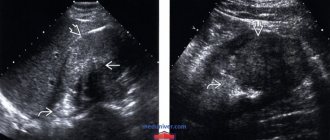
The formation, called “anechoic,” is an inclusion in any organ. It does not reflect, but rather absorbs the ultrasonic beam. The term itself does not indicate a specific diagnosis. This is just a property of this inclusion. An anechoic formation that appears can sometimes be normal, but in another case it can be a serious pathology.
Anechoic formation absorbs ultrasound radiation
In this article you will learn:
Concept of the term
To correctly understand the term, you need to remember what ultrasound is and what principle it is based on. The sound, which has a high frequency and is called “ultrasound,” cannot be heard by the human ear. The principle of operation of the device used to perform ultrasound is based on radiation and then processing of the reflected signal (reception of the so-called echo). The ultrasonic wave is generated by a transducer - a special sensor. It first produces it, and then reads a sound inaudible to humans, which is reflected from organs or other tissues. Depending on the frequency characteristics of the echo signal, a certain image appears on the monitor.
Dense tissues, as well as organs, appear light. Moreover, the higher this characteristic, the whiter the image on the screen. The densest tissues (bones) have the highest signal reflectivity.
If we translate the word “anechoic” from Latin, we get the term “incapable of reflecting sound.” Such inclusions appear as dark areas on the monitor screen. This property is inherent in liquid. In this regard, when performing an ultrasound, if dark areas are detected, suspicions of a cyst arise. This is what is usually filled with liquid.
During an ultrasound, an anechoic formation appears on the monitor as a dark area
How the research is carried out
To perform an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, the woman is naked to the waist, after which she lies flat on the couch, on the left side of the device. The procedure begins with an examination of the left breast, onto which a special transparent gel is applied (removes the air gap between the transducer and the skin).
Initially, the sensor is placed on the peri- and subareolar zones (around and above the nipple), where the doctor scans the breast in several positions. After examining the nipple area, the sensor begins to move from the periphery to the center clockwise. In this way, almost the entire area of the organ is assessed.
After completing the examination of the left gland, the doctor moves on to the right one. Sometimes, for better access, the patient is asked to turn on her left side, after which the condition of the glandular tissue of the mammary gland, its capsule, ducts, vascularization (blood supply) and surrounding structures is assessed using the previous algorithm. It is possible to perform an ultrasound in a sitting position.
How often can you do it
Despite the fact that ultrasonography is recognized as a safe method of functional diagnostics, the study should be done according to medical indications. Often the procedure is prescribed as a control for the treatment of the inflammatory process, before, during and after a puncture biopsy of the cyst.
Reasons for formation
Factors influencing the formation of an anechoic formation largely depend on its location. Causal factors vary significantly from case to case. It depends on the organ in which the process developed. A cyst that has an anechoic property often appears at an age considered reproductive. After menopause, it occurs much less frequently. Ovarian tumors in this case are rare due to decreased estrogen levels. In this case, the formations are more often benign in nature.
It is not always possible to pinpoint the exact cause of tumor growth.
The most common factor is considered to be hormone imbalance. It has a bad effect on the performance of the ovaries. After menopause, a cyst in the ovaries is possible due to inflammation, postoperative adhesions, or injury.
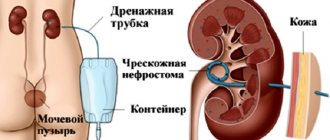
Urologists also cannot explain the reason for the appearance of a renal cyst. But some nephrologists argue that the culprit for the appearance of cystic elements is the improper development of the fetus in the mother’s womb. In addition, these formations can occur due to inflammation of the renal pelvis, stones formed in the kidneys, as well as due to infection of the organ.
Cysts on the ovaries most often form during reproductive age.
Ultrasound folliculometry on day 16
We started planning in January of this year. Until April 2014, I drank Yarina for 7 years. Then in April I quit, my first period came on time, the second didn’t come for two months, then it started on its own, the third came after 35 days on its own, and then disappeared from August to December, I went to the gynecologist, she said to call Duphaston, I called and then she said drink them for 3 months from 16-25 days of the cycle. She prescribed me to take hormones (the results are in my diary), she said that everything was basically normal, except for 17OH progesterone, which was a little too high. Ultrasound reveals multifollicular ovaries.
There was no ovulation during that cycle according to ultrasound.
I had an ultrasound done on day 16 of this cycle.
The uzistka says there won’t be ovulation, start drinking DUFASTON again. Why do I need it, maybe ovulation will be later (I think maybe my ovulation is late (because ovulation tests (the strip was just brighter than the control) I did and I feel sure that ovulation occurred when my periods came twice).
I’m at a dead end, I don’t know what to do. The gynecologist will tell me to stimulate myself, but I’m thinking maybe I shouldn’t start Duphaston this time, wait for my ovulation, or at least see when my period comes (Try to get pregnant yourself for a couple of months, don’t take any pills. Girls, has anyone had something similar???? Please advise(((
Ultrasound, today, is perhaps the main method for confirming and diagnosing problems with the female genital area. As a result of the examination, the doctor receives a visual picture of the pelvic organs and has the opportunity to assess their structure, shape, size, presence or absence of foreign inclusions. As a rule, the description of organs received from a diagnostician is more or less understandable even to patients who are inexperienced in matters of gynecology. Almost everyone knows what ovaries or uterus are, but a rare patient is familiar with the term M-echo. What is M-echo in relation to the female reproductive organs, and what are its standards?
Locations
Anechoic contents appear directly in the cyst itself in many cases. The tumor may appear in the following organs:
- Breast. Here the cyst is often found. If it is homogeneous, then it represents a dark area on the monitor screen. A complex cyst is visible during ultrasound in the form of objects with hyperechoic content. In the latter case, the mammologist necessarily conducts additional diagnostics to exclude a cancerous tumor. The contents can be formed due to hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorders, mechanical injury or inflammatory process in the organ.
- Thyroid. Here doctors can detect an anechoic avascular formation or adenoma, true, colloid, or pseudocyst. In order to determine the nature of the contents, the patient is prescribed tests.
Cysts in the mammary glands can form as a result of hormonal imbalance in women
- Uterus. This formation directly in the uterus can be detected during ovulation, degenerative diseases, leiomyoma, or in the period before menstruation. If such contents in the cervical area are small in size (less than 5 mm), then this is the norm for women who have given birth. The development of anechoic formation in this organ is also possible with cancer. Cases have been recorded when the contents were found in the fetus (a cyst was detected).
- Ovaries. An identified object in them often indicates the growth of a cyst. It may have a different structure. Often, the doctor suspects the development of a teratoma, cystadenoma (benign neoplasm) or cystadenocarcinoma (malignant neoplasm).
Small cysts located in the cervical area are considered normal for women who have given birth.
- Kidneys. In this organ, such content is a cyst, which is a round anechoic formation with rather thin walls. In the presence of polycystic disease, many of these formations are observed, and the kidneys are enlarged. Formation is often observed in abscesses, perinephric hematomas and cystic carcinoma.
- Liver. The presence of an echo-negative structure in the organ also indicates a cyst. Often additional diagnostics are required to obtain a complete picture of the pathology.
There are not only single-chamber, but also multi-chamber anechoic formations, which are also detected in the ovaries. The cyst can be single, but in many cases it is detected as multiple neoplasms.
Avascular cysts of the mammary glands
A breast cyst is a common, single or multiple pathology of the mammary gland cavity with liquid-like contents formed in the ducts. Usually, the disease is asymptomatic for a long time, and only after time does pain and burning sensations appear in the mammary gland.
These symptoms are worse before and during menstruation. A breast cyst is accompanied by inflammation and suppuration of the cystic cavity. The disease itself rarely degenerates into cancer, and, nevertheless, has an increased risk of developing a neoplasm. Often accompanied by dishormonal pathologies occurring in the sexual sphere.
Large cysts change the shape of the breast.
Physiologically, a cyst is a cavity bounded by a connective capsule and filled with non-inflammatory fluid. This pathology is a consequence of fibrocystic mastopathy.
The cavity is formed due to the enlargement of one gland duct, the accumulation of secretions and the gradual formation of a fibrous capsule. New growths are round, oval or irregular in shape.
The size ranges from a few millimeters and in difficult cases reaches five centimeters. An ordinary cyst has smooth and absolutely even internal walls.
As for the atypical cyst, on its walls it has growths inside the cavity.
Cysts can be either single or, in more complex cases, multiple. In polycystic disease, numerous cysts of different sizes combine to form multi-chamber clusters. The altered cystic tissue can occupy half or more of the gland tissue.
The cyst cavity may consist of benign cells, but it may also contain malignant cells.
A fatty cyst that is not associated with secretory tissue can develop in the chest area. It is formed as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland and its overflow with secretions. This disease is not a cause for concern.
The development of cysts in the mammary gland is influenced by hormonal balance. With excess production of estrogen and skewed hormonal balance, as well as when taking hormonal contraceptives, a disorder of sex hormonal regulation may develop, which leads to the formation of a cyst.
The development of cysts is provoked by: pathology of the thyroid gland, mastitis, ovarian dysfunction, inflammation of the genital organs.
The cysts are small in size and very rarely bother the patient. They are most often detected by chance, after undergoing a mammogram. Enlarged cystic formations cause pain, the mammary glands can be felt, and this manifests itself a few days before menstruation.
Large cysts filled with secretion are manifested by constant pain, pulling sensations, burning, and uneven compactions.
Breast cyst clinically manifests itself regardless of the menstrual cycle. Huge, giant cysts are defined by visible deformation of the mammary gland, redness and even bluishness of the skin.
Any inflammation in the cyst is characterized by fever, redness of the skin, and slight or even large enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes.
Palpable pain in the chest area.
Burning and pulling sensations.
Breast deformation.
Hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body is not uncommon. At such a moment, the ovaries secrete a higher than normal amount of estrogens, the main female sex hormones. This is what leads to tissue proliferation under the influence of estrogens, the epithelium of the mammary gland ducts, and swelling of its tissues. Such processes clog some ducts and form cysts.
In practice, a cyst is the main element of fibrocystic mastopathy. If the disease is diffuse in nature, i.e. equally distributed in the mammary glands, many small cysts appear. Nodular mastopathy is characterized by large nodes.
The female hormonal system is neurohumoral and controlled by the central nervous system. Any impact may cause the system to malfunction. The neurohumoral system is most sensitive to all kinds of psycho-emotional stress. First of all, the development of cysts is influenced by:
Long-term intellectual loads.
Constant emotional stress.
Frequent worries and stress.
Sensitivity to problems.
Abortion deals the biggest blow to the endocrine system. They are the ones who can cause problems in a woman’s body. Frequent abortions disrupt the functioning of the ovaries, provoke the release of large amounts of estrogens, and the maturation of cysts.
An increase in estrogen can cause excess weight, especially obesity. Since adipose tissue cells promote the production of estrogen, in obese women, the chances of developing hormone-dependent diseases increase.
Poor nutrition is another main cause of hormonal imbalance. Poor nutrition causes metabolic disorders, which sooner or later will affect the neuroendocrine system. Other endocrine glands and their work also affect the condition and activity of the mammary gland.
Any thermal procedures and ultraviolet rays stimulate the production of estrogen.
The formation of a cyst in the mammary glands can be caused by any injury. The risk of neoplasms also increases after surgery. Since breast tissue is very thin, it reacts to any physical impact. The use of oral contraceptives is a predisposing and common factor in the development of cysts.
Source: https://sklad-kotlov.ru/kista-molochnoy-zhelezy/avaskulyarnye-kisty-molochnyh-zhelez/
Anechoic formation that appears during pregnancy
During pregnancy, this formation is often detected at short notice:
- Before the sixth week of gestation, the baby is found at the top of the uterus. This is a fertilized egg. When performing an ultrasound, a hyperechoic rim is visible at the edges of the formation.
- In the ovary, a dark spot indicates the presence of a luteal or sometimes a follicular cyst. These formations subsequently resolve on their own.
- Ultrasound shows the same picture with the formation of a paraovarian cyst - a cavitary single-chamber neoplasm. It grows from the ligaments connecting the ovaries to the uterus.
During an ultrasound, the corpus luteum is also identified as a black spot. Thus, when identifying formations in the uterus, you should not panic. A dark spot may indicate the development of a normal pregnancy, indicate a corpus luteum or the appearance of a cyst that will disappear without intensive treatment.
Luteal and follicular cysts do not require treatment and resolve on their own
Is a follicular cyst dangerous?
The follicular type of cyst has the appearance of a single-chamber formation and can reach a diameter of up to 10 cm. As a rule, it is a single anechoic avascular formation with a thin capsule and liquid contents of uniform consistency. They have a characteristic feature of arising without specific reasons and, just as unexpectedly, after some time they resolve on their own. But if such a formation is diagnosed, it is better to regularly monitor its changes through ultrasound monitoring.
Corpus luteum cyst: what is it?
When a woman’s body prepares for ovulation, a special internal secretory gland is formed in it, designed to synthesize female sex hormones. It is she who is the yellow body. Both the formation itself and the functional cysts that arise on it are not capable of harming a woman’s health. They usually begin to regress 2-3 months after their appearance. It is recommended to remove such an anechoic avascular formation in the ovary, determined by ultrasound, only if its size exceeds the maximum permissible norms.
Diagnostics
To make an adequate diagnosis, doctors prescribe an ultrasound examination. However, it is often not enough. It is necessary to use additional diagnostic methods, which are:
Sometimes patients are given a blood test to determine their hormone balance. And to exclude the presence of a malignant tumor, the doctor writes out a referral for Doppler ultrasound.
If an anechoic area is detected, then most often the patient undergoes additional diagnostics a month later. Only after confirmation of its presence is the necessary therapy prescribed.
Treatment methods
The type of treatment chosen by the doctor depends on the stage of development of the tumor. Sometimes, when a cyst is detected, for example, in the ovaries, therapeutic intervention is not required. The types of therapy used in medicine are summarized in the table.
| Type of treatment | Methods used |
| Waiting tactics | This method is used only when identifying the functional type of formation. Most often, it disappears on its own after a period of several months. Therefore, the doctor is monitoring. If it does not go away, then medications are required. |
| Conservative therapy | Hormonal treatment is used. It is necessary to reduce the production of sex hormones. Oral contraceptives are used. The menstrual cycle and ovarian function are restored. |
| Surgical intervention | The method is used in the absence of the expected result or when the cyst degenerates into a cancerous tumor. |
| Aspiration method of therapy | It is used when the cyst has no signs of cancer. Using a nozzle used for puncture, its contents are removed from the formation. After which ethyl alcohol is poured into the growth, which destroys it. It is possible to use a special solution. |
The first stage of treatment is eliminating symptoms. In addition, doctors prescribe hormonal medications and iodine preparations. Medications must be prescribed by the attending physician. For these diseases, self-medication is prohibited, as it can cause negative consequences. Drug therapy is carried out only in cases where the cyst is small in size and does not grow. If it enlarges or becomes infected, doctors prescribe surgery.
Complications and prognosis
If the visit to the doctor occurred at an early stage of development of the anechoic area, then the patient can get rid of it quite quickly. Only a doctor, after conducting research, will be able to say whether this structure is pathological or not.
If the formation is not treated, some complications may develop, including:
- in the uterus there may be bleeding, death of tissue of the myomatous node;
- hydronephrosis or uremia, peritonitis or renal failure, as well as cancer may develop in the kidneys;
- in the liver - hepatomegaly, suppuration and even rupture of the formation;
- In the thyroid gland, the manifestation of cystic goiter, hypo- or hyperthyroidism, and osteoporosis is possible.
A detected benign neoplasm in the mammary gland rarely becomes malignant. If it is small in size, it does not pose a danger. Usually complications arise only in the presence of inflammation and suppuration of the cyst.
Encyclopedia of Ultrasound and MRI
This is the name for an inclusion in any organ of the human body that does not reflect ultrasound. This is not a final diagnosis, but only a description of the object being studied in a particular organ. Anechoic contents may be normal or pathological. In many cases, this depends on the anatomical features of the organ being examined.
Important! “Anechoic” means one that does not reflect ultrasound. On ultrasound diagnostics, such formations appear as objects of a darker color. Echogenicity, as well as echostructure, are the main concepts of ultrasound, as they are used in the study of any organ.
Anechoic contents and anechoic structure: what do they mean?
The echogenicity of a particular structure depends on its properties to absorb and reflect ultrasound. And this is due to the morphological features of the structure of the organ. This pattern is expressed in the following: the less liquid the object under study contains, the higher its echogenicity and it will be noticeable on the screen as a bright spot. Again, the more fluid it contains, the lower its echogenic properties, and it will appear dark in color on the screen.
An anechoic object is a sign of normality. Thus, during different periods of the monthly cycle, an echo-negative object may be in the ovary. This is the corpus luteum, a cyclically formed ovarian gland . Without it, the egg would not form. This body is impenetrable to sound and therefore appears dark on screen.
After the end of menstruation, the anechoic inclusion can be defined as the corpus luteum. If your period is late, it may indicate pregnancy.
Remember! Education with echo-negative properties can occur in many organs. When a doctor gives such an opinion, he does not make a final diagnosis. This will be done by other doctors who prescribed such a diagnosis.
An anechoic inclusion may be found in such organs.
Mammary gland If during diagnosis it was found in the mammary gland, most likely it is a cyst. In breastfeeding women, this may be a cavity that contains milk.
Breast cysts on ultrasound image
When the mammary gland contains a homogeneous cyst, it appears as a dark-colored object. A complex cyst is visualized as areas with hyperechoic inclusions. Then further diagnostics are carried out to exclude the presence of breast cancer.
Only a mammologist can determine exactly what a particular breast formation is.
Thyroid gland Anechoic formation in the thyroid gland can be:
- cyst (in this case it is a round formation with anechoic properties);
- false cyst (its walls are formed by glandular tissue, and the formation itself has a flocculent structure);
- adenoma (it has different visualizations, depending on its internal composition);
- colloid cysts are formed primarily from a lack of iodine in the diet).
Colloid cyst of the thyroid gland
To accurately determine the nature of the anechoic formation of the thyroid gland, additional tests are prescribed.
Uterus An anechoic formation of the uterine cavity is formed in the following cases:
- during the period of ovulation - this is fluid from the follicle (a variant of the physiological norm);
- with leiomyoma;
- for degenerative pathologies;
- when a hematoma forms in the suture area;
- before menstruation.
In the cervix of the uterus, an anechoic formation is observed in the following cases:
- if it is small (up to five millimeters) in size - this is the norm, this happens in women who have given birth;
- with a cyst;
- as a result of self-healing of ectopia;
- with an endometrial cyst;
- for cervical cancer.
There are cases of detection of an anechoic formation in the fetus. This is probably a cyst, but only a doctor can determine the final version.
Ovaries
An anechoic object in this organ indicates the presence of a cyst.
They are like this:
- follicular - with a dense structure and clear boundaries;
- endometrioid - with a hard capsule, with heterogeneous contents;
- serous (often this can be a manifestation of a more serious disease).
Serous ovarian cystadenoma on ultrasound
During pregnancy
This formation can also occur in pregnant women. If it is detected before six weeks, it is most likely a fetus. Luteal and follicular cysts are most often found in the ovary.
Kidneys Anechoic formations of the kidneys indicate that they contain a cyst. It is always anechoic, has thin walls and smooth borders, and is always round in shape. With polycystic kidney disease there are always a lot of such formations. At the same time, the kidneys increase in size.
Due to inflammatory pathologies, as well as some types of nephropathies, formations with heterogeneous echogenicity arise. Typically, such a conclusion from a sonologist indicates the need for further diagnostics.
There may be an anechoic formation near the kidney. This is a sign of a perinephric hematoma. The outlines of the organ are preserved.
Transcapsular rupture of the kidney: a- perinephric hematoma.
Finally, the presence of an echo-negative formation in the kidney indicates the presence of a cancerous tumor. As a rule, the contours of such a formation are unclear. Renal abscesses have the same contours.
Liver
Again, the presence of an echo-negative structure in the liver indicates the presence of a cyst. A simple cyst always has a round shape and gives a shadow. Other variants of such formations, as a rule, require additional diagnostics.
What does anechoic formation mean?
Often it indicates the presence of a cyst. Small cysts (up to five centimeters in diameter) regress after a few months. However, a cystic formation of a larger diameter turns out to be tolerant to treatment with special drugs. The treatment tactics are chosen only by the doctor, based on the patient’s characteristics.
Anechoic formation in patients over 50 years of age often indicates the malignant nature of the process. If we are talking about cancer, then prolonged deliberation about treatment becomes life-threatening.
Immediate treatment is prescribed when the tumor has caused complications in the kidneys: pyelonephritis, urolithiasis or arterial hypertension.
Avascular formation in the mammary gland - what is it?
What is avascular formation in the mammary gland and what are its consequences? The female breast consists of glandular structures and subcutaneous tissue. In the absence of pathology, the mammary gland has a homogeneous structure and smooth, clear contours.
However, on an ultrasound examination of the breast, a specialist can diagnose black shadows. These are hypoechoic formations. It is important to understand that avascular formations are just a description of the diagnosed picture.
This is not a diagnosis of a disease or a symptom of it.
Vascularization of the breast
The medical term “vascularization” itself implies the formation of new blood vessels in organic tissue. Their growth is associated with a rapid increase in organ volume, various diseases, and hypertrophy. Vascularization of the mammary gland is often observed with malignant neoplasms.
Increased vascularization can be diagnosed with increased production or decrease of certain hormones, hormonal imbalance, hyperfunction. Doctors identify several neoplasms in the mammary gland:
- cyst
- fibroadenoma
- lipoma
- avascular formation
A cyst is a cavity filled with fluid. Fibroadenoma develops from the fibrous structures of the organ. Lipoma is a tumor that is localized in fatty deposits. Avascular formation is a tumor without blood vessels and, in fact, blood supply.
Hypoechoic avascular formation: characteristic features
Many organic tissue structures are hypoechogenic. These are low density fabrics. In the mammary gland, low tissue echogenicity is not always a specific symptom of the disease. From a medical point of view, hypoechoic structures are a deviation from the norm (ICD-10 code).
The pathology is most common among women. The presence of a hypoechoic avascular formation indicates the development of:
- cysts
- adenosis
- glandular carcinoma
- benign tumor
- fibrocystic mastopathy
- fibroadenomas
A hypoechoic avascular formation has no capillaries and is a benign tumor. It may resemble cancer; the formation has clear boundaries. If the contours of the spot are blurred during examination, doctors diagnose adenosis.
A distinctive feature of the tumor is the darkened structure of the mammary gland. During ultrasound examination, pathological cells slow down the passage of the wave.
This is especially true for cysts with fluid. It is impossible to diagnose a cyst right away. After the ultrasound, a number of additional examinations and tests are required.
Sometimes the lump may be a tumor or galactocele.
Since when the gland is avascular, there is no blood supply to the tumor, it cannot degenerate into malignant. There is also no risk of its rapid further development.
Anechoic avascular formation: features
On the monitor during ultrasound examination, the anechoic formation looks like darkened roundness. These structures also do not allow ultrasound to pass through, so a specialist will quickly notice them during the examination. The formations are often benign in nature, but over time they can develop into malignant ones.
Focal pathology usually consists of soft, loose tissue. With the deposition of calcium salts, the echogenicity of the structures increases. The pathology is usually diagnosed as a cyst or galactocele.
Causes
There are certain factors that provoke changes in the structures of the mammary gland. Experts often associate the appearance of tumors with hormonal imbalances.
The outbreak occurs in the female breast for the following reasons:
- excess estrogen production
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives
- hormone replacement treatment
- thyroid diseases
- inflammation in the fallopian tubes
- ovarian diseases and dysfunction
- operations
Stress and depression can be prerequisites for the development of a tumor. They cause hormonal imbalances and affect hormone levels in the body. Provoking factors are also obesity and poor nutrition.
Symptoms
A tumor in the mammary gland does not cause any discomfort to a woman for a long time. Pathology can only be detected using ultrasound and additional Doppler mapping of the color circulation. As the tumor progresses, some breast lumpiness appears. A lump inside the breast can be detected by palpation.
Symptoms of a tumor also include:
- hyperemia of the skin
- breast tenderness
- feeling of fullness of the mammary gland
- burning
- breast deformation
- the appearance of discharge from the nipple
Sometimes the severity of symptoms depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. When infected, the temperature rises, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and the pain intensifies.
Diagnostics
A qualified specialist will help diagnose focal formation. The doctor will palpate the chest and send you for the necessary examination. You will need to be tested for estrogens, thyroid-stimulating hormonal substances, and prolactin.
An ultrasound scan of the mammary glands and genital organs is mandatory. Mammography, MRI, and Doppler sonography are also prescribed. If a tumor is suspected of being malignant, a biopsy is performed. The biomaterial is collected and histologically examined in the laboratory.
When a pathology is detected, a test for the tumor marker CA-15-3 is sometimes prescribed. Additionally, differential diagnosis is carried out.
How to treat
Therapy is prescribed only after a complete examination. For cysts and benign formations, comprehensive drug treatment is advisable. The following are used in therapy:
- anti-inflammatory drugs
- hormonal drugs
- herbal collections
To eliminate fibrocystic formation, the drugs Indinol and Fitonol are prescribed. They can be used for all types of tumors. Among hormonal drugs, medications containing gestagen and estrogen are prescribed - Duphaston, Estrogel, Utrozhestan.
To saturate the body with useful substances, various vitamin and mineral complexes are used. It is also important to provide adequate nutrition. It is recommended to eat a large amount of vegetables and fruits.
Effective homeopathic remedies are widely used as adjuvant therapy. Cyclodinone or Mastopol are taken for one month. Surgery is recommended when diagnosing a malignant tumor.
Traditional medicine can be used in complex treatment. Leaves of coltsfoot are applied to the lesion overnight. Then the chest is wiped with burdock oil in the morning.
You can prepare a healing mixture of honey, burdock rhizomes and castor oil. The compress with this homogeneous mass is left overnight. It is also recommended to make compresses on the chest with crushed pumpkin. To relieve pain and inflammation, a whole cabbage leaf is applied to the chest at night.
QUESTIONS ANSWERED BY SKVORTSOV VITALY ALEXANDROVICH, kmn, mammologist, plastic surgeon, oncologist of the State Clinical Oncology Department
QUESTION: Good afternoon! According to the results of ultrasound, in the upper inner quadrant on the left at 9 o’clock, 4 cm from the nipple, there is a hypoechoic formation with a fuzzy, uneven contour of 0.9X0.
7 cm, color circulation in which blood flow is visualized. The lymph node on the left is enlarged 1.5X0.7, the contours are clear and even. According to the ultrasound, there are signs of a space-occupying lesion in the right mammary gland (SUSP?), left-sided lymphadenopathy.
Doctor, is it cancer? What should I do? Where to begin?
ANSWER: Hello! Possibly cancer, but perhaps not! You need to get a mammogram, contact an oncologist, and he will refer you further! Usually a biopsy is done if possible! Immunohistochemistry is done.
According to ultrasound, your tumor is small, but there is an enlarged node in the armpit; sometimes such treatment begins with chemotherapy if the diagnosis is confirmed! In general, you need to be further examined and diagnosed.
It can also be a benign tumor with an enlarged lymph node. We need to figure it out!
QUESTION: Vitaly Alexandrovich, what is a hypoechoic formation in the mammary gland? This is according to the description of breast ultrasound.
ANSWER: Hello! This is a tumor and it is necessary to establish its nature: benign or malignant, then undergo the necessary treatment! To do this, you need to contact an oncologist.
QUESTION: Vitaly Alexandrovich, please tell us what an anechoic formation in the mammary gland is. Should I be worried about this?
ANSWER: Hello! This may be a malignant tumor and therefore you need to contact an oncologist to perform a puncture or biopsy of the formation! Next, you will be prescribed appropriate treatment!
QUESTION: Vitaly Alexandrovich, in the description of the ultrasound of the mammary glands it is written that in the axillary region the lymph node is hypoechoic. What does this mean? And is there any reason to worry? Thank you.
ANSWER: Hello! There is reason for concern; it needs to be verified to exclude a metastatic process!
QUESTION: Vitaly Alexandrovich, what are reactive lymph nodes? Thank you.
ANSWER: Hello! This means that they responded to some kind of disease or infection, and are not tumorous!
QUESTION: Vitaly Alexandrovich, hello! What is an anechoic formation in the mammary gland? Thank you.
ANSWER: Hello! It could be a cyst or other benign tumors; usually the ultrasound doctor gives an approximate conclusion about its nature!
QUESTION: Vitaly Aleksandrovich, according to the ultrasound description, the ultrasound shows a hypoechoic formation with an acoustic shadow with uneven edges, 14X17 mm. Could this be breast cancer? Should I do a biopsy?
Source: https://probotox.ru/venerologija/avaskuljarnoe-obrazovanie-v-molochnoj-zheleze-chto.html
The nature of the anechoic neoplasm
What is an anechoic formation? This is a situation in which there is the presence of a foreign body in the breast tissue, surrounded by a cavity. Thus, healthy tissues are protected from the negative effects of painful neoplasms. In accordance with ICD-10, code N63 “Unspecified formation in the mammary gland” was assigned.
If we turn to medical terminology, the word “anechoic” means how well a tumor-like inclusion can reflect ultrasound waves emitted by an ultrasound machine. The denser the structure of such a body, the higher the throughput of its tissues.
Focal neoplasms have the greatest echogenicity, but the air is considered anechoic, since it practically does not have the ability to reflect ultrasound.
In 99% of cases, an anechoic formation is benign in nature, and it can be:
However, under the influence of some negative factors it can turn into a cancerous tumor. True, the danger of such a change is very small, since the cyst can eliminate itself under the influence of hormonal fluctuations in the female body.
In addition, experts emphasize that an anechoic inclusion in the mammary gland is not considered a diagnosis, but only a preliminary result obtained during an ultrasound scan. In other words, the examination showed that there is some kind of deviation in the breast, but at this stage its exact nature is not yet known.
Types and forms
There are several types of anechoic neoplasms in the mammary gland:
- Cystic. They have a smooth and rounded configuration with distinct boundaries, and the contents inside are uniform and dark. If cysts are present in the plural, then this is most often a symptom of mastopathy.
- Solid. This type of echogenic formations in the mammary gland includes tumors and abscesses. They are characterized by an impenetrable structure and most often they have an irregular round or elongated shape, inside of which particles of different densities may be present.
- Mixed. They are characterized by an unfavorable course, and their structure has various variations.
Ultrasound allows you to identify the following types of tumor formations:
| Types of neoplasms | Characteristics |
| Cyst | Does not cause painful discomfort. In almost 99% of situations it is benign, but under favorable conditions it can become a precancerous condition. |
| Galactocele | A fatty cystic sac filled with homogeneous milky contents. Occurs in lactating women. Often not dangerous. |
| Fibroadenoma | Benign tumor. Most often diagnosed in young women as an iso- or hypoechoic formation. It has smooth, regular shapes and is enclosed in a thin capsule. |
| Oleogranuloma | Neoplasm of benign nature. Usually formed after a breast injury due to increased friability or necrosis of breast tissue. The peculiarity of oleogranuloma is that its internal contents consist of necrotic cells. Obvious signs are pain, deformation of the nipples and breasts, bloody exudate from the nipples. |
| Malignant tumor (cancer) | It has a significant volume and diffuse structure. When performing an ultrasound, attention is paid to its shape, density, size and degree of growth deep into the tissue of the mammary gland. A cancerous tumor is characterized by the presence of various inclusions, as well as a basic or mixed type of blood flow. |
Features of the condition
When examining a standard cyst, the doctor describes it as a homogeneous formation. If the cystic bodies have any special differences, then they are noted as hyperechoic inclusions. However, all these records do not confirm or reject the presence of cancer cells in the cysts. Malignancy can only be confirmed by biopsy.
Particular attention is paid to tumor bodies that have:
- uneven contour;
- additional inclusions;
- deformation elements.
It should be noted that avascular type tumors are pathological elements characterized by the absence of a vascular wall, so the possibility of their transformation into oncology is almost zero.
As a rule, malignant tumors have many vascular branches through which nutrients enter the tumor itself, thereby promoting its growth. In this clinical situation, biopsy and histology are necessary.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands with colorectal dosage: what it is and how it works, cost, reviews
Benign and malignant neoplasms occupy a leading place among all pathologies of the mammary glands.
The most effective and reliable diagnostic method for women of reproductive age is considered to be ultrasound of the mammary glands with Color Doppler. Sonographic examination in Doppler mapping mode makes it possible to identify small (more than 1 cm) tumors and make a differential diagnosis between a benign process and cancer.
Ultrasound of the breast with colorectal dosage – what is it?
Any echography (ultrasound) is based on the ability of human tissues and organs to reflect high-frequency ultrasonic waves emanating from a special sensor of the device. The transducer converts the signal into a gray scale image and displays it on a regular screen, which allows the diagnostician to assess the condition of the internal organs.
What is this - ultrasound of the mammary glands with color circulation? The Color Doppler mapping mode is aimed at studying the state of blood vessels and assessing the speed of blood flow in them.
When this function is turned on, the gray image of an organ or formation rich in blood vessels is painted in different colors (blue, red, green, etc.).
The method works on the ability of blood cells to reflect ultrasound (Doppler effect).
Indications for use
Indications for the use of ultrasound in Doppler mapping mode:
- the presence of palpable lumps and pain in the chest;
- the appearance of pathological discharge from the nipples;
- suspicion of the appearance of tumors, relapse of cancer;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes for the mammary glands (sub- and supraclavicular, axillary);
- changes in the nipple (retraction, appearance of a “lemon peel”) and the appearance of one or both glands;
- as a screening examination for hereditary predisposition to breast cancer in women under 45 years of age;
- detection of genital, extragenital endometriosis, uterine fibroids, cervical dysplasia;
- monitoring the effectiveness of hormonal therapy;
- before and after plastic surgery (correction, implantation).
Men may be referred for ultrasonography of the mammary glands if gynecomastia is suspected, if a tumor is detected in the testicular tissue, or during long-term hormonal treatment (more about breast ultrasound in men).
Preparation for ultrasound of the mammary glands with color doppler
There is no special preparation for the study. You must have a disposable diaper and napkins with you to remove the gel. There is no need to treat the breasts in any way (with alcohol or other antiseptic).
You should also take with you a referral, an outpatient card or medical history, and previous ultrasound reports of the mammary glands, if any. The examination is absolutely painless and harmless.
On what day of the cycle is a breast ultrasound performed?
Such requirements are associated with the fact that the mammary glands, like the uterus, undergo a number of changes under the influence of hormones of the hypothalamic-pituitary system. In the first half, ducts, lobules and vessels are better visualized in them. After ovulation, the breasts swell, the milky ducts expand, and the blood supply increases. Such changes can significantly complicate diagnosis.
If a woman comes for a test in the second half of her cycle, the doctor will probably conduct the test. However, if cysts, tumors or galactoceles (dilation of intralobular ducts) are suspected, he may prescribe a repeat procedure immediately after the end of menstruation.
How the research is carried out
To perform an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, the woman is naked to the waist, after which she lies flat on the couch, on the left side of the device. The procedure begins with an examination of the left breast, onto which a special transparent gel is applied (removes the air gap between the transducer and the skin).
Initially, the sensor is placed on the peri- and subareolar zones (around and above the nipple), where the doctor scans the breast in several positions. After examining the nipple area, the sensor begins to move from the periphery to the center clockwise. In this way, almost the entire area of the organ is assessed.
After completing the examination of the left gland, the doctor moves on to the right one. Sometimes, for better access, the patient is asked to turn on her left side, after which the condition of the glandular tissue of the mammary gland, its capsule, ducts, vascularization (blood supply) and surrounding structures is assessed using the previous algorithm. It is possible to perform an ultrasound in a sitting position.
How often can you do it
Despite the fact that ultrasonography is recognized as a safe method of functional diagnostics, the study should be done according to medical indications. Often the procedure is prescribed as a control for the treatment of the inflammatory process, before, during and after a puncture biopsy of the cyst.
Results of breast ultrasound using colorectal dosage
It should be understood that normally in prepubertal girls and menopausal women, adipose tissue predominates in the structure of the mammary glands. This is due to the influence of hormonal levels. Most of the breasts of women with active reproductive function are represented by the glandular component (lobules and ducts).
Possible pathologies of the mammary glands and their ultrasound signs:
- Galactocele (dilation of part of the intralobular duct). Often observed after injuries, breastfeeding. On the screen, an expanded hypoechoic liquid formation is detected in the thickness of the lobule.
- Fibroadenoma (a benign tumor of connective and glandular tissue) is visualized as a round or oval formation with clear contours. Has a homogeneous structure, reduced or slightly increased echogenicity; a peripheral type of blood flow is characteristic (when the vessels surround the tumor during CDB).
- Mastitis (acute inflammation of the gland). The doctor detects a diffuse change in the echogenicity of the breast tissue, expansion of a large number of ducts, increased blood flow and swelling of the skin and subcutaneous fat.
- Breast cancer . These can be single or multiple formations of various sizes, irregular shapes, with bumpy contours, and a heterogeneous structure. Often they reveal calcifications (small hyperechoic dots) and a mixed type of blood flow. Changed lymph nodes are often detected.
In addition, cysts, lipomas, adenomas, and age-related involutive changes are detected.
What are the advantages of the method, the specialist explains in this video.
Advantages of ultrasound with color circulation
Ultrasound of the mammary glands is the method of choice for diagnosing the pathology of this area in women of reproductive age. The survey has a number of advantages:
- no need for preparation;
- relatively low cost;
- the ability to perform on an outpatient basis, “at the patient’s bedside”;
- highly informative, harmless and painless.
Possible contraindications
There are no contraindications to breast ultrasonography. The exception is a common pustular lesion of the skin in this area, which is extremely rare.
Examination during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Ultrasound is harmless even during pregnancy and lactation. No special preparation is required from women, the indications are the same. At the time of breastfeeding, echography can be prescribed if there is severe pain and pathological discharge from the nipples, redness of the skin, or a sudden cessation of milk secretion.
What is the price
The price of ultrasound of the mammary glands with colorectal dosage in Moscow varies from 1000 to 3500 rubles (more details about where to undergo the procedure). The price includes the examination itself, the provision of a disposable diaper, wipes for removing the gel, and a doctor’s report.
Reviews
Reviews of the study are mostly positive:
“The procedure was quick and painless. Fortunately, everything turned out to be normal, although she complained of chest pain.”
Christina, 37 years old
“The first ultrasound revealed a small fibroadenoma, so far the doctors are just observing. I was pleased with the speed and high accuracy of the examination.”
Maria, 42 years old
Source: https://uzi.guru/myagkie-tkani/zelezy/molochnaya/vidy/uzi-molochnyh-zhelez-s-tsdk.html
Reasons for the development of pathology
Experts name several reasons contributing to the development of tumor-like anomalies in the structure of the mammary glands.
| Causes | Features of pathological influence |
| Chronic stress and negative emotions | Stressful situations provoke hormonal imbalance. There is an increased synthesis of progesterone, prolactin, cortisol and estrogens. In turn, excess levels of these hormones contribute to the manifestation of tumor-like bodies in the mammary gland. |
| Exposure to ultraviolet rays | Frequent and excessive taking of ultraviolet baths in a solarium or on the beach promotes the active production of estrogens. Excessive presence of these hormones causes the growth of tumor-like bodies in the breast. |
| Breast injury | Domestic bruises. Injury to the bust in an accident and other similar situations. |
| Abuse of high temperature procedures | Prolonged stay near a warm source, frequent visits to saunas, baths, and even the use of warm compresses can also lead to the development of a pathological process in a woman’s breast. |
| Operations | Breast surgery, including mammoplasty, sometimes leads to the appearance of cysts and other formations. |
| Genetic predisposition | The formation of tumor-like cavities can be inherited. |
| Hormonal imbalance | Most often, sharp hormonal fluctuations in the female body occur: - during puberty; - during pregnancy; - with the onset of menopause; - in the presence of thyroid disease. |
| Illiterate use of medications | Improper use of hormone-containing drugs, including oral contraceptives, often leads to an imbalance in the hormonal system, which can become a favorable situation for the manifestation of anechoic neoplasms. |
How dangerous is an anechoic neoplasm?
An anechoic inclusion in the mammary gland of insignificant size does not cause serious harm to the patient’s health. However, if infection enters its cavity and the subsequent development of inflammation and abscess formation can lead to a number of complications.
The following signs indicate the development of complications:
- Breast tenderness.
- Breast swelling.
- Hyperthermia.
- Uncomfortable feeling.
- Distinct deformation of the gland.
Two-chamber neoplasms create a more dangerous clinical situation, as they have an increased ability to transform into a malignant state. Multilocular cysts often contain growths that can only be removed surgically.
In addition, doctors do not exclude the possibility of the following clinical situation:
- Prolonged growth of the cyst can provoke the manifestation of mastopathy.
- Modification of a cyst into a malignant tumor, but such an anomaly occurs in isolated situations.
- The growth of the formation and its rapid increase in size can lead to compression of surrounding tissues, muscles and blood vessels.
If there is an anechoic inclusion in the breast structure, you should not worry or panic, since the possibility of malignancy is the same as in healthy women. If a tumor is detected in a timely manner, the treatment result is always positive.
Symptoms
A tumor in the mammary gland does not cause any discomfort to a woman for a long time. Pathology can only be detected using ultrasound and additional Doppler mapping of the color circulation. As the tumor progresses, some breast lumpiness appears. A lump inside the breast can be detected by palpation.
Symptoms of a tumor also include:
- hyperemia of the skin
- breast tenderness
- feeling of fullness of the mammary gland
- burning
- breast deformation
- the appearance of discharge from the nipple
Sometimes the severity of symptoms depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. When infected, the temperature rises, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and the pain intensifies.
Effect on the condition of the female breast during pregnancy and lactation
In some women, when carrying a fetus or breastfeeding, an anechoic inclusion forms in the breast tissue. How dangerous is its presence and how can it affect, for example, the quality of breastfeeding?
Experts note that during pregnancy, the appearance of a cyst itself is not as harmful as a hormonal imbalance, which most often provokes the formation of a cystic formation.
Doctors recommend that expectant mothers first get rid of the provoking cause, that is, regulate hormonal levels, and then eliminate the anechoic body. However, one cannot ignore its presence either, hoping that over time it will disappear on its own. Such inaction can lead to the development of:
- fibrocystic mastopathy;
- cystadenopapilloma (the presence of the latter increases the risk of cancer several times).
In relation to breastfeeding women, they are often diagnosed with a special type of cyst - a galactocele, which is of benign origin. The cavity of the neoplasm is filled with mother's milk. In some cases, such a cyst may appear after a woman abruptly stops lactation, or appears 8-10 months after the end of breastfeeding.
In this situation, treatment is required, since the tumor can cause mastitis and suppuration. However, the presence of a galactocele is not a reason to stop breastfeeding. The doctor will prescribe medications that will not harm the baby.
Types of cysts
Cystadenomas of an anechoic structure that occur inside or near the ovary are of the following types:
- follicular. Formed from a follicle. This element must rupture, then during ovulation the egg is released. In the presence of a follicular ovarian cyst, rupture does not occur;
- formation of the corpus luteum. Appear when fluid accumulates at the site where the egg exits the follicle;
- serous. They are smooth-walled growths formed from serous tissue that covers the ovaries and contains fluid inside;
- paraovarian. These forms of ovarian cysts are dense, form near the reproductive organs, and can reach large sizes.
Proliferating (cystomas) and non-proliferating (cysts) formations are formed in the body of the ovary. Cavities with liquid contents have different sizes: from 23 mm to 57 cm or more.
Cysts:
- follicular. The most common type of tumor formation. The reason for the appearance is a violation of the processes of reverse development after rupture of the follicle. There is liquid under the thin shell of the spherical formation. In most cases, with the onset of the next menstrual cycle, the follicular cyst resolves. Otherwise, drug therapy is required to resolve the cavity with fluid,
- dermoid. A rare type of benign formation. A congenital tumor is formed due to an incorrect process of ontogenesis. A specific feature is the presence of dysgerminogenic inclusions: skin, hair, teeth,
- paraovarian. A specific feature is the location of the cyst around the ovary. Liquid contents accumulate in the tissue of the gonad, an increase in formation occurs, neighboring structures experience pressure from the enlarged organ,
- Corpus luteum cyst. A specific formation is formed in the luteal (second) phase of the cycle, after the release of the egg. In some cases (against the background of hormonal abnormalities), the involution process occurs with disturbances. A thin membrane forms around the corpus luteum, and fluid accumulates inside. If the cyst does not resolve during pregnancy and grows to 6 cm or more, then surgery must be performed to prevent complications. When the cavity ruptures, hemorrhage occurs, acute pain in the abdominal area is disturbing,
- endometriotic. The cyst develops against the background of endometriosis (particles of the inner layer of the uterus penetrate into neighboring structures, grow, and provoke secretion in the tissues). When an endometrial (chocolate) cyst develops, menstrual blood accumulates inside. In the absence of treatment, an increase in tumor formation, rupture of the endometriotic cyst with spillage of liquid contents into the peritoneum is possible. The consequence is the development of a dangerous complication (peritonitis).
Cystoma:
- serous. A tumor formation is formed due to cell proliferation, accumulation of serous contents,
- cystadenoma or papillary cystoma. Formation formed from papillary epithelium. A cavity with a heterogeneous structure; during development, papillomas appear on the body. A dangerous type of cystoma, high risk of complications,
- mucinous. The formation develops against the background of proliferation of glandular epithelial cells. The mucous secretion mucin accumulates in the cavity.
Based on their morphological structure, there are several types of cysts:
- homogeneous formations with irregularly shaped partitions, complete or incomplete separation of chambers,
- element with low echogenicity and homogeneous structure,
- in the cavity of the formation there are zones with an average degree of echogenicity,
- in a homogeneous element there are smooth or mesh structures (closer to the walls of the cavity), each with a diameter of 10 to 15 mm.
On a note! Cystomas are multi-chamber formations; in the absence of timely treatment, the tumor grows, the diameter exceeds 810 cm. More than 80% of all neoplasms are benign, but when exposed to unfavorable factors, cell malignancy occurs and ovarian cancer develops.
Carrying out diagnostics
An anechoic formation in the mammary gland appears on the screen of an ultrasound device as an oval or round area that “beats” ultrasound signals. In this case, the boundaries of the body appear as clear, limited lines and do not have internal echogenic signals.
Usually the size of the cystic formation does not exceed 2-8 mm, however, if many cysts are observed, they often merge into one by dissolving the dividing membrane. In this situation, a tumor-like focus with multiple chambers and membranous particles will appear on the monitor.
As an additional examination, the following is used:
- Mammography.
- CT, MRI.
- Blood test for hormones, tumor markers.
- General blood sampling.
- General urine examination.
- Liver and kidney tests.
If the presence of malignant cells is suspected, a biopsy and histology are recommended.
Features of therapeutic therapy
Treatment is prescribed not immediately after an ultrasound scan, which showed the presence of an anechoic neoplasm in the cavity of the female breast, but on the basis of the data obtained from a full examination of the body.
As mentioned above, anechoicity is not a final diagnosis, but just a clinical picture that appears on the screen during an ultrasound scan.
Taking medications
Drug therapy is usually prescribed to help stabilize hormonal levels:
| Drugs | Name of medications |
| Vegetable origin | Phytolon. Indinol. Klamin. |
| Containing iodine | Iodomarin. Iodine active. |
| Anti-inflammatory | Diclofenac. Ibuprofen. Wobenzym. |
| Homeopathic | Mastiol Edas 127. Galium-Heel. Mastodinon. Mastopol. Cyclodinone. |
| Sedatives | Novopassit. Persen. Valerian. Phytosed. Motherwort. |
| Hormone-containing | Duphaston. Progestogel. Morning. Estrogel. |
| Vitamin and mineral complexes | Alphabet. Aevit. Complivit. Vitrum. Ascorbic acid. |
Application of surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is practiced in cases where the size of the cyst is more than 2.5 cm, the pathology is accompanied by discomfort and pain, and conservative therapy has not yielded positive results.
With a single formation, doctors advise the woman to remove it using sclerotherapy. The main essence of the operation is to introduce a special chemical substance into the cyst, which reduces its volume with further gluing of its walls. Manipulation is carried out using a thin needle.
If there are several cystic bodies whose walls thicken, sectoral resection under general anesthesia is prescribed. This operation is especially relevant if the patient has a history of oncology.
Therapy with folk remedies
An anechoic neoplasm in the mammary gland can also be treated using alternative medicine methods, but only with medical permission and when its origin is known exactly. Every woman, before using one or another traditional prescription option, should not forget that self-medication is fraught with serious complications, especially if the tumor is malignant.
For the preparation of home medicines the following are used:
- St. John's wort.
- Coltsfoot.
- Mint.
- Beet.
- Burdock.
- Cabbage.
- Carrot.
- Aloe.
| Means | Application |
| Herbal infusion | You will need 10 g of burdock and St. John's wort and 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 3 hours, strain and take 2 tbsp. before meals 3 times a day. |
| Beetroot compress | To prepare a compress, grind raw beets into a fine paste, measure out 100 g of mass and pour in 1 tbsp. apple cider vinegar. Apply for 1-2 hours, additionally covering with film on top. |
| Cabbage applique | Lightly chop the cabbage leaf and apply it to the problem area of the chest, preferably at night. |
| Carrot compress | Grate the vegetable on a fine grater and form a flat cake from the prepared pulp, which is also best used before bed. |
| Herbal compress | The coltsfoot grass is kneaded to release the juice and applied as a compress for 4-6 hours. |
| Burr oil | Natural oil is spread in a thin layer on the sore breast 1-3 times a day. |
| Tinctures | Prophylactic use of tincture of burdock root or walnut partitions is useful. |