The herpes virus, penetrating the human body, attacks the mucous membrane of any organ. Herpetic cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder caused by virus particles entering the walls of the organ. Infection occurs through sexual contact. Advanced cystitis can damage the reproductive and urinary functions of the patient’s body, so it is important to strictly adhere to the therapeutic regimen.
Relationship between diseases
A situation often occurs when one disease leads to the development of another. Diagnosis is complicated by the fact that it is impossible to determine the time of manifestation of a secondary infection. Based on numerous studies, it has been revealed that herpes is highly likely to lead to damage to the urethra. Since the causative agent is a virus, cystitis is a non-bacterial type.
Herpes causes an inflammatory process in the carrier of the pathogen or sexual partner. The infection can be transmitted not only through sex, but also through oral sex.
Herpes is highly likely to lead to damage to the urethra.
Therapy
Therapeutic therapy for herpetic cystitis in women is selected based on diagnostic results. Includes three main areas - antiviral therapy, restoration of immune functions, elimination of pathological symptoms.
- Antiviral treatment consists of prescribing well-proven drugs - Acyclovir, Oxolin, Valacyclovir, Khalepin, Famciclovir. For recurrent symptoms, use drugs and analogues of Ofloxacin, Lomefloxacin or Levofloxacin.
- To strengthen the immune system, immunostimulant drugs (Tiloran, Taktivin, Lavomax) and vitamin complexes (Supradin, Vitrum, Centrum) are recommended.
- As a symptomatic treatment, non-steroids, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are prescribed (according to the manifestations of clinical signs) - Ibuprofen, Papaverine, Nurofen, No-shpa or Drotaverine.
The course of treatment and dosage of drugs are individual for each patient.
Risk factors for infection
Doctors identify several predisposing factors such as:
- Female. A high risk of infection exists in women due to the specific structure of the genitourinary system.
- Inflammatory processes in the prostate gland in men.
- Pregnancy period. Against the background of changes in hormonal levels, a decrease in immunity occurs.
- Injury to the mucous membrane of the genital and urinary organs.
- Use of intrauterine devices. If the contraceptive is not suitable or is installed incorrectly, the flow of urine from the urethra is disrupted.
- Complicated childbirth. When the genital organs are overstretched, the tissues are injured. This process provokes the activation of a viral infection and its entry into the urinary system.
- Changes in hormonal levels. A decrease in hormone secretion leads to disruption of vaginal mucus secretion. As a result, the vagina becomes vulnerable to pathogenic flora.
Due to changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy, a decrease in immunity occurs, which can cause herpes.
A high probability of infection of the urethra is observed during various procedures that involve the installation of catheters.
Routes of transmission of the virus
There are several ways to get herpes:
- Hematogenous route. The pathogen enters the urinary system and contributes to the occurrence of sepsis.
- Lymphogenic pathway. The virus penetrates from foci of infection that are located in the pelvic organs.
- Ascending path. The pathogen enters from the urethra.
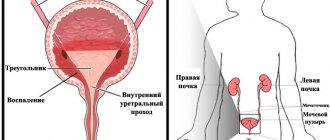
- Descending path. Herpes infection is located in the kidneys and spreads through the ureters.
- Contact path. The virus passes from one person to another through close contact.
- Sexual path. Infection of the body occurs after unprotected sexual contact with a carrier of herpes.
- Household way. Involves using someone else's hygiene products, clothing or towels. Herpes can spread from the lips to the genitals if hygiene rules are not followed.
Descending path. Herpes infection is located in the kidneys and spreads through the ureters.
Many factors can trigger a herpes infection. But its development will begin only in an organism where the immune system is greatly weakened.
Causes, diagnosis and treatment of herpetic cystitis
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! The only remedy for CYSTITIS and its prevention, recommended by our subscribers! Read more…
The herpes virus can affect various systems and organs, and the bladder is one of those organs that are most often infected. The state of the immune system plays a huge role in the body's ability to resist infection. Sometimes herpetic cystitis is not easy to identify, because the symptoms of bladder diseases can differ significantly from the symptoms that are inherent in the herpetic process.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
The most common manifestations of pathological changes in the urinary system are painful urination and frequent urge to urinate, especially at night. In most cases, herpes causes inflammation of the bladder in the carrier or partner, not only during sexual intercourse, but also during other types of intimacy (for example, oral sex).
Herpes infection of the bladder occurs through microscopic cracks. Once inside, the virus travels to the roots of the nerve in the spinal cord and settles there.
Untreated herpetic inflammation can cause damage to the walls of the bladder, resulting in the formation of numerous ulcers and scars. This causes the elasticity of the bladder to decrease. When filled with urine, it is no longer able to stretch as physiologically necessary, so the urge to urinate and pain often occur.
What factors can trigger the disease?
So, the disease develops by introducing an infection into the genitourinary system. This can happen for various reasons.
- Physiological features of the genitourinary system. The urinary tract in women is two times shorter than in men, so the risk of infection with herpes from the outside is higher for them. Pregnant women and men with an enlarged prostate are also at risk.
- The presence of genital herpes in one of the sexual partners. The risk of damage to the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system increases with intense and frequently repeated sexual intercourse. As a result, a favorable environment for the development of the disease is created.
- An incorrectly selected intrauterine device can disrupt the natural flow of urine, which leads to incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Menopause period. The female body cannot produce enough mucus from the vagina, which prevents the growth of bacteria. As a result, favorable conditions are created for the development of the virus.
- Natural birth. When passing through the birth canal, the child is at high risk of contracting the bladder with the herpes virus. It is not difficult for the virus to penetrate from the outside into any organ of the baby’s genitourinary system.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body. During menopause, a woman's body may experience hormonal imbalance. With a sharp drop in estrogen levels in the blood, the likelihood of developing cystitis increases.
- Patients who have had a urethral catheter installed to perform various medical procedures are also at risk.
What symptoms indicate herpetic inflammation?
Recognizing the symptoms of cystitis is not so easy because of their similarity to the symptoms of many other diseases. In this regard, it is important to correctly establish a diagnosis in the early stages so that the disease does not go too far and cause irreversible consequences.
The most common symptoms of the disease are:
- acute pain that occurs during sexual intercourse; feeling that the bladder does not empty completely;
- constant desire to urinate, regardless of the time of day (night and day);
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- chills and mild fever;
- pain in the lower back and pelvic area.
In elderly patients, the disease may be accompanied by chills, lethargy, fatigue, and confusion.
In an infant, cystitis caused by the herpes virus can be expressed by lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
It is also important to note that the intensity of the symptoms of the disease may vary from patient to patient.
Diagnostic methods
A medical examination for suspected herpetic inflammation of the bladder includes the following types of diagnostics:
- biopsy of the bladder wall;
- cystoscopy;
- examination of prostate secretions (for men).
The patient also submits urine and blood samples for analysis:
- blood test for the presence of antibodies to the herpes virus;
- culture or catheterization of a urine sample;
- a screening test to recognize herpes.
Treatment and preventive measures
To date, there are no methods to completely cure the herpes virus. And if the correct treatment was not prescribed and the patient did not take immunomodulatory drugs, multiple recurrences of bladder inflammation are possible throughout the year.
Directions for treatment of herpetic cystitis:
- symptomatic therapy;
- activities aimed at strengthening the body;
- therapy with antiviral drugs.
In addition, in the treatment of this type of cystitis, methods of increasing immunity such as herbal medicine, massages, the use of biogenic drugs, and physiotherapy are effective.
Considering the fact that in men the disease is secondary, because it develops against the background of a viral infection of the prostate or urethra, the doctor prescribes procedures such as:
- dilation of the urethra,
- prostate massage,
- laser reflexology.
Using a condom reduces the risk of transmitting herpes from a sick sexual partner to a healthy one.
Hygiene after sexual intercourse is important. It is recommended to give preference to neutral soap rather than scented ones. It is better not to overuse douching and excessive washing, so as not to disrupt the normal balance of the natural microflora of the genital organs. You need to ensure that the vaginal area remains clean and dry at all times. To avoid infection, washed areas should be wiped from front to back. These hygiene rules must be followed daily.
It is also necessary to pay attention to underwear that comes into contact with herpetic ulcers. It is better to wear underwear made from natural fabrics, which will ensure normal air circulation.
During menstruation, it is recommended to use tampons rather than sanitary pads. In the case of sanitary pads, the risk of developing herpetic inflammation of the bladder increases, since various bacteria accumulate on sanitary pads due to the warm and humid environment.
Consequences of the disease
Genital cystitis caused by the herpes virus in women can cause complications associated with the reproductive system. One of the most difficult consequences is the development of herpetic salpingopharitis. Symptoms of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder occur simultaneously with skin rashes and gradually disappear as manifestations on the skin subside or against the background of combined antiviral treatment.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
Complications develop gradually, the possibility of their occurrence is determined by the severity of the disease and the quality of the prescribed treatment. Most often, complications arise if exacerbations of the disease occur six or more times during the year and there is no systemic antiviral treatment.
Herpetic inflammation of the bladder cannot go away on its own. That is why the doctor, when prescribing treatment, must select the appropriate medications to prevent the development of more serious diseases. In most cases, relief is noted already on the first day of treatment.
By secret
- Incredible... Chronic cystitis can be cured forever!
- This time.
- Without taking antibiotics!
- That's two.
- During the week!
- That's three.
Follow the link and find out how our subscribers do it!
×
Symptoms
In most cases, herpes does not always make itself felt. The severity of the disease will depend on the severity of the inflammatory process. There are several symptoms of pathology in the form of:
- increased urge to urinate;
- acute painful sensations, which intensify during sexual intercourse or emptying the bladder;
- development of fever with headaches, aches in muscle structures;
- feelings of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- pain in the lower abdomen, lower back and perineum;
- leakage of urine.
Herpes can manifest itself in the form of acute painful sensations, which intensify when the bladder is emptied.
Such symptoms adversely affect the general condition of the body. The patient feels weakness, malaise, and decreased performance. Bloody urine appears.
Why does the disease develop?
There are 2 types of herpes simplex virus (HSV):
- HSV type 1 most often causes lesions on the face and upper extremities.
- HSV type 2 is isolated from lesions in the lower part of the body.
However, a direct relationship between antigen specificity and the localization of herpetic lesions was not found.
The vast majority of people are infected with the herpes simplex virus. In 40% of cases, primary infection occurs in childhood through airborne droplets. The immune response to infection is most often weak and goes unnoticed.
Sometimes herpetic rashes appear. Under the influence of external factors (sharp changes in climatic zones, hypothermia, stress, intoxication) and internal factors (diseases of internal organs, changes in hormonal levels), the immune system weakens and cannot resist herpesvirus infection. HPV multiplies rapidly and forms lesions.
There is a close relationship between the likelihood of herpetic cystitis and a person’s sexual activity. The pathology most often develops between the ages of 20 and 29 in people who begin sexual activity at an early age and have many sexual partners.
Diagnostic methods
To determine what caused cystitis, you need to undergo a diagnostic examination. It includes:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis;
- PCR research;
- immunoenzyme reaction;
- bacteriological culture of urine.
In severe cases, an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys, as well as cystoscopy after the disappearance of signs of an acute course, are required.
Diagnostics helps to identify pathology
Herpetic urethritis is difficult to identify, because it is similar to a lot of other diseases of the urinary system. At the same time, obvious signs of a herpetic lesion are sometimes completely absent. A high-quality and comprehensive examination, which is carried out in medical centers and hospitals, will help to trace the relationship between a number of ailments and the true cause of the disease. During the examination, the patient will be asked:
- donate blood to check changes in general indicators;
- bring urine for analysis to identify fragments of blood and mucous membrane of the bladder;
- undergo a specific test to detect antibodies to the herpes virus;
- do an ultrasound of the problem organ to see pathological changes, erosions and ulcers;
- have your urine cultured to make sure that the inflammation is not caused by bacteria, and if the result is negative, discontinue antibiotic treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of herpetic cystitis is based on reducing the activity of the viral agent, eliminating unpleasant symptoms and preventing the development of complications. During drug therapy, you must adhere to some recommendations:
- Refuse sexual intercourse. Treatment is carried out for both partners.
- Drink plenty of fluids. This will help remove viruses and toxins from the bladder faster.
- Limit the consumption of salt, spices and herbs. These substances contribute to stagnation of urine in the kidneys.
- Eliminate sour, spicy and fried foods from your diet. Such products irritate the mucous membrane of the bladder.
- The diet should consist of foods that have a diuretic effect: vegetables, fruits, fruit drinks, soups.
Drug therapy involves the use of:
- Antiviral drugs: Acyclovir, Famciclovir. They speed up the healing process and prevent the generalization of infection.
- Immunostimulating agents: Amiksin, Lavomax. Increases the body's resistance to viruses and stimulates the production of antibodies.
- Uroseptics: Canephron, Urolesan. The preparations include medicinal plants. They have antiseptic, healing and diuretic effects. Prevents the degeneration of cystitis into a chronic form.
- Antispasmodics and analgesics: Drotaverine, Diclofenac, Spasmalgon. It is necessary to take for severe pain in the abdomen and when urinating.
The duration of the treatment course is 5-7 days.
Clinical symptoms of the disease
The first signs of the disease can appear in a patient completely unexpectedly, since the virus has the ability to pass from a latent state to an infectious form at any time, regardless of the absence or presence of a clinic. Due to the identity of the symptoms with cystitis of bacterial origin, this type of damage to the bladder tissue is quite difficult to immediately identify in the initial period, since the symptoms are manifested by general signs of cystitis:
- painful sensations during intimacy;
- frequent false urge to micturate (the act of urination), which does not stop even during night sleep. At the same time, there remains a feeling of a filled urinary reservoir;
- pain during movements accompanied by nagging pain in the suprapubic and lumbar zones;
- possible fever. Especially in patients with concomitant chronic pathologies, which can cause attacks of headaches and loss of strength;
- Blood may appear in the urine.
A distinctive feature of the symptoms of herpetic cystitis in women is due to the multifocal nature of its manifestations. With herpes infection of the urethral canal, tingling and itching appears during micturition. Characterized by unilateral enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes and their soreness. On the skin around the anus, on the genitals, vaginal mucosa and uterine cervix, hyperemia (severe redness), swelling and itching appears, followed by the eruption of herpetic blisters.
A week later they open, forming weeping, painful wounds. The process of tissue regeneration (recovery) lasts up to two weeks. In the case of a primary acute process, restoration of the skin will last a month or more. In half of the patients, the clinical picture of herpes cystitis is recurrent in nature, which causes difficulties in treatment.
Weakened immune defense contributes to chronic disease with frequent exacerbations of symptoms.
Possible consequences
Herpetic cystitis is considered one of the dangerous diseases. Gradually, the virus leads to physical damage to the walls of the bladder, the formation of ulcers and scars. The resulting defects cause loss of elasticity of the urethra. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease can lead to:
- to manifestations of the walls of the urinary organ;
- to sclerosis of muscle structures;
- to generalization of infection with further damage to the nervous system.
Most often, cystitis causes the development of pyelonephritis or urethritis.
Most often, cystitis causes the development of pyelonephritis.
For women
Frequent relapses of herpetic type bladder damage are dangerous for pregnant women. A viral infection leads to the development of fetal defects, miscarriage or premature birth. When the genitourinary system is damaged in women, the likelihood of an inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes increases. Impaired patency makes it difficult for the egg to pass through, which leads to infertility.
For men
The pathogen in herpetic cystitis in men spreads from the penis and affects the testicles, vas deferens and prostate gland. This process adversely affects erectile function and conception.
In the absence of timely treatment, inflammation of the bladder develops into viral prostatitis.
This disease is the first stage of sclerosis of the genital organ.
Herpetic cystitis
- What is herpetic cystitis
- Causes of herpetic cystitis and predisposing factors
- Symptoms of herpetic cystitis and mechanism of infection
- How is herpetic inflammation of the bladder diagnosed?
- Prevention and treatment
Despite the fact that 90% of all known infections of the urinary system are caused by bacteria, doctors have established that the pathology of organs in this area can be of viral origin.
Often in medical practice there are cases when a patient’s existing disease gives rise to the development of another pathology, while he himself may not be aware of its presence. The situation is complex, because it is not always possible to record the moment of the onset of the development of a secondary infection, establishing their relationship with the underlying disease.
Numerous studies have shown that a well-known viral disease such as herpes is highly likely to cause inflammation of the bladder mucosa. Since the pathogen is of viral origin, we should talk about non-bacterial cystitis.
By its nature, the herpes virus is polytropic in nature - it is capable of infecting all human organs and systems, but the bladder is one of the most vulnerable organs susceptible to infection. Of course, the state of the immune system is of great importance.
The role of herpes infection as a source of cystitis development is often underestimated. This is primarily due to symptoms unusual for the herpetic process that accompany bladder disease.
What is herpetic cystitis
Herpetic (non-bacterial) cystitis is a comprehensive term: it implies various manifestations of many physical pathologies of the urinary system. The most common of them are: dysuria (painful urination) and nocturia (the urge to urinate mainly at night for an unknown reason).
Most often, herpes causes inflammation of the bladder in the carrier himself or in his sexual partner during any type of intimacy, which includes a broader concept than just sexual intercourse. For example, contact of mucous membranes during oral sex can also expose a person to the development of cystitis.
Due to the wide range of consequences, the disease is dangerous: scientists agree that over time, herpetic cystitis can lead to physical damage to the walls of the bladder, forming multiple scars and ulcers on their surface.
The resulting defects cause loss of elasticity of the bladder - when filled with urine, it cannot stretch to its fullest extent. The process is accompanied by pain, causing frequent urge to urinate.
Causes of herpetic cystitis and predisposing factors
- Physiological features of the body structure: women have a much higher risk of infection, since their urinary canal (urethra) is half as long as a man’s, which increases the likelihood of infection with the herpes virus from the outside; Also at risk are men whose prostate is enlarged and pregnant women.
- Increased sexual activity, provided that one (or both) partners have genital herpes: frequent and intense sex increases the chances of physical damage to the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system, which becomes a favorable environment for the development of herpetic cystitis.
- An intrauterine device installed for the purpose of contraception: incorrect selection of the device and its subsequent discrepancy with the woman’s physiological data can cause a restriction of the normal flow of urine, which will not allow it to be completely emptied.
- Menopause: During this period, women produce less vaginal mucus, a natural flora that can stop bacteria from multiplying, which becomes a favorable environment for the virus to multiply.
- Natural (vaginal) childbirth: this process is a high risk factor for infection of the bladder with the herpes virus, because during the birth of a child, all the birth canal is open, which means it is easy for the virus to penetrate one or another organ of the genitourinary system.
- Hormonal changes or disturbances: In most physiological periods, there is a hormonal imbalance in a person. In women, for example, it can occur during menopause. The risk of infection with herpetic cystitis increases due to a sharp drop in the level of estrogen in the blood and, as a result, the inability to resist viral infections.
In general, genitourinary tract infections account for a large proportion of hospital-acquired infections, especially among those patients who have undergone various procedures using a urethral catheter.
Symptoms of herpetic cystitis and mechanism of infection
The intensity of symptoms may vary from person to person. The most common ones are the following:
- an urgent need to urinate frequently both day and night;
- acute pain during intimacy;
- presence of blood in the urine (hematuria);
- mild fever and chills;
- feeling of bladder non-emptying;
- pain in the lower back and pelvic area.
Manifestations of herpetic cystitis in infants are lack of appetite, diarrhea or vomiting. In older people, the disease may be accompanied by lethargy, confusion, fatigue, and chills.
The symptoms of cystitis are very similar to a number of other diseases, so it is important to establish the correct diagnosis in the early stages of the disease.
Infection occurs as follows: the herpes virus enters the bladder cavity through microscopic cracks. Once inside, it moves to the roots of the nerve near the spinal cord, settling there forever. This does not mean that the connection between the two diseases cannot be dissolved, and that they themselves cannot be treated - the fact only indicates a high probability of the occurrence of herpetic cystitis.
How is herpetic inflammation of the bladder diagnosed?
First of all, the doctor conducts a survey and examination of the patient and, having learned that he has genital herpes, has every reason to associate this viral disease with inflammation of the bladder.
Medical examination includes cystoscopy, biopsy of the bladder wall; Laboratory examination of prostate secretions is relevant for men. An informative examination is laboratory blood testing, as well as a urine test.
The most relevant are the following:
- standard blood testing for the presence of antibodies to herpes viruses;
- a quick screening test to identify herpes (in its latent form, if there are only symptoms of bladder inflammation);
- culture or catheterization of a urine sample: having learned about the viral origin of herpes, not only antibiotic therapy, but also antiviral treatment is planned.
Prevention and treatment
- Couples who want to minimize the risk of transmitting herpes to their partner should always practice safe sex.
- Particular attention should be paid to clothing that comes into contact with herpetic ulcers - it should not touch healthy mucous membranes. In addition, it is recommended to wear underwear made of cotton - natural fabric guarantees air circulation.
- Practice good hygiene after sex. Try using neutral soaps rather than scented ones. Avoid douching and excessive washing, as this makes it difficult to maintain the normal balance of the natural flora of the genitals. Maintain proper daily hygiene. Keep the vaginal area clean and dry—always wipe washed areas from front to back to prevent infection.
- During menstruation, tampons are a better alternative to sanitary pads. Sanitary pads can collect bacteria, creating a moist and warm environment, thus increasing the likelihood of developing herpetic cystitis several times.
Cystitis caused by the herpes virus does not tend to go away on its own. When planning his treatment, the doctor first of all prescribes antiviral drugs, since one disease should not provoke the development of another. Most patients will experience the beneficial effects of medications after the first day of treatment.
It should be remembered: all forms of sexual contact carry great risk. To get competent advice, diagnosis and treatment, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
You can learn about the development and characteristics of herpes below:
Prevention
You can prevent the simultaneous development of cystitis and herpes if you follow some recommendations:
- Use condoms during sex.
- Avoid using scented personal care products.
- Keep your genitals dry and clean.
- Wash yourself properly.
- Wear underwear only from natural materials.
- Women should not use tampons during their periods.
To prevent the simultaneous development of cystitis and herpes, women are not recommended to use tampons during menstruation.
If a person is a carrier of the virus, then he should eat right, avoid stress and hypothermia, and visit a doctor regularly.
Establishing diagnosis
For a preliminary conclusion, the presence of clinical signs is sufficient. To prove the viral nature of the disease, a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test is prescribed.
In addition, the following analyzes and studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound – diagnoses the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence of ulcers and hemorrhages.
- Blood and urine tests show indirect signs of the disease.
- Cystoscopy - reveals the presence of rashes on the mucous membrane of the bladder. Allows you to determine the degree of its damage, the presence of complications in the form of ulcers and perforations.
- Taking a smear from the urethra allows you to determine the type of bacterial infection and is used for PCR.
After passing the examination, a final diagnosis is made and therapy is prescribed that affects the cause of the disease.
Genital herpes: symptoms, photo of the disease
Have you been trying to cure PROSTATITIS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Among the world's population aged 20 to 50 years, an infectious disease such as genital herpes is increasingly being diagnosed. Both men and women are susceptible to the disease. The prevalence among children is quite low.
The patient complains of itching and burning, which is typical when painful herpetic sores and blisters appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals.
- Genital herpes: what is it?
- Causes of the disease
- Characteristic signs of genital herpes
- Features of genital herpes in men: symptoms and photos
- Features of genital herpes in women: symptoms and photos
- Recurrent form of herpes
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment of genital herpes
Available statistics indicate that more than 70% of the inhabitants of our planet are infected. Doctors explain the mass infection, first of all, by the ease of transmission of the virus and the difficulty of its treatment.
Genital herpes: what is it?
Genital herpes usually affects the mucous membranes of the genital organs, as well as the areas of skin located next to them. Having carefully examined the herpes in the photo, it is worth noting that it is difficult to draw a conclusion about the true causative agent of the disease based on the affected areas of the skin. The accompanying symptoms do not provide a clear enough idea of the nature of the infection. Only a dermatologist can determine the exact cause of the disease after reviewing the results of special tests.
Herpovirus exists in two forms. The first type of virus most often manifests itself on the face and upper body, while the percentage of relapses is quite small. The second type primarily affects the genitals and lower extremities.
Both forms of herpes simplex, after infection of the body, are found in the form of rashes on the lips, penis or vagina.
The virus uses a contact route to enter the human body through mucous membranes. Being thin and delicate layers of tissue lining the openings of the body, they become a good conductor for herpes infection.
As soon as the virus enters the blood or lymph, it immediately penetrates cellular structures and instantly adapts to the new environment. This rapid adaptation of the virus makes it difficult to suppress its activity. Both types of herpes can be easily detected in the organic fluids of infected people: semen, vaginal secretions, saliva.
The danger of herpes is that by neglecting timely medical care, the patient risks developing other sexually transmitted infections, prostate and cervical cancer. In addition, herpes infection provokes immunodeficiency states and disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. It is especially worth noting that genital herpes threatens the health of a pregnant woman and her unborn child. Such an infection can cause premature birth, the risk of embryo developmental defects increases, and spontaneous miscarriage or fetal death cannot be ruled out.
Thus, if you discover any signs of this disease, you should immediately consult a dermatovenerologist.
Causes of the disease
Any person can become a carrier of the herpes virus, regardless of the stage of the disease - asymptomatic or in the acute phase.
Factors creating a risk of infection with herpovirus:
- Constant change of sexual partners
- Oral-genital sexual contact
- Using a public toilet
- The virus is transmitted through kissing or using other people's objects or personal hygiene items. You can become infected with genital herpes due to the use of foreign hygiene attributes, for example, towels, only if the integrity of the mucous membrane or skin is damaged. Herpes penetrates into the body due to the presence of cracks or wounds. However, the chances of becoming infected with herpes due to household contact are minimal if you follow basic rules of personal hygiene. Based on laboratory diagnostic studies, scientists agreed that the survival rate of the virus outside the human body is low. At normal temperature and humidity levels, the virus will not last more than one day. Metal surfaces allow the virus to survive for about three hours, and wet fabrics for about five hours.
- The herpes virus can be acquired through blood transfusion, when donor blood is transfused or a non-sterile medical instrument is used.
- Transplantation method of infection at the time of organ transplantation.
- Poor living conditions
Infection in children can occur through airborne droplets. While in the womb, the embryo sometimes becomes infected through the mother's blood. Often, newborns become infected through the mother's birth canal affected by herpes.
Characteristic signs of genital herpes
Common signs of genital herpes infection are common for men and women:
- Blisters appear on the genital area
- With local infection with herpes, small blisters are filled with liquid contents and are localized in the lips, mouth, and genitals.
- The infected area begins to itch, and there is a burning and tingling sensation.
- At sites of infection, redness on the skin and mucous membranes is noticeable.
- After the vesicles have ruptured and fluid has leaked out, small ulcers form in this area, constantly secreting serous fluid.
- After about a week, the ulcers are replaced by crusts
- The patient has palpable enlarged inguinal lymph nodes
- At an early stage, the temperature rises, headache and muscle pain appear, and the person becomes feverish.
- Increased frequency of urination
Signs of herpes are sometimes found on the inner thighs, buttocks and anus. There are cases when the blisters spread throughout the rectum.
Features of genital herpes in men: symptoms and photos
The clinical picture of genital herpes in men is marked by painful rashes:
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! D. Pushkar told how to defeat prostatitis at home...
Such a pleasant treatment for prostatitis for 147 rubles...
- On the head of the penis and tissues of the foreskin
- Herpetic rash spreads to the mucous membranes of the urethra and urethra
- The lesion affects the external genitalia, coronary groove and scrotal tissue
- Redness with blisters reaches the area of the upper inner thigh
- Characteristic symptoms also appear near the anus
In the male body, herpes manifests itself suddenly. A man may feel a strong burning and tingling sensation in the area of the penis. Almost until the moment of exacerbation, genital herpes cannot be recognized. There are no severe symptoms, no discomfort.
Genital herpes is dangerous for men due to the following complications:
- Herpetic cystitis. The man feels constant weakness and drowsiness, and spasms periodically occur in the groin area. After finishing urination, a burning sensation is felt.
- Herpetic urethroprostatitis. Pain when urinating, feeling of heat.
- Proctitis. False urge to go to the toilet, constipation, feeling of a foreign body in the rectum.
Features of genital herpes in women: symptoms and photos
According to statistics, genital herpes in the fairer sex is recorded much more often. This is largely due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the reproductive system.
A woman should be alerted to painful and itchy red spots affecting the external and internal genital organs.
Redness and blisters appear around the anus. Herpes often affects the vaginal walls and cervix. There is a strong itch inside. After a few days, the rashes transform into superficial erosions, causing discomfort. These injuries will heal within two to three weeks.
Many women who experience genital herpes complain of copious whitish or clear vaginal discharge. Urination causes burning.
Consequences of herpetic lesions of the genital organs in women:
- Vaginal dryness
- Mechanical irritation causes the formation of cracks that heal poorly and constantly bleed
- Development of secondary infection in the form of regular vaginal discharge causing itching and burning
- Condylomas may appear if there is a papillomavirus infection in the body
Recurrent form of herpes
Genital herpes, which is prone to relapses, creates conditions for the extinction of systemic and local immune responses, which entails the development of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system. The recurrent course of herpetic disease leads to the activation of papillomavirus, the development of oncological formations in the cervix, vagina and rectum. Constant episodes of exacerbation that occur after a short remission disrupt the normal rhythm of sexual life. This creates an obstacle to forming a family and having children. Problems in the sexual sphere have a negative impact on the emotional background and lead to depression.
A crushing blow to the immune system is caused by bad habits, hypothermia, physical and mental stress, and hormonal imbalances. All together gives impetus to the exacerbation of herpes.
The recurrent form of genital herpes is less aggressive than the primary episode of the disease. Characteristic redness and blisters worsen in the previous areas and do not affect new areas. They can be detected on the first day of exacerbation of the herpovirus. Antiviral substances cause mutations of the virus, as a result of which herpes changes into an atypical form. It is characterized by:
- The edematous form is marked by hypermia and swelling of the mucous membranes of the genital organs
- The itchy form manifests itself with severe itching and burning in the genital area, swelling is mild
- Ulcerative-necrotic form
- Isolated cracks of a single nature
- Unusual localization of lesions
Atypical forms of genital herpes in men are registered less frequently than in women. This form of herpes is dangerous due to the spread of infection.
Low-symptomatic forms rarely bother patients and make themselves felt by microcracks and mild itching. Usually there is no subjective symptomatic picture at all. For accurate diagnosis, virological testing is required.
With each relapse, immunocompetent cells are lost. Due to their losses, secondary immunodeficiency develops. The affected immune cells are no longer able to produce antiviral interferon bodies.
Diagnosis of the disease
The specialist makes a diagnosis based on a visual examination of the patient and special laboratory tests:
- A swab is taken from the vagina or urethra
- The patient donates blood for immunoenzyme indicators IgG, IgM
- The fluid released from herpes blisters is taken for polymerase chain reaction.
- Cultures are identified by sowing, and the infectious agent is studied using an electron microscope.
Treatment of genital herpes
Whatever treatment strategy is chosen, unfortunately, it is almost impossible to completely get rid of the herpes virus. Having penetrated the human body, the virus is able to persist in nerve cells for life. In this case, all efforts should be devoted to reducing the symptoms of genital herpes, and complete recovery should be forgotten. The patient is required to do everything possible to alleviate the course of the disease and reduce relapses.
For successful and quick treatment, the moment of contacting a venereologist plays an important role. The earlier the patient makes an appointment, the more effective the results of therapy will be. As a rule, those who go to a medical facility on the first day of illness are less susceptible to complications than others.
For men and women, doctors most often prescribe medications for the treatment of genital herpes: acyclovir, famaciclovir, penciclovir, ribavirin.
Antiviral drugs are used on the basis of tablets and ointments. The active components of these medications are aimed at preventing the spread of the virus and reducing symptoms. The regimen for taking antiviral drugs is agreed upon with the doctor. Your doctor may recommend analgesics and antihistamines to relieve itching and burning.
The ointment is used topically, applying a thin layer to treated and dried areas of the skin.
If the infection has affected the mucous membranes of the vagina or anus, then antiviral suppositories are prescribed.
Usually the course of treatment lasts 10–14 days.
The meaning of prevention appears if the patient often experiences relapses of genital herpes. For prevention purposes, a three-month course of medications is prescribed - this can reduce relapses by half.
To maintain the functioning of immune cells in order to reduce the frequency of relapses, special vaccines are prescribed that stimulate the production of their own interferons.
An artificial immunostimulant, cycloferon, has proven itself to be the best treatment for herpes. It is used in the form of tablets and liquid ointment. The ointment contains the antiseptic benzalkonium, which can eliminate secondary infection.
Barrier contraception during sexual intercourse is the best way to prevent primary infection with genital herpes. Unfortunately, a condom does not provide a complete guarantee that a person will not become infected. The virus can enter the body through unprotected areas of the body.
Basic measures to prevent genital herpes:
- Protected sex
- Maintaining personal hygiene standards
- Timely diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases
- Rejection of bad habits
- Compliance with the work and rest schedule
- Healthy eating
- Avoidance of stressful conditions
How are herpes and cystitis related?
There is a relationship between cystitis due to the herpes virus and sexual contact. The risk group consists of people 20-29 years old who begin sexual activity early or often change partners.
HPV usually enters the bladder through the genitourinary tract. So a common reason why herpetic cystitis develops is herpes on the partner’s genitals. During sexual intercourse, viruses constantly act on the mucous membrane. Microtraumas of the membranes of the genitals with the urethra are also possible, and even minor damage to them already creates conditions for the active reproduction of HPV. Pathology is also caused by herpes on the lips. In case of insufficient hygiene, the causative agent of the disease is transferred to the hands.
The herpes virus quickly spreads through the genitourinary tract and reaches the bladder. Infection occurs through microcracks in the walls of the organ.
The risk of contracting an infection is higher when a urethral catheter is inserted and during hormonal imbalance. Normally, the mucus produced by a woman’s body inhibits the penetration of pathogens into the genitourinary tract. Its formation may decrease due to insufficient hormone synthesis. Infection also becomes more likely if the uterine device is placed incorrectly if it disrupts the normal flow of urine.
The causative agents of the disease penetrate from the urethra into the bladder through a descending route - with blood and lymph flowing from the pelvis. It happens that infection is caused by the sweating of media with pathogenic microorganisms to the bladder from neighboring organs. HPV first affects the kidneys and ureters, and then the bladder mucosa.
In women, symptoms of bladder inflammation caused by HPV vary depending on the state of the immune system. However, the most common symptoms are the following:
- Increased urge to go to the toilet and painful urination. The same symptoms are characteristic of other forms of cystitis, so the diagnosis can only be made after tests.
- Blood in the urine. Even its slight staining may indicate pathology.
- Increasing the volume of urine excreted at a time.
- Frequent and painful urges in the evening.
- Feeling of a constantly full bladder.
- Fever, chills.
- Pain and discomfort in the lower back, pelvis, lower abdomen.
- Fatigue and drowsiness.
It is impossible to independently differentiate the symptoms of cystitis against the background of herpes from the manifestations of other genitourinary pathologies. It is important to see a doctor at an early stage of the disease, only this will avoid complications.
Diagnostic search
The effectiveness of the treatment process for herpes cystitis depends on high-quality diagnosis, since the clinical picture of the disease is similar to the manifestation of many genitourinary pathologies. Basis of the survey:
- Laboratory testing of urine and blood, which helps identify necrosis-affected lesions on mucous tissues.
- Confirmation of the viral nature of the disease is provided by bacteriological analysis of urine (tank culture).
- Ultrasound of the bladder. The examination helps to identify the presence of ulcerative lesions, which is typical for the viral genesis of the disease.
- Diagnosis of PRC using tissue biopsy from the walls of the bladder reservoir. This is the only sure way to detect the herpes virus in mucosal tissue cells.
Even more interesting:
Echinococcal liver cyst surgery
Apple cider vinegar for dandruff reviews
How to properly treat the disease
The bad news is that herpes can deeply damage the surface on which it reproduces. It easily penetrates the submucosal and muscular layers of the organ, leaving extensive scars and multiple ulcers on the tissue. Subsequently, the bladder loses its ability to fully stretch and contract. Accordingly, each filling of the organ with urine will cause sharp pain, and emptying will be incomplete. Hence - stagnation of urine and subsequent inflammation in the bladder. Vicious circle.
With improper treatment or lack thereof, herpetic cystitis becomes chronic. This means that the disease will torment the patient for the rest of his life and each new exacerbation will only worsen the situation.
Difficulties in diagnosis
Due to the fact that the symptoms of herpetic cystitis do not have clear features, and bacterial inflammation is easily associated with viral inflammation, diagnosing herpes as the root cause of the disease is problematic. It is impossible to detect the virus in a general analysis and bacterial culture of urine - viruses are not sown.
At the first stage of the examination, the doctor collects a detailed medical history, including finding out whether the patient has had cases of herpes. Subsequent visual examination shows the presence or absence of characteristic rashes on the genitals. If, simultaneously with inflammation of the bladder, a herpetic lesion is detected anywhere on the body, this is a good reason to suspect that the cause of cystitis is herpes.
Then comes the turn of laboratory tests:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- urogenital smear;
- PCR;
- screening test for herpes;
- cystoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- biopsy of bladder tissue.
In men, an additional study of prostate secretion is performed.
Treatment regimen
The bad news is that there is no complete cure for herpes. Therefore, all measures to combat the disease come down to the following points:
- Symptomatic treatment . This includes painkillers, antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory drugs: “No-spa”, “Papaverine”, “Ibufen”, “Diclofenac”, etc.
- Antiviral therapy . Medicines such as Acyclovir, Famciclovir, and Valacyclovir are effective in the fight against herpes.
- Strengthening the immune system . For this purpose, immunomodulatory drugs and multivitamin complexes are prescribed.
- Diet and drinking regime . The patient's diet should include plenty of fresh vegetables, fruits, grains and lean meats. Excluded from the diet: salty, fried, smoked and spicy foods. In addition, it is necessary to drink enough water.
- Physiotherapy.
If a bacterial infection has joined the main process, the doctor will prescribe an antibacterial drug depending on what pathogen was detected.