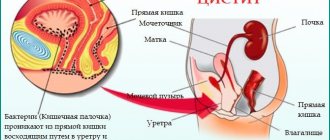
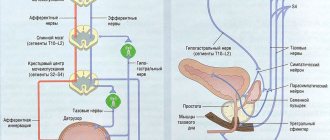
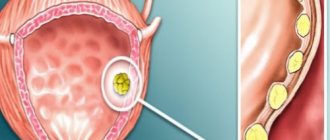
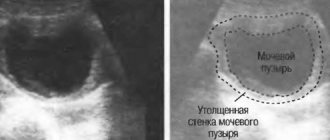
A bladder polyp is the appearance of benign formations on the mucous surface of the organ. Polyposis is more common in men near retirement age. It is characterized by an asymptomatic course and develops over a long period of time. The disease leads to complications, the growth is prone to degeneration into malignant tissue. ICD-10 code C67 – bladder tumor.
The node consists of a body, a stalk or a wide base, which supplies the formation with nutrients.
Types of warts
Warts are benign tumor-like growths of the skin.
The cause is the human papillomavirus. They look like a nodule on the skin. The main treatment is removal. Found in 90% of the world's population. There are also non-viral warts, for example, senile warts, or keratomas.
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
One of the latest domestic developments for the treatment of genital warts - Vartocid - read more
Causes of warts
The cause of warts is the human papillomavirus. Read more about HPV
The virus penetrates the skin through microdamages - scratches, abrasions. It is integrated into the chromosomes of epidermal cells and the cells become ugly - a wart grows. This cell proliferation is benign.
And only one type of wart - senile keratomas - does not have a viral cause.
Types of warts
Modern medical classification distinguishes the following types of warts:
- flat warts (or juvenile warts),
- ordinary or vulgar warts and their variety - plantar warts (or spinules),
- filiform warts (or acrochords),
- genital warts (or genital warts),
- senile warts, or age-related (or seborrheic keratosis).
Flat warts (juvenile)
Read more about flat warts here.
- flat view,
- flesh-colored or light brown,
- 1-2 mm rising above the surface of the skin,
- located on the face or back of the hands,
- appear in children and adolescents, in the area of skin irritation, cuts, scratches.
Common warts (vulgar)
Detailed article about vulgar warts - go
- This type of wart also appears more often in young people.
- Another name is simple warts.
- They are rounded elevations on the skin, up to 5 mm in height, initially flesh-colored, and then grayish or brown in color, gradually growing.
- A small “daughter” wart may appear next to the large “mother” wart.
Another type of common wart (photo below) is plantar. It is also called “spike”. These varieties are located on the sole of the foot or on the palm. And they look like a thorn grown on the skin, dense, slightly painful, sometimes making it difficult to walk, since it is painful for a person to step on this place.
Read a detailed article about spines.
Filiform warts (papillomas, or acrochords)
More details about this type: link.
These types are located:
- on the face,
- on the neck,
- in the armpit areas,
- under the mammary glands in women.
They are rounded elevations above the skin, on a thin stalk (see photo).
They occur in people over 40 years of age, but most often in the elderly. Should be distinguished from molluscum contagiosum.
Genital warts (genital warts)
A very detailed article about anogenital warts (condylomas) is here.
This type of wart is characterized by its location (in intimate places). The cause is human papillomavirus types 6, 11, 13, 16, 18. Genital warts have the appearance of a growing cauliflower. Color – dark flesh, closer to brown.
Such condylomas are located in the groin area and in intimate places - in the anus, labia majora, and in the penis area. The location itself suggests that the main route of transmission is sexual. And another place where genital warts can be located is the oral cavity.
Senile (age-related) warts
Read more about this type of wart here.
This is the last type of wart in the classification. They have nothing to do with true warts. The cause of the appearance of such warts is not a virus, but seborrheic keratotic growths on the skin of old people.
It first appears as age spots, then a small growth on the skin (on the head, neck, body) of a grayish, brown or black color, covered with seborrheic scales (dandruff). After removing the scales, the papillary outgrowths on the skin are exposed. Sometimes age-related warts literally merge on the human body into one conglomerate. Seborrheic keratoma should be distinguished from Clark's dysplastic nevus (read more about dysplastic nevus) and from melanoma.
So, as we see, the modern classification distinguishes five types of warts. The first four of them are true (caused by HPV). The fifth type (senile) - appear not as a result of viral infection, but as a result of skin growth with seborrhea in old people.
In ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision), warts are classified as viral skin lesions:
B07 Viral warts
The following types of warts have been moved to other sections of ICD 10:
- anogenital (venereal) warts (in the old way - genital warts) - in section A63.0 (sexually transmitted diseases)
- papilloma of the bladder - in section D30.3 (benign formations of the urinary organs)
- cervical papilloma - in section D26.0 (benign formations of the uterus)
- laryngeal papilloma - in section D14.1 (benign formations of the respiratory system)
Make an appointment for a paid appointment with a dermatologist in Moscow for tomorrow
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Basic principles and methods of treating warts and papillomas:
- laser removal (detailed article about laser removal),
- radio wave removal using the Surgitron device (more about this method),
- cryodestruction - cauterization with liquid nitrogen and its analogues (Wartner cryo, etc.) - read more about cryodestruction,
- treatment with celandine and super celandine (read here),
- treatment with cauterizing drugs (solkovagin, solcoderm, verrukacid, collomac, duofilm, lapis pencil),
- strengthening the immune system - taking immunomodulators (polyoxidonium, roncoleukin, etc.) and natural methods (detailed article about methods of strengthening the immune system - link),
- taking antiviral drugs (epigen, isoprinosine, panavir, etc.)
- Vartocide is a local immune drug for the treatment of genital warts on the genitals.
- How to gently remove a spine from a child?
- What is the main cause of warts? Frogs?
And now - a useful video on the topic of the material:
I also recommend reading these materials:
Medicinal herbs for treating kidneys and bladder
August 10, 2020 Vrach
Herbal medicine is a unique method of traditional medicine that allows you to achieve enormous success on the path to recovery without using pharmaceutical drugs. Herbs for the kidneys have a lot of useful properties: anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, diuretic, stone-dissolving. However, like all medicines, plants have indications and contraindications.
Benefits and properties of medicinal herbs
As a rule, phytotherapeutic methods are used to treat certain groups of patients for whom potent drugs are contraindicated: young children, the elderly and pregnant women. For them, taking medications with potent substances is unjustified, since they can cause irreparable harm to a weakened body. In nature, there are many medicinal plants that perform the same functions as medicines, but they do not have side effects and have a gentle effect.
Traditional medicine is indicated to combat various types of kidney diseases:
- immuno-inflammatory – glomerulonephritis;
- infectious-inflammatory – cystitis, pyelonephritis and urethritis;
- nephrolithiasis – urolithiasis.
To choose the right herbal collection, it is important to take into account the type and nature of the disease, as well as the characteristics of the patient’s body. A remedy that helped one person can harm the health of another, even if they are diagnosed with the same pathology. Healing plants that help with disorders of the kidneys and the urinary system as a whole are divided into 3 types:
- Decongestants or diuretics - improve the flow of urine and remove excess fluid from the body, thereby eliminating edema and preventing its re-formation. Birch buds, rose hips, horsetail and knotweed have similar properties.
- Anti-inflammatory – have a bactericidal effect, due to which the drug inhibits the inflammatory process and fights the cause of its formation. The most effective are the leaves of lingonberry, elecampane, bearberry, St. John's wort and corn silk, but it is recommended to use them not individually, but in the form of collections of 2-4 plants.
- Cleansing – help remove sand and stones from the kidneys naturally. It is extremely important to select such herbs in accordance with the type of stones formed. For urolithiasis, cinquefoil, meadowsweet, cocklebur and burdock root are usually prescribed.
In addition to the therapeutic effect, all medicinal herbs have a general strengthening effect on the body. They contain a large amount of vitamins and microelements. Thus, taking herbal medicines helps boost immunity, which in turn helps restore damaged tissues and improves the functioning of the urinary system.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that herbal medicine is a gentle method of treating kidney diseases, it has a number of contraindications and limitations:
- Pregnancy. Most herbs are capable of removing calcium from the body of the expectant mother, which can lead to improper formation of the fetal skeleton.
- Urine retention. In the presence of inflammatory processes that have caused a violation of excretory function, the use of plants with a diuretic effect can cause severe pain in the ureter and lead to its rupture.
- Allergies. If you are hypersensitive to one or more components of the collection, it is prohibited to continue treatment.
- Kidney and heart failure. Some folk remedies are prohibited from being taken by patients with chronic pathologies, as there is a high risk of exacerbations or complications.
- Advanced stage of ICD. With a long course of the disease, very large stones form in the pelvis, which must be eliminated exclusively by surgical methods. Taking medicinal decoctions can provoke the movement of stones that clog the urinary canals.
Medications for the bladder
You can prepare herbal mixtures yourself or buy them ready-made at the pharmacy. The duration of administration, as well as the composition of the collection, is selected individually. The course of treatment can last from two weeks to two months, then, after a short break, the treatment is repeated.
The most effective herbs for the bladder are yarrow, plantain, bearberry, and birch leaves. Therefore, in the fight against bladder inflammation, the following fees are used:
- Plantain, bearberry, birch buds, knotweed grass. Pour a handful of the collection with a liter of clean water and leave for at least twelve hours. Then warm up for ten minutes. Take one hundred milliliters four times after meals.
- Corn silk, calendula, flax seeds, birch leaves, licorice root, bearberry. Pour a handful of the mixture into a liter of water, leave for at least twelve hours, and warm up. Take three times, fifty milliliters after meals.
- Yarrow, birch buds, bearberry. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of the mixture. Take three times throughout the day after meals.
Before using any decoction, you should consult your doctor. An experienced specialist will evaluate the advantages of a particular collection over others, and will explain how to properly prepare and take a medicinal decoction. It is important to remember that each plant has its own indications and contraindications, so self-medication may not only be useless, but also harm the body, aggravating the course of the disease.
Medications for kidney stones
Today, there are several dozen recipes for preparing natural medicines at home, and some of them are more than 100 years old. The necessary herbs can be purchased at the pharmacy, but sometimes you need to collect them yourself, for example, if you need fresh rose hips or other plants. Mainly to combat disorders of the urinary system, decoctions and tinctures are prepared, which are drunk before or after meals, but in some cases compresses and sitz baths are more effective.
In the early stages of ICD, the following tinctures should be taken:
- Urate stones are effectively dissolved by tea made from birch buds, rose hips, flax seeds, parsley and strawberry leaves. Place 1 tsp in a 0.5 liter jar. each ingredient, pour boiling water and leave for 6-7 hours, after closing the lid. Drink the infusion for 1-3 months, 3 times a day, 150 ml, with the addition of honey.
- A collection of immortelle, lingonberry leaves, motherwort, sweet clover and crushed dry madder root will help remove phosphate deposits. Mix the herbs in equal parts, pour boiling water in a ratio of 0.5 liters of water per 2 tablespoons. mixture, cover and leave overnight. Take the drug 50-60 ml up to 7 times a day.
- For oxalates, it is recommended to take an infusion of mint, cornflower, bearberry and wintergreen leaves mixed in equal proportions. Place the mixture in a thermos, fill it with boiling water and leave for 7-8 hours. Drink the medicine 3 times a day, 80 ml.
Anti-inflammatory herbs
One-component herbal decoctions will help cure inflammatory diseases:
- A drink made from corn silk suppresses inflammation, lowers blood pressure and eliminates swelling. Place 15 g of dried crushed herb in a container, pour a glass of boiling water and cook for 10 minutes in a water bath. Then strain the broth and drink 50 ml every 3 hours.
- For pyelonephritis, the most effective is yarrow tea. To prepare it you need 1 tsp. plants and 250 ml of boiling water. The tea should be steeped for half an hour, then strained and drunk in small sips throughout the day.
- Horsetail is a diuretic herb with an anti-inflammatory effect. For the decoction you need only 15 g of dry horsetail and 0.5 liters of cold water. Bring the medicine to a boil and cook over low heat for 7 minutes. Drink 150 ml 3 times a day.
Herbal baths and compresses
To get rid of pain in the area of the affected kidney or in the lower back, it is recommended to apply compresses and take herbal baths. A compress of 100 ml of vegetable oil, yarrow, marshmallow and chamomile has a good therapeutic effect. All ingredients must be mixed in an enamel container and simmered over low heat for 5 minutes. Then soak a small piece of cloth in the oil mixture, apply it to the sore spot, wrap it in cling film and wrap yourself in a blanket or terry towel. After an hour, you can remove the bandage and carefully remove any remaining oil from the skin.
If kidney disease is accompanied by cystitis, warm baths with healing decoctions are often prescribed. Among the most effective recipes is a herbal mixture consisting of eucalyptus, sage, birch leaves, currants, chamomile and horsetail. The ingredients are mixed in equal quantities and poured with boiling water in a ratio of 1 liter to 3 tablespoons. herbal mixture. The finished strained broth is poured into a bath of hot water and placed in it in a sitting position for 15 minutes.
Using medicinal herbs to treat the kidneys and bladder in conjunction with drug therapy, you can significantly speed up the healing process and get rid of symptoms. In addition, herbal medicine can be used to prevent diseases of the urinary system and increase the protective functions of the body.
Bladder papilloma: how growths are treated
Among all cases of papillomavirus manifestation, bladder papilloma is quite rare, the treatment of which, however, requires a serious approach. This formation is initially benign, but is potentially dangerous. There is a high probability of transformation of its cells into malignant ones, which can rarely be diagnosed in the early stages due to the long asymptomatic course of the disease.
What is papilloma in the bladder?
The neoplasm in this organ is most often located on its inner surface and resembles a wart on a thin stalk of a white-pink hue. Its structure is fleecy, consists of small accumulations of tissue, and the consistency is soft. Over time, it becomes shorter, the threads thicken, and the formation takes on the appearance of a homogeneous large growth with a keratinized surface.
Such papilloma is characterized by growth into the deeper layers of the walls of the organ and into the muscle tissue, and when transformed into a malignant type, metastases begin to spread.
In common parlance they are called polyps, but doctors do not accept this name. It is included in the international classification of diseases and has an ICD 10 code D30.3.
Causes of bladder papillomas
Today it is known that such growths arise as a result of high activity of HPV in the human body. This virus can never be cured, and its carrier may not even suspect that he is infected throughout his life, since manifestations of the virus occur only when exposed to certain negative factors and a decrease in immunity. Experts still cannot say why tumors appear in the bladder.
Some luminaries of science are inclined to post-traumatic etiology, others suspect that the cause of the disease is work in chemical production, where a person had long-term contact with certain types of paint and varnish products, especially aniline type. The harmful influence of carcinogens, which are now filled with food products on store shelves, cannot be ruled out. There is also an opinion that heavy smokers are at risk of receiving such a “gift”. Autoimmune diseases, impaired renal function, stagnation of urine - all this also increases the likelihood of developing neoplasms.
The disease occurs in men and women. However, according to statistics, it is diagnosed less often in women. The age group at risk is people from 40 to 60 years old.
Symptoms of papillomas in the bladder
In women, the symptoms of this disease manifest themselves in the same way as in men:
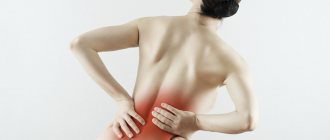
pain in the groin area or lower back;
traces of blood or reddish streaks in the urine;
discomfort or pain, pain when urinating;
the organ is not completely emptied, the urge to urinate is very frequent;
Emptying is carried out with considerable effort.
If you detect blood in your urine, you should immediately consult a doctor. This indicates a dangerous condition when the growth grows into the deep layers of the walls of the organ or breaks off.
Diagnosis of manifestations of papillomavirus in the bladder
Tumors can be detected in several ways, depending on their location and volume:
if the growths have already become large, a specialist can identify them by palpation, but only if they are localized on the outer wall of the organ;
if the tumors are attached internally, they can only be detected by ultrasound or computed tomography. This is suitable in cases where their size exceeds 1 cm;
in the initial stages, when the accumulation of tissue has not yet reached 1 cm, the diagnosis can be made after cystoscopy, during which the bladder is examined (when it is full) with special optical instruments. During this procedure, the doctor may also do a biopsy if pathological tissue growth is detected. Then a microslide of the bladder papilloma will be examined to determine the type of cells: benign or malignant.
In addition, a number of laboratory tests are carried out:
general analysis of urine and blood;
study according to Nechiporenko;
blood chemistry;
in men, a special prostate antigen is determined;
the presence of microbial and sexually transmitted diseases is investigated, etc.
The full range of measures is prescribed by the attending physician.
Modern methods of treating growths
if the growth has not yet affected the muscle tissue, then it is removed in the safest way - using electrical resection;
Once the growth tissue has penetrated the muscle, deeper surgical penetration is required. In this case, some part of the organ has to be removed. And if a large volume is affected, then sometimes the entire bladder. In this case, further plastic surgery is performed to create a reservoir from part of the intestine;
The most gentle is radiation treatment, which allows you to leave the organ unchanged. However, it does not have the desired effect in many cases, and very strong inflammatory processes often occur during therapy;
the most dangerous and destructive is radical cystectomy. In women, in addition to the bladder, the urethra, uterus and anterior vaginal area are removed, while men are left without the urethra and prostate.
In the early stages, the growth can be removed in a gentle way, but advanced cases require a radical approach. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the slightest dysfunction of the body and promptly contact a specialist.
Urethral polyp: what is it and why is a urethral polyp dangerous?
Urethral polyp is an area of study in oncology, urology and surgery. The appearance of polypous lesions is often a secondary pathological process.
Neoplasms often form on the affected tissue of the urethral canal. The localization of growths can also be different.
To assess the degree of cancer risks, you should consult a doctor for differential diagnosis.
What is a urethral polyp?
Urethral polyp is a benign neoplasm caused by chaotic division of mucosal cells due to multiple predisposing factors. The disease occurs in men and women. Morphologically, polyps have a soft structure with smooth, dense outlines.
Typical localization in men is the entrance to the prostate and the seminal tubercle from the urethral lumen. Histologically, such polypous fragments are filled with fibrous tissue. In women, such a growth is prone to rapid generalization. A few years later, polyps cover the entire urethral cavity, resembling multiple polyposis.
The danger of a growing polypous lesion is:
- the barrier of the urethra,
- the occurrence of various urological pathologies, including urinary retention, which is life-threatening.
The clinical picture often resembles inflammation of the organs of the urogenital system and the course of sexually transmitted diseases.
The ICD-10 urethral polyp code is D 30.4. This category also includes the polyp of the external opening of the urethral canal. The classification of diseases helps determine whether the pathology belongs to genitourinary and kidney diseases.
Classification and types
Taking into account the predominant benign quality of polypous foci, it is customary to classify neoplasms into:
- epithelial (otherwise, urethral);
- paraurethral (otherwise, nonepithelial).
In the first case, neoplasms originate from inside the mucous membranes and glands of the urethra. In the second case, the neoplasms originate from muscle and connective tissue structures.
- Epithelial tumors are considered: urethral caruncles, condylomas, papillomas, polypous neoplasms.
- Non-epithelial lesions are characterized by: fibromyomas, neurofibromas, fibromas, angiomas.
Papillomas
Urethral papillomas are papillary neoplasms (single or multiple).
Among them are:
- squamous,
- multilayer epithelial papillomas,
- transitional cell neoplasms.
Papillomas have a wide base with a long stalk (dimensions barely reach 1 cm). The surface is smooth, soft consistency. Papillomas are round in shape, and the color varies from gray-pink to burgundy. Papillomas resemble many warts, represented by conglomerates and crowded clusters. Papillomas are localized closer to the outer part of the opening of the urethra.
Condylomas
Condylomas are growths of the mucous membrane in the form of a cone or papilla, localized mainly along the ring to the external opening of the urethral canal.
Based on their histological structure, capillary condylomas or warts are distinguished. Warty neoplasms have a yellowish or white tint, a wide base, and an excessively dense consistency.
Capillary ones have a soft structure; such polypous condylomas have a purple color.
Polyps
A polyp is essentially a soft, vascularized tumor-like neoplasm, often pedunculated. The surface of the polyp's body is lined with squamous epithelium. The polyp itself in appearance resembles a drop of a bright red hue, often with foci of obvious erosive lesions.
Caruncles
Caruncles are a type of polyp; they have a small red hue and a soft structure and density. The surface of such a polypous lesion is furrowed. The abundance of vascularization and blood supply increases the risks of regular trauma and bleeding. Caruncles usually grow closer to the external opening of the urethral lumen.
Main types of nonepithelial growths
All nonepithelial tumors usually have a mixed morphological structure and are quite rare in clinical practice. These include fibroids, fibromyomas, myomas. Such pathologies occur in women in the vaginal cavity and urethra. The sizes of pathological neoplasms are large, from a small cherry to a medium chicken egg.
Angiomas are urethral tumors filled with an abundant vascular component. The usual localization is the exit from the urethral canal. Angiomas are more likely than other polypous and tumor-like lesions to bleed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_aYmF88mos8
Given the tight attachment of the polyp to the mucous structures, the neoplasm often bleeds and is damaged. The aggressive environment and uric acid inside the urethra is also an irritating factor.
Note ! In the early stages of development, urethral polyps rarely give characteristic symptoms, however, as they grow, the signs of pathology increase, accompanied by:
- discomfort,
- urinary disorders,
- pain,
- the appearance of blood in urine.
Dimensions and location
The size and location of polyps are varied, which is determined by the gender of the patient. In men, small pedunculated polyps, no more than 0.5 mm, form in the urethra. Broad-based tumors are often localized at the exit to the prostate gland.
As the tumor grows inside the mucous membranes, glandular tissue is involved in the pathological process, increasing the risk of malignancy of the tumors. When localized along the lumen of the urethra or at the very outlet of the urethra, patients note pain and painful urination, the appearance of blood impurities in the urine.
In women, polyps are usually localized at the entrance to the vaginal cavity, often spreading to the cervical canal. Urethral polyps in women vary in size, from 0.5 mm to 10 cm. When growths form in women, clinical manifestations are always late, which is due to the peculiarities of the anatomy.
Signs of polypous lesions can appear with concomitant inflammation of the bladder and ureters, sexually transmitted diseases, and urolithiasis.
The appearance of atypical discharge from the urethral canal always requires consultation with a doctor.
We will tell you more about the features of the manifestation of urethral polyps in men and women, as well as about methods of treating the pathology in the following publications.
The cause of infertility in many women is polyps in the ovaries. Neoplasms are considered benign, but the risks of their malignancy are high, which is why it is so important to seek medical help in a timely manner. How to treat cervical polyps without removal, read more here. It is important that the treatment of neoplasms is carried out by a specialized specialist.
Predisposing factors
Clinicians do not identify any one reason that directly affects the formation of polypous structures in the urethral canal. However, the main factor is the inflammatory process of an infectious nature.
Among these diseases, especially:
- gonorrhea;
- purulent urethritis;
- damage by chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma;
- genital herpetic infection;
- trichomoniasis;
- HIV infection;
- syphilis;
- bacterial or viral prostatitis;
- cystitis or complicated urolithiasis.
Prerequisites for the inflammatory process are poor intimate hygiene, lack of sexual discipline and frequent changes of partners. Weakened immunity is an important aspect of frequent exacerbations of chronic infectious diseases of bacterial, fungal or viral origin.
The appearance of atypical discharge from the urethral canal always requires consultation with a doctor.
Polyps are the result of chaotic compensatory division of mucosal cells in response to a serious inflammatory process and damage to the surface epithelial layer.
Indirect factors are:
- endocrine dysfunction;
- renal failure;
- chronic infections of the genitourinary system (with rare exacerbations);
- complications after therapeutic and diagnostic procedures;
- childbirth and pregnancy in women;
- injuries.
The risk group includes patients over 45 years of age, taking hormonal drugs, with a burdened clinical history.
Polypous lesions of the urethral canal are practically not found in young children.
What is the danger of a urethral polyp?
Unfortunately, the main danger lies in the absence of pronounced clinical symptoms in the early stages of the formation of pathological foci. Small growths or non-epithelial tumors can become malignant and transform into a malignant process.
Considering the predominantly benign nature of the pathological process, the risks of malignancy remain, but increase with a hereditary predisposition or the presence of other oncological foci.
Other dangers are:
- Development of chronic cystitis, urethritis - with a neoplasm in the urethra, the bladder or ureters become more vulnerable to an infectious environment;
- Hematuria syndrome - the appearance of blood in urine in any volume and a prolonged course of the symptom often leads to the development of iron deficiency anemia, the risk of blockage of the urinary canal with a blood clot;
- Pyelonephritis or nephritis - pathogenic environments can pass through the ascending canal to the renal structures, contributing to the development of acute inflammation;
- Infravesical obstructive changes - a complication develops against the background of the growth of a polyp, which simply clogs the urinary duct and impairs urinary drainage.
Find out what pain in the urethra and purulent discharge indicate from this video:
Urethral polyps are pathological neoplasms, predominantly benign, but oncologists always leave the risk of possible cancerous degeneration of cells. When the first symptoms appear, it is important to react in time, consult a doctor and together formulate an adequate treatment strategy.
Read about the causes of endometrial polyps in the uterus of a nulliparous girl in this article.
You can make an appointment with a doctor directly on our website.
Be healthy and happy!
Source: https://polipunet.ru/lokalizacija/mochevoj-puzyr/polip-uretry
Urethral polyp
A urethral polyp is a benign neoplasm of the urethra. The ICD10 code is N34.2. Women suffer from urethral polyps approximately 1.5 times more often than men. This is explained by the anatomical features of the urethral mucosa. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose the disease using modern research methods.
Urologists take an individual approach to the choice of surgical method for removing polyps in the urinary canal. Before surgery, antibacterial therapy is carried out with the latest generation antibiotics. Complex cases of urethral polyps are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. The medical staff is attentive to all the wishes of patients.
Causes of formation of urethral polyps
The exact cause of the formation of urethral polyps has not been established. Urologists believe that the cause of polyps in the urethra may be the following factors:
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system (chlamydia, urethritis, mycoplasmosis, human papillomavirus);
- Hormonal dysfunction;
- Mechanical injuries of the urethra;
- Impaired blood supply to the walls of the urethra.
Urethral polyps often occur in premenopausal and menopausal women.
Urethral polyp according to ICD 10 – Online medicine
Anyone can experience a urinary system disease such as a urethral polyp. The problem is typical for both women and men.
However, females are more likely to encounter this disease due to the structural anatomy (see pictures) of the urethra.
In men, the urethra has a more elongated shape, exceeding in size the length of this element of the urinary system in women.
Statistics say that the diagnosis of urethral polyp accounts for no more than 5% of all recorded tumor pathologies.
Symptoms of urethral polyp
In the early stages, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. As the urethral polyp grows, the following symptoms appear:
- Difficulty urinating;
- Spraying urine;
- Burning, itching and discomfort in the urethra during and outside urination;
- Sensation of a foreign body in the urethra.
A bleeding urethral polyp (ICD 10 code – N34.2) is manifested by the appearance of blood in the urine (urethrorrhagia). Women may experience pain during intercourse. In the later stages of the disease, a tumor-like formation can completely block the lumen of the urethra and cause acute urinary retention.
By structural type
Based on histological characteristics and structural units, polyps are classified into:
- Glandular or adenomatous. The structure of the pathological growth is based on the cells of the glands of the gastric cavity. Usually the polyp is benign in nature and only in 5% of all clinical cases does it malignize into carcinoma. Despite this, for clinicians these numbers are high, making all the reasons for surgery justifiable.
- Hyperplastic. A common type that is least likely to transform into an oncological tumor. The mucosa is constantly exposed to hyperplastic processes. If the volume of the polyp is insignificant, then there is usually no particular cause for concern regarding cancerous transformations. Symptoms and discomfort in patients begin to appear as the leg grows, torsion, and bleeding.
- Hyperplasiogenic type. The polypous structure consists of the regeneration of glandular cells of the stomach, due to a violation of their regenerative processes.
The juvenile type of stomach is distinguished separately. The disease occurs mainly in childhood. Localized in the antrum of the stomach and intestines. The body structure of the growths is usually filled with a cystic component. The size varies from 5 to 20 mm.
All tumors can be pedunculated or without it. The classic growth has a stalk, a base and a body. Such neoplasms are least susceptible to cancer and grow into the stomach cavity. Flat ones without legs gradually grow deep into the structures of the mucous epithelium and are most prone to cancerous transformations.
Methods for diagnosing urethral polyps
To identify neoplasms in the urethra, urologists at the Yusupov Hospital use a full range of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Urological examination;
- Cystourethroscopy;
- Urine culture;
- Microscopy of a smear from the urethra;
- PCR diagnostics.
The sooner a patient seeks medical help from urologists at the Yusupov Hospital, the higher the chance of quickly curing the disease, avoiding the development of possible complications and relapses.
Treatment of urethral polyp
The only effective way to treat a urethral polyp is surgery. Urologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform urethral polyp removal using the following modern methods:
- Electrocoagulation (excision of formation using high-temperature exposure to electric current);
- Cryodestruction (destruction of the polyp by ultra-low temperature);
- Radio wave surgery (removal of overgrown tissues using radio wave radiation);
- Transurethral resection.
Wedge-shaped resection of a urethral polyp is performed when the polyp is located at the external opening of the urethra. Innovative methods for treating urethral polyps include removal of urethral polyps with a laser or Surgitron radioknife. This method ensures minimal trauma and damage to soft tissues, painlessness and absence of blood loss, rapidity of action and a minimal recovery period.
Prevention of urethral polyps consists of using barrier methods of contraception to protect against sexually transmitted diseases, timely seeking medical help, and annual preventive examinations with a urologist. If you have the first signs of a polyp of the urethra, contact the Yusupov Hospital. Call by phone. The contact center is open every day, seven days a week, 24 hours a day. You will be scheduled for an appointment with a urologist at a time convenient for you.
Neoplasm of undetermined or unknown nature of the urinary organs (D41)
Excludes: renal pelvis (D41.1)
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without other instructions.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
†
— code of the main disease. The main code in the dual coding system contains information about the underlying generalized disease.
*
- optional code. An additional code in the double coding system contains information about the manifestation of the main generalized disease in a separate organ or area of the body.
Acute cystitis in the ICD 10 classification
It is not uncommon, when receiving a hospital report (especially when undergoing diagnostics in private clinics), in the diagnosis column, you can see a not entirely clear set of numbers and letters. This code is nothing more than the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, or abbreviated code according to ICD 10. Acute cystitis, like any other disease, has its own specific unique code, which is understandable to any professional physician.
International classification
The ICD is an international system (medical standard) designed to designate various diseases and their forms, founded in 1855 at the Paris International Statistical Congress. Throughout its existence, the system has been constantly improved and refined.
This is a special-use document that contains all the information about the disease: name, causes, number of deaths, factors leading to mortality, and so on. This standardization is accepted in all countries; it contains all diseases known to medicine, each of which is assigned to a specific class and has its own unique code.
Due to the constant development of world medicine, with the introduction of new methods of diagnosis and treatment, as well as the emergence of new diseases, periodic additions to existing standards are required. Such additions are carried out every ten years; one of the latest was the introduction of Latin letters from A to Z.
Acute cystitis in the ICD system
Acute cystitis is a painful inflammation of the bladder mucosa, accompanied by frequent urination. According to the ICD 10 standard, it has the following form - N30.0, where N30 is the general group of all forms, and the number after the decimal point indicates one or another type.
Here's what this classification looks like:
- Genitourinary diseases N00-N99
- Diseases of the urinary system N30-N39
- Cystitis N30
- Acute cystitis N30.0
Now, when you see a diagnosis with a strange code, you will understand that this is just a medical duplication of a particular disease. As a rule, such a code is prescribed not for the patient, but mostly for the specialists involved in his treatment.
We recommend that you read other useful publications:
- Chronic cystitis in the ICD-10 classification.
- Urinary tract infections in the ICD registry.
Causes, symptoms and treatment methods for urethral polyp (ICD-10 – D30.4)
Any urethral polyp that is benign must be treated. According to medical statistics, they begin to actively develop under the influence of external and internal factors. In just 6 months, specific growths invade the urinary and gallbladder, gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory organs.
Timely medical care helps prevent the rapid spread of benign tumors. Until a preliminary diagnosis is made, it is worth refraining from treatment with folk remedies.
Main causes and risk factors for polyp formation
The disease is strictly female in nature. The reasons lie in the specificity of the formation of epithelial-type tumors in the body of the fair sex. Less commonly, the culprit is the anatomical structure of the urethra. During diagnostic procedures, the doctor begins the examination with the external opening of the urethra and urethra. The disease, which occurs in 4-5% of patients with complaints of pain in the urethra, is not dangerous.
From an anatomical point of view, the appearance of polyps on the urethra in women indicates an active growth process of fibrous tissue. It is characterized by red or brown color. The average size of a neoplasm ranges from 0.2 mm to 1.5 cm. Doctors always conduct several tests so that a polyp is not confused with a papilloma. In the second case, we are talking about the appearance of a loose surface. In appearance it looks like cauliflower.
Despite studies of the disease, doctors cannot with a high degree of probability draw conclusions about risk factors. They name exposure to negative environmental conditions and poor nutrition. Doctors believe the most likely culprit is a malfunction of the hormonal system. It is accompanied by poorly noticeable symptoms, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor.
Often the reasons for the formation of polyps in the urethra should be sought in a previous pregnancy. Long-term use of potent drugs can cause illness. Much less often, polyposis is provoked by a poorly treated infection or a late noticed inflammatory process:
- disruption of proper blood supply to the walls of the urethra;
- chronic urethritis;
- chlamydial infection;
- human papillomavirus infection.
Growths in the gallbladder
According to studies conducted by the Ministry of Health, about 6% of the population is susceptible to polyps in the gallbladder.
Unlike the previously discussed formations in the bladder, which are most characteristic of men, this type of growth is characteristic of the female half of humanity. According to statistics, up to 80% of cases occur in women over 35 years old.
Such formations were first discovered and described by the German doctor R. Vikhrov in 1857. During the same period, the first assumption about the causes of the disease appeared. The main emphasis was on the occurrence of problems with fat metabolism in the body. Until now, this is one of the main reasons that causes the occurrence of neoplasms.
The international classification assigned this type of disease codes K80 to K87, as well as D37.6.
Types and causes of occurrence
The classification of neoplasms echoes the previously discussed polyps. It consists of 2 large groups - true and false formations. Representatives of the first group are characterized by the growth of epithelial tissue, the second are “cholesterol plaques”, deposits on the mucous membrane of the gallbladder. Also, pseudopolyps include formations caused by inflammatory processes in the body.
Classification of polyps
False polyps
Cholesterol type Pseudopolyp, formed by cholesterol-type deposits on the walls of the organ. It is most typical and most common in men.
Inflammatory type Pseudopolyp, caused by excessive growth of the epithelium, provoked by inflammatory processes occurring in the body.
Rarely develop into a malignant tumor.
True polyps
Adenomatous type Originates from the epithelium (its glands) located on the lining of the gallbladder.
Papilloma A neoplasm, in the early stages, of a benign type. It is characterized by the presence of many “papillae”, with the help of which it spreads over the surface of the organ.
More often than others they cause cancer.
Medical professionals identify the following reasons for the development of polyps in the gallbladder:
| Cause | Description |
| Genetic predisposition, heredity | The patterns of the occurrence of growths from the heredity factor have been identified. In particular, this pattern is characteristic of “true polyps”. Even if among distant relatives there were cases of the formation of tumor-like neoplasms (regardless of which organ was affected), the risk automatically increases. Also, heredity plays an important role in the susceptibility to diseases, the course of which can cause the development of polyps. |
| Diseases that cause inflammatory processes in the gallbladder | The formation of growths (usually false polyps) caused by inflammatory processes is associated with “stagnation” of bile secretion. It is characterized by pain, especially after eating food rich in animal fats. As a result of “stagnation,” the walls of the gallbladder become thicker and become deformed. Against this background, there is a danger of polyp formation. The “risk group” includes, in particular, diseases such as cholecystitis, which have both chronic and acute forms. |
| Metabolic failure | One of the main reasons for the occurrence of cholesterol-type growths. Metabolic disorders lead to increased cholesterol levels both in human blood and in bile. Its excess is “deposited”, including on the walls of the gallbladder. Over time, such deposits increase in size and “fossilize” (due to the presence of calcium salts). The danger of such deposits is that they practically do not bother the wearer, who, accordingly, does not rush to the doctor. This leads to the fact that negative symptoms occur when the volume of growth reaches a decent size. |
| Impaired movement of bile and malfunction of the bile ducts | This cause can be characterized as an atypical secretion of bile into the duodenum. Which leads to an imbalance in the digestive system caused by the inability to break down fats normally. In addition, stagnation of the bile itself in the bladder is recorded, provoking the occurrence of neoplasms. |
In practice, the development of the disease is preceded by not one, but several causes.
Symptoms
The manifestation of certain symptoms depends not only on the type of growth, but also on its location. The most “unpleasant” location is the bladder neck or bile ducts. Due to obstruction of fluid flow into the intestines. Which leads to the appearance of “obstructive jaundice” in the patient.
In other locations, the symptoms will not be so “bright”.
The main manifestations of a polyp are:
| Symptom | Description |
| Painful sensations | Attacks of pain are caused by the “inflating” of the bladder due to excessively accumulated bile or its excessively frequent contraction, which is determined by the body’s attempt to “push out” the accumulated fluid. The pain is located on the right side, under the ribs. Defined as a “dull ache.” As a rule, it is episodic in nature, like contractions. Occurs after drinking alcohol, eating high fat foods, or stress. |
| Jaundice | An increase in the specific gravity of bilirubin (bile pigment) in the patient’s blood leads to yellowing of both the human skin and the eye sclera. This is due to the fact that excess bile, not entering the digestive system in sufficient quantities, having completely filled the volume of the bladder, “looks for a way out”, entering the blood. In addition to changes in pigmentation, indicators of “obstructive jaundice” are: - nausea; - vomit; - itching of the skin; - dry, tight skin; -pain in joints/muscles; - darkening of urine; - temperature increase. |
| Colic in the liver area | Attacks characterized by sudden, sharp pain on the right side, under the ribs. Occurs due to disturbances in the outflow of bile. It is more typical for “stones” in the gall bladder, but it also occurs with polyps, when the growth has a fairly long “leg”. The painful shock occurs suddenly and is quite strong. It is difficult for the patient to stay in one place, he tries to move to relieve the pain. Increased heart rate and increased blood pressure are possible, and the skin becomes covered with perspiration. At the same time, changing body position, with this type of pain attack, does not bring relief. |
| Bitterness in the mouth, nausea, vomiting | A symptom characteristic of polyps, it can be both pronounced and have “blurred” manifestations. These manifestations are caused, again, by stagnation of bile secretion. A failure in the flow of bile into the digestive system makes it impossible for the body to break down and absorb fats. At the same time, the patient begins to lose weight. Bitterness, in turn, is caused by bile entering the stomach. |
In addition to those mentioned, the following symptoms may occur that indicate a growth:
- dark urine;
- pale/wet skin;
- elevated temperature;
- bloating.
Diagnostics
To identify growths in medical practice, both laboratory and instrumental methods (ultrasound, endoscopy) are used. Moreover, medical test data are indirect signs of diagnosing polyps. And the basis for referral, for example, for an ultrasound examination.
When considering test results, pay attention to:
Blood
The following indicators have been increased:
- bilirubin (more than 17 micromol/liter);
- alkaline phosphatase (more than 120 units/liter);
- cholesterol (5.6 mlmol/liter and above)
I'm pissing
- presence of bilirubin;
- the content of such a component as urobilinogen is less than 5 mg/liter.
Feces
Absence or reduced content of the bile pigment - stercobilin (gives feces their characteristic color).
Negative tests, against the background of pain symptoms characteristic of such neoplasms, are the basis for medical examinations. It is their result that will become the basis for the choice of further treatment - surgical or medicinal.
To identify polyps and study them, use:
Ultrasound diagnostics During the examination, the gall bladder on the device’s monitor looks like a darkened, monochromatic oval with thin light walls. If there are growths, they are distinguished by light formations of heterogeneous colors. They are located from the walls of the organ into its interior. Depending on the type of neoplasm, its components (for example, stem, cap) can be determined. A feature of polyps that facilitates their diagnosis is their static nature - when the patient’s body position changes, the object does not move, but remains motionless (unlike “stones”).
Ultrasonography With this research method, an ultrasound probe is inserted into the patient through the mouth into the duodenum. Using high-frequency waves, the condition of the gallbladder is monitored. This method is effective in detecting even the smallest growths. Among the disadvantages, it is worth noting the procedure of “swallowing” the sensor, which will not bring pleasant sensations to the patient.
Tomography is an additional diagnostic method. Using tomography, the location and structure of growths (even the smallest ones) are revealed. High detail of the image helps to examine existing damage and additional abnormal changes in both the bladder and bile ducts. This type of research helps to understand the causes of the disease. This method is simple and effective, the only drawback is the cost.
Surgical intervention
Surgical procedures are prescribed by a doctor in cases where there is a high probability of a benign tumor developing into a malignant one.
The main indications include:
- the volume of the polyp exceeds 10mm;
- there is a dynamic growth in education;
- the growth develops in “tandem” with other chronic diseases (for example, cholecystitis);
- the neoplasm is not single, there are multiple growths;
- hereditary predisposition to cancer;
- Along with the polyp, stone deposits are present in the gall bladder.
During the surgical procedure, the gallbladder itself is removed along with the growth. Depending on the size of the growth, the operation is performed either by “piercing” the abdominal cavity with subsequent insertion of surgical instruments (90% of cases) . Or using a full incision - if the growth reaches a size of more than 1.5 cm.
Drug treatment
Treatment of formations with medications has low effectiveness. As a rule, it is used to eliminate diseases that caused tumor growth (for example, eliminating cholesterol deposits). Or eliminating the pain that accompanies the disease (painkillers, choleretic drugs).
Clinical manifestations of pathology
The disease, which has a unique ICD-10 code, manifests itself depending on the degree of organ damage and the strength of the immune system. Among all the symptoms, discomfort or pain during urination ranks first. Mistakenly, ladies begin to treat themselves for kidney problems, but the true cause of the ailment is hidden elsewhere. If during the first 5-6 days the patient does not receive professional treatment, then the following symptoms develop against the background of weakening of the body:
- burning;
- itching;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness;
- problems with urination;
- other.
When prescribing tests, the attending physician will pay special attention to the presence of blood clots in the urine. If any are detected, we can say that the neoplasms have damaged the ureter. Polyps are very fragile in structure. If for some reason they are injured in the ureter, then minor bleeding immediately manifests itself.
The transition of the disease to a chronic form is characterized by 2 common symptoms. Most often, the stream during urination is practically uncontrollable. The resulting growths make it unnatural. Women who have a very large polyp experience the most problems.
The most effective treatments
Regardless of the general symptoms, a urologist treats the disease. Unlike many diseases, where early diagnosis helps shape the therapeutic course, polyps in the early stages are extremely rarely visible. Modern equipment is not able to correctly identify them inside a person. We can talk about making a preliminary diagnosis at the moment when the formation reaches a certain size or provokes external symptoms.
Before treatment, the urologist asks the patient to take blood and urine tests and undergo urethroscopy. For subsequent treatment, a visual examination is best. The doctor has the opportunity to confirm or refute a previously made assumption.
What is a bladder polyp?
Under some circumstances, the mucous membranes of the genitourinary region may change and grow. Due to this phenomenon, benign neoplasms called polyps are formed. Growths localized on the mucous membranes of the bladder cause polyposis of the organ. The polyp is represented by the proliferation of superficial mucosal tissue, forming separate growths that are attached to the base with the help of a stalk (see photo). Some polyps may not have a stalk. Depending on the causes and nature of the disease, the quantitative indicator of polyps varies. These may be single tissue growths or multiple polyps. The main danger of the disease is the possibility of malignant degeneration of cells. And also, with significant growth of polyps, changes in the anatomical structure of the organ and associated problems in the form of impaired urinary function may occur.
Doctors reveal the cards: polyps in the bladder. How are bladder polyps treated in men?
Under some circumstances, the mucous membranes of the genitourinary region may change and grow. Due to this phenomenon, benign neoplasms called polyps are formed. Growths localized on the mucous membranes of the bladder cause polyposis of the organ.
The polyp is represented by the proliferation of superficial mucosal tissue, forming separate growths that are attached to the base with the help of a stalk (see photo). Some polyps may not have a stalk. Depending on the causes and nature of the disease, the quantitative indicator of polyps varies.
These may be single tissue growths or multiple polyps. The main danger of the disease is the possibility of malignant degeneration of cells.
And also, with significant growth of polyps, changes in the anatomical structure of the organ and associated problems in the form of impaired urinary function may occur.
Description
A bladder polyp is a tumor that appears on the surface of the bladder.
Methods for detecting tumors in the bladder
At the Ros-Vet Center, a number of studies are carried out that make it possible to most likely detect signs of neoplasms in the bladder, including transitional cell carcinoma in dogs. The disease does not have pronounced symptoms, so a standard diagnostic algorithm is used:
- urine test and general clinical analysis. Cystitis is excluded, although with neoplasms there may be an infectious process that causes inflammation;
- If an obvious neoplasm is palpable, or characteristic signs appear, an x-ray is prescribed to rule out stones in the bladder. The survey image shows only the stones, but not the tumor;
- use contrast radiography, cystoscopy, ultrasound;
- Cytological examination of the sediment reveals tumor cells.
Using urethrocystoscopy, you can visualize a neoplasm, get its full image on the screen and give an assessment and prognosis for the disease.
A veterinary nephrologist can understand how much the tumor has grown, what structures around it are involved in the pathological process, and whether there are signs of spread to other organs and tissues.
Based on the conclusion, a rough forecast can be given. So, when diagnosing bladder cancer, it is believed that the animal will live:
- up to 4 months, if the tumor has spread beyond the bladder;
- up to 2 to 3.5 months, if lymph nodes and distant organs are affected.
The maximum that an animal owner can count on is 8-9 months, in the case where the neoplasm is small, it has not spread beyond the bladder and there are no metastases in the lymph nodes.
Causes
The development of polyps in the bladder area is caused by a combination of reasons or one of the following factors:
- burdened heredity,
- intrauterine pathologies,
- metabolic disorder,
- bad habits (alcoholism, smoking),
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary tract,
- chronic endocrinological disorders,
- prolonged lack of personal hygiene,
- stagnant processes in the organ,
- lack of normal physical activity (as a result of illness),
- serious errors in nutrition, incorrect gastronomic habits,
- injuries, stress reduction of immunity.
When identifying the disease in question, it is not always possible to determine the exact cause of its occurrence.
Prevention
It is possible to prevent the development of a polyp.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=57mZ-u62zeQ
To do this, you must always adhere to the following rules:
- Use a condom during sexual intercourse.
- Use means to strengthen the immune system.
- Lead a correct lifestyle.
- If alarming symptoms occur, visit a gynecologist or urologist.
- Timely eliminate pathologies in the functioning of the pelvic organs.
- In case of hormonal disorders, it is correct to stop them.
We also advise you to read this article: “Treatment of candidal urethritis in women.”
Symptoms of urethral polyp
In the early stages, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. As the urethral polyp grows, the following symptoms appear:
- Difficulty urinating;
- Spraying urine;
- Burning, itching and discomfort in the urethra during and outside urination;
- Sensation of a foreign body in the urethra.
A bleeding urethral polyp (ICD 10 code – N34.2) is manifested by the appearance of blood in the urine (urethrorrhagia). Women may experience pain during intercourse. In the later stages of the disease, a tumor-like formation can completely block the lumen of the urethra and cause acute urinary retention.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Polyps in the bladder are a pathology that does not always make itself felt with clear clinical manifestations. Often, the diagnosis is revealed during a general examination or examination aimed at other ailments.
But under some circumstances, special signs of the disease can still be detected. The following symptoms should be the reason to consult a doctor:
- pain in the lower abdomen,
- congestion,
- difficulty urinating,
- burning in the genital area and pain in the bladder after bowel movement,
- in men, decreased erectile function,
- in women, decreased or complete absence of sexual desire,
- lethargy, apathy, irritability.
Important! During the inflammatory process, body hyperthermia with values up to 38 degrees can be observed.
All of these symptoms may indicate a number of other diseases not related to bladder polyposis. To clarify the diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist.
Transitional cell carcinoma
Neoplasms (tumors) of the bladder are rare in dogs and cats, but more than 70% of them are transitional cell carcinoma. The infrequent detection of tumors is explained by the age of the animals; after 11 years, they have a lot of visible, clinically evident pathologies, while cancer makes itself felt already in the last stages of development.
More often, the neoplasm is localized at the neck of the bladder, gradually blocking the lumen and disrupting the flow of urine. In males, the urethra and prostate are involved in the pathological process.
An obvious symptom is difficulty in the outflow of urine, frequent “empty” urges, drops of urine with blood are often mistaken for ICD.
Incorrect treatment does not bring results, although the tumor itself is difficult to access, surgical intervention is difficult, and given the age-related risks, it is impossible.
The reasons for the formation of mutations in the cells of the transitional epithelium lining the inside of the bladder are not known for certain. According to assumptions, the following are in first place:
- prolonged exposure of urine to the urinary mucosa;
- consumption, inhalation of harmful substances (carcinogens).
In recent years, according to the observations of veterinarians, cases of the development of neoplasms in the bladder in dogs have become more frequent due to the treatment of lawns with phenoxy herbicides.
Clinical symptoms do not appear at the initial stage of tumor formation; dogs and cats behave normally. Often the first manifestations of tumors are similar to urolithiasis or urethritis, which forces animal owners to intensively treat non-existent pathologies, thereby giving cancer cells the opportunity to capture “new territories”.
The reason for a complete examination should be the following symptoms: hematuria, frequent urination, hydronephrosis, poor urinary output. With metastasis, signs of damage to the lymph nodes and bone tissue (hypertrophic osteopathy), manifested by lameness, appear.
Diagnosis of the problem
The level of modern diagnostic medicine allows us to easily identify this disease.
Source: https://alkomir.net/vrachi-raskryvayut-karty-polipy-v-mochevom-puzyre-kak-lechatsya-polipy-v-mochevom-puzyre-u-muzhchin/
Causes
The development of polyps in the bladder area is caused by a combination of reasons or one of the following factors:
- burdened heredity,
- intrauterine pathologies,
- metabolic disorder,
- bad habits (alcoholism, smoking),
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary tract,
- chronic endocrinological disorders,
- prolonged lack of personal hygiene,
- stagnant processes in the organ,
- lack of normal physical activity (as a result of illness),
- serious errors in nutrition, incorrect gastronomic habits,
- injuries, stress reduction of immunity.
When identifying the disease in question, it is not always possible to determine the exact cause of its occurrence.
Causes
Urology refers to congenital strictures of the ureter as cicatricial changes in the wall of the duct due to existing hereditary anomalies, as well as its compression at the intersection with blood vessels (for example, the accessory renal vessel). The causes of acquired stricture are damage to the ureter as a result of operations and various instrumental procedures (ureteral stenting, ureteroscopy, etc.), trauma, bedsores from stones, urinary infections (tuberculosis, gonorrhea) and inflammation of surrounding tissues (periuteritis), radiation damage. In tuberculosis, multiple scar strictures of the ureter form in areas subject to infiltration and ulceration. Post-radiation strictures of the ureter are observed, as a rule, in the pelvic region and can be associated with radiation therapy for cancer of the prostate, rectum and female genital organs. Ureteral strictures after urological surgical interventions (ureterolithotomy, reconstruction of the ureteropelvic segment) can be observed in any part of the ureter.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Polyps in the bladder are a pathology that does not always make itself felt with clear clinical manifestations. Often, the diagnosis is revealed during a general examination or examination aimed at other ailments.
But under some circumstances, special signs of the disease can still be detected. The following symptoms should be the reason to consult a doctor:
- pain in the lower abdomen,
- congestion,
- difficulty urinating,
- burning in the genital area and pain in the bladder after bowel movement,
- in men, decreased erectile function,
- in women, decreased or complete absence of sexual desire,
- lethargy, apathy, irritability.
Important! During the inflammatory process, body hyperthermia with values up to 38 degrees can be observed.
All of these symptoms may indicate a number of other diseases not related to bladder polyposis. To clarify the diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist.
Diagnosis of the problem
The level of modern diagnostic medicine allows us to easily identify this disease.
A number of studies and tests are used to identify polyps:
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary tract,
- cystoscopy, cystography,
- general and detailed urine analysis,
- biopsy,
- MRI.
Also, to make a diagnosis in each specific case, other diagnostic measures can be taken to clarify or exclude certain pathologies.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of ureteral stricture is established based on the results of ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound examination of blood vessels, X-ray contrast examination, CT scan of the kidneys and MRI. Carrying out three-dimensional ultrasound angiography with a diuretic load allows you to simultaneously see the dilated section of the ureter above the stricture and evaluate the renal vessels. X-ray contrast urography (excretory, infusion, retrograde) makes it possible to visualize kidney tissue and the urinary tract, determine the narrowing of the ureters, the extent of strictures, and assess the decrease in the excretory capacity of the kidneys. In complex cases, CT or MRI are used, which additionally identify diseases of adjacent organs and tissues that affect the kidneys and ureters.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there is no drug treatment for this problem. With the help of drugs, you can only relieve pain and correct other accompanying conditions: stop the inflammatory process, strengthen the immune system, increase the body's resistance.
To relieve spasms and eliminate pain, use No-Shpu, Analgin, Papaverine or other antispasmodics and painkillers. If an infectious lesion is detected in a given area, antibacterial or antifungal therapy may be prescribed.
The mainstay of treatment for bladder polyps is surgery. Resection or cystoscopy may be used to remove polyps. A number of clinics practice laser removal of polyps. In all cases, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. The recovery period after treatment, subject to recommendations and appropriate therapy, passes quickly and without consequences.
Traditional methods
It is important to understand that traditional medicine recipes are not suitable for completely eliminating polyps in the bladder. Homemade remedies will only help support the body during and after the main treatment and prevent the development of complications. Some herbal infusions are effective in preventing the growth of polyps. You should consult your doctor regarding the use of any home medicine.
Infusion of celandine
The medicinal plant, celandine, is famous for its ability to stop tumor processes and block tissue proliferation. For bladder polyps, you can use the infusion. To prepare, you need to pour two teaspoons of dry suspension of celandine with 200 grams of boiled purified water. Cover the container with a lid and leave to infuse for 2.5 hours. The finished infusion should be strained and taken 1/2 cup between meals in the morning and evening. It is recommended to drink the infusion heated to a comfortable temperature.
St. John's wort infusion
St. John's wort is a medicinal herb that is effective in enhancing immunity and relieving inflammation. The infusion is prepared from 500 ml of boiling water and 30 grams of dry suspension of St. John's wort. The product should infuse for 2-3 hours. Then the infusion is filtered and drunk in small sips throughout the day.
Chamomile tea
Tea made from dry suspension of chamomile will help strengthen the immune system and reduce inflammation. To prepare the drink, you can take special bags of dried herbs or scattered herbs. Tea is prepared from one teaspoon of herb per 200 ml of boiling water. Infuse the herbal drink for 20 minutes. If necessary, the product should be strained and sweetened with 1 tsp. natural honey (if there is no allergy).
Polyps in the bladder may not cause any trouble to the patient for a long time. However, pathology should not be taken lightly. Any benign neoplasm increases the risk of malignant degeneration. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment are fundamental points that will help eliminate the risks of developing dangerous complications.
Folk remedies
The possibility of using certain homeopathic components depends on the patient’s individual tolerance to various herbal infusions.
Based on the above, before starting to take these medications, you should consult with your doctor.
If there are no contraindications, consider the recipes offered to its readers by the Messenger of a Healthy Lifestyle.
Recipe 8. Tubage
(HLS 2007, No. 16, p. 14)
For polyps, tubage (a procedure that stimulates the flow of bile from the bladder) is also effective. Recommended tubes with:
- 25% magnesium sulfate,
- sorbitol,
- tansy,
- xylitol,
- motherwort.
For preparation:
- 1 tbsp. one of these preparations is poured with boiling water (1 tbsp.).
- The warm infusion is taken in small sips.
- After which you need to lie down, placing the heating pad on your right side.
Lie down for 2 hours.
The procedure is performed no more than 1 procedure every 7 days.
Recipe 9. Celandine juice
(HLS 2010, No. 3, p. 10)
Dilute the squeezed celandine juice with vodka in a ratio of 2:1 (2 parts juice - 1 vodka).
Reception according to the scheme (dilute in 100 ml of water):
- 1st week – 8 drops;
- 2nd week – 0.5 tsp;
- 3rd week – 2/3 tsp;
- 4th week – 1 tsp.
Take 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
After a break (28 days), the course is repeated.
Recipe 10. Celandine decoction
(HLS 2010, No. 1, pp. 18-19)
- 1 tbsp. dry celandine.
- 1 tbsp. water.
- Pour boiling water over the herb. Leave in a thermos for 2 hours.
Take 1-2 tbsp. l. For 30 days.
If necessary, repeat after 10 days.
Recipe 11. Washing with celandine
(HLS 2010, No. 1, pp. 18-19)
The use of enema washes consists of 3 stages.
1 At the first stage, a solution prepared from warm water (2 l) and celandine juice (1 tsp) is used. The enemas themselves are given before bedtime. The duration of this stage is 15 procedures. After which there is a 15-day break and transition to the next stage.
2The second stage is characterized by an increase in the content of celandine in the solution. For the same 2 liters of water and juice, add 1 tbsp. The frequency and frequency are the same - once a day, 15 days. The break after the second stage will also be 15 days.
3At stage 3, the dosage is doubled again and is now 2 tbsp per 2 liters of heated water. Another 15 procedures are done at night.
If it is not possible to use the plant juice, then it is possible to prepare an infusion from dry herbs, using the technology from recipe No. 10. In this case, the dosage in stages will be 1 tbsp, 3 tbsp. and 4 tbsp respectively.
Recipe 12. Herbal tincture
(HLS 2010, No. 1, pp. 18-19)
- Dry leaves of celandine.
- Chamomile flowers.
- Mix herbs in equal parts.
- 1 tbsp. pour 1 tbsp of the resulting mixture. boiling water, let it brew for 7-8 hours.
The duration and frequency of administration is similar to prescription No. 10.
Recipe 13. Herbal mixture
(HLS 2012, No. 10, p. 22)
- St. John's wort;
- calendula;
- immortelle;
- calamus root;
- chamomile;
- corn silk.
1 tbsp. collection is poured with boiling water (1 tbsp.), Infused. Take 100 ml orally half an hour before meals, 3 times a day.
Course – 60 days.
In addition to collecting, these herbs can be taken separately, preparing an infusion according to the same principle.
Recipe 14. Burdock root
(HLS 2005, No. 10, p. 22)
(HLS 2010, No. 1, pp. 18-19)
- Several burdock roots + 2l. water.
- Wash the rhizomes and chop them.
- Add water, boil.
- Continue boiling over low heat for 10 minutes.
- Drink instead of water throughout the day.
[/wpsm_list]
Duration of treatment – 60 days.
If bitterness appears after the procedure, stop further use of this treatment.