Gonorrheal urethritis is a specific disease caused by gonococci. In almost half of women, the disease can be complicated by inflammation of the pelvic organs, which then leads to the formation of an ectopic pregnancy and infertility.
This problem is considered a venereal disease, in which infection of the genitourinary organs occurs during unprotected sexual relations. Sometimes the reason lies in contact with ordinary things, on which the pathogen can remain active for up to twenty-four hours. It happens that at the time of birth the disease is transmitted from mother to baby.
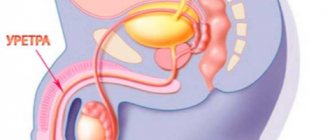
The infection process occurs as follows: bacteria enter the mucous membrane and begin to slowly destroy it. Gonococci not only destroy the epithelium, but also change its appearance, as a result of which the tissues become abnormal. An inflammatory process is formed that can spread even to the tissues located under the mucosa. The disease, as it were, prepares a path for itself leading to the area of the urethra, located in the back.
As a result of such a negative impact, pus begins to be released, which is the products of tissue decomposition. Its hue is often greenish, yellow or gray.
Gonorrheal urethritis begins to progress three to five days after infection. Bacteria penetrate everywhere and can not only multiply, but also remain in the body for a long time, and then again have a detrimental effect on the human body.
Description of the disease
Gonorrheal urethritis is caused by the gonococcal bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This pathogen settles exclusively on the mucous membranes. Therefore, it most often affects the urethra. The vagina is an unfavorable environment for its reproduction.
The bacterium penetrates into white blood cells, so it can easily move around the body and not react to the reaction of the immune system and some antibiotics.
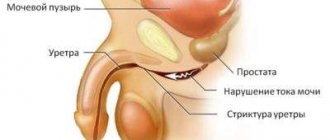
When Neisseria gonorrhoeae gets on the mucous membrane, it destroys it. In the absence of therapy, the membrane may change. Scars and cysts form. Over time, the gonococcal infection reaches the back of the urethra, thereby affecting the entire urethra.
The incubation period takes up to 10 days. In rare cases - up to 30. If symptoms are detected, immediately consult a doctor, as there is a risk of complications.
A common cause of infection is unprotected sexual intercourse with a casual partner. If treatment is ignored, the patient becomes a carrier of the disease.
Gonococci are the main cause of the disease
Gonococcal urethritis, better known as gonorrhea, is a disease with a rich history. It is described in the works of ancient scholars and even the Bible as a source of ritual impurity. Subsequently, the infection received many “popular” names - clap, French disease, hussar runny nose.
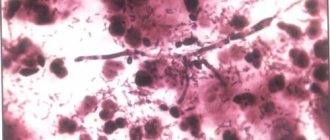
The causative agent of STIs, gonococcus, was discovered in 1879 by Neisser. Gram-negative diplococci of the genus Neisseria are paired microbial cells resembling coffee beans that face each other with their concave sides. The sizes of bacteria range from 1.0×0.7 to 1.25×0.8 microns.
The pathogenicity of gonococcus is determined by the presence of several factors:
- pili ensure attachment of pathogen cells to the epithelium of the urethra, vaginal wall, and oral cavity;
- the capsule allows you to achieve antiphagocytic activity of the microbe;
- The outer membrane protein Por promotes the intracellular survival of bacteria;
- Opa protein mediates tight attachment to the cytoplasmic membrane and penetration into the intracellular space of the epithelium;
- The Rpm protein protects gonococcal surface Ags from the action of bactericidal antibodies;
- LOS is a liposaccharide that has a toxic effect on the human body;
- IgAl protease – destroys one of the immunoglobulins of the body’s defense system;
- beta-lactamase (detected in 85-90% of cases) is an enzyme that destroys the beta-lactam ring of penicillin antibiotics.
The mobility of these microorganisms is sharply limited. Although they are quite stable in the human body, they quickly die in the environment. Heating to 40-45 °C, the action of soap solution, antiseptics and most antibiotics, are destructive for them.
Note! Unlike the external environment, in the human body gonococci quickly become resistant (resistant) to antibiotics. Today, most strains of the gonorrhea pathogen produce beta-lactamase (penicillinase).
The source of gonorrheal urethritis is always a sick person. Infection occurs through sexual contact, less commonly through the use of common household items (towel, washcloth, underwear). A special form of gonococcal infection - blenorrhea - develops in newborns while passing through the infected birth canal of the mother.
Reasons for appearance
There are several reasons for the development of gonorrheal urethritis. Among them:
- Frequent casual sex;
- Unprotected sex, including anal and oral;
- Neglecting to wash hands after visiting a public toilet, saunas and baths;
- Using another person's personal care products;
- Infection caused by a specialist during an intimate massage.
If you take responsibility for your health, use contraception and follow the rules of personal hygiene, then the risk of contracting the disease is reduced to almost zero.
Types of gonorrheal urethritis
There are several types of gonorrheal urethritis:
- Spicy. This form is the most common. In this case, the mucous membrane of the genital organ becomes inflamed and the size of the urethra decreases. Sharp pain occurs when urinating. Sometimes gray discharge is observed.
- Chronic. If left untreated, the acute form of the disease becomes chronic. This is also possible with ineffective therapy. At the same time, the patient has practically no pain and cutting in the genital area. In most cases, discharge is absent or present in small quantities.
- Latent. This type of disease does not manifest itself with any symptoms. Despite this, a person is a carrier and during unprotected sexual intercourse infects his partner. The duration of this form is up to 10 days. Then it turns into acute.
Chronic gonorrheal urethritis is divided into:
- Granulation;
- Infiltrative;
- Desquamative;
- Urethral adenitis.
All men and women should be periodically observed by a venereologist, especially if they have random unprotected sex in their lives.
You may be interested in: Bacterial urethritis: symptoms and treatment
Symptoms
Acute and chronic types of the disease have different severity of symptoms.
We can say that an acute form of the disease is developing if the infection occurs within two months. If more time has passed, we can talk about the development of a chronic form of the disease. The symptom of gonorrheal urethritis varies in intensity, depending on the form and severity of the disease, the presence of concomitant diseases, and the state of the immune system. The first manifestations of the disease, which occur within a week after infection, are pronounced discharge from the urethral opening, having a yellowish or grayish color, and impurities of pus are present. This symptomatology is complemented by cutting, burning, and painful sensations during miction. If the inflammatory process occurs in the anterior part of the urethra, the general condition of the patient is satisfactory. If the inflammatory process spreads to the back of the urethral canal, body temperature becomes febrile, severe weakness, headache and muscle pain appear.
The chronic form of the disease occurs in patients who have not been treated or have not completed treatment of the disease in its acute form, if the body’s protective functions are weakened, if the posterior parts of the urethra are involved in the inflammatory process.
With the development of a chronic form of the disease, the symptoms are not clearly expressed. A person experiences itching, burning, and tingling in the area of the urethra. When emptying the bladder, a tingling pain is felt. The discharge is usually light, mixed with pus and mucus. Most often, this symptom occurs in the morning after waking up.
Symptoms of gonorrheal urethritis in men
Signs of gonorrheal urethritis in men:
- Changes in the color and clarity of urine;
- Burning and cutting during urination;
- Pain syndrome in the pelvic area;
- Inflammation and hyperemia of the head of the penis;
- Purulent discharge.
If the disease is not treated, it develops into a chronic form. At the same time, the risk of complications increases. The peculiarity is that half of the patients had no symptoms at all. The other half had mild aching pain, and also in the morning, during the first urination, a small amount of pus with blood came out.
The determination of treatment and medications for gonorrheal urethritis in men is carried out only by a specialist. If symptoms are detected, you must contact a urologist and undergo all the necessary tests.
Diagnostic and treatment measures
The main goal of diagnosing the disease is not its differentiation - the specificity of the symptoms of gonorrheal urethritis does not allow it to be confused with other pathologies. However, a thorough examination of the patient is very important, as it allows doctors to determine the etiology of the disease, excluding other (non-bacterial) causes of the onset of the inflammatory process.
The main diagnostic measure used to detect inflammation of the walls of the urethra is:
- bacterioscopic examination of a smear of the contents of the urethra to detect pathogens;
- bacteriological analysis to isolate a pure culture of gonococcus and select the most effective treatment by testing the sensitivity of bacteria to a particular group of antibiotics.
Based on the data obtained, infection therapy is prescribed, including:
- etiological effect on bacteria with antibiotics;
- immunological reinforcement of the body.
Etiological treatment measures
Antibacterial medications are prescribed to the patient by doctors who have identified a specific type of pathogen during diagnosis. The prescribed drugs are regularly changed, since the peculiarity of gonococci is their ability to adapt to one antibiotic and are weakly susceptible to its effects. It is possible to effectively treat gonorrheal urethritis only by periodically replacing penicillin (this is the main remedy for fighting bacteria) with fluoroquinolones or cephalosporins.
Of the penicillin antibacterial medications, doctors most often prescribe to patients:
Recommended topic:
Genital herpes
- Benzylpenicillin;
- Bicillin;
- Ampiox;
- Levomycetin.
The following remedies are used as a replacement for purulent urethritis:
- Tetracycline;
- Erythromycin;
- Olethetrin;
- Kanamycin;
- Claforan;
- Ketoceph.
In cases where the cause of the disease is not only gonococci, but also other bacteria attached to them, doctors prescribe a course of several types of antibiotics.
Alternative measures
The second direction of treatment for gonorrheal urethritis is immunological therapy, which is necessary not only to support the body’s defenses, weakened by a bacterial infection, but also to strengthen internal organs that are harmed by prolonged use of antibiotics. For these purposes, it is recommended to use:
- Potassium orotate;
- Methyluracil;
- Glycerama;
- Aloe extract;
- Trypsin;
- Plasmol.
A course of treatment with both antibiotics and immunomodulatory drugs is prescribed by a doctor. Both types of drugs have a number of contraindications and can cause complications.
On the recommendation of a doctor, you can turn to traditional medicine, the remedies of which will help defeat bacteria, improve urination, relieve pain and provide an anti-inflammatory effect. For gonorrheal urethritis, the following recommendations are useful:
- drink more fresh cranberry juice;
- brew and take 2 times a day, 350 ml of infusion, brewed in 750 ml of water, 3 tbsp. l. finely chopped black currant leaves;
- eat blackcurrant berries, make juices from them or add them to teas;
- prepare a healing potion: pour parsley (70 g) with milk (200 ml), heat over low heat until the liquid has almost completely evaporated, then strain and drink 1 tbsp every hour. l.;
- Brew cornflower flowers (1 tbsp of dry raw material) in 350 ml of boiling water, then leave for 1 hour, strain and drink in three doses per day.
Important: doctors consider traditional medicine to be an auxiliary method of combating gonorrheal urethritis, since it does not have a therapeutic effect on gonococcus bacteria, but only helps relieve the main symptoms.
Symptoms of gonorrheal urethritis in women
Symptoms of the disease caused by gonococcal infection in women include:
- Pain in the lumbar and lower abdomen;
- Purulent discharge from the vagina or urethra;
- Failure of the menstrual cycle;
- Increased body temperature;
- Cramping pain in the uterine area.
If these symptoms are detected, it is recommended to immediately contact a gynecologist, who will take an anamnesis and issue a referral for testing. If necessary, the patient will be sent to a venereologist.
When does discharge appear?
The incubation period for gonorrheal urethritis ranges from 3 to 10 days. In this case, symptoms may not appear at all.
When feeling the head of the penis, a man feels the presence of seals that were not previously observed. A pain syndrome appears that intensifies during urination. After the end of emptying, light discharge with blood flows from the urethra. They are called terminal hamaturia.
In advanced cases, discharge occurs throughout the day. This happens even in a dream.
Is it possible to cure the disease?
The use of modern medications allows the patient to recover. Treatment time largely depends on the stage of the disease. It is easiest to treat the acute form. In most cases, the course lasts about a month . An effective method is complex treatment using different groups of drugs.
Taking medications is prescribed only by a doctor . It is also advisable to use antiseptic agents, which include Miramistin, Collargol, Dioxidin.
In more advanced cases, the doctor prescribes physiotherapy.
IMPORTANT : During the acute phase, the use of physiotherapy is prohibited.
If the infiltration has grown, the doctor performs instillation , introducing a special solution into the canal. If a hard infiltrate is observed, the patient undergoes bougienage of the urethra using metal bougies. If granulation is observed, the patient is cauterized once a week.
Complications
Complications of gonorrheal urethritis occur not only in the chronic form, but also in cases of fresh disease. In the second case, negative consequences rarely appear due to the fact that the disease is sluggish.
Complications of gonorrheal urethritis in men:
- Morganite. Hyperemia and nodules appear.
- Colliculitis. This is a disease characterized by inflammation of the seminal tubercle. Pain occurs in the lumbar and lower abdomen. In rare cases, bleeding occurs. The urethra is not visible due to inflammation.
- Inflammation of the tizonium glands. Nodules with a diameter of up to 0.7 mm are formed, which are located around the frenulum. In advanced cases, it develops into a gland abscess.
- Paraurethritis. It does not manifest itself symptomatically, but the man’s paraurethral ducts become inflamed.
- Acute prostatitis. Symptoms include frequent urination and pain in the genital area. In rare cases, body temperature rises to 39 degrees.
Complications in women:
- Cystitis. Disease of the genitourinary system. Cystitis. Characterized by the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen.
- Endometritis. The upper part of the lining of the uterus becomes inflamed.
- Colpitis. The second name is vaginitis. Irritation of the mucous membranes of the vagina.
- Vestibulitis. Various inflammations in the vulva in women.
If a woman develops gonorrheal urethritis while carrying a child, this may result in premature rupture of amniotic fluid. The child is born premature. The most terrible consequence for a girl is infertility.
You may be interested in: Acute urethritis: symptoms and treatment
Diagnostics
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to undergo diagnostic tests. Sometimes a person is infected with several diseases. To do this, the patient turns to a venereologist, who writes out referrals for research.
Diagnostics include:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- urethral swab;
- ELISA;
- three glass sample;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- urethroscopy;
- PCR;
- bac sowing
Based on the results of the analysis, the doctor will identify the root cause of atypical symptoms and prescribe treatment.
To take tests, a man and a woman should prepare:
- take a shower with soap in the evening;
- urination should be at least 2 hours before examination;
- do not have sex 2 days before taking tests;
- do not use antibacterial drugs for external use per day.
Some tests cannot be taken during the menstrual cycle, as the results will be distorted.
If there is heavy discharge in the morning before the examination, it is washed off with water without the use of soap or other intimate hygiene products.
Treatment
Treatment of gonorrheal urethritis in some cases takes a long time. The treatment regimen is prescribed by a venereologist after receiving test results. Antibiotics are most often used. However, gonococcal bacteria have developed immunity to penicillin over time, so tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones and other groups of drugs are prescribed.
In most cases, a venereologist prescribes complex treatment for gonorrheal urethritis. This is due to the fact that with weak immunity, the chance of re-infection increases significantly.
Drugs prescribed for the treatment of the disease:
- Levomycetin;
- Ampiox;
- Ofloxacin;
- Claforan;
- Tetracycline;
- Erythromycin;
- Dioxycycline;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ceftriaxone.
Various forms of drugs are used:
- injections;
- candles;
- pills.
In addition, it is necessary to follow a diet to normalize the functioning of the genitourinary system. It is strictly forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, spicy and fried foods.
In parallel, immunomodulators are being taken. The genitals are treated with an antiseptic (Miramistin and Chlorhexidine)
Treatment tactics for acute and chronic forms
Often the primary complication of urethritis is cystitis. When the infection spreads through the genital tract of a woman, endometritis and colpitis develop. The most dangerous and serious complication is infertility.
The consequences of an advanced infection, as you can see, are serious, so it is important to promptly pay attention to alarming symptoms and consult a specialist. Treatment for uncomplicated urethritis does not require hospitalization and can be carried out at home. A woman must follow all the recommendations and instructions of the doctor, and also regularly see him for examinations and monitoring the results of the therapy. The basis of treatment is antibiotic therapy.
Initially, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs in order not to waste precious time (since the infection quickly spreads through the genitourinary system and testing for the sensitivity of the infection to antibiotics takes a lot of time).
Prevention
Gonorrheal urethritis is a disease that appears due to human fault. To prevent the risk of infection, it is recommended to follow the following preventive measures:
- Use a condom during sexual intercourse;
- Avoid casual sex;
- Do not use other people's underwear and towels;
- After casual sex in the first 2-3 days, consult a venereologist, even if there are no symptoms;
- Wash your hands after visiting public places, especially toilets;
- Carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
If there is a person with such a disease in the family, then all family members should take responsibility for prevention. You cannot use personal hygiene items of an infected person. His clothes should be washed in hot water. After drying, clothes and towels are ironed with a hot iron.
If accidental sexual intercourse does occur, then after it you need to wash yourself using antibacterial soap. Chlorhexidine and Miramistin are purchased for disinfection. They treat the genitals and urethra. The procedures make sense in the first 2-3 hours after sex.