Diseases of the genitourinary area are considered one of the most common among all pathologies in men. This is a whole group of diseases with similar symptoms. One of them may be residual urine - ischuria, when the bladder does not empty completely.
Normally, men may have an insignificant accumulation of urine (up to 50 ml). In the presence of pathological processes in the body, the volume of unremoved fluid can be up to 1 liter. This phenomenon can lead to serious complications (hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis). The first signs of urinary obstruction require early diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Why does residual urine occur?
Deviations from the norm are more common in older people. This is due to weakened MP tone. Insufficient contraction of the walls leads to the fact that the organ cannot expel urine in full. This symptom may also appear due to the following factors:
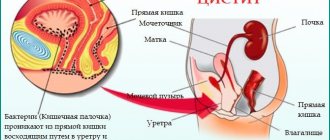
- Presence of infection (cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, etc.);
- Anatomical pathologies (as for the male body - prostate adenoma, prostatitis; for the female - cysts, ureterocele, urethral adhesions, etc.);
- Taking medications whose side effect is weakening the tone of the bladder (diuretics, hormonal, etc. medications);
- Nervous overstrain, which leads to weakening of central nervous system control over the process of urination.
If urine is not excreted from the body for a long time, the patient will soon feel a deterioration in health:
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of bladder;
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Urinary incontinence.
Stagnation of urine leads to increased pressure in the bladder. Ignoring this problem over time leads to all sorts of complications:
- MP infection;
- The appearance of inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system;
- Impaired kidney function, pyelonephritis, stone formation, renal failure.
Stagnant urine is a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which can lead to the development of bullous cystitis, so the symptoms of the pathology cannot be ignored and it is necessary to contact specialists in a timely manner.
Residual urine most often appears in childhood. The reasons for this phenomenon may be hidden behind bladder dysfunction, namely:
- Insufficient contraction of the walls of the bladder, as a result of which urine is not pushed out of it in full;
- Disruption of the sphincter, that is, the wall that is located between the bladder and the muscles blocking the urethra. As a result, urine stagnates in the bladder and does not come out.
In medical practice, the phenomenon of residual urine is truly of great importance. After all, if urine remains in the human body and is not removed from it for a long period of time, then this leads to a rapid deterioration in well-being.
Following urinary incontinence, a person develops symptoms such as the urge to urinate frequently, insufficient urine output, urinary incontinence, and bladder infection.
General concepts
The muscular layer of the bladder wall (desutor) takes part in the process of urination. It relaxes and stretches under the pressure of accumulated urine, resulting in an increase in bladder capacity. At the same time, the muscles of the urethra, pelvic floor and cervix contract to prevent the free flow of urine.
The desutor's ability to contract is limited. The more urine accumulated, the higher the pressure inside the bladder and the stronger the contraction of the desutor. As emptying occurs, intravesical pressure drops and contractile function weakens. The stretching and contraction of the muscle layer is automatically controlled by the CNS (central nervous system).
With strong stretching and increased pressure in the bladder, that is, when the bladder is completely filled, the nerve endings are irritated, afferent impulses enter the brain, and the urination reflex is triggered.
If there are no obstacles in the way of urine outflow, the bladder is completely emptied. When pathology occurs, when the pressure decreases, the contractility of the desutor is not enough to overcome the obstacle, and part of the urine will remain not removed from the bladder. Uroflowmetry allows you to check the correctness of urination processes.
Uroflowmetry is a diagnostic method for determining the volumetric rate of urine evacuation from the urethra during bladder emptying. The task of diagnosis is to find out the condition of the external and internal urethral valves (sphincters), the ability of the bladder to contract and the patency of the urethra.
Diagnosis is prescribed when diseases of the lower parts of the genitourinary system are suspected: adenoma (benign tumor) and cancer (malignant tumor) of the prostate, narrowing (stricture) of the urethra, disruption of the valves and others. The procedure is carried out using a uroflow meter and computer processing of the data obtained.
Uroflowmetry includes four methods:
- standard;
- simplified;
- pharmacological;
- with determination of residual urine.
The last diagnostic option is carried out as follows. During the examination, the patient empties the bladder into a special funnel (men standing, women sitting). Sensors connected to the funnel record: the time of onset of urination, the duration of the process, the average and maximum rate of excretion and the volume of urine entering the funnel over a certain time.
Causes
This symptom can manifest itself due to various pretexts, and some of them are not even related to pathologies of the genitourinary system. Conventionally, they can be divided into several categories.
All reasons causing the appearance of residual urine can be divided into several groups:
- neurological nature;
- inflammatory-infectious;
- obstructive;
- independent pathologies (diverticulum, urethral stricture).
In men, this disease can be caused by a variety of diseases. These include cystitis in acute or chronic form, neurogenic bladder, inflammation of the urethra, inflammation of the prostate gland, prostate adenoma, narrowing of the lumen of the urethra, cystolithiasis (bladder stones), small bladder.
Diseases of the peripheral nervous system, in which the innervation of the pelvic organs is disrupted, also play an important role. In men, residual urine can be observed with atony or decreased tone of the bladder.
How dangerous is the pathology?
If the first symptom occurs, you should seek help from a doctor and undergo a diagnosis. If you do not pay attention and the disease progresses, urine will stagnate in the bladder and pathogenic flora will begin to multiply in it. This will lead to the onset of an infectious-inflammatory process. Additionally, stagnation of urine increases the chance of stone formation. Due to the increase in pressure, residual urine will rise to the kidneys and provoke:
- hydronephrosis;
- pyelonephritis;
- renal failure.
Normal residual urine in the bladder: in men, women, children
There is an acceptable level of residual urine. If the volume of urine that remains in the bladder after urination does not exceed 10% of the total volume before emptying, then this is a normal phenomenon that does not require medical intervention.
In women, men or children, the amount of urine remaining in the bladder after emptying differs significantly. The permissible value for women and men is no more than 50 ml. For children, the normal balance depends on the age group:
- Newborns - up to 3 ml;
- Children under 1 year – up to 3-5 ml;
- Up to 4 years – 5-7 ml;
- Up to 10 years – 8-10 ml;
- Up to 14 years – 11-20 ml;
- Teenagers 14-18 years old – up to 40 ml.
At the initial stages, exceeding the norm usually does not manifest itself as severe symptoms. The patient does not feel pain or significant discomfort. It’s just that the process of emptying the MP occurs a little more often and shorter than usual.
The norm of residual urine for men and women is 30−40 ml. The figure of 50 ml is considered critical. This means that the normal flow of urine is disrupted in a person, and diseases develop. As for the norms of residual urine for a child, they are as follows:
- in newborns 2−3 ml;
- in babies under one year of age 3−5 ml;
- in children 1−4 years old, this norm is 7−10 ml;
- 4−10 years — 7−10 ml;
- 10−14 years - 20 ml;
- for adolescents under 14 years of age, the norm is no more than 40 ml.
Ultrasound examination is considered the most popular and effective type of diagnosing internal organs for pathology.
Determining residual urine allows you to find out what state the body is in now, and whether there are any disturbances in the functioning of its systems. To obtain true results for an ultrasound, you need to prepare properly and follow the instructions.
Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine - what is it?
The ultrasound examination procedure allows not only to determine the amount of residual urine in the patient, but also to obtain a visual picture of the internal state of the bladder - the appearance of its walls, their thickness.
Diagnostics makes it possible to assess the functional capabilities of an organ. It can be carried out even for bedridden patients - the device is easily transported and does not emit harmful ions.
The principle of the study is based on the ability of ultrasound to be reflected from the surface of organs and transformed into an image on the screen.
Norm of residual urine
When the process of emptying the bladder is completed, some urine sometimes remains in the bladder. This is not typical for a healthy person.
However, if the remaining urine does not exceed a tenth of the total volume, this is normal.
Errors in results
Determining the volume of residual urine can quite often have false positive results. Why is this happening? Because the measurement should normally be carried out exactly when the person went to the toilet. That is, literally in 5 minutes he should come to the diagnostic room. But this is an ideal option.
As a rule, a decent amount of time passes between the last urination and the ultrasound examination. During this time period, a portion of urine begins to accumulate in a person.
Another factor that may influence false results is taking diuretic medications or drinking large amounts of water the day before. For example, if a person drank a diuretic before taking the test, then his urine begins to rapidly accumulate - approximately 10 ml of urine per minute. It is easy to calculate that in 10 minutes a person collects 100 ml of urine in his bladder.
Some patients are unable to go to the toilet normally in a hospital setting due to certain uncomfortable conditions. Accordingly, they will have an excess amount of urine.
In order for the result of determining residual urine to be reliable, it is imperative to carry out the analysis at least 3 times (preferably more).
Signs and complications
Urine, which remains in the bladder cavity after urination, not only causes a large amount of discomfort, but is itself an alarming symptom, the severity of which directly depends on its quantity.
Residual urine is an important clinical sign, as it leads to dysfunction of the upper urinary tract and is a consequence of pathological processes leading to functional disorders of the bladder.
The main symptoms accompanying excess residual urine are:
- increased urge to urinate;
- weak or intermittent stream;
- the need to strain the abdominal muscles in order to begin the process of urination or prevent its interruption;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary tract.
In the absence of timely treatment, the risk of developing inflammatory processes increases, since stagnation creates a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic microflora and the formation of stones. Impaired urine flow can also lead to the development of hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis and renal failure.
Prostatitis disease
BPH is benign prostate hyperplasia. Its characteristic feature is an increase in the volume of the prostate gland, which leads to an increase in the total number of tissue cells. Due to hyperplasia, tissue compaction occurs.
Many people believe that prostate adenoma is a tumor, but this is absolutely not true. 30% of men over 50 years of age are diagnosed with this disease. Very often, prostatitis is the cause of poor urinary emptying. Disorders of the prostate gland provoke its active growth.
At the initial stages, a person does not feel any changes, but after some time the process of urination becomes more difficult. This is due to thickening of the walls of the urinary tract. The man notices that the stream of urine becomes weaker; in order to fully empty the bladder, it is necessary to use a little effort (tighten the muscles).
If the disease remains untreated for a long time, constant straining during urination significantly weakens the muscles, they become less sensitive. Sensitivity soon disappears, which leads to incomplete emptying during urination. Doctors call this condition paradoxical ischuria, when one is unable to relieve oneself due to the lack of muscle tone.
Causes of the symptom
Residual urine is just one of the various symptoms found when the genitourinary tract becomes blocked and becomes inflamed. But if its appearance is associated with neurological disorders, then such a problem is much more difficult to detect, in particular, if the problem is in a small child.
If before this you felt like a healthy person, then the first sign of urinary retention will be the presence of a sluggish urge to urinate. This symptom develops gradually, like organ atony. This can be felt by several signs.
If you have a diverticulum, there will be no pressure or pain, but urination will occur “in two steps.” First a large portion will come out, and then a meager one. This process occurs because first the bladder itself is emptied, and then the diverticulum that appears there.
When you leave the toilet, but you have the feeling that there are still remnants of urine inside, this is the first alarm bell and a symptom of bladder disease. Symptoms also include unstable or intermittent urine flow or when it comes out in drops.
In addition, the presence of a symptom such as continuous urination after straining the muscles of the abdominal wall also determines health problems.
Doctors associate other symptoms with diseases that provoke the appearance of final urine. Thus, urolithiasis is characterized by frequent urination, pain in the bladder area, and the appearance of blood in the urine. Patients also experience itching and burning when urinating. The pain usually gets worse after exercise or hard work.
Residual urine is a clear sign of diseases of the genitourinary system, but it cannot be the only symptom. Additionally, a man can experience:
- feeling as if the bladder is not completely emptied;
- burning and pain when urinating;
- disorders of sexual life (dysfunction, pain during ejaculation or sexual intercourse);
- the stream of urine becomes thin;
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the lower back or pubic area;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- swelling of the glans penis and redness of this area.
Over time, men with these symptoms become less inclined to urinate. They go to the toilet less often, their desire becomes less pronounced.
What does stagnation of urine mean - definition
The amount of urine that is present in the bladder after urination is called residual. Even a minimal excess of the permissible volume is a deviation.
Normally, the indicators should not be more than these numbers (ml):
- newborns – 1-2;
- children under one year old – 3-5;
- children under 5 years old – 7;
- children under 10 years old – 7-10;
- children 10-14 years old – 10-20;
- teenagers, adults – 30 ml.
Urine stagnation is considered to be a prolonged excess of this indicator or a one-time detection of residual urine in a volume of 40-50 ml (in an adult). Congestion in the bladder occurs frequently regardless of gender and age, although it occurs less frequently in children than in adults.
Urinary retention occurs:
- complete – anuria is registered, the patient feels the urge, but cannot go to the toilet;
- incomplete - urination occurs, but a certain amount of liquid always remains in the bladder.
A more detailed classification of urinary retention is as follows:
- acute complete - occurs suddenly in the form of a cessation of urine output;
- acute incomplete - urine is released from the overcrowded organ in small portions;
- chronic complete - such patients need artificial drainage of the bladder for a long time;
- chronic incomplete - a person regularly urinates in scanty portions, and there is almost always stagnation (the volume of residual urine can reach 0.5-1 l);
- paradoxical - the organ is overstretched with urine, it constantly comes out drop by drop spontaneously.
Stagnation of urine is also called ischuria, the ICD pathology code is R33. Without treatment, this disease inevitably provokes infectious processes, and if it continues for a long time, it causes the development of urolithiasis. Each time the bladder stretches more and more, pain and other symptoms begin.
Diagnostics
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, it is necessary to accurately measure the volume of residual urine. It is not possible to conduct an accurate study at home, so it is necessary to resort to medical diagnostics.
Analyzes.
First, the doctor must collect anamnesis, palpate the area of the bladder and prescribe general blood and urine tests to the patient.
The method that will determine the volume of residual urine in the bladder is abdominal ultrasound.
But more often an x-ray is performed with a contrast agent. For the data obtained to be reliable, it is necessary that the study be carried out with a full bladder and 5-10 minutes after emptying it. Before diagnosis, the patient must comply with several conditions:
- Do not take diuretic medications and significantly exceed the volume of fluid consumed;
- Before diagnosis, there should not be a long delay in urination, otherwise the walls of the organ will stretch and after the first void the results may be unreliable.
In practice, not all conditions are always met, which can cause a false positive result, so studies are often carried out several times.
Also used for diagnosis is the catheterization method.
Which is more suitable for adult patients. This method allows you to more accurately determine how much urine remains in the bladder after emptying, but has the disadvantage of requiring the use of a catheter, which can damage the bladder or urethra.
In the early stages of the formation of an increased volume of residual urine, the pathology is easily corrected with the help of drug therapy, but in advanced cases, a more radical method is often used - surgery (cystostomy of the bladder), so it is necessary to monitor your health and seek medical help in a timely manner.
This process consists of several neurological, urological, laboratory tests and interviews. When you first visit a urologist, you will be prescribed the following procedures.
- Ultrasound of the bladder and pelvic organs. This study is carried out in two phases. The first is when the bladder is full to measure its volume and size. The second ultrasound is 5-10 minutes after emptying. To ensure accurate results, calculations are carried out at least three times. There are special formulas for calculating the amount of liquid, which require the following parameters:
- height;
- width;
- length of the ultrasound shadow of the bladder.
If the patient is currently taking diuretics, or before the examination, drank drinks or ate foods that could irritate the organ for examination, then the doctor must be warned about this, since the diagnosis may be erroneous due to these influencing factors.
Ultrasound is considered a non-invasive method, since the rate of residual urine in men and women is not determined accurately. But it is used more often due to its general availability.
- Clinical analysis of blood and urine, urine culture to determine bacterial infection.
- Cystoscopy and contrast urography – if necessary. The first type of examination is prescribed as a last resort, as it is quite traumatic. But it quite accurately indicates the volume of residual urine, if any was detected.
Do not forget that the calculation of volume and urine analysis for prostatitis and other diseases in which this symptom appears may turn out to be erroneous during ultrasound and other examinations due to nervous strain.
To determine the volume of residual urine, you need to resort to medical diagnostics. At home, you will not be able to determine exactly how much urine remains in the bladder and how much comes out of it. Therefore, the method of catheterization of the bladder or the method of abdominal ultrasound is used.
Determining the presence and quantity of residual urine is the main purpose of the examination, which includes asking the patient for the presence of clinically significant symptoms. Next, instrumental research methods are carried out, the list of which includes:
- studying the dynamics of changes in stream pressure during urination (urofluometry);
- orthostatic urine test;
- measuring pressure in the bladder at different moments of urination (cystometry);
- assessment of the contractility of the muscular layer of the bladder walls (electromyography);
- study of the functional state of the sphincters and urethra (urethroprofilometry);
- Ultrasound of the bladder before and after urination;
- Ultrasound of the prostate gland.
Laboratory research methods:
- clinical urine analysis (determining the presence of bacteria, proteins and nitrogen in the urine);
- clinical blood test;
- determination of prostate specific antigen (PSA).
A reliable method for determining the amount of residual urine is the direct catheterization method. But due to the difficulties associated with its implementation (invasiveness, risk of damage to the urethra, provocation of inflammatory processes), assessment of the amount of residual urine is mainly carried out using ultrasound.
This deviation is dangerous because at the first stage of development it does not have pronounced symptoms. This contributes to the progression of the disease and it enters a more severe stage.
At the second stage, the manifestations are already more obvious. But even now they can be confused with a common cold, as they are chills, fever, and lower back pain.
Therefore, it is very important to determine the residual volume of urine. If it exceeds the norm, then this is the first symptom of disease.
Determination of residual urine is a rather complex process and consists of a set of measures:
- laboratory diagnostics;
- urological studies;
- neurological research.
Men with cystitis should be referred for examination. Diagnosis of this pathology includes collecting the patient’s history and complaints, external examination, and palpation.
Data from laboratory and instrumental studies are of great importance. These include general blood and urine tests.
A urine test reveals the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells, mucus may be present, and many epithelial cells. This is not the norm for men.
If there is increased acidity of the urine, this may indicate a tuberculous nature of cystitis. To confirm the diagnosis of cystitis, smears are taken from the urethra and a urine culture is done.
This makes it possible to identify the pathogen.
Of the instrumental research methods, ultrasound is used. Not only the bladder, but also the kidneys, prostate and other pelvic organs of men are subject to examination. Cystography, uroflowmetry, and less commonly biopsy are also used. To prevent residual urine from accumulating in the organ, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease.
Treatment includes the use of antibacterial agents. Before this, the type of pathogen is determined using PCR. The most effective are drugs from the group of fluoroquinolones, macrolides and tetracyclines. Of great importance for sick men is bed rest, exclusion from the diet of foods that irritate the mucous membrane, and alcohol. Diuretics and antispasmodics can be used.
How to determine the presence of pathology?
The purpose of diagnosis is to correctly determine residual urine. For this purpose, the patient is asked about the manifestations that he had to encounter. Then he is prescribed a general urine and blood test and a specific test to determine the presence of adenoma and prostate cancer. Instrumental research methods include the following procedures:
The disease can be diagnosed using cystometry.
- uroflowmetry;
- orthostatic urine test;
- cystometry;
- electromyography;
- urethroprofilometry;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Ultrasound of the prostate.
To determine the residual urine volume (RVV), an ultrasound examination is performed in 2 stages. To begin with, a diagnosis is made with a full bladder. Then they ask the patient to empty the bladder and sit for 15 minutes, and then again examine the changed organ on the monitor of the device. The difference in size and volume visible on ultrasound is calculated using standard tables.
Treatment of the disease
Laser contact vaporization – it is used in the treatment of BPH only when the volume of the affected organ does not exceed 30 cm3. In this case, the tumor is removed with a laser using the contact evaporation method. The operation is minimally invasive and is performed under direct visual control, which is provided by modern endoscopic equipment.
Contact laser resection - this operation to remove an adenoma is considered the most complex intervention, requiring extensive experience and skill of the surgeon. This method of treating BPH is similar to transurethral resection, but it is performed using a laser. In this case, the affected gland tissue is removed with a controlled laser pulse.
Residual urine is not a separate disease, but only one of its symptoms. In order for there to be a normal bowel movement, it is necessary to eliminate the factor that violates it. The following measures may be taken.
- Removing the inflammatory process.
- Restoration of urinary tract patency. An operative or conservative method can be chosen.
- Normalization of bladder contractility.
For neurological disorders, more complex therapy will be required. Both surgical and medical methods can be used here.
If you are diagnosed with bladder atony, the doctor will prescribe medications that restore contraction skills. When the organ spasms, muscle relaxants are prescribed.
If they do not help, then a surgical procedure called selective dorsal rhizotomy is performed. During this, the doctor isolates the bundle of nerves of the spinal cord - only those that are responsible for the spastic contraction of the bladder, and dissects them.
The main thing is to adhere to complex therapy, which will act not only on the symptoms, but also on their causes.
If you identify these symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor, because only he can correctly diagnose the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment.
mochaanaliz.ru
Treatment of urinary retention in severe cases involves catheterization with a rubber catheter. This treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting; it will not be possible to insert a catheter correctly at home (the catheter is inserted into the urethra).
A permanent catheter is inserted for several days and treated with solutions of Furadonin, Nitroxoline, as well as other antibacterial agents.
At home, you can apply warm water to your genitals to promote urination. If this method turns out to be ineffective, then a 2% Novocaine solution or Pilocarpine solution is injected into the urethra. Do not try to insert a catheter at home, as this may cause a bladder infection.
med.propto.ru
Residual urine in the body is not a disease, it only indicates its presence. That is why, first of all, it is necessary to determine the causes of excess urine. In addition, you need:
- restore the patency of the urinary canals;
- relieve inflammatory processes;
- restore the bladder's ability to contract.
Basic principles of treatment:
- it must be comprehensive;
- The treatment process must not be interrupted under any circumstances;
- The doctor must choose a course with minimal side effects.
Neurological abnormalities are considered much more complex. In this case, unfortunately, surgical and medical intervention cannot be avoided.
If the patient has atony, the doctor prescribes medications that will help the bladder restore its contraction function. For its spasms, muscle relaxants are often prescribed.
If all attempts are in vain, then an operation has to be performed, during which the doctor dissects in the spinal cord those nerves that form spastic contractions of the bladder.
etopochki.ru
The remaining urine in the bladder is one of the criteria for assessing the functioning of the entire urinary system.
By determining the residual amount of urine, one can judge the presence of a variety of pathologies, which, as a rule, require immediate treatment.
Normal residual urine in the bladder
Under no circumstances is the urethra completely emptied. A small urine residue is acceptable, and the norm for this indicator is 10% of the total urine volume.
In a healthy adult, urea volume is 320–350 ml in women and 350–400 ml in men. Therefore, the normal residual urine value is 35–40 ml.
A urine residual of 50 ml is considered to be a critical indicator. This amount of urine leads to stagnation, the development of a large number of bacteria, and intoxication of the body.
Urine residue levels in children vary depending on their age:
- newborn babies up to 3 months – 2 – 3 ml;
- at 1 year – up to 5 ml;
- 2 – 4 years up to 7 ml;
- 4 – 10 years up to 10 ml;
- 10 – 13 years – 20 ml;
- adolescence (14 – 16 years) – 25 – 35 ml;
- adults – 35 – 40 ml (in some cases up to 50 ml).
Attention! The dangerous amount of residual urine, established by world experts, is only 50 ml, but in some diseases, this value can reach 500 ml, causing bladder overflow.
The remainder of the urine is formed due to various pathologies, and not all of them are related to the genitourinary system. All reasons can be divided into 3 groups:
- Obstructive.
- Inflammatory and infectious.
- Neurological.
Effective methods and general rules of treatment
Treatment depends entirely on the underlying cause that caused residual urine, and is primarily aimed at restoring the patency of the urinary tract. It may include etiotropic therapy, catheterization and surgery.
- Etiotropic therapy. Taking anti-infective, antiviral drugs, antibiotics that help suppress unfavorable microflora (if the cause is infectious cystitis or urethritis). For urolithiasis, agents are used to help dissolve and quickly remove stones from the kidneys. If the cause is a neurological disorder, treatment is aimed at restoring control of muscle tissue. Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
- Surgical intervention. If we are talking about kidney failure or deformation of the bladder, only surgery can correct the situation. Surgery is also performed for urolithiasis, if the size of the stones is too large and medications are unable to remove them.
- Catheterization. If the residual urine is too large, a special catheter is installed in the urethra for its painless removal. The patient's urethra is first disinfected, after which a catheter lubricated with glycerin is gradually inserted. The process is quite painful and unpleasant. As a rule, a catheter is placed for a certain time (5-6 days) while the patient is in the hospital, but in rare cases a permanent catheter is installed.
What are the treatment methods for prostate adenoma?
There are two main treatment tactics for managing patients suffering from prostate adenoma - the use of medications and surgical methods for removing the tumor. The decision to choose one or another method of therapy is made by the doctor together with the patient, depending on the size of the benign tumor, the stage of the disease, its clinical symptoms and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
The optimal treatment tactics are carefully selected for each patient individually.
Herbal preparations
In this case, medicines based on aspen bark, pumpkin seeds, fanleaf palm fruits, nettles, etc. are used.
As a result of many scientific studies, scientists have determined that some plants are able to eliminate bladder outlet obstruction of the urethra and relieve the unpleasant symptoms of prostate adenoma, as effectively as 5-alpha reductase inhibitors.
It is for this reason that herbal preparations are widely used in the treatment of various prostate pathologies. Medicines containing herbal components not only reduce the size of the affected gland, eliminate inflammation and swelling of this organ, but also prevent further growth of the tumor.
The advantage of using such drugs is their mild and safe effect on prostate adenoma. But these herbal preparations are effective only at the early stage of the disease; at later stages of BPH, they are preferred to be used only as part of a combination treatment, together with alpha-blockers.
Alpha adrenergic blockers
The following drugs are used - Tamsulozosin, Alfuzosin, Terazosin and Doxazosin. The drugs from this list quickly and effectively relieve urethral irritation and urinary obstruction, and eliminate urinary retention. The result of using these funds appears within 1-4 days of treatment.
Important signals of distress
Symptoms of difficulty urinating are:
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder or weakness of urination;
- jet splitting;
- frequent urination in small volumes;
- pain and discomfort;
- general malaise;
- erectile dysfunction;
- discharge from the urethra.
Incomplete bladder emptying in men is rarely a separate disease. Pathology is evidence of another disease - prostatitis or prostate adenoma. In women, such disorders are a sign of cystitis or urethritis, occurring in acute or chronic form, postpartum complications or genital herpes.
Urethral stones are a pathology that develops against the background of a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder and prolonged symptoms. Stones cause dysuria, are signaled by blood in the urine, and form in the ducts and cavities, disrupting the natural cycle of formation and excretion of urine.
The symptoms should not be taken lightly. Incompletely excreted urine can become a source of bacterial damage and inflammatory reactions. If the listed symptoms appear, a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed for a long time. Otherwise, serious complications are possible that are difficult and long to treat.
Medical therapy
In advanced situations, therapeutic measures consist of inserting a rubber catheter and removing excess urine from the bladder artificially. Such therapy is possible only in a hospital setting; self-medication is unacceptable. At home, it is impossible to correctly place a catheter in the urethra.
This device is introduced for 2-3 days; it must be constantly treated with various antibacterial agents (Nitroxoline, Furadonin).
Treatment at home involves treating the external genitalia with heated water, this stimulates urination and elimination of excess urine. If this method is ineffective, Novocaine or another drug prescribed by the doctor is injected into the urethra. It is not recommended to insert a catheter at home; this can lead to infection of the organ and the development of additional inflammatory processes and infections.
It is important to seek medical help in a timely manner. This will make it possible to carry out less painful treatment and prevent pathological and inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
If a person does not see a doctor...
In a healthy person, the bladder should normally empty completely, without any residual urine. Only 10% of the remaining urine is allowed, depending on the age of the patient, that is, in a child it will be 3-5 ml of urine, in an adult – up to 50 ml.
If the volume of residual urine exceeds the permissible norm, this indicates that the person has begun to develop urological infectious or inflammatory processes. To truly confirm or refute the diagnosis, it is necessary to very accurately measure the amount of residual urine.
At the same time, it is important that certain conditions for the process of urination are observed - comfortable psychological conditions, a familiar, non-painful posture when urinating.
If a certain person has a disturbance in the process of urination and does not seek medical help and does not investigate this situation in any way, then in this case the person begins to develop pathologies.
The sign of residual urine in the bladder leads to the emergence and rapid development of kidney diseases, namely:
- To the development of chronic pyelonephritis;
- To the formation of kidney stones (in most cases, this problem can only be solved surgically);
- To urethritis;
- Hydronephrosis;
- Impaired kidney function and renal failure as such.
In the early stages of dysfunction of the bladder and the formation of residual urine in it, this condition can still be corrected with the help of medications. In advanced states of the disease, they resort to hospitalization and treatment through surgical methods.
When a lot of fluid accumulates in the bladder and the patient cannot empty it naturally, he undergoes catheterization. People for whom the procedure is contraindicated, for example, with urethral sphincter spasm, may receive an injection of botulinum toxin into the sphincter area to relax the muscle.
In some cases, the patient is given a temporary urethral stent with a validity period of three to six months. It is a cylinder of thin (1.1 mm in diameter) wire spiral made from organic material, which soon dissolves.