If there is a violation of the outflow of urine, a nephrostomy in the kidney is used. A passage is artificially created for the proper removal of urine. According to statistics, the main reason is manipulation, the presence of large stones that clog the canal, as a result of which urine accumulates in the pyelocaliceal structure. The complex operation is performed exclusively in specialized clinics under general anesthesia.
What is a nephrostomy?
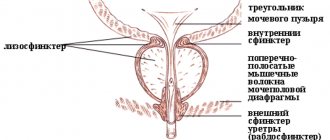
This is a drainage catheter in which one end is fixed in the renal pelvis, and the opposite end is brought out from the lumbar side and connected to a urinal. The outflow of urine occurs into a urine collection bag - connected to the catheter directly or through a connector tube. With the help of a nephrostomy catheter, emptying is carried out without involving the urethra, urinary ducts and bladder.
A nephrostomy is installed by a doctor during a surgical operation, which is performed using ultrasound or X-ray machines to eliminate the risk of damage to the renal artery or pelvis. This operation is called nephrostomy.
Contraindications
The decision on the need to promptly restore the outflow of urine is made by the doctor individually in each case. Surgical intervention may be prohibited if:
- persistent increase in blood pressure that cannot be controlled with medication;
- pathologies of the blood coagulation system;
- treatment with anticoagulants.
When is a nephrostomy necessary?
Nephrostomy can act both as a temporary solution to problems with excretion, and palliative, i.e. continuous post-operative care that supports the functioning of the body. Most often, this is required after operations to remove cancerous tumors - if doctors were unable to preserve enough tissue for the normal functioning of the organ.
Indications for nephrostomy are as follows:
- cancerous tumors of the kidney or other organs of the urinary system,
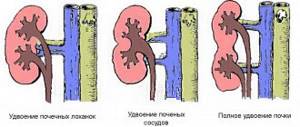
- hydronephrosis - progressive expansion of the pelvis and calyces in the kidneys due to impaired urine outflow, which leads to atrophy of kidney tissue,
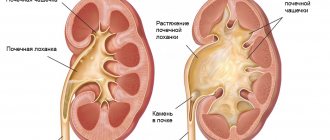
- urolithiasis with large calculi (stones),
- tumor metastases compressing the pelvic organs,
- ureteral obstruction.
Nephrostomy restores urine output and prevents the development of inflammation that leads to kidney failure - both acute and chronic.
However, nephrostomy also has contraindications:
- diseases that interfere with blood clotting,
- taking anticoagulants - drugs that thin the blood;
- uncontrolled high blood pressure.
In the first two cases, there is a risk of fatal bleeding, and in the third, the patient may experience a stroke and (or) cardiogenic shock.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for nephrostomy does not differ from usual preoperative measures.
Blood (biochemical and general analysis) and urine (for culture and composition) are given for analysis. Blood clotting and sugar levels are controlled.
The affected kidney is examined using ultrasound and radiography. If necessary, additional studies may be prescribed - urography, CT scan of the kidneys or retroperitoneum.
- What is doubling of the left kidney?
The anesthesiologist determines the patient's response to anesthesia.
The need for antibacterial therapy is determined by the presence or absence of infections in the genitourinary system. If any are present, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to eliminate the inflammatory process.
Patients should refuse liquid food and milk 8 hours before nephrostomy. Non-alcoholic drinks can be taken at least 2-3 hours before surgery.
Installation of nephrostomy: surgery
First, the doctor must explain to the patient how to care for the nephrostomy and what restrictions it imposes on lifestyle. Then the doctor begins diagnostic procedures. They are divided into 2 categories:
- laboratory tests (general and biochemical analysis of blood, urine, coagulogram - a set of tests showing blood clotting),
- instrumental studies (excretory urography, kidney ultrasound, computed tomography).
After the doctor determines that there are no contraindications, a date for the operation is set. It is performed either under general anesthesia or local anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition. The procedure itself takes 15-30 minutes. There are 3 techniques for installing a nephrostomy:
- open surgery (intraoperative method) - the doctor makes an incision in the lower back to the kidney, with the help of several sutures he sews the fat capsule to the skin and cuts the kidney, and then the pelvis. A tube is inserted there, which the doctor also sews to the skin, and then the rest of the incision is sutured,
- laparoscopic drainage installation - used during laparoscopic surgery to remove a tumor. The main difference from the first method is that operations are performed through a very small incision, up to 0.5-1.5 cm. The main instrument is a laparoscope, a tube with a lens system attached to a video camera.
- percutaneous puncture – the most common, because least traumatic. In addition, patients tolerate it best, which is important when it comes to the elderly, children or pregnant women. The doctor pierces the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles and tissue of the kidney with a puncture needle, watching the monitor to get into the pelvis as accurately as possible without causing damage to other tissues. Following the needle, he inserts a drainage tube and connects it to a urinal.
Patients, as a rule, recover quickly - on the first day after surgery they can move around the ward. The doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics lasting 5-7 days to prevent the development of an infectious process. Within 2-3 days after nephrostomy, blood may appear in the urinal due to damage to the renal vessels, but after 3 days the bleeding should subside. If there is still blood in the urine bag after 3 days, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Algorithm
Step-by-step preparation
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a standard urine test.
Previously, a patient with a diseased kidney that requires the installation of a nephrostomy undergoes a standard set of tests and is examined by specialized specialists. The results of a study on general blood and urine parameters, coagulation, determination of glucose levels and bacteriological culture will be required. The patient must consult with an anesthesiologist and conduct a test reaction, in which individual tolerance to the drugs is studied. Hardware studies include ultrasound and urography. Medication preparation is not required; it will be relevant if infectious or bacterial lesions are identified. All this is necessary to study the functional characteristics of the excretory system and the rate of its accumulation in the CLS. 14 hours before the operation you should give up dairy and fatty foods; 3-4 hours before the operation water is not allowed.
Execution Features
Classic procedure
Drainage performs both permanent and temporary functions. After completing its task, the nephrostomy is removed. Open surgery is carried out through a strip incision to the organ capsule, where the catheter is inserted directly into the kidney. This method of intervention is rarely used, since there is a high risk of infection, as well as the rehabilitation period will take much longer.
Minimally invasive method of intervention
Percutaneous puncture nephrostomy is performed through an opening made in the lumbar region. It passes through the skin and muscle tissue, then a drain is placed in the kidney. The manipulation is carried out under ultrasound control, the image is displayed on the monitor and with the help of this the surgeon regulates the movements. The entire procedure takes no more than half an hour. Percutaneous percutaneous nephrostomy has a number of advantages: after a day, the patient moves freely and the recovery period is reduced several times. Postoperative complications are minimized due to the fact that it is possible to hold your breath for a short time and install the catheter without damage. The nephrostomy channel is fixed in several ways:
- using a pelvic loop;
- an inflating balloon;
- to the skin (most often used).
Postoperative period, how is the recovery going?
It is important to promptly empty and wash the urine reservoir so that the contents of honey mushrooms do not enter the kidney.
If the nephrostomy was removed by puncture, then after the manipulation the patient goes home the next day. The patient must carefully ensure that the tube does not fall out; if this cannot be avoided, then it should be inserted back within 24 hours. The procedure is performed exclusively by a doctor. The wound must be monitored and washed regularly to avoid inflammation. The tube is also washed, since urine residues can provoke the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into the organ. It is very important to regularly flush the urine collection tank; if it overflows, urine will flow back to the organ. It is convenient to install 2 tubes at once: saline solution is injected through one, and the solution with residual sand, stones, and other things flows out through the other. Many people live happily with drainage for many years; the main condition is timely replacement of the nephrostomy.
It is important to follow a therapeutic diet that will not overload the body and the kidney in particular.
Caring for a nephrostomy at home
Nephrostomy, being a foreign object for the human body, requires constant care in order to prevent infection. The skin around the tube insertion site should always remain dry, clean and free of inflammation. There should be no pus coming out of the hole - and if this happens, you should immediately call a doctor. Nephrostomy care includes:
| washing with saline solution and antiseptics (for example, drugs such as chlorhexidine or furatsilin), | |
| applying a sterile bandage to the site where the operation was performed - and for the first 2 weeks it is changed daily - this is done by medical staff or relatives, | |
| after the wound has healed, the bandage should be changed if necessary - when it gets wet or dirty, | |
| timely and regular emptying of the urine bag, | |
| Every 2 weeks, the doctor should examine the area where the nephrostomy is installed. |
Patients are also prohibited from physical exercise and heavy lifting, i.e. this can lead to injury, kinking of the drainage tube, which, in turn, will cause serious complications. The catheter should always be placed in exactly one position.
General information
The main danger is the absence of urine outflow for a long time, which causes irreversible destruction of nephrons - the functional units of kidney tissue.
As a result, the kidneys lose the ability to perform their main function - filtering blood. Kidney failure develops.
Nephrostomy is an operation to install an artificial pathway device to drain urine from the collecting-pelvic area through the kidney tissue and abdominal wall into an external container (urinal).
Structurally, the outlet channel - nephrostomy - is a drainage tube (catheter) made of polymer material, one end of which is located in the renal pelvis, the other in a urinal bag attached to the patient’s body.
In most cases, when normal urine flow is restored, the nephrostomy is removed.
However, with large-scale and irreversible damage to the urinary tract or kidneys, the catheter may remain in the patient’s body for life.
Nephrostomy replacement
Changing the tube is necessary because urine contains mucus, salts, and fibrin, which form sediment that impairs the patency of the catheter. The doctor replaces the tube every 2-3 months, on an outpatient basis. But the urinal should be changed independently at least once a week, and more often if an odor appears.
Possible risks
There are primary (operative) and secondary (postoperative) complications of renal nephrostomy. During the manipulation, there is a risk of damage to the pararenal artery with the development of bleeding into the retroperitoneal space with the formation of a hematoma, which can become infected, which will require abdominal surgery. Less often, incorrect treatment is carried out against the background of detection of blood in the urine during the first day, as a consequence of a breakthrough of the resulting perioperative hematoma.
There are more risks with abdominal surgery, most often urinary leakage, bleeding, and kidney infection. Secondary disorders develop in the form of postoperative pyelonephritis, which is characterized by its aggressive nature and resistance of the infection to antibiotics. Eliminating the disease will require more expensive medications and a longer recovery period. Therefore, if your temperature suddenly rises to 38 °C or higher, you should urgently call a doctor.
Stoma removal
Indicators of successful treatment, after which the nephrostomy can be removed, are:
- formation of a fistula tract to ensure the natural outflow of urine (in patients with severe pathologies);
- restoration of normal urine drainage through natural urinary drainage channels.
Typically, drainage is carried out for 10-15 days. Pregnant women are not recommended to use nephrostomy for more than 4 days due to the high risk of developing disorders. In any case, removal of the nephrostomy is prescribed by the attending physician based on the results of control tests and assessment of the degree of restoration of urinary diversion function. An equally important indicator is the absence of irreversible diffuse damage to the renal parenchyma (fiber).
Nephrostomy: general information
The operation involves draining the kidney by introducing a nephrostomy - an artificially created path for urine drainage, passing through the tissues of this organ and in the lumbar region into an external container - a urinal.
The drainage itself, simply put, is a tube in the kidney for the outflow of urine. The length of the nephrostomy tube, or nephrostomy, in the kidney is determined by doctors individually for each patient. Usually this is 10 - 15 days, and pregnant women are not recommended to exceed the period of 4 days. There are cases of severe pathologies when it is used throughout one’s life.
Purpose of the drainage tube
Most often, nephrostomy is necessary for the treatment, primarily of symptomatic, cancer patients. It is carried out, including when providing palliative care. The indication for such surgery is the presence of a malignant tumor compressing the ureter and, accordingly, preventing the natural exit of urine from one or both kidneys.
Drainage can be prescribed for acute urolithiasis, in cases where the patient is inoperable (due to age or general condition), as well as when this disease is combined with cancer. Nephrostomy is necessary to prevent such severe consequences of fluid accumulation in the kidneys as hydronephrosis (pathological expansion of this organ) and pyelonephritis (inflammation leading to irreversible destruction of the kidney tissue and the occurrence of acute failure against this background). With such consequences, organ dysfunction is almost impossible to correct.
Under certain circumstances, nephrostomy can be performed to gain access to the upper urinary tract, to install special stents, to administer chemotherapy, and also as a stage for future surgery. Also in medical practice there are examples of kidney drainage for further research.
Rehabilitation period
After nephrostomy surgery, the patient is transferred to outpatient therapy, instructions are given such as eliminating stress and salt from the diet, ensuring proper care and keeping the wound absolutely clean. At first, care for the equipment is carried out with the help of medical workers, but then the patient will be able to care for the wound at home independently with the help of household members.
Pregnant women with a nephrostomy say that in this position it is very difficult for a woman to walk with drainage, but it allows her to save the kidney and the baby, so after giving birth they in most cases thank the doctors for the opportunity for a happy motherhood.
Childbirth with a nephrostomy usually involves a caesarean section, although a natural delivery is also possible. It all depends on the patient’s condition during pregnancy and the reason why the nephrostomy was installed.
A fairly popular question is how long people live after surgery. The patient can easily live with a nephrostomy for many years. It will be changed periodically, as necessary. The main thing is to take proper care of it, wash and treat the wound daily. Also, with nephrostomy, a salt-free diet is necessary. Treatment table No. 7 provides favorable conditions for renal activity and facilitates the functioning of the organ. Metabolic processes in the kidney structures are restored. In addition, a salt-free diet significantly improves urination processes. In the video about childbirth with a nephrostomy in the kidney: