Urology
1896
no comments
The appearance of stones in the human body has been recorded in the distant past. The first stones were discovered in mummies. It is known that even Isaac Newton, Peter I and Napoleon suffered from this disease. Why and how do kidney stones occur, and how to prevent this phenomenon?
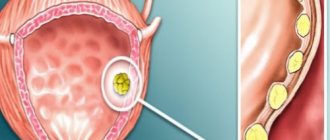
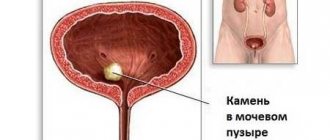
Cystolithiasis is a disease caused by the formation of stones, dense formations in the bladder, ureter and kidneys. The number of stones in the human body can vary from one to several hundred. And their diameter varies from 0.8 mm to 11-13 cm. Cases have been recorded when the mass of the stone was more than 2 kg.
Causes
The most common cause of stone formation in adult patients is bladder outlet obstruction - a violation of the free outflow of urine due to an obstruction in the bladder neck or urethra. Blockage of the lower urinary tract can be caused by stenosis of the bladder neck (Marion's disease), prostatic hyperplasia or prostate cancer in men, urethral strictures (after trauma, surgery, inflammation).
The mechanism of stone formation is associated with the inability to completely empty the bladder, stagnation and concentration of residual urine, leading to the loss of salt crystals. Stone formation is facilitated by a neurogenic bladder, its prolapse in women with cystotele, and existing defects in the internal muscular layer, including diverticula.
Sometimes, in the presence of stones in the kidneys and upper urinary tract, migration of small stones along the ureter is observed with their further appearance and persistence in the bladder. The presence of foreign bodies (stents, ligatures, catheters and other foreign objects) in the bladder can cause the deposition of salts on them and the formation of stones.
Bladder stones can be a consequence of reconstructive operations for stress urinary incontinence and inflammatory changes in genitourinary infections, the result of parasitic diseases (genitourinary schistosomiasis) and radiation therapy. In children, the appearance of stones in the bladder is often caused by existing balanoposthitis, complicated by phimosis and narrowing of the external opening of the urethra.
Causes of the disease
Cystolithiasis affects about 1-3% of the population. Moreover, men are much more susceptible to the disease than women.
The disease can appear as a result of inflammation of infectious and non-infectious origin. In the case of infectious inflammation, the culprits of the disease are microorganisms, and non-infectious inflammation is caused by physical and chemical factors.
Below we will consider the main causes of stones.
Infravesical obstruction
It is a blockage of the urinary tract that prevents the natural flow of urine. Initially, when such a problem arises, the body copes with it on its own. The muscle thickens, which causes an increase in pressure. Due to the increased pressure, urine flows down the urethra. Over time, muscle wasting occurs, leading to decreased muscle tone. Such problems lead to incomplete emptying, which is a favorable condition for the formation of stones.
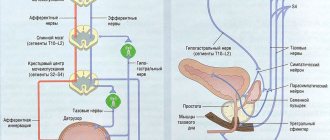
Disturbance of innervation of the bladder
The retention and emptying of urine is regulated by a special mechanism - muscles called the detrusor and internal sphincter. The detrusor is responsible for stretching the bladder when fluid accumulates and for producing contractions that help empty it. The internal sphincter maintains urine retention. Dysfunction of one of the innervation departments leads to impaired urination, and as a result, the formation of stones.
Other reasons
- Inflammatory processes. Affects the genitourinary system. May appear as a result of undergoing radiation therapy;
- Finding foreign objects in the organ. These items may be fragments of suture material, a catheter;
- Damage to the inner muscle wall;
- The appearance of a diverticulum (protrusion of the wall);
- Consequence of reconstructive surgery performed to prevent urinary incontinence caused by a stressful situation.
Urogenital cystosomiasis
Appears as a result of human infection with helminths and their active activity in the body, which affects the genitourinary system.
Concretions are divided according to certain characteristics. These include:
- Quantitative indicator. It is possible to have one or several stones;
- Diameter. Both very small and very large stones are detected;
- Hardness and softness. Stones can feel either soft or hard to the touch;
- Degree of roundness. There are stones with a rounded, that is, smooth surface, and with protruding points.
Metabolic disorders contribute to the accumulation of insoluble salts - the material from which stones are formed.
Factors predisposing to the formation of stones are:
- The predominance of spicy and sour foods in the diet, consumption of foods containing animal protein, refined sugar. Frequent intake of acidic foods causes an increase in urine acidity, which is favorable for the formation of stones;
- Insufficient amount of vitamins, minerals and trace elements for the body;
- The presence of metabolic diseases - diabetes mellitus, fermentopathy (impaired enzyme activity), gout;
- The presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- The presence of diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary organs (cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis);
- Dehydration caused by poisoning or infectious disease.
Types of stones
You can detect the symptoms of crystalline and salt formations in the bladder yourself. How exactly the presence of stones manifests itself depends on the nature of their origin and size.
- Oxalates. Such stones have an uneven surface and a hard structure. When oxalates move along the walls of the bladder or through the urinary canals, their jagged edges damage the mucous membranes. Symptoms in this case are acute pain and the presence of blood in the urine.
- Phosphates. These stones are softer in structure than oxalates, although they come from the same calcium salts. The presence of phosphates can be determined by the presence of light flakes in urine, pain during urination and frequent interruptions of the stream.
- Urats. It is possible to detect urate in the bladder only after taking a urine test. The smooth surface of this type of stones does not damage the internal tissues and membranes, which means there is no pain.
In addition to the listed stones, there are also struvites, cystines and other mixed formations.
Epidemiology of cystolithiasis
This type of bladder pathology is common. It is widespread throughout the world. Most countries are experiencing an increase in the incidence of urolithiasis. The highest incidence rates are typical for countries such as Spain, Great Britain, the Netherlands, France, Hungary, etc. Most often, urolithiasis occurs in the north of Australia, Asia Minor and the south of North America.
In our country, bladder stones are very common. In urological and surgical practice, this is one of the most common diseases. Of all urological ailments, bladder stones account for approximately 30-40%. After inflammatory processes, they occupy a solid second place in the ranking structure of diseases of the genitourinary system. The disease affects mainly people aged 20 to 55 years, that is, the adult, working population. Men suffer from stones quite regularly. As for the elderly and children, they are less susceptible to this pathology. This prevalence is largely related to the lifestyle of the population.
Indications
If conservative treatment is ineffective, chronic periodically exacerbating bladder infections, regular pain in the lower abdomen, blood in the urine or acute retention, they resort to removing stones from the bladder.
Transurethral methods for removing stones are indicated when they are visualized instrumentally and there are no obstacles to the extraction or spontaneous release of small particles of fragmented formations.
The indication for open surgery is the detection of a purulent inflammatory process or urethral stricture in the patient, the inability to visualize stones, and the presence of large stones that cannot be crushed.
[7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13]
Types of stones
How the disease will manifest itself depends on the size of the urinary stones, their number, component composition, as well as the presence of additional diseases in the patient.
Calcium stones are the most common (in 80% of cases) - they are rightfully considered the most dangerous, difficult to remove and dense (it is extremely difficult to crush them).
Calcium stones are classified according to their chemical composition:
- Oxalate
- Phosphate
- Urate
- Struvite
- Cystine
- Mixed stones
Oxalate . They have a brown color, an uneven surface, due to which they scratch the mucous membrane. If a patient has oxalate urinary stones, the urine often turns scarlet and urination becomes painful. They contain salts of oxalic acid.
Phosphate . Gray stones that are not very durable. They contain salt (containing phosphorus), making them easy to crush. Appear due to metabolic failure. Signs of phosphate stones include light-colored flakes in the urine, pain in the lower abdomen, and difficulty urinating.
Urate . Smooth stones that do not cause irritation or damage to the mucous membrane. They appear most often as a result of dehydration, so they are found mainly in residents of hot areas and those who suffer from gout. Urate stones can only be detected using a urine test.
Struvite . The cause of these stones is bacteria. They negatively affect urea, provoke an alkaline reaction, which results in the formation of phosphate, carbonate, ammonium and magnesium precipitation
– this contributes to the formation of struvite stones.
Cystine . A rather rare type of stone that looks like a crystal with six edges. Appears as a result of cystinuria, a disorder caused by an inborn change in metabolism. The level of cystine in the patient's urine is constantly elevated.
Mixed . This type of bladder stone, as the name suggests, consists of different salts and has a layered pattern.
Symptoms
Common symptoms indicating the possible presence of bladder stones in men are:
- pain in the lower abdomen, genitals, perineum;
- acute pain, stinging, severe discomfort when urinating;
- the presence of blood in the urine, changing its color to red or brown;
- cloudiness of the urine, the presence of flakes and crystals in it;
- interruption of the stream during emptying of the bladder;
- frequent urge to urinate, which occurs mainly during fast walking, physical effort and during shaking in transport.
When cystolithiasis occurs against the background of infections, patients experience a deterioration in their general health and symptoms that are characteristic of infectious diseases:
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- headaches and aches in the limbs;
- lack of appetite.
The presence of stones or sand in the bladder sometimes does not cause any of the listed symptoms and does not cause inconvenience to the patient.
- Bladder stones - folk remedies
Folk remedies
It is advisable to treat urolithiasis not only with the help of surgery or drug therapy, but also with various folk recipes. Today, a sufficient number of such agents are known, the effectiveness of which has been proven by laboratory studies. It goes without saying that it is strictly forbidden to prescribe one or another remedy for yourself - you should first undergo an appropriate consultation with your doctor.
The most popular and effective folk recipes that help men get rid of bladder stones:
- Dandelion infusion
This plant is known for its diuretic functions. Thanks to this, blood circulation in the genitourinary system will be significantly improved. Consequently, the flow of urine will increase, which will entail the washing out of stones. You can prepare a decoction as follows: take two teaspoons of dried herbs, pour a glass of boiling water over them, stir and cook this mixture for 15 minutes in a water bath. It is strongly recommended to drink the prepared broth immediately after it has cooled slightly.
- Lingonberry decoction
Another effective diuretic. It should be prepared as follows:
- 2 tablespoons of berries are poured into 200 ml of boiling water;
- the mixture is boiled for half an hour in a water bath;
- after this, the broth should be carefully filtered;
- the finished decoction will retain its beneficial properties throughout the day;
- It is recommended to drink 70-100 ml of the product at a time, approximately three times a day.
- Knotweed infusion
Knotweed effectively fights stones by destroying their structure. You need to take a thermos, pour about one teaspoon of knotweed into it, and pour 250 milligrams of boiling water. You need to infuse the product throughout the day. The finished infusion must be drunk three times, that is, within 24 hours. It is advisable to drink the product half an hour before meals.
- Infusion of birch leaves
This remedy will quickly relieve the unpleasant symptoms of urolithiasis. It is very simple to prepare - you need to brew about two grams of dried leaves in a glass of boiling water. It is important to drink approximately 2-3 glasses of the drug per day. At the same time, it must be fresh, that is, it is not recommended to cook it with a reserve.
- Cranberry juice
A very simple way to treat the symptoms of bladder stones in men. It is enough to drink two glasses of this natural juice a day, which helps to significantly reduce the concentration of calcium in the urine. This substance is known to be the main building material for stones.
Cranberry juice, due to its specific taste, may not always be suitable for treatment for certain men. In this case, it can be replaced with natural orange juice or lemonade (also real). Both drinks contain citric acid, which regulates the balance between citrate and calcium in urine, preventing the possibility of new stone deposits forming.
- Wild carrot seed infusion
Take three tablespoons of seeds, pour in about 600 ml of boiling water, and then let it all sit for about 12 hours. After settling the product, it must be thoroughly filtered. It is recommended to take 200 grams three times a day. The infusion, if desired, can be replaced with regular carrot juice - it is also very healthy. However, you need to take it as carefully as possible - no more than one tablespoon three times a day. But carrot juice is ideal for complex therapy, because it can be treated for six months.
- Carrot decoction
Take one carrot, grate it and pour 750 grams of boiling water. You need to insist for about 10-12 hours. Take three times a day, so that you drink all 750 ml. You can be treated with this remedy for a month, then you need to take a short break.
- Apple vinegar
Bladder stones in men can be effectively treated with regular apple cider vinegar. Even a ten-day course of treatment is enough to experience significant positive changes in the body.
During the day you need to drink six tablespoons of this remedy. Given the high concentration of the substance, which causes a very specific taste, it can be diluted with a small amount of clean water. After ten days, apple cider vinegar therapy is discontinued. If necessary, treatment can be resumed after a certain break - in about a month.
It is important to understand that only natural apple cider vinegar is suitable for treatment. The one that is widely available in grocery stores is completely unsuitable, since it contains a significant amount of foreign impurities, including those of chemical origin.
- Potato peel decoction
This medicine has a destructive effect on all types of stones localized in the bladder. Dissolution occurs as quickly as possible and, what is very important, completely painless. Preparing a decoction is very simple - you need to take a handful of freshly cut peels and boil it in prepared clean water (about half a liter).
At one time you need to drink one glass of potato medicine. There should be 2-3 such receptions per day. A significant advantage of this folk remedy is that it can be combined with other infusions and decoctions made from medicinal herbs.
Diagnostics
Detection of stones in the urinary tract does not currently cause any particular difficulties. This is due to the prevalence of diagnostic methods.
The most common of which are:
- Laboratory examination of urine. In this case, when taking a general urine test, you can identify indirect signs of metabolic disorders, expressed by the appearance of certain types of salts, the most common of which are oxalates and phosphates. This is also the appearance of bacteria, epithelial cells and red blood cells. It is impossible to accurately determine the presence of a stone in the bladder using this method, but it is possible to suggest the presence of pathology, as well as encourage other laboratory methods.
- Biochemical and general clinical blood tests. It can only indirectly suggest the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, while it is not possible to accurately identify the affected area.
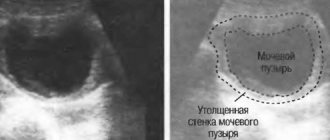
- Ultrasound examination of the bladder. Currently, this is one of the most informative methods for determining its presence, size, and structure. Based on some characteristics, one can draw a conclusion about the expected nature of the formation and the presence of accompanying changes, the inflammatory process, etc.
- Cystoscopic examination. A method that is used either for an acute process, or in case of difficulties with other diagnostic methods. It is invasive and requires the patient to be put under anesthesia. In this case, endoscopic equipment is inserted into the bladder cavity through the urethra, allowing visualization of the bladder cavity. If necessary, stone removal can be performed.
- Carrying out a cystogram with a contrast agent. In this case, a contrast liquid is injected through the urethra, which fills the bladder cavity. As a result, the doctor may note a filling defect, which will be evidence of the presence of a space-occupying formation in the bladder. Excretory urography also has a similar mechanism of action. This method is radiological and has limitations in use due to possible radiation exposure.
- Computed tomography method. Currently, it is quite valuable in diagnostic terms, as it allows you to accurately determine the size, structure and density.
Bladder cold
To treat a cold in the bladder, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, which must be taken if symptomatic therapy does not bring results.
A cold organ can be cured with the following medications:
- Uroprofit – helps relieve spasms, has an anti-inflammatory effect. It consists of biologically active substances that normalize the urinary system, improve kidney function, and reduce the risk of re-inflammation.
- Adenostop - the drug is made on the basis of an extract of the herb, cocklebur. Relieves swelling and kills pathogenic microflora.
- Abaktal is an effective medicine in the fight against infectious diseases. Can be used as a single agent or in combination with other antimicrobial drugs.
- Macropen - has an antibacterial effect.
- Levofloxacin is an antimicrobial drug.
- Augmentin - has a bactericidal effect on the inflamed organ.
- Diclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. In addition, it has analgesic and antipyretic effects.
- Ibuprofen - helps relieve inflammation and reduce pain during bladder infection.
- Lincomycin is an antibiotic that belongs to the lincosamide group. It has a bactericidal effect on the inflamed urinary system, suppressing protein synthesis in the microbial cell.
- Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Has a bactericidal effect against colds. Penetrating into the cell, it acts on intracellularly located pathogens.
Bladder stones are a fairly common disease in which stones of various sizes form in the organ.
Sometimes they appear in the ureter.
People of any age are susceptible to the disorder.
Based on the composition of salts, stones in the bladder are divided into groups :
- Carbonate stones;
- Oxalates;
- Urats;
- Phosphates.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of the pathological process is the key to making the correct diagnosis and accordingly prescribing a course of treatment. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient undergoes a series of tests and, based on their results, he is given a diagnosis.
- Ultrasound of the bladder. A non-invasive research method that allows you to obtain informative diagnostic results in a short period of time. The presented diagnostic method will allow us to determine both the size, shape, and localization of the tumor in the bladder cavity.
- Cystoscopy. A diagnostic method using a special apparatus, a cystoscope. It is this that is injected into the urethra and the bladder, kidneys and urethra are examined from the inside. It allows you to determine the size and mobility of stones, their appearance.
- General urine analysis . Helps determine the amount and volume of hematuria and crystals in its composition, the level of pathogenic microflora that contributes to the appearance of stones or is the result of their development in the patient’s bladder.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. Morning urine is collected for testing and laboratory testing is carried out on the same day. Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko takes into account the level of leukocytes - up to 2,000 in 1 ml, erythrocytes - up to 1,000 in 1 ml, as well as cylinders - up to 20 in 1 ml.
- X-ray of the bladder or its area . Allows you to identify stones in the bladder, but only if the latter have a layer of calcium in their structure. Otherwise, only a slight darkening will be visible in the image, without the ability to diagnose the size of the stone in the bladder.
- Diagnostics using a computer or magnetic tomograph . Computed tomography or the use of a magnetic tomograph in the process of identifying stones in the bladder is a painless, informative method of hardware diagnostics. Provides complete and informative examination results, makes it possible to obtain images in different projections - allows you to determine the size and localization of tumors.
- Administration of contrast agent, intravenous urography . Cystography and intravenous pyelography are diagnostic methods based on the introduction of a contrast agent into the genitourinary system. After the contrast agent is administered, X-rays are taken to show the location and size of the stone in the bladder.
Diagnosis
At the initial stage, the doctor diagnoses stones by palpating the area above the pubic bone. The first sign of the presence of stones is the detection of an enlarged bladder by palpation. Then a rectal examination is performed to identify prostate pathology.
Next, a general urine test is taken to determine the presence of salts from which stones are formed. Also, with the help of a general analysis, the presence of infections in the genitourinary organs, which contributed to the formation of stones, is revealed.
Another effective examination method is ultrasound. Using this method, it is possible to determine the location, size, shape and number of stones. The advantages of ultrasound are low cost, low time consumption, and the absence of surgical intervention.
Using computed tomography, a cross-sectional image of the bladder is taken, which makes it possible to detect even minor formations.
Carrying out a survey X-ray allows you to notice stones also in the ureters and kidneys. With its help it is possible to determine the number, diameter and location of stones.
But, some stones have an X-ray negative property, that is, they cannot be seen during an X-ray.
An effective examination method is intravenous pyelography. Its essence lies in the production of X-ray images before and after the introduction of a contrast agent into the human body through the veins. Once in the urinary system, the substance helps to identify even the smallest stones in the kidneys, bladder and ureters.
Complications
Complications of urolithiasis should be considered impaired renal function, which often leads to inflammation of the latter and the formation of an abscess in its cavity. This condition most often ends with an operation, the scope of which may even involve the removal of this organ.
With bilateral renal colic, when the outflow of urine from both kidneys is impaired, blood poisoning, which is called uremia, can develop. In such a situation, the condition of the patients deteriorates sharply and approaches critical. Uremia can threaten death for patients, so it is necessary to be extremely careful in the treatment of urolithiasis in order to prevent such a condition in time.
general information
Depending on the composition, they differ in color, shape, quantity and degree of hardness.
Based on their shape, they can be rounded, smooth, with spikes, polyhedrons, or fragments of a coral kidney stone.
Smooth ones are the most difficult to feel, since they do not injure the internal walls, and no pain symptom is observed. As a result, the patient is unaware of the formation for a long time.
The composition influences the treatment method: large crystals that are not able to leave the body on their own are artificially reduced in size. For this purpose, drugs are prescribed that dissolve the formations.
Different medications are used for different formulations, and some cannot be dissolved at all.
Stones is a general term. In practice, it is applied to formations larger than 1 mm. Crystallized salts less than 1 mm are called sand.
Depending on what acid they were formed from, stones are:
- oxalate – oxalic acid;
- phosphate – phosphoric acid;
- carbonate – carbonate acid;
- urate – uric acid;
- cystine – cystine amino acid;
The first three types belong to the calcium group, since each acid contains calcium salts, which serve as the basis for crystallization. Calcium stones occur in 70% of all cases of urolithiasis.
The formations are dangerous because they interfere with the normal functioning of the urinary system. In addition, they are formed in the kidneys, which leads to organ failure.
The disease is accompanied by severe pain when urinating and is fraught with development into a chronic form. Requires mandatory treatment from a specialist.
Treatment of bladder stones
If the deposits of conglomerates have not become widespread, conservative treatment of bladder stones in men is possible.
Having found out what the stone consists of, the doctor can prescribe a combination of drug therapy with the nutritional system. The diet prescribed for men and women with the formation of bladder stones depends on the chemical composition of the stone - phosphate, oxalate, urate or mixed type. To eliminate symptoms, stop pain and prevent recurrent stone formation, effective and safe drug therapy has been developed.
Preparations are used based on the perennial herb Goldenrod - Goldenrod (Solidágo virgáurea). The herbaceous plant of the Asteraceae family received its Latin name in the scientific classification from the word solidus - healthy, strong. It helps remove stones and prevents the formation of new conglomerates. If concomitant infectious diseases of the genitourinary system are detected, antibiotics are prescribed. Pain and colic are eliminated with the help of antispasmodics.
Treatment
Treatment of bladder stones is surgical. Surgery is not performed on small stones, in severely ill patients with renal failure or other pathologies, in immobile patients, or in very elderly patients. In these patients, attempts can be made to dissolve bladder stones with medication, but this is rarely effective.
Treatment of bladder stones in men always involves eliminating the cause of bladder outlet obstruction. Otherwise, repeated stone formation cannot be avoided. That is, the prostate adenoma will definitely be removed, the urethral stricture will be excised, the diverticulum will be removed, and the foreign body will be removed.
Patients who cannot be operated on are advised to take drugs that dissolve stones (nephradoz, rovatinex, prolit, urolesan). Sometimes it is possible to dissolve large stones, especially if they are urates or phosphates.
The stone can be removed using cystolithotripsy - crushing. It is used if the stone is located in the cavity of the bladder or at the mouth of the ureter. For bladder stones, the contact method of crushing stones, that is, ultrasonic grinding, is more often used. Using this method, it is possible for men and women to crush the stone into small fragments, which will be excreted independently in the urine under the influence of medications in the postoperative period.
Patients wonder if crushing a stone hurts? No. This manipulation is performed under spinal anesthesia.
Other stone removal operations:
- Laser crushing. The most optimal, as it allows you to destroy dense stones and shortens the recovery period after surgery
- Using DLT (external lithotripsy, when the calculus is broken by a shock wave of air through the skin). Most often used for kidney disease.
- Open surgery. The entire stone is removed, and the bladder is sutured with absorbable sutures. You will have to walk around with a urinary catheter for 7-10 days after the operation.
- Cystolitholapaxy is removal with an instrument through the urethra during cystoscopy or through a vesical fistula on the anterior abdominal wall. Removing stones from the bladder in women is easier, since the urethra in women is shorter and wider, which makes it easy to insert an instrument.
The postoperative period after crushing is easier, since there are no incisions on the body or on the organ itself. While in the hospital for the first days after surgery, a person may excrete small fragments of crushed stones in the urine; how many of them will be released is not known in advance. Doctors know how to speed up the passage of a stone or its fragments after lithotripsy. Conservative therapy is prescribed:
- For better removal of small grains of sand: canephron, rovatinex, blemarene, spilled
- To relax the urethra and urinary cervix in men, adrenergic blockers are prescribed, making the lumen of the urethra wider, which helps remove fragments: Omnic, Urorek, Focusin, Dalfaz
- Antibiotics and antispasmodics are required.
Taking tablets that affect the chemical composition of stones together with surgical treatment leads to complete recovery.
Urinary disorders that occur after the operation are relieved after a month. To treat hematuria, hemostatic injections or tablets are used.
Traditional medicine knows how to remove a stone from the bladder. Traditional methods of getting rid of stones involve taking herbs (knotweed, bear's ear, lingonberry leaf, currant, dill seed, orthosiphon, half-palm, goldenrod, madder, hop cones, birch buds, corn silk). 4-5 herbs are taken in equal proportions and mixed. 1 or 2 tablespoons of the mixture are poured with boiling water, infused for an hour and drunk in several doses a day. This way you can expel the stone and completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease.
After a few weeks of taking herbal infusions, a person will feel that a stone has passed. What to do? The main thing is not to throw it away, but to take it to the laboratory for analysis of its chemical components. Subsequently, it will be possible to take medications to prevent the disease.
Manifestations of urolithiasis
Symptoms indicating stones developing in the bladder are varied. When lowering the stone into the bladder, the patient experiences acute pain in the lumbar back; the urine contains sand and salts, and inclusions of blood.
If the calculus is formed in the urinary cavity, the symptoms will not be so pronounced, however, they will show themselves as an admixture of blood in the urine, pain, which intensifies when visiting the toilet or having sexual intercourse.
Other symptoms of pathology are also identified:
- attack of dull pain radiating to the back;
- blood in urine;
- change in the visual composition of urine - it is more cloudy and thick, has an unpleasant odor;
- bothered by frequent urge to go to the toilet and painful urination;
- the stream may break off during urination.
If your urine changes its consistency and color for no apparent reason, sediment appears in it, and you are bothered by attacks of pain radiating to the lower back, you should immediately visit a urologist and undergo a full and comprehensive examination.
What preventative measures should be taken?
Stones can form again, so it is necessary to carry out prevention to prevent the recurrence of stones.
To be proactive, doctors advise:
- Strictly follow all doctor's instructions when taking medications;
- Increase fluid intake;
- Treat cystitis in a timely manner;
- For men over 50 years old – visit a urologist once a year and treat prostate diseases;
- Compliance with a diet prescribed taking into account the detected metabolic failures and the composition of the stones;
- Timely removal of foreign bodies from the bladder or changing catheters;
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Sport;
- Correct lifestyle;
- Balanced diet;
- It is necessary to dress according to the weather;
- If any, even the smallest signs of this disease appear, you should consult a doctor.
In the future, it is necessary to take measures to prevent recurrence.
Further observation by a urologist, examination of metabolic processes and ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder every six months.
If the underlying disease is neutralized, the prognosis after healing of the stones is positive. If the causes of stones are not eliminated, the formation of stones in the urinary organ and kidneys may recur.
Surgery
Today, the main surgical methods for treating bladder stones include:
- How to get rid of bladder stones without surgery
- Transurethral cystolitholapaxy - after cystoscopy and identification of the stone, a special energy device (mechanical, pneumatic, ultrasound, electrohydraulic, laser) crushes the stone under the control of the surgeon’s eye, after which the crushed stone is removed through a cystoscope. It is the method of choice for treatment in adult patients. Relative contraindications for the use of the method are a small bladder volume, pregnancy, and the presence of a pacemaker in the patient.
- Percutaneous suprapubic litholapaxy (the method of choice for treatment in children) - the method allows you to more quickly and safely crush the stone and isolate stone fragments. The method is contraindicated in patients who have previously undergone operations on the pelvic organs, the lower floor of the abdominal cavity, or with a small volume and insufficiently filled bladder.
- Open suprapubic cystolithotomy - allows you to remove stones of significant size, stones that cannot be crushed by the above methods, stones attached to the wall of the bladder. The method is also used if combined prostatectomy (adenomectomy) or surgical treatment for bladder diverticulum is necessary.
What are the indications for surgical treatment of bladder stones?
- Lack of effect from drug therapy.
- Recurrent bladder infections.
- Acute urinary retention.
- Uncontrollable pain in the lower abdomen.
- Hematuria (blood in the urine).
Treatment can be carried out under local, spinal and general anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia method depends on the patient's comorbidities and the decision of the anesthesiologist.
Types of bladder medications
The list of bladder treatments includes types of medications such as:
- antibiotics;
- herbal medicines;
- antispasmodics;
- painkillers.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics have a wide range of effects. They create the necessary concentration of the active substance in the urine to treat pathogenic microflora.
To improve the health of the bladder, the doctor prescribes the drug Monural, which is prescribed once. This method of use helps reduce the side effects on the body from taking the antibiotic. Monural is not prescribed for the chronic form of the pathology. One tablet of this product eliminates microorganisms.
Herbal remedies
In case of remission or in the absence of acute forms of the disease, the doctor prescribes herbal medications. Such medications have virtually no side effects, are not addictive, can be used in long courses and are an effective method in the fight against the disease.
Commonly used herbal remedies include:
- Monurel. The component on which this biological additive is created is cranberry. The drug is effective in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms and E. coli.
- Bearberry - helps cope with cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis, and kidney diseases.
- Canephron is prescribed for the treatment of chronic infections, and also as a drug that prevents the formation of urinary stones. Canephron does not cause side effects if the patient does not have individual intolerance to the components.
- Cystoit-GF. Prescribed for acute chronic cystitis.
- Phytolysin. It is used in the presence of diseases such as cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, urethritis.
- Urolesan. It has antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodics relax smooth muscles, thereby relieving spastic pain. They help with the urge to urinate, urinary incontinence and nocturnal enuresis.
This type of drugs includes:
Painkillers
For pain and severe cutting in the urinary system, the doctor may prescribe painkillers such as:
Possible consequences of ureterolithiasis
Late diagnosis and long stay of stones in the ureter lead to the appearance of the following pathologies:
- inflammation caused by bacteria causes pyelonephritis;
- the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the blood can provoke sepsis;
- expansion of the renal pelvis, due to difficulty urinating, leads to hydronephrosis;
- inability of the kidneys to synthesize and excrete urine - renal failure;
- narrowing of the ureteric canals causes pathological strictures of the ureter.
Diagnosis of the disease
Understanding why stones form is possible through the integrated use of diagnostic methods, these include:
- X-ray of the bladder;
- general urinalysis, biochemical blood test;
- ultrasonography;
- using a cystoscope to examine the condition of the mucosa;
- cystogram.
Also, diagnosis of stones in the bladder and kidneys may include the use of computed tomography. This popular research method allows you to find out the number, type, and size of stones. Based on the data obtained, the doctor prescribes treatment according to a specific regimen.
Nutrition
The diet for a patient with bladder stones does not play such an important role as for kidney stones, but still some rules should be followed. The diet of a patient with cystolithiasis should be adjusted in such a way that water-salt metabolism in the body is normalized. To do this, you need to limit your consumption of table salt and generally reduce your daily diet.
If you have urates, you should avoid the following foods:
- broths;
- chocolate;
- cocoa;
- coffee;
- liver;
- kidney;
- fried and spicy foods.
It is also recommended to limit fatty and meat dishes in the evening meal.
For oxalate stones, a diet low in oxalic acid is needed. It is necessary to limit in the diet:
- tomatoes;
- sorrel;
- spinach;
- green salad;
- potato;
- carrot;
- dairy products;
- oranges and grapefruits;
- chocolate;
- meat broths;
- fats;
- meat of young animals.
If the stones have a phosphate composition, then the patient needs nutrition that promotes the oxidation of urine. To do this, you need to diversify your menu with fish, meat, flour products, lard, and vegetable fats.
To prevent the formation of new stones, it is necessary to reduce the concentration of urine; for this it is important to adhere to the correct drinking regime. It is recommended to drink as much fluid as possible, preferably mineral water. For uric acid stones, the patient is prescribed Borjomi, Essentuki and others. For phosphates and oxalates - “Izhevsky Spring” or “Narzan”. The patient should drink at least 2–2.5 liters of mineral water per day.
Benefits of diet
By adjusting your diet, you can prevent the formation of stones. Also, a properly selected diet will promote the natural removal of stones. To select a diet, it is necessary to find out what type of stones the patient has:
- If oxalates are detected, you should stop taking products containing oxalic acid. You cannot drink tea, eat salads with sorrel or beets, or chocolate. Fresh fruits are recommended, including grapes and pears.
- When phosphates cause discomfort, you need to drink as many acidic drinks and fruit drinks as possible. Milk and calcium-containing foods should be avoided. Bakery products and meat will benefit. This diet cannot be followed constantly, otherwise stomach upset may occur.
- If urates are detected, you will have to completely abandon legumes, meat and fish. You can cook porridge with milk, vegetarian soups and salads.
With any type of stones, you need to drink a lot so that when you empty your bladder, the accumulated salts come out. You should reduce your salt intake and start taking vitamin A. You need to eat in small portions, but at least five times a day. It is advisable to avoid fast food, products with preservatives and other chemical additives.
Treatment of urolithiasis should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. To avoid the formation of stones, it is necessary to be examined promptly. Men over 45 years of age who suffer from prostatitis are especially susceptible to this pathology. Pregnant women should also undergo regular screening.
What are the types of bladder stones?
Bladder stones are the result of a metabolic disorder that will result from urolithiasis. Oxalate, struvite, phosphate, cystine, urate and mixed aggregates are formed from accumulated mineral salts and acids.
If the urine content is incorrect, the concentration of salts in the urinary system increases pathologically. The composition of urine is disrupted, the precipitate that falls out crystallizes and forms stones. The chemical composition of the “blockages” of the urinary tract is always different; its study makes it possible to clarify the symptoms and prescribe the correct treatment.
Bladder stones tested in adults are composed of uric acid in about half of the cases. Children's stones are made from calcium oxalates and phosphates and other elements.
Bladder stones are soft and hard formations, single and multiple, round and hard, with a rough, layered and smooth surface, in the form of spikes and polyhedrons. They vary in size and location. There are small and very large. There are specimens with a diameter from 1 millimeter to 10 centimeters.
Bladder stones are formed as a result of poor nutrition, metabolic disorders, and congestion, leading to urolithiasis.
Medications and folk remedies in the treatment of the disease
How to remove a stone from the bladder? Medications for removing bladder stones are no different from those used to dissolve kidney stones.
These include:
- "Spilled";
- "Urolesan";
- "Cyston";
- "Phytolysin";
- "Allopurinol"
- "Canephron";
- "Blemaren" and the like.
The active ingredients of the drugs increase the amount of urine excreted and change its properties, promoting the dissolution of stones. Medicines are selected depending on the type of stones.
Diet is of great importance for the dissolution of stones. It must be selected correctly.
By type, stones are divided:
- carbonate - contains calcium carbonate;
- phosphate - from calcium phosphate;
- urate - consist of uric acid;
- oxalate - from salts of oxalic acid.
Oxalates and urates are the most common. There are also stones of mixed nature, struvite - do not dissolve, cystine stones.
If you do not determine the type of stone and the structure of the stone, traditional medicine can be harmful. For example, for phosphate stones, decoctions of dye madder are used,
And for urate - kidney tea, horsetail decoction, lingonberry tea, decoction of elderberry flowers and stinging nettle.
Oxalates are dissolved with an infusion of herbal tea - horsetail, greater celandine and smooth hernia are taken in equal parts.
If it is not possible to determine the type of stone, or the stones are composed of sediments of several types, then it is better to coordinate the selection of medications and folk remedies with a doctor.
You can only change your drinking regime on your own - if you have stones in the bladder, you should drink 0.5-1 liters more fluid than in a healthy state.
The amount of liquid is increased by using clean water, dried fruit compotes or fruit drinks, and eating grapes and watermelons.
Diagnostic tests
A visit to the doctor involves a visual examination of the patient, collection of complete data - anamnesis of the disease, life history, followed by the collection of blood and urine samples.
The specialist will need:
- Urinalysis (general);
- Urography, using x-ray;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- Computer, magnetic resonance imaging;
- Contrast cystoscopy.
These measures are aimed at finding out how stones leave the excretory organ, as well as the intensity of dysuria - pain, burning sensation accompanying bladder emptying, and the degree of progression of hematurgy.
Rectal palpation gives results only for large stones - cystoscopy allows you to study in more detail changes in the structure of the urinary organ - the integrity of the mucous membranes, protrusion of the walls, neoplasms, the presence of a narrowing of the cervix.
The sand and stones present are determined by diameter, quantity, and composition. Multislice computed tomography makes it possible to examine the smallest particles of formations.
A comprehensive study helps to make an accurate diagnosis and determine how to remove stones most effectively without damaging internal organs.
Prevention
In fact, it is quite difficult to prevent the formation of stones that form due to natural causes. We can only advise you to immediately consult a doctor at the first symptoms and treat urinary tract infections before they cause stone formation.
However, you can reduce the likelihood of stone formation by leading a healthy lifestyle. Drink plenty of water, on average 6 to 8 glasses per day. Consult your doctor about the best diet for you, but in any case, try to avoid large amounts of fatty foods, as well as salt and sugar. Smoking and taking drugs also put a lot of strain on the kidneys as they try to filter out harmful chemicals. If they accumulate, they can easily form stones.
Causes of bladder stones in women
Discomfort and unpleasant symptoms during urination should alert you; these may be the first manifestations of urolithiasis.
Provoking reasons are:
- heredity;
- poor nutrition (frequent consumption of foods that contain uric and oxalic acid, eating spicy, sour and bitter foods);
- inflammatory process in the bladder, trauma;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- abnormal structure of the urinary tract;
- endocrine diseases leading to calcium metabolism failure;
- poor physical activity;
- diseases of the kidneys and digestive system (ulcers, gastritis, colitis);
- disturbance of material metabolism;
- foreign body;
- spinal injury, osteoporosis.
Bladder stones (symptoms in women are provoked by numerous factors) occur under the influence of geographical and climatic influences. During the heat, sweating increases and the concentration of salts in the bladder increases. Hard water promotes the formation of stones.
Bladder stones in pregnant women
Stones in a woman who is carrying a child are formed due to the following reasons:
- the presence of sand or small formations before fertilization has occurred;
- disruption of metabolic processes as a result of low mobility of a pregnant woman;
- the appearance of edema due to double load on the kidneys (urine concentration increases, the expectant mother consumes less fluid);
- abuse of canned foods and semi-finished products, insufficient amounts of fruits and vegetables in the diet.
The first symptoms of bladder stones appear more often in late pregnancy in women. This is due to the deposition of calcium, which is removed from the body more slowly during this period.
Sources used:
- https://doctor-365.net/kamni-v-mochevom-puzyre/
- https://simptom.info/urologiya/kamni-v-mochevom-puzyre
- https://ilive.com.ua/health/operaciya-po-udaleniyu-kamney-iz-mochevogo-puzyrya-metody-i-reabilitaciya_125526i88956.html
- https://urohelp.guru/mochevoj-puzyr/mochekamennaya-bolezn.html
- https://fraumed.net/kidneys-urination/kidney-stones/kamni-v-mochevom-puzyre.html
- https://farmamir.ru/urologiya/mochekamennaya-bolezn/kamni-v-mochevom-puzyre-u-muzhchin-prichiny-obrazovaniya-simptomy-klassifikaciya-i-lechenie/
- https://opochk.ru/kamni-v-mochetochnike-lechenie/
- https://omuzh.ru/urologiya/kamen-v-mochevom-puzyre-lechenie
- https://healthperfect.ru/kamni-v-mochevom-puzyre-simptomy.html
Where do they come from?
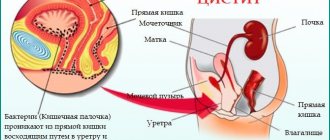
The appearance of stones in the bladder (calculi) can have various causes. Most often, deposits accumulate due to bladder outlet obstruction - partial blockage of the urinary outflow channels.
When the urinary tract is narrowed or blocked, urine is not completely cleared from the bladder cavity. The remaining urine crystallizes over time, forming stones of different shapes and sizes.
When a stone forms in the bladder itself, it is called primary. If the stone has descended from the kidneys into the bladder , then they speak of the presence of secondary stones.
In men, obstruction of urine flow is often caused by:
- prostate enlargement;
- narrowing of the urethral canal;
- phimosis;
- other diseases or physiological changes.
Among women:
- pathological changes in the bladder in the cervical area;
- displacement of the bladder due to uterine prolapse.
In addition, regardless of gender :
- Kidney stones appear as a consequence of diseases collectively called “neurogenic bladder.” The peculiarity of these diseases is the disruption of connections between the bladder and the nervous system.
- Foreign bodies in the genitourinary area (for example, a contraceptive device or suture materials) can also cause stone formation by affecting the urinary tract.
- An unsuccessful operation to treat incontinence can cause cystolithiasis if, in the postoperative period, there is a violation of the outflow of urine and it accumulates in the bladder cavity.
- Some external factors contribute to the formation of stones, such as drinking hard water, dehydration, and vitamin deficiency.
Prognosis and prevention
Predicting the development of disease in the bladder and kidneys depends on what causes problems with the flow of urine.
The outcome of therapy will be favorable if the cause of the pathology is eliminated, but medical statistics indicate that after removal of bladder stones, relapses may occur in half of the patients.
If the body is prone to the formation of stones, it is necessary to take this into account and adhere to a healthy lifestyle, reducing the consumption of salty, sweet, fatty and spicy foods, as well as giving up alcohol and cigarettes.