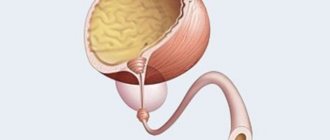
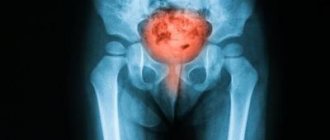
The human bladder is a hollow muscular organ located in the pelvis. Depending on the fullness of urine, its shape changes: when filled, it has a pear-shaped shape; when emptied, the organ becomes saucer-shaped, as its walls collapse after urination. The absence of pathologies on ultrasound is indicated by the symmetry of the organ, clear, even contours and echo-negativity (its structure does not reflect ultrasound waves well). If echogenic formations are found in its cavity, this indicates the development of pathogenic processes. Such an echogenic formation can be a fine suspension or sediment. In this article we will tell you what a suspension in the bladder detected on ultrasound in adults and children means, whether it poses a danger to human health and how to treat it.
Suspension in the bladder on ultrasound, what is it?
Suspension in the bladder (MB) consists of tiny solid particles of various salt compounds. This is not sand coming from the kidneys, with which suspension is often confused, since it has a different origin and composition.
The suspension is formed by salts of the following acids:
- oxalic acid - oxalates;
- urinary - urates;
- calcium salts of phosphoric acid - phosphates.
Suspension is not considered a disease, but is a sign of some pathological process leading to an increase in the concentration of salts and their accumulation.
Healthy urine should contain a certain amount of dissolved salts, and their excess should be excreted.
Classification
The suspension is classified by origin, particle size and degree of echogenicity.
Based on its origin, the suspension is divided into:
- primary - the formation of such a suspension is caused by an increased concentration of salts in the urine. This condition causes a slowdown in the flow of urine naturally, and as a result of stagnation of urine, salt crystals fall out, forming a sediment;
- secondary - the suspension is formed due to small crystals that are separated from large formations localized in the kidneys or ureters. They enter the bladder along with urine and settle there. Such particles are formed in pathologies of the urinary system and their diagnosis is usually difficult.
According to particle size:
- fine - particle diameter no more than 0.05 mm, usually pure salts;
- coarse - consists of large particles and, in addition to salt crystals, has inclusions of epithelium and blood cells. Such sediment is a harbinger of the formation of stones, and in the case of surgery, its consequence.
According to the degree of echogenicity:
- Echogenic suspension - formed by small salt salt crystals, cholesterol and high concentration urine. This is a sign of stagnation in MP.
- Hyperechoic - sediment is based on large particles that are ready to transform into stones. In this case, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment.
Why is the formation of suspended matter dangerous to health?
The detection of suspended matter on an ultrasound examination is only a harbinger of the underlying pathology, but it must be dealt with in the same way as the cause.
Remember that the formation of sand and stones in the bladder directly depends on the concentration of salts in the urine: the higher it is, the higher the risk of disease.
The appearance of sediment can also lead to other complications.:
- Changes in MP walls . Constant irritation and stagnation of urine leads to hypertrophy of the walls of the bladder, which in turn causes pain when urinating. Moreover, hypertrophy can be uneven: some areas become too thick, others become too thin, which threatens perforation (rupture) of the wall and spillage of contents into the abdominal cavity.
- Atony - frequent urge to void the bladder can suppress the urination reflex. And in this case, congestion and the formation of stones will not be the most important problem; the risk of developing paralysis of the bladder is more dangerous.
The development of such severe complications is very rare, since pain will force a person to seek medical help much earlier.
Development of prostate adenoma
An increase in androgen metabolism in prostate cells plays a major role in the development of adenoma. An increase in the activity of 5α-reductase in the epithelium of the prostatic glands leads to an increased conversion of the male hormone (testosterone) into 5α-dehydrotestosterone. As a result, growth factors are activated, causing proliferation of stromal cells in the prostate gland.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreators
(T-testosterone, 5eR-5α-reductase, DHT-5α-dehydrotestosterone, AR-androgen receptor)
Causes of suspension in the bladder in adults
Excessive concentration of salts in urine, leading to stagnation of urine, can develop against the background of many pathologies. Clinicians note that most often a suspension is formed due to diseases of an inflammatory nature.
Most often, suspension is formed against the background:
- Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. The processes accompanying this disease provoke stagnation of urine, and, as a result, an increase in the concentration of salts in the urine, which is already increased due to inflammation. Which leads to the formation of suspension. After adequate therapy it will disappear. This is the most common cause of sediment in MP;
- Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the renal pelvis. The reason for the high concentration of salts in this case is impaired renal function, that is, we are talking about the formation of a secondary suspension;
- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra. The cause of stagnation of urine and all subsequent phenomena is the narrowing of the urethra;
- Endometriosis and inflammation of the ovaries in women, if untreated, sooner or later negatively affects the bladder;
- Surgical intervention . Even a successful operation of the genitourinary system can lead to a temporary failure in its functioning. This means that a suspension may form, obstructed urine flow and hematuria (the presence of blood in urine);
- Foreign bodies in the bladder and ureters also cause mechanical sediment formation, as they complicate the function of the ureter;
- Injuries to the organs of the urinary system - with any damage, the functioning of the organs is disrupted and urinary tract is no exception. Violation of its function is expressed in stagnation of urine, as a result of which a suspension is formed;
- Urolithiasis . Particles separated from stones and sand enter the MP with urine. And since this disease has an increased concentration of salts, the outflow of fluid is difficult. As a result, the particles cannot be completely removed from the organ cavity and accumulate in it.
The suspension can also form against the background of infection with parasites, such as worms or schistosomes. Such cases are more common in Asian countries.
Any diseases associated with impaired urine outflow and stagnation can cause the formation of suspension.
Stages of BPH
Stage I (grade 1 prostate adenoma). There is sluggishness of the urinary stream, a strong urge to urinate (with the greatest severity at night), frequent and somewhat difficult urination. Stage II. There is thinning and pronounced sluggishness of the urinary stream, a feeling of incomplete emptying develops due to the formation of residual urine, impaired renal function and acute urinary retention are possible. Stage III.
Paradoxical ischuria occurs: there is no muscle tone in the bladder, the patient is unable to urinate, which causes the bladder to overflow, but at the same time urine is spontaneously constantly released in the form of drops. Impaired renal function becomes more pronounced, the upper urinary tract expands.
Causes of sediment in the bladder in children
The formation of suspension in childhood is not necessarily associated with any pathological processes.
The reason for the formation of sediment can be the usual physiological processes of the formation of the genitourinary system. Also, suspension can appear due to a basic lack of water. After all, children do not yet know how to control the amount of liquid consumed, which can provoke an increase in the salt content in urine.
The main thing is that the child does not experience pain or discomfort when emptying the bladder.
If any unpleasant symptoms are observed that the baby complains about, it is necessary to seek medical advice and diagnostics: ultrasound and other studies. We have already written about how an ultrasound of the bladder is performed in children in a separate article.
If during the diagnosis a primary disease is discovered - the cause of the formation of the suspension, then the child will be prescribed therapy.
In most cases, sediment appears against the background of inflammation, so the young patient will be prescribed antibacterial therapy with drugs such as: Sumamed, Amoxiclav or Azithromycin.
As for herbal medicines included in the treatment regimen, their list does not differ from that recommended for adults. We will cover the treatment for adults below.
Clinical manifestations
It is impossible to notice the symptoms of the presence of suspension in the bladder immediately after its formation, since it is not removed from the organ cavity along with urine for a long time. For example, if a person seeks medical help for cystitis, then while receiving treatment, he may not even know when there was sediment in his bladder.
Typically, the signs are not given by the presence of suspension, but by the pathology that caused its accumulation.
A person should be wary of:
- obvious cloudiness of urine, acquisition of an unusual color and smell;
- pain in the groin area and lower abdomen - characteristic symptoms for most MP pathologies;
- difficulties with urination, for example, urine comes out in an intermittent stream, it is not possible to empty the bladder at one time;
- frequent urge to urinate, accompanied by pain - usually these signs indicate an increased content of salts in urine, since it irritates the lining of the organ;
- hematuria. Blood in the urine can appear due to mechanical damage, and when sediment exits through the urethra, and with kidney dysfunction - a more severe complication.
The presence of sediment in the urine can be observed only after it has settled. And if the particles are very small and their number is minimal, then only after centrifugation.
Ureterocele
One of the rare anomalies of the ureters, in which there is an expansion of all layers of the intramural part of the ureter; bulges into the cavity of the bladder on one or both sides. A ureterocele is difficult to differentiate from a diverticulum or hydatid cyst located at the orifice of the ureter. Early diagnosis of ureterocele is of great importance, as it allows timely relief of the patient from possible dilatation of the upper urinary tract, development of pyelonephritis and secondary cystitis.
Source: health-medicine.info
How much does it cost to order the drug sofosbuvir and daclatasvir
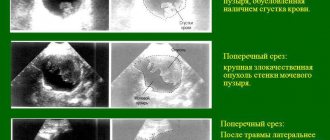
Suspension in the bladder on ultrasound
In most cases, sediment in MP does not manifest itself in any way and its visual determination is not possible. You can see the suspension on an ultrasound, more often if you suspect another pathology of the genitourinary system.
Using ultrasound examination, areas of echogenicity, their intensity and nature are determined, which makes it possible to clarify the level of salt concentration.
In addition, the ultrasound procedure of the bladder allows you to assess the general condition of the urinary tract.:
- shape;
- the presence of stagnation;
- wall thickness.
The doctor pays attention not only to the presence of sediment as a consequence of pathology, but also to changes in the organ caused by the disease.
However, it happens that urine becomes echogenic not against the background of pathology from the organs of the genitourinary system, for example, due to its increased concentration if a person has not emptied the bladder for a long time. In order to avoid such situations, you need to properly prepare for the study.
It is necessary to drink 1-1.5 liters of water an hour and a half before the examination so that the bladder is well filled and the results of the ultrasound examination are reliable.
Additional diagnostics
In addition to ultrasound examinations, to understand the full picture of the pathological process,:
- blood test to determine the presence of inflammation;
- urine analysis to determine the type of salts that form the suspension and to determine the true reason for its formation. For example, phosphates in most cases indicate kidney disease.
- intravenous pyelography - contrast radiography of the kidneys (according to indications). The study allows us to assess not only the condition of the kidneys, but also their functions, which is of great importance for identifying primary pathology.
The reasons for the formation of sediment may be different, so to identify them, the doctor may prescribe other diagnostic measures.
Treatment
The doctor develops treatment tactics based on diagnostic data and the nature of the pathology. The appearance of sediment is only a consequence and its elimination will undoubtedly alleviate the patient’s condition, but will not get rid of the cause.
However, if an ultrasound examination revealed an echogenic fine suspension that settled when sand came out of the kidneys or after crushing stones, then it is enough to follow a plentiful drinking regime and a special diet to facilitate the removal of particles. If you want to learn about the symptoms and folk remedies treatment of sand in the bladder in women and men, go here.
Basic principles of treatment:
- Relief of pain;
- Relief from difficulties when emptying the bladder;
- Reducing the salt content in urine and removing sand and stones (if any);
- Strengthening immune defense;
- Treatment of primary pathology: inflammatory process, bladder dysfunction.
Drug therapy
In most cases, the suspension is formed against the background of various inflammatory processes.
The standard therapeutic regimen includes:
- Prescription of antibiotics - Monural, Nitroxoline, Norfloxacin, Furazidin, Cefixime, Palin in order to suppress inflammation, destroy harmful microflora and restore normal functioning of the organ. You can quickly relieve inflammation with the help of installations of sea buckthorn oil and Miramistin into urine.
- To relieve pain, No-Shpa, Drotaverin, Baralgin, Spazmalgon are indicated. Clinicians also recommend the use of suppositories such as Voltaren.
- In order to normalize the outflow of urine and empty the bladder cavity, therapy with plant-based uroseptics is prescribed: Canephron, Cyston, Urolesan, Fitolysin, Uronefron. It is recommended to combine the use of medications with the use of decoctions of horsetail, chamomile or dill seeds, as well as lingonberry and cranberry juices. If a bladder infection is detected in women, douching with infusions of horsetail and chamomile is additionally prescribed.
- If urinary incontinence occurs , then taking Detrusitol is indicated.
- To stimulate the immune system, you can take Uro-Vaxom.
This regimen is applicable for the treatment of MP; for pyelonephritis, the therapy will be different.
Drinking regime and nutrition
The success of treating such pathologies directly depends on adherence to proper drinking and nutrition.
- Drink more fluid, then the urine will be less concentrated and suspended particles will be more easily washed out of the bladder. You can drink water, weak teas, dried fruit compotes, fruit drinks, but you will have to forget about coffee and alcohol.
- Do not over-salt your food - daily salt intake should not exceed the age norm.
- All winter preparations: pickles and marinades, as well as smoked meats, spicy and canned foods and dishes will have to be excluded from the diet.
- Those with a sweet tooth should avoid sweets of any kind, as they contain a large amount of salts.