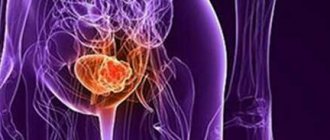
It has been revealed that over the past few years, an increasing number of people have begun to complain of pain in the peritoneal area. Bladder cancer is more often diagnosed in males. The risk group consists mainly of those who smoke too much. It is smoking that most often provokes the development of malignant tumors. If a disease is detected, you should immediately contact a specialist who will prescribe the necessary examinations and treatment. Among them, transurethral resection of the bladder (TUR) occurs.
Indications for bladder resection
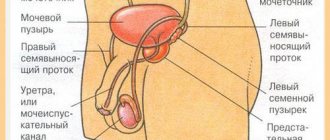
TOUR of the bladder is a surgical intervention without incisions of the skin or soft tissues, with the purpose of examining the internal part of the organ, collecting samples for a biopsy, and eliminating a malignant neoplasm. The operation is performed by inserting instruments through a cystoscope into the peritoneum through the urethra. In this case, any damage to the urethra is completely excluded.
Surgery is indicated only in the early stages of cancer. Transurethral resection is performed at the initial stage of tumor development, before metastases damage neighboring organs or tissues.
Transurethral resection of the bladder allows you to remove a malignant tumor without making incisions in the skin and muscles. When performing the operation, special thin instruments with a built-in camera are used, which allows you to visualize the internal walls of the organ and the process of removing the tumor on the monitor.
Transurethral resection of the bladder is the primary treatment for cancers detected at an early stage.
What are the advantages of the method?
Transurethral resection is often used for malignant tumors of the bladder, which is explained by certain advantages:
- Using this method, it is possible to establish an accurate histological diagnosis, as well as determine the extent of the pathological process.
- The stage of cancer is determined, and it is also determined whether tumor cells have penetrated the muscle walls of the organ.
- A clinical prognosis is established, as well as factors against which a relapse of the disease may occur.
- The location of tumors, their size, configuration, and number are revealed.
- The cancerous growth is removed.
With the help of transurethral removal, it is possible to solve a variety of problems. This is an undeniable advantage of surgical intervention.
Contraindications for surgery
Contraindications to bladder surgery are:
- narrowing of the lumen of the ureter;
- the presence of chronic extragenital diseases;
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- general and genitourinary infectious diseases.
If these pathologies or disorders are present in the body, surgical intervention is completely contraindicated. In such a situation, the specialized doctor resorts to other methods of treating the existing pathology.
To whom is manipulation indicated and contraindicated?
The operation is performed only if the person has appropriate indications. Manipulation is recommended for acute delay or chronic emptying, which indicates obstruction of the bladder.
If pain and a feeling of heaviness appear in the lower abdomen, surgery is recommended. It is indicated for inflammatory diseases of an infectious nature. Surgical intervention is necessary for adenoma, renal failure and other pathological processes that interfere with the complete removal of fluid from the body. For hematuria, the use of this treatment method is also recommended.
Despite the effectiveness of surgical intervention and the postoperative period, TUR of the bladder has certain contraindications for:
- narrowing of the urinary canal;
- development of varicose veins in the bladder neck.
If infectious processes are observed in the reproductive system or urinary tract, then surgery is not recommended. Contraindications to surgery are
How to prepare for transurethral resection?
Before performing a TUR of the bladder, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
- For 3–10 days before surgery, the patient is in the hospital under full medical supervision. Blood and urine tests, an electrocardiogram and a chest x-ray are performed.
- An anamnesis is collected by the therapist and anesthesiologist to eliminate possible risks during the operation, since the patient may have pathologies that are included in the list of contraindications for transurethral resection.
- From the evening until the operation itself, it is forbidden to eat.
- On the eve of the TUR of the bladder tumor, a cleansing enema is given and the hair in the groin is shaved.
- Before the actual resection of the bladder, the patient is given antibacterial drugs that prevent possible infectious infection.
These manipulations and medical preparatory recommendations are carried out without fail, since the success of surgical therapy depends on their implementation.
How to use Diclofenac 100 correctly?
Diclofenac 100 is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to relieve symptoms of inflammatory diseases. It does not affect the cause of the pathology, therefore it cannot be used as an independent therapeutic agent. It has a large number of side effects, so it is used as prescribed by a doctor.
Latin name
Diclofenac.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Release forms and composition
The drug is available in the form:
- Long-acting tablets, enteric film-coated. Each contains 100 mg of diclofenac sodium, hypromellose, corn starch, magnesium stearate. Tablets are packaged in blisters of 10 pcs. The package contains 2 contour cells and instructions.
- Rectal suppositories. They are white or yellowish in color and torpedo-shaped. Contains 100 mg of active substance. Packed in plastic cells of 5 pcs. The cardboard box contains 2 cells.
- Gel for external use. Supplied to pharmacies in tubes of 40 g. 10 g of gel contains 100 mg of diclofenac.
Mechanism of action
Pharmacodynamics
Diclofenac has the following actions:
- suppresses the activity of cyclooxygenase, preventing the development of processes of conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins;
- prevents platelet aggregation;
- reduces the intensity of autoimmune inflammatory reactions;
- slows down the production of proteoglycan in cartilage tissues.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered orally or rectally, the drug is completely absorbed into the blood. The rate of absorption may be slowed when the tablets are taken with food. The maximum concentration of the active substance in the blood is achieved after 2 hours. Almost 100% of the dose taken is bound to plasma proteins.
Diclofenac quickly penetrates into soft tissues and synovial fluid. 35% of the active substance is excreted in the feces. The remainder of diclofenac is converted in the liver and leaves the body in the urine. The half-life is 6 hours. When applied externally, the substance accumulates at the site of inflammation.
Indications for use of Diclofenac 100
The list of indications for the use of tablets, gel and suppositories with diclofenac includes:
- inflammatory processes in various parts of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic joint disease, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, osteochondrosis, bursitis, tenosynovitis);
- pain syndrome of various origins (toothache and headache, sciatica, sciatica, neuralgia, muscle and joint pain, pain due to cancer);
- post-traumatic pain syndrome;
- early postoperative period, accompanied by severe pain;
- painful menstruation;
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system (inflammation of the appendages, bladder, prostate);
- upper respiratory tract infections accompanied by inflammation and severe pain (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis);
- inflammation of the middle ear.
Contraindications
The drug is not prescribed for:
- individual intolerance to the active substance or auxiliary components;
- bronchial asthma combined with sinus polyposis;
- ulcerative gastrointestinal diseases;
- frequent rectal bleeding;
- inflammatory diseases of the large intestine;
- decompensated heart failure;
- previous coronary artery bypass surgery;
- hyperkalemia;
- lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
How to take Diclofenac 100
The tablet is swallowed whole, washed down with plenty of boiled water.
The long-acting drug is taken at 100 mg per day. After reducing the intensity of pain, they switch to maintenance doses (50 mg per day).
The gel is applied to clean skin 2 times a day.
For pain in the kidneys
For diseases of the excretory system accompanied by pain, it is recommended to administer rectal suppositories.
The daily dose of diclofenac is 100 mg. The suppository is administered at night, after cleansing the intestines.
Before or after meals
It is recommended to take the tablets after meals.
Side effects when taking Diclofenac 100
The severity of side effects depends on the dosage of the drug and the individual sensitivity of the body.
Most often there are:
- signs of damage to the digestive system (unstable stool, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, increased gas formation, ulceration of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum, inflammation of the pancreas);
- interstitial inflammation of the kidneys and bladder;
- neurological disorders (headaches, poor coordination of movements, agitation, sleep disturbances, chronic fatigue, irritability, inflammation of the membranes of the brain);
- signs of damage to the respiratory system (pneumonitis, respiratory depression, attacks of bronchial asthma);
- allergic manifestations (erythematous rashes, urticaria, anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema);
- skin reactions (eczema, redness and burning in areas where the gel is applied, increased skin sensitivity to sunlight);
- dysfunction of the hematopoietic system (decrease in the number of leukocytes, granulocytes and platelets, aplastic anemia, hypoprothrombinemia);
- other undesirable consequences (increased blood pressure, impaired taste, swelling of the face and lower extremities).
Overdose
Acute overdose contributes to the development of convulsive syndrome and severe renal failure. In large doses, diclofenac has a pronounced hepatotoxic effect and inhibits the activity of the central nervous system. Treatment begins with cleansing the stomach and taking enterosorbents. Further therapy is aimed at eliminating signs of overdose and maintaining vital functions.
Features of application
During pregnancy and lactation
The drug is not prescribed in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. In the 1st and 2nd trimesters it is used with caution.
Diclofenac passes into breast milk, so breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment.
In childhood
Diclofenac is not prescribed to patients under 18 years of age.
For impaired renal function
Severe renal failure, accompanied by impaired creatinine excretion, is included in the list of contraindications to the use of Diclofenac 100.
For liver dysfunction
The drug is not recommended for use in cases of severe liver dysfunction.
Effect on concentration
Diclofenac may cause side effects that reduce reaction time and concentration. During the treatment period, they refrain from controlling complex mechanisms.
Drug interactions
With other drugs
Diclofenac slows down the excretion of cardiac glycosides and lithium preparations, so simultaneous use of these drugs is undesirable.
The medicine reduces the effectiveness of antihypertensive substances.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
When taken simultaneously with potassium-sparing diuretics, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases.
Diclofenac enhances the negative effects of cyclosporine on the excretory system.
Simultaneous administration with anticoagulants increases the likelihood of bleeding.
Alcohol compatibility
Ethyl alcohol enhances the hepatotoxic effect of diclofenac, therefore, during the treatment period, refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages.
Storage conditions and periods
Tablets, gel and suppositories are kept in a place protected from light at room temperature.
Medicines are suitable for use within 24 months from the date of issue.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Is it sold without a prescription?
It is impossible to buy Diclofenac without a prescription.
What is the price
The average price of 20 tablets is 35 rubles; 40 g of gel will cost 30 rubles; 10 rectal suppositories cost 42 rubles.
Recipe in Latin
RP: Tab. Diclofenaci 0.100 DS
Analogs
Analogues of the drug include:
- Diclofenac-Akrikhin;
- Diclofenac-Retard;
- Dicloberl;
- Diklak;
- Ortofen;
- Voltaren;
- Diclovit.
Reviews from doctors
Antonina, 47 years old, therapist, Ryazan: “Diclofenac is a time-tested anti-inflammatory drug. The action occurs quickly and lasts up to 24 hours. The drug copes well with joint pain, dental pain and headaches. Due to the high risk of liver and gastrointestinal damage, I do not recommend using the drug for more than 5 days.”
Ivan, 54 years old, rheumatologist, Moscow: “I often use Diclofenac in my practice. This medicine helps to cope with severe pain associated with deformation of cartilage and bone tissue due to arthritis and arthrosis. The low price of the drug makes it accessible to all categories of patients. The disadvantages include the frequent occurrence of side effects from the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system.”
Patients' opinions
Alina, 44 years old, Dolgoprudny: “Due to sedentary work, my back often hurts. This makes it difficult to sleep at night and move normally. In such cases I use gel with diclofenac. It begins to act approximately half an hour after application. After several uses I forget about back pain for a long time. Rarely there is redness of the skin, which goes away after a couple of hours.”
Svetlana, 38 years old, Pskov: “I take Diclofenac tablets for headaches, joint and toothaches. They are characterized by low price and high efficiency. I suffer from arthritis, which is accompanied by a feeling of stiffness and swelling of the joints. After taking Diclofenac, these unpleasant symptoms disappear.”
Leukoplakia of the bladder often occurs in a chronic form, in which healthy tissue of partial epithelium is replaced by squamous cells. Damaged areas are covered with keratinized scales; the walls of the bladder are not able to protect themselves from the aggressive effects of some components of urine.
The pathological process leads to a lot of complications and a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being. Contact your doctor for help in a timely manner, do not delay your visit. Correct therapy, in most cases, copes with unpleasant symptoms and significantly improves the patient’s condition.
- Causes
- Clinical manifestations
- Diagnostics
- General rules and methods of treatment
- Medications
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
- Folk remedies and recipes
- Surgical treatment options
- Leukoplakia of the bladder during pregnancy
- Possible complications
- Prevention measures
Causes
Disease code according to ICD-10 No. 32, translated from Greek “leukoplakia” means “white plaque”, which is associated with the appearance of altered bladder tissue. Plaques in the disease are off-white, yellowish or gray in color. The formations can be clear or with uneven edges; in advanced cases, the patient’s entire bladder is covered with such plaques.
Leukoplakia can affect other mucous membranes in the human body. The disease often occurs in women, which is due to the anatomical structure of the urethra in the fair sex.
The path of pathogenic microorganisms entering the bladder is often ascending (from the external genitalia they penetrate into the bladder area along a descending path (the infection penetrates with the influx of blood from the kidney, lymph, uterus and its appendages). In this case, the causative agent of the disease is staphylococcus, Proteus, often - Escherichia coli.
Factors influencing the development of the pathological process are:
- long-term use of an intrauterine device;
- abnormal structure of the patient’s urinary system organs;
- course of endocrine diseases;
- chronic course of inflammatory pathologies of nearby organs;
- frequent change of sexual partners, non-use of contraceptives;
- remote foci of inflammatory processes in a chronic form (tonsillitis, sinusitis, carious teeth);
- hypothermia, stress, irregular sleep;
- weakened immune system;
- age matters. More often than other patients, women after thirty years of age suffer.
Often, several negative factors together lead to the appearance of bladder ailments.
Learn about nutrition and diet guidelines for kidney stones in men and women.
Read about the symptoms of hydrocalycosis of the left kidney and the treatment of the pathology at this address.
Clinical manifestations
The main sign of bladder pathology is dull pain in the pelvic area. Many patients complain of pain when urinating. Unpleasant sensations can be of varying degrees of severity, depending on the stage of development of the disease and the characteristics of the course of the pathology. Bladder disease manifests itself as sharp pain when urinating.
During periods of exacerbation of the pathology, the symptoms of leukoplakia are accompanied by signs of acute cystitis: incomplete emptying of the urinary organ, intermittent flow, pain during urination, patients complain of a deterioration in their general condition. The symptoms of leukoplakia are very similar to cystitis, so many women experience chronic pain in the pelvic area due to improper treatment. Only through additional research does it become clear that the patient did not suffer from cystitis, but from leukoplakia.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of leukoplakia of the bladder are often confused with the clinical manifestations of cystitis, and an incorrect diagnosis is often made. A thorough diagnosis will help prevent this situation.
The correct diagnosis can be made using specific studies:
- laboratory Biochemical and general blood test: the study helps determine the level of hormones and glucose. The patient’s urine is taken for analysis to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to antibiotics; a smear from the urethra/vagina is additionally indicated (if a woman came to the appointment);
- hardware: ultrasound of organs, cystometry, cystoscopy of the bladder, urethra (sometimes a biopsy is required).
If leukoplakia of the bladder is suspected, the doctor prescribes all of the above studies. The most informative analysis is cystoscopy, which allows you to determine the specific location of the changed tissue. A punch biopsy (a piece of pathological tissue is taken for examination) allows one to reliably determine the nature of the pathology (malignant or benign), which is important for choosing treatment tactics.
General rules and methods of treatment
How to treat leukoplakia of the bladder? Difficult diagnosis complicates the treatment of pathology. After determining the root cause of the disease, the specific causative agent of the pathology, the doctor prescribes treatment. Elimination of all concomitant diseases (urological, gynecological, other organs and systems) is required.
Medications
Conservative therapy for leukoplakia of the bladder includes a set of drugs aimed at relieving unpleasant symptoms; they act on the causative agent of the disease and the affected areas of the organ.
Effective medicines:
- antibiotics of different groups (destroy pathogenic bacteria);
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- general strengthening medications that increase the body's resistance to various pathogenic microorganisms;
- Instillation (irrigation of the walls) with drugs that are analogues of glycosaminoglycans (heparin, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin) will help protect damaged bladder walls.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Procedures aimed at stopping the inflammatory process, triggering tissue regeneration, eliminating the adhesive process, which accompanies the chronic course of leukoplakia, are widely used.
Physiotherapeutic treatment includes:
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- microwave radiation.
Folk remedies and recipes
The use of natural drugs helps reduce the pathological process and restore the epithelial layer.
Proven means:
- goldenrod. Pour two tablespoons of the selected raw material into a glass of cold water and wait four hours. Drink the resulting infusion throughout the day. The duration of therapy is several weeks;
- rose hip. Take 50 grams of rosehip roots, add 400 ml of water, boil for half an hour. Cool the resulting product, strain, drink 200 ml three times a day;
- Mix flax seeds in equal proportions with honey. Take a tablespoon of natural medicine daily, washed down with water or tea.
Surgical treatment options
Failure of conservative therapy or the presence of serious complications, doctors have to resort to surgery. Sometimes the only way to eliminate pathology is surgery. In most cases, they resort to TUR (transurethral resection).
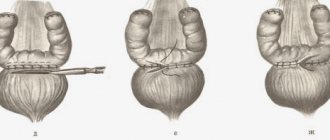
The operation is performed using a cystoscope, which is inserted into the urethra, then into the bladder cavity. A special loop at the end of the device is used to remove damaged tissue. The device is equipped with a light device, which allows the doctor to act carefully, preserving the organ, removing only unusable tissue.
Learn about the symptoms of a kidney cyst, as well as how to treat the disease with folk remedies.
Effective methods of treating acute pyelonephritis with antibiotics are described in this article.
At https://vseopochkah.com/bolezni/drugie/tuberkulez-pochek.html read about how kidney tuberculosis is transmitted and how to treat the disease.
Leukoplakia of the bladder during pregnancy
Any pathological process can complicate pregnancy. The course of the disease in the early stages of pregnancy can provoke spontaneous abortion and the development of abnormalities in the fetus, especially chlamydia, trichomonas, and papillomavirus.
The course of the disease in the second trimester of pregnancy leads to the development of complications:
- placental abruption;
- Doctors often encounter premature births;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus, anomalies of its development.
Pregnancy against the background of bladder disease proceeds pathologically. During this period, any surgical interventions are prohibited, only the use of antibacterial therapy is permitted. Full therapy is carried out after the birth of the child.
Chronic cystitis in most cases becomes the cause or consequence of leukoplakia. In case of frequent relapses of the inflammatory process in the bladder, it is recommended to undergo a biopsy of the mucous membranes of the organ to avoid the formation of cancer.
Possible complications
The danger of leukoplakia lies in the fact that the walls of the organ lose their elasticity during the inflammatory process. As a result, the bladder cannot cope with the task, it holds urine only for half an hour, then it begins to flow out. Against the background of this pathology, renal failure develops, which without proper treatment leads to death.
Also, some scientists consider pathological processes in the bladder to be a precancerous condition. Incorrect or untimely treatment of the disease can lead to the development of cancer.
Prevention measures
Special recommendations will help prevent the development of pathology:
- take care of the prevention of sexually transmitted infections, regularly visit a gynecologist/urologist;
- promptly treat pathologies of internal organs;
- strengthen your immune system.
Find out more useful information about the development features and treatment options for leukoplakia of the bladder after watching the following video:
How is surgery performed?
A TOUR of the bladder is performed under anesthesia. A cystoscope is inserted into the bladder cavity through the urethra. To prevent damage to the mucous membrane, irrigation is performed with a sterile solution that completely fills the bladder. This manipulation simplifies the visibility of the surgical field and the malignant neoplasm.
The inserted device is equipped with a special loop, which removes the tumor and damaged tissue. The cut tumor is immediately removed from the bladder. If the tumor is too large, it is removed in parts in several stages. After cutting the tumor, the surface is cauterized. This can protect against the spread of the inflammatory process and bleeding.
The resulting pathological tissues are sent for histological examination, the results of which will be ready in 5–7 days.
What you need to know about TUR operation for prostate adenoma
Transurethral resection of the prostate is a minimally invasive operation to remove pathologically overgrown prostate tissue through access through the urethra . Despite the apparent simplicity of the technique, the operation requires high professionalism of the doctor. The likelihood of developing complications after a TUR of the prostate largely depends on the type of instrument and the patient’s health status.
Indications and contraindications for TOUR
The main indication for TUR is hyperplasia (prostate adenoma). The prostate gland hugs the part of the urethra just below the opening of the bladder. As prostate tissue grows, the lumen of the urethra decreases, as a result of which the neck of the bladder suffers from oxygen starvation.
As a result, the man begins to suffer from urinary retention or leakage. TUR involves the removal of excess tissue that interferes with normal urination . The prostate itself (the capsule with tissue remains) remains in place.
It cannot be removed using the TUR method due to the extensive venous network (important venous plexuses will inevitably be damaged).
When is a TURP of the prostate gland recommended?
- Patients for whom maintaining sexual function is important.
- For obesity and the presence of cardiovascular pathologies.
- In case of relapse of adenoma.
- Localized prostate cancer (which can be completely removed from the gland).
TUR is carried out in cases where previous methods (conservative, hyperthermia) were ineffective.
The operation is performed using a resectoscope - a hollow tube through which instruments are brought into the surgical area.
Resectoscope with loop General scheme of TUR
Contraindications for TOUR:
- Arthrosis and other pathologies of the hip joints that prevent the legs from spreading to the sides (this is the position the patient is in during TUR);
- Urethral strictures (impossible to insert the device);
- Bladder capacity less than 100 ml;
- Tumors and defects of the bladder walls;
- Varicose veins of the urethra and bladder neck;
- Severe concomitant diseases.
Advantages of the TOUR:
- There are no cuts or scars.
- Short recovery period.
- The bladder is not injured.
After a TUR, the tissue can be examined for the presence of malignant cells, and after the laser it is completely evaporated.
Types of TOUR
Depending on the type of cutting element (loop), the following types of TUR are distinguished:
- Monopolar : one pole is the knife, the other is the body. To conduct impulses, liquid must constantly circulate between them. An outdated but still used method. It is fraught with severe bleeding, the development of TUR syndrome, and is dangerous for those suffering from cardiovascular diseases. Used only for TUR of the prostate with a volume of no more than 80 cm3 - to quickly remove tissue, otherwise too much electrically conductive solution will be absorbed into the blood.
Urologist, surgeon Maxim Aleksandrovich Ryabov talks about the indications, the course of the operation, and the consequences of transurethral resection of the prostate
- Bipolar : both poles are at the ends of the loop, resulting in a high temperature, effectively sealing the vessels. Saline solution is used as an auxiliary fluid, which is not dangerous to the body. You can spend more time on the operation and remove the nodes better. The method is suitable for excision of formations with a volume of up to 150 cm3, as well as for patients with cardiovascular diseases.
- Plasmokinetic : a “super pulse” is formed around the loop - a plasma corona, which compacts and seals the cut tissue, but does not overheat the surrounding tissue.
Plasmokinetic transurethral resection of prostate adenoma is recognized by most urologists as the least traumatic and most effective method of treating hyperplasia.
Preparation
List of preliminary tests (valid for 30 days):
Be sure to tell your doctor about all the injuries you have suffered to the brain and spinal cord, and about the medications you are taking. Antibiotics are prescribed before and after TUR. You should not eat food 8 hours before; on the day of surgery you must cleanse your intestines.
Operation technique
For TUR, spinal anesthesia is usually used as pain relief - an injection into the spine. During the operation, the patient may feel pressure and touch, but not pain. If there are contraindications, endotracheal anesthesia is used, in which the respiratory function is performed by a special apparatus.
Spinal anesthesia before TOUR
The patient is placed on a urological chair or operating table with his legs spread apart, the groin area is treated with an antiseptic solution and covered with sterile sheets. The groin must first be shaved or hair removed using hair removal cream.
Urethral zones
A lubricating antiseptic gel is first injected into the urethra, and then the resectoscope itself. The place to which the device is inserted is indicated in the figure below by number 5 (prostatic part of the urethra):
First, the bladder is examined, the condition of the closing sphincter is assessed, and then the hyperplasia is removed (layer-by-layer excision with a loop). Bleeding vessels are immediately coagulated (cauterized) with a loop.
Cutting tissue during TUR
The doctor monitors all actions on the monitor. In a number of clinics there are two of them, one of which is turned towards the patient if he is under spinal anesthesia and wants to see the progress of the operation.
Source: https://muzhchina.info/prostata/adenoma/tur
Postoperative period after TOUR
The postoperative period is the most important. If medical recommendations are not followed, the likelihood of developing complicated situations increases significantly.
Immediately after the operation, the patient is fitted with a system that washes the bladder with a special solution. The solution is supplied through one channel, and exited in another way. The system is removed when a clean solution, without blood clots, enters the urinal. The duration of bladder cleansing is 3–5 days. After removing the catheter, it is necessary to monitor the quality of urine. It should be a light shade. It is unacceptable for blood to appear in the urine.
On the first day, the patient is allowed to drink up to 1.5 liters of water, but only if there is no nausea or vomiting. You need to drink in small sips. After 24 hours, the patient can eat food, but must adhere to a strict diet.
It is forbidden to eat salty, fried and smoked foods, any baked goods, and saturated fatty broths. Juices, teas, fruit drinks can be drunk in unlimited quantities.
To prevent infection of the body, the patient is recommended to take antibacterial drugs prescribed by the doctor.
Until complete recovery, the patient is prohibited from lifting weights, moving a lot, playing any sports, driving a car, and any sexual activity is not recommended.
Urological condom after prostate surgery
Indications for surgical removal of prostate adenoma are:
- Severe narrowing of the urethra with disruption of the bladder, when a large volume of urine is retained in the latter;
- Bladder stones;
- Chronic kidney failure;
- Acute urinary retention, repeated many times;
- Bleeding;
- Infections and inflammatory changes in the organs of the genitourinary system.
For large tumors, when the volume of the prostate exceeds 80-100 ml, the presence of many stones in the bladder, structural changes in the walls of the bladder (diverticula), preference will be given to open and the most radical operation - adenomectomy.
If the tumor and gland do not exceed 80 ml in volume, then transurethral resection or dissection of the adenoma can be done. In the absence of a strong inflammatory process, stones, or small adenoma, endoscopic techniques using a laser or electric current are preferred.
Like any type of surgical treatment, the operation has its contraindications, including:
- Severe decompensated pathology of the heart and lungs (due to the need for general anesthesia, risk of bleeding);
- Acute renal failure;
- Acute cystitis, pyelonephritis (operate after the elimination of acute inflammatory phenomena);
- Acute general infectious diseases;
- Aortic aneurysm and severe atherosclerosis.
It is clear that many contraindications can become relative, because the adenoma needs to be removed one way or another, so if they are present, the patient will be referred for preliminary correction of existing disorders, which will make the upcoming operation the safest.
The main indication for TUR is hyperplasia (prostate adenoma). The prostate gland hugs the part of the urethra just below the opening of the bladder. As prostate tissue grows, the lumen of the urethra decreases, as a result of which the neck of the bladder suffers from oxygen starvation. As a result, the man begins to suffer from urinary retention or leakage.
When is a TURP of the prostate gland recommended?
- Patients for whom maintaining sexual function is important.
- For obesity and the presence of cardiovascular pathologies.
- In case of relapse of adenoma.
- Localized prostate cancer (which can be completely removed from the gland).
TUR is carried out in cases where previous methods (conservative, hyperthermia) were ineffective.
The operation is performed using a resectoscope - a hollow tube through which instruments are brought into the surgical area.
Resectoscope with loop
Contraindications for TOUR:
- Arthrosis and other pathologies of the hip joints that prevent the legs from spreading to the sides (this is the position the patient is in during TUR);
- Urethral strictures (impossible to insert the device);
- Bladder capacity less than 100 ml;
- Tumors and defects of the bladder walls;
- Varicose veins of the urethra and bladder neck;
- Severe concomitant diseases.
Advantages of the TOUR:
- There are no cuts or scars.
- Short recovery period.
- The bladder is not injured.
After a TUR, the tissue can be examined for the presence of malignant cells, and after the laser it is completely evaporated.
Removal of the prostate is performed in cases where conservative therapy is powerless. In most cases, this is an oncological process. Sometimes prostatectomy is performed for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Enlargement of an organ due to inflammation is not a reason for surgery. The following indications for prostate removal are distinguished:
- Initial stages of prostate cancer.
- Calculous prostatitis is accompanied by urination problems and hematuria.
- Benign organ hyperplasia - adenoma.
Cancer is considered the main indication for organ removal. Prostatectomy is performed only for stages 1 and 2 of the disease. In these cases, the oncological process is limited to the prostate tissue.
If the prostate is not removed promptly, the cancer can spread throughout the body.
The operation is performed on men under 70 years of age, since somatic pathologies are contraindications to its implementation.
Prostate adenoma leads to enlargement of the organ. As a result of this disease, sexual weakness and impaired urination are noted. If benign hyperplasia progresses and therapeutic treatments are ineffective, prostatectomy is performed.
There are several ways to remove the prostate. The choice of method depends on the prevalence of the pathology. Removal of an organ can be complete or partial. Surgical options include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate gland. It is characterized by partial removal of tissue, which is performed through the urethra. Resection is performed laparoscopically. It is performed for benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Prostate incision. Such a surgical intervention involves dissection of organ tissue. It allows you to expand the lumen of the urethra and prevent compression of the urethra. An incision is made in the prostate gland, but the organ is not removed.
- Radical prostatectomy. It is carried out for tumor formations and severe benign hyperplasia. The gland is removed together with the lymph nodes. Access to the organ can be different - perineal, suprapubic and retropubic. Open surgery is dangerous due to the development of complications.
- Laser intervention. It is considered more preferable as it reduces the risk of bleeding. Laser removal of the prostate is performed for benign prostate hyperplasia. There are several methods for performing this manipulation. Among them are vaporization (evaporation), enucleation and laser resection of adenoma.
Currently, less traumatic surgical procedures are preferred. These include laser removal of adenoma and transurethral resection. However, in some cases it is impossible to replace open surgery with other methods.
Possible complications
The first 2 weeks after a TUR of the bladder, you may experience unpleasant symptoms during urination:
- small portions of urine outflow;
- burning and pain in the urethra;
- frequent and unbearable urge to urinate.
If after two weeks such manifestations have not disappeared, you should consult your doctor. The presence of blood in the urine can last up to three weeks. In this case, you need to drink more fluid so that the ureter is washed out faster.
If blood in the urine is observed for more than three weeks, you should consult with your doctor, as this may be a sign of complications after TUR of the bladder or the opening of internal bleeding.
It takes a long time for complete recovery after surgery. Doctors recommend avoiding sex, physical activity, and eating fatty foods. The patient needs to be regularly examined by the attending physician in order to monitor the general condition of the body and prevent a possible relapse of the development of a malignant or benign tumor. Further drug therapy depends on the histological diagnosis and test results.
Possible consequences
After surgery, a variety of undesirable effects may occur. Their number and severity are directly influenced by the individual characteristics of the patient. In most cases, the consequences of transurethral removal manifest themselves as:
The above symptoms may occur when emptying the bladder or involuntarily. To eliminate problems with bladder emptying, it is recommended that a person drink still water in large quantities.
In some cases, patients may experience severe bleeding. That is why after surgery, blood pressure and pulse rate are constantly monitored, which makes it possible to immediately provide first aid.
If a large cancerous formation is removed, this leads to the presence of one or more holes in the walls. They should tighten, after which the urination process will improve. For this purpose, a catheter or a special cystostomy device is installed.
Due to individual characteristics or if the operation is performed incorrectly, the patient may experience undesirable consequences, which are recommended to be eliminated in a timely manner.
conclusions
Transurethral resection is a gentle surgical technique. The operation has a number of advantages, including:
- no damage to the skin and soft tissues;
- speed of the operation;
- accuracy of histological diagnosis;
- complete elimination of malignant formation.
Before surgery, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis and be examined by a therapist and anesthesiologist to identify concomitant pathologies. If there are any contraindications and the tumor is not operable, the attending physician resorts to other treatment methods.
Why is the tour scheduled?
Indications for resection are:
- excision of urinary tumors;
- examination of the neoplasm (characteristics of tumors, severity of lesions) - this is an important nuance for prescribing subsequent therapy;
- general diagnosis for concomitant diseases, examination of the urinary cavity for the occurrence of a tumor process;
- taking material for analysis; the need to study the material to identify cells of a malignant nature.