A bladder polyp is a benign tumor that develops from the transitional epithelium of the bladder wall. Polyps do not have a tendency towards persistent malignant degeneration, but this possibility increases with age. For a long time, a polyp can remain undetected and be discovered only after tearing or in case of large growth.
Polyps in the bladder can develop into a malignant tumor with age
What are formations and why are they formed?
A bladder polyp is a benign neoplasm that grows from the transitional epithelium as a result of pathological tissue proliferation.
As a rule, they form on the inner walls of the bladder. With rapid changes in the metabolic processes of the body, active division of cells of the mucous membranes occurs, during which the focal appearance of these formations can be monitored.
There is no specific disease or reason why polyps appear in the bladder in men, since absolutely any change in the usual state of the body can trigger the process of polyp formation. The main risk group includes men who are monitored for:
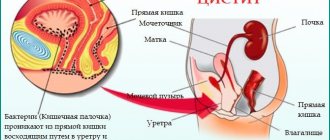
- Various diseases of the urinary system (especially inflammatory ones) . In more than 90% of cases, polyps can be found in patients suffering from cystitis, orchitis, folliculitis, and urethritis.
- Immunity . A weakened immune system is unable to fully renew the body's cells. As a result of active division, the cells are not burned, but accumulate in various places, forming small tumors - polyps.
- Genetics . If a person has a family history of patients suffering from any kind of neoplasm (benign or malignant), then there is a huge risk of polyp formation. Such people should take more care of their health and, in case of any chronic or severe viral diseases, undergo a thorough medical examination.
There are also additional factors that can affect the development of polyps:
- Destabilization of the body's hormonal system . It occurs due to pathological changes in the body or with the artificial administration of hormonal drugs. Bladder polyps can very often be observed in men with diabetes who regularly undergo insulin therapy.
- Unprotected sex . Most often, polyposis is transmitted sexually, and their formation can be concentrated not only in the bladder.
- Exposure of the body to toxic or harsh chemicals . If a person inhales fumes from paint, gasoline and other similar substances for a long time, his mucous membranes become deformed, provoking their active division, which leads to the formation of formations.
- Exposure, radiation . Any radiation sickness is accompanied by pathological disorders in the structure of the body.
- Nervous system disorders . These include diseases such as epilepsy, akinesia, neurasthenia, neuritis, myelitis, fibromyalgia. Ordinary stress, emotional tension or depression can cause tumors.
- Poor nutrition . Polyps are nothing more than a tumor. Large amounts of fatty, fried and spicy foods often lead to the formation of tumors in various internal organs.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking . Alcohol and tobacco significantly increase the risk of tumors.
Neoplasms of various types, including bladder polyps, arise as a result of hypothermia. With a sharp drop in body temperature, the lymph nodes throughout the body become inflamed, which contribute to the development of various neoplasms in the form of tumors, papillomas and polyps.
Polyps in the bladder in men: removal, causes, symptoms and diagnosis
Proliferation on the mucous surface of the bladder is called a polyp. The formations rise above the surface of the bladder cavity and are benign.
However, in men, in the presence of undesirable factors and various concomitant pathologies, bladder polyps can develop into a malignant form, which can lead to serious complications.
What causes the growth of bladder polyps in men and how they can be dealt with is explained in detail in the material below.
Causes and symptoms of polyps in the bladder
Benign growths on the walls of the bladder are formed under the influence of certain factors and causes. Including:
- Genetic predisposition;
- The presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- Disorders in the metabolic processes of the bladder;
- Poor environment and smoking.
Important: Men who have had similar cases should pay special attention to their health. And the connection with age is directly related. This means that if a relative is overgrown at 45 years old, then the descendant at this age should pay special attention to himself.
It is worth understanding that the initial stage of the pathology is asymptomatic. In this case, height is determined by chance during external examinations. When the polyp has already reached an impressive size and is probably injured, the clinical picture of the growth of polyps in the bladder is as follows:
- The color of the urine changes from the usual straw yellow to pale pink. This indicates bleeding in the bladder.
- Pain when urinating when a growth has formed in the area of the ureter, obstructing the flow of urine.
- Frequent chronic inflammatory processes in the bladder in the form of cystitis.
Diagnosis of polypous neoplasm
Bladder polyps in men are diagnosed using modern hardware. Such methods include:
- General urine analysis. Allows you to detect blood, protein and leukocytes in the urine, which indicates inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
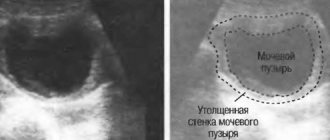
- Ultrasound of the bladder. Allows you to see the tumors themselves, assess their size and structure.
- Cystoscopy. The procedure is performed by injecting a cystoscope into the bladder cavity through the urethral canal. A mini camera is used to assess the condition of polyps and their appearance. Using the device, you can also take tissue samples for histological analysis (detection of malignant polyp degeneration).
- Cystography. X-ray examination of the bladder using X-ray contrast agent. The substance colors tumors a certain color if they are benign or malignant.
You might be interested in: How to give an enema to cleanse the intestines at home?
Important: The absence of polyps means that they are born into a malignant tumor.
Treatment methods for bladder polyps
To overcome bladder polyps in men, either popular methods, conservative therapy or surgery can be used. However, in any case, treatment tactics are prescribed by a urologist or andrologist.
Traditional methods
In the popular treatment of growths of the bladder walls, the use of the following agents is recommended:
- Fresh parsley and dill in sufficient quantity.
- Purity in the form of tinctures. The tincture is made from herb and water. The ratio is 1 tablespoon per 500 ml of boiling water. Everything was mixed and poured within an hour. The finished infusion is drunk in three servings throughout the day.
- Herbal potion. Here you need to mix the leaves of horsetail and birch (4 parts each), calendula, celandine and sage (3 parts each) and wheat (roots 2 parts). Mix them all and collect 3 tablespoons. Pour them into boiling water (1 liter) and let them soak in the steam bath for another 45 minutes. Ready for peeling and drink up to 75 ml 3-4 times a day.
- Pumpkin seeds and egg yolk. Here you should mix 3 tablespoons of dried pumpkin seeds and 3 chicken yolks. All this should be carefully filled with vegetable oil (0.25 l) and kept in a water bath for 20 minutes. The finished product should be placed in a container and refrigerated. Take 1 spoon of the product 30 minutes before breakfast in the dining room. The duration of treatment is 10 days.
Medication methods
There is no cure per se for bladder growth. Only in rare cases, endoscopic injection of medicinal solutions into the cavity of the affected organ can be used to fight cancer.
Surgical intervention
In such cases, surgical removal of polyps in the bladder in men is indicated:
- Rapid growth in education;
- polyps on the wall of the bladder (polyposis);
- The presence of blood in the urine and permanent damage to the formation;
- Anatomical localization of a polyp obstructing the flow of urine (growth of a formation at the entrance to the ureter);
- Risk of growth into a malignant tumor.
Today, growths can be removed through the urinary tract by endoscopic insertion into the bladder cavity using a special cystoscopic device. Or better said, a diathermocoagulator is introduced into the organ cavity.
Using a special belt, they caught the knot and electrocuted his leg. In this case, the wound surface is cauterized.
Using a special mini-camera, the doctor observes the process.
Important: The operation is performed under general anesthesia. This operation is not dangerous for the patient.
It is worth knowing that the postoperative time with this procedure is short. The patient recovers within a short time. After 3-4 days the patient can return to their normal lifestyle. It is important to monitor every six months to prevent relapses or detect them early. If the pathology does not reappear within the next two years, an examination can be performed once a year.
Prognosis and prevention
As for the prognosis for polyps in the bladder, in 10% of cases the growth degenerates into a malignant tumor. This can be avoided with early diagnosis.
In other cases, the patient's prognosis is good. However, it should be borne in mind that in 9% of cases growth can be repeated.
Among the preventive measures to prevent the growth of polyps, the following stand out:
- Balanced diet;
- Quit smoking;
- Optimal drinking conditions;
- Timely and high-quality treatment of infections and inflammations of the genitourinary system.
Everyone should understand that false shame, due to which the patient does not rush to see a urologist even with obvious symptoms of pathology, plays a bad role for the patient.
All doubts should be clarified as soon as possible, and if the clinical picture is suspicious, a doctor should be consulted. Only a specialist in the field of genitourinary medicine can properly treat problems of the genitourinary system.
Remember that delays can be expensive.
Rating for this publication: ( 2
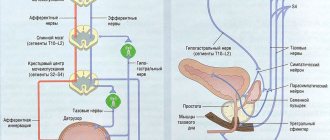
Main manifestations of the disease
Polyps that are small in size have absolutely no external manifestations, so the patient can live for several years, or even his whole life, with the disease, unaware of its presence. As the pathology progresses, neoplasms can degenerate and increase in size. A bladder polyp has the following symptoms:
- Presence of blood and pus in the urine . Too large tumors stretch the inner wall of the bladder, tearing the surface layer of the epithelium. Pus appears as a result of the inflammatory process of the bladder, which is accompanied by pain and heaviness.
- Frequent urination . Growths formed in the bladder block the urethral meatus. A person constantly feels the need, and urination is accompanied by severe pain in the bladder. The pain symptom occurs gradually, from mild discomfort to the absolute impossibility of emptying the bladder.
The symptoms are very similar to prostate inflammation. Men often self-medicate without additional examination, but painful bladder symptoms do not go away, but only get worse.
Polyps in the bladder in men and women - symptoms and treatment
A polyp is an abnormal growth of the mucous membrane. Bladder polyps in both men and women are associated with lifestyle factors, such as smoking or exposure to harmful chemicals, but the exact cause is unknown.
Causes of polyps
It has been established that a certain parasitic infection known as schistosomiasis is associated with the development of bladder polyps, which are the result of the secretion of parasitic eggs in the tissues of the walls of this organ, leading to the formation of polyps.
Schistosomiasis is associated with the development of bladder polyps
Bladder polyps develop more often in men and are usually diagnosed after 55 years.
A combination of growth factors increases a person's susceptibility to bladder polyps. Chronic inflammatory disorders, along with genetic variants, increase the chances of developing them. A person with a family history of bladder polyps is more likely to get them.
Bladder infections, such as chronic cystitis, lead to chronic inflammation of the urinary tract system. This condition leads to the proliferation of the mucous membrane of the bladder, causing it to protrude into the organ cavity in the form of a polyp. Although this does not occur in all cases of chronic cystitis, it is common if the conditions are right and the person's genetics support the development of polyps.
Polyps can be of different sizes
Bladder polyps come in different sizes, from a few millimeters to centimeters in diameter. They come in a variety of forms, but most appear as an abnormal growth of tissue attached to the surface of the tissue lining the stem or stem.
Polyps can occur in other places besides the bladder, including the colon, stomach, nose, ear, and uterus in women. Bladder polyps are asymptomatic in most patients at an early stage.
It is possible that a person will not notice polyps in the bladder, which makes them difficult to detect. However, there are many common symptoms of MP polyps that need to be monitored, e.g.
Finding blood when urinating is one of the typical symptoms of bladder polyps, but it is also not one of the most common. Most likely, these growths in the bladder are found because the patient is concerned about the frequency of urination.
However, the presence of blood in the urine often leads to further investigation to determine the cause.
Diagnosis of bladder polyps
For symptoms of bladder polyps in both women and men (urinary problems such as increased urination frequency or bloody urine), the most common test will be a urine test. This helps the doctor determine the presence of red blood cells and rule out a possible cause of infection.
In cases where bladder polyps are the cause of symptoms, the next step to diagnosis is ultrasound. This procedure uses sound waves at the upper limit of human hearing to measure distance. Ultrasound can be used to determine if there are abnormalities in the structure of the urinary tract, such as polyps.
Once polyps have been noticed on ultrasound, further testing is necessary. They often take the form of endoscopic examination of the bladder or cystoscopy. This test uses a very small camera at the end of a tube that must be inserted into the bladder. This gives a direct image of the mucous membrane.
Ultrasound is required to determine the cause of symptoms
This test allows the doctor to determine the size and appearance of the abnormal growth inside the bladder. Often, an endoscopic tube is critical to diagnosing this disease, as it can be used to remove tissue or perform a biopsy for diagnostic testing. A biopsy provides conclusive results about whether a polyp is cancerous in nature.
You may be interested in: Wen on the gums of an adult - 2 methods of removal and treatment methods
If the polyp does turn out to be cancerous, it can be completely removed, although cystoscopy is part of the procedure to remove bladder polyps.
Chemotherapy drugs can also be used to treat cancer.
If polyps are found in the bladder at a later stage, the cancer may have already spread to the removed muscle and tissue around the bladder, and surgical removal of the bladder may be possible.
Removing polyps from the bladder
People preparing for bladder polyps should refrain from urinating for an hour before surgery.
Your doctor may prescribe the type of pain reliever to take before surgery. The patient is placed on the operating table with legs extended and treated with antiseptic and local anesthesia in the genital area.
The patient may choose general anesthesia, but this is not necessary for such a quick operation.
The doctor slowly inserts a thin cystoscope, a narrow tube-like instrument, through the urethra and up the bladder. The patient should not feel anything at this moment.
Once the cytoscope is in place, the doctor fills the bladder with sterile saline so that the small camera at the end of the cytoscope can easily see the inside of the bladder.
He then cuts out the polyps using a small instrument through a cytoscope or destroys the tissue with an electric current and removes the instruments from the body. No stitches are needed as there are no visible cuts on the body.
Adenoid removal occurs quite quickly
After adenoid removal, the patient may feel pain while urinating and may notice some blood in the urine. Your doctor may prescribe a pain reliever and advise you to drink plenty of water to flush out the saline solution and speed up recovery.
Prevention and complications
Since the presence of benign polyps is strongly associated with smoking, it is best to quit smoking altogether to prevent it from recurring. Middle-aged men are more likely to develop polyps, but this does not mean that women cannot develop bladder polyps.
People living in highly urbanized areas are more likely to develop polyps, so fresh air and healthy foods may have some benefit in preventing the disease.
Complications that can result from untreated polyps include possible malignancy and metastasis, as well as chronic inflammation and pain.
Bladder polyps almost never go away on their own, so it is recommended that the person suffering from them have the polyps surgically removed as quickly as possible. Most patients who have polyps removed can walk and return to work the next day.
Very often, bladder polyps are not cancerous. In this case, they do not pose a real danger, although they can cause great discomfort. However, if the polyps are malignant, then cancer treatment is usually very successful, provided it is detected at an early stage. The survival rate for bladder cancer polyps is extremely high.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
To identify this disease and establish an accurate diagnosis, doctors prescribe the following types of studies:
- Complete blood test for the presence of antibodies.
- Extensive urine analysis.
- Ultrasound examination of the bladder.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the bladder.
- If cancer is suspected, the doctor may additionally prescribe a biopsy.
After a series of studies, if the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor prescribes a cystoscopy. This is a study that is carried out using a special apparatus - a cystoscope.
This is a very unpleasant procedure during which a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the bladder through the penis. This procedure makes it possible to study the type and size of growths.
Establishing diagnosis
A recurring symptom or several indicates the need for medical attention. You need to contact a nephrologist or urologist. If there are no narrow specialists, then you need to see a therapist.
The doctor examines the patient and records clinical manifestations. Then diagnostic examinations and laboratory tests are prescribed. For targeted treatment, the exact cause of the growth is identified. Research is carried out using the following methods:
- General urine analysis. Inflammatory and infectious processes and the state of the body are identified.
- Ultrasound. The procedure refers to the most revealing study. Ultrasound determines the site of development of the node, the structure and area of growth, dimensional characteristics, and the surface of the bladder.
- Cystoscopy - helps to determine the structural structure of the polyp, makes it possible to obtain material for a biopsy to identify malignant degeneration. Creates a visual image of the urinary system.
- MRI. Prescribed if cystoscopic examination is contraindicated.
- Cystography is an x-ray examination using contrast liquid that helps identify hidden foci of growth.
Diagnostic methods are selected individually. It all depends on the patient’s condition and clinical manifestations. To exclude tuberculosis and syphilis, a Wasserman reaction test and pathogen analysis are prescribed.
A polyp is determined by chance or in complicated forms of the disease.
How is polyposis treated?
Only after basic and additional studies of polyps in the bladder have been carried out, the doctor can prescribe individual effective treatment. There are three main methods for eliminating polyps:
- Drug treatment . In the presence of small foci of tumor growth, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, such as: Omeprazole, Prednisolone, Ciprofloxcin, Dexamethasone, Airtal, Lincomycin, Cipran and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, will be effective. The drug itself and the dosage are prescribed by the doctor, according to the individual characteristics of the body.
- Surgical removal. Partial surgery is performed using a cystoscope during the diagnostic period. If the polyps are small, the cystoscope trims the stalk of the foreign body, which will later be released along with the urine under the influence of diuretics. If large growths are found, a full-fledged operation is required.
- Chemotherapy . In cases where polyps degenerate into malignant nodes and there is a high risk of cancer, the doctor prescribes a course of chemotherapy.
After successful removal of polyps, the patient is prescribed restorative treatment aimed at normalizing all functions of the urinary system.
Diet after removal of lesions
After removal, it is recommended to use semi-liquid meals to reduce the load on the intestines, low-carbohydrate foods. It will be useful to follow a slag-free diet in the first 3 days after surgery (see what a slag-free diet is before a colonoscopy).
A sample menu for 3 days looks like this:
- 1 day . For breakfast, grated porridge without milk, green tea. Lunch - vegetable broth, beet salad with prunes. Afternoon snack - thick jelly. For dinner - a glass of warm kefir.
- Day 2 Steam omelette, biscuits, milk. Lunch - chicken broth with crackers, jelly. Afternoon snack - berry pudding, toast. Dinner - mashed potatoes, steamed cutlet.
- Day 3 Rice milk porridge, cottage cheese casserole. Lunch - soup with chicken breast and homemade noodles. Afternoon snack - crackers and jelly. Dinner - fish balls, boiled vegetables.
Gradually, the menu is enriched with calories. No special changes in the menu are expected for polyps of cystic structures. Compliance with the rules of food discipline requires minor adjustments.
Traditional methods of treating pathology
Conservative treatment with folk remedies is not able to eliminate polyps in the bladder, but is excellent as a prevention and relapse of this disease in men. There are two doctor-approved folk recipes against polyposis:
- The first remedy is prepared on the basis of egg yolks, vegetable oil and pumpkin seeds. To prepare, you will need 5 fresh egg yolks, ground pumpkin seeds (5 tbsp) and 200 ml of vegetable oil. All this must be mixed, boiled and taken cold, one tablespoon at a time before bed.
- Decoction of celandine herb. Approximately 20 grams of celandine herb are poured into 1 liter of boiling water and allowed to brew for 3 – 4 hours. The resulting decoction is filtered and taken three times a day, 100 ml, half an hour before meals. Celandine has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and diuretic properties.
It is worth remembering that folk remedies can be used as additional or preventive measures, but not as the main treatment.
Possible complications
In many cases, bladder polyps do not appear, and the person is not even aware of their existence. But there are cases when, due to various pathological changes in the body, polyps begin to actively grow and degenerate. This can lead to a number of complications, such as:
- inflammation of the bladder and the entire urinary system;
- chronic cystitis and cholecystitis;
- prolonged prostatitis;
- necrosis of the bladder as a result of inflammation;
- If left untreated, polyps tend to degenerate into malignant neoplasms (cancer cells).
All this can be avoided. It is necessary to undergo a timely medical examination, including a urologist, monitor your diet, exercise and give up bad habits. Rest plays an important role. In order for the body to be able to fully recover, it is necessary to maintain a sleep schedule.