviations, its negative effect begins, ending in inflammation, bacterial cystitis.
The danger of wands for women
Having penetrated into the lower parts of the woman’s genitourinary system (vagina, urethra), pathogenic flora causes colpitis and urethritis. If the patient ignores the symptoms for a long time and does not see a doctor, then the infection not only takes root in the above organs, but also begins to rise higher.
In this case, the bladder (cystitis), uterus (endometritis), appendages (adnexitis) and kidneys (pyelonephritis) are affected.
Pathologies caused by E. coli in women last a long time, often become chronic and are difficult to treat. Often the process has a hidden course, that is, the patient feels normal, but inflammation is present in the body. This pathology is often aggravated by hypothermia, colds and even stress.
E. coli and cystitis, as a consequence, are a particular risk for females. As the pathology progresses, patients may experience colpitis. This infectious and inflammatory disease affects the mucous membranes of the vagina. Without treatment, it leads to serious complications, including infertility.
This type of bacteria also provokes the development of urethritis. The disease is caused by inflammation of the urethra.
Ignoring the main symptoms often causes the development of pyelonephritis. In women, the disease lasts for a long time. There is a risk of developing a chronic form.
There are cases when the disease does not manifest itself in any way, so there is no effect on the general condition and well-being of the patient. Most often, symptoms can be felt under the influence of hypothermia, stressful situations or a cold.
Reasons for the penetration of bacteria into the urinary organs
There are many factors that contribute to the attachment of bacteria to the wall of the bladder. One of them, the most common, is insufficient perineal hygiene. Once you wash yourself poorly, the disease can manifest itself.
E. coli also appears in the bladder:
- Due to problems with immune defense;
- For intestinal infection;
- For other diseases of the urinary system - pyelonephritis, prostatitis, urolithiasis;
- When the natural acidic reaction of urine changes;
- Due to inflammatory vaginal processes, for example, with colpitis.
Even pregnancy can sometimes cause cystitis.
Some hormonal changes, the uterus pressing on the pelvic organs, difficulties in normal hygiene of the genital organs in the later stages - all this can contribute to cystitis, which develops due to E. coli in the organ.
Symptoms of bacterial cystitis
At first, if a person has a strong immune system, then E. coli may not make itself felt. When symptoms do begin to appear, they are so severe that the person immediately seeks medical help. Thanks to this, it is possible to diagnose bacterial cystitis in a timely manner and promptly begin its therapy.
Bacterial cystitis, caused by E. coli, manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- frequent urination, gradual decrease in the amount of urine;
- feeling of a full bladder;
- painful sensations in the abdomen and groin;
- the need to make an effort to start the process of urination;
- burning, pain and stinging in the genitals during bowel movements;
- cloudy, concentrated urine mixed with blood and pus;
- strong unpleasant odor of urine;
- weakness, general malaise;
- signs of intoxication.
Such a complex of symptoms cannot go unnoticed; a person almost immediately seeks medical help. Particular attention should be paid to increased body temperature. If the temperature is high, this may indicate kidney inflammation, which requires immediate treatment.
The first step is to remove all pathogenic microorganisms from the bladder. For this purpose, the doctor prescribes an antibiotic, taking into account the test results and the general condition of the patient. Acute cystitis is treated with antibacterial agents for 3-5 days, and chronic cystitis – up to 10 days.
Self-treatment of bacterial cystitis with antibiotics is unlikely to bring positive results. Even if you manage to get rid of the symptoms, the root cause will not go away, as a result of which the disease recurs after some time.
E. coli is resistant to many antibiotics, so only the attending physician can select a truly effective drug. The most effective antibiotic to which E. coli has no resistance is Monural.
To get rid of E. coli in the bladder and cystitis, the doctor may prescribe medications:
- nitrofurans;
- probiotics;
- bifidobacteria;
- cephalosparins;
- diuretics;
- uroseptics;
- antispasmodics and painkillers;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- medications for tissue hypoxia;
- immunostimulants, vitamins.
Drug therapy for bacterial cystitis may include herbal remedies and folk remedies, but they only act as additional treatment, along with antibiotics.
Types of disease
The risk of getting an infection is highest before the onset of menstruation or immediately after it, when changing partners, when leading a promiscuous sex life, due to refusal to use barrier contraception.
Infectious cystitis
This species has different routes of infection:
- Hematogenous. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the blood as a result of cuts, transfusions, that is, directly into the human blood.
- Contact. Failure to comply with sanitation measures, use of dirty medical devices.
- Descending. The infection descends into the bladder from other organs and takes hold in the mucous membrane of the bladder.
- Rising. Viruses enter the urethra through infected objects and things.
- Lymphogenic. The infection passes through the lymph.
Non-infectious cystitis
This type of disease has another name - honeymoon cystitis. The disease occurs at the beginning of sexual relations. This is explained by changes in the woman’s body systems, especially hormonal ones. Immune activity decreases at this time. Breaking the hymen exposes the tissues around it to irritation from clotted blood proteins. Irritation activates the occurrence of cystitis.
It is possible to diagnose cystitis as a complication of another disease.
Transmission routes
E. coli bacteria are often spread through the oral or fecal route. Together with feces, the stick gets into the soil and water, and from there onto plants, including agricultural ones. Infection occurs when drinking contaminated water, unwashed vegetables and fruits. Accompanied by stomach pain, diarrhea, vomiting.
Another reason for the penetration of E. coli into the body can be unwashed hands after using the toilet or contact with soil. Poor quality products, dysbacteriosis, long-term use of medications (for example, antibiotics) can provoke an increase in the number of rod-shaped microorganisms in the intestine, from where they enter the bladder.
Transmission of infection can occur through contact and household contact, although this method is quite rare. Happens in preschool and educational institutions, hospitals, families through shared dishes, medical instruments, pots, etc.
Penetrating into the urethra, the intestinal bacterium attaches quite firmly to the walls. It can be washed away by a stream of urine, which has a slight bactericidal effect. If favorable conditions exist, the stick takes root in the mucous membrane, after which it penetrates the bladder in an ascending manner. Most often this happens for the following reasons:
- pregnancy, during which inevitable compression of the bladder occurs;
- urolithiasis, causing urinary disturbances and stagnation of urine;
- prolonged holding, when a person is unable to urinate in time;
- promiscuous sex;
- hypothermia;
- disruption of the natural protection of the genitourinary system due to infectious diseases;
- diabetes mellitus, kidney pathologies that cause deviations in the acid-base balance and chemical composition of urine;
- treatment of oncology with radiation and chemotherapy, which negatively affects the urethral mucosa;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene requirements.
From there, the bacteria enters the kidneys, which will lead to serious illness.
In men
The penetration of intestinal bacteria from the male penis into the urethra causes inflammation. It proceeds rather sluggishly, becomes chronic, and is difficult to treat.
Most often, infection occurs during sexual intercourse with a partner whose vagina is infected with intestinal bacteria. Another reason is unprotected anal sex.
The peculiarity of the male body is such that a pathogenic microbe from the urethra usually penetrates not into the urinary organs, but into the genitals. Therefore, they rarely suffer from pyelonephritis and cystitis, unlike the fair sex. In guys, E. coli causes orchitis and epididymitis. A carrier of the infection can infect a sexual partner with the bacteria.
Among women
Infection of the female genitourinary organs is not uncommon. As a result, chronic diseases arise that are severe and difficult to treat. Rod-shaped bacteria enter the genitourinary organs from feces, where they are found in quite a large number. This happens for the following reasons:
- Incorrect washing from the anus forward to the labia. Bacteria are transferred by hand to the external genitalia and then inside.
- Selection of tight underwear, thongs. Mini panties allow fecal matter left after bowel movements to enter the vaginal area.
- Rare water procedures. In women who do not maintain personal hygiene, fecal residues accumulate on their skin and underwear, which will inevitably lead to infection of the genitourinary system.
- Unprotected sex with a man suffering from orchitis, chronic prostatitis, epididymitis, caused by intestinal bacteria. In this situation, the partner can become infected through sperm.
- Anal sex alternating with vaginal sex. When unprotected penetration into the rectum, the bacterium enters the vagina through sexual toys or the penis.
During pregnancy
The detection of a pregnant bacillus in urine tests or a smear indicates that this microorganism is located in the woman’s genitourinary organs. If laboratory tests did not show anything before, it means that the expectant mother’s defense system fought it well. Pregnancy itself cannot provoke the appearance of bacteria, therefore, the woman was already its carrier. The immune system stopped coping, and E. coli began to actively reproduce.
The risk of inflammation increases. To prevent the development of cystitis or pyelonephritis, the doctor recommends taking a course of antibiotics. The presence of pathogenic microflora in the vagina of a pregnant woman is undesirable. This can lead to colpitis, causing premature birth and polyhydramnios. There is a possibility of infection of the baby during childbirth or through amniotic fluid.
In children
Infection with E. coli can occur during pregnancy and childbirth from the mother. Certain physiological characteristics of children lead to the detection of bacteria in the urinary system. For example, vulvitis in girls is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia. Swelling allows fecal debris to enter the urethral area.
How to get rid of E. coli in the bladder
If a small concentration of E. coli is present in the bladder without causing inflammation, the person most likely will not know about it. In most cases, we are talking about how to cure cystitis caused by the Escherichia Coli bacterium.
Treatment for cystitis, caused by E. coli growing in the bladder, usually involves taking antibiotics. It should be noted that E. coli easily forms new strains, including those resistant to previously successfully used antibiotics. Usually, the doctor prescribes a broad-spectrum antibiotic empirically, but if the treatment does not give the expected effect, it should be adjusted taking into account the antibiogram - a bacterial urine culture test to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to various antibiotics. Currently, Monural (Fosfomycin), fluoroquinolones (norfloxacin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin), aminoglycosides (gentamicin), nitrofuran derivatives (nifuratel, furazolidone), penicillins (amoxicillin) are considered relevant. All antibiotics have side effects and contraindications, so the choice of antibiotic and its dosage is determined by your doctor. Antibiotics are prescribed with extreme caution to children, pregnant women and breastfeeding.
Acute cystitis can usually be cured with a short course of antibiotics. Chronic cystitis requires long-term use of antibiotics, which in this case affect not only the E. coli in the bladder, but also the E. coli that lives in the lower intestines and is a representative of the normal intestinal microflora. To avoid intestinal dysbiosis, probiotics are prescribed: Hilak Forte, Bificol, Colibacterin, containing specially selected strains of E.Coli.
For cystitis, it is important to drink a lot - compotes, fruit drinks, decoctions of medicinal herbs (bearberry, lingonberry leaf, rose hips, St. John's wort). During illness, salty, spicy foods, smoked foods should be excluded from the diet, and alcohol should not be consumed.
How the biomaterial is collected
E. coli in urine (causes and treatment require careful medical examination) is rarely present in the human body without causing characteristic symptoms. Patients often complain about existing disorders and the appearance of signs of pathological processes.
In this situation, the doctor prescribes diagnostic measures to establish an accurate diagnosis:
| Name | Description |
| General urine analysis | In laboratory conditions, the taken material is examined for the pathogen and its variety.
|
| Bacteriological culture | The causative agents of the disease are isolated from the collected urine and placed in favorable conditions for development and reproduction. The results make it possible to most accurately determine the causative agents of pathological processes and their sensitivity to certain antibacterial drugs. |
| Stool analysis (coprogram) | The results will help determine the type of bacteria that causes E. coli. |
Diagnostics requires careful preparation so that the results are as accurate as possible and the doctor can make a diagnosis. Based on the information received, medications are selected. Incorrect therapy will have serious consequences.
Diagnostics
In order to diagnose pathogenic microflora, it is necessary to pass appropriate tests of urine and feces. As a result of laboratory diagnostics, it is possible to identify the critical presence of pathological Escherichia, which provoked the inflammatory process. The presence of pathogenic microorganisms is a direct indication for therapy, including the use of antibiotics.
It is important to remember that in order to determine subsequent treatment and prescribe the correct antibiotics, you need to culture laboratory material and find out which bacteria are infesting the urinary and reproductive systems.
Sources used:
- https://no-prosprob.ru/kak-ubit-kishechnuyu-palochku-v-mochevom-puzyre/
- https://kupiviagru.info/cistit/kishechnaya-palochka-v-mochevom-puzyre.html
- https://pochkam.ru/mochevoj-puzyr-i-mocheispuskanie/kishechnaya-palochka-v-mochevom-puzyre-lechenie.html
- https://motiv-tarif.ru/kishechnaya-infektsiya-mochevom-puzyre/
- https://wmedik.ru/zabolevaniya/urologiya/kishechnaya-palochka-v-mochevom-puzyre.html
Symptoms of the disease
In most cases, the main symptoms of the disease are similar to other infectious lesions of the bladder. Often, against the background of general clinical manifestations, patients experience nausea, vomiting, weakness, fatigue or fever.
Among the most common symptoms are:
- Pain of varying degrees of intensity and nature. Most often this is a burning sensation or itching in the urethral area.
- Frequent urge to urinate. They often make themselves known at night.
- A specific, extremely unpleasant odor of excreted urine.
- The presence of various impurities in the urine, for example, flakes. It also often becomes cloudy.
- Difficulty urinating (requires some effort from the patient).
Elevated body temperature usually occurs when patients ignore primary clinical signs. It also manifests itself due to a large number of microorganisms that, under the influence of various factors, have entered the genitourinary system. As soon as symptoms become apparent, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination. After all, these signs can often indicate the development of other pathological processes.
Medicines for cystitis
Antibiotics. The following drugs are usually used to suppress E. coli: cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, aminopenicillins, aminoglycosides. The doctor will select a specific drug based on laboratory data, as well as the characteristics and predispositions of the patient himself. Acute cystitis is treated for 3-5 days; chronic cystitis is treated for about 10 days.
Probiotics. When treating with antibiotics, probiotics are always prescribed. Because antibacterial drugs affect not only the pathogenic flora, but also the normal microflora of the intestines and vagina. Therefore, taking probiotics for women is absolutely necessary in order to cure cystitis without getting candidiasis.
Immunomodulators. Also, in the treatment of cystitis, drugs that increase the body’s natural immunity are widely used.
Antispasmodics. To relieve pain and spasms, antispasmodics are prescribed; anti-inflammatory drugs also reduce pain and help eliminate infection. Also, if necessary, vasodilators are prescribed to improve blood flow and capillary permeability of the bladder.
Diet. During treatment, it is especially important to exclude sour, spicy, salty, too spicy and fried foods from the diet. Preference should be given to fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as steamed or stewed foods. In addition, it is important to receive a balanced diet; in winter, you can supplement it with vitamins. Fruit drinks with a sour taste, rosehip decoction, tea with lemon, herbal decoctions, etc. are very useful. Remember to drink enough water. This will speed up the washout of painful microflora, and therefore recovery in general.
Chronic cystitis and its treatment
Chronic inflammation of the bladder manifests itself as follows:
- the appearance of dysuria. When the mucous layer of the bladder is irritated and even a small amount of urine in the bladder leads to frequent, minor urination;
- feverish condition. Cystitis worsens and the temperature rises;
- frequent and painful urination. The part of the mucous membrane responsible for the urge to empty, located in the neck of the bladder, with cystitis is constantly irritated, and urination will be frequent and unbearably painful;
- The mucous layer of the bladder becomes thinner and ulcerated and becomes swollen. This makes the lower third of the abdomen very painful;
- sometimes nausea and vomiting;
- urine loses transparency, turbidity and heterogeneity appear in it;
- urine becomes mixed with blood. Damage to the mucosa threatens microhematuria (chronic hemorrhagic inflammation is accompanied by a large amount of blood).
Chronic inflammation is always accompanied by periods of remission and relapses.
We are looking at a chronic infectious process caused by Escherichia coli.
Although cystitis may also have a non-infectious course, or an infection other than E. coli.
The above symptoms of a chronic process are not specific.
Often caused by an infection in the urethral canal or vagina, or another pathology.
For example, a malignant tumor of the bladder, diverticulosis of the urethral canal or stones in the urethra.
The main factors contributing to the appearance of chronic inflammation of the bladder in women are:
- very tight underwear made of synthetic materials;
- failure to maintain intimate hygiene;
- active sexual activities;
- frequent hypothermia;
- lack of routine in visiting a gynecologist;
- irregular bowel movements.
E. coli enters the bladder in two ways: ascending or descending.
In the first case, the infectious pathogen enters the bladder through the urethra.
In the second, the upper parts of the MPS are affected first.
And then the inflammation turns into a bubble.
Factors provoking relapses of the inflammatory process in the bladder, chronic:
- foods that irritate the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system;
- irritating contraceptives (we are talking about vaginal contraceptives);
- birth control pills;
- intensive antibiotic therapy;
- oncopathology in the bladder.
The diagnosis of chronic inflammatory process in the bladder is made:
- after a thorough history of the disease;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- urine culture for microflora;
- STI testing;
- Ultrasound of renal and bladder tissue;
- cystoscopy.
Diagnostics are carried out in order to accurately establish that the cause of cystitis is E. coli and to draw up a plan and scope of treatment measures.
Treatment usually takes place within a week, to a maximum of ten days.
The therapeutic effect for this pathology consists of taking medications with general and local effects.
Treatment is accompanied by a special diet and adherence to a special drinking regime.
Treatment consists of taking antibiotics, uroseptics and immunovaccination.
You need to listen to certain tips and recommendations;
- drink plenty of unsweetened herbal teas and plain water;
- eat foods containing a lot of fiber (legumes, oatmeal, vegetables);
- remove any potential food allergens from your diet;
- saturate your body with food rich in antioxidants (colored fruits and vegetables);
- sharply limit your consumption of pasta and white bread products, as well as sweets;
- It is better not to eat red meat at all, but to consume white lean meat and fish;
- consuming olive, pumpkin, flaxseed or coconut oil is beneficial;
- avoid foods with trans fats (such as cookies and margarine);
- less stimulating products (such as coffee and alcoholic drinks and tobacco products);
- exercise for at least half an hour, five times a week;
- take vitamin-rich complex preparations with microelements and amino acids.
Also, uncomplicated chronic cystitis is well treated with traditional medicine.
They have a pronounced antifungal, antispasmodic and analgesic effect.
It is useful to add medicinal herbs to food and make herbal teas from them.
They also use herbal preparations.
Application both general and local (healing baths).
Therapy with medicinal herbs is necessary daily, without interruption.
They are treated with alfalfa, bearberry, burdock, butch, celery, dandelion, chamomile, cranberry, plantain, yarrow, echinacea and other medicinal herbs.
The main thing is not to delay in determining the cause of cystitis and timely and correct treatment.
General information
The approximate weight of all bacteria that live in the human body is two kilograms. E. coli forms within the first few days after birth. Normally, its level is 104–1010 CFU per milliliter of contents. It brings undoubted benefits, taking part in the formation of microflora, the process of digesting food and the synthesis of essential vitamins.
The number of bacteria in the body is controlled by various mechanisms. In cases where their basic functions are impaired, a person may develop various types of diseases. For example, diarrhea, severe meningitis, coli-septicemia.
During the examination of the patient, E. coli may be detected in an environment that is unusual for it - in the area of the genitourinary organs. Often such changes are caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules, and may occur against the background of decreased immunity or due to the influence of some other factors.
If E. coli lives in the organs of the genitourinary system in females, then most often it becomes the cause of the development of adnexitis, colpitis or other inflammatory diseases.
Infection is extremely dangerous during pregnancy, as it often contributes to the occurrence of intrauterine infection.
In male patients, the bacillus provokes an inflammatory process that affects the testicles or appendages, and can also cause the formation of prostatitis and urethritis.
Causes of cystitis
Urine has a bactericidal effect; it destroys all harmful microorganisms. That is why bacteria that accidentally enter the genitourinary system cannot provoke disease. They simply do not even have time to attach to the mucous membranes before they are washed away by a stream of urine. However, there are some factors that contribute to the development of inflammation.
The occurrence of bacterial cystitis is due to the following reasons:
- Decreased immunity, which can be caused by a variety of reasons - both stress and chronic diseases
- Pathological processes in the urethra, as well as in the upper urinary tract.
- Stagnation of urine, often occurring with urolithiasis or prostate pathologies.
- Regular violations of intimate hygiene rules. Very often, inflammation is caused by improper washing, as a result of which pathogenic microorganisms enter the urethra from the rectum.
- With inflammation of the prostate, accompanied by an increase in temperature.
- Changes in the bactericidal properties of urine due to kidney diseases, diabetes and other diseases.
- Reduced barrier properties of the urethra and compression of the urethra during pregnancy.
Women suffer from bacterial cystitis much more often than men, due to the structural features of the genitourinary system. In addition, the sphincter of the rectum, where pathogenic microflora is concentrated, is located much closer to the urethra in women than in men. In this case, it is much easier for E. coli to enter the urethra and cause inflammation.