The 21st century is the century of technology. But neither high technology nor the latest developments in pharmacology are able to completely rid humanity of oncology.
In Russia, about 300 thousand people die every year from various types of cancer. Among the fair half of humanity, the most common are breast cancer and cervical cancer. Bladder cancer in women is far from the last place.
Prognosis for poorly differentiated and highly differentiated cancer
The degree of differentiation of cancer is no less important. It determines the nature of cell development. Thus, the prognosis for highly differentiated bladder cancer is more favorable than for poorly differentiated one, since the cells within the tumor are clearly visible. They have regularly shaped nuclei and do not have the structures that are characteristic of normal tissue.
Poorly differentiated cancer causes dramatic changes in the structure of cells, which is why sometimes they cannot even be recognized. Such cells are also characterized by a high rate of division, which gives them a high potential for malignancy. For this reason, the prognosis for poorly differentiated cancer is worse than for highly differentiated cancer.
Stages of cancer in the bladder
The International Union Against Cancer has developed a system of tumor stages, nodes and metastases, which is used in the treatment of the disease:
- CIS is a preinvasive carcinoma limited to the epithelium.
- Ta is a papillary tumor limited to the epithelium.
- T1 – invasion of tumors into the mucous membrane.
- T2 – tumor invasion into muscle tissue.
- T3 – cancer invasion into fat tissue.
- T4 – Tumor involvement in adjacent organs such as the prostate, rectum or pelvic side wall.
- N+ – metastases to lymph nodes.
- M+ – Metastases.
More than 70% of all newly diagnosed bladder cancers do not invade muscle tissue, approximately 50-70% are Ta, 20-30% are T1, and 10% are CIS. Approximately 5% of patients have metastatic disease, which usually involves lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bone and central nervous system. Approximately 25% of affected patients are diagnosed with a muscle-invasive disease.
At stage 3
This stage is divided into several more substages, depending on where the abnormal cells begin to spread. Also the third stage is important. If the disease progresses to the fourth stage, the prognosis will be extremely unfavorable.
At the third stage, they often resort to surgery to remove the bladder, supplementing treatment with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Relapses occur in approximately 25% of cases. But survival rate for bladder cancer after surgery is higher than for other cancers, even in advanced forms. The prognosis is better in patients who do not face additional medical problems.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of cancer involves several laboratory and instrumental studies of the patient.
Laboratory tests may include various tests. For example, a routine urine test can detect microhematuria and suspect the disease.
Analysis for the presence of atypical cells (cytological examination) most often allows us to determine the recurrence of bladder cancer.
Tank culture (bacteriological examination) of urine helps to identify the presence of dangerous and harmful bacteria in the urine, since bacterial infections of the pelvic organs often give symptoms similar to oncology.
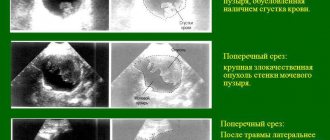
An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed on a full bladder. To do this, about an hour before the examination, you need to drink about 6 glasses of water at once. This type of study allows you to accurately identify the presence or absence of a tumor and its size. It is also possible to say with a high degree of probability whether the tumor has grown into neighboring organs.
Intravenous urography. For this purpose, a substance that stains the urinary tract is injected intravenously. A series of x-rays are then taken. Thanks to the X-ray contrast agent, visualization of the kidneys, ureters and bladder becomes possible.
Computed tomography allows us to see not only the organs that interest us, but those located nearby. It gives a clearer picture of what is happening than an x-ray.
Magnetic resonance therapy (MRI) of the pelvis is a more sensitive and painless examination method. It allows you to see the lymph nodes near the cancer tumor, which often metastasize.
Endoscopy is performed under local anesthesia. To do this, a thin tube with a microscopic video camera is inserted into the urethra (urethra) and bladder. This allows you to see the picture of what is happening from the inside, visualize various pathologies of the mucous surface and take tissue samples from suspicious areas of the bladder. This is followed by a series of laboratory tests of the samples taken. If the presence of cancer cells is confirmed, the patient should be examined immediately to determine the stage of the disease.
Cystoscopy is often used not only for examination, but also for the treatment of superficial cancer that does not require surgery.
During cystoscopy, very small tumors or flat cancerous lesions may not be visible and may be missed. For this purpose, Fluorescence or Photodynamic diagnostics (PD) is used. To do this, a special luminous substance is injected intravenously. When it enters an area affected by cancer cells, it begins to emit different colors. Depending on the image obtained, the specialist makes a conclusion about the presence of a tumor, its size and location.
Only after all the examinations and consultation with a pathologist and oncourologist can a diagnosis be made and treatment begin immediately, depending on the type of cancer.
At the moment, biopsy of the bladder mucosa remains one of the most common in our country.
At stage 4
Survival data is provided in official WHO statistics. According to it, the most unfavorable prognosis is observed for stage 4 bladder cancer. In the terminal form of the disease, the 5-year survival rate is 10%, i.e. 90% of patients do not cross this threshold.
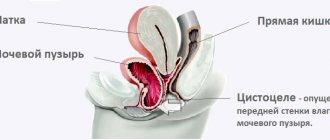
The tumor in the fourth stage spreads to neighboring organs: in men, to the prostate gland, and in women, to the vagina. Metastases also appear in the lymph nodes, abdominal cavity, and pelvic bones. In this regard, treatment is often palliative in nature and aims to prolong and improve the patient’s quality of life.
In order not to bring the disease to the last stage, it is worth contacting a urologist when the first symptoms appear. In our clinic you will be provided with qualified assistance. We have modern diagnostic and treatment methods. To make an appointment, you can use the online form or our clinic’s contact number.
All publications...
Causes of bladder cancer
The disease is characterized by rapid development, atypical cells form inside the mucous membrane of the organ. The most common causes of bladder cancer in women include:
- Smoking - this addiction destroys many organs and systems of the body. The harmful effect on the bladder is due to the fact that tobacco breakdown products are excreted through the urinary system.
- Working in a hazardous industry - contact with certain chemicals can negatively affect the walls of the bladder. Chemical industry workers are at risk.
- Unbalanced diet, predominance of fatty, fried, spicy foods.
- Radiation exposure often causes the development of malignant tumors.
- Pathologies of the urinary system, which, by disrupting the functioning of the organ, contribute to the development of cancer. Women suffering from chronic cystitis or schistosomiasis are at risk.
Determining the exact cause of the disease helps specialists choose the most effective therapy.
Classification
Oncopathology is characterized by several signs. Malignant neoplasms of the walls and mucous membranes have many histological varieties and stages of development. An important point for prescribing therapy is whether the patient has been diagnosed with invasive or non-invasive cancer. Knowledge of the classification of a dangerous disease allows you to select the optimal treatment option for each case.
Types and forms:
- non-invasive cancer. Favorable prognosis, benign course, no metastases;
- invasive cancer. Severe course, active growth of tumor cells through the walls of the bladder, spread to other organs.
Sometimes a non-invasive variety becomes invasive and the disease progresses.
On a note:
- the tumor can develop on the bottom, neck or body of the bladder;
- During a biopsy, doctors identify a certain type of cancer based on examination of tumor cells under a microscope;
- distinguish between spindle cell carcinoma, intercellular carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and other types of tumor;
- The symptoms of oncopathology are similar for different histological types.
Stages:
- 0 – the neoplasm is small in size, the tumor does not grow through the basement membrane, and other organs are not affected. Timely removal of affected tissue leads to recovery;
- 1 – the size of the tumor is small, but the penetration of altered cells of the bladder wall begins;
- 2 – tumor growth through the basement membrane, metastases appear in the inguinal lymph nodes;
- 3 – the size of the tumor increases, neighboring organs are often affected;
- 4 – when examined on a tomograph, doctors detect multiple metastases in other (distant) organs.
Classification of tumors according to the international TNM nomenclature:
- T – coding indicates the size of the tumor. From To to T4;
- N – presence or absence of tumor cells in the tissues of the lymph nodes. From No to N3;
- M – detection of distant metastases. From Mo to M1.
Treatment of the disease
It is advisable to remove a malignant tumor on the bladder at an early stage . Chemotherapy is used. Radiation therapy is used separately or in combination with others; in addition, immunotherapy can be used.
Operation
When the tumor is small, it is possible to use closed surgery to remove it. Using a catheter under video surveillance, a device is launched into the cavity that can remove the tumor. The resulting material is sent for histological examination. This method is also called transurethral resection.
Germination into the walls of an organ, a large spread of a neoplasm, sometimes creates a situation where it is best to remove the organ with infected neighboring cells.
Radical measures involve solving the problem of urination:
- creation of artificial urinary canals and urinals;
- formation of urine output into the intestines, in some cases it is discharged onto the skin.
Other treatment options for cancer:
- Chemotherapy. It can be used before surgery, as well as after it. If it is too late to perform surgery, chemotherapy is used to improve the patient’s well-being. An excellent effect is shown by a local procedure - intravesical chemotherapy. The person may be prescribed intravenous injections or medications.
- Folk methods. According to the recommendations of a specialist, in some cases celandine juice is included in the treatment of bladder cancer. The juice is prescribed to be used 0.5 tablespoon per day, the duration of treatment is one week. Take celandine juice with milk. If it is well tolerated, the dosage can be doubled. This course is determined to last a month.
- Radiation therapy. Used as an independent method or in complex treatment.
- Conservative treatment. The method of introducing the BCG vaccine into the bladder has shown itself to be positive. The result is superior to the effect after chemotherapy. Used in case of early stage of the disease. After surgery, this method is also recommended. It is prohibited to use it if a person has bleeding in the bladder or tuberculosis disease.
- Immunotherapy. In treating the patient, drugs are used that stimulate the body to better resist the disease.
Relapse
After surgery, a relapse is sometimes possible : a new tumor forms from the remaining malignant cells. The extent to which this option is possible will depend on the degree of differentiation and stage of tumor maturity.
Small superficial neoplasms are least likely to recur. A type of neoplasm with slight differentiation is capable of more rapid development.
Complete excision of the bladder along with tissues that may be affected by the cancer process has the most favorable prognosis regarding the development of relapse. If transurethral resection is used to remove a tumor, chemotherapy and BCG therapy are used to prevent relapse.
Survival prognosis
How successful the treatment will be depends on many factors:
- the method used for treatment;
- the degree of development or maturity of the pathology process;
- type of neoplasm.
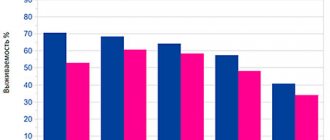
Often, transitional cell formation creates superficial tumors that, when initially removed, provide a good prognosis for survival. About seventy percent or more are healed from the disease.
If the bladder is completely removed, only half of people can live for five years. When treatment is supplemented with other modalities, such as radiation or chemotherapy , the survival rate improves slightly.
When treatment is carried out in the early stages of the disease, up to seventy percent of people can live for five years or more. Treatment of patients with bladder cancer, which has already reached the third stage, reduces the survival prognosis; up to twenty percent of people live for more than five years.
Disease prevention
Prevention of bladder cancer in men is as follows:
- You need to quit smoking.
- Live in an area with good environmental conditions.
- Avoid contact with chemicals, especially aromatic amines.
- Do not be exposed to ionizing radiation.
- Treat chronic inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system.
The danger of malignant tumors is that often at the initial stage they do not manifest themselves in any way or the person ignores the first symptoms . In these cases, a person learns about the diagnosis already when the disease is at its “blooming” stage and the prognosis for survival does not always sound optimistic.
Source
Reasons for the development of cancer pathology
The tumor process occurs against the background of negative factors. In some cases, doctors identify several reasons for changes in bladder cells.
Provoking factors:
- penetration of oncogenic infectious agents into the body: individual genotypes of human papillomavirus, Epstein-Barr virus;
- frequent contact with aniline dyes, benzene derivatives, smoking. The longer carcinogens act on the body, the higher the risk of cancer pathologies of various organs;
- microdamage to the bladder mucosa with regular insertion of a catheter, manipulation in the organ cavity in the treatment of acute and chronic pathologies;
- exposure to high background radiation or chemical compounds during man-made disasters;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic course of infectious pathologies (cystitis) against the background of a short urethra in women, frequent relapses that provoke damage to bladder tissue and tumor development.
Bladder cancer ICD code – 10 – C67. To clarify the location of the tumor, codes from C67.0 to C67.9 are used: anterior/posterior walls, triangle, neck, ureter, other parts of the affected organ.
See a selection of effective methods for treating postcoital cystitis in women.
Read about the symptoms of kidney abscess and treatment of the disease at this address.
Stages of the disease
If the oncological process in the bladder is not diagnosed in time, it will begin to progress rapidly, going through all the stages characteristic of a malignant neoplasm:
- First stage. The tumor is located in the mucous membrane of the bladder, but does not penetrate the muscle fibers. Cancer does not make itself felt by any manifestations. At this stage, the woman has a high probability of complete recovery.
- Second. Cancer grows into the smooth muscles of the bladder, but the process is still local. The chances of relapse-free recovery are reduced, but are still high if timely and sufficient therapy is prescribed.
- Third. The neoplasm increases in size and involves part of the fatty membrane, peritoneum, lymph nodes close to the lesion, and internal genital organs. Cancer cells spread with lymph flow and blood flow, forming new foci - metastases. The prognosis for women with this stage is unfavorable.
- Fourth. The tumor invades most of the pelvic organs, multiple metastases poison the organs with decay products, and the body is exhausted. The survival rate of patients with this stage is very short even with treatment.
Diagnostic methods
Timely consultation with a doctor and correct diagnosis are the key to successful treatment. The most informative method is considered to be cytoscopy. It involves a visual examination of the bladder, or more precisely, its internal cavity. During the procedure, biomaterial is collected for biopsy. In laboratory conditions, this material is examined by cytological and histological methods. Which provides confirmation or refutation of a previously diagnosed cancer. Cytoscopy also helps to find out the stage of the disease.
If the tumor is too small, a fluorescent control method is used. Using a cytoscope, contrast is injected into the cavity. It accumulates in tumor cells, due to which, when illuminated with blue light, it, regardless of size, will be visible in pink.
MRI and ultrasound are prescribed as an additional measure. The first technique makes it possible to determine whether other organs are affected. The internal structure of the tumor is also visualized. As for ultrasound, it shows the outer boundaries and saturation of the tumor.
Important! If the clinical picture is such that there is a suspicion of metastasis, an additional X-ray examination of the bones is performed.
Main symptoms
At first, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, even when the tumor has already begun to develop and grow.
After a certain time, the patient discovers blood in his urine, or hematuria.
As a rule, 90% of visits to the doctor with subsequent detection of a tumor are caused by this symptom.
It is also worth considering the specifics of the appearance of blood in the urine of women. What could this be, besides oncopathology of the bladder? Inflammatory processes such as cystitis are accompanied by similar symptoms. Hematuria sometimes occurs in pregnant women, without being a symptom of a dangerous disease. Also, bloody impurities can be detected during menstruation, which may be a sign of endometriosis. Of course, blood clots and streaks may actually be menstrual flow, but if the picture looks suspicious, not as usual, it is better to play it safe and consult a doctor.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on the stage and grade of the tumor at the time of diagnosis. Its purpose is primarily to remove the tumor. In the case of superficial tumors, simply removing the tumor may be sufficient.
If the tumor has penetrated the muscle wall, the entire bladder must be removed, an operation called cystectomy. Slowing the development of metastases and reducing the risk of surgical recurrence is often associated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Regular medical monitoring is maintained after treatment to ensure that the tumor does not return.