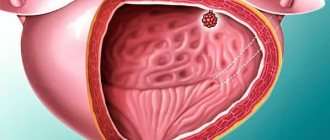
Bladder puncture is one of the optimal ways to empty the bladder. The fact is that there are a number of diseases in which a person cannot empty his bladder on his own. This negatively affects not only the organ, but also the body as a whole. Suprapubic puncture may also be prescribed for diagnostic purposes. It is believed that this technique is the most informative.
There are a number of contraindications on the basis of which puncture is not performed, but if you follow all the rules, the risk of complications is minimal.
Indications
Suprapubic bladder puncture has the following indications:
- inability to perform bladder catheterization;
- acute urine retention combined with the inability to empty the bladder naturally;
- severe injuries to the urethra;
- the need to obtain urine for laboratory testing (during the puncture process, urine is collected that has not come into contact with the reproductive organs, which will make it possible to see the most accurate picture of the pathological process when performing the analysis).
Suprapubic bladder puncture is an emergency procedure that is often performed in urological practice. The procedure is usually prescribed to patients who are unable to empty their bladder naturally. However, not so long ago the number of indications for puncture has increased.
During this procedure, the urologist frees the bladder from the biofluid accumulated in it by evacuating it through the abdominal wall. The procedure is carried out by puncturing the bladder with special medical devices.
Consequences and possible complications
When performing a puncture, there is a possibility of bleeding from the vessels of the bladder. But when the operation is performed correctly, this rarely happens. There is also a risk of injury to the abdominal organs and intestines. Today, puncture in many hospitals is carried out using a modernized method: ultrasound is used to control the process.
Specific complications include:
- Development of cellulitis of fiber.
- Bladder perforation.
Urine gets into the fiber that is located around the bladder.
The quality of the operation and its consequences depend on the surgeon. Therefore, the manipulation must be performed by a competent and experienced doctor.
Contraindications
- bladder injuries, bladder rupture;
- slight fullness of the bladder;
- tumor processes in the organs of the genitourinary system (both cancerous and benign);
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- operations in the area of the white line of the abdomen, undergone in the past;
- severe prostatitis, prostate abscess;
- pregnancy;
- problems with hemocoagulation;
- severe obesity;
- rapid course of cystitis;
- bladder tamponade;
- the presence of purulent wounds or scars in the area in which the intervention should be carried out;
- inguinal hernia;
- adhesions in the lower abdominal cavity;
- advanced form of ascites;
- displacement of the peritoneal organs or pathological increase in their volume.
Who is contraindicated for manipulation?
Bladder puncture, like other interventions in the human body, has a number of contraindications:
- incomplete filling of the organ cavity;
- coagulopathy;
- pregnancy;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- infection of the dermis at the puncture site;
- pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- cystitis;
- inguinal hernia, femoral hernia;
- displacement, stretching, enlargement of abdominal organs;
- previous surgery, where the peritoneal wall was cut along the line below the navel.
If the bladder is empty or half empty, the procedure is prohibited, as the risk of consequences increases;
Progress of the operation
If the bladder is full, puncture is performed quickly and easily. When there is a significant accumulation of urine in the organ, it increases. As a result, the walls of the bladder can reach all the way to the navel. It is also worth noting that the anterior wall of the bladder is absolutely not protected. It is not covered by peritoneum, and it simply adheres to the abdominal muscles.
Before starting the procedure, the patient lies down on the couch. At the same time, the sacrum rises slightly. The area in which the puncture will be performed is treated with an antiseptic solution. There should be no hair at the site of the operation, so if the patient has any, it is shaved off.
Next, through palpation examination, the urologist determines the highest point of the bladder and its approximate location. In some cases, a specialist may perform an ultrasound.
During the intervention, the patient does not feel any discomfort or pain, because a procedure such as bladder puncture requires preliminary local anesthesia. An anesthetic medication is injected into an area located approximately 4 cm above the pubic symphysis. The anesthetic is injected extremely carefully, along the midline of the abdomen.
To puncture the bladder itself, the doctor uses a needle, the length of which is 12 cm and the diameter is 1.5 mm. This instrument is inserted slowly and extremely carefully. The urologist gradually punctures the aponeurosis, muscles, fat and ultimately the bladder wall.
Having felt a puncture of the bladder, the urologist will advance the needle about 5 cm more and evacuate the biofluid. He can do this using a syringe or tube placed on the cannula of a needle. The removal of urine from the bladder should occur slowly, as haste can cause bleeding. To make the cooling process as easy as possible, the patient needs to turn on his side and lean forward slightly.
After all urine has been removed, the puncture site is disinfected and isolated from the external environment using a bandage. This will help avoid infection. If necessary, capillary puncture of the bladder can be repeated up to 4 times a day for 5-7 days.
Bladder puncture in men with adenoma
Have you been struggling with PROSTATITIS and POTENTITY for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day.
To improve potency, our readers successfully use M-16. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
According to statistics, every second man in old age and every third on average are faced with diseases of the genitourinary system.
Prostatitis is considered the most common; in addition, there are a number of diseases that seriously complicate the process of urination and are also difficult to diagnose in the laboratory.
To facilitate the examination process, bladder catheterization is used in men.
In general, the bladder catheterization algorithm involves inserting a small silicone tube into the bladder cavity through the urethra.
For certain indications, a catheter can be inserted not through the urethra, but by penetrating the peritoneum.
Also, such a procedure involves not only helping the patient, but also helping specialists in determining the origin of a particular illness, after which the correct approach to therapy is possible.
What is this procedure and why is it performed?
Bladder catheterization is one of the ways to maintain the functions of this internal organ during the period of treatment and recovery of the patient.
There are a number of diseases of the genitourinary system, as a result of which a man is unable to empty the bladder on his own, or the process of urination causes him severe pain and discomfort.
In this case, the catheterization technique is an indispensable procedure.
The purpose of this procedure is to completely empty the bladder, as well as administer drugs prescribed by a doctor and wash this internal organ if necessary. This procedure is actively used in the treatment of urological problems in men and women, and bladder catheterization in children is also acceptable.
Indications for the procedure
In order for the procedure to benefit the patient and also help the specialist in determining the etiology of the problem and making a diagnosis, it is necessary to use it only for specific reasons.
Indications for bladder catheterization are as follows:
- stones in the bladder, tumors, and adenoma;
- inflammatory process (cystitis);
- state of coma or shock;
- recovery period after surgery;
- for diagnostic purposes;
- for the purpose of administering drugs during treatment.
Only under such prerequisites can a specialist advise the patient to undergo catheterization, otherwise such intervention in the body can lead to complications.
Types of catheters
An experienced specialist, before carrying out such a procedure, must discuss the concept and goals of catheterization with the patient as a preliminary consultation. Next, it is necessary to consider the types of catheterization in order to select one or another option on an individual basis, taking into account the age, gender and health status of the patient.
Today, the following types of catheterization are provided:
To improve potency, our readers successfully use M-16. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
- rigid metal catheters;
- silicone catheters;
- rubber catheters 24-30 cm long.
In any case, the choice remains with the specialist as to how appropriate it is to perform catheterization with a soft catheter or a hard one, and in what cases each type of instrument is used.
In addition, catheters are divided into several types according to design details:
- The Robinson (Nelaton) catheter is a simple direct insertion method that is used for short-term catheterization in uncomplicated clinical situations.
- Thiemann system catheter - used in difficult clinical situations, such as adenoma, stenosis of the urethral canal. This rigid catheter is used due to its curved tip to allow passage.
- A Foley catheter is a flexible instrument with a special balloon that allows the device to be held. Such a balloon is used for bleeding from the source of the adenoma after it is removed by the surgeon.
- Petzer system catheter - this version of the catheter is used much less frequently than others, but usually for cystostomy drainage. That is, a separate tube is supposed to come out, bypassing the urethra.
For each type of catheter, a certain size, diameter, and overall dimension are assumed. Thanks to this variety, it is possible to eliminate the risks of trauma to the urethra and cases of blockage of catheter tubes.
Bladder catheterization algorithm
Performing catheterization on a woman or performing catheterization on a man are two completely different technologies that require a specialist to have knowledge, skills and experience in such matters. As for men, medicine provides certain rules for catheterization, that is, an algorithm. It consists of the following manipulations:
- first, the doctor must wash and disinfect his hands with chlorhexidine, and then put on medical gloves;
- the tip of the catheter is lubricated with a special moisturizer, liquid sterile glycerin or Vaseline (sterile lubricant);
- the man’s anus and external genitalia are washed;
- the patient needs to lie on his back, then spread his legs bent at the knees to the sides;
- the penis is treated with furatsilin;
- the soft catheter used is gradually inserted into the external opening of the urethra, after first retracting the foreskin and squeezing the glans penis in the area of the subcoronal groove, the skin of the glans must be pulled back (this will expand the urethral canal);
- after this, the specialist inserts the instrument further, slowly turning the catheter tube, thereby accompanying its advancement;
- if drops of urine appear at the drainage end of the catheter, then the procedure is being performed correctly;
- After precise adjustment of the tube, it is connected and fixed to the urinal of the device.
The technique of performing a metal catheter involves other methods of implementation:
- the rounded catheter is inserted downwards into the urethra;
- forward-directed drainage is inserted in such a way that the inclination of the penis is oriented towards the abdomen, as if pushing itself onto the catheter;
- if the end of the drain is brought to the posterior side of the urethra, a vertical landmark of the catheter is necessary to achieve penetration into the membranous region;
- in the process of penetration, the membranous section turns, its outer edge must be moved away from the abdomen by the doctor, thereby penetrating into the prostatic section and the bladder next.
Such manipulations are much more complicated than the first catheterization option, so they can only be performed by a doctor with experience in performing such manipulations.
Possible complications
Procedures such as catheterization and puncture have certain contraindications. If you do not take them into account, medical procedures can cause harm to health if the following negative factors contribute to this:
- insufficient compliance with antiseptic and aseptic standards;
- exaggerated force during insertion of the catheter tube;
- non-compliance with the algorithm for introducing the device;
- insufficient examination of the patient by a doctor.
As a result of such errors, catheterization can lead to serious complications, such as cystitis and urethritis, trauma, perforation and rupture of the urinary canal.
Since rinsing the bladder through catheterization is appropriate for purulent foci and inflammation of cystitis, tumors and stones, the doctor must carefully treat everything with antiseptic solutions.
It is also important to observe the length of time the instrument remains inside the urethra, as this can lead to injury to the mucous membranes, and the bladder becomes infected after catheterization.
Source: https://gemoglobin.top/prokol-mochevogo-puzyrja-u-muzhchin-pri-adenome/
Technique for performing renal cyst puncture
Before proceeding with the puncture, the patient undergoes all necessary tests. The technique is as follows:
- Depending on the location of the cyst, the patient lies on his stomach or side.
- Conducting local anesthesia. The puncture area is disinfected with a medical solution and then numbed.
- Preparing the ultrasound machine. This process is possible because the puncture needle has a special tip, which is visible on the screen of the ultrasound machine. This innovation allows for the most accurate removal of liquid.
- In preparation for surgery, the results of the study, in addition to the puncture zone, also determine its depth. This is necessary to prevent injury to blood vessels, organ parenchyma and other complications. Therefore, a mark is made on the needle, deeper than which entry is prohibited.
- Upon completion, the doctor makes a small, neat incision on the surface of the dermis, moves the tissues apart, fixes them, makes a puncture with a needle and removes the substance from the cyst capsule.
What could be the consequences?
Puncture of a kidney cyst is an operation carried out in accordance with all the necessary rules for carrying out interventions in the human body. The procedure is performed only in a clinical setting, after which the patient remains in the hospital for 3 days under the supervision of medical personnel. Usually, after this therapy, the patient recovers quickly and safely.
During the rehabilitation period, an increase in body temperature and swelling in the puncture area may be observed, which quickly disappear. Since the entire process is controlled by an ultrasound machine, miscalculations are excluded - puncture of the pelvis, large blood vessels. However, complications can still occur:
- bleeding into the renal cavity;
- opening of bleeding into the cyst capsule;
- the onset of purulent inflammation due to infection of the cyst or kidney;
- organ puncture;
- violation of the integrity of nearby organs;
- allergy to sclerosing solution;
- pyelonephritis.
Development mechanism
How the process develops largely depends on the origin of the pathology. For example, with a sudden rupture of the prostate capsule, the process proceeds as follows. Rupture and tension of the capsule occurs due to the growth of the prostate gland and obstruction in it.
There is constant pressure on the muscle that relaxes the bladder, as well as on the neck of the bladder. It is formed due to the fact that it is necessary to overcome infravesicular blockage. Changes in pressure inside the bladder and a large volume of the prostate gland create conditions that lead to capsule rupture. As a result, hematuria occurs.
Suprapubic puncture or bladder puncture is an emergency procedure that is often used in medical practice. This procedure is required when patients are unable to empty their bladder naturally. Recently, indications for puncture have become more numerous. The procedure is considered one of the safest compared to other methods of collecting urine. Puncture allows you to quickly empty the patient’s bladder of excess fluid by collecting it through the abdominal wall. The operation is carried out using a puncture method using special instruments.
Injection of sclerosing solution
Provided that the disease is not accompanied by inflammatory or purulent processes, then after pumping out the liquid, a sclerosing agent is injected into the empty space. Ethyl alcohol is often used for this. Its amount is equal to the 4th part of the volume of cystic fluid.
The injected solution is left inside the capsule cavity for 5 to 20 minutes (depending on the characteristics of the pathological disease), then removed. This is necessary to kill the cells that secrete cystic fluid and “glue” the cavity. Meanwhile, when the sclerosing solution is in the kidney, the patient experiences a burning sensation and pain.
When fluid is removed from the formation, it may contain blood and pus. The reason for this phenomenon is trauma that led to the formation of a cyst. In this case, after pumping out the liquid from the formation, drainage is installed, the cavity is washed and sanitized.
The drainage is left for 3-5 days to allow the inflammatory process to subside. Sclerosis is carried out 4 times, leaving the substance for 2-3 hours. Having completed the entire complex of manipulations, the drainage is removed.
Methodology
Specialists place the patient on the operating table depending on the location of the tumor.
The entire kidney puncture operation is carried out strictly under ultrasound supervision. Before inserting the needle, the doctor determines the puncture site and its angle. The device also allows for the depth of the puncture.
A specialized needle has a fixing tip that will prevent you from plunging deeper into the cyst than necessary. This procedure will help avoid unpleasant moments.
Once the patient has been given anesthesia, the specialist will make a small incision on the patient’s skin, then use a clamp to spread apart the skin tissue and subcutaneous fat. This procedure allows you to quickly restore skin tissue and shorten the rehabilitation period.
After penetration into the cyst, the wire aspirates the liquid contents.
If during puncture the cyst cavity is filled with pus, then drainage is installed and the cavity is completely sanitized. Then, a week later, sclerosing fluid is injected.
When the cyst cavity is absolutely clean, it is filled with sclerosant. Typically this is a volume of 20 to 25% of the initial volume.
During and after surgery, complications may occur in the form of bleeding inside the cyst. The amount of blood loss varies.
Experts warn the patient that if antiseptic rules are not followed, an inflammatory process may develop, with the formation of pus.
The patient lies down on the operating table. The position of the body depends on the location of the tumor. Then the doctor treats the surgical field with antiseptics and injects local anesthetics.
When performing a puncture, precision is required. It is very important not to touch the kidney parenchyma and blood vessels with the needle. Therefore, the entire procedure is carried out under ultrasound control. Using ultrasound, the surgeon determines the required depth and location of instrument insertion. After this, the doctor puts a special clamp on the needle.
The surgeon makes a small incision in the skin with a scalpel. The doctor then spreads the tissues apart and secures them with clamps. A needle is placed through the incision into the cystic cavity and the contents are evacuated.
The puncture is supplemented with the following procedures:
- sclerosis;
- drainage.
As already mentioned, the tumor may reappear after puncture. A kidney cyst of 3 cm or more often recurs. Therefore, in many cases the procedure is supplemented with sclerotherapy. An ethanol solution is injected into the cystic cavity. The amount of sclerosing agent should be 1/4 of the volume of removed fluid.
Ethyl alcohol is left in the cyst cavity for 5 to 20 minutes. During this time, the cells of the cyst walls die and stop producing fluid. The ethanol is then removed. If the procedure was carried out successfully, the walls of the cystic cavity stick together. This minimizes the likelihood of relapse of the pathology.
If pus or blood is found in the removed cystic fluid, then immediate sclerotherapy is contraindicated. In this case, drainage is done first. Special tubes are inserted into the cavity and it is cleaned and washed.
The drainage is left for 3 to 5 days until signs of inflammation completely disappear. During this time, the sanitation is repeated several more times. Then a sclerosing agent is injected and the drainage tubes are removed.
How painful is the procedure? This question interests many patients. Here is the opinion of those patients who had a kidney cyst punctured. Reviews report that no pain occurs during puncture and removal of fluid. This is due to the fact that the procedure is performed under local anesthesia. However, when a sclerosing agent is injected, most patients experience a strong burning sensation.
Carrying out diagnostics and a therapeutic course in some cases requires installing a catheter in the patient’s bladder. Most often, the tube is inserted through the urethra, but it is also possible to place it through the abdominal wall, located in front. The catheter performs the following important functions:
Postoperative period
Reviews of kidney cyst removal by puncture note that after the procedure, many patients had a fever. In addition, a large hematoma usually forms at the puncture site. However, such symptoms should not cause concern. This is the body's natural reaction to surgery. After a few days, the fever goes away, and the hematoma resolves within 1 to 2 weeks.
If the puncture went without complications, the patient is discharged from the hospital 2 to 3 days after the procedure. If drainage was used during the operation, the hospital stay may last up to 7 days.
At home, the patient must take antibiotics to prevent possible infection.
Within 7–10 days after discharge from the hospital, you must also follow the following recommendations:
- Wear a special bandage.
- Avoid physical activity.
- Do not take alcohol or diuretics.
- Eliminate spicy and salty foods from your diet.
2 weeks after the puncture, the patient must visit the doctor for an ultrasound examination. This is necessary to monitor the condition of the cavity.
If, during an ultrasound examination, the patient is determined to have re-production of cystic fluid, then dynamic observation is necessary for 2 months. If this process continues for six months, then the puncture is performed again. However, relapses of pathology after sclerotherapy are quite rare.
The development of specific complications after puncture is a rare occurrence. However, if medical workers neglected the rules of asepsis, then the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms leading to inflammation is likely.
Serious complications include:
- abdominal puncture;
- bladder perforation;
- injuries to organs located near the puncture organ;
- urine getting into the fiber that is located around the organ;
- purulent-inflammatory process in the fiber.
Despite possible complications and risks, puncture is sometimes the only method of helping the patient. The quality of its implementation and the patient’s postoperative period almost entirely depend on the experience of the surgeon.
If the postoperative course is successful after puncture of the cystic formation, the patient is discharged from the hospital on the 3rd day. After 14 days, the patient must undergo an ultrasound scan. During the examination, the doctor will evaluate the healing process (scarring) and whether a relapse has occurred.
If cystic fluid re-forms, nothing is done for 60 days, only monitoring is carried out. If the process progresses for more than 6 months, the patient is prescribed a repeat operation. However, the re-formation of cysts is an extremely rare phenomenon, which depends solely on the individual characteristics of the human body.
Any operation, even the most minor one, is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of tissues and interference with the functioning of internal organs. The recovery period after surgery can last about a month, depending on the characteristics of the body. Rehabilitation after puncture requires less time than other types of surgical intervention.
Within a few days after the procedure, the patient is discharged from the hospital. After 2 weeks, he is recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination in order to monitor the process of tissue healing and re-cyst formation.
At the early stage of recovery after puncture, there may be an increase in body temperature and pain in the puncture area on the abdomen. To relieve discomfort, painkillers are prescribed. In some cases, patients experience weakness, nausea, and bloating. After a few days, the symptoms go away on their own.
During the recovery period, the patient is advised to avoid any physical activity, maintain bed rest and proper nutrition. The diet should contain mainly easily digestible foods: low-fat kefir, crackers, soups, broths, boiled meat and fish.
Recurrent development of pathology is extremely rare and depends on the individual characteristics of each person’s body.
Main stages of the procedure
Suprapubic capillary puncture of the bladder in men and women is performed as follows:
- The patient lies on his back.
- The level of the upper part of the bladder is determined.
- Local anesthesia in the form of a novocaine solution is injected under the skin. Moreover, anesthesia is done in stages for each layer (skin, subcutaneous tissue, aponeurosis, muscles and prevesical tissue).
- Simultaneously with anesthesia, a needle begins to be inserted strictly perpendicular to the anterior pubic bone.
- After the needle has deepened 4-5 centimeters, urine should appear from the tube attached to the other end of the needle.
- To avoid bleeding from the blood vessels of the bladder, which can occur as a result of a rapid decrease in pressure, periodically clamp the outlet tube.
- After the bladder is completely emptied, the needle is removed and the puncture site is covered with a sterile napkin.
Trocar cystostomy of the bladder in men: operation, care – Website about
21.11.2019
The operation can be carried out either planned or urgently - after installation of the system, the patient is explained how to care for the cystostomy so that there are no complications. Bladder cystoma in men does not affect life expectancy, although it makes adjustments to the patient’s daily life.
What is a cystostomy
This catheter is more comfortable, flexible, does not create discomfort and has a lower percentage of complications. The entire installation process takes about an hour and is carried out in the clinic under anesthesia.
Advantages and disadvantages
- catheterization and evacuation of urine through a tube in the abdomen does not have a negative effect on the urethra, but with prolonged excretion of urine through a regular catheter, complications arise - in this, a suprapubic cystostomy definitely wins;
- the location of the urethral balloon near the neck of the bladder inevitably leads to further leakage of urine and its removal out along the outer walls of the catheter, which does not occur with a cystostomy;
- careful handling of the catheter significantly reduces the risk of it being pulled out;
- when the suprapubic catheter is obstructed, there are additional ways - the outflow of urine can be established through the urethra (very often such catheterization is carried out urgently if the patient cannot cope with the maintenance of the epicystostomy on his own);
- when installing a suprapubic cystostomy, men have the opportunity to be sexually active;
- It is easier for patients to maintain a catheter at the level of the suprapubic zone than below - caring for a cystostomy is possible without outside help, which cannot be said about catheterization through the urethra;
- the procedure for applying a cystostomy is not traumatic - if it is necessary to remove the tube from the bladder, then after the stoma a small scar remains, almost invisible;
- To prevent the possible consequences of tube blockage, a larger diameter, more suprapubic catheter can be used, which cannot be inserted into the urethra.
Disadvantages of the procedure
- in patients in the area where the cystostomy is applied, skin sensitivity increases, but most patients note that the discomfort goes away after a while;
- if a cystostomy is used incorrectly, there is a possibility of pushing the tube into the urethra and damaging it, but such cases are rare;
- some men may have problems with installation if they have significant body weight or fat deposits in the suprapubic area;
- the place where the tube is installed sometimes gets wet - this can be easily eliminated if you apply a bandage, but in other patients the wetting stops on its own;
- in rare cases, a suprapubic catheter causes spasmodic contractions of the bladder;
- there is still a risk of tube clogging, so men should carefully care for the system;
- According to some patients, cystostomy is less convenient than frequent catheterization, but this point of view is subjective.
Indications and contraindications
- if a man has an injury to the urethra or penis, which does not allow urine to be excreted;
- if a false urethra is present;
- if the patient has pathology of the bladder neck;
- if long-term catheterization is necessary in order to continue social activity and intimate life;
- for certain categories of patients with limited mobility (wheelchair users);
- if there is a need to frequently take urine samples for analysis, this is done through an intake valve;
- patients who cannot self-catheterize.
Contraindications to the installation of a urinary stoma are incorrect location of the organ, a history of hemophilia, detection of a tumor in the bladder itself or directly next to it. The reason for refusing to install a stoma may be the patient's excess weight if it interferes with the normal functioning of the system.
Installation process
- A bladder stoma is performed in a medical facility.
- Before performing surgery, doctors explain to the patient what tests need to be taken and how to properly prepare for the procedure.
Preparing for cystostomy
For those who are recommended for elective surgery, doctors prescribe the following tests:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- Ultrasound examination.
If there is a history of diabetes mellitus, the patient is examined by an endocrinologist. Before surgery, a man needs to drink a lot of fluid, then the organ will fill and straighten.
Progress of the operation
The operation is carried out in the following sequence:
- the skin in the puncture area is treated with an antiseptic;
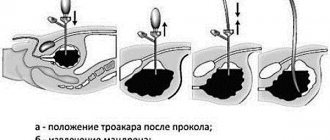
- a trocar is inserted into the formed hole along with a cystostomy;
- the trocar is removed, and the catheter itself remains in the bladder. It deepens approximately 2 cm from the walls of the organ to the inflating balloon;
- the outer edge is attached to the skin.
After the operation, the edges of the wound are treated. If a laparotomy was performed, sutures are placed and a urinal is attached. By the activity of urine excretion there, one can judge the correctness of the installation of the cystostomy.
Caring for a cystostomy
To ensure that the tube does not cause problems for the man and complications arise, it is necessary to properly organize care at home. This process is simple, but requires a responsible approach to performing all actions and strictly following all the recommendations of the urologist.
Here are some tips to help keep your cystostomy clean:
- any manipulations with the catheter must begin with washing your hands - it is very easy to get an infection, even if your hands visually seem clean;
- if the urine bag is attached to the leg, then it must be emptied when it is filled to half the volume;
- if urine is not collected in the receiver, but goes straight into the toilet, the catheter valve must be wiped every time;
- the skin in the pubic area must be washed twice a day, and more often if necessary (for example, in hot weather, with excessive sweating), keep an eye on the bandage around the tube - it can be removed after the hole has healed, but if the man continues to use the bandage, the fabric should remain clean;
- as a hygienic procedure for cystostomy, it is best to choose a shower rather than a bath - it can be taken daily, and the tubes themselves should remain in place during the washing process; it is necessary to rinse the catheter without bending or stretching, so that microcracks do not appear;
- Every day, patients need to drink at least 2 liters of water - this will make it possible to activate the functioning of the kidneys, promptly remove urine from the body and reduce the concentration of salts in the urine, which can be deposited on the surface of the tube and clog it;
- You should not drink large quantities of liquids that irritate the bladder: carbonated drinks, sour fresh juices, coffee and strong tea, you also need to protect yourself from constipation; To prevent accidental pulling out of the catheter, adhesive tape (surgical tape) is used;
- if the urinal is attached to the thigh, it needs to be moved from one leg to the other several times a day;
- on a long trip on vacation or on a business trip, it is recommended to take a second catheter with you in sterile packaging in order to change it in an emergency;
- during sexual activity, make sure that the tube does not move, then men get used to its presence;
- if a man wants to swim in the pool, it is recommended to change the urine bag to a smaller one at this time.
How to recognize complications in time
In order to prevent complications, doctors recommend training the bladder. The training is carried out after trocar puncture on the third day, after laparotomy - on the sixth day. In the future, the doctor will give all recommendations regarding the frequency of such training.
In parallel, it is important for patients to monitor urodynamic control indicators - they will help signal the onset of pathological processes and eliminate them in a timely manner. If there is a suspicion of a violation of urine formation, patients should immediately contact the clinic, where a control urine sample will be taken, a diagnosis will be made and appropriate treatment will be provided.
You also need to pay special attention to caring for the cystostomy - if everything is done correctly and in a timely manner, then complications during the use of the catheter will not arise.
Life expectancy with a cystostomy installed
Patients are often worried about how to live with a catheter so as not to harm their health. Of course, a hole in the skin with a direct entrance to an internal organ at first leads patients almost into a state of panic, especially at the postoperative stage, when the tissues are swollen and painful.
Not everyone believes that they can handle catheter care themselves. In fact, you can take care of your bladder stoma yourself, and the catheter in no way affects your life expectancy, although it requires special attention to your health.
Prevention of complications
As already mentioned, the main method of prevention is training the organ. It is also important to observe the rules of hygiene when caring for a cystostomy, because in some cases complications arise due to patients’ failure to comply with basic hygiene rules.
The catheter must be changed in a timely manner, and if the tube becomes clogged, the tube must be changed immediately, observing the state of health and one’s own sensations. If you have a fever and pain in the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor. Installed cystostomies do not cause problems if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Performing a cystostomy and installing a catheter to remove urine is a serious step that doctors decide to take in the absence of alternative treatment for the disease.
Patients should not despair - many people live with a cystostomy and lead almost the same lifestyle as healthy patients.
But the use of a catheter allows patients to live, because without it, the urinary organs will stop working, intoxication and death will occur.
Source:
Care with trocar cystostomy
Trocar cystostomy is a vital operation that is performed under local anesthesia. The indication for its implementation is acute urinary retention, which has developed against the background of various diseases. Below we will present the indications for the operation, the nuances of cystostomy, patient care after it, as well as possible consequences.
Trocar cystostomy involves installing a cystostomy, a medical instrument in the form of a catheter. The installed cystostomy temporarily takes over the functions of the urinary canal.
Below we discuss in what cases a patient requires a trocar cystostomy, or epicystomy.
Indications for trocar cystostomy
The purpose of a cystostomy is to help drain urine that has accumulated in the bladder. Indications for installation of a urinary catheter are:
The patient's inability to empty the bladder naturally
The cystostomy method is an alternative to urethral catheterization in men in cases where the urethra is compressed by an enlarged inflamed prostate gland, and the patient requires an adenomectomy. Cystostomy is also indicated for damage to the bladder neck or the presence of false urethral canals.
Source: https://uroscope.ru/bolezni-organov/troakarnaya-tsistostomiya-mochevogo-puzyrya-u-muzhchin-operatsiya-uhod.html