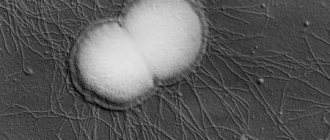
A sexual disease called trichomonas urethritis is characterized by a hidden course. The main route of transmission of infection is sexual. Less commonly, household infection occurs through objects infected by sick people: washcloths, toothbrushes, handkerchiefs. The pathogen remains viable on household items for two to four hours, depending on environmental conditions. Trichomonas urethritis in women most often occurs as a mixed protozoal-bacterial infection.
Causes of the disease
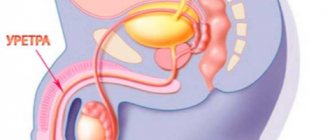
The causative agent of urethral trichomoniasis, flagellated Trichomonas, belongs to the category of pathogenic microflora, which has the simplest single-cell structure and reproduces through longitudinal division. Before entering the urethral canal, it settles in the walls of the vagina in women, and in men it initially penetrates the urethra, and then rises higher along its walls and settles in the tissues of the prostate gland. Taking into account the specific localization of the bacterial microorganism, the following reasons for the development of the disease in both sexes are identified.
Unprotected sex
It is extremely important to use barrier contraception during intimacy. Especially if a man or woman regularly changes sexual partners and is not completely sure that their loved one is 100% healthy and is not a carrier of this disease. Unprotected sexual contact leads to the fact that Trichomonas settles on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, enters the stage of the incubation period and, upon its completion, begins to build bacterial colonies with an increase in its numbers. From this stage the manifestation of the first symptoms of the disease begins.
Domestic infection
The sole use of personal hygiene products and other personal items is not only a sign of cleanliness or a developed sense of ownership, but also concern for one’s health. About 15% of all cases of Trichomonas urethritis are due to the fact that several people, one of whom carries the infection, used the same bath towel, toilet soap, shaving accessories (we are talking about hair removal in the intimate area), underwear, robe, poorly washed or ironed bed linen.
The contact and household route of infection is dangerous because often a person cannot understand how he acquired this disease and what specific actions caused the disease.
Intrauterine infection
In medical practice, there are clinical cases when, during gynecological registration, a woman is not examined well enough and the presence of an excessive amount of trichomonas infection in her vagina is not diagnosed - then the period of bearing a child passes with the presence of pathogenic microflora, which involuntarily penetrates along with the blood flow and into the body of the unborn child. As a result of this process, the baby is initially born with the disease.
The number of causative factors influencing the occurrence of trichomoniasis urethritis in a healthy person is very small, therefore, knowing about the sources of origin of the disease, you can easily protect yourself from the possible risk of getting sick.
Symptoms of Trichomonas urethritis
After the completion of the incubation period of Trichomonas division, which lasts on average 5-10 days, the first signs of the disease begin to appear. Symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- inside the urethra there is a burning sensation, constant itching and a sensation as if a small insect is crawling in the urinary canal (discomfort increases several times at the time of urination and in the evening, when the patient’s body is most weakened);
- white or gray mucus begins to periodically be released from the urethra, which does not have a specific odor, but causes a lot of discomfort to a person (this symptom is especially common in the male half of the population);
- body temperature rises, which in the acute course of the disease can reach 38 degrees Celsius and higher (the chronic form of the disease maintains the temperature within 36.9 - 37.3 degrees);
- the lymph nodes in the groin area become inflamed and become painful when palpated;
- in men, the disease may penetrate into the seminal vesicles and the appearance of pain in the testicles, which is acute and occurs in the form of attacks lasting from 5 to 20 minutes, and then the symptoms disappear.
The described signs of trichomoniasis urethritis appear from the first days of the development of the disease, if the patient has an acute or subacute form of the disease, or the characteristic symptoms manifest themselves gradually according to the principle of systematic deterioration of health. We recommend comparing the symptoms with ureaplasma and allergic urethritis, because they are similar in many ways.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis and determining the fact that it was Trichomonas that caused inflammation of the walls of the urethral mucosa requires a comprehensive examination and a series of diagnostic procedures, consisting of the following:
- bacterial culture from the urinary canal (the principle of selecting biological material for research is that the nurse takes a disposable and necessarily sterile cotton swab, and then runs its edge along the walls of the urethra for further laboratory research of the microflora and isolation of the Trichomonas strain);
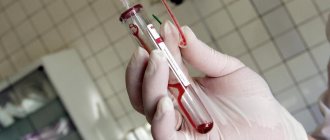
- blood from a vein for biochemical analysis (necessary to find out whether the infection has spread throughout the body and whether the patient has concomitant sexually transmitted diseases, since most of them have similar symptoms as Trichomonas urethritis);
- blood from a finger in order to conduct a clinical analysis and determine both the qualitative and quantitative composition of the blood (the level of glucose in the blood is also determined in order to exclude the factor of the patient having diabetes mellitus and its complications, which quite often manifest themselves in the form of inflammatory processes of the urethral mucosa );
- passing urine and excreting trichmonas (in the presence of an infectious pathogen, the concentration of the bacterial agent in the urine is at an extremely high level).
After receiving the results of the tests, the attending physician has comprehensive information about the health status of the patient’s genitourinary system and the treatment methods that need to be applied in a specific clinical case.
What it is?
Urethritis is an inflammation of the walls of the urethra and the entire genitourinary system. This disease often causes the development of prostatitis and infertility, as well as other genitourinary diseases.
History of the disease
In the development of Trichomonas urethritis, 3 main stages can be distinguished:
- acute inflammation;
- subacute inflammation;
- chronic inflammation
Prevalence and significance
Trichomonas urethritis occurs quite often in men, up to 90% of cases.
Risk factors
The provoking factors for the development of the disease are the following:
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- hypothermia;
- weakened immunity;
- lack of vitamins;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- poor nutrition;
- alcohol abuse;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic diseases of internal organs.
How and how to treat Trichomonas urethritis
Therapy for trichomoniasis urethritis is based on the patient taking medications that contain active components that have destructive properties against the cell membrane of trichomonas infection. To do this, the patient is prescribed a treatment course of the following medications:
- Metronidazole (taken for 7 days, 2-4 tablets per day after meals, with a small amount of liquid);
- Ornidazole (available in tablets, which are recommended to be taken 2-3 pieces 3 times a day for 10-14 days).
It is believed that these drugs are the only ones in their group whose effectiveness against Trichomonas urethritis has been proven in medical practice. It is extremely important to abstain from sexual contact and completely stop drinking alcohol during the treatment period, otherwise the therapy will not bring any positive results. After completing the course of treatment, it is necessary to be examined again 3 months later and, if an infectious agent is present, to be re-treated. Both sexual partners take the pills according to the same regimen. An additional advantage will be the joint enhancement of the effect of folk remedies against urethritis.
Therapy
Traditional treatment of Trichomonas urethritis includes the following drugs:
- nitroimidazoles;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- instillation of drugs into the urethra;
- painkillers;
- immunomodulators;
- vitamin complexes.
Nitroimidazoles (Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Tinidazole) are considered the only drugs that have proven highly effective in the fight against Trichomonas. The treatment regimen is selected for each patient individually. These medications can be prescribed to patients during pregnancy, for special indications and in lower dosages.
Antibiotics are part of the complex treatment of Trichomonas urethritis. They are necessary to get rid of bacterial infection. According to indications, the patient is given symptomatic therapy: pain relief, relief of inflammation. To strengthen the general condition, a course of vitamin therapy is often required.
To eliminate the risk of re-infection and further spread of the infection, the patient should be treated together with his sexual partner.
During the entire treatment period, it is necessary to limit physical activity, avoid hypothermia, completely avoid sexual intercourse and follow a special diet. Spicy, fatty, salty, smoked foods and alcoholic beverages should be avoided.
After completing the course of therapy, the patient and his sexual partner are re-examined. If the disease relapses, a second course of treatment is prescribed.
Complications
If the disease is not treated for a long period of time, or medications are used incorrectly, the patient may develop the following types of complications:
- inflammation of the ovaries, cervix and epithelial tissues of the reproductive organ itself;
- development in men of acute and chronic prostatitis with further erectile dysfunction and early onset of impotence, which occurs at a fairly young age;
- damage to the seminal vesicles and the synthesis of non-viable spermatozoa;
- male and female infertility;
- menstrual irregularities with premature onset of menstruation or their unreasonable delay;
- miscarriage of the fetus and outflow of amniotic fluid earlier than the physiologically prescribed period;
- inflammation of the foreskin of the penis with the formation of ulcers and purulent discharge.
Each of the described complications significantly affects the quality of life of a person suffering from Trichomonas urethritis. It is necessary to promptly respond to emerging symptoms indicating the presence of the disease and undergo examination by a urologist, dermatologist or venereologist. Women can seek medical help from a gynecologist.
Does Trichomonas urethritis occur in women?
In representatives of the fair half of humanity, this disease occurs as often as in men. The difference lies only in the intensity of the manifestation of characteristic symptoms. In women, the disease can last for several months, and sometimes even years, but the patient will think that this is another exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the appendages or cystitis. Therefore, it is very important that men and women periodically undergo a comprehensive examination of the body with smears from the walls of the mucous membrane of the urinary canal. Only in this case can you monitor the health of your genitourinary system and be sure that there is no Trichomonas in it.
Prevention
Like any disease, urethritis in men is much easier to prevent than to treat. Prevention of the disease consists of preventing infection.
This requires following some rules:
- personal hygiene, that is, using your own underwear and towels;
- refusal of sexual contacts with different partners;
men must use condoms during sexual intercourse;- in case of unprotected contact, you must immediately get tested in order to detect the disease in time;
- dress warmer in the cold season. It is important to especially protect your legs and groin area from the cold;
- shower regularly;
- exercise;
- visit a urologist once a year.