What is leukocyte esterase?
This biochemical compound is a hydrolytic enzyme of white blood cells. It is released into uric acid after the destruction of leukocytes, which are destroyed during the process of phagocytosis (intracellular breakdown), suppressing the vital activity of pathogenic agents and foreign microorganisms.
White blood cells play an important role in the immune mechanism, capturing and destroying pathogens of various diseases and inflammations with secreted enzymes. However, this inevitably leads to destruction of the biological structure of leukocytes.
As a result, esterase ends up in the urine and is excreted along with it from the body. The amount of this hydrolytic enzyme in urine indicates not only the presence of an inflammatory process, but also the nature of its course.
Normal indicators in urine analysis in infants and children over 1 year of age
The rate of white cells in urine in children varies depending on age, gender and physical development. The content of the substance is determined by examining urine sediment under a microscope. The normal amount in a healthy baby does not exceed 10 cells per microliter.
In infants, the quantitative indicator of leukocytes is somewhat overestimated. This is due to weak functional activity of the kidneys in the first days of life. In the absence of an inflammatory process, the number of leukocytes can reach nine units. For boys, the figure is slightly lower - about six.
READ ALSO: a child has low leukocytes in the blood: what to do?
In children over one year old, the norm is considered to be from one to eight cells. For most healthy children, the norm is one or two units.
Goals of the analysis
Leukocytes have the ability to penetrate organ tissue from the bloodstream to suppress the activity of microbial pathogens. The detection of a hydrolytic enzyme in uric acid increases the information content of laboratory diagnostics, since it is detected regardless of the content of white blood cells in it.
Often such an analysis is prescribed as a screening test to monitor the effectiveness of therapy:
- pyelonephritis;
- glamerulonephritis;
- urethritis;
- prostatitis;
- cystitis;
- amyloidosis.
Laboratory examination of the biomaterial allows us to identify pathological processes in the urinary system at an early stage, which greatly facilitates treatment. Elevated leukocyte esterase concentrations may indicate inflammation in the kidneys.
To clarify the diagnosis, additional examination is prescribed. Traces of adipocyte cells, which form the basis of adipose tissue, indicate a violation of metabolic processes, dystrophic changes in the abdominal and pelvic organs, and their infectious infections.
Leukocyte esterase in urine is present in increased concentrations in some pathologies of the reproductive system in women and in liver diseases. An important goal of such an analysis is to identify the inflammatory process at the initial stage of its formation and development.
An increased level of this enzyme clearly indicates attempts by blood cells to neutralize pathogenic pathogens that have penetrated the kidneys, bladder, and urethral cavity.
In most cases, in parallel with leukocyte esterase, signs of bacteriuria are detected - the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in uric acid, where they enter from the abdominal organs, genital system, and pelvis.
False indicators
When first examining a patient, the physician must pay attention to the patient’s condition, complaints and symptoms. Only after this are recommendations given for laboratory urine testing. Leukocyte esterase is determined after a chemical analysis of urine. To do this, paper strips soaked in a special substance are immersed in the patient’s urine. After a few seconds, the strip will become colored, and the amount of leukocyte enzyme in the sample can be determined by the hue.
To clarify the diagnosis, you need to undergo additional diagnostics, in the form of:
- Biochemical and general blood tests;
- Bakposeva;
- Ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- X-ray.
For each patient, the method of diagnosing kidney and urinary diseases is different. When choosing a study, the physician takes into account the patient’s age, his complaints, and the results of the preliminary examination. If white bodies are found in the urine, special therapy is prescribed. To quickly restore your health, it is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
How is a urine test deciphered?
The content of white blood cell hydrolytic enzyme is usually determined in biological fluid during a general or biochemical laboratory test, along with other characteristics.
Leukocyte esterase in urine and the level of its concentration are assessed in conjunction with such important indicators as:
- protein components;
- glucose;
- composition of microbial flora;
- bile pigments;
- ketone components;
- hemoglobin;
- elements of inorganic origin;
- epithelial cells and their derivatives.
A comprehensive study allows you to establish the overall clinical picture and minimize the likelihood of a false positive result. The increased content of this hydrolytic enzyme and the accompanying pathogenic microflora give urine a cloudy color.
Sometimes the phenomenon of sterile leukocyturia occurs, in which esterase is detected in the urine, but there are no pathogens. In this case, clarification of the results, additional examination, and repetition of the laboratory test are required.
To correctly interpret the results of the analysis, accurate anamnestic information and data on the use of medications that can affect the chemical formula of urine are required.
To establish the composition of the accompanying microbial flora, bacteriological culture is performed and a nitrate test is performed. The biomaterial is examined by microscopy or using special laboratory markers impregnated with a chemical compound that reacts with leukocyte esterase.
Benefits of Enzyme Research
Urologists and specialists in infectious pathology of the urinary tract like to prescribe this test as a screening test when monitoring the quality of treatment of pyelonephritis, urethritis, cystitis and other inflammatory lesions. After all, the presence of this enzyme indicates inflammation even in the case when there are no more leukocytes, and there are not even traces of their cells. This allows one to confidently, based on this indirect sign, suspect bacteriuria and an inflammatory infectious process, even if microscopy of the urine sediment did not show the presence of either leukocytes or microbial cells.
Of course, this result of the analysis should not be considered in isolation. Thus, traces of leukocyte esterase in urine must be taken into account together with the results of sediment microscopy, as well as with other reactions. Indirect markers of inflammatory lesions will be the presence of protein in the urine, its cloudiness, the presence of bacteria, and so on. Therefore, the reliability of microbial contamination of urine will be much higher if all these signs are simultaneously detected in the tests, and it will be possible to accurately make a diagnosis, including identifying the pathogen, based on the results of bacteriological culture. The only “minus” of sowing is that it can take several days, or even up to 2 weeks, for the growth of a pure colony and determination of the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics.
Interpretation and norm of content in urine
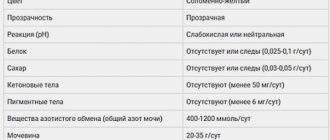
The level of the hydrolytic enzyme of white blood cells should not exceed 5 units in the field of view in men and 3 in women. A higher concentration may indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, urethral cavity or renal organ.
A semi-quantitative determination of the content of the phagocytic enzyme is performed as standard. In the results of the analysis it is about. If the level is below the minimum detection limit, the chemical will test negative for leukocyte esterase. An increased concentration of neutrophil cells is clear evidence of an inflammatory process.
Norm and content of leukocyte esterase in uric acid:
| Analysis result | Approximate concentration |
| negative | Below detection limit |
| Traces of phagocytic enzyme | 25 leukocytes/µl |
| + | 75/µl |
| ++ | 250/µl |
| +++ | 500/µl |
75 leukocytes per microliter of uric acid may indicate the initial stage of the inflammatory process or be associated with some side factors that affect the reliability of the analysis result. This requires clarification of the diagnosis.
Leukocyte esterase, contained in urine at a quantitative level of 250/μl, most often indicates bacterial infection of the kidney organ, urethral cavity or prostate in men. Consultation with a urologist is necessary.
If leukocytes are detected in a laboratory urine test in a concentration of 500 or higher, an acute stage of the inflammatory process is suspected. It is usually accompanied by painful symptoms and urological dysfunctions.
In men and women
Both sexes have both common clinical and biochemical signs of deviation from the norm in the content of the phagocytic enzyme in uric acid, as well as gender differences.
In men, an increase in leukocyte esterase levels can be caused by:
- inflammation of the prostate gland;
- balanoposthitis - bacterial infection of the head of the genital organ and the foreskin;
- prostate adenocarcinoma – malignant tumor destruction;
- phimosis - congenital or acquired narrowing of the lumen of the skin of the penis.
A urine test to measure white blood cell hydrolytic enzyme levels is not used to make a definitive diagnosis. It only serves as a basis for additional examination.
In women, deviations from the norm in leukocyte esterase levels are caused by a large group of factors, both pathological and natural physiological.
The first include:
- inflammation of the bladder and its mucous membrane;
- pyelonephritis – damage to kidney tissue;
- vulvovaginitis – a disease localized in the vaginal cavity;
- candidiasis;
- oncological neoplasms.
Common reasons for both sexes for increased levels of leukocyte esterase in urine are considered to be excessive static physical activity, fever, and antibiotic therapy with cephalosporins.
The level of the phagocytic enzyme may change when taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or using radiocontrast agents.
Indicators during pregnancy
In such a specific physiological state of the female body, a leukocyte esterase value of 6 units/μl of uric acid is considered normal. Exceeding the established indicator requires additional examination.
Hormonal changes and preparation of the body for childbirth lead to a slight increase in the release of the hydrolytic enzyme into uric acid. During conception, a significant accumulation of leukocytes is observed in the uterine organ. In this way, the body protects the embryo from pathogenic pathogens.
Leukocyte esterase in urine during pregnancy is always found in increased concentrations. Closer to childbirth, this value decreases. Otherwise, the woman is prescribed additional examination.
The clinical picture is considered pathological and requires treatment if, due to fetal pressure on the walls of the bladder, inflammation develops, muscle tone decreases and congestion occurs in the organ, which creates a favorable environment for the penetration of pathogenic pathogens.
The migration of leukocytes into the uterus is a natural protective mechanism of the female body during pregnancy. A large accumulation of these blood cells leads to an intensification of the production of a phagocytic enzyme, which is excreted through the urinary ducts.
Content in urine in children
In an infant, the content of the hydrolytic enzyme of leukocytes may slightly increase during teething. A value of up to 8 units is considered normal when examining biological fluid using microscopy.
The consequences of childhood infectious diseases lead to a slight increase in leukocyte esterase even when the vital activity of pathogenic agents is completely suppressed. In infants, inflammatory processes are often asymptomatic, causing only the phagocytic enzyme to exceed the established norm.
Esterase analysis, norm and deviations
In healthy people, when performing urine microscopy, the leukocyte content should not exceed 3 cells for men and 5 for women. Accordingly, if this indicator is elevated, then in all likelihood the urinary system is affected by infection. And the higher the content of white cells in the urine, the higher the LE level will be.
The determination of this enzyme is carried out using semi-quantitative analysis, that is, a study that implies something between the study of the quality and quantity of a substance. To carry it out, special test strips are used, and the rating scales for the results may vary slightly among different manufacturers.
The lower sensitivity threshold of this test is 5 leukocytes per field of view; if their number in the sample is less than or equal to the specified value, the result will be considered negative. When deciphering this analysis, pluses are used, and their number directly shows the level of concentration of the substance being studied.
So, for example, if the form indicates three pluses (+++), then this indicates a high content of leukocytes - more than 500 in 1 μl of biomaterial. The number of pluses is interpreted as follows. (+) – one plus is not conclusive evidence of the presence of a serious urinary system disease in the body.
The principle of the leukocyte esterase test and interpretation of materials
LE can be detected in small quantities in the initial stages of minor inflammations, such as cystitis or urethritis. Also, similar results are often determined during pregnancy or in people who were poorly prepared for collecting biomaterial.
One plus indicates the need for a repeat analysis, and in situations that are accompanied by pathological symptoms, the prescription of anti-inflammatory and diuretic drugs will be required. In addition, the patient is recommended to pay increased attention to personal hygiene, which will help avoid diagnostic errors in the future.
Leukocytes in a general urine test
(++) – two pluses, is considered a result indicating a strong inflammatory process occurring in the urinary system, in its lower and upper sections. This indicator often accompanies the acute form of cystitis and urethritis, as well as nephritis (inflammation of the kidneys).
In addition to increased PE, impurities of pus, mucus, protein and blood may be found in the urine of patients, which only once again confirms the presence of the disease. The secreted fluid is cloudy in appearance, and in most cases the patient has a high fever.
Such pathologies require immediate further examination to determine the inflammatory focus and the pathogen that caused it, as well as the prescription of antibacterial, supportive and, if necessary, analgesic therapy.
(+++) – three pluses means that the infection has spread to all or almost all parts of the urinary system. This condition requires immediate hospitalization of the patient and the prescription of powerful antibiotics.
If the disease is too severe, antibacterial agents are administered intravenously. As an additional examination, the patient is required to undergo ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys. The presence of a large number of pluses in the analysis form is sometimes a sign of kidney tuberculosis.
To confirm or refute the results of a urine test for leukocyte esterase, the doctor needs to compare the following data about the patient’s condition:
- medical history, during which you also need to find out what medications he is taking;
- data from bacteriological and microscopic analysis of urine;
- diagnostic results for nitrites, which is mandatory for people suffering from chronic diseases of the urinary system.
Diagnostic methods
An increased concentration of leukocyte esterase in biological material may be a sign of one or more pathologies of the internal organs, reproductive or urinary system.
Therefore, additional diagnostics are often required to clarify the diagnosis, determine the area of localization and anatomical and physiological characteristics of the inflammatory process. During such an examination, the genotype of the infectious pathogen or other reasons for the development of the pathology are determined.
In addition to urine analysis, the following is performed:
- generalized and biochemical blood tests;
- bacteriological culture;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- computed tomography of internal organs.
The doctor may prescribe a urography. It is performed using the urethroscopic method. A 3-glass test is often used. This method of laboratory diagnostics involves dividing the total volume of the obtained biological material into the initial, middle and final phases.
Leukocyte esterase in urine increases unevenly. Based on the principle of its distribution in different parts of urine, one can find out the reason for the increase in the volume of the hydrolytic enzyme of white blood cells.
Nichiporenko's diagnostic method involves determining the ratio of erythrocytes and leukocytes in 1 ml of uric acid. There is a 2-glass sample method, in which the middle phase is excluded, only the initial and final phases are taken into account.
With the Kakovsky-Addis method, biological material collected during the day is examined. Laboratory diagnosis using the qualitative analysis of leukocyturia involves supravital staining to determine the type of these blood cells.
For each patient, a method for determining the level of phagocytic enzyme is individually chosen. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe a biopsy and smear to analyze the composition of the microflora of the genital area.
The prednisolone test, which is able to detect latent leukocyturia, shows high performance. It is based on the biochemical aggressiveness of a synthetic glucocorticosteroid, which causes a short-term exacerbation of the inflammatory process.
The method of isolating formed components and sedimentary cylinders according to Addis-Kakovsky is not often used, since the cells are quickly destroyed during daily collection of biological material. More often, a similar 12-hour method is used, in which the leukocyte esterase detected during this period is recalculated for 24 hours.
The Amburge method of laboratory testing allows one to determine what is excreted in the urine in 1 minute. volume of phagocytic enzyme. Many pathological processes in the renal organ at the initial stage of formation have a vague clinical picture.
The Amburger diagnostic method is intended to clarify this. Regardless of the research method used, the level of leukocyte esterase should not exceed 5 units. Exceptions are children, pregnancy and the menstrual cycle. In the latter case, it is better to postpone the test.
Symptoms
Inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, which result in leukocyte esterase, have pronounced symptoms. Be sure to pay attention to the baby's condition. As the pathology progresses, the following warning signs may appear:
- The baby's urine becomes dark and cloudy;
- There is a frequent urge to urinate, which causes discomfort to the child;
- Body temperature rises.
The enzyme level in a child prone to allergic reactions may be higher than normal. Also, such indicators can be explained by a recent cold or teething.
A newborn’s own immune defense is still weak, and he has to expend a lot of energy while passing through the birth canal. If the results of a urine laboratory test cause concern to the doctor, additional diagnostics may be needed.
How to properly prepare for research?
Biological material should not be collected in household containers that are poorly suited for this purpose. Such containers may distort the analysis result. The reliability of the study of urine suspension is the key to correct diagnosis and the correct choice of therapeutic tactics.
Household containers contain microorganisms that can significantly affect the results of the study of biological material.
It is necessary to adhere to other important rules for preparing for the test:
- You should only use a sterile medical container purchased from a pharmacy for the appropriate purpose.
- Before the procedure for collecting urine, you need to thoroughly wash your hands and external genitalia to eliminate the influence of microbial factors on the result of the analysis.
- For hygienic treatment, it is advisable to use a large amount of warm water and toilet soap with antibacterial properties.
- The initial phase of urinary fluid must be poured into the toilet, and the middle phase must be carefully collected in a container.
For research, 50 ml of biological material is sufficient. The last portion of urine must also be flushed into the toilet. The container is tightly closed with the supplied lid, placed in a plastic bag and taken to the laboratory.
It is best to collect biological material in the morning before meals. An important nuance is the rapid decomposition of phagocytic cells outside the body. Therefore, it is recommended to collect urine immediately before visiting the laboratory.
Preparing for the test
In order to avoid having to subsequently treat a child for non-existent diseases, it is necessary to follow certain requirements when preparing and taking a urine test:
- Do not take antibiotics or other strong medications 2 weeks before the procedure, or warn about it.
- The day before the test, do not give babies ultrasounds, x-rays, or physical therapy.
- A few days before this, do not feed the child beets, bananas, chocolate, carrots, avocados, tomatoes, pineapples.
- The day before the test, do not give children foods that they have not yet tried, unhealthy or “not for children” food.
- The urine container must be sterile; it is preferable to use a container purchased at a pharmacy.
- The study requires the first morning urine, before breakfast.
- Before collecting urine, the child must be washed with soap.
- The first and final drops of urine are not taken into the container.
Peculiarities of children's research
An increase in the level of leukocyte esterase in a child indicates the likelihood of developing the same inflammatory processes as in adults. This could be cystitis, urethritis or pyelonephritis. Failure to maintain personal hygiene and take certain medications can distort the test result.
In children, there is a direct connection between allergic manifestations and an increase in the content of leukocyte hydrolytic enzyme in the urine. This is explained by the immune competence of white blood cells.
This result is considered to be false positive, that is, not related to the presence of an inflammatory process in the child’s body. An increase in the level of enzyme in the urine is observed after an acute respiratory infection.
With a normal level of leukocytes in the blood, excess release of esterase into urine is not a cause for concern. Therefore, the result of a study of urinary fluid in a child is assessed only in conjunction with a general blood test.
Physiological, immune and hormonal instability of the child’s body often leads to dysfunction of the urinary system. Some of them are virtually asymptomatic until they develop into an acute form.
A urine test for the content of a phagocytic enzyme is the only way to diagnose the inflammatory process at an early stage, when its suppression is a relatively simple set of therapeutic procedures.
Pathological causes
More often, the growth of esterase is associated specifically with diseases of the genitourinary organs:
- pyelonephritis;
- kidney abscess;
- cystitis;
- urethritis.
All these diseases are caused by bacterial flora, so leukocytes actively flock to the site of inflammation. They destroy bacteria and esterase is released into the urine.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the calyces, pelvis and parenchyma of the kidney. The disease is manifested by fever and pain in the lumbar region. Caused by hypothermia. An abscess is an abscess in the kidney. It is formed due to the ingress of microbial flora. The area of the kidney is destroyed and covered with a capsule. The disease is characterized by high fever, lower back pain, nausea and vomiting.
With cystitis, the bladder becomes inflamed. Hypothermia can be a provoking factor for infectious inflammation. Manifested by frequent and painful urination. Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra. In childhood, it often develops due to insufficient personal hygiene. During urination, the child experiences pain and burning in the urethra.
Esterase can be detected as traces in urine if the test was taken incorrectly or inflammation is just beginning
Leukocyte esterase during pregnancy
In this physiological state of the female body, white blood cells are produced more intensely than usual . This leads to an increase in the level of their hydrolytic enzyme uric acid.
If other diagnostic methods have not revealed microbial infection, and there are no symptoms of the inflammatory process, there is no reason for concern. During pregnancy, stagnation of urinary fluid is often observed, which contributes to the development of bacteriuria and pyuria.
In some cases, an increased content of white blood cells and their phagocytic enzyme indicates the development of candidiasis. It is recommended to conduct additional research and do bacteriological culture.
If an inflammatory process is detected, pregnant women are prescribed a special therapeutic regimen using drugs that have an established safety profile for the embryo.
In this physiological state, a slight increase in leukocyte esterase is normal, due to the protective functions of white blood cells, as well as compression of the bladder against the background of decreased muscle tone.
If the indicator is very high, it is worth paying attention to the content of protein components and red blood cells in uric acid. A comprehensive assessment will allow timely diagnosis of inflammation of the kidney tissue, in which such a clinical picture is observed. 6-8 units/μl of uric acid is normal during pregnancy.
Treatment
Treatment directly depends on the identified pathology and the established diagnosis. The goal of therapeutic measures is to eliminate the action of the factor that led to the development of this disease, etiological treatment (elimination of the root cause), leveling and reducing the intensity of the symptoms of the pathology. All this leads to a decrease in the manifestations of the disease and/or complete cure, which improves the well-being and level of functioning of patients.
Both conservative treatment methods and surgical measures are used.
Conservative treatment methods include:
- Pharmacotherapy. In this case, the therapeutic effect is achieved using drugs from various pharmacological groups. Most often, for diseases of the urinary system, drugs from the groups of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, hormonal (glucocorticosteroids), diuretics, etc. are used.
- Diet therapy. Depending on the pathology, a certain dietary table is prescribed (for example, diet 7A, 7B, etc.).
- Physiotherapy.
In severe cases or if conservative treatment is ineffective, surgery may be required.
Causes of increased leukocyte esterase
The level of hydrolytic enzyme in urine is affected by pathological disorders of various origins and localization. The leading role in a positive test result for leukocyte esterase belongs to cystitis.
Due to anatomical features, this disease is more common in women than in men. The cause of inflammation is the penetration of pathogenic pathogens into the bladder cavity.
Men are more often affected by urethritis, which is also associated with an increase in the hydrolytic enzyme of leukocytes in the urinary fluid.
Other common reasons include:
- urolithiasis;
- pyelonephritis – a complicated form of cystitis;
- interstitial nephritis - acute inflammation of the renal tubules;
- infectious prostatitis;
- tuberculosis;
- urogenital infections;
A slight increase in the level of leukocyte esterase is observed in chronic renal failure.
False results and their reasons
Physiological, hygienic and medicinal factors not associated with the development of the inflammatory process can increase the content of the hydrolytic enzyme of leukocytes in the urine.
The penetration of vaginal secretions into the biological material and the course of treatment with antibacterial drugs based on modified clavulanic acid distort the results of the analysis.
Increased concentrations of glucose and protein compounds can also artificially increase the level of leukocyte esterase. False-positive results are observed when urobilinogen (bile enzyme) is released into the urine and when taking cephalosporin antibiotics.
Leukocyturia and its types
Elevated leukocytes in the urine of a child or adult in medical practice are referred to as leukocyturia. The first classification is based on the clinical significance of leukocyturia, distinguished:
- true, when the cause of an increase in leukocytes in my child or adult is a pathology of the genitourinary system;
- false, when lymphocytes found in the urine are the result of improper preparation of the patient for the collection of biomaterial. For example, insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia in the presence of inflammation, minor injuries or bruises.
The dogma that human urine is sterile has not retained its relevance in the 21st century. Many studies have shown that moderate amounts of representatives of the normal microflora of the human body can be found in urine. However, leukocytes in the urine of infants and older children do not increase.
In this regard, leukocyturia of infectious and aseptic nature is distinguished. The first type is characteristic of infectious lesions of the urinary system, the second is the result of an allergic reaction, exposure to certain medications or glomerular nephritis (damage to the kidney glomeruli, as a result of which leukocytes diffuse freely into the urine in unlimited quantities).
Depending on the degree of deviation from the norm, leukocyturia is distinguished:
- insignificant - no more than 30 cells in the field of view of the microscope. It has no diagnostic value in the absence of concomitant symptoms of the disease. It can be triggered by improper preparation of the patient for the collection of biomaterial or daily fluctuations in all physiological parameters;
- moderate – up to 100 cells, typical for infectious infection of mild to moderate severity;
- severe - more than 100 leukocytes. The condition accompanies severe infectious and oncological diseases.
What should I do if my leukocyte esterase results are positive?
To clarify the diagnosis, a repeat test and additional examination are prescribed. Bacteriological culture is carried out. It helps to select an antibiotic to which the detected genotypes are highly sensitive.
An increase in leukocyte esterase is not an independent disease, but only a diagnostic sign that requires clarification. During the inflammatory process, in most cases, along with phagocytic cells, pathogenic microflora is recorded in the urine.
Prevention
The goal of preventive measures in this case is to prevent the development of diseases of the urinary system, as well as, in the case of already developed pathologies, to prevent the occurrence of complications.
Preventive measures include:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- Timely and adequate treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases (not only of the urinary system);
- Regular observation and conduct of prof. examinations by specialists;
- If there are any complaints or unnatural sensations in the area of the kidneys or other organs of the urinary system, you should immediately contact your doctor;
An important factor is mechanical contraception during sexual intercourse. You should also not have uncontrolled sex life. It is necessary to avoid casual sexual contacts, because urogenital infection can reach the kidneys through ascending spread. This will lead to the development of infectious inflammatory processes, which will be manifested in urine analysis by increased levels of leukocytes and leukocyte esterase.