Unpleasant sensations localized in the urinary area can reduce a person’s quality of life, so you need to be very attentive to your health. Discomfort of the genitourinary system can indicate the development of various pathologies: cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, the appearance of neoplasms, etc. All these problems make a person’s life unbearable, forcing him to give up many usual activities, they provoke insomnia and cause stress, as well as depression.
The occurrence of unpleasant sensations in the urinary area is a fairly common occurrence. They can be a temporary phenomenon or accompany a person almost always. Basically, such intimate difficulties confuse many people, so they rarely turn to a specialist, but in vain. Today, there are many diseases that cause discomfort in the urinary tract, but they can be successfully treated, so consultation with a specialist is simply necessary.
Urinary disorders can be caused by various reasons. They can be infectious, physiological or psychological.
Mechanism of urination
In fact, a healthy person may have more than 200 milliliters of urine in their bladder. This amount of liquid has a fairly strong effect on the walls of the urinary organ, on which there are special receptors associated with brain cells. And everything happens like with a doorbell button: urine presses on certain points, and the brain sends a signal to the sphincters, which, when relaxed, remove excess fluid from the body.
So the work of the bladder is the interaction of several organs of the body at once, and both the physical and emotional state of a person depends on the quality of this work.
Frequent urination in women without pain: causes
- Diuretic therapy. When taking diuretics, the number of urinations increases, and the volume of urine increases.
- Pregnancy. We will talk about this factor in more detail below.
- Nutritional features. Eating large amounts of spicy food, pickles, animal and vegetable fats irritates the bladder receptors and contributes to increased urination.
- Abuse of caffeine-containing drinks such as green tea, coffee, and alcohol, especially beer.
- Hypothermia of the lower extremities. Many people probably noticed that when they were cold, the urge to go to the toilet “in a small way” became more frequent. This can be considered a normal reaction of the bladder after hypothermia.
- Psycho-emotional shocks. During stress, the body's cells suffer from oxygen starvation, one of the manifestations of which is frequent urination.
- Period. Before menstruation, fluid is retained in the female body, so with the arrival of menstrual periods, it begins to be excreted in the urine, as a result of which urination becomes more frequent.
- Climax. During the period when a woman’s reproductive function fades, hormonal and metabolic changes occur in the body, which contribute to increased frequency of urination.
Causes
The sensation of a full bladder appears due to several factors:
- Obstruction in the urinary tract. In this case, even if the brain gives the command to remove urine, it simply cannot come out. The path can be cluttered by various tumors, inflammations, and so on.
- Neoplasms. They can also make you feel like your bladder is full. Neoplasms include not only stones, but urethral stricture and even prostatitis.
- Atony or hypotension. These are disorders in the functioning of muscles, which is what the bladder is. At its core, it is either constant tension or a relaxed state.
- Diseases. Bladder fullness in women, men and even children can be caused by cystitis, urethritis, hyperplasia, descending appendicitis and enterocolitis.
- Incorrect brain processing. This is the so-called imaginary urinary retention.
For some, this feeling occurs simply because their urinary organ is too small and fills up quickly.
If we talk about women, then such a symptom may occur due to salpingo-oophoritis, uterine fibroids and other diseases of this kind. When inflamed, the organs of the reproductive system tend to increase in size and put pressure on the bladder.
Treatment approaches
Treatment of this pathology begins with eliminating the root cause of the disease. If the factor causing the feeling of a full bladder is an infection, then antibacterial or antiviral therapy is mandatory. If you have urolithiasis, the doctor prescribes drugs that can dissolve small stones. If the size of the stones is large, then crushing of the stones is used.
In case of urethral stricture, the only way to solve the problem is through surgery.
If the disease is explained by a psychological factor, then the patient is prescribed sedatives and psychotherapy is recommended.
In the case of formations of a benign and malignant nature, the tumor is excised; if malignancy is confirmed, chemotherapy and radiological irradiation are used.
There are a number of ways to diagnose the causes of the feeling of a full bladder, which can significantly improve the well-being of a sick person:
- when urinating, you need to relax, do not squeeze the muscles of the bladder and abdomen;
- You definitely need to retire and find the most comfortable place;
- you can’t rush, as it’s difficult to empty your bladder;
- palm pressure on the suprapubic area will make it much easier to defecate;
- to stimulate deurination, you can use the sound of water pouring;
- during the act of emptying an overfilled bladder, the process cannot be interrupted (some use this technique as training), as this creates an even greater disturbance.
If all of the above methods are ineffective, then the doctor inserts a urinary catheter.
In case of acute urinary retention, emergency catheterization is performed. The external opening of the urethra is disinfected, lubricated with Vaseline and then a catheter is inserted, then its terminal part is inflated. With this, it is secured. The exception is situations in which the cause of the disease is prostatitis or stones. In this case, the catheter is prohibited from use, as it can aggravate the process.
Conclusion
Feeling your bladder full is a big problem that needs attention. The success of treatment directly depends on a correct diagnosis. Untimely and incorrectly selected therapy can lead to serious complications, which will be very difficult to cope with. That is why a doctor should treat such an “illness”. Be healthy.
ATTENTION! All information on the site is for informational purposes only and does not claim to be absolutely accurate from a medical point of view. Treatment must be carried out by a qualified doctor. By self-medicating you can harm yourself!
Diagnostics
Whether your bladder is actually full or not can be determined by having it diagnosed by a qualified specialist. He will direct you to do several tests and procedures:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and kidneys;
- culture of urine for microflora;
- general blood analysis;
- excretory urography;
- general urine analysis.
They may also prescribe magnetic resonance therapy or computed tomography. The doctor will definitely be interested in many details to select the most correct diagnosis and treatment. For example, he may be interested in whether there is pain when urinating, how often the feeling of fullness occurs, and so on.
Correct diagnosis will improve quality of life
Diagnosing the causes of overactive bladder is critical to the patient's quality of life.
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor uses the following methods:
- History: includes a conversation with the patient about the clinical history of the disease. The patient is asked whether he has had episodes of urinary incontinence, how many times he gets up at night, whether he often feels an urgent need to urinate, whether he has time to get to the toilet, or whether involuntary losses occur.
- Examination: carried out by examining the abdominal cavity and genitourinary apparatus. In women, a pelvic examination is performed to look at the condition of the pelvic floor muscles; in men, a prostate examination is performed.
- Level 1 tests: necessary for differential diagnosis with diseases such as cystitis, irritable bowel syndrome, urinary tract infections and the presence of bladder or kidney stones.
- Urodynamic test: Used to evaluate the filling and emptying of the bladder to rule out urinary stasis (meaning the bladder does not empty completely during urination), which can lead to symptoms similar to overactive bladder syndrome. This test can be combined with uroflowmetry, which evaluates the volume and flow rate of urine.
- Other level 2 tests: to rule out dangerous diseases such as tumors in the bladder or changes in muscle contractility. These studies include cystometry, electromyography and urethrocystoscopy.
This disease is indicated if a person has the desire to go to the toilet more than eight times a day. It is important to determine the cause of such hyperactivity, so first of all it is necessary to do a general urine test and culture for the presence of urinary tract infections. An ultrasound of the bladder will help rule out surgical problems and also determine the amount of urine remaining after urination.
Women need to be examined by a gynecologist, men – by a urologist for prostate diseases.
You will have to visit a neurologist to check general reflexes as markers of neurological diseases.
And finally, to complete the picture, the doctor may suggest keeping a urination diary for several days, which will show how often and in what volume they occurred. This observation diary can replace a urodynamic study: special equipment records all contractions of the bladder, which, in fact, cause the desire to go to the toilet.
It is prescribed when there are suspicions of urological problems. If the diagnosis of “overactive bladder” is obvious, then the doctor limits himself to studying the patient’s diary.
Some symptoms
Constant sensations of bladder fullness are already an unpleasant symptom, but often it does not occur alone. Many people note difficulties with the process of urination in the form of cutting sensations or complete incontinence.
Some noted pain and aches in the lower back or side above the waist. This is often accompanied by elevated body temperature and chills. In difficult situations, the urine becomes cloudy and even contains blood. Is it worth talking about the unpleasant odor that comes from urine?
With independent palpation, you can find that the bladder is enlarged. This is clear evidence that urine does not leave the organ completely, swelling its walls. Frequent urges with a small amount of discharge cannot be ruled out.
The process of urination
The human bladder is capable of holding 300 ml of urine for 5 hours.
The walls of the organ are covered with receptors, from which signals are sent to the center, which is responsible for urination. It is located in the sacral region of the spinal cord. This area controls bladder activity through stimulation through parasympathetic nerve fibers. Under the influence of signals from the nerves, the walls gradually tense up, and the sphincters of the organ, on the contrary, relax, this is how the bladder is emptied, that is, at this moment urine comes out of the bladder.
Return to contents
Help from specialists
A full bladder is a sign of many genitourinary diseases, and a specialist will do everything to find the source of the discomfort.
If the feeling of constant fullness is caused by stones or sand, then the doctor will do everything to completely remove it from the body. This means that pain and other symptoms may increase during therapy. But such therapy does not last long, and along with the passage of the stone, the unpleasant feeling of fullness goes away. In some cases, such as when the stone is too large, surgery is required.
Treatment of infectious diseases or constipation helps to completely get rid of the unpleasant symptom. Then not only does the pressure on the organ decrease, but other unpleasant symptoms such as pain when urinating and increased body temperature also disappear.
What to do if you feel discomfort?
You can get rid of an unpleasant symptom only after identifying the cause of its occurrence and treating the underlying disease. First of all, you should consult a urologist. To make a diagnosis, the following examinations are necessary:
- Bacterial culture of urine.
- Blood analysis.
- Ultrasound examination of the bladder.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and prostate.
Treatment is selected depending on the cause of the discomfort. It is not recommended to take any medications on your own. Symptomatic therapy will not bring results; it is useless to fight discomfort without treating the underlying disease.
The feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder is one of the common complaints in diseases of the genitourinary system. Therefore, the doctor will have to conduct differential diagnostics to make the correct diagnosis.
conclusions
A feeling of fullness in the bladder is an excellent sign from the body about health problems. Some people prefer to block this signal with various sedatives or antispasmodics.
This symptom is like a bright light bulb that helps to notice and eliminate the disease in time before it causes irreparable harm. Timely diagnosis of any disease reduces not only pain and other symptoms, but also reduces financial costs, and also reduces the likelihood of ending up on the operating table.
The feeling of a full bladder is a physiological phenomenon if it goes away after urination and is not accompanied by pain and burning. But if the feeling of a full bladder is constant, this may indicate the development of the disease, so it is best to consult a urologist with such a symptom.
A frequent feeling of a full bladder worries pregnant women in the later stages. This condition is a variant of the norm, since it is caused by fetal pressure on the bladder, and not by a pathological process. In this case, the symptom will go away on its own after delivery.
Oncological diseases
Any inflammatory diseases occur with acute symptoms, except for cases of chronic inflammation. In addition to the constant fullness of the bladder, there are always symptoms of malaise, deterioration in performance, dull or cramping pain in the lower abdomen and pressure in the urethra.
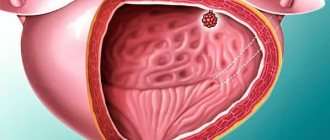
Bladder cancer in the initial stages is asymptomatic, which makes timely diagnosis and initiation of therapy difficult. Quite often, the development of a malignant process is indicated only by a feeling of fullness of the bladder, pain and discomfort are completely absent.
The same symptoms can accompany prostate cancer. Due to the compression of the tissues of surrounding organs by the enlarged prostate, the bladder is constantly filled. Additionally, pressure is observed in the anus. As a rule, in the initial stages of cancer there is no significant discomfort at all. In this regard, it is important to consult a specialist in a timely manner to make a diagnosis. The earlier cancer is detected, the better the prognosis for the patient.
Main Factors
The constant sensation of a full bladder is a serious disorder that significantly impairs a person’s quality of life. The patient cannot work normally, he constantly wants to go to the toilet, but no urine is released at all, or only a few drops come out.
Various pathologies can cause this condition:
- and or inflammation of the bladder.
- A feeling of a full bladder in men can occur due to prostatitis.
- Inflammatory process in the urethra.
- Inflammation in the pelvis, which leads to irritation of the bladder.
- Disruption of nerve conduction in the pelvis.
- Oncological disease.
- Narrowing of the urethra.
The feeling of a full bladder in women most often occurs against the background of cystitis. In this case, the pathology is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, burning sensation when urinating, and sometimes blood may appear in the urine.
Some more factors...
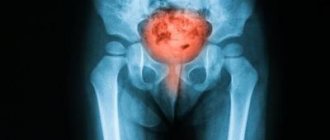
But these are not all the reasons that people complain about when they notice residual urine and pain when emptying the bladder. It happens that the problem occurs against the background of a fracture of the pelvic bones and trauma to the urethra - in most cases in representatives of the stronger sex. Less commonly, such discomfort is a consequence of a disorder of the nervous regulation of the muscular membrane of the bladder or inadequate functioning of the sphincters of this organ. It can be caused by hemorrhages in the spinal cord, compression of the vertebrae, etc.
Acute urinary retention is often reflexive in nature. That is, it is observed in a person in the first few days after he has undergone surgery on the pelvic organs or has suffered from severe stress. Sometimes the disease is diagnosed in completely healthy people who regularly drink alcohol.
often has a reflex character. That is, it is observed in a person in the first few days after he has undergone surgery on the pelvic organs or has suffered from severe stress. Sometimes the disease is diagnosed in completely healthy people who regularly drink alcohol.
Treating the Feeling of a Full Bladder
If your bladder seems full, but no urine is coming out, you should definitely visit a urologist. The specialist will send you a test, based on the results of which treatment will be prescribed. Therapy can be different, it all depends on the cause of the unpleasant symptom.
Most often, a constantly full bladder in women occurs due to inflammation, so the doctor can prescribe appropriate therapy:
- taking antibiotics;
- taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- taking diuretic medications and fruit drinks;
- bed rest;
- physiotherapeutic treatment;
- proper nutrition;
- taking vitamins.
If a full bladder is associated with cancer, then the patient will be referred to an oncologist for further evaluation. In this case, surgery may be required.
Frequent night urination in women: causes
Frequent urination in women at night can also be caused by both physiological conditions and various diseases.
The appearance of nocturnal nocturia can be caused by menstruation, pregnancy and menopause.
If we talk about diseases, frequent night urination in women is most often a symptom of urethritis, cystitis, diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus, chronic renal failure and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Why is this happening?
Pathologies of the genitourinary system manifest themselves as follows:
First.
After going to the toilet there is a feeling of a full bladder.
Second.
The patient again and again experiences the urge to urinate. This is inconvenient, especially if it is not possible to have bowel movements as often.
Third.
When urinating, other symptoms of the disease may be felt, such as burning and stinging.
In most cases, this condition is caused by the presence of urine that remains in the organ cavity. Obstacles prevent its outflow from moving normally.
Sometimes the reason that the bladder does not empty completely is atony, in which it cannot contract normally. The tone of its walls is weakened, and the muscles can no longer support it in the desired position.
Some patients have no obstacles to the outflow of urine, however, it is still not completely eliminated from the body, and the person always wants to go to the toilet. This may indicate the presence of erroneous signals received by the brain.
This condition is typical in the case of the development of certain pathologies: adnexitis, appendicitis, salpingoophoritis
etc. Prolonged stress, shock and nervous strain can also act as a psychological cause.
The problem cannot be left to chance. After all, constant bladder fullness worsens the quality of life and can have serious consequences. Urine that remains in the organ is a good breeding ground for bacteria, which can trigger an inflammatory process.
In what cases does it occur and why?
The sensation of bladder fullness can manifest itself in different ways. For example, if after urination the patient feels that...
In some cases, it is also observed when the bladder fills up in a short period of time.
In this case, other symptoms may be observed that indicate the presence of a particular disease. These are painful sensations, stinging, burning, which intensifies during the process of emptying the bladder.
The following unfavorable factors can lead to a feeling of a full bladder in men and women:
- Inflammatory processes in internal organs located in close proximity to the bladder (inflammation of the kidneys, appendix). In this case, the bladder may be almost empty, but it seems to the patient that it is full;
- The formation of solid elements in the urine, urinary elements, which irritate the mucous membrane of the organ and interfere with its normal emptying;
- Tumor formations of benign or malignant form that arise in the cavity of the bladder;
- Pathologies or damage to the spinal cord, which leads to disruption of nerve conduction of the tissues of the pelvic organs;
- Bladder;
- Deformation of the walls of the urethra, when its lumen becomes narrower or grows together completely;
- Weakness of the muscle tissue of the organ, its damage, as a result of which the muscles of the organ cannot fully contract during the process of urination;
- Changes in stool, constipation. As a result, the size of the intestines increases, and accordingly, the pressure on the bladder increases;
- Disturbances in brain activity when it sends erroneous signals that the bladder is full.
There are also causes of pathology that are typical only for women
. These include various types of female diseases of the genitourinary system, such as adnexitis, fibroids, inflammatory processes affecting the ovaries.
The feeling of a full bladder can also occur in healthy women during the period (in the 2nd trimester). This phenomenon is considered normal, since the enlarged uterus puts pressure on neighboring organs.
In men
the development of this symptom is often provoked by diseases such as adenoma, sclerosis and prostate cancer.
Associated symptoms and types of diseases
To accurately make a diagnosis, it is necessary to evaluate the accompanying symptoms of the diseases.
Prostate diseases
The patient complains of pain in the lower abdomen and has problems with erection. The urine stream is weak and intermittent, and blood may be released. With a malignant prostate tumor, the patient loses weight and develops a fever.
Urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis
Often incomplete emptying of the bladder in women can indicate the development of and. These diseases are accompanied by burning, stinging and pain during urination. This may cause a headache and a rise in temperature. The urine becomes cloudy. With inflammation of the kidneys, pain is felt in the lower back and abdomen.
Bladder stones
Expressed in renal colic and severe pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen. Its signs also include traces of blood in the urine, frequent trips to the toilet, the number of which increases with movement.
Adnexit
This is a female disease in which the body temperature rises, pain is felt in the groin, and discharge may be observed. The woman feels insufficient emptying, she is tormented by chills, weakness, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Hypotension
Along with urination disorders, the patient experiences problems with the gastrointestinal tract, tension in the pelvic muscles, and painful sensations. A person constantly feels the presence of fluid in the bladder, the act of urination itself is sluggish and weak. Chronic disease provokes fecal and urinary incontinence.
Urethral stricture
The narrowing of the urethra prevents the patient from adequately urinating. The flow of urine is weak, accompanied by a constant feeling of a full bladder. Pain appears in the pelvic area and when going to the toilet, there is blood in the urine.
Overactive bladder
This diagnosis is often made by excluding other diseases. Incomplete emptying of an overactive bladder is rare. This disease is characterized by frequent urination, urgent and strong urges. In some cases, urinary incontinence occurs.
Other pathologies can also cause the unpleasant sensation: diabetes, sciatica, spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis. A feeling of a full bladder can be a consequence of serious illnesses, so if this symptom occurs, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder due to injury, hypothermia, hormonal disorders, blood stagnation. It is often caused by complications after infection of nearby organs. The chronic form of the disease is practically asymptomatic. characterized by a feeling of incomplete emptying, discomfort and pain at the end of urination. Blood appears in the urine, discomfort or aching pain is felt in the lower abdomen. Inflammation often spreads to the kidneys and causes pyelonephritis. Antibiotics are used as treatment. Antispasmodics are suitable for pain relief. It is also necessary to take diuretics and follow a special diet.
Which doctor should I contact?
A urologist diagnoses and treats diseases of the genitourinary system. A woman may need to have her ovaries and uterus examined. Then the urologist will refer the patient to a gynecologist, who will take a smear from the vagina to rule out the presence of infection. A urologist also treats diseases of the genital organs in men.
There is no need to be embarrassed to tell the doctor about your problem. A detailed description of the symptoms will help him diagnose the disease more quickly. It is better to choose a high-class specialist, because health and even life are at stake.
Prostatitis
Inflammatory process in the prostate gland. Predisposing factors include hypothermia, congestion, previous infections, and sedentary work. Chronic prostatitis often occurs immediately. It is characterized by a sluggish course and erased symptoms. Patients are concerned about discomfort in the perineum during urination and defecation. Possible under voltage. The acute form of the disease is more pronounced. It is accompanied by severe pain spreading throughout the groin area. . A strong increase in temperature is possible. Significant inflammation threatens the formation of an abscess and infection of other organs of the genitourinary system. Patients are prescribed antibiotics, massage, and physiotherapy. It is important to boost your immunity and give up bad habits.
Diagnosis and treatment
After taking a history, the doctor determines changes in the size of the bladder by palpation. He usually prescribes the following studies:
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Urine culture;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary organs;
- Cystoscopy;
- Contrast urography.
In some cases, a CT or MRI may be required. Only after the results of the examination can the doctor accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the root cause of the pathology.
To eliminate infectious diseases, a course of antibiotics and antibacterial agents is prescribed; in the presence of urolithiasis, drugs to remove stones are prescribed. If the illness is psychological in nature, the doctor usually prescribes sedatives that calm the nervous system.
Some gynecological diseases, due to which the bladder is not completely emptied, require the use of hormonal drugs. In cases, the patient may be prescribed surgery.
Unfortunately, even complete relief from unpleasant symptoms cannot guarantee that a person will not be bothered by relapses in the future.
Any person experiences the feeling of a full bladder several times a day. To get rid of it, a healthy person just needs to go to the toilet.
However, urination does not always lead to the desired result - a feeling of fullness may remain. Such a violation is a signal of a problem in the urinary system or, less commonly, a sign of a malfunction of other systems.
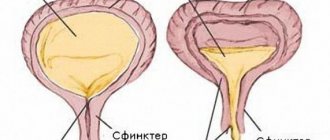
The structure of the bladder is a reservoir where urine accumulates, with locking sphincters. There are two sphincters, one of which a person controls consciously. They are located at the junction of the bladder and the urinary canal - the urethra.
When the bladder is full, its walls stretch, an urge arises, but one of the sphincters holds back urine as long as the person wants it. When urinating, it relaxes the sphincter, urine comes out through the urethra. Normally, up to 20 ml of urine can remain in the cavity.
After urination, some of the fluid may be retained, causing a true feeling of fullness. Urine is either not excreted at all, then up to one liter of liquid can accumulate in a full bladder, or not all of it is evacuated. Pathology is considered to be an accumulation of more than 50 ml of fluid. Urine cannot be removed for two reasons:
- there is a mechanical barrier to its outflow;
- the muscles involved in the process of urination are weakened.
Features of different types of pathology
A true sensation of bladder distension is more common in men.
Tumors, stones, and anatomical abnormalities of the urinary tract can act as mechanical obstacles.
A false feeling of fullness is said to exist if there is no urine in the bladder, but the urge remains. This condition occurs due to signals generated in:
- brain or spinal cord;
- the organ itself;
- surrounding tissues.
Most often, a false sensation of incomplete emptying is recorded in women with bladder dysfunction.
In recent years, doctors have noted an increase in the number of patients with this pathology, which occurs without changes in the qualitative composition of urine. This proves that neuroendocrine pathologies and mental changes more often become a source of dysuria.
In pregnant women, the growing fetus puts pressure on the bladder, causing an unpleasant feeling that it is full, even with little urine.
Drinking diuretic drinks, such as those containing alcohol, caffeine or aspartame, causes a false urge.
Any feeling of fullness, if it occurs constantly, requires contacting a urologist.
Urethral strictures
Scarring in the urethra caused by inflammation or mechanical damage. With this pathology, there is no opportunity to urinate normally. You have to work hard. The stream is weak and splashes to the sides. . The process of urine outflow is accompanied by severe pain. The disease threatens complete fusion of the urethra. Urination becomes impossible, so a tube is inserted into the peritoneum to allow fluid to flow out into the urine bag. Surgery to dissect scars and urethroplasty is indicated as treatment.
Causes of feeling a full bladder
The sensation of a full bladder after urinating may occur periodically or be constant. It occurs due to pathology or the influence of physiological factors.
Bladder overflow can be caused by:
- drinking plenty of fluids (more than 2.2 liters per day),
- taking substances that stimulate the urinary system.
In these cases, discomfort does not indicate illness; it can be eliminated by reducing the amount of fluid consumed or replacing medications.
A separate group of causes of the feeling of fullness of the bladder includes neuroendocrine, iatrogenic (spinal cord injuries due to operations, manipulations) factors and mental disorders.
A constant feeling of a full bladder is possible with diseases of neighboring organs - the small intestine, appendix, ovaries.
Main Factors
Why doesn't my bladder empty completely? Urine retention occurs if its outflow is obstructed. Possible reasons for this:
- Mechanical compression of the urinary canal:
- full intestines with constipation;
- enlarged uterus;
- tumors, neoplasms;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- enlarged prostate gland.
- Urethral obstruction due to:
- blockage with stones, blood clot, pus, foreign bodies;
- urethral strictures;
- neoplasms.
- Detrusor weakness.
Features in men and women
In a man, the feeling of a full bladder most often occurs when the urinary tract is obstructed due to prostate pathologies (adenoma, prostatitis). Hyperplasia of the central lobe of the prostate leads to compression of the urethra. It becomes difficult to pass urine through the narrowed channel. For this reason, the bladder begins to fill with remaining urine.
A common cause of urinary stagnation is urethral pathology. A narrowing of the urethra (stricture) is more often observed in men due to its large length. Stricture is caused by injuries to the urethra (most often), infectious diseases (gonorrhea), and chemical burns during self-medication.
In women, the feeling of fullness often turns out to be false, its sources:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- bladder stones;
- fibroids, endometriosis.
The cause is irritating signals coming from the bladder or other organs, most often when they are inflamed. Painful impulses in women provoke contraction of the bladder, intravesical pressure increases, which causes a feeling of fullness. Similar inflammations can occur in men, but in women they are recorded more often. The female urethra is wider and shorter, which facilitates rapid upward penetration of microorganisms. Sexual intercourse causes the transfer of bacteria from the vulva to neighboring organs.
The urinary and genital organs of women have a close anatomical location, common blood supply and innervation. This creates the prerequisites for the mutual involvement of the urogenital organs in pathological processes.
Stones can also block the urinary tract, causing fluid to accumulate. The calculus can close the entrance to the urethra only at the moment of urination, then the process suddenly stops. When changing body position, urine output is restored. In addition, stones injure the mucous membrane of the bladder, causing pain impulses.
Bladder dysfunction with endometriosis or fibroids is caused by two factors: tissue compression and hormonal imbalance affecting the organ's receptor apparatus. In women, a feeling of a full bladder without pain occurs when:
- menses,
- pregnancy.
Pathological causes of frequent urination in women
Diseases of the urinary system are the most common cause of frequent urination. Let's look at these diseases.
Cystitis. This disease is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. Women suffer from cystitis more often than men, since the female urethra is shorter and thicker than the male urethra, which facilitates the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the bladder from the external environment.
With cystitis, there is pain in the lower abdomen, and urination becomes more frequent and is accompanied by pain and burning. Also, after going to the toilet, a woman experiences a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder and the urge to urinate. In addition, there may be urinary incontinence and the appearance of pathological impurities in it, causing it to become cloudy.
Urethritis. Urethritis is an inflammation of the urinary canal that is caused by various pathogens.
Urination with urethritis becomes more frequent, accompanied by itching, pain and burning in the urethra.
Pyelonephritis. This disease is an inflammation of the renal pyelocaliceal system, which is caused by pathogens. Frequent urge to urinate is characteristic of chronic pyelonephritis. Women also experience lower back pain, body temperature rises, shivering, and the urine becomes cloudy due to the admixture of pus and blood.
Urolithiasis disease. Frequent urination with blood is often a sign of urolithiasis, since stones can damage the lining of the urinary tract, causing pain and bleeding. Also, symptoms of this disease may include interruption of the stream of urine, pain in the lower abdomen and along the urinary canal, which radiate to the inner thigh and genitals.
Atony of the bladder. With this disease, the walls of the bladder have weakened tone. Atony of the bladder is manifested by a frequent urge to urinate, during which a small amount of urine is released.
Overactive bladder. This condition is a complication of other diseases of the urinary system, in which the activity of the nerve receptors in the walls of the bladder increases, which is manifested by a frequent urge to urinate.
Uterine fibroids. In the initial stages of the disease, only menstrual irregularities, lower abdominal pain, and metrorrhagia are present. After the tumor reaches a significant size, it begins to compress the bladder, which is expressed by a frequent urge to urinate.
Prolapse of the uterus. This condition leads to displacement of all organs that are located in the pelvis, in particular the bladder. Therefore, patients suffer from heavy periods, pain in the lower abdomen, uterine bleeding, as well as frequent urination and urinary incontinence.
Frequent and excessive urination in women can be caused by pathology of the endocrine system, for example, diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus.
Diabetes. With this disease, the body does not have enough insulin, resulting in increased sugar levels in the blood and urine. Glucose is able to carry water molecules, so when it is actively excreted from the body in urine, it takes water with it, causing frequent urination.
Diabetes insipidus. This disease is characterized by severe thirst and an increase in daily diuresis due to a malfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
The appearance of frequent urination in diseases of the heart and blood vessels is explained by the fact that during the day fluid accumulates in the body tissues, which is actively excreted at night, causing nocturnal nocturia.
Estrogens in the body are responsible not only for the possibility of egg fertilization, but also for the muscle tone of the vagina and urethra. These hormones promote active blood supply to the organs of the genitourinary system, including the urethra. Due to this, the normal tone of the muscular lining of the urinary canal is maintained.
Therefore, when hormonal levels change dramatically in women during menopause, a weakening of muscle tone is observed in the urethra, which is manifested by increased urination. In addition, during menopause, many women suffer from urinary incontinence.
Also important in the occurrence of frequent urination in women who do not have a menstrual cycle is the fact that estrogens affect the secretion of immunoglobulins, the sensitivity of the receptors of the bladder and urethra.
During menopause, women may complain of frequent urination at night and during the day, urinary incontinence and a feeling of bladder fullness. Also, after the decline of reproductive function in women, the risk of developing infectious processes in the urinary tract increases significantly. Therefore, it would not hurt for women with this problem to be examined by a urologist.
Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder and associated symptoms
Regardless of the etiology, an overfilled bladder itself becomes the cause of the development of diseases and the appearance of some associated symptoms.
- With prolonged overfilling of the bladder, the muscle wall stretches, atony of the organ muscles and stretching of the sphincters develops. Weakness of the sphincters that hold urine allows it to come out in separate drops or leak.
- Accumulated urine is a good environment for the rapid development of microorganisms. Therefore, constant stagnation of urine and a feeling of fullness of the bladder are often accompanied by a complication in the form of infectious inflammation.
- One of the signs of acute inflammation is pain. Therefore, the feeling of incomplete emptying in women is often accompanied by pain during urination.
- Trying to get rid of the feeling of a full bladder, men and women often go to the toilet and strain hard and for a long time when urinating. This increased work of the detrusor leads to hypertrophy, which deforms the ureter and interferes with the movement of urine from the kidneys. Stagnation of urine in the upper urinary tract triggers pathological mechanisms in the kidneys.
- Concentrated urine in the bladder and kidneys is a good environment for the formation of stones.
Related pathological conditions
Some symptoms are not associated with bladder fullness, but accompany this feeling in women and men:
- Pain syndrome outside of urination. The intensity and localization are determined by the organ in which the pathological focus is located. Severe pain is typical for acute conditions, mild pain is typical for indolent inflammation and slow onset of urine passage.
- Disorders of the urination process. They may be a manifestation of irritation:
- frequent and painful urination;
- imperative urges;
- increased urge at night;
or obstruction:
- difficulty urinating;
- thinned stream;
- increased duration of urination.
- Sudden irresistible urges that do not end with urine output.
- Urinary incontinence. Dripping urine without urge occurs due to weakness of the sphincters and pelvic floor muscles. A sharp contraction of the sphincter and detrusor leads to an acute urge, accompanied by rapid uncontrolled release of urine - the person does not have time to get to the toilet. This type of involuntary urination is observed with cystitis, neoplasms, and urolithiasis.
Practice shows that up to 70% of women over 40 years of age lose control of urinary continence and only 3-20% express a desire for treatment.
- Body temperature rises to subfebrile levels, higher only with inflammation of the kidneys.
- Bladder swelling occurs gradually, which is why painful sensations are not always present.
- Blood and discharge in the urine. Fresh blood in the urine appears with tumors of the urethra and bladder, stones or hemorrhagic cystitis. White flakes in the urine are clots of mucus that appear when the organs of the urinary system become inflamed. Yellow or green discharge and an unpleasant odor indicate purulent inflammation. Brown flakes are a sign of glomerulonephritis.
- Sexual disorders. An increase in symptoms leads to a weakening of sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, disappearance of nocturnal erections, and a decrease in the frequency of intercourse.
If any of these symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor, despite the sensitivity of the problem. Even a combination of several symptoms will not allow the urologist to make an accurate diagnosis - additional research will be necessary.
Frequent painless urination in women during pregnancy: causes
Frequent urination in women with pain, which is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms (cutting and burning in the urethra, lower back pain, the appearance of blood and pus in the urine, increased body temperature, general weakness, increased sweating, etc.) may indicate inflammation of the organs genitourinary system.
Most often, the above symptoms are observed in diseases such as:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis.
Frequent urination in women with sexually transmitted diseases is explained by the fact that the organs of the reproductive and urinary systems are closely connected. Therefore, an infectious process that has developed in the bladder or urethra can spread to the genitals and vice versa. For example, many women experience a combination of inflammation of the urethra and vaginal mucosa.
The infection can enter the genitals through an ascending route, that is, from the urethra to the vagina and further to the uterus and appendages. And also from the vagina to the urinary canal, bladder and even kidneys.
The reason for frequent and painful urination in women may lie in irritation of the vaginal mucosa, for example, if the rules for using hygienic tampons are not followed.
In addition, there is frequent urination after sex, which is also associated with irritation of the vaginal tissue. This condition is transient, so pain and burning in women goes away the next day. But it should be noted that at this time the protective mechanisms of the irritated mucosa are weakened, so there is a risk of pathogenic microbes entering the body.
If frequent and painful urination after sexual intercourse bothers a woman for several days, then it is necessary to visit a urologist to be examined for a urinary tract infection.
During pregnancy, a woman may experience many inconveniences, such as nausea, drowsiness, general weakness, back pain, as well as painless frequent urination, which is normal.
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes changes in hormonal levels, metabolism, and an increase in the volume of circulating blood, which creates additional stress on the urinary system. For example, amniotic fluid is renewed every 2-3 hours, which cannot but affect the pregnant woman’s diuresis.
But the most significant factor that provokes very frequent urination in women during pregnancy is the increase in the size of the uterus, which puts pressure on the bladder, forcing it to empty. There is also a tendency - the longer the period, the more frequent urination. Moreover, frequent night urination is also typical for pregnant women.
In addition, during pregnancy, troubles such as spontaneous release of small portions of urine during coughing and laughter can also occur. But even this is considered the norm while waiting for a baby.
Frequent urination during pregnancy, which causes pain in the lower back and/or lower abdomen, bloody or purulent discharge from the urethra, increased body temperature, burning in the urethra, require immediate consultation with a urologist. The listed symptoms are characteristic of diseases of the genitourinary system and can negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus.
Diagnostics
The examination of the patient is aimed at identifying the cause of the pathology in order to prescribe the correct therapy. It is quite difficult to establish the cause of violations. After reviewing your medical history and taking into account your symptoms, your general practitioner will order general tests.
Women may be referred for additional examination of the genital organs to a gynecologist; in men, the prostate gland is examined. It is possible to prescribe an ultrasound, CT with contrast (urography) or MRI. Informative methods are cystoscopy and cystography.
Diagnostic methods
The list of diagnostic measures that the patient must undergo includes:
- general urine analysis and bacteriological culture;
- general blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of organs such as kidneys, bladder, prostate (for males), ovaries (for females);
- cystoscopy - in order to study the condition of the bladder mucosa.
If a patient has ambiguous test results, he is prescribed other procedures for a detailed examination and establishment of an accurate diagnosis. For these purposes, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT), scintigraphy, and X-ray of the urinary tract with contrast are performed. After all the studies are completed and the doctor has the results in hand, he diagnoses the patient and prescribes the necessary treatment.
Return to contents
Treatment
If you constantly feel like your bladder is full, you need professional medical help. Self-treatment results in unpleasant consequences: injury to the urethra when trying to insert a catheter, infection, and possible rupture of the organ in the absence of therapy.
Treatment is carried out after the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis. In an emergency, the patient is given a urethral catheter to remove fluid. Depending on the type of disease, treatment with medications or surgery is prescribed. For spasms, antispasmodics are prescribed, pain is relieved with analgesics. Cystitis and other pathologies of inflammatory etiology are treated with antibiotics. Tumors, strictures, and blood clots are removed surgically.
Prostate adenoma is treated depending on the stage of development - conservatively or surgically. Small stones are dissolved with drugs, the choice of which is determined by the origin of the formations; large ones, in case of difficulty in the outflow of urine, are removed surgically. Treatment of neurogenic excessive contractions of muscles and sphincters is carried out with anticholinergic blockers. When muscles weaken, exercises are prescribed to restore their tone and diet.
What are the characteristic signs to use to diagnose the disease?
Since a large number of diseases can provoke a feeling as if the organ is full, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis before prescribing treatment. When making a diagnosis, not only the patient’s symptoms are taken into account, but also diseases of any nature that he had previously suffered from, gender and age. According to statistics, women are more often susceptible to diseases of the genitourinary system.
Return to contents
Inflammation of the urinary system
With the development of the inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system, the most common diseases are cystitis and urethritis. If you do not pay attention to the felt filling of the bladder and other manifestations, the disease will develop into pyelonephritis. Most often it is women who get sick due to physiological characteristics. Characteristic manifestations of the inflammatory process:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- burning and stinging when urinating;
- temperature increase;
- headache;
- cloudiness of the urine and the appearance of a whitish tint.
Return to contents
Prostate diseases
Prostatitis and prostate adenoma are always accompanied by an increase in the size of the organ (edema). Swelling provokes pressure on the urethra, it is more difficult for urine to come out and there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The main signs indicating prostatitis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- a weak, intermittent stream when a man relieves himself;
- involuntary leakage of a certain amount of urine.
Also, swelling and similar symptoms are characteristic of the development of impotence. If the patient has prostate adenoma, in addition to the previously listed signs, weight loss and prolonged elevated temperature will be added. In addition to prostate tumors, neoplasms can also occur in other organs of the genitourinary system. The appearance of blood in urine is a signal of the onset of bladder cancer.
Return to contents
Diseases associated with gynecology
Impaired bladder emptying indicates the presence or onset of adnexitis. A characteristic sign of this disease is an increase in body temperature and constant pulling pain in the lower abdomen. The pain is often one-sided, but can also occur on both sides at the same time. Discharge uncharacteristic of a healthy person is observed from the urethra.
Return to contents
Stone formation
The inability to fully empty the bladder is a manifestation of a narrowing of the lumen of the urinary tract. Quite often the paths are clogged with stones of various origins. This problem is accompanied by sharp pain, sometimes with acute attacks in the lumbar region, and a burning sensation in the urinary tract. Urolithiasis requires immediate treatment, so when the first symptomatic manifestations appear, the patient should consult a doctor.
Return to contents
Innervation disorders
The feeling of fullness is also caused by damage to the nerves that are responsible for urinary function - the neurogenic bladder. Disruption of the innervation of the bladder in a patient is accompanied by problems with the release of urine to the outside, since the functioning of the bladder itself fails. Problems with the passage of signals from the nerves also appear due to severe diabetes.
If the innervation is disturbed in other organs of the genitourinary system, they affect the performance of the urinary function. The organ is not able to produce sufficient contractions to completely empty itself. Because of this, the cavity is filled with urine residues. These consequences cause:
- multiple sclerosis;
- lesions in the spinal cord;
- hernias compressing the spinal cord.
Due to lethargy, the bladder not only does not completely empty, but also begins to stretch. This process is not accompanied by pain due to the fact that the increase in size occurs gradually, and impulses from the nervous system practically do not pass through the organ or are absent. Moreover, even if the organ is greatly stretched, the patient regularly observes a small amount of discharge from the urinary tract.
Return to contents
Questions to ask your doctor
- What type of incontinence do I have?
- What is the likely cause of my incontinence? Is this cause treatable?
- If so, will this relieve my incontinence? When will I feel relief?
- Should I do Kegel exercises? How often?
- Will a bladder training program help manage incontinence?
- Does it make sense to make some lifestyle changes?
- I am very embarrassed about my incontinence. How can I minimize symptoms until I recover?
(No Ratings Yet)
Loading…
Principles of therapy
If the cause of the disease is unclear and there is no proper treatment, complications will not be long in coming.
An overfilled bladder causes stagnation of urine both before and after urination - this is a common cause of discomfort; various bacteria actively multiply in residual urine, the inflammatory process can spread to other parts of the urinary tract - to the ureters, urethra, even reaching the kidneys - and cause pyelonephritis. Therefore, with this symptom, there is no need to waste time and be examined carefully.
If there is a bacterial etiology, for example, inflammation of the bladder in women due to the anatomical features of the structure, treatment is carried out with antibiotics. Antispasmodics relax and help relieve pain during spasms, while analgesics eliminate pain of a non-spasmodic nature. In the presence of tumors, stones, strictures, or bladder ruptures, surgical treatment is required, of various types, the choice is quite wide. Small stones are removed conservatively by dissolving them with herbal remedies; in case of problems with other organs, the underlying disease is treated, for example, in case of constipation, cystitis is secondary and will go away after
uropraktik.ru
Overcrowding during pregnancy
The pregnancy period is difficult for every woman. The body of the expectant mother, all its organs and systems, are being rebuilt, preparing for the difficult life period of bearing a child and childbirth.
At the very beginning of pregnancy, the size of the fetus is still very small, however, the uterus is already beginning to rebuild: the size of the organ increases, its walls become thicker.
During pregnancy, the level of the hormone progesterone increases in a woman’s body, as a result of which the bladder sphincter becomes weaker.
Over time, as the fetus grows, the size of the uterus increases, and it begins to put pressure on neighboring organs , including the bladder.
This leads to a decrease in the size of the organ cavity, and, accordingly, to a greater rate of its filling with urine. As a result, the pregnant woman feels a frequent urge to urinate .
Closer to the expected date of birth, the uterus rises slightly, partially extending into the abdominal cavity, while the pressure on the bladder decreases, and the frequency of the urge to empty the organ decreases.
Diagnostic measures
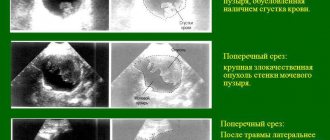
To get rid of these unpleasant and painful sensations, proper diagnosis and consultation with a doctor is necessary. In addition to analyzing complaints, the doctor will definitely prescribe general blood and urine tests; urine is cultured for bacteria and their sensitivity to antibiotics is determined, an ultrasound examination of all pelvic organs, ureters, and the kidneys themselves is performed, an X-ray with a contrast agent is performed (detects tumors, parasites, stones); if the picture is unclear, cystoscopy of the bladder is performed.
Cystoscopy is a painful procedure, performed with local anesthesia, but allows a thorough examination of the inner surface of the vesica urinaria. If the etiology is unclear, MRI and CT are prescribed. Since there are many factors for the occurrence of bladder pathology, several diagnoses are being studied to accurately determine the cause. Therefore, diagnosis may take more than one day, but this is necessary to choose the optimal treatment. One difficult diagnosis is, for example, overactive bladder.