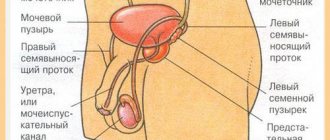
Today, cystoscopy is increasingly used for visual inspection of the internal mucous membrane and the cavity of the urinary bladder in men and women.
The value of this method is that it can help detect serious diseases even at the earliest stages of their formation.
Cystoscopy of the bladder in men and women is an excellent alternative to surgery, as well as a unique way to diagnose and treat all kinds of disorders and their causes.
The study is currently widely used in urological practice, which has made it possible to significantly reduce the development of complex forms of oncological pathology with metastasis and complications of chronic diseases, leading to a significant deterioration in a person’s quality of life.
What is cystoscopy?
Cystoscopy is an endoscopic procedure for the purpose of examining and analyzing the condition of the internal walls of the organs of the urinary system. Manipulations are carried out using a cystoscope placed in the urethra and then directly into the bladder. The device is a long tube with a complex optical device, thanks to which it is possible to record various changes in the condition of the walls and disease of the bladder.
There are three types of cystoscopy procedure.
- Rigid. It is performed under local anesthesia and is used to perform a biopsy. With its help, you can remove the affected areas of the organ.
- Flexible. Anesthesia is injected directly into the urethra, and the patient remains awake during the manipulations. However, if you need to remove the affected part of the organ or perform a biopsy, you will have to do cystoscopy again using general anesthesia.
- Fibrocystoscopy. It is performed under general anesthesia and is used not only for examination, but also for surgical operations.
Safety and Consequences
The usual consequences are aching pain and discomfort after the procedure. Such consequences are considered natural. Painkillers are not prescribed as they thin the blood, which can cause bleeding in the bladder.
Neglect of safety, in which sufficient attention is not paid to patient hygiene and the cleanliness of the device itself, is the most common case of subsequently causing problems such as infection.
In order to prevent possible infection, antibacterial agents are sometimes prescribed.
Due to minor injuries to the urinary tract that occur during the passage of the tube, a small amount of blood may appear in the urine. In this case, it is recommended to drink more water to normalize the microflora of the urinary tract.
Traumatic consequences in the urethra, as a rule, occur in men due to insufficiently careful insertion of the tube or if the process is carried out in the presence of an adenoma.
There is a reaction to anesthetics that makes it difficult to urinate.
When is cystoscopy prescribed?
There can be many conditions for undergoing cystoscopy of the bladder in women and men:
- purulent or bloody discharge in the urine (hematuria or pyuria);
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- urinary tract infections;
- regular pain in the pelvic area;
- urolithiasis disease;
- chronic cystitis;
- abnormal cells in urine;
- polyps, tumors in the urethra or bladder detected by ultrasound, magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- urinary retention due to inflammatory processes in the prostate gland or due to narrowing of the urinary canal.
Cystoscopy can also be used for therapeutic purposes:
- removal of stones;
- elimination of tumors and polyps;
- stopping bleeding;
- removal of obstructions.
Why is the procedure performed?
Cystoscopy is the examination of the mucous membrane of the bladder, as well as the urinary tract. The procedure is carried out using a special device called a cystoscope - hence the name of the procedure. Thanks to it, you can reliably assess the current state of the mucous membranes of the urethra and bladder, which will allow you to diagnose the early stages of pathologies, as well as carry out a number of treatment procedures without surgical intervention.
Contraindications
Cystoscopy is contraindicated if:
- exacerbation of inflammation in the bladder: urethritis or cystitis;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels, previous myocardial infarction;
- pregnancy (the walls of the bladder are close to the uterus and careless insertion of a cystoscope may damage the walls of the reproductive organ).
In this case, patients are prescribed gentle ultrasound examinations or excretory urography.
Indications
Indications for cystoscopy are:
- The need to determine the causes of bloody impurities in urine;
- In the presence of previously identified interstitial cystitis;
- In the presence of enuresis in children and adults, especially in the absence of effect from the therapy;
- For chronic cystitis, if treatment does not provide complete elimination of the pathological process, which periodically worsens;
- If laboratory diagnostics showed the presence of cells of atypical origin, since such a finding often indicates the development of tumor processes;
- It is used as one of the therapeutic techniques in the treatment of urolithiasis;
- Performed for patients with hyperplasia of prostatic tissue, narrowing or blockage of the ureteral structures;
- In the presence of frequent urination of unknown etiology.
Cystoscopy of the bladder and urethral structures is necessary; alternative diagnostic studies cannot detect small formations, determine their origin, nature and extent of spread.
For example, ultrasound diagnostics is not able to detect polyps and small ulcers in the bladder structures, while the cystoscopic method shows in detail and accurately the presence of pathology. He can detect any tumor neoplasms, determines their nature, reveals that there are stones in the bladder, inflammatory foci and traumatic injuries to mucous tissues.
Preparation
The preparatory process before surgery requires strict adherence to the recommendations of doctors.
- Refrain from eating on the day of the examination if cystoscopy will be performed under anesthesia.
- Do not empty your bladder for an hour.
- Stop taking medications, in particular painkillers, anticoagulants, aspirin, insulin, and drugs for the treatment of arthritis.
- You may need to take a urine test.
Before starting manipulations, the doctor is obliged to inform the patient about the possible consequences of cystoscopy. This study belongs to the category of invasive and sometimes leads to undesirable consequences:
- bladder infection;
- development of cystitis;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- damage to the urethra;
- perforation (puncture of the walls of the bladder with subsequent leakage of urine beyond its boundaries).
However, if the operation is performed professionally, the risk of complications is minimal. At the end of the doctor’s instructions, the patient signs a special form, thereby confirming consent to the procedure.
Types of cystoscope
The cystoscope can be rigid or flexible. This long and thin instrument is hollow inside. It has an optical mirror system. It transmits the image to the monitor. The cystoscope is also equipped with lighting lamps that improve visibility.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder: preparation for the study of women and men
If necessary, the inner tube of the cystoscope is used to deliver medication directly to the bladder mucosa, inject saline into the organ to increase visibility, and remove excess urine. Also, using this device and a cutting loop, you can cauterize tumors and ulcers and take tissue samples for analysis.
Depending on the purpose of cystoscopes
There are operating rooms, catheterization rooms, examination rooms, universal rooms and special rooms.
Operating cystoscopes
are used during medical procedures in combination with semi-rigid surgical instruments.
Using catheterization cystoscopes
Catheters are installed on the ureters.
A viewing cystoscope is intended for rinsing and examining the bladder.
.
To special cystoscopes
include pediatric cystoscopes, cystoresectoscopes and cystolithotriptors.
Children's cystoscope
They have a small diameter and are used for examining and treating children.
Cystoresectoscope
The following medical procedures are performed: resection of the prostate gland, if it is affected by cancer or adenoma; resection of tumors and papillomas of the bladder using high-frequency current under visual control; transurethral electroresection of the bladder neck affected by sclerosis.
Using a cystolithotripter
Mechanical crushing of stones in the bladder is carried out.
Features of the event
Cystoscopy takes place in a urologist’s office, a cystoscopy office, or in a hospital, depending on the complexity of the operation. Several health professionals are participating in the study:
- urologist;
- anesthetist;
- nurse;
- pathologist (if a biopsy is needed).
The procedure for bladder cystoscopy in women and men is as follows:
- The patient sits on a chair with his legs slightly raised and bent.
- The doctor treats the genital area with antiseptic drugs.
- Before use, the cystoscope is lubricated with sterile glycerin.
- The device is inserted first into the urethra and then into the bladder.
- The bladder is emptied and filled with fluid (150-200 ml) so that the doctor can examine the walls of the organ. Before the examination, the bladder cavity can be washed with a solution of furatsilin.
- The mandrin is removed from the device and the optical system is inserted in its place.
- The doctor applies an electric current and begins the examination, rotating the cystoscope clockwise.
- If treatment is necessary, other instruments may be used during cystoscopy or samples may be taken for research.
The duration of the procedure depends on the type of device and the disease and ranges from 15 minutes to 1 hour. For example, when catheterizing the ureter, cystoscopy will take about an hour, while for a routine examination 10-15 minutes are enough. Much will depend on the qualifications of the doctor.
After the procedure, the patient may remain in the hospital for some time. It is prohibited to drive or engage in professional activities on the day of the examination. The doctor may advise you to drink more liquid to eliminate the burning sensation and dilute the urine, prescribe painkillers or medications that reduce the acidity of urine. There are no dietary restrictions. A warm bath will be useful to relieve discomfort.
After cystoscopy, the patient may experience unpleasant symptoms:
- frequent urination;
- fever;
- pain in the pelvis and lower back;
- blood in urine;
- burning sensation when emptying the bladder.
If the symptoms are very bothersome and do not go away within 24 hours, you should consult a doctor.
How is diagnosis carried out?
There are two types of cystoscopes for research - flexible and more rigid:
- The rigid one is equipped with multiple lenses for viewing from all angles, while the second option takes advantage of its flexibility.
- Flexible cystoscopes allow for a less painful procedure and generally avoid some complications.
The patient is placed on a special urological chair in a supine position, with legs widely spaced and knees bent.
The genitals are treated with an antiseptic to prevent infection. In the case of therapeutic cystoscopy, general anesthesia is performed; in others, spinal and local anesthesia is used.
Having pre-treated the end of the cystoscope with petroleum jelly, the specialist carefully and smoothly inserts the tube into the urethra and directs it into the bladder. As you move through the tube, a special solution is injected in order to better see the walls of the urinary tract.
When the bladder is full, excess fluid is drained through the cystoscope tube.
The duration of the diagnostic procedure usually takes from 15 to 40 minutes, but the time can increase to two hours if therapeutic actions are necessary.
With a therapeutic cystoscopy through a tube, the doctor may do procedures such as removing polyps and administering medications or performing a biopsy.
How it is done and what cystoscopy of the bladder shows can be found in the video:
Features of the procedure for men, women and children
Cystoscopy of the bladder in women is faster than in men. The location of the organs of the genitourinary system in women is more free, and it is easier for the doctor to find an approach to the bladder. While any specialist can handle the examination of female organs, analyzing the bladder in men requires special skills. The most difficult study is considered to be for prostate adenoma.
Cystoscopy in children is most often performed under general anesthesia due to their excitability and requires skill, since the procedure uses devices with a tube of a smaller diameter.
Advantages and disadvantages of cystoscopy
The main advantages of the survey can be considered:
- High information content. Cystoscopy allows you to identify malignant tumors at the earliest stage of their development, which has a beneficial effect on treatment results.
- Possibility of performing treatment procedures during diagnostics.
- Get results quickly.
- Lack of specific training.
- Possibility of choosing the method of pain relief.
Procedures in government institutions are performed free of charge.
Its main disadvantage is the need to meet a number of conditions for a successful result:
- The urethra must be sufficiently patent for the endoscope.
- The bladder must be of sufficient volume.
- The liquid introduced into the cavity of the bladder should remain transparent. The presence of pus or blood in the organ makes visualization of the walls difficult.
- Severe pain and the urge to urinate should be absent, since the patient’s anxiety makes diagnosis difficult.
Cystoscopy is a technically difficult manipulation to perform. It should only be performed by a qualified doctor. In this regard, district clinics rarely have the opportunity to conduct it.
Women's reviews
Patients perceive bladder cystoscopy differently. Among women, reviews of this procedure are mainly focused on the pain of the process. From the stories of forum visitors, we can conclude that cystoscopy is a painful procedure, but doctors do not always give anesthesia even to children.
On the one hand, the study is informative for the doctor. Many women report that only after this analysis they were able to cure chronic diseases. On the other hand, cystoscopy is extremely unpleasant and dangerous for the patient.
Tools used
When performing cystoscopy, a cystoscope is used - an endoscopic device equipped with an optical system. A long tube is inserted into the urethra, at the end of which there is an optic and lighting system that improves visual examination.
This tube is hollow inside, which allows you to insert additional instruments through it (forceps for tissue collection, diathermoelectrodes for cauterizing erosions, blood vessels and removing polyps) or infusing medicinal liquid.
In urology, a rigid (stiff) or flexible (fiber optic) cystoscope is used.
When choosing the first option, the doctor examines through the eyepiece of the optical system.
In a flexible endoscope, a miniature video camera is located at the end of the tube, so all the information goes to the computer, that is, the image can be seen on the monitor.
Features of rigid cystoscopes
The use of a rigid (metal) cystoscope during cystoscopy allows for a detailed study of all tissue structures of the bladder and urethra.
Rigid tubes spread the tissue well and provide maximum magnification during examination, but due to their rigidity the procedure is somewhat painful.
Metal cystoscopes are mainly used when performing cystoscopy in women, since their urethra is shorter compared to men’s, so the discomfort is not as pronounced.
Rigid cystoscopes are necessarily used when diagnosis needs to be combined with treatment, for example, with cauterization of erosions or crushing stones. The instruments required for manipulation are inserted through a rigid tube more accurately and provide maximum access at the time of surgery.
Features of flexible cystoscopes
Fiber optic cystoscopes have a smaller diameter, which, combined with their flexibility, ensures the least painless insertion.
Flexible tubes easily penetrate hard-to-reach places, following the curves of the urethra and bladder. But the information of the examination often depends on the correct advancement and position of the tube, so anesthesia may be administered to the patient to relax.
Cystoscopy with a flexible cystoscope is mainly prescribed for men and children. This method is suitable for women if treatment is not expected during endoscopic diagnosis.
Application of anesthesia
Let's decipher the concepts of general and spinal anesthesia.
Anesthesia helps put a person into a state where there is no pain.
If the anesthesia is spinal, pain relief is performed with an injection into the spine. The doctor injects an analgesic into the cerebrospinal fluid. The result is that there is no pain for the person, since the lower part of the body temporarily loses sensitivity.
General anesthesia (narcosis) is carried out by intravenous injection and a special mask. Provides complete shutdown of consciousness. Not only will the person not be in pain, even after the procedure he will not remember how the cystoscopy was performed.
What it shows: survey results
The results of cystoscopy allow the urologist to understand what processes are occurring inside the bladder and how dangerous the formations previously detected on ultrasound are. Before the procedure, it is important to thoroughly cleanse the intestines, go without food for 12 hours to avoid distortion of the results and complications, and facilitate the insertion of the cystoscope.
The results of the study reveal:
- calculi (stones that appear when salts are deposited);
- tumors;
- cysts;
- injury to the walls of the bladder;
- inflammatory processes;
- abnormalities of organ development;
- chronic type of cystitis;
- papillomas;
- internal bleeding in the bladder;
- polyps.
General concept of the procedure
Few people know how cystoscopy is performed and what this type of diagnosis is. The procedure allows you to determine the most insignificant formations on tissues with maximum accuracy.
This type of diagnosis is resorted to when other methods have not shown an accurate picture of the disease. Cystoscopy is an endoscopic examination method that provides information about the nature of tumors: whether they are malignant or benign.