Classification of the disease
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys (ICD-10 code - N13) is a pathological disease from the section of urology, in which an increased fluid content .
This occurs due to a disruption in the process of urine outflow, and this disruption contributes to the development of inflammatory processes in the parenchyma - renal tissue consisting of functional cells.
Hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, the pathology manifests itself in the child immediately after birth. The acquired type of disease may have less obvious symptoms and most often occurs against the background of other kidney damage.
Any of these types of pathology can occur in one of the following forms :
- Obstructive.
- Double sided.
- Chronic.
- Terminal.
Ureteral obstruction occurs as a result of obstruction of the normal flow of urine. The simplest and most common form, which is characterized by discomfort in the kidney area, the functions of which are impaired.
Clinical manifestations are almost always absent, and the disorder can only be detected using ultrasound, while such an examination shows a slight expansion of the renal cavities, and the parenchyma remains in a normal state and is not subject to inflammatory processes.
Usually one of the kidneys is affected - the right or left, but the disease can spread to two organs at once, and the parenchyma most often becomes thinner and inflamed.
The cause of such damage is excessive accumulation of fluid, as a result of which irreversible pathological processes develop in the renal pelvis.
The disease occurs in a latent form, the symptoms are not obvious.
It is characterized by complete atrophy of the parenchyma, resulting in the development of renal failure and, as a result of such irreversible processes, in most cases the disease leads to death.
Read our article about what kidney failure is.
Hydronephrosis is also classified by severity :
- The 1st degree is characterized by stretching of the renal pelvis, which is subject to excessive pressure from a full bladder. The kidneys, although they increase in size, function normally in the first stage.
- At grade 2, the pelvis stretches even more, and the renal calyces also undergo stretching. This leads to compression of the parenchyma, in which atrophic processes develop, and kidney function is impaired.
- Hydronephrosis of the 3rd degree leads to irreversible atrophic processes of the kidney tissue, as a result of which the organ itself begins to die.
Preventing the disease from progressing to the terminal stage is possible only with timely diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Any therapeutic and surgical methods are useless .
(The picture is clickable, click to enlarge)
Types of disease according to the nature of localization
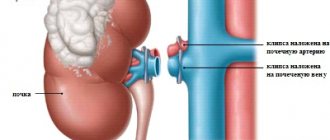
Removal of an organ or resection of its part occurs in two available ways:
- open (laparotomy) nephrectomy;
- closed (laparoscopic) nephrectomy.
Each of these approaches has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the preference in choosing each of them depends on the underlying disease, the severity of the patient’s condition and the extent of the process.
If we are talking about emergency surgical intervention, then patients are unconditionally referred to open surgery, thanks to which the doctor can assess the extent of the problem as much as possible and conduct a complete inspection of the lesion.
Based on the nature of localization, they are distinguished:
- unilateral;
- bilateral ureterohydronephrosis.
Unilateral ureterohydronephrosis is diagnosed most often. The bilateral form of the disease is observed in only 5% of the total number of patients. Also, this form of damage to the renal system is very rarely observed in children.
Depending on the damage to the kidney, ureterohydronephrosis on the right or ureterohydronephrosis on the left may develop. In view of this, abdominal pain can be supplemented by pain in the right or left hypochondrium.
Also in official medicine, the disease is distinguished by the degree of obstruction:
- refluxing - expansion of the ureter along the entire length;
- obstructive – expansion of the ureter only in the upper section;
- combined - simultaneous narrowing of the ureter and cystic reflux.
Causes of the disease
Basically, the disease develops due to blockage of the internal urinary ducts , and most often this occurs when stones enter the ureters, blocking the movement of urinary fluid.
In men and women, the causes of this disease may be different. Among male patients, this disease is most often observed with prostate cancer, which blocks the urinary tract, increasing in size due to inflammatory processes.
Also, an increase in this organ can occur due to the formation of a benign prostate tumor.
In women, this disorder is often diagnosed during pregnancy , when pressure on the ureters is exerted by the enlarged uterus. Pathology also develops against the background of ovarian or cervical cancer.
Other common reasons include:
- changes in the structure of the tissues of the urinary tract and kidneys;
- strictures;
- cysts of various origins;
- urinary tract dyskinesia;
- narrowed lumen of the ureter;
- abnormal or abnormal location of the ureter and renal arteries;
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system;
- formation of scar tissue in the post-traumatic period;
- reflex disorders leading to difficulty in the outflow of urine as a result of damage to the spinal cord;
- endometriosis;
- entry of tuberculosis pathogens into the bladder.
All categories of patients are also characterized by non-pathological causes - this is compression of the ureters during cold-related inflammatory processes affecting organs located in the genitourinary tract.
What are the typical symptoms?
In the initial stages, hydronephrosis does not manifest itself and is asymptomatic, but some indirect signs may appear that are characteristic of the pathologies that caused hydronephrosis (for example, with urolithiasis, which results in blockage of the ureters, the patient experiences lower back pain).
As the pathology develops, patients may experience the following symptoms:
- severe pain from the kidney affected by hydronephrosis;
- dull pain in the lower back in any position of the body;
- increased blood pressure;
- the pain syndrome may transfer to the right side of the abdominal cavity;
- constant bloating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- with urolithiasis - the presence of blood in the urine.
In some cases, an associated infection may develop during the disease - in such situations, the patient’s body temperature rises significantly.
general information
Often, bedsores appear in patients who are bedridden or wheelchair-bound. Bedsores are a serious complication of the underlying disease, requiring separate treatment and rehabilitation. Pressure ulcer damage to the skin and tissues can be avoided if preventive recommendations are followed. According to statistics, the percentage of pressure sores in patients undergoing treatment in a hospital reaches 29%. And in patients who have suffered a spinal injury, the incidence of bedsores reaches 60%. High-quality care reduces this figure to 8%, a figure achieved in UK clinics.
Diagnostic methods
The examination begins with a physical diagnosis, during which the specialist palpates the kidney area and evaluates the patient's response. After this, general urine and blood tests are prescribed, the results of which can determine the presence of inflammation in the kidney area.
But the main diagnostic methods that allow you to get a complete picture of the disease are:
- urography;
- Ultrasound (to assess the condition of the tissues of the renal apparatus);
- MRI and CT (if it is difficult to determine the causes of the disease);
- cystoscopy of the bladder;
- in any case, an x-ray of the kidneys is prescribed (see photo), which is performed using a contrast agent. This method often allows you to accurately determine the cause of urinary tract obstruction.
Treatment and outcome of the disease
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys is treated with medication and surgery. The first method is relevant in the early stages of the disease and if the lesions are still reversible .
Treatment is performed only in a hospital setting and involves the use of the following groups of medications:
- hormonal agents (when diagnosing fibrosis in the retroperitoneal region);
- antibiotic drugs (to prevent and eliminate bacterial infections);
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- drugs that lower blood pressure;
- the use of drugs containing alkali (to dissolve stones in urolithiasis).
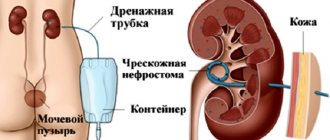
In later stages, such conservative therapy is ineffective, and the patient undergoes surgery to install a nephrostomy tube .
A nephrostomy is an artificial urinary canal, which is a catheter and is installed during a surgical operation.
The nephrostomy is installed directly into the renal pelvis and, passing through the tissues of these organs, comes out, draining urinary fluid into a urinal. The procedure for installing a nephrostomy tube (nephrostomy) can be performed in one of three ways :
- open surgery;
- laparoscopy;
- puncture.
The type of operation is determined based on the degree of tissue damage and the general condition of the patient.
In general, any of these operations involves making punctures or incisions in the kidney area and inserting a catheter, which is subsequently connected to an external urine bag.
Treatment prognosis can be favorable only if treatment is started in the early stages of hydronephrosis.
In the case of bilateral damage, the prospects are not so good: most likely, the person will have to undergo hemodialysis for life, and sometimes a transplant of the affected organs may be necessary.
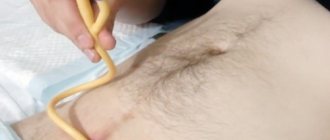
Nephrostomy installation
Type of nephrostomy kit
A nephrostomy tube is installed by a urologist or surgeon in a sterile operating room/manipulation room. Often the intervention is performed for emergency reasons without preparation, for example, in case of a blocking stone in the ureter and the impossibility of stenting it through the bladder. Deep anesthesia is not required.
After anesthesia and treatment of the surgical field under the control of an ultrasound or X-ray machine, a radiopaque substance is injected directly into the renal collecting system using a puncture needle, then a nephrostomy tube is installed along the conductor string. Next, the auxiliary components are removed, and another portion of the radiopharmaceutical is poured into the catheter and pictures are taken.
Sometimes, as part of preoperative preparation, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is performed to clarify the anatomical features. Today, there are many nephrostomy systems from different manufacturers, with varying prices and fixation methods: loop (the catheter is held in place by forming a loop), balloon (air or liquid is introduced through a special outlet, an inflating balloon, etc.). Additionally, immobility of the nephrostomy is ensured by skin sutures and a bandage.
Prevention
You can notice the development of renal hydronephrosis in time and prevent it by following the following preventive recommendations:
- people aged 35 years and older are recommended to visit a urologist and nephrologist 1-2 times a year;
- if you are predisposed to kidney disease, hypothermia must be avoided;
- all infectious lesions of the urinary tract and kidneys should be treated in a timely manner to avoid complications.
a healthy diet and giving up bad habits such as alcohol abuse and smoking can also reduce the risk of developing such pathologies
Home Hydronephrosis congenital urolithiasis
N13 Obstructive uropathy and reflux uropathy
Kidneys
In accordance with the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, this disease is designated by several codes:
- 13.0 - hydronephrosis, in which the connections of the pelvis and urinary tract are disrupted;
- 13.1 - hydronephrosis, in which the urinary tract is narrowed;
- 13.2 - hydronephrosis with obstruction of the kidney and ureter by a stone;
- 13.3 - other forms of disease of unspecified origin.