Kidney dialysis (hemodialysis) – what is it?
This procedure consists of cleaning the human blood from harmful waste products of the body and stabilizing the water-electrolyte balance artificially.
Dialysis is not able to heal the kidneys or slow down inflammatory or regressive processes in the kidney tissues. Its goal is to maintain the functionality of all body systems until the moment when the patient’s excretory organs can again perform this task or until a transplant is performed. Very often, if there are a number of indications and/or if transplantation is not possible, the procedure must be carried out for life.
Dialysis is a general concept; based on the method of implementation, hemodialysis, peritoneal and intestinal dialysis are distinguished. However, the last two types are less effective and are used, as a rule, in the presence of contraindications to hemodialysis, or as a temporary measure.
It is not obvious, but the procedure requires psychological preparation. The question here is not so much how long people live on kidney dialysis, but how prepared a person is for this procedure and possible restrictions in everyday life after it (diet, medication).
What is hemodialysis?
Kidney dialysis is a procedure that helps cleanse the human body of harmful substances, waste, and toxins, that is, it performs the same role as the kidneys.
The procedure consists of injecting a person with a special solution to cleanse his body using a special apparatus. The solution is passed through semi-permeable membranes with pores; it is through these membranes that various unnecessary substances are removed from the blood. The specifics of the procedure and the membranes used depend on the type of dialysis.
Cleansing the body requires quite a lot of time - from several days to several weeks, but there are solutions that speed up this process. Depending on how damaged the kidneys are, people live on dialysis either for a short period or for the rest of their lives.
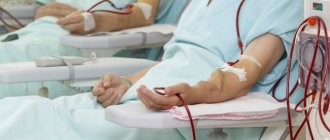
Hemodialysis is a completely artificial filter system, which is used to cleanse a person’s blood of toxins and remove excess fluid accumulated in it from the body. The procedure is carried out using a special blood filtering device.
Bilateral catheters extend from it. They are injected directly into the patient's vein.
The blood purification itself is carried out in a hemodialyzer. A specially prepared dialysate (chemical solution) is supplied to it through one outlet, and through the other, unpurified blood is passed through, which passes through a special double-sided membrane.
It is similar to a sieve or filter with tiny holes through which only substances with a molecular weight not exceeding a certain value can pass. The cleaning solution itself—the dialysate—is prepared from purified water and certain acids and salts in a given ratio.
The set of substances depends on the condition of each individual patient.
Blood purification becomes possible due to the difference in the density of the substances involved in dialysis (the blood itself and the dialysate), as a result of which the biological elements contained in it become equalized.
Excess fluid is removed from the patient's body through ultrafiltration or reverse osmosis, which is made possible by the difference in pressure on both sides of the membrane. That is why blood pressure readings before, during and after the procedure are of great importance.
The human urinary system is responsible for removing toxins from the body and filtering decay products. If for some reason the kidneys fail to fulfill their purpose, toxins accumulate in the body, leading to intoxication, which can be fatal.
Kidney dialysis is a replacement method for artificially cleansing the body. It frees the body from decay products formed during metabolic processes and cleanses the blood of harmful impurities. During the process of hemodialysis, colloidal substances are filtered, which do not dissolve, but only clog blood vessels and flows.
There are several ways to perform dialysis.
Kidney hemodialysis is an artificial filtering system through which the blood is purified.
It consists of several double-sided catheters (inserted into the patient’s vein) and connected to a hemodialyzer, through one outlet of which a special dialysate (chemical solution) is supplied, and through the other, blood is “distilled”, passing through a special double-sided semi-permeable membrane.
Due to the different densities of substances (blood and the dialysate itself), blood diffusion occurs, as a result of which the concentration of biological substances is equalized.
Dialysis - what is it? Manipulation involves filtering waste products from the bloodstream. If the kidneys do not perform their function, and toxic substances, collecting in the body, can lead to intoxication, then this is dangerously fatal.
This procedure is considered a replacement method for artificial cleansing of the human body. There are 2 types of dialysis:
- Hemodialysis.
- Peritoneal.
Each of them has its own contraindications, advantages and performance characteristics. Blood purification is performed using an “artificial kidney” device.
Hemodialysis
Indications for hemodialysis procedure
Hemodialysis sessions, as a necessary life-sustaining measure, are prescribed for acute and chronic renal failure to cleanse the kidneys of endotoxins, but can also be recommended for the following pathological conditions:
- glomerulonephritis;
- poisoning from products containing alcohol;
- the presence of plant or chemical poisons in the body;
- overhydration (excess fluid), which cannot be treated with medication and is life-threatening (pulmonary or cerebral edema);
- disturbance of water and electrolyte balance in the body;
- state of overdose as a result of violation of the medication regimen.
It is worth noting that the attending physician can only recommend hemodialysis; the decision is made by the patient himself, who must be provided with comprehensive information about possible side effects.
In what cases are there contraindications?
Hemodialysis is not performed for patients with cirrhosis, tuberculosis, bleeding, or pregnant women.
The procedure is performed only if there are indications for hemodialysis. Since the procedure is not very well tolerated by the body. It is important to know the absolute contraindications to its implementation. Patients with liver cirrhosis, tuberculosis, and bleeding are under no circumstances allowed to undergo dialysis. If the patient is pregnant and is diagnosed with acute renal failure, it is worth consulting with a doctor about the possibility of the procedure. If there are contraindications to the procedure, the doctor will tell you what to do and what alternative is available in order to live through this difficult period without complications.
How long do they live with this procedure?
Not so long ago, a diagnosis of chronic renal failure left no chance of survival. The hemodialysis procedure, prescribed for life, helps support the body of such patients. For how long? But here everything is not so simple.
Every patient asks the question, how long do they live on hemodialysis according to modern statistics? The term often stated is 15 years. The psychological attitude of the patient is very important here - you need to show a little will, without this the process of adaptation to the procedure may take a long time, someone may need the help of loved ones - and this is also not forbidden.
We should also not forget that quite recently we could only talk about 3 or 7 years of life, however, equipment is being improved, the procedure itself is becoming more streamlined, and during his life on hemodialysis, the patient may have the opportunity to undergo a transplant - after that the need in dialysis it will simply disappear.
Do not forget that medicine does not stand still and can provide patients with medications that compensate for some “weakness” of the body after the dialysis procedure.
So there is no need to despair and remember that earlier (and even more so now) there were known cases when people lived on this procedure for decades.
Life-altering complications of dialysis
The human body is not always able to adequately respond to this not entirely natural procedure. It is important to distinguish between unwanted symptoms associated with adaptation to dialysis and systemic problems.
The first is a temporary phenomenon, they may require only symptomatic correction, and, as a rule, fade away as one gets used to the procedure.
More serious side effects of the sessions include:
- pressure surges and heart rhythm disturbances;
- anemia;
- epileptic seizures;
- diseases associated with the spread of microbial flora in the body - sepsis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis;
- large-scale disturbance of water and electrolyte balance.
In these cases, the following measures will help:
- constant monitoring and correction of a number of indicators;
- adequate drug therapy;
- following a diet and taking vitamins.
Also, the cause of complications may be conducting sessions in the presence of contraindications:
- mental disorders or susceptibility to them;
- tuberculosis;
- oncological diseases accompanied by metastases;
- arterial hypertension and pre-stroke condition;
- a number of blood diseases (anemia with impaired formation of red blood cells, cancer, clotting abnormalities);
- diabetes.
At the same time, if the likelihood of death is high, the procedure can be performed even if there are contraindications.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to exclude interference in the procedure by human and technical factors. As a result, the following undesirable effects may occur:
- equipment malfunctions;
- incorrectly selected dialysate composition;
- entry of air particles into the bloodstream;
- obstruction of the hardware catheter;
- introduction of infection into the blood during the process of dialysis or preparation for it.
At the same time, if the rules of equipment operation are observed and the personnel are properly qualified, the likelihood of such cases is very low.
Possible complications
After dialysis, side effects may occur, which are expressed in a sharp decrease in the level of red blood cells in the blood, the development of anemia and a drop in blood pressure. In some cases, dialysis causes nausea and vomiting, and may cause seizures. Patients with heart disease may experience neurological problems, dizziness, and weakness. They may develop a disease called pericarditis, an inflammation of the heart sac. Dialysis is carried out in a hospital setting, in intensive care wards, so the occurrence of side effects or unexpected complications is under the control of specialists who will be able to notice the pathology in time and take appropriate measures to eliminate it. It must be remembered that the occurrence of side effects after hemodialysis significantly reduces life expectancy. Such a response from the body may also indicate possible rejection of the donor organ that was transplanted into the patient.
Factors that help prolong life
Undoubtedly, the severity of the underlying disease and the general condition of the body play a big role. But the following points can also affect life expectancy:
- In order to start using this technique, you should not wait for complete kidney failure. If there are indications, it is better not to delay the procedures.
- You should adhere to the session regimen prescribed by your doctor.
- You need to be careful about the choice of medications used and, if possible, the clinic in which the sessions are held.
- You should not remain silent about eating disorders or emerging ailments - this information may be important for correcting the procedure regimen.
- You will need to make changes to your daily diet - food should be rich in proteins and contain a limited amount of salt, some spices and water. It is advisable to avoid canned food, smoked meats and foods rich in potassium. Diet is a necessary condition, especially relevant during lifelong dialysis.
Cost of hemodialysis
The procedure is considered relatively expensive. Those wishing to undergo chronic hemodialysis should be aware that the cost varies in different clinics and countries. The total amount is made up of several factors:
- patient's severity;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- level of respectability of the medical institution.
In private clinics, the expense item includes:
- care services provided by staff;
- payment for the ward;
- additional expenses.
The amount indicated in the price list is paid in a lump sum upon admission to the medical center at the time of conclusion of the contract. It must match the one named by the doctor providing the consultation.
| Country where hemodialysis is performed | Total cost of the procedure and stay in the clinic |
| Russia | Moscow – 97,650 rubles; St. Petersburg – from 14,500 rubles; Rostov-on-Don – from 13,000 rubles. |
| Israel | “Assuta”, “Hadassah” - from 300 dollars. |
| Germany | – from 200 euros. |
| USA | New York - 250-300 dollars. |
But situations often arise when the procedure can be performed free of charge. Only in this case we are not talking about treatment abroad or private clinics. Patients in critical condition undergo urgent hemodiafiltration.
How long do they live on hemodialysis after kidney rejection?
Kidney rejection after transplantation leads to the development of renal failure, characterized by small amounts of urine output and a low glomerular filtration rate.
Pathology is an absolute indication for hemodialysis. In case of kidney dysfunction, patients are prescribed a lifelong course of hardware treatment. How long they live on kidney dialysis is of concern to every patient.
This method of blood purification is relatively new and has been used in practice for about 40 years.
Decades ago, people with kidney failure died early.
Kidney dialysis has become a salvation for patients with kidney rejection or poor organ function: no specialist can say for sure how long they live using this treatment method.
Today, the need for artificial blood purification is not a death sentence, but only a necessary measure that allows one to prolong the life of patients.
The lifespan of artificial blood purification depends on the professionalism of doctors, the availability of the necessary equipment and the attitude of the patient himself to his health.
According to statistics, the average life expectancy of dialysis patients after kidney failure is 15 years. If neglected, it can be reduced by half. With kidney dysfunction, a person's immune system is greatly weakened, and any concomitant disease can be fatal.
Most people suffering from kidney failure do not die from this pathology, but from complications caused by other diseases.
In addition, the blood purification procedure itself poses some danger, since it is not suitable for everyone. If the first dialysis was successful, then the person is guaranteed to increase the likelihood of extending his life by 6-10 years.
Quality of life and prognosis
If you have doubts about the benefits of hemodialysis, it is worth considering how long people live agreeing to an unpleasant procedure. According to statistics, extracorporeal blood purification increases life expectancy by 15-20 years. Important conditions: sessions cannot be postponed until the next day or skipped; It is forbidden to stop taking prescribed medications on your own and break your diet.
If you do not transplant the affected organ, but regularly use the “artificial kidney” device, you can live another 20 years, but then you will have to “sit” on the procedure for life. In this case, the patient dies not from kidney failure, but from inflammatory or infectious diseases and their consequences. This is due to a severe weakening of the immune system, against the background of which any pathogen can cause irreparable harm to health and life.
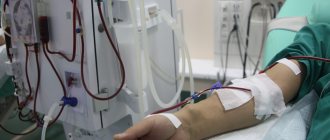
Artificial kidney filter
The hemodialysis procedure is carried out using special equipment that performs the functions of the kidneys outside the human body. To do this, access is provided to the artery and vein, into which special systems are inserted that are connected to the dialyzer. It purifies the blood. The movement of blood is carried out using a perfusion device and is displayed on the monitor.
Necessary substances enter the blood from the hemodialyzer. To prevent the formation of blood clots, coagulants are introduced into the system. The processed dialysate solution is excreted, and the purified blood enters the bloodstream.
The duration of the procedure can vary from 4 to 12 hours, and the number of times it is performed is prescribed individually depending on the patient’s condition: 3 times a week or 1 time a day.
The question of how much hemodialysis costs can be answered unequivocally: not cheap. The average cost of one procedure is about 3,500 rubles.
What equipment is used for hemodialysis?
Kidney hemodialysis is performed using a medical device “artificial kidney”, which allows you to cleanse the blood of urea, potassium, phosphorus, sodium and improve the patient’s physiological condition several times.
An innovative blood purification apparatus consists of the following elements:
- a device through which blood is collected and moved in the direction of purification;
- a dialyzer designed to filter blood;
— valve for supplying cleaning solution;
— monitor.
Passing through the device, the blood restores its normal salt and acid-base composition.
Causes
The reasons why patients are doomed to live on hemodialysis are health problems associated with kidney dysfunction. Indications for the procedure:
- Acute or chronic renal failure (ARI and CRF). The goal of dialysis is to perform the functions of the kidneys without involving them in the process.
- Diabetic nephropathy is a disease that is a complication of diabetes mellitus, which results in hardening of the kidney filters due to elevated blood sugar levels. The procedure is contraindicated for diabetics who have reached the age of seventy.
- Poisoning of the body caused by methyl alcohol, poisons or drugs. Acute intoxication leads to damage to kidney tissue and the development of renal failure. The purpose of the procedure is to detoxify the body and remove toxins from the kidneys.
- Overhydration is a condition in which the amount of fluid in the body is several times higher than normal. If it occurs, there is a risk of pulmonary and cerebral edema. The procedure is aimed at removing excess fluid from the body and eliminating swelling.
- Electrolyte imbalance. It occurs as a result of dehydration of the body with frequent vomiting and diarrhea. Dialysis is carried out to eliminate the disorder.
Devices for conducting and principle of operation
Plate type dialyzer
The apparatus system includes plates through which the acid concentrate passes. The plate connections consist of cylindrical channels and a special fluid flows through them. The upper part of the formation is covered with a membrane through which blood flows. The device has a complex structure and operation, but has a lot of positive aspects, including the ability to control the intensity of filtration and a reduced risk of blood clots.
Capillary dialyzers
Capillary dialyzers for hemodialysis are among the most convenient and safe.
The membrane of the device is made of biologically inactive substances, so the device is considered one of the safest and most effective in treatment. Hemodialysis sets are made of tubes arranged in parallel and ensuring blood circulation and filtration. The likelihood of infection with this cleaning method is minimal. This type of hemodialysis unit cleans the blood faster, which is why it is more popular.
In cases where it is impossible to perform hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis is prescribed.
Contraindications
Kidney hemodialysis is a rather complex procedure, the implementation of which has a number of contraindications. Their list includes:
- infectious process in the body;
- mental disorders;
- epilepsy;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- cancerous tumors;
- heart failure;
- severe form of arterial hypertension;
- blood clotting disorder;
- poor vascular condition;
- the first days after myocardial infarction.
Hemodialysis is stressful for the body, so when it is carried out, constant monitoring of the patient's condition is necessary. The dialysis machine must be selected taking into account the patient’s vital signs, because in case of kidney failure, dialysis will have to be carried out for a long time.
Side effects
The majority of patients endure dialysis painfully, feeling unwell during and after the session. Life expectancy depends on the degree of adverse effects from the procedure.
Adverse reactions of dialysis are as follows:
- decreased levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells (anemia);
- a sharp drop or increase in blood pressure;
- asthenic syndrome - weakness, drowsiness, apathy, headache;
- leg cramps;
- itching of the whole body during dialysis;
- nausea with vomiting;
- heart rhythm failure;
- osteoporosis - “softening” of bones due to lack of calcium;
- During dialysis, there is a high risk of air embolism, since the blood circulation rate through the system is 150–250 ml/minute.
Filtering the blood from unnecessary substances through dialysis is stressful for the body. Therefore, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems are possible. The risk of their formation is small, but it is not always possible to completely avoid it. The following side effects are observed:
- pressure changes in blood capillaries,
- numbness of the limbs,
- inflammatory process in the lining of the heart muscle,
- anemia,
- changes in hearing, vision,
- pain in the back, chest,
- damage to bone tissue,
- nausea, vomiting,
- slowing, increased heart rate.
There have been cases when patients during dialysis experienced an allergic reaction to a constituent substance of the dialysate solution. Neurological signs or mental disorders can develop with prolonged use of the procedure. The patient begins to feel oppressed by constant manipulation and attachment to equipment. There is an imbalance of substances that occurs after frequent diffuse transfusions.
Diet for hemodialysis
Life on dialysis becomes more difficult. When switching to it, you must follow a special diet and completely abandon bad habits.
Such patients should exclude fried, spicy, salty foods, smoked foods, marinades, flour products and coffee from their diet. It is recommended to limit the consumption of legumes, milk, cheeses and nuts.
The main emphasis in nutrition should be on fresh vegetables and fruits. It is allowed to include boiled eggs, chicken, lean beef and rabbit meat in the menu.
The hemodialysis diet must include calcium. It is even recommended to add synthetic preparations rich in this element to food.
The fact is that long-term hardware treatment often leads to the development of osteoporosis, characterized by a decrease in bone density.
How long do they live after kidney dialysis? This question is of interest to all patients who are faced with organ pathology. Indeed, this procedure is vitally important, and if it is not carried out on time, it can be fatal. Those who are prescribed hemodialysis are well aware that at a certain time they must report to the hospital without delay. Kidneys play an important role in the human body. They cleanse the blood of toxins, excess salts, organic compounds, remove fluid, and ensure the synthesis of substances that control blood pressure. We can safely say that the kidneys are a powerful filter through which 1,700 liters of blood are purified per day.
Preventive actions
Patients with risk factors for the development of progressive chronic kidney disease must be tested to detect proteinuria, hematuria, and leukocyturia. For some categories, testing for microalbuminuria is indicated at intervals of 1-3 years. Patients with the following parameters should undergo observation and regular examinations:
- age (over 60 years);
- cardiovascular pathology, including arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- kidney disease in close relatives;
- history of urinary tract infections;
- taking drugs that have nephrotoxicity.
The minimum scope of examinations includes the Zimnitsky test, bacteriological examination, detection of daily protein loss, ultrasound examination, excretory urography.
The goals of preventive medical examinations for early detection of disease or risk factors in patients with renal pathology are:
- monitoring the functional capacity of the kidneys for timely referral to dialysis centers;
- maintaining remission with the use of prophylactic agents;
- detection of the disease in the active stage;
- observation and rehabilitation measures.
Continuous improvements in replacement therapy methods have increased the life expectancy of patients with lost kidney function by decades. The most significant causes of mortality are complications associated with the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Meanwhile, the state of the patient’s mental health is also considered an important factor. There are no guarantees for recovery and there is no exact period of how long a particular patient with impaired renal function will live, but in addition to other concomitant pathologies, a person’s state of mind plays an important role. In this regard, psychotropic drugs and non-drug methods for treating depression and anxiety are used in therapy as indicated. Accurate adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician and a positive attitude in people undergoing therapy directly affects how long patients on hemodialysis live.
You can share your experience of undergoing replacement therapy in the comments. Take care of yourself and your loved ones!
How long do they live after kidney dialysis? This question is of interest to all patients who are faced with organ pathology. Indeed, this procedure is vitally important, and if it is not carried out on time, it can be fatal. Those who are prescribed hemodialysis are well aware that at a certain time they must report to the hospital without delay. Kidneys play an important role in the human body. They cleanse the blood of toxins, excess salts, organic compounds, remove fluid, and ensure the synthesis of substances that control blood pressure. We can safely say that the kidneys are a powerful filter through which 1,700 liters of blood are purified per day.
brief information
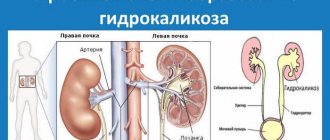
The kidneys function in unison: they filter the same amount of fluid every day. If atrophy of one of them occurs, then the second copes with the necessary function alone. People with one kidney can live their entire lives, but the load on the organ increases significantly. Therefore, patients with one kidney are given the necessary recommendations to maintain their health. It happens that both kidneys stop working due to serious pathologies. In such cases, a procedure called dialysis becomes a salvation.
People who have various kidney diseases need to avoid bad habits, abuse of salt, spicy and smoked foods. Also, with some pathologies of the organ, renal failure can develop, so patients require constant monitoring.
If a person is indicated for kidney hemodialysis, then first of all it is necessary to carry out psychological work so that the patient is in the right mood for the procedure and understands the importance of its implementation.
Transplantation as an alternative to dialysis
In various countries, annually 60-100 patients per 1 million population require renal replacement therapy (RRT) due to the development of end-stage chronic failure of the filtering organ. Until recently, this sounded like a death sentence. Today medicine offers three main methods of maintaining the lives of people with this diagnosis.
It is important to know! Despite constantly improving medical technology, chronic hemodialysis has many negative side effects and circumstances that worsen the patient’s well-being. Therefore, it can be considered as an intermediate therapy.
Patients with a transplanted organ (if rejection does not occur) can live as before, and their quality of life is much higher. Despite the fact that from an economic point of view this method is considered unprofitable due to its high cost, it is an option of choice for end-stage chronic renal failure.
Description of the hemodialysis procedure
Hemodialysis began to be practiced almost 40 years ago. The procedure has proven itself well, so it has been improved over time. This allows us to save and prolong the lives of young people. Dialysis is prescribed if the kidneys lose their filtering function. This cleaning method effectively filters the blood, releasing metabolic products from it and safely removing them from the body. Dialysis exists in two types:
Each method has its own advantages, contraindications and implementation features. To understand what hemodialysis is and the content of this procedure, it is necessary to recall kidney function. Essentially, its goal is to purify the blood through a device called an “artificial kidney.” Through an artery or vein, the blood enters special equipment containing filters. Thanks to these devices and a sterile solution, the blood is completely cleansed of toxins and poisons, after which it is returned to the patient’s body.
In this procedure, the person is seated in a special chair and connected to a machine, after which the blood is filtered for several hours.
Hemodialysis is required to be carried out 2-3 times a week, taking into account the patient’s age, height, weight, and the presence of underlying diseases. Sometimes they are limited to one procedure.
But most often it is carried out until a kidney transplant is performed.
During hemodialysis, nothing changes in the protein composition of the plasma. This filtration method is indicated for those patients whose arteries and veins are easily accessible. Thanks to the hemodialysis procedure, the following goals can be achieved:
- get rid of uremic toxins and colloidal substances;
- stabilize the electrolyte composition;
- normalize blood pressure by removing fluid.
Many patients believe that they can avoid this procedure by following a strict diet, but by doing so they miss the opportunity to preserve partial kidney function. It is necessary to begin the hemodialysis procedure as soon as doctors report its need. Refusal of medical help can lead to complete loss of the kidney. Timely hemodialysis will prolong life for a significant period.
Types of procedure
Hemodialysis is divided into several types depending on whether the procedure is carried out in a hospital or at home, as well as on the functionality of the device.
Also distinguished:
- hemodialysis;
- peritoneal dialysis.
In the first case, an artificial membrane is used to filter the blood, and in the second, the peritoneum is used.
Depending on the location of the procedure, hemodialysis is distinguished:
- at home;
- outpatient;
- during inpatient treatment.
Hemodialysis at home involves the purchase of a special device by a person.
Outpatient procedures are performed in the hospital on a first-come, first-served basis three times a week, but the equipment is more specialized. The duration of the procedure is 4 hours.
Kidney dialysis is a rather complex process that requires medical equipment and special solutions. The procedure involves purifying liquids from foreign impurities using a semi-permeable membrane. There are two types of dialysis, each of them has its own specifics and frequency.
| Kinds | How is it carried out? | Advantage |
| Hemodialysis | 3-4 times a week | Possibility to carry out the procedure at home |
| Short duration of the filtration process | ||
| Peritoneal | Every 6 hours | No risk of bleeding |
| No strain on the heart |
Depending on the characteristics of the procedure and the devices used, there are different types of dialysis.
Hemodialysis is a procedure performed using a machine called an “artificial kidney.” The principle of its operation is as follows:
- Blood that requires purification passes through a filter into a container (dialyzer) with a special solution.
- The dialyzer purifies the blood.
- Purified blood goes back into the body.
Hemodialysis is reserved for patients whose veins and arteries are clearly visible, and is performed under the supervision of a doctor who monitors that the machine does not remove too much fluid from the body. This procedure is carried out for 3-4 hours 3 times a week. Under no circumstances should you miss a session even once.
At the moment, modern medicine has multiple capabilities that make it possible to treat all kinds of renal pathologies.
Unfortunately, not in all cases medicine can create conditions that provide the patient with the opportunity to live as long as he wishes, without resorting to additional procedures.
If the kidneys are unable to perform their natural functions, not only does the person’s health deteriorate, but also a serious danger arises in which even a doctor will not be able to answer in the affirmative how many people live with such a pathology.
Kidney dialysis is performed using a special machine called an “artificial kidney” in the medical industry. It is this device that is designed to drive away all the blood, cleansing it.
Dialysis can also be carried out in another way, when the patient’s abdominal cavity acts as a cleansing membrane.
The first method using an “artificial kidney” is called hemodialysis. Using special tubes, the patient’s blood is pumped into the apparatus, where it undergoes systemic purification, and then re-enters the human body.
How long such a procedure lasts depends on several factors, but there is no doubt that a sufficient amount of time will have to be spent on such a procedure.
Peritoneal dialysis is aimed at injecting a special solution into the patient’s abdominal cavity aimed at purifying the blood. This method is as safe as possible, since after a few hours (the doctor decides exactly how long), the injected solution is naturally eliminated from the body.
Unfortunately, it is simply impossible to completely clean the blood in one session, so patients have to undergo such forced cleansing as many times as the doctor indicates. In particular, this number reaches three times if hemodialysis is performed.
If the patient is prescribed kidney dialysis, then the number of sessions increases, by how much also depends on several factors.
The patient should also take into account that neither hemodialysis nor kidney dialysis can eliminate the underlying pathology; they are only focused on maintaining the functioning of the kidneys, which allows patients to live, despite the existing serious pathologies.
What is the difference between peritoneal dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis is also aimed at filtering blood, but the procedure itself differs in the way it is carried out. Cleansing is carried out using a special solution, which is injected into the abdominal cavity through a catheter for several hours. Almost 2 liters of dialysate is poured into the peritoneum, the membrane of which serves as a natural filter. Toxins, wastes, and breakdown products enter the dialysis solution over a period of 4–12 hours. After the “holding time”, all the fluid from the peritoneum is drained along with the “waste”. The procedure is called drainage and takes about 30 minutes. And after that, the sterile solution is poured again, and the process is repeated.
What is it and why is it done?
Hemodialysis is a set of actions performed to purify the blood. The manipulation is carried out using a special apparatus. In common parlance it is called an “artificial kidney.” It is a selective permeable membrane through which the patient's blood is passed. The design of the device may change, but the general principle of operation is always the same - with the help of an artificial kidney, harmful substances are removed from the blood. The following are excreted from the human body:
- excess water,
- urea and alcohol,
- excess electrolytes,
- medications,
- toxic substances,
- creatinine
The procedure can be prescribed for kidney failure and a number of other problems.
How long can you live with dialysis?
Since this procedure is indicated for serious diseases, which in themselves already pose a danger to human existence, the question logically arises of how many years people can live with kidney dialysis. No doctor can answer this question with certainty.
Much is determined by the stage of the disease, the patient’s age, general health, and the presence of other pathologies.
A lot depends on the behavior of the patient himself, on his mood and desire to follow all the doctors’ recommendations. Dialysis is indicated for the following ailments:
- acute or chronic renal failure;
- diabetes mellitus;
- acute poisoning with toxins;
- electrolyte imbalance;
- drug overdose;
- overhydration (when standard treatment is ineffective).
These conditions themselves are complex and can be fatal, so dialysis cannot be delayed. And life expectancy directly depends on whether the patient adheres to a diet, carries out the procedure regularly, and whether he behaves correctly after hemodialysis. In the last century, some people lived more than 25 years. Over half a century, medicine has stepped forward, but for most people this method may be inaccessible due to the high cost of the procedure. Previously, those on hemodialysis died more often due to the fact that the body “without kidneys” was greatly weakened.
Even a common cold could lead to death, but more often patients suffered from intestinal problems or pneumonia. Now doctors provide patients with everything they need to prolong life. The case of a woman who was on hemodialysis for more than 30 years is included in the Russian Guinness Book of Records.
Although there are no exact statistics, the average life expectancy of people on dialysis is 14–20 years.
If a transplant is performed after dialysis, a person can live for about 55 years. How long a patient will live with kidney dialysis also depends on the quality of the drugs that have to be taken.
It is no secret that medicines may be counterfeit and of poor quality, equipment may be cheap, and specialists may be unqualified. All this can lead to a shortened life span due to complications or errors by medical staff. Therefore, it is worth choosing a dialysis center with good reviews and reputation.
Where is hemodialysis performed?
Hemodialysis (indications for it were described above) is carried out in urological clinics. Options using foreign experience are possible, but for chronic diagnoses this option is unprofitable both in terms of cost and in terms of permanent stay abroad.
Entire departments have been set up to carry out this serious medical procedure. Since it requires expensive equipment, which is often not enough to serve a large flow of patients with kidney problems, hemodialysis has to be done on a first-come, first-served basis. Due to the additional physical inconvenience, many patients refuse to continue treatment.
Only patients who are above average can afford hemodialysis at home.
How to prolong life after dialysis
To reduce the burden on the body, doctors usually prescribe a strict diet for patients. Protein products are introduced into the diet and those containing a lot of potassium and phosphorus are excluded. During dialysis, it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of potassium in the blood, as its excess leads to heart rhythm disturbances and death. You should limit your consumption of table salt to avoid swelling. If you violate the diet, you must notify your doctor, as you may need to change your hemodialysis regimen. The doctor will explain how long life can be extended if the regimen is followed, but the chances for “obedient” patients are high.
Sometimes dialysis is the only option for kidney failure. But with the right attitude, a person can live normally for another 20–30 years. The main disadvantage is that the patient is tied to the dialysis center. But thanks to modern technologies, you can sleep during the procedure, listen to music on headphones or watch your favorite TV series on your tablet. Over time, patients get used to this lifestyle and try to lead it fully, setting aside time for communication, entertainment and hobbies.
How to make the right decision?
How often have you thought about whether it is worth continuing dialysis? There are many factors that lead to one choice or another. But, sooner or later, it needs to be done.
We'll make it easier. Let's consider and compare the reasons why you should and should not continue treatment.
Reasons to continue dialysis
Reasons to stop dialysis
- Condition has improved
- This allowed us to return to the previous rhythm
- Complications during treatment are compensated by good health after it
- Food restrictions don't bother you
- Family and friends insist that you continue to fight
- You still have many unachieved goals that you can achieve with the help of dialysis
- You are not satisfied with the quality of life
- During regular trips home and to the hospital, your health worsens
- Eating restrictions interfere with normal life
- I want to enjoy the taste of my favorite dishes
- Family and friends support the decision to stop dialysis
- You realize that you have achieved and received everything you wanted from life.
The main thing to always remember is that after stopping the procedures, patients live for several weeks.