Indications for research
Despite excellent health in youth, sooner or later every woman is faced with the need to diagnose her bladder. The reason for this can be both age-related changes in the body and a number of unpleasant symptoms. Diagnosis of the bladder and kidneys has a number of indications, among which the following can be noted:
- pain in the lower abdomen, which is periodic or constant;
- frequent urge to urinate, constant feeling of bladder fullness;
- visible impurities of blood or pus in the urine;
- urine has a strong odor and has changed color;
- small amounts of urine;
- pain when urinating.
Against the background of the above symptoms, a person may experience an increase in body temperature, decreased performance, increased heart rate, and may experience profuse sweating. If there are pathological changes in the process of urination, it is necessary to consult a urologist as soon as possible. It is likely that there is an inflammatory process or other pathological changes in the organs of the excretory system.
Diagnosis of urogenital infections
Discounts for friends from social networks!
This promotion is for our friends on Facebook, Twitter, VKontakte and Instagram! If you are a friend or subscriber of the clinic’s page &laqu.
Resident of the microdistricts "Savelovsky", "Begovoy", "Airport", "Khoroshevsky"
This month, residents of the Savelovsky, Begovoy, Airport, and Khoroshevsky districts.
The term “ urogenital infections ” refers to all inflammatory diseases transmitted during unprotected sexual intercourse of any type with an infected partner (STI), and a significant part of infections that “dormant” until their time in the human body. It is also customary to include chlamydia and syphilis in this group, despite the fact that these diseases can also be transmitted through household means - through an unsterile syringe, during blood transfusion, during childbirth, or through the use of common household items.
The source of infection is viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa. They are usually divided into:
- absolutely pathogenic (pathogens of syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, genital herpes, genital mycoplasmosis, etc.);
- conditionally pathogenic (Escherichia coli, enterococcus, streptococci, staphylococci, Klebsiella and many others), that is, present in healthy people and causing inflammation under certain conditions.
Leading symptoms
Bladder pathology can have different origins, but many diseases have similar symptoms.
The following warning signs deserve special attention:
- pain in the lower abdomen and groin area;
- dysuric phenomena: difficulty urinating, frequent urge to empty the bladder, urinary incontinence, weak or intermittent stream of urine;
- increase or decrease in the daily volume of urine excreted;
- itching, burning or pain when urinating;
- the appearance in the urine of impurities of pus or blood, sediment, flakes, sand;
- increase in body temperature.
SYMPTOMS OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
In newborns with urinary tract infection, the symptoms of the disease are nonspecific:
vomiting, irritability, fever, poor appetite, low weight gain. If your baby experiences at least one of the listed symptoms, you should immediately consult a pediatrician.
Clinical picture of urinary tract infection in children of the preschool age group
– these are most often dysuric disorders (pain and pain when urinating, frequent passage of urine in small portions), irritability, apathy, and sometimes fever. The child may complain of weakness, chills, pain in the abdomen and in its lateral parts.
School age children:
- In school-age girls with urinary tract infections, the symptoms of the disease in most cases are reduced to dysuric disorders.
- In boys under 10 years of age, body temperature often rises, and in boys 10–14 years of age, urinary disorders predominate.
Symptoms of UTI in adults are increased frequency and disturbance of urination, fever, weakness, chills, pain above the pubis, often radiating to the sides of the abdomen and lower back.
Women often complain of vaginal discharge, men - of discharge from the urethra.
The clinical picture of pyelonephritis is characterized by pronounced symptoms: high body temperature, abdominal and lumbar pain, weakness and fatigue, dysuric disorders.
We recommend reading:
Laboratory methods for examining the bladder
Initially, the doctor will conduct a detailed survey of the patient to understand the condition of her kidneys and the bladder itself. Symptoms are collected, as well as information about chronic diseases that are present in the body. Next, the bladder is palpated and laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed. Among the laboratory tests, a urine test is prescribed, which will be examined using several methods:
- analysis according to Nechiporenko - consists of a single urine collection and studying the exact number of cylinders, leukocytes and red blood cells in 1 ml;
- analysis according to Zimnitsky - involves collecting biomaterial 8 times a day;
- bacteriological analysis - consists of determining the causative agent of a particular disease by searching for infectious agents.
Urinalysis is the most routine diagnostic method, however, it is mandatory, as it allows you to determine inflammatory processes in the bladder, as well as suggest changes in kidney function. Before checking the bladder in women using a laboratory method, it is not recommended to take medications or use antiseptics, as this may distort the results. Accurate information about the patient’s condition can be obtained an hour after collecting the biomaterial. With each subsequent hour, bacteria and microorganisms begin to multiply in the urine, which affects the accuracy of diagnosis.
Using a microscope, a laboratory employee studies the composition of the biomaterial and compares the content of leukocytes, erythrocytes and other components with the norm. Based on the information received, the doctor can indirectly assess the patient’s condition. As a rule, a urine test is not enough to make a diagnosis; additional diagnostic techniques are needed. The composition of urine does not reflect visible changes in the organ, as well as the presence of stones and tumors.
How to properly collect urine?
The result of the study, and, consequently, the prescribed treatment, depends on the correct collection of biological material. When collecting urine, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Urine collection is carried out after washing to prevent dirt from getting into the urine.
- You should wash from front to back.
- It is recommended to collect the morning portion of urine, but the first part must be released, and then what remains is collected in a container.
- If a woman is on her menstrual period, then before collecting tests, a tampon must be inserted into the vagina; this is also necessary if there are gynecological infections.
Principles of treatment
The treatment regimen will depend on the cause of the disease.
Conservative treatment is indicated for inflammatory processes in the bladder, some forms of urolithiasis and neurogenic dysfunction.
For some bladder diseases, drug treatment is indicated
To eliminate the problem, the following drugs are used:
- Antibacterial and antifungal agents (for inflammatory diseases of the bladder, taking into account the identified causative agent of the disease).
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs - to eliminate pain and reduce body temperature.
- Antispasmodics - to relieve muscle spasms, improve urine flow and facilitate the removal of stones.
- Litholytic therapy is the prescription of drugs that dissolve bladder stones.
- Diuretics are drugs that increase urine output.
- Herbal infusions to enhance diuresis, eliminate intoxication and stimulate the immune system.
If bladder stones do not pass on their own, instrumental lithotripsy is indicated: shock wave or laser. During the procedure, the stones are crushed and then exited through the urethra in the form of fine sand. The choice of a specific technique will depend on the size and location of the stone, as well as on concomitant pathology.
Surgical treatment is indicated for the following conditions:
- large bladder stones or in the absence of effect from conservative therapy;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- abnormalities in the development of the bladder that prevent the normal flow of urine;
- purulent complications of cystitis.
The extent of surgical intervention is determined based on the form of the disease and the severity of the patient’s condition. Removing stones and tumors allows you to radically get rid of the disease and avoid the development of serious complications.
Prevention of bladder diseases includes timely treatment of any pathology of the urinary tract and prevention of the spread of infection from the urethra. Regular visits to the urologist will allow you to identify the problem in time and take the necessary measures to eliminate it.
- How to check your bladder
- What tests will show kidney stones?
- Why do they donate morning urine?
Common diseases
Diseases of the female genitourinary organs most often appear at a certain stage of development. If we consider the urinary system, its most common diseases are:
- pyelonephritis. An inflammatory disease that occurs in the kidneys is most often concentrated in the renal pelvis. It can occur on one kidney or on both. In most cases, it has a bacterial etiology;
- urethritis. The disease is caused by inflammation of the urethra (urethra), caused by a viral infection or the influence of pathogenic bacteria. The course of the disease can be acute or chronic;
- urolithiasis disease. Characterized by a large accumulation of protein and salts in the structure of urine, resulting in the formation of stones in the bladder or other ureters;
- cystitis. Inflammation of bladder tissue. The mucous membrane can be affected, as a result of which the functioning of the organ is disrupted.
(The picture is clickable, click to enlarge)
Common diseases of the female reproductive system include:
- vaginitis An inflammatory process occurring in the mucous membrane of the vaginal walls. Has a bacterial etiology;
- chlamydia. The disease, as a rule, is sexually transmitted and is characterized by the presence of pathogenic chlamydia bacteria in the vaginal microflora;
- thrush (candidiasis). Fungal pathology, which is caused by the spread of yeast fungi. May affect vaginal mucosa and skin;
- uterine fibroids. A benign formation of hormonal etiology, which can occur inside the uterus or in its outer walls;
- ovarian cyst. A benign formation located on the body of the ovary can transform into malignant;
- cervical erosion. Caused by damage to the epithelium or the wall of the uterine cervix;
- endometriosis. Characterized by the proliferation of the inner mucous layer of the uterus. In some cases, it may spread to the vagina or abdominal cavity.
Any disease of the female genitourinary system requires treatment. In some cases, surgery is necessary.
Weak sphincter and urinary incontinence
When the muscles in the sphincter in the bladder are relaxed, urine leaks out uncontrollably, a condition called incontinence. This disease can develop in men and women for various reasons, but primarily this is due to weakness of the sphincter due to a stroke, diagnosed diabetes mellitus, frequent constipation and heart failure. Weakness of the bladder sphincter also occurs when taking certain medications. Pathology is also detected in men, although much less frequently than in women.
More on the topic: How is an X-ray of the bladder performed?
There are several types of urinary incontinence:
- Urge incontinence caused by hyperactivity in the urethral canal. With a strong urge, urine is released;
- stress incontinence, which occurs most often after surgery. Urine is released when laughing, coughing or sneezing against the background of weak pelvic floor muscles;
- functional incontinence due to acute mental illness;
- mixed incontinence, when several types are combined;
- Overflow incontinence, when the bladder is filled to its maximum and it is not possible to keep such a volume inside.
Functional significance of the system
The genitourinary system (genitourinary apparatus) is a complex of organs that perform reproductive and urinary functions. Anatomically, all components are closely interconnected. The urinary and reproductive systems perform different functions, but at the same time complement each other. If one of them malfunctions, the second one also suffers. The main functions of the urinary system are:
- Removal from the body of harmful substances formed in the process of life. The main part of the products comes from the digestive system and is excreted in urine.
- Ensuring a balanced acid-base balance in the body.
- Maintaining water-salt metabolism in the correct state.
- Maintaining functionally significant processes at the level necessary for life.
If there are problems with the kidneys, substances that have a toxic effect are no longer excreted from the body in the required volume. As a result, harmful products accumulate, which negatively affects human life. The reproductive system ensures reproduction, that is, reproduction. Thanks to the proper functioning of the organs, a man and a woman can conceive a child.
The gonads provide the production of hormones necessary for reproductive activity and the functioning of the body as a whole. Violation of the production process has a negative impact on the functioning of other systems (nervous, digestive, mental). The gonads perform mixed functions (external and intrasecretory). The main and main task is the production of hormones necessary for childbirth. In men, the gonads produce testosterone, in women - estradiol.
Hormones influence such vital processes as: metabolism; formation and development of the genitourinary system; growth and maturation of the body; formation of secondary sexual characteristics; functioning of the nervous system; sexual behavior. The substances produced enter the human blood and are transported to the organs in its composition. Once distributed throughout the body, hormones affect many systems and are important for vital functions.
Physiology of the Bladder
Urination is a complex physiological act that involves the process of simultaneous relaxation of the external and internal sphincter with synchronous contraction of the bladder muscles. The muscles of the perineum and abdominal muscles take an active part in urination.
The urea has very elastic walls. In the case of normal functioning of the receptors, the signal about the urge to void enters the brain when the volume of urine reaches 160-170 ml.
The anatomical features of the human bladder structure allow it to accommodate a urine volume of no more than 1000 ml (based on average values). Due to the weakened muscles of the organ, the process of excretion and accumulation of urine becomes chaotic and uncontrollable.
According to medical statistics, such problems are most often observed in older women and young children. When the muscle walls of the bladder lose tone, the brain stops receiving neural signals that indicate it is full. Such communication disorders are fraught with atony (incontinence) and provoke the process of uncontrolled urine release.
Why are urogenital infections dangerous?
As the name itself suggests, these infections affect the human genitourinary system, that is, the inflammatory process is initially concentrated in the organs and structures of the urogenital tract, although later, if left untreated, it can affect other parts.
There is a lot of debate about who is more dangerous from genitourinary infections - women or men. Thus, women are more susceptible to contracting urogenital infections due to the characteristics of female physiology. While in men, some dangerous STIs occur without any symptoms, which significantly delays the detection and treatment of the disease.
There are no “winners” in this dispute and there cannot be. Infectious diseases of the genitourinary area can lead to chronic inflammatory processes; cause erectile dysfunction, prostatitis and infertility in men, inability to become pregnant (female infertility) or bear a child to term in women; cause damage to the nervous and immune systems, kidneys, liver, spinal cord and brain; lead to the formation of malignant tumors.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
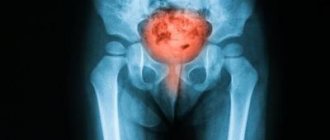
Diagnosis of the bladder can also be carried out using instrumental methods; one of these methods is x-ray. The examination involves injecting a special contrast agent into the woman’s urethra. Immediately after administration of the drug, an x-ray of the bladder is taken. The image clearly shows how the contrast agent spreads and whether there are any obstructions in the ureters. Also, by examining the bladder in this way, it is possible to diagnose diverticula, tumor growths in the lumen of the bladder, foreign bodies, stones, fistula tracts and other pathologies of the organ.
Endoscopic examination of the bladder is also used quite often. The cystoscopy method is used to examine women. Urinary assessment is carried out using a special endoscope instrument - a long tube with a mini camera at the end. The image is transmitted to a computer monitor, which is monitored by a doctor. The endoscope is brought into the lumen of the urethra and extended into the cavity of the bladder. This diagnostic option gives the doctor a comprehensive picture of the patient’s condition; he can assess the integrity of internal structures, as well as detect tumors and problem areas.
It should be noted that cystoscopy can develop into a surgical procedure, for example, to remove polyps. The procedure itself is not painful; the only consequences after it may be cystitis or urethritis, which can be easily eliminated with medications on an outpatient basis. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. A day before the procedure, you need to give up gas-forming products and also do a cleansing enema.
CT and MRI are the most modern and highly accurate diagnostic methods; their only drawback is the high cost of the examination, which not every patient can afford. Examination of the bladder is carried out by scanning the organ with X-rays. The doctor gets the opportunity to evaluate the layer-by-layer structure of the organ and see its three-dimensional image on a computer. The patient lies motionless while the doctor observes the procedure from the next room. In general, the procedure lasts twenty minutes and is completely painless.
Sometimes, for the accuracy of the procedure, contrast is used, which the patient drinks twice - the first on the evening before the examination, and the second immediately before the examination of the kidneys and bladder. This allows fabric textures to be more visible to equipment.
Based on the information received, the doctor can accurately make a diagnosis after the first procedure. Before checking the bubble in this way, a detailed study of the patient’s condition is carried out; there is a possibility that the contrast agent will cause an allergic reaction in the person.
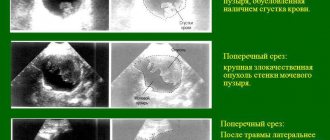
You can get information about the kidneys and bladder using an ultrasound examination. This is the most accessible and fastest method of obtaining results of the condition of internal organs. The procedure is carried out by scanning human organs with ultrasound beams of a certain frequency. The resulting image is marked on the screen, as is the case with CT and MRI. The difference is that it is impossible to obtain a three-dimensional image during the examination; only direct projection is available, but this also provides a certain amount of information about the structure of the organ.
Ultrasound
TRUSY
When wondering how to check the bladder and kidneys, you should pay attention to a non-invasive, highly informative, quick and painless method - ultrasound diagnostics.
Today this is the main screening method. If previously ultrasound machines were only available in large centers, now they are available even in small medical institutions in small settlements.
Main advantages of the method:
- speed of implementation and decoding;
- painless and harmless;
- low price;
- high diagnostic value;
- the ability to immediately visualize all organs of the genitourinary system.
The examination can be carried out using two methods:
- Classic - through the abdominal wall, is simple and therefore more often used;
- Transrectal (insertion of the sensor into the rectum). This method of access is somewhat more complicated and not entirely pleasant, but it is possible to more clearly visualize those areas of the bladder and kidneys that are poorly visible with conventional ultrasound. TRUS is more indicative from a diagnostic point of view.
Indications for ultrasound
The access method is chosen by the attending physician, based on clinical manifestations or to clarify the diagnosis.
Reasons for referring a patient for examination may include:
- pain in the lower abdomen, lower back or shingles;
- various problems with urination;
- the presence of mucus, suspended matter, sand, blood and other abnormal particles in the blood;
- bacteria, epithelial cells or leukocytosis in TAM;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms.
Important. Ultrasound can show the presence of a tumor in the examined organ, but this method cannot assess the malignancy of the pathology.
Preparation
To obtain reliable data, it is important to properly prepare for the study. The main condition is that the bladder must be completely filled with urine.
To do this, it is recommended to drink a liter of water an hour and a half before the test. Simply put, the study is carried out when you want to urinate. This is necessary to ensure that the walls of the organ are in the most stretched state.
It is also desirable to avoid increased gas production because a distended esophagus may interfere with visualization. To do this, you should drink the drug “Espumizan” a day before (during meals); the package contains instructions that indicate the optimal doses for each specific case.
Home treatment
In addition to taking medications, people who suffer from this problem should limit their consumption of alcoholic beverages, strong tea and coffee. It is also worth excluding all smoked meats, pickles, fatty and fried foods from your diet. Such food provokes irritation of the mucous membrane of the bladder, causing the urge to empty.
With this problem, it is recommended to drink as much fluid as possible (preferably plain water) to enhance kidney function. The thing is that concentrated urine promotes the formation of stones and sand in the organ, which then leads to inflammatory processes in the bladder.
Cystitis can also be a complication of tuberculosis
Infectious cystitis caused by Trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasmas, gonococci, Koch bacilli is called specific. Nonspecific cystitis is a disease caused by opportunistic bacteria that constantly inhabit the body.
Infrequent types of cystitis are those caused by purpura, actinomycosis and schistosomiasis.
The route by which pathogens enter the bladder may vary. Depending on it, cystitis is divided into descending, ascending, lymphogenous and hematogenous. Ascending infection (from the urethra) in male patients is quite rare. Cystitis in men is most often descending (in the case of a kidney infection), as well as hematogenous and lymphogenous.
There are also cystitis of a non-infectious nature. They can be caused by:
- surgeries or diagnostic procedures on the bladder;
- radiation exposure to the body, for example, during radiation therapy of the prostate gland;
- bladder injuries caused by foreign bodies, such as stones;
- chemicals that are excreted in the urine and cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
Cystitis is also divided into primary and secondary. In the first case, the disease begins on its own, directly in the bladder. In the second, cystitis is caused by some other pathological processes in the body.
Secondary cystitis, in turn, is divided into cystitis of intravesical and extravesical origin. For example, stones in the bladder and neoplasms of this organ are intravesical causes, and diseases of other organs (prostate adenoma, pyelonephritis) are extravesical.
If the area of inflammation is the bladder triangle, then such cystitis is called trigonitis. Also, depending on the location of inflammation, cervical and diffuse cystitis are distinguished. With cervical cystitis, only inflammation is observed at the neck of the bladder. The diffuse form of the disease manifests itself in inflammation of the entire wall of the organ.
Depending on how severely the bladder wall is affected, the following forms of cystitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal,
- hemorrhagic,
- cystic,
- ulcerative,
- phlegmonous,
- gangrenous.
The mildest form, affecting only the superficial layers of the walls, is catarrhal. In the gangrenous form, the pathological process leads to necrotization of the walls. To determine the extent of the disease, cystoscopy followed by a biopsy is used.
Factors contributing to the appearance of cystitis in men:
- hypothermia of the body;
- decreased immunity;
- stress;
- conscious urinary retention, rare emptying of the bladder;
- kidney and prostate diseases;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- diseases accompanied by the occurrence of foci of infection (tonsillitis, sinusitis, furunculosis, dental diseases, etc.);
- spinal injuries;
- diabetes;
- alcohol abuse.
Complications of cystitis may include paracystitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the bladder), pyelonephritis, sclerosis of the bladder walls, perforation of the bladder walls, inflammation of the kidneys (as a result of vesicoureteral reflux).
Prevention
To achieve the best results in strengthening your bladder, it is worth making a number of adjustments to your usual lifestyle. First of all, you must adhere to the diet recommended by your doctor even after the condition of the genitourinary system improves. You need to give up addictions and drinking carbonated drinks, strong tea and coffee.
It is important to undergo a full diagnostic examination for the presence of inflammatory processes affecting bladder tissue. It is strongly recommended not to expose your body to hypothermia, and to avoid stressful situations and heavy physical activity.
Doctors assure that it is quite possible to prevent the occurrence of such health problems. Elderly people should insulate their legs and lower back and avoid hypothermia. It is also worth fighting constipation, since problems with bowel movements often lead to weakening of the bladder muscles.
Other preventive measures:
- Avoiding heavy lifting
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene of the perineum
- Weight control
Female genitals
The anatomy of the genitourinary system is represented by a complex of genital (genital) organs, which are divided into internal and external. The main functional significance is reproduction (reproduction). Male and female reproductive organs differ significantly. In representatives of the fairer sex, the genitourinary apparatus, and specifically the part responsible for reproduction, is presented in the form of external organs (labia and clitoris) and internal organs (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, vagina).
Rules
The kidneys and the bladder itself are examined only when it is full. The patient is required to drink two liters of fluid before the procedure. It should be regular or mineral water, but not carbonated. The patient lies down on the couch, and the doctor moves a special sensor over his abdomen; for people with excess body weight, a rectal examination is recommended. The sensor is inserted through the rectum. The procedure is completely painless and takes no more than half an hour. The person receives the results of the procedure on the same day or they are announced by the doctor during the procedure. This efficiency makes ultrasound the most popular diagnostic method.
Today, there are a huge number of research methods that make it possible to assess a person’s condition in a few moments. This is very encouraging, because as you know, a correct diagnosis is half of successful treatment. Despite this, many patients still hesitate to see a doctor, endure discomfort and painful symptoms, attributing everything to fatigue and a cold. This attitude towards the body is unacceptable; the sooner you contact, the sooner you will get rid of the disease that is eating you from the inside. There is no need to be afraid or ashamed, there is nothing shameful in the fact that you want to be healthy, in addition, there are many studies that do not cause either psychological or physiological discomfort to the patient.
Male genitals
The male organs of the genitourinary system (genitals), like the female ones, are divided into internal and external. Each segment is necessary to perform reproductive activities. The external genitalia are represented in the form of the penis (penis) and the scrotum (the cavity in which the testicles are located). The internal organs include:
- The testes are paired sex glands that produce sex cells (sperm) and steroid hormones. Their formation and descent into the scrotum occurs already during embryonic growth. The ability to move remains throughout life, which helps protect the genitourinary system from external factors.
- The vas deferens is a paired male reproductive organ. It is presented in the form of a tube, the length of which is approximately 50 cm. The vas deferens continues the accessory duct of the testicle. In the prostate, a connection occurs with the ducts of the seminal vesicles and the ejaculatory canal is formed.
- Seminal vesicles are paired glands in the form of oval-shaped sacs. Their functional significance is based on the production of protein secretion, which is an integral part of the seminal fluid.
- The epididymis is a long narrow duct (6-8 m) necessary for the passage of sperm. The ripening, accumulation and further transportation of germ cells takes place in the canal.
- The prostate gland is an exocrine gland located below the bladder. Functions of the organ: production of prostate secretion, which is included in sperm; restriction of exit from the bladder during erection; control of hormone production. The substance produced by the gland dilutes the seminal fluid and gives activity to the germ cells.
- Cooper's glands are a paired organ located deep in the urogenital diaphragm. During erection, the glands produce a transparent mucous secretion that facilitates the penetration of the penis into the vagina and the movement of seminal fluid.
The male reproductive system is a complex set of organs that closely interact with each other. Correct performance of functions is only possible with balanced operation of the entire system. Often, pathological disorders of one organ provoke diseases of others, and in complicated cases leads to loss of reproductive ability.
Features of the male genitourinary system
The bladder in men communicates with the narrow and long urethra, which passes through the penis. The urea is adjacent to many organs of the reproductive and excretory system:
- ureters;
- seminal vesicles;
- prostate;
- rectum;
- vas deferens;
- urethra.
Injuries and infectious inflammation of any of them are fraught with damage to the urinary tract. Untimely treatment of diseases leads to complications - sexual impotence, infertility.
Common symptoms of bladder disease in men
In 80% of cases, urinary tract pathologies in men are secondary, that is, they arise as a complication of damage to the organs of the reproductive, digestive, nervous or immune systems. Clinical manifestations depend on the cause of bladder dysfunction. But many symptoms are nonspecific, so when they appear, seek help from a doctor.
Signs of bladder disease:
- pain in the suprapubic region;
- intermittent stream;
- urinary incontinence;
- hematuria;
- difficulty urinating;
- change in the color and clarity of urine;
- discomfort in the groin;
- excretion of urine in small portions.
Damage to the walls of the organ leads to disruption of detrusor tone, which is why 90% of men experience urinary disorders.
If the disease is provoked by harmful microflora - bacteria, fungi, viruses - symptoms of intoxication appear. Men complain of muscle weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, and fever.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
The causes of cystitis in women include:
- hypothermia;
- gynecological diseases;
- urological diseases, including bladder diseases.
The symptoms of cystitis are very pronounced, making it quite easy to recognize the disease. However, the final diagnosis is made by a gynecologist or urologist based on certain tests, after which treatment is selected.
Symptoms of cystitis:
- pain in the urinary area;
- pain throughout the entire process of urination or only at the end;
- a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder immediately after urination, constantly wanting to go to the toilet;
- bleeding when urinating with severe forms of inflammation;
- temperature rise.
Bleeding with this pathology is dangerous, as it can lead to urinary tamponade: blood can clog the urethra, which will lead to stagnation of urine and stretching of the urinary tract. Also, when bacteria penetrate, blood poisoning can begin. The infection can spread to the kidneys.
It is important to start treatment on time to prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
To make a correct diagnosis and to determine the nature of the inflammation, it is necessary to undergo certain tests.
Transitional cell cancer of the bladder is a striking example of this: the neoplasm is formed from the epithelium lining the inner wall of the organ. At the initial stage, the disease is asymptomatic, which makes it dangerous, since the tumor is often diagnosed late, when it reaches a large size.
Bladder cancer is an oncological pathology characterized by the appearance of a malignant neoplasm on the inside or in the walls of this organ. The tumor disrupts the functioning of the bladder and can metastasize over time.
The classification of transitional cell cancer of the bladder is of two types: the first characterizes the localization of malignant neoplasms, and the second indicates the degree of their maturity.
Depending on the location, bladder cancer can be:
- superficial;
- invasive;
- metastatic;
- zero.
Malignant neoplasms lead the list of “killers” of humanity; they can appear in different organs and tissues. The greatest risk of tumor formation is found in structures that quickly divide, that is, epithelial cells of different types.
Transitional cell cancer of the bladder is a striking example of this: the neoplasm is formed from the epithelium lining the inner wall of the organ. At the initial stage, the disease is asymptomatic, which makes it dangerous, since the tumor is often diagnosed late, when it reaches a large size.
Bladder cancer is an oncological pathology characterized by the appearance of a malignant neoplasm on the inside or in the walls of this organ. The tumor disrupts the functioning of the bladder and can metastasize over time.
The word “transitional cell” explains the mechanism of tumor appearance. It develops in the zone of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
The classification of transitional cell cancer of the bladder is of two types: the first characterizes the localization of malignant neoplasms, and the second indicates the degree of their maturity.
Symptoms of concomitant diseases in men
Symptoms of cystitis and prostatitis are similar:
- frequent urination;
- night urges;
- pain and cramps;
- mucus and blood in the urine.
The same symptoms occur with inflammation of the prostate gland. Without analyzing urine and prostate secretions, it is impossible to determine from the symptoms what disease a man has: cystitis, prostatitis, or both at once. Sometimes even test results do not give an accurate answer.
But prostatitis has a peculiarity: it develops against the background of stagnation, for example, during sedentary work. This is not typical for cystitis. But painful urination is characterized by cystitis, not prostatitis.
In men, cystitis can occur in a healthy body (primary) or against the background of other inflammatory processes (secondary):
- Primary develops in the bladder without any associated diseases.
- Secondary develops against the background of existing diseases. It is their complication. It is the secondary one that is typical for men after 45 years of age. Most often it manifests itself with prostatitis or the growth of prostate adenoma.
How to treat?
Diseases of the female genitourinary system are most often associated with inflammatory processes. Therefore, to suppress pathogens, you should take an antibacterial drug . However, only a doctor can prescribe an antibiotic based on tests and identification of the pathogen.
The course of antibiotics should be completed completely, otherwise untreated diseases may become chronic.
In addition, along with antibacterial tablets, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulating agents .
Treatment of neoplasms (fibroids, cysts) may be limited to taking hormonal medications , or may lead to surgery.
In addition to drug treatment, you can, with the consent of your doctor, resort to traditional medicine. For this, herbal mixtures and berries are used as decoctions (chamomile, blueberries, leeks, dill seeds, steelberry roots). In addition to herbal decoctions, a decoction of viburnum with honey is used for inflammation of the urinary tract.
Cystitis therapy
Treatment of male cystitis includes following a diet, bed rest, and taking medications. You can get rid of bladder pain in men using folk remedies. You will first need to consult a urologist.
During the treatment of cystitis, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, herbal medicines and anti-inflammatory drugs. If there is severe pain in the urinary tract, and the inflammatory process occurs in an acute form, the following antibiotics are recommended for men:
- Nolitsin is an antibacterial drug that belongs to the pharmacological group of fluoroquinolones. The active component of this drug is norfloxacin. The drug is taken 2 times a day for 6 days if a man has acute pain. For chronic pathology, treatment lasts 6 weeks.
- Palin is an antibiotic of the quinoline group. It is prescribed against gram-positive and gram-negative microbes that provoke pathological processes in the urinary system.
- Monural is a modern antibiotic that affects all pathogenic microbes. With its help you can quickly get rid of cystitis.
- Nitroxoline is effective against fungi and various microbes. It is prescribed to relieve pain from cystitis and other bladder diseases in men.
In addition to the above antibiotics, you can take Furagin, Rulid, Nevigramon. The list of drugs and their dosage is prescribed to each patient individually.
How to treat genitourinary infections in women
Treatment of the genitourinary system is carried out with antibiotics. Their need and type of drug are determined by the attending physician. Violation of his recommendations and the system of taking medications, instead of the expected recovery, can cause complications and infertility in the end.
In addition to antibacterial agents, diseases of the genitourinary system are eliminated with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators and other auxiliary agents.
For example, gardnerella requires taking a medicine that restores the vaginal microflora.
Which doctor should you contact?
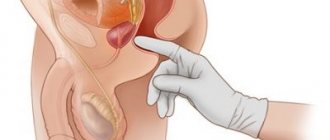
Bladder diseases in men are treated by a urologist. If there are complaints of dysuric disorders, the doctor must examine the genitals and palpate the prostate gland. If necessary, the man is referred for further examination to:
- endocrinologist;
- proctologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- andrologist.
If during an ultrasound examination benign or malignant formations are detected in the bladder, an oncologist should be consulted. In case of immunodeficiency, you will need to visit an immunologist.
How to check your bladder
The set of diagnostic measures depends on the nature of the symptoms, their severity and associated complications. To identify pathologies of the urinary system, ultrasound or cystoscopy and urine tests are required.
Examinations for urinary dysfunction in men:
- culture of a urethral smear;
- PCR diagnostics;
- clinical urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder.
In doubtful situations - with neoplasms, foreign bodies in the organ - multispiral cystourethrography is prescribed.
FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF UTI:
- congenital anomalies of the genitourinary system;
- functional disorders (vesicoureteral reflux, urinary incontinence, etc.);
- concomitant diseases and pathological conditions (urolithiasis, diabetes mellitus, renal failure, nephroptosis, multiple sclerosis, kidney cyst, immunodeficiency, spinal cord lesions, etc.);
- sexual life, gynecological operations;
- pregnancy;
- advanced age;
- foreign bodies in the urinary tract (drainage, catheter, stent, etc.).
Elderly people are a separate risk group. Infection of the genitourinary tract in them is facilitated by epithelial failure, weakening of general and local immunity, decreased secretion of mucus by cells of the mucous membranes, and microcirculation disorders.
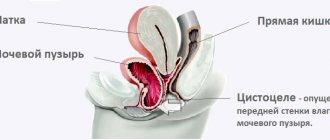
Urinary tract infections develop 30 times more often in women than in men. This occurs due to certain features of the structure and functioning of the female body. The wide and short urethra is located in close proximity to the vagina, which makes it accessible to pathogenic microorganisms in case of inflammation of the vulva or vagina. The risk of developing a urinary tract infection is high in women with cystocele, diabetes mellitus, hormonal and neurological disorders. All women during pregnancy, women who began sexual activity early and have had several abortions are at risk for developing UTIs. Lack of personal hygiene is also a factor contributing to the development of urinary tract inflammation.
As women age, the incidence of UTIs increases. The disease is diagnosed in 1% of school-age girls, 20% of women aged 25–30 years. The incidence reaches its peak in women over 60 years of age.
In the vast majority of cases, urinary tract infections in women recur. If UTI symptoms reappear within a month after recovery, this indicates that the therapy was insufficient. If the infection returns a month after treatment, but no later than six months, it is considered that re-infection has occurred.