One of the most common parasitic diseases of the genitourinary system is kidney worms. Pathology occurs regardless of the patient's age and gender. The predominant route of infection is nutritional: penetrating the body with food or water, helminths feed for a long time on the nutrients present in it. The pathological phenomenon requires immediate medical intervention.
Worms in human kidneys, symptoms of helminths in them
A helminthic infestation can affect any organ.
Helminths, entering the human body, can live there for a long time. They actively reproduce and feed at the expense of their owner. A parasitic disease can manifest itself in different ways, which is why a patient can be treated for a long time for other diseases and not know what he really has. Most often, parasites live in the digestive organs, but are there worms in the kidneys? Some types of worms can travel throughout the body through the bloodstream. They are found in different organs; there is practically no place where they cannot live. For example, worms in the human kidneys can be very dangerous to health. They quickly destroy organ tissue and thereby interfere with its normal functioning. Due to the presence of worms in the kidney tissues, inflammation can begin, and pyelonephritis often occurs.
Such uninvited guests can also cause the formation of kidney stones, as well as non-healing fistulas. Thanks to the vital activity of worms, general immunity is reduced; they can become a trigger for the formation of cysts and tumors.
Symptoms of worms in the kidneys may not be pronounced at first. But over time, there is a gradual decline in organ function, and kidney failure may even occur. The patient begins to suffer from headaches, irritability and constant fatigue. The following symptoms will help you suspect something is wrong:
- bad breath;
- pressure surges;
- swelling of the ankles;
- dull pain in the lower back;
- anemia;
- indigestion;
- bleeding gums.
It is almost impossible to recognize a parasitic disease on your own. That is why, if you have the above symptoms, you must undergo an examination.
Just about health: what you need to know about worms so as not to become their victim
Preventive medicine specialist Ekaterina Stepanova
continues to talk about the most important parameters of the body, which are important to always keep under control.
© Pixabay
It is so created by nature that there are many around who want to live in comfortable and satisfying conditions of our body, for example, worms or helminths. Do not underestimate uninvited lodgers - they can cause very serious damage to our body, even death.
They are not visible, but they are there
Since we live in society, invasion (translated from Latin as “invasion”, “invasion”, in modern medical language means infection, most often with helminths, worms - Sputnik) usually becomes a problem for an entire family or team. And although we do not eat raw food and observe, for the most part, sanitary conditions, infection with worms is not at all uncommon. According to statistics, helminthiasis ranks second after respiratory diseases!
In addition, for a long time you may not be aware of uninvited tenants. The symptoms and clinical picture of invasion are often very similar to other diseases. It can be completely asymptomatic. This is not surprising, because parasites are living beings, and they do not need to be detected at all.
Therefore, diagnosing their presence can be difficult. About 150 species of parasites can live in humans.
© Pixabay
The eggs of many parasites mature in the ground
Children are the most defenseless against parasites, so parents simply have to be twice vigilant and attentive to their child’s complaints.
If a child is 4-5 years old and is diagnosed with “biliary dyskinesia” or something like that, this is a reason to be wary.
This disease is not typical for childhood, unless you feed your child barbecue, olives and smoked meats every day.
Any diagnosis that is uncharacteristic for a child is a reason to suspect helminth infection. For example, if a diagnosis of epilepsy is made, and there was no one in the family with such a diagnosis, it is worth ruling out helminthic infestation.
The most dangerous tenants
There are a great variety of helminths in nature. We will look at the most common in our region, the order of so-called roundworms
.
The most common of them are pinworms, roundworms, and toxocara (another name is canine roundworm).
© Pixabay
Pinworms.
The disease they cause is called
enterobiasis
. Such tenants most often move in due to poor personal hygiene. Usually children bring them home, and adults are automatically included in the company.
Pinworms are small worms that live in the small intestine. But sometimes they can enter the brain and the retina of the eye, causing corresponding disorders. In the small intestine they eat the best food, rich in vitamins, enzymes, proteins...
In the morning, pinworms crawl into the anus area and lay fertilized larvae. If a child sleeps without panties or pajamas, then, tossing and turning in his sleep, he shares the larvae with the bed, toys, blanket, and everything he touches with his buttocks. Larvae can survive on things for quite a long time - up to 6 months. This is the danger of re-infection (reinvasion).
Often parents cannot understand how the child became infected again, but meanwhile, it is very easy to let the tenant back in.
If a child infected with pinworms sat without underwear, for example, on a blanket, and then you shook it off and then vacuumed the carpet, then the larvae can be spread throughout the room with the flow of blown air.
And you can become infected just by breathing such air. The life cycle of a larva is 21 days, but if reinfestation occurs, this story can last for years.
© Pixabay
After swimming in a pond, it is best to take a shower and wash your pet thoroughly.
Enterobiasis can signal itself in different ways. Sometimes symptoms of acute respiratory infections may appear, and the person does not even suspect that he has not caught a cold, but has become a landlord. Sometimes a child may complain of abdominal pain, poor sleep, runny nose, cough, be tearful, or have allergic reactions. If there are no epidemics during this period, then parents should think about whether they have pinworms or not.
An infected child may have a greatly increased appetite, but after eating there will be a feeling of nausea, abdominal pain, and abnormal bowel movements. And although the baby eats abundantly, he will be weak and lethargic. Parasites take up to 60% of a person’s energy.
Diagnosing enterobiasis is not difficult - to do this, you need to scrape the eggworm.
The whole family should undergo treatment, and not just the person who has been diagnosed with parasites.
The consequences of infection can be:
- acute intestinal conditions: flatulence, colic, appendicitis, peritonitis;
- urinary tract infections, vaginitis, are especially dangerous in young children.
Roundworms
.
Parasitic roundworms up to 40 cm long cause ascariasis
. Ascaris feeds on blood, so it is classified as a dangerous worm. Lives mainly in the intestines, but can sometimes penetrate other organs. It is not difficult to identify the roundworm - it is pink if hungry and red if well-fed.
Ascaris eggs are found in the ground, where they mature. When the temperature rises above 16°C, the larvae become active. They can reach a person through unwashed hands after sandboxing or working in the ground, unwashed vegetables, fruits, and berries.
The route of the parasite is approximately as follows: earth - human mouth - folds of the stomach - circulatory system - portal vein - liver lymph node - through the vein up into the lungs - bronchial lymph nodes - along with a cough, re-swallowing into the esophagus - stomach - intestines - sticks to the capillary of the mucous membrane and sucks blood .
© Pixabay
To avoid becoming a landlord to “strangers,” wash your hands as often as possible
One roundworm drinks 40 milliliters of blood per day. But, as a rule, one is not enough. They always have a big company. Roundworms are a very organized form of helminths.
Scientists endow them with the simplest intelligence, since the path of their development is surprising in complexity.
The male looks for a female in the human intestine, the female lays fertilized eggs there in the intestine, the person empties, the eggs fall into the ground with the feces and everything goes in a circle again.
Roundworms live 1.5 years. If a new addition does not occur, the person is considered cured, but loses enough health.
Roundworms can cause anemia. The disorders that roundworms cause in the body can sometimes be irreversible:
- intestinal obstruction, perforation of the intestinal wall;
- anemia of various etiologies;
- acute cholecystitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis and so on, depending on the place where the parasite has settled.
Toxocara,
or canine roundworm. They are dangerous because they constantly move throughout the body, living wherever they like: eyes, joints, heart, brain. Toxacara is often confused with roundworm - but it is always white.
The needs of Toxocara coincide with the needs of our cells. Therefore, she receives our cellular nutrition first, and we receive all that is left.
© Pixabay
Important! Toxocara is capable of simulating the clinical picture of any disease, depending on which organ it is currently located in. Symptoms can range from runny nose to schizophrenia.
Therefore, if you have not been examined for toxocariasis, then your clinical diagnosis is 50% correct, especially if you returned from southern countries. There are also types of parasites that are transmitted through insect bites!
Diagnosis: skin scraping and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for Toxocara antigen.
How to protect yourself from “strangers”?
One hundred percent - no way, but some measures need to be taken.
If you are going to travel to distant countries, then a necessary safety condition will be to contact a parasitologist. We need to find out the epidemiological situation in the country, what helminths live there, and how one can become infected with them.
It is very important to regularly conduct protoparasitic preventive programs. But it is better to do this after consulting a doctor, otherwise you risk doing more harm to your body than good.
Treat chemicals against worms with caution and thoughtfulness. Don't forget, worms are LIVING organisms that feed on the same cellular nutrition as we do. And it is impossible to kill helminths without causing harm to the body.
When the worms decay, severe intoxication is formed; the body has to expend effort to neutralize the cadaveric poison. Therefore, it is necessary to use anthelmintic drugs. And it doesn't have to be pills.
An alkaline environment (washed herbs, spices, washed pumpkin seeds), water with the correct pH creates conditions for worms to escape!
How to keep unnecessary tenants out?
Everything here is quite simple; most of these rules are familiar to us from childhood. But we don’t always comply with them. To avoid getting infected, you need to:
- wash your hands before eating and be sure to wash them after using the toilet. As soon as you remember that you have hands, wash them.
- You cannot walk around the apartment in street shoes - always change into house slippers;
- pets - dogs and cats - should not be in the kitchen (worm larvae are quite light and can be lifted from the animal’s fur by the air flow without any problems and spread everywhere);
- the animal’s bowl must be washed exclusively in the bathroom, and not in the kitchen, so as not to infect the family dishes;
- It is necessary to wash the animal’s paws after going outside;
- vegetables and fruits must be washed with a 1% soda solution; you can soak them in a weak vinegar solution for 15 minutes;
- The worms have very tenacious suckers, and it is impossible to wash them off with water alone. Everything that you bring from the store in bags (milk, sour cream, cheeses, eggs) must be washed with soap, since rodents can run around in the warehouses where it is all stored - carriers of various diseases, including worms.
- In summer, swim only in those bodies of water where sanitary services allow it. And it is better if it is a river, and not the standing water of some dam. Do not swallow water when swimming;
- in summer cottages, sanitize the garden - all types of onions, peas and garlic kill worm larvae. So change their planting locations more often;
- In spring and autumn, conduct anti-parasitic programs for the whole family. And it’s better not to get carried away with pills, but to make prevention safe. Give preference to all types of onions, garlic, wild garlic, radishes, radishes, hot peppers, turnips, white cabbage, eat pineapples, grapefruits, strawberries, cranberries, blackberries, corn, lemons, ginger, dill, sorrel, herbs and spices more often. If at least one of the products is on your table every day, you will protect yourself and your family!
In the midst of spring and nature's renewal, renew yourself and your family. And let no uninvited guests spoil your joy of enjoying life and excellent well-being.
Source: https://sputnik.by/society/20170422/1028446774/ostricy-askaridy-toksakary—kak-ponyat-chto-rebenka-glisty.html
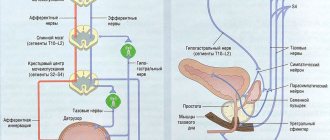
Kidney helminths – schistomatosis
Schistomatosis is a serious disease that requires immediate treatment.
It can be caused by trematodes, but fortunately, this type of parasite lives in the tropics and is rarely found in our area. Both animals and people can carry the disease. The helminth can enter the body through the skin or stomach. At first, the disease manifests itself clearly: the temperature rises, diarrhea and vomiting appear. Then these manifestations pass, and the chronic course of the disease begins. The parasite selects one organ and can live there for many years. For example, if it has settled in the kidneys, then the patient may suffer from dull pain in the lower back. Often this is the only symptom, but if a person goes for examination, pus and worm eggs will be found in the urine.
Worms in the kidneys - echinococcosis
This disease is also quite rare; you can get infected from a sick dog, as well as from wild animals and poorly washed vegetables and fruits. The worm that causes this disease can also travel through the bloodstream throughout the body. It most often affects the lungs and liver, but sometimes occurs in the kidneys.
In this case, the patient may be tormented by a dull pain in the lumbar region; when palpated, the organ may be enlarged. The parasite, entering the organ, strengthens there and forms a cyst, which reaches an impressive size. It puts pressure on the organ and prevents it from functioning normally. If the cyst bursts, the patient may feel acute and unbearable pain.
Worms in the kidneys are rare, but damage to this organ often leads to serious health problems. Unlike the liver, the kidneys do not regenerate, so they need to be protected. At the first signs of helminthic infestation, it is advisable to immediately get examined and undergo the necessary course of treatment.
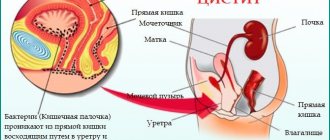
Parasites of the kidneys and urinary tract
Parasites of the kidneys and urinary tract
- these organisms most often belong to the class of worms, flukes, which are introduced into the body through swimming or drinking contaminated water.
Echinococcus kidneys. Etiology and definition
Echinococcal blisters have been repeatedly found in the kidney (1-3% of all cases of echinococcus), although they are much less common in it than in the liver.
Usually only one kidney is affected, and the parasite is located in its very substance and only as an exception - between the tissue of the organ and the renal capsule.
The size of echinococcal blisters can be quite significant (up to 20 cm or more in diameter).
Clinical phenomena usually occur only by the time the tumor can be felt through the abdominal walls. However, even in this case there may be no subjective disorders. And only subsequently does a painful feeling of pressure gradually arise. The tumor is usually approximately round in shape.
Its relationship to neighboring organs (especially the colon) is the same as was indicated when describing renal tumors. The seemingly characteristic sensation for echinococcus, the so-called trembling of the hydatid, which appears during jerky palpation of the tumor with the palm of the hand, is observed extremely rarely.
Relatively often, the echinococcal bladder opens into the renal pelvis.
In these cases, severe colicky pain usually occurs, reminiscent of colic due to kidney stones, and individual echinococcal blisters or at least fragments of membranes, hooks, etc. are excreted in the urine.
Such attacks can be repeated quite often and in the case of prolonged blockage of the urinary tract (bladder, ureters) can cause a severe picture of the disease.
Often in such cases the phenomena of secondary pyelitis and cystitis are associated. The spread of echinococcus to other organs is much less common. Several times, renal echinococcus was observed to burst into the lungs, and echinococcal blisters were released during expectoration. Sometimes, especially after injury, the echinococcal bladder becomes inflamed, suppurates and leads to general pyaemia.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of renal echinococcus is possible only when it is possible to detect a tumor related to the kidney, and when parts of the echinococcus are isolated in the urine or during a test puncture. The fact that you should be very careful with a test puncture was already mentioned above.
Most often, echinococcus is mixed with hydronephrosis (see the corresponding chapter) and, in women, with ovarian tumors. Sharp eosinophilia in the blood, observed in almost all animal parasites, can sometimes direct one's thoughts on the right path or support the diagnosis of echinococcus.
Forecast
The prognosis is not always unfavorable. After opening and single or repeated emptying of the echinococcal bladder, a complete recovery was eventually observed. It goes without saying that the existence of renal echinococcus is associated with various dangers (bladder suppuration, etc.). The general course of the disease is always long.
Effective therapy is only possible through surgery. Symptomatically, for local inflammatory phenomena, ice is used, for colic - morphine, sometimes mechanical means (catheter).
Parasites schistosomum (distomum) haematobium (bilharzia)
Schistosomum (Distomum) haematobium (Bilharzia) is a parasite belonging to the class of flatworms, flukes (flukes) and is found in Egypt, Ethiopia, Africa and Asia Minor
Definition. Etiology
Infection occurs through water when swimming or drinking, if parasite eggs get into the latter along with the urine of patients with genitourinary schistosomiasis.
Embryos (miracidia) hatched from eggs in water first penetrate the liver of an intermediate host - a water snail - where they develop. Then they, in the form of cercariae, fall back into the water and look for their final owner - humans.
While swimming in contaminated water or during field work, parasites pierce human skin, penetrate the veins and here they develop into adult schistozomas.
After prolonged puberty, egg deposition begins again in the pelvic veins (the parasite’s favorite place of residence). The natives are affected, of course, much more often than Europeans.
Parasite Schistosomum haematobium
As already mentioned, the kidney parasites Schistosoma haematobia live primarily in the branches of the portal vein, especially in the venous plexus of the bladder and genitourinary system. They lay their eggs in the mucous membrane of the renal pelvis, ureters and bladder in such large quantities that the tissue is stuffed with them.
The consequence of this is extremely severe inflammation, ulceration with subsequent narrowing, stone deposits, bladder stones, etc. Sharp inflammatory changes are also observed in the genitals (bilharzia of the genitourinary system).
The consequence may be tumor-like spread of tissue in the genital parts (Bilharz tumors), from which cancer often develops. The course of the disease is very protracted.
The main symptom of schistosomiasis or bilharzia is prolonged hematuria (the presence of blood in the urine), which is subsequently joined by local inflammatory phenomena, especially signs of severe cystitis.
Intestinal bilharzia
A parasite related to the one described above (Schistosomum Mansoni) enters the human body in the same way. However, it settles primarily in the intestinal veins and, due to accumulation in the intestinal wall, causes dysentery-like phenomena, which are expressed in inflammatory and polypous changes in the intestinal mucosa, especially the rectum (intestinal bilharzia).
Bilharz tumors of the rectum, anus and thigh can be a consequence of intestinal schistosomiasis.
Treatment
Tartarus stibiatus has a direct specific effect on worms and their eggs. Every other day, 0.05-0.1 one percent solution is poured into a vein. This treatment is continued for a month, then the pauses are increased. At the same time, local treatment of cystitis, etc. is carried out.
Eustrongylus gigas parasite
The parasite, found in some animals (dog, wolf, marten) and extremely rarely also in the human renal pelvis, is similar in size and color to an ordinary earthworm. It apparently causes severe pyelitis with bleeding, colic, etc.
Filariasis. Parasitic worm Filaria sanguinis Bancrofti (Bancrofti)
Human blood filament, a roundworm, acquired particular clinical interest after it was identified as the cause of tropical chyluria by the studies of Otto Heinrich Wucherer in Bagia (1868) and Lewis in the East Indies (1870). and some other similar diseases
- lymphatic swelling of the scrotum
- Elefantiasis Arabum
- chylous ascites, etc.).
The geographical distribution of the disease covers almost all tropical and subtropical regions. Most often it was observed in
- Africa
- Brazil
- Antilles
- throughout East Asia,
- in the southern ocean region of Australia, etc.,
- also in Spain and North America.
The adult threadworm (Filaria Bancrofti) is a worm about the thickness of a horsehair. It is very difficult to find in a person. Females have a length of 7 - 9, males 4 - 5 cm. Infection occurs through the bite of insects (such as Culex and Anopheles) that have sucked blood containing filariae.
When bitten by an infected insect, larvae (Ftilleborn) are transmitted to a person. They penetrate the epidermis and are carried into the body by the lymph current. After a long period of time, about a year, their development into a sexually mature filament ends.
These latter collect in the lymphatic vessels around the cisterna chyli, seminal tract and testicles, as well as in the lymphatic glands, mainly in the groin area. Here the females release young individuals, the so-called microfilariae, into the circulating blood, which are usually born alive.
These young larvae swim in the blood by the millions. However, they are found in skin vessels only at night (Microfilaria nocturna). Mosquitoes fly out at night and therefore can easily transfer the parasite from one person to another.
In the initial stages, the symptoms of filariasis are so mild that the accidental detection of microfilariae in the blood can be extremely puzzling to the doctor. Subsequently, fever, anemia and typical diseases of those areas of the body in the lymphatic vessels of which filariae are located occur.
The disease is accompanied by inflammation and expansion, and subsequently also thickening of the lymphatic vessels, chronic stagnation of lymph with all the ensuing consequences (chronic hyperplasia of connective tissue, elephantiasis).
Frequently observed in tropical countries, shapeless changes in the affected parts of the body, elephantiasis of one or both lower extremities, scrotum (see Fig. 3), labia, less often the hands, are a consequence of filariasis.
Fig. 3 Elephantiasis of the scrotum in filariasis
Mguya, Zanzibar
Worms in the kidneys
One of the most common parasitic diseases of the genitourinary system is kidney worms. Pathology occurs regardless of the patient's age and gender. The predominant route of infection is nutritional: penetrating the body with food or water, helminths feed for a long time on the nutrients present in it. The pathological phenomenon requires immediate medical intervention.
Complications
Diagnosis of parasites in the kidneys
Helminths are diagnosed using laboratory and instrumental methods. It is necessary to undergo urine and blood tests to detect parasites. To identify schistosome and echinococcus in the kidneys, serological tests, methods using a contrast agent, and the Katsoni reaction are carried out. Ultrasound examination (US), computed tomography (CT), and radiography are also prescribed. This allows you to determine the degree of damage to the organ, its structure, detect cysts and localization of worms.
What can worms in the kidneys lead to?
There are a number of complications that can result from worms inside the kidneys:
- Renal failure, pyelonephritis.
- Varicose veins.
- The disease causes inflammation of the epididymis, resulting in epididymitis.
- In women, inflammation of the vaginal mucosa occurs, which causes pain during sexual intercourse.
- Once in the stomach, helminthic masses cause vomiting, constant nausea, damaging the mucous membrane, they form erosions, as a result of which the organ suffers - gastritis occurs.
Helminthiasis in men can provoke prostatitis. Worms in the kidneys of a child can even cause irreversible processes and death.
Symptoms indicating the presence of parasites in the human body
Infections of the human body caused by the presence of parasites are more common than it seems at first glance. They can cause serious health complications in both adults and children. There are several types of infections depending on their size and whether the parasites are in the human blood or on the surface of the body.
Typical symptoms of parasitic infection in the human body
Microparasites (malaria) can exist in the human body, which can only be seen under a microscope.
The next group is macroparasites - round and flatworms (nematodes, tapeworms, etc.), which can often reach enormous sizes in the body of an infected person.
The presence of parasites in the body is not limited to the intestines; they often affect the lungs, liver, muscles, brain, blood, skin and even eyes.
Symptoms of the presence of parasites in the human body depend on the type of parasite itself and its toxic waste:
- chronic diarrhea caused by poor absorption of food;
- chronic constipation, flatulence and bloating (especially after eating) or any other digestive problems, including heartburn, abdominal pain and cramps, mucus or blood in the stool, intestinal problems, etc.;
- puffy eyes and dark circles;
- fever;
- pancreatitis;
- nausea, loss of energy, lethargy and depression;
- chills, weakness.
Parasites and skin
Symptoms of skin parasite infestation primarily include itching. Due to tissue inflammation, the number of white blood cells that protect the body increases.
This reaction often causes skin irritation. A person may even have a food allergy.
Parasites release toxins, and the skin, which is the largest organ, tries to get rid of them. As a result, various skin problems arise.
Signs of a parasite infestation include:
- dry skin and hair;
- hair loss;
- allergies and allergic reactions to food;
- itching in the nose, skin or anus;
- eczema, stomatitis;
- swelling;
- a feeling of “something crawling under the skin”;
- jaundice, etc.
Parasites and the nervous system
Toxins secreted by parasites can affect the central nervous system in humans. Uncertainty and nervousness are often caused precisely by the presence of unwanted organisms in our bodies.
Signs of parasites in the human body related to the central nervous system:
- rapid and frequent mood swings;
- anger and irritability;
- nervousness;
- depression;
- forgetfulness and disorganized thinking;
- anxiety;
- anxiety;
- slow reflexes;
- attention disorder.
Infection with parasites poisons the body. The body reacts to them even when it is resting, because it is at night that the manifestations of parasitic infections are most pronounced.
Infected people often wake up at night, especially between 2:00 and 3:00, as the liver tries to remove toxins from the body.
This causes the following signs of the presence of parasites in the human body:
- insomnia and sleep disorders;
- grinding teeth during sleep;
- night sweats and increased salivation.
Signs of the presence of parasites in the body are often not diagnosed for a long time; “pests” can live for a long time in the body of their owner undetected, consuming the basic nutrients they receive from food.
Parasites in the body often force a person to eat a lot. In this case, the infected person cannot gain weight.
Other symptoms of infection in the body
Parasites can travel in almost all soft tissues, including joints and muscles, where they form cysts and inflammation. These symptoms of parasites in the body are often mistakenly considered to be arthritis or muscle pain.
Parasite toxins also often accumulate in joints and muscles, causing muscle spasms and pain, pain in the joints, abdomen, chest, rheumatic pain, and rapid heartbeat. What signs appear depend on the affected system or organ.
Parasites are also often responsible for problems associated with the urinary and excretory systems. Their larvae, after inhalation, “wander” through the respiratory system, causing the following symptoms:
- acute bronchitis;
- asthma;
- pneumonia;
- cough;
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat;
- difficulty swallowing;
- bad breath and many others.
Symptoms of parasites in the human body can be quite atypical, and some types of helminths can be very difficult to identify. This is due, in particular, to complex diagnostics: it is often necessary to perform 3-6 stool samples to eliminate false results. However, in practice, just one negative conclusion is enough for the patient to refuse.
Of course, parasites are not hidden behind all diseases, but they often take part in the occurrence of some of them. For example, roundworms manifest themselves in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract as bloating and flatulence. Many of them can lead to intestinal blockage and constipation. Roundworm eggs can be ingested with unwashed vegetables.
Pinworms in the body often cause nausea and diarrhea; they easily penetrate the intestinal wall into the vascular system and can lead to:
- hemorrhoids;
- discharge in women;
- inflammation of the bladder;
- blockage of the bile ducts.
Parasitic infections are often at the root of health problems such as tissue damage (which makes weak areas easier to attack by viruses and bacteria).
Dizziness and parasites
In the case of the presence of parasites in the human body, symptoms and treatment are closely interrelated. This applies, for example, to vertigo (dizziness). Our ancestors already noticed a connection between flukes and dizziness. All trematodes (there are several types) reduce metabolism, clog bile ducts, worsen liver function, and increase cholesterol levels.
Even the largest human parasite, the broad tapeworm, is relatively common. Infection occurs more often in fishing areas. The source is freshwater fish – marinated or smoked.
Tapeworms in dogs and cats, although not common in humans, are no exception.
What can parasites lead to in the body?
They can provoke the development of a number of serious diseases; however, their role in the occurrence of such diseases is often not taken into account.
- Parkinson's disease can be caused by a combination of several major parasites: Trichomonas vaginalis, with blood that has penetrated to the brain, Treponema pallidum, often congenital, Nocardia asteroids, Echinococcus tapeworm, as well as other parasites.
- Parasite larvae migrate to the larynx and pharynx, easily accumulate on the thyroid gland, and cause an autoimmune process (which is typical for multiple sclerosis). Multiple sclerosis is caused by dysenteric amoeba (Entamoeba histolytica), echinococcus (Echinococcus multilocularis), borrelia, sometimes gonococci or meningococci, etc.
- The situation is similar with ankylosing spondylitis, the culprits of which are often echinococci and tapeworms that have penetrated the spinal canal and depress the peripheral nerves.
- Epilepsy and dizziness. The cause may be large parasites (tenia, tapeworm, tapeworm) either in the cerebellum or in the inner ear. A bacterial load is often present.
The cysts of some parasites have a multi-layered protective shell, which is why they are practically indestructible. A living larva can survive up to 30 years (Trichinella). Various lumps under the skin can form worms, trichinella, and echinococcus tapeworm.
How to remove parasites from the body?
To remove parasites from the human body, it is first of all important to cleanse the entire digestive system. A clean intestine with well-developed muscles is not a good place for intestinal parasites.
Step 1: Herbal remedies play an important role in colon cleansing. The most effective are the following:
- chamomile;
- tansy;
- yarrow;
- oak bark;
- immortelle;
- sagebrush;
- buckthorn bark.
A good method is to consume onions and garlic. Pumpkin seeds can also treat parasitic infections.
If you cannot overcome the problem on your own, you need to contact a specialist who will prescribe anthelmintic drugs.
Important! During treatment, all family members and animals living in the same house must undergo a therapeutic course to avoid re-infection.
Step 2: Increasing your fiber intake speeds up the time it takes for undigested food debris to travel, thereby avoiding sedimentation, which reduces the quality of the soil for parasite colonization.
Step 3: Prevent vitamin deficiencies. Adequate intake of vitamins, minerals and nutrients is essential to fight parasitic infection.
Step 4. Determine the source of infection and prevent infection:
- It is important to avoid contact with known sources of infection, such as rodent droppings, cat feces; contact with dogs is inadvisable;
- you must be careful when drinking water and/or swimming in water whose quality is unknown;
- to prevent bites from blood-sucking insects that can carry parasites, you need to wear protective clothing;
- Before eating, you should wash all fruits and vegetables in clean water - this will also help avoid infection;
- Water from potentially contaminated sources should not be used to water vegetables.
Children are especially susceptible to parasitic infestation; worms are often present in children's bodies in large quantities. Therefore, it is extremely important to teach them proper hygiene - washing their hands after using the toilet, playing outside and before eating.
Symptoms
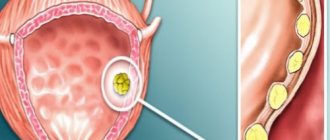
At the initial stage, symptoms of worms in the kidneys may not appear. Increasing in size, the hydatid cyst causes the following symptoms:
- urinary retention (due to bladder compression);
- lower back pain;
- pronounced impairment of functional activity - a sign indicating that the organ is damaged.
The listed symptoms are of concern when the enlarged cyst in which the parasite is located affects the nervous and vascular structures.
Filaria cause weakness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, hyperthermia and fever. The presence of schistosomes is manifested by general symptoms: pain localized in the lower abdomen, impaired urine output, and hematuria. The degree of presence of blood in the urine can vary from slight sediment to large clots, which are favorable conditions for the development of anemia.
Rehabilitation after illness
Since all anthelmintic drugs are quite powerful antibacterial agents, after their use it is necessary to undergo a course of restoring normal intestinal microflora. It is carried out using drugs from the group of probiotics, which can be purchased at any pharmacy even without a doctor’s prescription.
The most serious complication of echonococcosis is considered to be chronic renal failure, which develops due to the progressive growth of the cyst and damage to the renal parenchyma. Such a complication can be prevented only by promptly operating the patient.
In addition, with the same disease, arterial hypertension of renal origin can also develop. Poor in terms of prognosis is the fact that arterial hypertension often does not disappear after surgery.
The most dangerous complication of filariasis is blockage of lymphatic and venous vessels. In the first cases, elephantiasis or elephantism develops. The disease is manifested by swelling of the lower extremities due to stagnation of lymph. The legs, over time, increase in size several times, which gives the pathology its name - elephantiasis.
First of all, it is necessary to adhere to sanitary and hygienic standards. Heat treatment of food before consumption is extremely important. Especially when it comes to raw meat and fish, which very often become sources of helminth infection. Any vegetables and fruits must be washed under running water before consumption. Any dairy products, especially homemade ones, must be checked before consumption. If they do not pass official sanitary control, then it is better to consume them only after heat treatment. It is imperative to check the expiration date on store-bought dairy products.
In the prevention of filariasis, it is very important to combat the carriers of this disease - various types of mosquitoes. In countries with hot climates, special programs have been developed to exterminate such pests. Anyone planning to visit such countries should remember personal protective equipment against insects, as well as vaccination, which is carried out for such people for epidemiological reasons.
Collapse
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of helminthic infestations includes the following measures:
- A thorough medical history is taken to determine the likely causes of infection. Complaints such as pain in the right side from worms should always be voiced to a doctor.
- Laboratory tests of stool, blood, scraping of anal contents, urine analysis, vaginal secretions and discharge from the head of the penis. Eggs are identified during the analysis process. The specialist's attention is drawn to the increased concentration of eosinophils in the blood - this is also a harbinger of helminthiasis.
- The bladder is examined using ultrasound, CT and endoscopic examinations are performed: the listed methods allow us to understand how much the parasites have damaged the kidney parenchyma.
A biopsy of the cyst is also performed, based on the data from which the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed.
Diagnosis of kidney echinococcosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out with a non-parasitic kidney cyst, tumor, tuberculous lesion, abscess. the final diagnosis is established based on morphological examination data.
Diagnostic plan for suspected kidney echinococcosis:
• general urine analysis:
only if there is a communicating cyst or when it breaks into the pelvis, daughter blisters are visualized under microscopy. Microhematuria, proteinuria, and leukocyturia are often detected.
• general blood analysis.
In some cases, an increased number of eosinophils, accelerated ESR, and leukocytosis are diagnosed. With long-term hematuria, a decrease in hemoglobin levels is possible.
• urea, serum creatinine.
Their level is used to judge the preservation of the functional capacity of the kidneys.
• specific studies.
Tests for detecting antibodies to echinococcosis antigens do not allow confirming the diagnosis in all patients. In modern parasitology, RLA, RNGA, RIFA, etc. are used. The combination of various tests for echinococcosis increases the accuracy to 90%.
Instrumental diagnostics include:
• Ultrasound of the kidneys.
Sonograms show daughter cysts, hydatid sand, and membranes. When the position of the body in space changes, it is noticeable that some elements move, like falling snow.
• CT/MRI.
The results of CT/MRI are quite comparable in diagnostic value. Tomograms visualize a rounded neoplasm with a clearly demarcated double wall and daughter cysts along the inner edge of the mother cyst or throughout the entire cavity.
• Cystoscopic examination.
Cystoscopy is performed to evaluate the bladder. Hyperemia of the mucous membrane is not a pathognomonic sign, but when the contents of the kidney cyst rupture into the urinary tract, one can see the discharge of daughter vesicles from the ureter.
Considering that kidney echinococcosis is often combined with damage to other organs, the lungs, liver, spleen, brain, etc. are examined.
Treatment options
- In the acute phase of a parasitic infection, the patient is prescribed therapy for the purpose of detoxification and desensitization. In severe clinical cases, glucocorticoids are prescribed. Specific therapy involves the prescription of anthelmintics: specific drugs are prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the identified causative agent of the disease.
- Treatment involves taking antihistamines and enterosorbents, which is necessary to remove the larvae from the blood.
- The final stage of the therapeutic approach involves the use of probiotics - they stabilize the natural intestinal microflora.
The patient follows diet therapy - food should be easily digestible and contain little fat.
While undergoing anthelmintic therapy, it is important for the patient to maintain personal hygiene, since many people, neglecting this rule, cause re-infection. Conservative methods are effective only at the initial stage of the condition: if helminthiasis has caused a wide range of lesions, surgery will be required.
Even if the parasites are localized only in the kidneys, the body suffers comprehensively, so the patient’s primary task is to contact an infectious disease specialist and receive adequate treatment. There are many ways to remove worms from the kidneys, but each of them must be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the general condition of the person and the characteristics of his body.
Conservative treatment
For cystic echinococcus, albendazole and mebendazole are used. The dosage of drugs is calculated individually by the doctor and depends on the patient’s weight. The course of treatment is about a month and is repeated several times with a break of two weeks. Drug therapy can be combined with surgery. In recent years, praziquantel has been prescribed concomitantly with albendazole. Treatment with these drugs gives a positive result in approximately 50% of cases.
Surgical intervention for cystic echinococcus is now extremely rare. The reason is the high mortality rate among patients. On average, it is 2% during the initial operation, and during subsequent operations the figure increases. Complications and relapse are recorded with a frequency of 2 and 25%, respectively. After the development of treatment methods with tablet drugs and invasive intervention, they are trying to refuse operations.
Worms in human kidneys, symptoms and treatment with drugs
One of the most common parasitic diseases of the genitourinary system is kidney worms. Pathology occurs regardless of the patient's age and gender. The predominant route of infection is nutritional: penetrating the body with food or water, helminths feed for a long time on the nutrients present in it. The pathological phenomenon requires immediate medical intervention.
Treatment
How to get rid of parasites in the kidneys? To combat them, the doctor prescribes medications, mainly in the form of tablets. Such drugs may be: Vermox, Levamisole, Albendazole and their analogues. The principle of their action is that the smooth muscles of the parasite are paralyzed.
The course of treatment usually takes no more than 1 week. During this period, you should take medications that support the functioning of the renal system, as well as vitamins to maintain body tone.
Important! Six months after recovery, you need to take another 1 course of the drug for prevention!
What can worms in the kidneys lead to?
There are a number of complications that can result from worms inside the kidneys:
- Renal failure, pyelonephritis.
- Varicose veins.
- The disease causes inflammation of the epididymis, resulting in epididymitis.
- In women, inflammation of the vaginal mucosa occurs, which causes pain during sexual intercourse.
- Once in the stomach, helminthic masses cause vomiting, constant nausea, damaging the mucous membrane, they form erosions, as a result of which the organ suffers - gastritis occurs.
Helminthiasis in men can provoke prostatitis. Worms in the kidneys of a child can even cause irreversible processes and death.
Types of parasites
Three types of helminths can live in human kidneys .
Some cause moderate harm to health, others cause death.
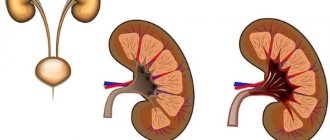
The most dangerous kidney parasite is Echinococcus. A person is an intermediate host for it, but the larva that has settled in the kidney has the most detrimental effect on health.
Fortunately, echinococcus affects people tens of times less often than roundworms or pinworms. In addition, it rarely settles in the kidneys, preferring the liver or lungs.
Echinococcus is a small tapeworm 3-5 cm . Its larva causes the disease echinococcosis, accompanied by the formation of parasitic cysts in organs and tissues.
When the kidney is damaged, the larva is carried into the organ with arterial blood, anchors in the cortex and forms a cyst. The left kidney is most often affected .
As a result of invasion, the organ is displaced, the calyces and pelvis expand, and the renal epithelium atrophies. A calcareous capsule with a diameter of several millimeters to tens of centimeters can form around the parasite.
Echinococcosis is contracted by ingesting parasite eggs. This happens through contact with domestic and farm animals, working with hides and wool, through food and water.
The cause of renal schistosomiasis is small parasites of the trematode schistosoma haematobium, which penetrate the kidneys when swimming in natural bodies of water. The disease is typical only for tropical climates. Urogenital schistosomiasis is especially common in Africa and the Middle East.
A classic sign of pathology is the presence of bloody discharge in the urine. If the disease is neglected, the kidneys, bladder and ureters will become covered with scars. At the last stage of the disease, a cancerous tumor of the bladder may appear.
In women with advanced schistosomiasis, the genitals are affected and bleeding from the vagina begins. In men, the prostate and testes are injured. Long-term schistosomiasis leads to complete destruction of the kidney and infertility.
The causative agent is the nematode Dioctophyme renale, which has a very large size. Female worms reach a meter in length. As a result of infection with dioctophimosis, the kidney may atrophy.
Damage to the body by parasites is a disease that can last a long period. Helminths can exist in the body for years due to the vitamins and microelements consumed by humans. Some worms, together with the blood flow, can conduct their life activities in any organ. Parasites often appear in the kidneys. The presence of worms in this organ is dangerous to health. After all, they quickly destroy kidney tissue, resulting in kidney failure.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, symptoms of worms in the kidneys may not appear. Increasing in size, the hydatid cyst causes the following symptoms:
- urinary retention (due to bladder compression);
- lower back pain;
- pronounced impairment of functional activity - a sign indicating that the organ is damaged.
The listed symptoms are of concern when the enlarged cyst in which the parasite is located affects the nervous and vascular structures.
Filaria cause weakness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, hyperthermia and fever. The presence of schistosomes is manifested by general symptoms: pain localized in the lower abdomen, impaired urine output, and hematuria. The degree of presence of blood in the urine can vary from slight sediment to large clots, which are favorable conditions for the development of anemia.
Kinds
Damage to the genitourinary system is a consequence of infection of the gastrointestinal tract and blood. After penetrating into the stomach and reproducing there, the larvae (eggs) of worms penetrate the blood and are transported through the vessels to the bladder, where they successfully continue to develop.
The following types of helminths can be found in urine:
- schistosome;
- filariasis;
- pinworms.
Schistosoma
After entering the sewer, worm eggs may end up in water with which a person comes into contact. It is in this way (through water) that infection occurs.
Schistosoma enters the body not only through the oral cavity, but also through the skin (in the presence of an open wound or even microtrauma).
The process of the worm entering the bladder causes symptoms:
- weakness;
- abdominal pain;
- malaise.
After this, there are no signs of damage for several months. Then the patient notes:
- urinary retention;
- pain when urinating;
- blood in the excreted urine.
Schistosoma causes diseases such as swelling of the urinary canals, kidney stones, inflammation of the kidneys, cystitis, pathologies of the genital organs and tumors of the affected organ.
Filariasis
Filariasis is quite dangerous because from the first stage it causes dangerous inflammatory processes. After the larvae penetrate the body, the patient's lymph nodes begin to swell, and the skin becomes covered with a rash. Then the vessels rupture, and urine is mixed with lymph. As a result:
- urine changes color to milky white;
- Fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
If treatment is not carried out, then it occurs that this can be seen in the photo:
Complications
This pathology is characterized by the accumulation of large amounts of fluid in the lower extremities.
Echinococcosis
Symptoms of worm infestation begin to appear after two to three weeks:
- weakness;
- general malaise;
- skin rashes and itching;
- pain in the urinary area;
- difficulty urinating;
- kidney pain.
Pinworms
The most common type of helminth found in humans is pinworms. These are small roundworms, no more than one centimeter in size. The cause of infection is neglect of the rules of individual and general hygiene.
The most common disease in humans associated with helminthic infestations is enterobiasis, caused by pinworms. Enterobiasis affects people of any age group, but most often these are children of preschool and primary school age. But adults are not insured either, especially if there is a child in the family.
How do you get pinworms?
Infection with enterobiasis occurs according to the following scheme: adult pinworms (females) undergo a fertilization procedure in the lumen of the cecum, after which they begin to move towards the rectum and anus in order to crawl out to lay eggs. Considering that pinworms are helminths that are active mainly at night, egg laying occurs precisely during this period. The standard place for laying is the skin of the inner surface of the thighs, buttocks, and perineum. The female lays eggs and dies. It can also be torn when a person scratches the itchy skin, which also leads to the release of eggs.
The source of infection is a person suffering from enterobiasis. The development and spread of this pathology is facilitated by violation of the rules of personal hygiene and household hygiene.
Symptoms
In approximately 60% of adults suffering from enterobiasis, this disease occurs without any characteristic symptoms. The most common symptom of this disease is a feeling of itching in the perineum and anus. Such itching occurs most often in the evening or at night, when female pinworms migrate.
The feeling of itching can cause sleep disturbances, resulting in a person developing fatigue, increased irritability, and general malaise.
In general, enterobiasis in adults and children is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe or partial loss of appetite;
- increased irritability, emotional instability, tearfulness;
- sudden loss of body weight;
- urinary disorders may occur (enuresis, painful urination);
- nausea, vomiting;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- pain, redness and bleeding of the skin in the anus;
- painful sensations in the abdominal area that do not have a clear localization.
The causative agents of this disease do not have the ability to penetrate the tissues of internal organs, so their migration throughout the human body is limited to the gastrointestinal tract. However, while in the female body, pinworms can enter the vaginal lumen and cause characteristic symptoms of vulvovaginitis (vaginal discharge and itching).
In rare cases, in women, pinworms can migrate into the lumen of the urethra and provoke the development of inflammation of the bladder (cystitis). According to one theory of the occurrence of inflammation of the appendix of the cecum (appendix), pinworms living there are to blame.
Signs
The most valuable symptom of this disease from a diagnostic point of view is itching in the anus, which is especially noticeable at night. Often a person can visually detect the presence of adult pathogens on bedding or underwear. And also in stool or on toilet paper when going to the toilet, especially during this itching. Outwardly, they look like light-colored small worms.
The presence of such signs is 100% a reason for diagnosing enterobiasis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this disease is not difficult and is quite simple. There are several simple procedures that allow you to determine with absolute accuracy the presence of helminthic infestations in the intestines. For children of preschool and primary school age, such tests are mandatory and must be carried out regularly. An adult needs to visit a doctor of his own free will.
Mandatory diagnosis of enterobiasis in adults should be carried out if a person works in a children's team (educator, teacher). The main methods for determining the presence of helminthic infestations include scraping for enterobiasis and a tape test.
Scraping can be carried out independently, in the morning, preferably immediately after waking up. To do this, you need to scrape the skin around the anus with a special cotton swab, after which the cotton swab should be placed in a special container and sent to the laboratory for research.
To obtain the most accurate results, this procedure must be carried out at intervals of 3-4 days.
Another method is the tape test, which has gained particular popularity in pediatric practice. In adults, this technique is used much less frequently.
Coprological examination (stool analysis) for enterobiasis is a low-informative method, because eggs are laid by adults on the surface of the skin, and they rarely enter the feces.
Treatment
To treat this disease in adults and children, special anthelmintic drugs are successfully used. The main treatment should be supplemented by a set of hygienic measures, the observance of which will avoid the re-entry of pathogens into the body.
If enterobiasis is detected in one person, not only he, but also all members of his family should be treated for this disease. For drug therapy of this disease, the following names of anthelmintic drugs are used:
- Mebendazole (Vermox). This drug is capable of influencing the nervous system of pathogens, resulting in their rapid death. As a rule, treatment with this drug involves taking it three times, with an interval of 3 weeks.
- Pyrantel pamoate/ebonate. This representative of anthelmintic drugs is not only the most popular, but also the safest of all drugs in this group. Its use is permissible even during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Albendazole (Vormil, Nemozol). It is a potent drug that is effective against any form of enterobiasis pathogen. Equally suitable for treating both adults and children. The dose should be selected by the attending physician depending on the age and weight of the patient.
In severe cases of the disease, as well as in cases of damage to the urinary tract, a combination treatment is used, which combines the drugs Ivermictin and Vermox.
Along with anthelmintic drugs, drugs are prescribed whose action is aimed at correcting the microflora of the large intestine (probiotics). Upon completion of the course of treatment, it is necessary to conduct a control examination of the scraping for enterobiasis. A three-time negative test result with an interval of 14 days proves a complete cure for the disease.
The list of necessary hygiene rules during the course of treatment includes:
- washing hands thoroughly after each visit to the toilet;
- regular cutting of fingernails;
- daily change of bed linen;
- Bed linen should be washed exclusively in hot water. After drying, the laundry must be ironed on both sides.
- in the room where a person suffering from enterobiasis lives, it is necessary to carry out daily wet cleaning;
- during treatment, a person should wear underwear with tight thigh bands, which will prevent the spread of pinworm larvae;
- Antihelminthic medications should be taken by all members of the family in which the sick person lives.
Complications
The most common complication of this disease is intestinal dysbiosis. This phenomenon is caused by the fact that adult pathogens are capable of causing a persistent disturbance in the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic microflora in the intestine through the release of metabolic products.
Late diagnosis of enterobiasis can lead to the entry of pathogen larvae into areas where the skin is scratched. This, in turn, provokes the appearance of foci of suppuration in the area of the buttocks, thighs and perineum.
In especially severe cases, massive helminthic infestations during enterobiasis can lead to the development of inflammation of the appendix and peritonitis, which occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the intestinal walls.
Consequences
Those waste products that are capable of being massively released by adult specimens of the enterobiasis pathogen can cause a sharp and persistent decrease in immunity, and also have a significant impact on the central nervous system.
Prevention
Large-scale prevention of this disease among the population is carried out by the relevant health authorities. For the purpose of personal prevention, it is enough for each person to follow the following rules:
- Hand washing should be done before each meal, after visiting the toilet and changing bed linen.
- Fingernails should be trimmed regularly.
- Underwear must be changed daily.
- Food products should not be left uncovered to prevent pinworm larvae from getting in with dust particles.
It is safe to say that enterobiasis is a fairly serious disease that at any age must be promptly diagnosed and treated according to existing therapeutic regimens.
- Schistosomes.
- Filaria sanguinis hominis.
- Pinworms.
Urogenital schistosome
The first symptoms of this disease are the presence of blood in the urine, first a few drops at the end of urination, later in any portion. This symptom appears approximately 4-6 months after infection, but there is no pain when urinating.
The waste products of the worm cause intoxication of the entire human body, and the lymphatic system can also be mechanically injured. The worm obstructs the passage of lymph, causing tissue expansion, which can lead to elephantiasis.
The development of the disease itself occurs in several stages:
- The appearance of an allergic reaction in the form of a rash on the skin, the lymph nodes enlarge and become painful.
- Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and their rupture, which leads to chyluria (when urine mixes with lymph, causing it to become gelatinous and milky white in color) and chylous ascites (accumulation of lymph in the abdominal cavity).
- Development of elephantiasis.
In case of infection, the following symptoms first appear: mild malaise, weakness, fatigue and other manifestations. Later, constant pain syndrome, renal colic, and sometimes skin itching may appear. It is the daughter blisters that break off from the cyst that can be detected during a urine test.
This small thread-shaped worm up to 1 cm long causes a human disease - enterobiasis. It lives in the small and large intestines, as well as in the cecum. They attach themselves to the mucous membrane using suction cups, which causes small hemorrhages and inflammation of the mucous membrane. All this is accompanied by abdominal pain similar to contractions, the appearance of mucus in the stool and a frequent urge to go to the toilet.
Female pinworms lay eggs on the folds of skin around the anus. If improperly washed, eggs can enter the genitals, causing inflammation of the genitourinary system. Pinworms can also penetrate the urinary tract, causing bedwetting.
Sometimes, especially in girls and women, female pinworms get into the urine, where they are found.
Roundworms are bisexual. Female 25-40 cm, male – 15-25. The body is spindle-shaped with pointed ends and whitish-yellow in color. One worm can lay up to 250 thousand eggs per day, which mature in the environment for up to forty-two days. Infection occurs through ingestion of mature eggs, from which larvae hatch. Moving with the bloodstream, the larvae spread throughout the body.
- acne;
- the appearance of seborrhea;
- early wrinkles may appear on the face of a person with intestinal infestations;
- the skin takes on a pale, unhealthy tint;
- nails break;
- hair splits and falls out intensively;
- Numerous papillomas appear on the body.
Similar manifestations on the epidermis occur when Trichomonas, Giardia or other protozoa (most often a combination of them) settle in the human gastrointestinal tract.
Enterobiasis (a form of helminthiasis caused by pinworms) is characterized by the following external symptoms:
- children experience slow growth;
- the earlobes of pinworm-infected babies are underdeveloped;
- fingers are shortened;
- the size of the ring finger may exceed the length of the middle finger;
- Also, children with enterobiasis have a narrow forehead, eyes are often different in size, and alopecia is often observed.
In addition to the fact that helminths that live in the small intestine and stomach of a person provoke the appearance of a number of external signs, their presence in the human body can also be indicated by various malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs.
Obviously, intestinal invasions primarily cause signs of disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, constipation, diarrhea, bloating and other signs).
The most typical symptoms are:
Almost all types of helminths move throughout the body of the “host”, choosing the best place where they can “settle”. Intestinal worms are no exception. Such migration of helminths in the human body is certainly accompanied by painful sensations in the muscles, bones and joints.
- eczematous;
- the disease provokes the development of atopic dermatitis;
- symptoms similar to urticaria occur;
- The patient is experiencing acne.
Destroyed helminth eggs are transformed into foci of inflammation that form on the walls of the rectum or colon. This phenomenon is called granuloma and requires treatment.
Another symptom that there are eggs, larvae of worms or their adults in the patient’s body is a sharp and significant change in his body weight. Weight loss is associated with digestive dysfunction, but an uncontrollable feeling of hunger appears when a person’s blood sugar level drops sharply (this is a kind of response of the body to the released toxins of helminths).
Toxins released by worms in the body of children and adults irritate the central nervous system, causing the patient symptoms such as increased nervousness and a feeling of constant anxiety.
Intestinal helminthiasis often manifests itself as chronic fatigue syndrome. Its symptoms include the following disorders:
- general weakness;
- periodic changes in body temperature;
- memory impairment;
- inability to concentrate one's attention on one object for a long time.
And, of course, the most obvious symptom that there are certain types of helminths in the human intestines is an immune malfunction in the body. This phenomenon is due to the fact that the active life of worms is accompanied by the release of a substance such as immunoglobulin A, which significantly weakens the natural protective reaction of the “host” body to bacteria, viruses, infections and other foreign organisms.
It is possible to remove worms by taking a certain medicine once, but there are cases when the treatment of intestinal helminthiasis lasts for several weeks, or even months.
What medications help fight against intestinal helminths? In the pharmacy you can find the following effective tablets:
- broad-spectrum drug Pyrantel (especially good for children);
- Vermox tablets;
- Kombantrin;
- drug "Dekaris";
- Vermox tablets;
- The drug "Nemozol" has a wide spectrum of action.
Treatment of intestinal forms of helminthiases caused by protozoa (for example, Giardia) is carried out using the following medications:
- The drug “Tinidazole” helps to cope well with infestations in children and adults;
- specialists also use Furazolidone tablets;
- The drug Metronidazole helps to quickly remove helminth eggs from the intestines of children;
- treatment of intestinal invasions is also carried out with Paromycin.
It is no secret that any pharmaceutical drug (tablets or capsules) has a toxic effect on the body of an infected person. That is why antihelminthic treatment is always accompanied by the presence of various side effects. The most common of them include:
- constipation or diarrhea;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- stomach ache;
- increased nervousness and other unpleasant symptoms.
A remedy such as baking soda will help you cope with the disease at home - it will successfully replace any toxic drug. The product is diluted in a small amount of water, and the finished product is used as an enema.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of helminthic infestations includes the following measures:
- A thorough medical history is taken to determine the likely causes of infection. Complaints such as pain in the right side from worms should always be voiced to a doctor.
- Laboratory tests of stool, blood, scraping of anal contents, urine analysis, vaginal secretions and discharge from the head of the penis. Eggs are identified during the analysis process. The specialist's attention is drawn to the increased concentration of eosinophils in the blood - this is also a harbinger of helminthiasis.
- The bladder is examined using ultrasound, CT and endoscopic examinations are performed: the listed methods allow us to understand how much the parasites have damaged the kidney parenchyma.
A biopsy of the cyst is also performed, based on the data from which the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed.
Diagnosis of the disease
To identify parasites in the kidneys, you should contact a specialist who will refer you for certain tests. There are several types of research for the presence of the disease:
- stool analysis. Does not always show reliable results and requires repeated research. But it is the simplest and most accessible;
- blood analysis. Allows you to identify parasite antigens;
- ultrasound examination of organs. When cystic formations appear, a biopsy is performed under ultrasound guidance;
- endoscopy;
- PCR method. The most reliable analysis identifies a foreign individual at the DNA level.
The most effective way to diagnose a disease may be to carry out several types of tests in a comprehensive manner.
Important! After completing the course of treatment, you should get tested again! This is necessary to ensure that the parasites are completely eliminated.
Treatment options
- In the acute phase of a parasitic infection, the patient is prescribed therapy for the purpose of detoxification and desensitization. In severe clinical cases, glucocorticoids are prescribed. Specific therapy involves the prescription of anthelmintics: specific drugs are prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the identified causative agent of the disease.
- Treatment involves taking antihistamines and enterosorbents, which is necessary to remove the larvae from the blood.
- The final stage of the therapeutic approach involves the use of probiotics - they stabilize the natural intestinal microflora.
The patient follows diet therapy - food should be easily digestible and contain little fat.
While undergoing anthelmintic therapy, it is important for the patient to maintain personal hygiene, since many people, neglecting this rule, cause re-infection. Conservative methods are effective only at the initial stage of the condition: if helminthiasis has caused a wide range of lesions, surgery will be required.
Even if the parasites are localized only in the kidneys, the body suffers comprehensively, so the patient’s primary task is to contact an infectious disease specialist and receive adequate treatment. There are many ways to remove worms from the kidneys, but each of them must be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the general condition of the person and the characteristics of his body.
Invasive treatment
Invasive treatment means laparoscopic surgery using drainage and partial cystopericystectomy. A preliminary course of albendazole significantly reduces the risk of relapse and simplifies the intervention process. Thanks to the medication, intracystic pressure is reduced, due to which previously punctures were refused, since there was a high risk of developing anaphylactic shock due to fluid leakage.
Now, thanks to the use of modern techniques and medications of the latest generations, it has been possible to reduce the incidence of anaphylactic shock to 0.1% (overall mortality 0.05%).
The puncture is performed under the cover of albendazole and under the guidance of ultrasound or CT. To carry it out, a needle or catheter is used. The choice depends on the size of the cystic formation. When performing an invasive procedure, an anesthesiologist must be present next to the surgeon and auxiliary medical personnel. First, the doctor removes a small amount of fluid. It is examined under a microscope for the presence of viable protoscolex. If they are detected, the cyst is completely removed.
From a diagnostic point of view, puncture is the only way to make a diagnosis, which has a 0% probability of error.
Types of worms in humans
Worms, or helminths, are parasitic worms that live off animals and plants, feed and reproduce inside living organisms. You and I are no exception.
– According to statistics, every third inhabitant of the Earth is infected with parasitic worms. It is assumed that there is not a single adult person during whose life not a single worm has settled in his body, says general practitioner, family doctor Aigul Kharisova , known online as @doctor_aygul.
In everyday life, people call almost all parasitic worms worms, without thinking about how many species of these unpleasant creatures there actually are.
Among all the parasitic worms that can exist in the human body, there are three main groups:
- nematodes related to roundworms: pinworm, whipworm, trichinella, roundworm;
- tapeworms, or flatworms related to cestodes (various types of tapeworms, tapeworms and echinococci);
- fluke parasites, or trematodes, causing opisthorchiasis, fascioliasis, schistosomiasis, paragonimiasis and other ailments.
Herbs and plants against worms for humans
There is not a single person who is not infected with worms or parasites. Most pathologies begin precisely because of parasitic infestations. Therefore, periodically all living creatures must be expelled from the body. Antihelminthic drugs are recommended to be taken 2 times a year. These medications have contraindications and side effects. It is safer and no less productive to get rid of parasites and worms with the help of medicinal plants. Herbs are available to everyone, and recipes have been tested for centuries.
Fund selection principle
Researchers have noticed that the death of parasites and worms occurs due to high temperature inside the human body and slight dehydration.
Microorganisms that are dangerous to people do not like bitterness, acidity, or pungency.
The ancient sages said: “If you want to live sweetly, eat bitter things. If you want to live bitterly, in illness, eat sweets.” By what principles are herbs selected to expel worms and parasites from the human body:
- Plants with a pungent taste increase the temperature inside the body.
- The pungent taste relieves itching, kills parasites, and provides an antiseptic effect.
- Burning foods open blood vessels, remove blockages, and remove mucous waste from worms.
- You can slightly dehydrate the body with the help of bitter plants. Bitterness removes toxins and destroys parasites; provides bactericidal, antipyretic, antifever effects.
- Most parasites do not like an acidic environment.
List of plants and herbs dangerous for worms
- Carnation. Thanks to its burning and pungent taste, it destroys worms. The aromatic spice improves the condition of the bloodstream and promotes the elimination of waste products of parasites.
- Wormwood and all its species. The most popular medicine in folk medicine for the treatment of helminthic and parasitic infestations. Used dried and fresh, in tinctures, decoctions, and for enemas.
- Black walnut. Effectively destroys dangerous microorganisms. It provokes a number of side effects, so it cannot be used for a long time.
- Red pepper. The burning taste increases body temperature, which parasites and worms do not like.
- Rosemary. Medicinal herb and spice for vegetable and meat dishes. Effective for the prevention of helminthiasis.
- Chamomile. The plant strengthens the immune system, helps cleanse the intestines, and neutralize the effects of helminth poisoning.
- Cumin (seeds). Used in the complex treatment of infection with tapeworms and nematodes.
- Angelica. Has an anthelmintic effect. Relieves the symptoms of infestations (muscle pain, abdominal pain).
- Calendula. Restores tissue damaged by worms.
- Cascara. Natural laxative. When the parasites are poisoned, it helps remove them from the body.
Treating worms with herbs
It is recommended to start therapy with nutritional therapy:
- For one or two weeks we eat only vegetarian food. Parasites also love meat and often enter the human body through meat products.
- The next stage is fasting. The goal is to deprive worms and parasites of their nutritional environment. On the first day you can drink water, herbal teas, and sour fruit juices (apple). Add garlic.
- The next day, take a tablespoon of castor oil in the morning. This will speed up bowel cleansing. During the day - mint tea, papaya juice, pumpkin seeds, fresh vegetables.
- Third day of fasting – juices. Carrots, cabbage, cucumbers, beets, etc. help cleanse the intestinal tract. You can eat fresh vegetables, pumpkin seeds, amaranth.
- Day four – we add decoctions of medicinal plants.
The existence of worms and parasites will make barberry, valerian, dandelion, ginseng, and myrrh even more unbearable.
Folk recipes
Antihelminthic therapy: practice of famous doctors
Russian threesome
Method of Doctor of Medical Sciences V. A. Ivanchenko.
3 herbs are used: tansy flowers, wormwood leaves, clove seeds. Together, these plants provide a powerful antiparasitic effect. In addition, these are the strongest antiseptics that cleanse the human body even of microparasites.
Daily values of herbs for cleaning:
- tansy – 3 g,
- wormwood – 1 g,
- clove powder – 1.5 g.
Secrets of application:
- To measure such small quantities of food, you will need an electronic kitchen scale.
- A single dose of each herb can be placed in a capsule. Take any pharmaceutical medicine in capsule form and remove the powder.
- It is better to take all ingredients at the same time.
The procedure for cleaning the human body from worms:
Day 1. Divide the daily dose of each herb into three times. Take half an hour before meals.
Day 2. Before breakfast and lunch, drink 1 g of tansy, 300 mg of wormwood and 0.5 g of fresh clove powder.
Day 3-7. We drink herbs in full dosage, divided into 3 doses.
Contraindications to the use of the method:
- stomach ulcer;
- erosive gastritis;
- pregnancy;
- menstruation;
- hypertension.
Threesome by Heldy Clark
She suggests using a concentrated tincture of unripe black walnut skins, wormwood leaves and clove powder. In this composition, the medicine destroys adults, larvae and eggs of pathogenic microorganisms in the human body.
Antiparasitic treatment:
Day 1. Drink 1 drop of walnut alcohol tincture, dissolved in half a glass of water (not hot!) on an empty stomach. A pinch of wormwood, crushed into powder. Take 1/5 tsp of clove powder. 3 r. in a day.
Day 2. 2 drops. nut tincture + ¼ teaspoon of wormwood. Cloves - ¼ tsp. three times a day.
Day 3. 3 drops. alcohol tincture of black walnut + 1/3 tsp. ground wormwood. Clove seeds - 1/3 tsp. three rubles in a day.
Day 4. 4 drops. tinctures + half a teaspoon of wormwood. Cloves - in the same dosage.
Day 5. 5 drops. tinctures + 0.75 tsp. wormwood + cloves (according to the same scheme).
Day 6. 2 tsp. Dissolve the tinctures in a glass of water. If a person’s weight is over 70 kg - 2.5 tsp. Wormwood – 1 tsp. Cloves in the same dosage.
Day 7-10. Walnut tincture and clove powder - in the same dosage. Gradually increase the dose of wormwood by 0.25 tsp.
Day 11-14. Tincture - the same dose. We bring the dosage of wormwood to half a tablespoon (can be divided into 2-3 doses if it is difficult to take at once). Clove powder – 1 tsp. once a week
Day 15-20. We drink walnuts and wormwood in the same dosages daily. And cloves - once a week.
In the future, take the maximum dose of plants once a week. And so throughout life. If the human body is heavily infected, then treatment must be repeated after 2 weeks.
Cleansing according to G. Malakhov: wormwood + fasting
Worms and parasites affect almost every person. Therefore, everyone needs to systematically take a decoction of wormwood orally and douche with it.
Recommendations by G. Malakhov:
- Roll the wormwood flower into a ball of bread. Eat before or after meals.
- Drink a cup of tea three times a day. 1 tsp dry wormwood, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes.
- The same infusion must be douched periodically, morning and evening.
- During fasting - fasting. 5-10 days 3-4 times a year. The timing is individual (listen to how you feel).
The bitter taste of wormwood stimulates and tones a person. This is not only an excellent remedy for parasitic infestations. It is also a cure for a lazy intestine, gallstone disease, kidney stones, poor circulation, obesity, and metabolic disorders.
Treatment of worms in humans
The treatment of worms in a person is carried out by a general practitioner if the patient is an adult, or by a pediatrician if the worms are in a child.
“You should never self-medicate in the case of worms: the drugs used in the treatment of helminth infections are quite difficult for the body,” notes Dr. Aigul Kharisova .
Typically, in the treatment of worms in humans, complex therapy is used, the purpose of which is not only to destroy the parasites, but also to eliminate the consequences of their vital activity. Therefore, it is unlikely that it will be possible to manage with anthelmintic drugs alone. In addition, it is often necessary to treat all family members, because people in a narrow circle easily infect each other.
Along with medications, vitamins and enzymes that improve digestion may be prescribed. For more effective treatment of worms, a person will have to follow a diet and limit carbohydrates: sweets, flour.
“If there are animals in the house, they definitely need to undergo anthelmintic therapy twice a year, otherwise all treatment efforts will be in vain,” says general practitioner Aigul Kharisova .
Honey and honey water for worms and parasites: beneficial properties and how to use
The beneficial properties of honey have been known since ancient times. People have used it for centuries to treat various diseases. The properties of honey and honey water to remove parasites and worms from the body are also known.
Beneficial features
For the full therapeutic effect, honey must be diluted with raw water. This drink is identical to blood plasma and has full medicinal properties. You need to take the drink in the morning on an empty stomach. Honey and honey water against parasites have the following beneficial properties:
- Normalizes intestinal function.
- Softens fecal stones.
- Cleanses the intestines.
- Introduces waste and toxins.
- It rids the body of worms and parasites, as they die in the honey solution.
- Has an antibacterial effect.
- Fights viruses.
- Treats fungal diseases.
- Restores the microflora of the stomach.
- Reduces cholesterol levels.
- Improves metabolism.
- Reduces appetite.
Honey also has many beneficial properties:
- Eliminates swelling by absorbing excess moisture.
- Contains a huge amount of vitamins and microelements.
- Compensates the balance of nutrients in case of malnutrition and non-compliance with the diet.
- Strengthens the immune system.
- Accelerates the removal of bile from the body.
- Liquefies stones in the gall bladder, pancreas and spleen.
- Improves intestinal motility.
- Tones the body.
- Calms the nervous system.
- Normalizes sleep.
- Has an antifungal effect.
- Promotes fat burning.
- Restores the skin.
- Slows down oxidation processes in tissues that contribute to aging (antioxidant effect).
- Cleanses body cells and blood vessel walls.
To achieve maximum effect, it is recommended to drink water in one gulp. This will help open the stomach and allow fluid to enter the duodenum.
Worms and parasites, settling in the human body, lay eggs and larvae. Also, as a result of the vital activity of helminths, rotting products remain. They are the source of bad breath. Drinking honey and honey water will help solve this problem.
When using this remedy to treat worms and parasites, many people wonder whether water helps expel them from the human body. Yes, it helps, but such a drink will not destroy the helminths themselves. It blocks their vital activity and further reproduction. It also cleanses organs affected by worms from their waste products. Doctors recommend drinking a 30 percent solution (a teaspoon of honey per glass of raw water) of honey water in the morning immediately after waking up and before going to bed.
Indications for use of honey water
People with the following diseases should pay attention to this method of treatment:
- Parasites in the intestines and other organs (giardia, protozoa, worms, pinworms, ascorides).
- Constipation and dysbiosis.
- Stones in the kidneys, pancreas and spleen.
- Fasting, diets, eating disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency and autoimmune conditions.
- Liver dysfunction, swelling.
- Lazy bowel syndrome.
- Excess weight and body fat.
- Bad breath.
- Increased gas formation in the stomach.
Contraindications to the use of honey and honey water
As with taking medications, the use of this drink has a number of restrictions:
- Allergic reactions to honey and bee products.
- Diabetes.
- Stomach ulcer and gastritis.
- Liver dysfunction.
- Heart diseases.
- Upper respiratory tract diseases: asthma, bronchitis.
- Stagnation of bile.
How to use honey water
To prepare the drink, you need to take natural honey. It is best to purchase it in special beekeeping stores, at fairs and from trusted beekeepers. When buying honey in a store, pay attention to the labels on the jars. The word R AW means "raw" or unpasteurized. Pasteurized honey (PURE) does not contain beneficial enzymes. The water temperature should be warm, about 30 degrees. You cannot pour hot water over honey, as this will reduce the amount of nutrients in the amber drink. You should drink the finished drink immediately after preparation.
To remove worms and parasites, it is recommended to use the following recipe:
- 1 tsp honey.
- 200 ml. cold raw water.
Dissolve honey completely in water. Drink in one gulp before meals. For additional benefits, add other ingredients to the drink.
Pay attention to such an ingredient as cinnamon.
Honey water with cinnamon
- Pour 1 teaspoon of cinnamon into a glass of hot water.
- Leave for half an hour.
- Add honey to the cooled cinnamon.
- Drink 2 times a day, ½ glass.
This drink not only helps remove parasites and worms, but also normalizes weight.
Honey water with ginger
- Ginger root, 7 cm in size, peel and grate.
- Pour 1 cup boiling water.
- Cool and add 1 teaspoon of honey.
- Squeeze the juice of half an orange and a lemon.
In combination with ginger, honey water acquires a tonic and healing effect.
Honey water with vinegar
- Take one teaspoon each of apple cider vinegar and lemon juice.
- Add 200 ml raw water.
- Add 1 teaspoon of honey.
Helminths will quickly leave the body after taking such a drink, since they cannot tolerate an acidic environment.
Honey water with garlic
- Dilute 1 teaspoon of honey with 1 glass of raw water.
- Squeeze 1 clove of garlic.
- Mix all ingredients.
This drink will remove parasites, rid the body of waste and toxins, and strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
Use during pregnancy
In addition to a large number of beneficial properties, you need to remember that honey is a strong allergen. Therefore, during pregnancy you need to drink honey water with caution. It is better to consult your doctor first.
Expectant mothers who have not previously had an allergy to this product can safely drink this healing drink.
Women who are breastfeeding should not drink amber drink in the first 2-3 months of the baby’s life. Next, the pediatrician should explain how to properly use honey water.
Children should not be given this drink until they are two years old.