Causes of diseases
If we consider the diseases separately, then in practice the most common is the advanced stage of candidiasis, in which the infection spreads to the urinary tract and reaches the bladder. As a result, cystitis develops. That is why it would be more logical to consider the causes of thrush or cystitis separately.
Thrush
Candidiasis occurs due to the external introduction of the fungus onto the mucous membrane or its appearance inside the body due to disorders of a different nature. The causes of thrush are combined into the following list:
- weakening of the immune system of any nature;
- hormonal imbalances associated with pregnancy, menopause and any other factors;
- an unbalanced diet, for example, eating high-carbohydrate foods can trigger the development of thrush;
- taking medications that affect microflora, including antibiotics;
- dysbiosis of various etiologies, developing in the intestines and genitourinary system;
- infection through a partner;
- injuries of the urinary tract, birth canal;
- insufficient hygiene, including during menstruation.
There are also secondary reasons for the development of thrush associated with wearing synthetic underwear, using inappropriate cosmetics for intimate hygiene, and so on.
In some cases, candidiasis is diagnosed when the infection “drops” from the bladder, during colds or hypothermia.
Cystitis
Such provoking factors include the development of candidiasis, ureaplasmosis and other gynecological pathologies that spread to the urinary system.
In addition to the spread of bacteria from the genitals, cystitis may appear due to the following reasons:
- hypothermia, colds of the bladder;
- decreased immunity;
- urolithiasis or release of sand, advancement of stones;
- hormonal disorders, including changes during pregnancy;
- insufficient hygiene.
The causes of thrush and cystitis are largely similar, so the diseases themselves sometimes occur simultaneously, as a result of each other.
Thrush and cystitis are characterized by certain symptoms, but in the case of simultaneous pathologies, the symptoms are combined. Such conditions cause particular discomfort to the patient and are dangerous due to the occurrence of subsequent complications for reproductive and genitourinary function.
The following symptoms are typical for signs of thrush:
- Itching, burning of the genitals. The sensations may temporarily disappear after sexual intercourse, urination, or reappear for no apparent reason.
- The discharge is of a cheesy type, light milky, white in color.
- Inflammation, enlargement of the genital organs.
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during sexual intercourse, accompanied by a burning sensation.
The longer the fungus progresses on the mucous membrane, the more intense the symptoms appear, the lesions grow and spread to the mucous membranes of other organs.
Signs of cystitis are mainly determined by problems with urination. Typical symptoms are:
- Pain when emptying the bladder. It is especially felt at the beginning and at the end of the process.
- Burning, itching.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Frequent urge to urinate, but little or no urine output.
- The urine becomes cloudy and may contain blood clots, mucus, or pus.
- Temperature increase. With the initial development of pathology up to 37.5, with acute inflammation higher values may be recorded.
The symptoms of cystitis and thrush have a certain similarity, but an accurate diagnosis can only be established after special studies, including a smear on the microflora.
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene;
- reducing the risk of hypothermia;
- timely treatment of infectious diseases.
If there are changes in natural discharge or concerns when urinating, you should seek advice and take a smear to check the flora. These simple steps will help prevent the development of complications in gynecology and urology.
Treatment during pregnancy and lactation, in children
During pregnancy, the question of whether thrush can provoke cystitis is especially acute. On the one hand, most drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy, on the other hand, an untreated bladder infection is even more dangerous and can lead to the development of diseases in the fetus.
The advisability of prescribing a particular drug during pregnancy is determined by the ratio of the expected benefit for the patient and harm to the unborn child. The key role in this situation is played by the woman’s condition and well-being. In some cases, if severe complications of cystitis have developed, and the treatment has caused serious harm to the health of the pregnant woman, the question of terminating the pregnancy may be raised.
During breastfeeding, the situation is somewhat simpler - it is necessary to temporarily interrupt lactation, cure diseases of the female genital area, then restore milk production if the woman wants to continue breastfeeding.
To avoid such problems, it is recommended to undergo examination and treatment for microflora that causes bladder infections while planning pregnancy.
Girls before puberty rarely suffer from thrush, cystitis, or their combination. But if a teenager is diagnosed with these diseases, you will have to spend a lot of time to find a drug that is suitable for the child.
Prevention
Relapses and spread of candidiasis in general (no matter where) are a sign of immunodeficiency - temporary and local or general. To avoid them, you should not allow it to decrease - due to frequent colds, physical and emotional stress, exposure to several harmful factors at the same time (city smog, smoking, alcohol abuse, inactivity, excessive or insufficient hygiene, tight synthetic underwear)
The condition of the urinary tract is well affected by not having the habit of tolerating the urge, wearing warm high-waisted trousers or long jackets in winter, and drinking a sufficient amount of fluid (1.5-2 liters, but you should drink more only in hot weather).
Diagnostics - modern methods
It is impossible to determine a gynecological or urological disease by symptoms alone; special tests and studies must be carried out to identify cystitis. If, during examination on the chair, there are external signs of the development of thrush and cystitis, and the patient’s complaints complement this assumption, then a set of diagnostic measures is prescribed. They include the following procedures:
- Blood and urine analysis. Research of biomaterials and comparison of indicators with standards provides information about ongoing processes in the body. For example, an excess of leukocytes may indicate the development of inflammation and so on.
- Biochemical blood tests. The analysis helps determine the level of functioning of all organs and the structure of metabolic reactions. The indicators of glucose, cholesterol, urea, phospholipids and other compounds are compared.
- Three-glass urine sample. Prescribed for elevated values in a general urine test, which indicate inflammation. The three-glass method helps to determine in which part (kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra) pathological processes develop.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. It is carried out to identify the exact number of formed elements for an accurate diagnosis of inflammation.
- Study of secretions. An analysis or smear is taken at the first visit to the gynecologist; it is necessary to study the biocenosis or state of the microflora in a woman. It is one of the informative methods for detecting pathogenic organisms.
- Selection of the optimal antimicrobial agent or determination of the sensitivity of the flora to various types of antibiotics and antifungal components;
- Colposcopy or visual examination of the vagina, cervix and uterus itself, as well as adjacent tissues and organs for pathological lesions. It is carried out using a special device - a colposcope.
- Cystoscopy. Examination of the bladder and ureter using an invasive method using a special compact device.
A set of diagnostic measures allows you to determine the condition of the genitourinary system, identify the type of bacteria that provoked inflammation, find out the structural changes in damaged tissues, and obtain other information necessary to select the optimal type of treatment. In case of simultaneous detection of cystitis and thrush, the regimen is adjusted for each disease.
Can there be complications?
Against the background of incompletely cured vaginal candidiasis and cystitis, severe complications may develop , spreading to the pelvic organs and urinary tract. The kidneys are most often affected. Often, when diagnosed, women are diagnosed with cysts in the kidneys.
The infection that remains in the body destroys the walls of the bladder and weakens the blood vessels. Such changes impair the process of urination. In severe cases, surgical removal of the bladder becomes inevitable. Cystitis often recurs, becomes chronic and can cause female infertility.
Simultaneous treatment of candidiasis and cystitis
Specialists select a treatment that will not only eliminate the manifestations of both diseases, but also the main cause of their occurrence and development. The patient follows the doctor's orders at home, sometimes while on bed rest. First of all, medications are used.
- Antibacterial drugs (Amoxicillin, Monural, Nitroxoline).
- Uroseptic medications are not antibiotics, effective in the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (Furamag, Furagin).
- Antifungal drugs (Clotrimazole, Izol, Canesten, Miconazole).
- Vaginal (antimycotic) suppositories (Pimafucin, Diflucan, Livarol, Chlorhexidine).
Cystitis caused by bacteria is successfully treated with a herbal preparation with diuretic and antispasmodic effects - Urolesan. For external use, antifungal ointments are used - Diflucan, Decamine, Clotrimazole. The course of treatment is at least 2 weeks, medications are prescribed individually
It is important to complete the treatment and follow all the doctor’s instructions. Candidiasis may affect fertility
Traditional medicine
Your doctor will advise you on how to treat thrush and cystitis using traditional recipes. He will help you choose the best products with effective action. These could be the following methods:
- They use the antiseptic properties of garlic that affect candida. Prepare the juice, dip a sterile cotton or gauze swab into it, place it in the vagina overnight, and remove it in the morning. Use for 10 days, then as recommended by a doctor. If there is a strong burning sensation, remove the tampon and stop using it.
- St. John's wort decoction treats thrush. 2 tablespoons of dried herbs are poured into 2 liters of cold water, boiled for 20 minutes, filtered. Use for douching - no more than 2 times a day, 3 days in a row.
- The anti-inflammatory effect of chamomile helps treat cystitis and thrush. 20 g of herb are poured with boiling water (500 ml), left for 1 hour. Used for douching in the same way as St. John's wort.
- An infusion of dried calendula flowers has an antimicrobial effect. It is prepared from 20 g of raw materials, poured a glass of boiling water, and kept over low heat for 15 minutes. Infuse for an hour, filter, use for douching after sleep and at night, 14 days.
- Dill helps cure cystitis. The seeds of the plant are ground, 10 g of this flour is poured into a glass of boiling water (200 ml), and left for 1 hour. Take 200 ml of strained infusion once a day in the morning before meals. Course – 1 week.
- Baking soda relieves itching and reduces vaginal discharge. Dilute 10 g of soda in 200 ml of boiled water. Use for washing - 2 times a day, 2 weeks.
- Folk remedies cannot cure diseases; they are effective in combination with medications.
Disease Prevention
During treatment, the doctor recommends adjusting your diet:
- remove salty, fatty, spicy foods from the diet;
- limit sweets, alcoholic drinks, cheese curds;
- increase the amount of sour dairy products, vegetables, herbs.
Strict adherence to intimate hygiene standards is necessary, the use of clean underwear made from natural fabrics, not very tight
Timely treatment of foci of infection in the body is important - this will prevent the development of thrush and cystitis
When prescribing antibiotics, be sure to take probiotics to prevent dysbiosis (Yoghurt, Linex). Douching should not be abused, as this can cause disruption of the microflora of the female genital organs. You need to undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist and urologist at least once a year.
An active healthy lifestyle and exercise can also help prevent the disease. Taking vitamin complexes as prescribed by your doctor and preventing stressful situations and nervous tension will strengthen your immune system. Following these simple preventive measures will help to effectively prevent the development of cystitis and thrush and maintain health.
Effective therapy for pathology
Effective treatment of many urological and gynecological diseases includes general recommendations that promote successful recovery. These include proper, regular intimate hygiene, including the menstrual period, a balanced diet that excludes harmful high-calorie foods, protected sex with a new partner and other well-known rules that are not always followed by women.
Treatment for concurrent thrush and cystitis may include the following:
- Antifungal drugs, the purpose of which is to destroy the development of Candida fungi.
- Probiotics. Auxiliary products for restoring natural microflora, they contain beneficial bacteria and have a positive effect on the condition of the mucous membranes.
- Uroseptics. They can be of medicinal origin or herbal. The purpose of taking them is to block the spread of infection in the urinary system; they have an antibacterial effect and are excreted along with toxins in the urine.
- Immunomodulators. Substances that help improve the functioning of the immune system and the general protective functions of the body.
- Vitamins. The use of vitamins B and E is considered especially valuable. Complexes of all essential vitamins will be useful.
- Suppositories for thrush and cystitis. Local treatment is considered one of the most effective, so the use of vaginal suppositories is recommended. They may contain antibacterial components, antifungal, anti-inflammatory compounds.
The patient is prescribed complex therapy; the list of drugs may vary depending on the stage of the disease, the causes of its appearance, and the general condition of the body.
Treatment methods
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination. The patient undergoes a smear test for flora, PCR to determine sexually transmitted infections, and bacterial culture. To detect cystitis, it is necessary to undergo urine tests, including culture.
Usually, when cystitis and thrush are combined, the fungal infection will initially be eliminated. This is due to the fact that cystitis should be treated with antibacterial drugs, which can aggravate the course of thrush. Moreover, cystitis often occurs against the background of thrush.
Gynecologists use the following treatment algorithm.
- Elimination of the cause of candidal inflammation.
- Use of antifungal agents.
- After suppressing the signs of thrush, an antibacterial drug is prescribed.
Medication
There are many medications available to treat thrush. Medications can be used in the form of:
- suppositories or suppositories;
- vaginal tablets;
- creams, ointments, gels;
- solutions;
- tablets and capsules.
All medications are conventionally presented as agents of local or systemic action. For thrush, topical medications are often used. This method of treatment allows you to inject the medicine directly into the affected area. Tablet drugs are usually used in combination with local agents to treat chronic conditions.
Before starting treatment you must:
- maintain sexual rest;
- Healthy food;
- exclude alcohol.
Treatment includes exclusively medications prescribed by a doctor. If signs of pathology disappear, the course of treatment should be continued at the dosage recommended by the doctor. Pregnant women are prescribed drugs for topical use in the second and third trimesters.
Gynecologists prescribe medications that are represented by the following groups:
- triazole derivatives: Diflucan and Flucostat;
- polyene group: Nystatin and Natamycin;
- imidazole group: Candide and Clotrimazole.
In gynecological practice, agents with a combined effect are quite popular. Drugs such as Terzhinan and Polygynax are effective due to the inclusion of several antifungal components in the composition.
For the treatment of cystitis, which begins after the elimination of thrush, antibiotics are used. Doctors usually prescribe antibacterial drugs of the nitrofuran group. Antifungal medications containing an antibiotic are sometimes recommended. Combination drugs:
- Levorin;
- Natamycin;
- Pimafucin.
To relieve symptoms, it is recommended:
- compliance with bed rest;
- plenty of warm drinks;
- using a diet that excludes disease-causing foods;
- taking painkillers;
- regular genital hygiene;
- timely change of linen, which should be made from natural fabrics.
In order to prevent relapses, you should remember the need to treat your sexual partner.
Folk
Many medicinal herbs have been officially recognized by official medicine and have proven their effectiveness. Herbs have a mild effect and have a minimum of side effects
However, experts recommend using medicinal herbs with caution and only on the advice of a doctor.
As a rule, folk remedies are not used independently. They have anti-inflammatory and regenerating effects and help eliminate unpleasant symptoms. The use of exclusively folk remedies in treatment is not able to completely eliminate diseases, but only alleviate painful symptoms.
Gynecologists recommend using the following herbs:
- chamomile;
- aloe;
- calendula;
- yarrow;
- Oak bark;
- nettle.
To treat the genitals, you can use a soda solution. To prepare the solution, you need to dissolve a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water. The solution can be used once or twice a day before administering medications.
Treatment of cystitis is carried out with antibacterial drugs. However, traditional medicine can also be used to relieve symptoms. An infusion of lingonberry leaves, which should be drunk in small portions, quickly and effectively eliminates pain when urinating and reduces the number of urges.
Potatoes boiled in their jackets have antiseptic properties. The potatoes along with the peel must be mashed and used as a steam bath to warm the genitals.
Is thrush due to cystitis?
As we already know, an integral component of complex therapy for cystitis is antibiotic therapy, which leads to an imbalance of microflora. At this time, active growth of fungi and the development of thrush are observed. It should also be taken into account that in case of chronic cystitis, or often recurrent processes, long-term antibiotic therapy with repeated courses is provided, which greatly increases the risk of the possible development of thrush.
Regardless of which of the pathologies provoked the development of the other, they can occur in parallel, which the patient does not always suspect. Similar, outwardly almost indistinguishable symptoms and a sharp deterioration in condition do not always allow us to determine the root cause. It is believed that only a professional is able to accurately determine the nature of the pathology
How to independently determine whether it is cystitis or thrush, a number of characteristic distinctive signs that you should focus on will help
Therapeutic measures
Cystitis is a fairly common disease. In order for its treatment to be effective, it is necessary to determine its nature, that is, to identify the infection (bacterial, fungal) that provoked its appearance. To do this, it is necessary to conduct a diagnostic study.
Patient examination
For this purpose, if unpleasant symptoms appear, the patient should consult an experienced urologist or gynecologist. Diagnostics occurs in several stages:
- Examination of the patient. Such an examination is necessary to examine the patient’s external genitalia to identify external signs of the disease.
- Anamnesis collection. An experienced doctor will carefully review the patient's medical history to determine whether he or she has had a previous bacterial or fungal infection.
- Blood analysis. A general analysis is carried out, as well as a serological study to identify antibodies that are produced in response to the proliferation of Candida fungi.
- General urine analysis. At the same time, they donate morning urine. They study the color of urine and its smell. Under a microscope, the level of squamous epithelium, leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine is determined. An increase in their number indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. You can also detect yeast in urine DPS-1150.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). This procedure is performed when the bladder is full. This method allows you to see signs of the inflammatory process in it.
After identifying the disease and making a diagnosis, a specific course of treatment is prescribed. It is aimed at:
- destruction of fungus not only in the urinary tract, but throughout the entire body;
- elimination of accompanying symptoms;
- pain relief;
- restoration of the mucous membranes of the genitals and urinary tract.
Drug effects
As a rule, drug therapy is indicated for such a disease. It helps to effectively and quickly cope with the infection, as well as relieve a person from unpleasant symptoms. The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Systemic antifungal agents. For bacterial cystitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. But for candidiasis, such therapy is contraindicated.
In this case, the following tablets for thrush will help, which enter the general bloodstream and are able to fight infection even in the internal organs:
- Futsis;
- Ketoconazole;
- Miconazole;
- Hexicon and others.
Nystatin;
- Pimafucin.
Ketoconazole.
Veronika Andreevna, 34 years old: “My stomach began to hurt badly and strange discharge appeared from the vagina. Even the temperature rose. I got scared and went to the gynecologist. After examination and a series of tests, candidal cystitis was diagnosed. The doctor prescribed Ketoconazole tablets and Nurofen for fever. I was treated for a week, after which everything went away.”
Diagnostics and therapy
To determine what caused the disease, as well as to determine treatment measures, the doctor prescribes a number of tests, including a general blood and urine test, as well as biochemistry. An ultrasound examination and a vaginal smear are also performed.
Often taking antibiotic drugs prescribed for various diseases, including cystitis, leads to the destruction of good microorganisms along with pathogenic ones. But candida fungus is a conditionally pathogenic fungus; they multiply and lead to the development of dysbacteriosis and thrush.
What should I do? Diseases should be treated in a comprehensive manner. First, it is necessary to restore the intestinal microflora and mucous membranes. Products containing probiotics help in their health. It is especially useful to use:
- yoghurts;
- kefir;
- cheeses;
- yeast-free bakery products.
Asparagus, legumes, bananas, and oatmeal are beneficial. It is forbidden to eat sweets, yeast baked goods, spicy, fatty foods, too salty foods, marinades, and smoked foods.
Symptoms
The severity of manifestations depends on the nature of the dysfunction of the immune system. If the inflammatory process begins from the surface of the vaginal mucosa, both Candida fungi and other representatives of opportunistic flora can participate in it. Thus, both a mixed infection and true candidiasis can develop.
If bacterial vaginosis is mild, thrush can occur as a carrier state. In this case, inflammation is controlled due to a sufficient amount of lactobacilli. There is no clinical picture for candidiasis.
As a rule, candidiasis leads either to recovery or to the development of an inflammatory process. Recovery is possible only in the absence of provoking factors and an adequately functioning immune system. If the number of lactobacilli continues to decrease, recurrent thrush develops over time, which is characterized by periods of exacerbations and remissions. With prolonged progression of chronic thrush, cystitis often occurs.
Typically, exacerbations of cystitis and thrush are associated with exposure to provoking factors, for example, taking antibiotics or hypothermia. With co-infection, symptoms may vary. However, patients are usually concerned about the following manifestations:
- itching, burning in the vagina, which may intensify in the evening and at night, when walking, hygiene procedures;
- feeling of dryness and pain during sexual intercourse;
- curdled discharge with a sour odor;
- cloudy discharge that, when dried, leaves yellow spots on the laundry;
- pain, pain and burning when inflammation spreads to the urethra, that is, meaning urethritis;
- pain, frequent urination when the bladder is involved in the inflammatory process, that is, in the case of cystitis;
- swelling and redness of the vaginal mucosa;
- rash in the form of small blisters, which is accompanied by itching;
- white coating on mucous membranes that bleed when trying to remove it;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- purulent discharge from the urethra;
- frequent urge to urinate.
Signs of intoxication may also appear, which are caused by the activity of bacteria and fungi. The woman is worried about weakness, decreased performance, and low-grade fever.
Often women ignore the signs of candidiasis and cystitis, which contributes to the transition of the disease to the chronic stage. Symptomatic treatment helps to get rid of unpleasant sensations, but with each subsequent exposure to an unfavorable factor, an exacerbation of cystitis and thrush is possible.
In a chronic course, the signs of cystitis and thrush are not intense. The discharge may be cloudy and normal in appearance. A woman may be bothered by frequent, painful urination. Symptoms persist for several days and then usually decrease until the next exacerbation.
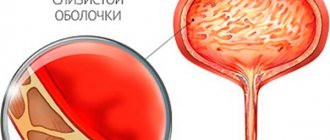
Clinical manifestations of candidal cystitis
Cystitis caused by Candida fungi is characterized by the same symptoms as regular cystitis: discomfort and burning in the perineum, painful and frequent urination in small portions, sometimes with a small admixture of blood (terminal gross hematuria). This type of cystitis does not respond well to antibiotic therapy, and sometimes the symptoms even worsen during treatment.
More details about the manifestation of thrush are described in the video:
If the patient has any of the above risk factors for candidiasis, then in case of a urinary tract infection it is necessary to examine the urine not only for the presence of pathogenic bacteria, but also fungi, and they “grow” on other media. Candida enters the urinary tract ascending from the intestines and vagina, or through the blood, hematogenously.
Treatment of candidal cystitis involves the use of antimycotic drugs (Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, etc.) in individually selected dosages. When prescribing treatment, a thorough diagnosis is necessary to determine the spread of fungi to other organs. It should also be borne in mind that purely fungal inflammation of the bladder in the absence of severe diseases is rare; more often fungi are associated with bacteria, which requires combined treatment.
Vaginal candidiasis and cystitis
Normal, bacterial cystitis and thrush often go hand in hand. If a woman suffers from vaginal candidiasis, she will be bothered by severe itching, burning, and copious curdled discharge. These symptoms cause severe anxiety and impair performance and mental stability. Sexual intercourse becomes painful and unpleasant.
If thrush is not treated, then after a while moderate urination disorders will occur, caused by irritation of the urethra with discharge. You can distinguish cystitis from thrush precisely by the presence of these secretions, which indicate the active proliferation of fungi in the vagina. Their color can vary: from white to yellowish-greenish, light brown. Many people think that with cystitis there is discharge, but this is not so. In women, there is no discharge of bacterial origin due to cystitis; urinary disorders come to the fore.
It may happen that candidiasis spreads from the vagina to the urethra, bladder, thereby causing fungal urethritis and cystitis. However, as mentioned above, this rarely happens, only if the body is severely weakened.
Thrush and cystitis
Cystitis and thrush are two unpleasant ailments that often occur in the genitourinary system of the female body. Moreover, they can develop against each other, complicating an existing disease.
And the whole point is in the anatomical structure of the female body, where the urethra is located next to the entrance to the vagina. What are the consequences of a disease called candidal cystitis?
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day.
Why do diseases occur?
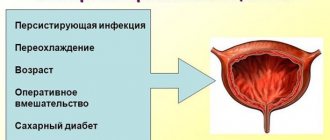
Experts confirm that these two diseases form a vicious circle and develop due to the following reasons:
- Disturbances of bacterial microflora, which can be caused by E. coli, staphylococci, enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, fungi.
- Infection with an infectious pathogen that is sexually transmitted (STD).
- Taking antibiotics.
- Diseases can be caused by hormonal disorders that occur during pregnancy;
- Disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- Diabetes;
- Prolonged placement of the catheter in the urethra;
- Chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Blood diseases;
- Damage to the mucous membrane of the urethra and vagina;
- Violation of hygiene rules;
- Hypothermia;
- Constantly wearing synthetic or tight underwear;
- Prolonged sitting;
- Difficulty defecating.
Most often, cystitis and thrush occur simultaneously against the background of several predisposing factors.
How do these ailments manifest themselves?
Both diseases are not asymptomatic.
For example, thrush, the development of which is caused by Candida fungi, may not manifest itself at all at first. But with the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, symptoms still appear in the form of:
- whitish coating on the surface of the labia majora and minora;
- curdled vaginal discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- severe itching in the genital area;
- discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse.
Cystitis is an inflammatory process in the bladder that can also begin without clear signs. In this case, the girl may attribute frequent urination to other reasons, for example, cold weather. However, more obvious signals follow that cannot be ignored:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- itching and burning sensations when urinating;
- difficulty urinating;
- the urine is cloudy, if the disease is not treated immediately, then a bloody purulent admixture appears in it;
- the urge to urinate becomes more frequent.
Treatment for thrush and cystitis
The basis of treatment is the use of antibacterial agents.
It is worth noting that candidiasis is of fungal origin, which means that drugs with a broad spectrum of action not only will not help, but can also aggravate the course of the disease.
Antibiotics from the nitrofuran class effectively fight fungi.
Our readers successfully use CystoBlock to treat cystitis. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
If cystitis is complicated by candidiasis, the specialist may also prescribe a course of antibiotics with a narrow spectrum of action:
For cystitis, treatment is supplemented by taking diuretics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Preference is given to herbal preparations:
You can also improve your condition with the help of renal and urological herbal infusions and teas.
The listed medications do not get rid of thrush, but they are also not capable of causing intensive fungal growth.
It is important to consult a doctor and adhere to the prescribed dosage, especially when taking antibiotics
Etiological (causal) factors of cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder is caused primarily by bacterial flora. In more than 90% of cases, such bacteria are Escherichia coli, enterococci, saprophytic staphylococcus and proteus. In other, more rare cases, the causative agents are Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a number of other microorganisms and... mushrooms. This may explain the discharge due to cystitis.
Fungi of the genus Candida are the most common cause of cystitis of fungal origin. It must be said that these microorganisms are part of the human microflora; they are also found in many healthy people in the oral cavity, intestines, and vagina. But in healthy people they are in an inactive dormant state. In order for the fungi to begin to multiply and penetrate into tissues, causing a disease - candidiasis, the body must be exposed to strong weakening factors.
Risk factors for genitourinary candidiasis
These include:
- Pregnancy.
- Dysbacteriosis caused by taking (especially repeated) broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Diabetes. This disease, in addition to impaired carbohydrate metabolism, is characterized by decreased immunity, and increased sugar levels and glucosuria form an excellent breeding ground for Candida fungi.
- The presence of a long-standing catheter in the urinary tract.
Other causes of candidiasis, not only on the mucous membranes, but also on internal organs, include: HIV infection, cancer, tuberculosis, blood diseases, long-term treatment with glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants. Also risk factors are severe operations and injuries, peritoneal dialysis, etc.
How to identify cystitis and not confuse it with other diseases?
Incorrect diagnosis of any disease leads to the use of the wrong treatment methods that are needed in a particular situation. The result is a lack of positive dynamics, and in the case of inflammation of the bladder, this is also fraught with the transition of an acute process to a chronic one. It’s better not to think about the question of how to determine cystitis yourself. At the first sign that some kind of malfunction has occurred in the body, you need to contact a specialist. Of course, there are several points that will help you suspect the development of this particular disease in the body and distinguish it from other problems with similar symptoms.
How to suspect acute cystitis?
Most often, doctors identify acute cystitis in women, whose anatomical features contribute to the easy penetration of pathogens through the urethra into the bladder and the development of the inflammatory process. Fortunately, microbes alone are not enough to trigger pathological reactions. The body must be affected by factors that reduce its protective properties, which allows harmful agents to attach to the surface of the mucosa and begin their life activity. Often, it is the identification of predisposing factors that allows one to suspect the development of cystitis in a patient.
Reasons provoking the condition
All potential causes of cystitis can be divided into two large groups. The first includes universal factors that affect representatives of both sexes. Secondly, those that act exclusively on women. We should not forget about the points that make it possible to classify a particular person as at risk for bladder inflammation.
Universal causes of cystitis and related issues:
- Past infectious diseases of the genitourinary system or sexually transmitted diseases.
- Intestinal dysbiosis, problems with stool in the form of frequent constipation.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- Stagnation of urine in the bladder, provoked by physiological (the habit of tolerating) or pathological (impaired functioning of internal organs) reasons.
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle, which leads to impaired blood supply to the bladder.
- Long-term use of strong medications, alcohol abuse, ingestion of toxins into the body.
- Weakening of the body's immune defense as a result of vitamin deficiency, stress, immunodeficiency, hypothermia, chronic fatigue.
To all this we can add several reasons that are unique to women. These may be periods of pregnancy or menopause, which reduce the body's resistance to external factors. Recent or chronic inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system. In some cases, acute cystitis becomes a consequence of abuse of the douching procedure or its improper implementation.
Symptoms of the inflammatory process
Of course, taking into account only the possible causes of the disease, it is difficult to accurately make the correct diagnosis. When examining a patient with suspected cystitis, the doctor pays a lot of attention to his complaints.
The acute disease is very pronounced and is characterized by a number of nonspecific symptoms.
Acute inflammation of the bladder is characterized by the following:
- Frequent urination. It is often accompanied by cutting or burning at the beginning and end of the process. There may be false urges or urine output in small portions.
- Pain appears in the lower abdomen. It seems that the bladder was not completely emptied.
- Increased body temperature. This symptom is present very often, but the thermometer numbers do not rise above 38ºC.
- Urine may change color. Sometimes it becomes cloudy due to the presence of pus or turns pink due to blood.
The listed symptoms give a certain idea of the patient’s condition, but treatment is not prescribed on their basis alone. The doctor must use laboratory tests and other modern diagnostic methods. Without them, therapy may not be effective enough and even dangerous.
Methods for diagnosing acute cystitis
To make a final diagnosis, a general urine test is taken from the patient. If infectious cystitis is suspected, urine is cultured for microflora and the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics is determined. In the case of women, a gynecological examination and smear taking will not be superfluous. Recent sexually transmitted diseases are an indication for testing for STDs. An ultrasound scan of the kidneys and bladder will determine whether cystitis is caused by damage to the internal organs.