Urinary retention in the human body quite often causes the formation of kidney stones, prostate adenoma, paralysis of the bladder and damage to its tissues. In order to avoid such consequences, it is necessary to rinse the bladder using solutions. Doctors often use Furacilin solution to rinse the bladder.
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe a diuretic, usually along with antibiotics. A diuretic may help flush out the infection from the bladder. But in the acute stage of the disease they are limited, since they significantly limit the beneficial properties of the liquid.
Urine has excellent antibacterial properties, which do not require additional medications if the body is healthy. In particular, for cystitis, this treatment regimen is used in cycles.
It is important to remember that along with urine, not only infections and bacteria are washed out of the body, but also microelements that are beneficial to the body.
The need to rinse the bladder
A similar catheterization procedure is performed for those patients who cannot remove urine from the bladder themselves. When inflammation occurs, a person must regularly rinse the urinary tract.
Such diseases, accompanied by inflammation, are formed due to an infection that has entered the body, as well as the presence of favorable conditions for its development. This could be staphylococcal bacteria, influenza, sinusitis, tonsillitis, any infectious diseases or E. coli.
In some cases, flushing the bladder may become necessary when taking medications for a long time that cause changes in the mucous surfaces of the bladder and urethra.
How to rinse the bladder through a catheter in patients who have undergone catheterization: Miramistin, Furacilin, boric acid (3%), chlorhexidine (2%) and dioxidine diluted 1 to 40.
Rinse the bladder according to a certain procedure, since if the rules are not followed, you can burn the mucous membrane of the canals and the surface of the bladder. If such a situation arises, doctors perform repeated rinsing with infusions of herbs that can regenerate soft tissue. The membranes can also be injured when stones move through the genitourinary system during treatment.
Indications for rinsing
Flushing allows damaged tissue to heal faster, which speeds up overall recovery. The indications are:
- urolithiasis disease;
- BPH;
- infections of any kind in the urinary tract;
- inflammation of organs and tissues;
- stagnation of urine;
- planned cystoscopy;
- a long course of medications, the side effects of which include a pathogenic effect on the bladder.
There are several contraindications in which flushing the bladder is prohibited even in a hospital setting. These are, first of all, injury to the sphincter in the bladder, gonorrhea and acute inflammation of the urethral canal.
In this case, treatment is carried out exclusively with medications, and the therapy lasts much longer, since it is impossible to directly influence the source of inflammation.
Why is a catheter placed?
Many diseases of the urinary system are accompanied by a symptom such as ischuria. Retention of urination when the bladder is full is a frequent companion to urolithiasis, tumor diseases, problems with the prostate gland in males, severe inflammatory processes, narrowing of the urethra of a traumatic nature, etc.
Most often a catheter is placed in a cat, since this pathology leads to obstruction of the urinary tract. Urinary retention can be acute or chronic. In the first case of ischuria, catheterization is a vital procedure. When a plug of urinary sand forms in the urethra, obstruction develops. Signs of urinary retention in a cat are as follows:
- urinating in the wrong places, outside the tray;
- frequent urges, the pet takes the appropriate position, but urine is not released;
- the animal is worried and screams when going to the toilet;
- urine is released in drops, often with;
- palpation of the lower abdomen reveals a tense bladder. It becomes hard and increases in size to the size of a chicken egg.
When the urethra is completely blocked, the pet often takes the appropriate position on the toilet, but not a drop of urine is released. In this condition, general intoxication of the body quickly develops, and there is a risk of developing acute renal failure and painful shock. If veterinary care is not provided to the animal within 2-3 days, death occurs.
The benefits of furatsilin
It is important to know!
Doctors are shocked: “Comprehensive kidney treatment exists. " Read more.
Furacilin can be classified as a disinfectant that effectively fights infection. It is used both for external treatment of the genital organs and for internal rinsing.
The composition of furatsilin promotes accelerated tissue healing and elimination of inflammation. The solution is able to destroy pathogens, eliminates purulent processes and inflammation in the bladder. Substances in furatsilin prevent bacteria from dividing.
Furacilin is used in a course in the form of washing the urinary canals, the duration of which depends on the severity of the disease and its spread. As a rule, unpleasant symptoms can be avoided after 2 weeks.
Tips to make life easier for a patient with artificial urinary diversion
Despite modern drainage materials that prevent the proliferation of microflora, acute inflammatory processes occur frequently during long-term catheterization. To minimize this risk, the tubes must be properly cared for. As a rule, recommendations are indicated in the hospital extract.
If there is a functioning epicystostomy and the patient is predisposed to urolithiasis, it is necessary to rinse the drainage daily with a solution of furatsilin. The doctor will tell you more specifically about the tactics of action after assessing the individual characteristics.
When urinating through a urethral catheter, the patient's condition must be closely monitored, especially if brain activity is impaired. Urethritis often develops against the background of a weakened immune system during catheterization, so if long-term urine diversion is planned, epicystostomy is considered a safer method.
The urethral catheter is also washed with antiseptic solutions; in case of severe inflammation, antibiotics and instillations are prescribed: Dioxidine (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, etc.) is administered through the installed drainage and left in the bladder for 15-20 minutes. If your health worsens or your temperature rises, the catheter is removed and the issue of another method of urine diversion is decided upon.
Important! Before any manipulation, be sure to coordinate all actions with your doctor.
Caring for a nephrostomy is somewhat more complicated; its processing requires special skills. It is unacceptable to administer fluid under pressure, as this can lead to rupture of the kidney. It is better if this procedure is carried out by a specialist.
Patients who are examined by the ITU (medical and social examination) and recognized as disabled can receive urinals, catheters, systems with urocondoms and some care products for free. To obtain medical documentation, you must contact the clinic at your place of residence.
Urinals
The urinal collects urine. The urine bag is attached to a catheter, a tube that is placed in the bladder. You may have a urinary catheter with a urine bag if you suffer from urinary incontinence, urinary retention, have had surgery that made a catheter necessary, or have other health problems.
How does a urine bag that is attached to the leg work?
Urine from the bladder flows through a catheter into a urinal attached to the leg. The urine bag can be hidden under a dress, skirt or pants. You can move freely with the urine bag throughout the day. There are many types of urinals - all different sizes and shapes.
At night you will need to use a bedside urine bag.
Where to attach a urine bag to your leg?
Attach the urine bag to your thigh using Velcro or elastic strips. Make sure the urine bag is positioned below the bladder. This will prevent urine from flowing back into your bladder.
Emptying the foot bag:
Always empty your urine bag in a clean bathroom. DO NOT touch the urine bag or the catheter opening to any surfaces in the bathroom (toilet, walls, floor, etc.). Empty the bag at least two or three times a day or when the bag is two-thirds full.
Follow these step-by-step instructions when emptying the foot bag:
- Wash your hands thoroughly
- Lower the urine bag below your hip or bladder as you will be emptying it.
- Keep the urine bag over the toilet or over the special container given to you by your doctor
- Open the drain hole at the bottom of the urine bag and empty it into the toilet or container
- Do not allow the urine bag to touch the toilet rim or container neck
- Rinse the drainage hole of the urine bag with alcohol using a gauze or cotton swab
- Carefully close the drainage hole of the urine bag
- Do not place the urine bag on the floor. Reattach the urine bag to the leg
- Wash your hands again
Replacing a leg urinal
Change your urine bag at least once a month. If the urine bag smells bad or looks dirty, replace it sooner.
When replacing the urine bag, follow these instructions:
- Wash your hands thoroughly
- Before disconnecting the urine bag, close the end of the catheter. Do not touch the end of the catheter tube and urine bag to any surface, including your hands.
- Disinfect the end of the catheter using a cotton swab or gauze swab moistened with alcohol.
- Disinfect the connecting hole of the leg urine bag with a swab soaked in alcohol, if this is not a new urine bag.
- Attach the catheter to the urine bag. Make sure the connection is tight and there is no urine leakage.
- Attach a leg bag to your leg.
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
Disinfection of a foot urine bag
Disinfect your nighttime (bedside) urine bag every morning. Disinfect the foot bag every evening before replacing it with a bedside (night) bag.
- Wash your hands thoroughly
- Disconnect the catheter from the urine bag. Attach the catheter to a clean urine bag.
- Rinse the used urine bag by filling it with a solution of 2 parts white vinegar and 3 parts water. Or you can use 1 tablespoon of chlorine bleach diluted in half a glass of water.
- Close the valve of the urine bag with disinfectant liquid. Shake the urine bag.
- Leave the urine bag with the disinfectant solution for 20 minutes.
- Then drain the solution and dry the urine bag, placing it with the drain hole down.
Contact your doctor if:
- You are not sure how to attach, disinfect, or empty a foot bag.
- Your urine bag quickly fills up.
- You are worried about skin irritation or wounds.
You have symptoms of infection (burning when urinating, fever or chills).
How to dilute the rinsing solution?
In order to rinse the bladder with Furacilin, it is necessary to use its concentration of 1 to 500. For this purpose, two tablets of the drug must be diluted in one glass of boiled water, warm enough not to cause discomfort. You can get rid of crystals in the liquid by straining the sediment through layers of bandage or gauze. Washing is done three times a day.
The solution can only be used for treatment, but not for prevention.
The prescription is prescribed by the attending physician, who knows the patient’s medical history and observes the symptoms. Using the solution in the wrong concentration or with the wrong catheter can only make the situation worse.
What is a reusable urine bag
A reusable device for storing urine - a medical “duck” (taking into account anatomical features) for men or women, made of plastic, glass, metal. This allows for disinfection and reuse of the product, even on different patients.
A more primitive version of a reusable urinal bag is a bedpan.
Washing procedure
To rinse the bladder, the patient must take a position in which he will be comfortable during the procedure. To do this, you need to lie on a flat surface, spread your hips and bend your knees slightly. At the same time, the pelvis is raised slightly to improve the penetration of fluid inside.
The use of special tools also involves an Esmarch mug made of plastic or silicone, with an inserted tube. Before starting the procedure, you need to prepare the syringe by boiling it in boiling water for a couple of seconds. Antiseptic preparations and solutions are used to clean hands.
The first step is to wash the urethra, as well as treat the catheter with furatsilin solution. Then the catheter is inserted smoothly forward until the involuntary release of urine begins. As soon as urine begins to come out of the catheter, this indicates its correct installation. You must wait until all the urine comes out.
Next, the catheter is connected to a syringe, through this system a furacilin solution is poured into the bladder. How much of the drug to administer depends on the individual course of the disease, as well as the characteristics of the patient’s body. Washing with furatsilin must be stopped if the patient has an irresistible, persistent desire to deurinate. As soon as the syringe is disconnected from the catheter, the solution begins to flow through it.
During the manipulation, the catheter sometimes becomes clogged with mucous masses. Then it must be washed with a special solution. The procedure is carried out until the liquid becomes clear. As practice shows, 10 repetitions are sufficient, with about 2 liters of solution used for each procedure.
Cystostomy for washing
It is important to know!
Doctors are shocked: “Comprehensive kidney treatment exists. " Read more.
If a patient has damaged urinary organs, he needs a drainage system that is installed for a long time. In this case, the bladder can be flushed through the cystostomy. This method involves removing urine from the body, but not from the urethra, as in the case of conventional lavage, but through the abdominal cavity.
Cystostomy is performed in a hospital setting because abdominal incisions and anesthesia are required. In order to avoid infection, the device must be changed every month, and for washing it is used 2 times a week.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=D7mynFmlxQc
There are also negative properties of this method, but in some cases it cannot be avoided. The negative consequences of such a procedure may be:
- mechanical damage to the intestinal surface;
- rotting of the incision sites in the peritoneum;
- inflammatory processes of the bladder;
- bleeding at the sites where the drainage system is installed;
- allergy to the installed device.
How to change a urinal?
It depends on the type of urine bag. The urinal described above changes as follows:
1) Prepare a clean urine bag.
2) Separate the urine bag tube from the catheter (drainage).
3) Drain the urine from the used urine bag, place it in a plastic bag and set it aside.
4) Connect a clean urine bag to the drain.
5) Use a measuring stick to check the size of your stoma.
How to care for the skin around the stoma?
See gastrostomy skin care.
What to do with used colostomy bags, urinals, and rubber probes?
If a colostomy bag or urinal bag cannot be replaced with a new one, they can be used several times. In such cases, urine or feces is poured into the toilet and, for the purpose of disinfection, colostomy bags (urinal bags) are washed with water, then filled with a 3% chloramine solution for 1 hour, then washed again with water.
If the patient does not use this colostomy bag (urinal bag), it is placed in a plastic bag and thrown into a garbage container, the rubber tube (tube) for feeding through a gastrostomy tube at home is washed with warm boiled water (to wash away food debris), then with a solution furatsilin 1:5000 and again with warm boiled water. The probe is boiled for at least 30 minutes.
Similar actions are possible if the patient is not HIV-infected, does not have Botkin’s disease, and a colostomy bag, urinal bag or rubber tube is used individually.
What to do if the patient is bothered by the smell of urine? feces?
In this case, we can recommend:
— follow a diet (see below);
— when changing the urinal, first pour a little (50
ml) 0.1% solution of rivanol, or furatsilin 1:5000, which, according to
In addition to the antiseptic effect, they help eliminate odor;
- use deodorants;
- ventilate the room;
- change the urine bag or colostomy bag as needed.
Where and how to wear a urine bag? colostomy bag?
We can recommend sewing a special bag for the urine bag and attaching it to your belt.
Attention!
The level of the urinal (and therefore the bag) must be lower than the level of the cystostomy. Therefore, most often patients wear them in trousers.
The colostomy bags described above are attached with adhesive tape, which protects the skin from irritation, so patients are advised to wear tight swimming trunks to help fix the colostomy bag.
Can the patient bathe?
It is possible, but it is better to do it in parts with the help of relatives, so that water does not get into the stoma. After washing, be sure to treat the skin around the stoma.
What can the patient eat?
Features of nutrition through a gastrostomy tube - see the module “Principles of therapeutic nutrition”.
Nutritional considerations for ileostomy and colonostomy: fatty spicy foods and consumption of large amounts of carbohydrates are not recommended (they cause fermentation and increase the smell). It must be remembered that eating onions, garlic, eggs, cabbage, and peas causes increased gas formation. Smoking on an empty stomach speeds up the release of intestinal contents. In order to expand the diet, the patient should be advised to record in a notebook his observations of stool consistency, stool frequency, gas formation and odor. You should eat slowly and calmly, at least 3-4 times a day. With cystostomies, you need to drink more fluid, preferably cranberry juice or tea with lemon, so that less mucus is formed, which clogs the catheter (drainage).
What to do if a patient with an ileostomy or colonostomy has constipation?
In this case, an enema is used (500-600 ml of water or 200 ml of vaseline oil).
Before inserting the tip, lubricate the glove with Vaseline and insert the end into the fistula (stoma) to determine the direction of the overlying intestine.
Attention!
Be sure to warn the patient that in case of signs of inflammation of the stoma (redness, pustules, etc.), as well as in case of urinary retention, blood in the urine, consult a doctor immediately!
Tracheal stoma
Tracheostomy is an opening in the trachea. Tracheostomy in surgical practice is used for long-term maintenance of free patency of the upper respiratory tract, which can be impaired due to acute stenosis (narrowing) of the larynx caused by the presence of a foreign body, trauma, burn, diphtheria, allergic edema, tumors and other reasons.
Tracheostomy can be temporary (for example, foreign body, allergic edema, diphtheria) or permanent (a burn of the larynx and subsequent scarring, laryngeal tumors).
As a result of the operation (tracheostomy), a tracheostomy cannula is inserted into the opening of the trachea, which consists of two tubes: external and internal, tubes of the same length, the internal one is fixed to the external one using a special latch-lock. The outer tube is fixed with a gauze bandage to the neck: the ends of the bandage on one side and the other are threaded through the “ears” of the outer tube and tied at the back of the neck. Both tubes (cannula) can be metal or plastic.
To prevent skin irritation, gauze is placed on the skin under the outer tube in several layers with a cut to the middle, the so-called “panties”. Otherwise, caring for the skin around a tracheostomy is the same as for the skin around a gastrointestinal tract stoma. Caring for the tracheostomy itself is different from caring for other stomas. Its main task is to maintain the patency of the trachea and cannula. After surgery, care is provided by a nurse and then by the patient. In the first days, the inner tube is removed twice a day, cleaned of mucus with cotton-gauze swabs, washed with boiling water (disinfectant solutions irritate the upper respiratory tract) and reinserted. If the inner tube is replaced with a new one, then only a sterile one is installed (in order to prevent the transmission of infection from one patient to another). To prevent the mucous membrane of the trachea from drying out, the tube is covered with a damp gauze curtain. Toilet of the trachea and bronchi involves suctioning out viscous contents using an electric suction device. Before suctioning, humidified oxygen is inhaled, and 3-5 ml of a warm, sterile bicarbonate solution is instilled into the trachea (through the stoma) to thin out thick mucus. Enzyme solutions (for example, chymotrypsin) dilute sputum even better.
With a tracheostomy, unhumidified and unheated air enters the lungs, which leads to drying of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tree. Therefore, it is necessary to use a special humidifier that is installed in the room or hang wet sheets on radiators. Prolonged exposure to a tracheostomy tube can cause tracheobronchitis, which can only be prevented by good tracheostomy care.
Questions regarding the features of daily tracheostomy care by the patient himself or his relatives
How to care for your skin?
The same as for the skin around the gastrointestinal tract. The peculiarity is that several layers of gauze are placed under the outer tube. The nurse should teach all this.
How to care for the inner tube?
If necessary, clean it of mucus and rinse with hot boiled water.
How to avoid congestion in the respiratory tract?
The patient independently instills a warm soda solution into the cannula (1 teaspoon per glass of warm boiled water) or chymothrinsin, or any other enzyme aimed at liquefying mucus and sputum. Then he clears his throat.
How to make verbal contact with a patient?
Warn that when talking you need to cover the opening of the handset with your fingers.
CASE STUDY OF NURSING PROCESS
Situation:
During home visiting, a nurse from the surgical clinic of the clinic visited a patient with a colonostomy.
Stage 1 - collection of information (survey): the patient complained of an unpleasant odor from her stoma, she was embarrassed to go to the store, walked late at night so as not to meet friends, and began to sleep poorly. From the conversation it became clear that the patient loves sauerkraut and onions, eats them often, eats at different times, and tries to eat less often: 2 times a day.
Upon examination: there are no signs of inflammation of the skin around the stoma; there is a strong unpleasant odor from the colostomy bag.
The patient's needs are impaired: to be clean, to avoid danger, to communicate, to sleep.
Stage II - making nursing diagnoses (patient problems):
1) unpleasant odor from the stoma
2) restless sleep
3) social loneliness,
Priority diagnosis (problem): unpleasant odor from the stoma.
Stage III - planning.
Short-term goal: after 1-2 days, the patient realizes that her problem can be managed by following all the nurse’s recommendations.
Long-term goal: The patient will consistently follow the nurse's instructions and will not be bothered by the odor from the colostomy bag.
Plan:
1) the nurse will talk about the need to follow all her recommendations aimed at eliminating the patient’s problem 10
minutes daily for 5 days;
2) the nurse will teach the patient how to properly disinfect a colostomy bag or replace it with a new one, and timely empty the colostomy bag;
3) the nurse will teach the correct use of deodorants (1.5-2 ml
to the bottom of the colostomy bag);
4) the nurse will check that the patient is properly caring for the skin around the stoma;
5) the nurse will talk about the patient’s individual nutrition
10-15 minutes for 5-7 days (eat at the same time, exclude sauerkraut, onions and other gas-forming foods);
6) the nurse will recommend ventilating the room more often;
7) the nurse will visit the patient for a week - daily, for a month once a week, then once a month in order to identify new problems and monitor the implementation of previous recommendations.
Stage IV - Implementation. The nurse implements the planned plan of nursing interventions.
The stage is Evaluation. The patient follows the nurse's recommendations. The unpleasant odor has decreased significantly. The goal has been achieved.
Literature
1. Mukhina S.A., Tarnovskaya I.I. “Theoretical foundations of nursing”: Textbook. - 2nd ed., revised and supplemented. – M.: GEOTAR – Media, 2008
2. S. A. Mukhina, I. I. Tarnovskaya “Theoretical foundations of nursing” / Textbook M.: Rodnik, 2001. – 296 p.
3. Kaligina L.G., Smirnov V.P. Fundamentals of Nursing: A Guide to Medical Procedures. – Federal State Educational Institution “VUNMC Roszdrav”, 2006. – 432 p.
4. Fundamentals of nursing: Algorithms of manipulation: textbook / N.V. Shirokova et al. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2010. - 160 p.
5. Mukhina S.A., Tarnovskaya I.I. Practical guide to the subject “Fundamentals”
nursing": textbook. – M.: GEOTAR. Media, 2009 – 512 p.
6. Manipulations in nursing / ed. A.G. Chizha. – Rostov n/a: Phoenix. 2010. – 318 p.
Catheter Care
The procedure uses a Faley catheter, which can be flushed by both the patient and people close to him. Furacilin solution for such a catheter is purchased at the pharmacy, or can be made with your own hands. To do this, you need to dilute two tablets of the drug in warm boiled water in a volume of 400 ml.
The resulting product is filtered through a layer of triple gauze. The syringe for procedures is used in a volume of 5 ml; before carrying out the manipulation it must be disinfected for several seconds in boiling water.
A tube is disconnected from the urinal, the end of which is treated with furatsilin solution. The solution is drawn into a syringe and placed in a tube, after which slow administration begins. As soon as the entire solution is injected, the syringe is removed and the liquid begins to flow out. The catheter needs to be flushed once a day.
This method of eliminating bladder infections is very common, since the medicine acts directly on the source of inflammation. Furacilin for such purposes is a universal remedy that copes with various bacteria, while restoring the surface of the mucous membrane of the urinary canals.
It is prohibited to carry out the procedure on your own and use the drug to flush the genitourinary system without a doctor’s prescription.
How do I flush my Foley device?
To flush the Foley catheter, large volume syringes are used - fifty or one hundred milliliters. Immediately before washing the device, the syringe must be scalded with boiling water. Washing is carried out with warm saline solution.
If blood or some sediment was noticed in the urine, then a warm solution of furatsilin will be used for rinsing at the rate of two tablets per one and a half glasses of warm boiled water. It is important to strain the solution to remove any undissolved tablet pieces. The resulting solution is drawn into a syringe.
The urinal tube is disconnected. Its end is wiped with a solution of furatsilin. We insert the syringe and inject the solution; this should be done slowly. After entering all the contents, the syringe is removed, and the liquid itself flows out of the catheter.
Urinary catheter care
Wash the skin around the catheter with soap and water twice daily to avoid irritation and infection. In addition, wash the patient after each bowel movement. After washing thoroughly, with light movements, dry the skin.
When wiping after bowel movements, washing and drying the perineum, women should move from front to back to prevent bacteria from the rectum from entering the catheter and urinary tract.
Rinse the urine bag with water daily. You can add a 3% solution of table vinegar to the water at a ratio of 1:7.
Empty the urine bag every 3-4 hours.
Always keep the urine bag below bladder level.
Tell your doctor immediately if urine begins to leak from the catheter, abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness, or blood or flakes in the urine. If the catheter is clogged and causes pain, it must be replaced immediately.
Never pull on the catheter. Disconnect the catheter only to flush or replace it, or to empty the urine bag.
Reasons why urine leaks: the catheter is too thin, the balloon is not inflated enough, the catheter or urinal tube is kinked, the catheter is blocked.
If the outflow of urine stops, the reasons may be:
The catheter installed in the bladder can be washed by the patient himself or his relatives. A warm saline solution is used for rinsing. If sediment or flakes appear in the urine, rinse the catheter with furatsilin solution. At home, you can prepare a solution from two furatsilin tablets dissolved in 400 ml of boiled water. Strain the solution through a double layer of gauze. You can buy a ready-made solution at a pharmacy. Also suitable are a 3% solution of boric acid, dioxidine diluted in a ratio of 1:40, miramistin, and a 2% solution of chlorhexidine.
If a therapeutic effect on the mucous membrane of the bladder is required, rinsing can be done daily. In other cases #8212; as needed.
We hope that our recommendations will help you. If you have any problems, please contact the hospice organizational and methodological department by phone: (499) 245-76-04, from 8-00 to 17-00. Or by phone (499) 245-00-03, around the clock.
Urologist, andrologist Vykhino-Zhulebino, Lyubertsy
Caring for the urine bag. How to do this correctly?
In a urological patient, the urine bag performs the function of collecting urine, that is, it is a soft reservoir for storing urine during the day and night. The urinal is attached to a catheter, cystostomy - a tube that is installed through the urethra or through the abdominal wall into the bladder for the purpose of drainage for incontinence, urinary retention, and postoperative planned drainage of the bladder.
How does a urine bag work? How to attach it?
Urine from the bladder flows through a catheter into a urinal (M), which is usually secured to the leg. Its volume is usually 750 ml. M can be hidden under a dress, skirt or trousers. You can move freely with it throughout the day. There are many types of M - of all possible sizes in volume and shape. At night, it is more rational to use the bedside M, since it is usually larger in volume - from 1.5 liters.
Where is M attached to the leg?
M is attached to the leg using Velcro, elastic or elastic strips in the knee area, one of the fasteners is above it, the other is below. It is necessary to ensure that M is located below the bladder. This will prevent the bladder from refluxing urine and also ensure its free outflow.
M should be emptied in a clean bathroom. Do not touch it or the catheter opening to any surfaces (toilet, walls, floor, etc.). Empty the urine bag at least two or three times a day or when it is two-thirds full.
Step-by-step instructions for emptying the urine bag:
- wash your hands thoroughly
- lower the urine bag below the hip or bladder
- keep the urine bag over the toilet or over a special container
- open the drain hole at the bottom of the urine bag and empty it into the toilet or container
- Do not allow the urine bag to touch the toilet rim or container neck
- Wash the drainage hole of the urinal with alcohol using a gauze or cotton swab
- carefully close the drainage hole of the urinal
- wash your hands again
The urine bag must be changed at least once every two weeks. If an unpleasant odor appears from the urine bag or a large amount of salts or cloudy urine is visible, then it needs to be replaced sooner.
- you do not know how to attach, disinfect or empty a foot bag
- M gets full quickly
- concerned about skin irritation or wounds
- concerned about symptoms of inflammation (burning in the urethra, fever or chills).
Urinary catheter care
Wash the skin around the catheter with soap and water twice daily to avoid irritation and infection. In addition, wash the patient after each bowel movement. After washing thoroughly, with light movements, dry the skin.
When wiping after bowel movements, washing and drying the perineum, women should move from front to back to prevent bacteria from the rectum from entering the catheter and urinary tract.
Rinse the urine bag with water daily. You can add a 3% solution of table vinegar to the water at a ratio of 1:7.
Empty the urine bag every 3-4 hours.
Always keep the urine bag below bladder level.
Tell your doctor immediately if urine begins to leak from the catheter, abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness, or blood or flakes in the urine. If the catheter is clogged and causes pain, it must be replaced immediately.
Never pull on the catheter. Disconnect the catheter only to flush or replace it, or to empty the urine bag.
Reasons why urine leaks: the catheter is too thin, the balloon is not inflated enough, the catheter or urinal tube is kinked, the catheter is blocked.
If the outflow of urine stops, the reasons may be:
The catheter installed in the bladder can be washed by the patient himself or his relatives. A warm saline solution is used for rinsing. If sediment or flakes appear in the urine, rinse the catheter with furatsilin solution. At home, you can prepare a solution from two furatsilin tablets dissolved in 400 ml of boiled water. Strain the solution through a double layer of gauze. You can buy a ready-made solution at a pharmacy. Also suitable are a 3% solution of boric acid, dioxidine diluted in a ratio of 1:40, miramistin, and a 2% solution of chlorhexidine.
If a therapeutic effect on the mucous membrane of the bladder is required, rinsing can be done daily. In other cases #8212; as needed.
We hope that our recommendations will help you. If you have any problems, please contact the hospice organizational and methodological department by phone: (499) 245-76-04, from 8-00 to 17-00. Or by phone (499) 245-00-03, around the clock.
Warnings
- If you have a central or peripheral venous catheter, only a qualified professional should remove it. Extraction on your own can have serious consequences.
- If you notice the following symptoms, call your doctor or go to the hospital emergency room right away: you feel the urge to urinate but cannot go to the toilet; you have severe back pain or swelling in the abdominal area; you have a high temperature; you feel sick or vomit.
Bladder rinsing technique: what and how to rinse with?
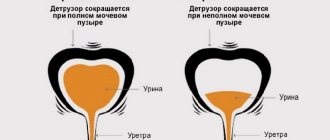
Bladder lavage is necessary to treat diseases of the urinary system.
This procedure leads to rapid healing of damaged tissues, which means the patient’s recovery. How and with what to wash the bladder we will consider further.
When done #8212; readings
Indications for the procedure are:
- Inflammation of organ tissue.
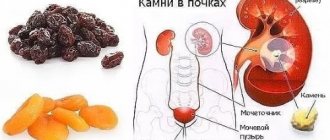
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Stagnation of urine.
- BPH.
- Improper flow of urine.
- Cystitis.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary system.
- Before performing cystoscopy.
- With long-term use of medications that cause bladder pathologies.
What and how are they washed?
Flushing techniques vary depending on the devices and medications used.
Through a catheter
The following medications are used for flushing through a catheter:
technique :
First, the patient is placed on the couch. He should bend his knees and spread them apart. The doctor treats the external genitalia with an antiseptic.
Then a catheter is taken, which is pre-washed in Furacilin solution . It is carefully inserted into the urethra. When it reaches the bladder, urine will begin to be released. The specialist waits for all the urine to come out.
Next, a syringe filled with medication is attached to the catheter. The drug enters the bladder through the catheter. The amount of medicinal solution may vary. It all depends on the volume of the patient’s bladder. As a rule, 200 ml of solution .
It is introduced gradually over several minutes. The administration of the medication is stopped when the bladder is full and the patient expresses the desire to evacuate. The syringe is disconnected and the urine is allowed to exit through the catheter.
Urine can be dark or mixed with impurities . The procedure for administering the medicine is repeated another 8-10 times until the urine becomes clear.
The procedure ends with the administration of a small amount of medication so that the bladder is not completely full. The catheter is carefully removed from the bladder through the urethra.
The external genitalia are again treated with an antiseptic.
The patient needs to lie down for 20 minutes to achieve maximum effectiveness, then he is allowed to get up and get dressed. The procedure is considered completed.
Through a cystostomy
The following medications are used for rinsing:
It is more difficult to perform rinsing using this method, since it is first necessary to carry out an operation to install the tip of the cystostomy into the bladder. How to do it:
The operation takes 30-35 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia.
Only when the cystostomy is installed are rinses performed.
A person every three days to carry out the washing procedure. Her technique is like this:
The patient can lie down for 5 minutes , then stand up. The procedure is complete.
How to rinse your bladder at home?
To carry out the procedure at home, medications :
Before using the medicine, it must be diluted with water in a ratio of 1:1000 .
You should not use alcohol for rinsing, since in addition to alcohol, it contains various additives that can damage the tissue of the bladder.
Inflammatory processes can only get worse, so it’s better not to take risks .
To perform rinsing correctly, you will need: a Janet syringe, a catheter, a container into which the secreted liquid will fall. It is desirable that the catheter be rubber. Rinse the bladder according to the instructions:
The medicine must be administered at least 8 times. By this time, the urine should become clear and clean.
- After this, the catheter is carefully removed, and the genitals are again wiped with an antiseptic.
- Blood in urine.
- The occurrence of infections.
- Organ inflammation.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Burning during urination.
- Redness and itching of the external genitalia.
- Difficulty urinating.
- Pyelonephritis.
It is recommended to lie down for at least 30 minutes and avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting.
It is enough to carry out this procedure at home once every two days . The patient should be assisted by relatives during the procedure. It will not be easy to cope with this task on your own.
How to rinse the tube from the bladder?
It is very important to keep the tube clean so that germs do not accumulate in it and infection does not occur.
Rinse the tube immediately after use. To do this, you need to dilute a special solution: mix Furacilin solution and clean water in a ratio of 1:5000 .
Instead of Furacilin, you can use a solution of Potassium Permanganate. The proportions remain the same.
The tube is placed in a container with the solution for 15-20 minutes , then removed and wiped with a sterile cloth. Before using the tube, you need to do this procedure again.
It is very important that it remains sterile, as a dirty tube can cause infection.
Possible complications after the procedure
The following complications may arise if the technology of the washing process is violated or the recommendations of specialists are not followed:
What is pyelonephritis read in our article.
Bladder lavage is an effective procedure that helps eliminate diseases of the urinary system. If the procedure is performed correctly and regularly, the patient’s likelihood of recovery is high.
How to install a bladder flushing catheter #8212; watch in the video:
Many bladder diseases are accompanied by congestion. This complicates the course of the pathological process, provokes additional irritation of the walls of the organ and their inflammation. In such cases, washing the bladder has a good therapeutic effect. This procedure promotes accelerated elimination of metabolic products. In addition, it becomes possible to treat the inflamed walls of the bladder with an antiseptic solution, which leads to relief of the patient’s condition.
How to restore the bladder after a catheter?
After the procedure there is a recovery period
. The procedure itself may cause discomfort and even pain.
The recovery process includes resting the patient for the first two weeks
. It is shown to lie down a lot, because physical fatigue can lead to complications. You should also not lift weights for the first month.
The patient should try to empty the bladder himself, even if it is not easy at first. Liquid may come out in small quantities at first. We must try to relax him as much as possible, not be nervous or worry.
Gradually, the functions of the bladder and urinary tract are normalized. Usually, patients recover in the first days; by 3-4 days any pain and discomfort disappear, urine is excreted correctly, and the amount is within .
In severe cases, the patient may need diapers
. Liquid may come out very unexpectedly. This is completely normal during the recovery period.
Gradually, the functions of the bladder are normalized, and the person learns to control the process of urination.
The first week you need at least 2-3 times a day
treat the urethra with antiseptics to prevent inflammation.
Bladder catheterization is a serious procedure that helps in treating the bladder and examining its condition. A correctly performed procedure will help the patient recover.
How and how to flush a catheter in the bladder if it is clogged, learn from the video:
For various pathologies of the urinary system in animals, catheterization is often used. The catheterization procedure when spontaneous urination is impossible in pets requires certain qualifications and is usually performed in specialized institutions. But there are situations when animal owners have to perform the procedure themselves. Therefore, the questions of how to remove a catheter from a cat, whether this can be done at home without having special skills, are more than relevant.
Read in this article
Indications for the procedure
The main indication for bladder rinsing is acute inflammation, accompanied by impaired urine outflow. In urology, this technique is most often used for cystitis. This disease is typically associated with a secondary infectious process. However, it does not develop instantly, but only under the influence of certain factors. It could be:
- tonsillitis;
- staphylococcus;
- sinusitis;
- flu.
In addition, bladder lavage is recommended for paralysis of the body. The procedure must also be used before diagnosing pathologies of the organs of the excretory system. Also among the indications it is worth noting the long-term use of certain medications.
Why is this procedure needed?
Indications for catheterization are:
- Acute urinary retention. The causes may be neoplasms (tumors) and urolithiasis.
- Inability to urinate on your own. This situation often occurs after operations with infusion therapy. A person wants to urinate, but is unable to do so due to spinal anesthesia.
- Administration of medications (antibiotics, decoctions and infusions of herbs, antiseptics).
- Obtaining urine for the purpose of laboratory research.
- Carrying out an X-ray examination of the bladder using dyes.
This procedure can be single or multiple, short-term or long-term. Do not confuse catheterization with cystoma. In the latter case, urine is surgically removed through an opening in the abdominal wall, bypassing the urethra.
Possible contraindications
Only a doctor can prescribe such a procedure if there are appropriate indications. The specialist must take into account the patient’s health condition. After all, rinsing the bladder does not always give a positive therapeutic effect. In what cases is intervention contraindicated?
- Injuries and mechanical damage to the organs of the excretory system.
- Blocking of the urethra with a calculus.
- The presence of neoplasms, including benign ones, in the bladder.
- Prostatitis in acute form.
- Spasm of the urethra.
- Some sexually transmitted diseases.
These are not all contraindications. Therefore, it is worth mentioning once again about the need for preliminary consultation with a doctor and a diagnostic examination.
Technique
Many specialists first perform a manual bladder massage on the animal before inserting a catheter. Often this manipulation leads to the resolution of the urinary plug formed in the urethra and the spontaneous passage of urine.
The procedure for installing a catheter is painful for animals, especially for cats, whose urethra is narrower. Therefore, veterinary specialists most often use sedatives and anesthesia. In very rare cases, catheterization is performed without the use of anesthesia. As a rule, older animals with heart problems are prescribed painkillers.
Catheterization is usually carried out by a veterinarian with an assistant
. The animal is fixed in a lateral position. Hair in the perineal area is cut off and disinfected. The cat's penis is pushed out of the prepuce and a catheter pre-lubricated with sterile Vaseline is inserted into the urethra. To facilitate insertion, the foreskin of the penis is pulled back. Using careful movements, the device is inserted into the bladder. Cats are given painkillers that are injected into the vagina.
If there is obstruction of the genitourinary tract and difficulty installing a catheter, rinsing the urethra with saline solution is used to wash away the sand. After inserting the catheter, a special cuff is used to secure it, which is sewn to the animal’s skin. Then a urine collection system is attached. To prevent loss, the catheter is secured to the pet's tail in such a way that there is no tension on the sutures. It is advisable to put a special collar on the cat.
This is why it is not possible to change the catheter yourself.
Preliminary preparation
Before prescribing manipulations, it is imperative to check the patient’s excretory system. This is done to assess bladder capacity. The volume of the organ can be measured by estimating the amount of urine released during one act of urination. The use of medications during this procedure is not recommended. Their help should be resorted to only if there is purulent secretion in the urethra.
Psychological preparation of the patient is carried out by a doctor. The specialist should explain the algorithm for flushing the bladder and tell what materials and medications are used. The patient should not have any fears or questions related to future intervention.
Urinal system + catheter
Bedside urinal
Urinal with fastenings
If a patient has undergone urological surgery with unnatural urinary diversion, a urinal bag is more often used, which can be emptied as it fills. It is disposed of after a few days, since the product cannot be sterilized. In this case, the urinal is connected to a catheter (drainage tube).
Often the urine collection bag has an adjustable drainage hole to drain the contents. More advanced models have a valve that prevents the reverse flow of urine, which helps prevent the upward spread of microbial flora in the urogenital tract. The volume, material and methods of fastening urinals vary. Some devices are equipped with a pad that prevents skin irritation at the point of contact.
Currently, urinals are popular, which allow urine to be drained through a special hole with a tap without disassembling the entire system (without disconnecting from the drainage tube), have graduations for assessing the volume of liquid and anti-reflux protection. The bag itself is divided into 2 parts, which when filling does not make it noticeable due to the tight fit of the leg. The corrugated tube does not bend, and its smooth inner surface prevents the spread of bacteria. The material of the uroreceiver restrains the smell inside and does not make noise when walking.
According to most urologists, such urinals are the best.
Which medicine should I choose?
The basis of solutions for washing the bladder is selected taking into account the disease that caused congestion. In the vast majority of cases, Furacilin is used. Sometimes doctors insist on using Penicillin or Collargol. These medications help fight the infection. The substances included in the composition prevent further division of pathogenic elements.
For preventive rinsing, plain water or boric acid (2%) is used. The solutions must first be warmed to room temperature. It is prohibited to use cold liquids. This can provoke spasm, resulting in additional injuries to the organ.
Optimal cleaning agents
At home and within the walls of a medical institution, the following means are used to wash the bladder cavity:
- Furacilin solution (antiseptic).
- Protargol solution.
- Penicillin (broad-spectrum antibacterial drug).
- Distilled water.
- A weak solution of boric acid.
- Potassium permanganate solution.
- Miramistin.
- Chlorhexidine.
- Dioxidine.
- Physiological solution of Sodium chloride.
Washing with diuretics and Heparin is not carried out. The injected liquid should be warm. Cold solutions should not be administered.
How to prepare the solution
To obtain a cleaning solution for rinsing the bladder, you must:
- grind 2-3 tablets of Furacilin;
- add 400-500 ml of boiled or distilled hot water;
- mix thoroughly until the medicine is completely dissolved (if necessary, strain);
- cool to room temperature.
Algorithm for the procedure
To carry out the procedure, it is necessary to follow a clear algorithm of actions. First, let's look at how to flush the bladder through a catheter.
The patient should lie down in the most comfortable position for the manipulation. Doctors usually suggest sitting on a couch. The patient lies on his back, bends his knees and spreads them, slightly lifting the pelvis.
The specialist attaches the syringe or Esmarch device to a tripod. In relation to the patient, they are located at a height of approximately 0.5 m. Initially, the anterior area of the urethra is washed. For this purpose, a catheter is installed in the urethra and smoothly advanced until the outflow of urine begins. This sign indicates that he has reached the “final point”. After this, the doctor waits until the entire bladder is completely emptied.
At the next stage, a syringe is attached to the catheter, and a medicinal solution is pumped into the organ. The most common choice is to wash the bladder with Furacilin. It is filled until the patient feels the urge to urinate. After this, the syringe is removed. Spontaneous outflow of previously administered fluid occurs through the catheter. At this point the procedure can be considered complete. To obtain a lasting therapeutic effect, the patient must remain in a supine position for about 30 minutes.
Washing technique
When performing catheterization, the algorithm must be strictly followed. To carry out the procedure you will need:
- antiseptic solution or anti-infective solution;
- sterile disposable gloves;
- Janet syringe;
- Foley, Tieman, Kasper, Pezzer or Nelaton catheter;
- antiseptic (alcohol);
- urine collection container;
- Vaseline for lubricating the catheter;
- sterile cotton balls;
- tweezers (they grab the instrument);
- sterile forceps (clamp).
Catheters can be soft or hard (metal). The former are used more often. They are rubber tubes consisting of a balloon, a passage for urine and inflation of the balloon, and the tube itself. Their length ranges from 12 (for women) to 40 cm (for men).
When flushing the bladder, you must follow the following sequence of actions:
- Reassure the patient and establish a trusting relationship with him.
- Isolate the person. A screen is used for this.
- Conveniently position the patient. He should be lying on his back with his legs spread apart.
- Place a container to collect urine between the person’s legs.
- Draw up the rinsing solution in advance.
- Wash the patient or wipe the external genitalia with a disinfectant.
- Wash your hands and put on gloves.
- Draw the rinsing solution into the syringe. Its temperature should be around +37ºC.
- Take out the catheter and lubricate the tube with Vaseline (this is necessary for better glide and to prevent injuries).
- Find the urethral opening and carefully insert the catheter with the rounded end first. It is advanced slowly until urine is removed.
- It is easy to press on the pubic area at the end of the procedure, when urine stops flowing.
- Connect the Janet syringe to the tube and inject the solution.
- Apply the clamp and remove the syringe.
- Place the other end of the tube in the tray.
- Remove the clamp.
- Remove the catheter.
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Process materials.
Flushing the bladder through a cystostomy
A cystostomy is another device that is also used to flush the bladder. However, the algorithm of actions is somewhat different from that with the use of a catheter. In this case, the outflow of fluid occurs through the abdominal cavity. Using a cystostomy, flushing the bladder is recommended for those patients for whom it is impossible to insert a catheter due to injury or damage to the urethra.
This device is usually installed for a long time. The tube is replaced once a month or more often. The organ cavity is washed using antiseptics or medications. The procedure is repeated several times until the solution finally becomes clear. A special drainage bag is used to drain fluid. It is usually installed just below the level of the bladder. After washing is completed, the skin around the cystostomy is treated and a bandage is applied.
Rules to help avoid complications
1. Despite the fact that the urine bag can be used for several days, it is a disposable medical product, i.e. no need to try to wash it, boil it, wipe it with alcohol, etc. Just replace the bag with a new one.
2. If urine does not flow into the urinal, pain or fever appear - immediately call an ambulance. Do not wait to see a urologist; the sooner the flow of urine is restored, the lower the risk of serious complications.
3. Remember that according to the laws of physics, for adequate outflow of fluid, the level of the urine collection bag must always be below the level of the bladder. Otherwise, there is a risk of acute inflammation: cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis, etc.
4. Before you go to sleep, secure the urine bag to the bed.
5. Make sure that the tubes are not kinked or tangled (corrugated tubes are more reliable).
6. Make sure the tap is closed.
7. Do not allow the bag to be completely filled; drain the urine when it reaches 1/2 or 2/3 of the volume.
8. Before replacing the urine bag, do not forget to sanitize your hands.
9. Try to drink more liquid, this will reduce the concentration of urine and reduce the process of salt formation.
10. Eliminate rich broths from meat, chicken or fish, offal, sausages, smoked meats, and marinades from your diet.
11. Visit a urologist regularly and have your urine tested at least once every 2-3 weeks (unless otherwise prescribed).
Uroseptics, antibiotics and litholytic (stone-dissolving) agents prescribed by a doctor help prevent/reduce the inflammatory process.
Features of washing at home
Before starting any treatment, consultation with your doctor is necessary. Despite the apparent simplicity of washing, this procedure is sometimes accompanied by certain difficulties.
It is worth noting that the situation is easiest with the female body from a technical point of view. After all, the urethra has a small length. For men, the procedure is fraught with some difficulties. For example, the length of the urethra is already about 25 cm, it has several narrowings. In this case, all manipulations should be carried out with extreme caution and skill.
First, the catheter must be lubricated with Vaseline. It should be moved along the urethra very smoothly, making rotational movements. In places where anatomical narrowings are present, the man should be asked to take 4-5 deep breaths. This way you can avoid severe pain and relax the muscles. If a spasm occurs, it is recommended to stop the procedure immediately. After relaxing the body, you can begin manipulation again. The catheter continues to be deepened until the first drops of urine come out.
Sometimes you have to resort to using a metal tool. The need to use this type of catheter is due to pathological changes in the male body. We are talking about diseases such as prostate adenoma and urethral stricture. Rotational movements with a metal catheter are prohibited, as the risk of mechanical damage to the walls of the organs increases.
Features of children's urinals
The main purpose of children's urinals is to provide comfortable urine collection for babies. This device makes life much easier for young parents who know very well what a problem it is to collect tests and how difficult it is to “predict” the moment when their child wants to go to the toilet. Today, urinals for babies help solve this pressing problem, with the help of which you can collect the required amount of urine for analysis without problems and stress for babies and their parents.
Urinary bags for babies are a simple bag with a hole that is attached to the baby's skin with Velcro.
This device is absolutely safe to use and does not threaten the slightest discomfort for the baby, especially if you use models that take into account the anatomical characteristics of babies of different sexes.
The bags of children's urine collection bags are made of polyethylene. Using Velcro, the device is securely attached to the skin, as a result of which all urine falls into the bag. There are markings on the bag that make it possible to control whether a sufficient amount of material has been collected for analysis. Standard pediatric models are designed to draw up to 100 milliliters of liquid.
Many parents are concerned that the Velcro used to attach the device to the skin may cause pain, discomfort or irritation to the baby.
However, in fact, it is absolutely safe thanks to the use of a special adhesive composition that does not contain any harmful substances. After the urine collector has fulfilled its function, it can be easily removed, and no marks will remain on the baby’s skin.
Separately, mention should be made of the attachments for the opening of the bag, which take into account the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of representatives of both sexes.
There are three types of children's urinals:
- for boys;
- for girls;
- universal.
Urine bags with oval holes are universal. They are suitable for babies of both sexes. However, the use of specialized urine collection bags is more comfortable. For boys, the hole has an ovoid shape, pointed downward, and for girls, it is more rounded, with branches on the sides.
Complications after manipulations
Flushing the bladder should not be accompanied by severe pain. The appearance of discomfort usually indicates an illiterate procedure or excessive stretching of the organ. In such a situation, it is necessary to stop all manipulations and allow the liquid to come out calmly. In what other cases should rinsing be suspended?
- Urethral spasm or difficulty inserting a catheter.
- Bleeding.
- Incorrect selection of the drug, as a result, burns the mucous membrane.
- Infection of the bladder due to insufficient aseptic processing of instruments.
If the solution does not flow back, this indicates a blockage in the catheter tubes. The cause of this problem is mucus. To dissolve it and continue all manipulations, it is necessary to rinse the catheter with a special product.
In order to prevent these complications, it is better to perform the procedure in a hospital setting and under the constant supervision of a doctor.
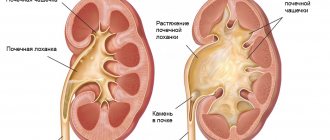
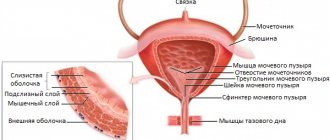
A urological catheter is a hollow tube that can be installed through the urethra or surgically through the skin into the urinary tract (with the tube coming out above the pubis). In the second case, the catheter will be called a cystostomy.
After bladder catheterization has been performed, the catheter must be carefully maintained. This is necessary to ensure that medical equipment works correctly to prevent infections of the urinary organs. Usually, after installation, doctors themselves tell patients how to care for the bladder catheter.
When are urinals installed?
Urinary receivers are inserted into the bladder through the urethra. They are installed when the patient needs to reduce pressure in the bladder area, for example, in the postoperative period when the bladder ruptures or other injuries, during operations or when urination is difficult. But there are cases when installing a urinal through the urethra is prohibited or irrational. These cases include:
- long-term installation;
- rupture of the urethra as a result of trauma;
- operations on the urethra;
- benign formations of the prostate gland.
In such a situation, doctors resort to surgical removal of an artificial canal - a cystostomy. It is located above the pubic area.
Basic care
Urinary catheter care includes the following:
- Every time after going to the toilet, the patient should clean the genitals with warm water. It is important for women to watch the direction of their hand when washing. Movements should be from front to back. In this way, transfer of infection from the rectum to the catheter can be avoided.
- The area in which the catheter is installed should be periodically inspected under good lighting. This will help to detect the inflammatory process in time and, if necessary, begin treatment.
- In the area where the catheter is installed and where it comes out, you need to wash the skin. It is recommended to do this twice a day.
- The urinal should be located below the level of the bladder.
- The system must be secured using a special bandage.
- Urine should be drained from the reservoir every 3 hours.
- The container in which urine is collected must be rinsed daily. If the tank is disposable, it needs to be changed on time.
- It is strictly not recommended to use any sprays, powders, gels or creams in the area where the catheter comes out.
Caring for your external urinary catheter involves regularly disinfecting it. It is important not to handle the tube in the area of the skin outside (if the patient has a cystostomy) and in the area of the external opening of the urethra (with a urethral catheter). For these purposes, it is recommended to use Chlorhexidine bigluconate 0.05%. The procedure must be performed daily.
Patients who have a catheter installed should reduce their consumption of spicy, salty and smoked foods. A complete abstinence from alcohol and cigarettes will be helpful.
Preparing for installation
Preparation for the procedure includes the following steps
:
- A few days before the procedure, the patient is examined by a doctor to ensure that there are no contraindications.
- 1-2 days before the procedure, it is better to avoid spicy, fatty foods, alcoholic and sweet carbonated drinks.
- A few minutes before the procedure you need to wash yourself.
- The patient then goes to the treatment room, where he is prepared even more thoroughly by a specialist.
- The doctor treats the genitals with an antiseptic and tells the patient about the upcoming actions.
After this, the patient is ready for the procedure, for the insertion of a catheter.
Flushing the catheter
Normally, after surgery and correctly performed catheterization, flushing the catheter is not required. Emptying the bladder itself is already a prevention of the infectious process.
In order for the natural cleansing of the urinary system to occur more efficiently, the patient may be prescribed herbal preparations. Cranberry juice will also be useful for cleansing.
To understand whether a flushing procedure is necessary, the patient must pay attention to how the drainage functions.
If the urine is clean and it flows freely through the catheter, flushing is not necessary. In this case, it is enough to simply replace the catheter with a new one once a week (although in practice, replacement usually occurs every 2 weeks). As for the cystostomy, it needs to be changed every month. This should be done by people with medical education. Replacing the catheter yourself at home is fraught with infection and injury to the urinary organs.
Flushing the bladder catheter may be necessary in the following cases:
- cloudy urine;
- the appearance of salts, flakes, sediment in the biofluid;
- periodic clogging of the tube.
In all of the above situations, flushing the bladder through a catheter should be done every 12-24 hours.
In particularly advanced cases, when the tube is severely clogged with crystals, more careful care of the urinary indwelling catheter is required. Then washing should be carried out up to 4 times a day. In this case, a large volume of liquid should be used. In this case, the catheter is replaced more often.
Cleaning products
Flushing the urinary catheter is usually done using the following means:
- Furacilin;
- Potassium permanganate (in proportion 1:10000);
- Dioxidin (before use it must be diluted with saline in a ratio of 1:40);
- Miramistin;
- Boric acid (2% solution);
- Chlorhexidine (2%).
To flush the catheter with Furacilin, you can use either a ready-made solution purchased at a pharmacy or tablets. If we talk about how to rinse a urinary catheter with Furacilin in tablet form, then doctors recommend making a special solution for this.
This is done like this: 1 part of Furacilin is added to 5000 parts of distilled water. As a result, the patient will receive a solution of Furacilin 0.02%. To make the drug dissolve faster in water, it can be brought to a boil.
Before flushing the urinary catheter, you need to wait until the solution cools to a comfortable temperature. Thus, to prepare 100 ml of a 0.02% solution, you need to use 1 tablet of Furacilin, 0.1 g each.
It is important to note that a drug that is ideal for one patient may be useless or even harmful for another, and vice versa. The urologist will tell you exactly what to use to rinse the catheter in the bladder and what dosage of the drug to use.
Washing procedure
If the patient decides to flush the catheter, then the procedure algorithm and care of the urinary catheter must be followed as accurately as possible. Amateur activity in this case is categorically not encouraged. To flush the catheter you need to use a syringe, the volume of which is 50-100 mg.
Before rinsing the bladder catheter, the patient should place the syringe in boiling water for a few seconds, wash their hands with soap, and then wipe them with cotton wool soaked in alcohol.
At the end of the preparatory activities, the solution prescribed by the specialist is drawn into the syringe. The tube is disconnected from the urine bag, and its end is treated with an antibacterial solution. Next, a syringe is inserted into the tube and the prepared solution is gradually and slowly injected from it. It is better to start with small portions (approximately 20-30 ml). After all the liquid has been injected, the syringe is removed.
The injected solution flows out of the tube on its own. These steps must be performed three times. It is worth noting that flushing the bladder catheter in men may be more difficult than in women. This is due to the fact that men have a longer and narrower urethra.
To avoid unpleasant sensations, a man needs to relax as much as possible. To better understand the essence of the procedure and avoid mistakes, you can watch a video on how to flush the bladder through a catheter.
Bladder catheterization in men - procedure technique
Catheterization is a medical procedure that involves inserting a hollow tube into the urethra. The special tube is called a “catheter” and is where the procedure gets its name. It is performed to drain the bladder cavity.
Catheterization is necessary for therapeutic and sometimes diagnostic purposes. The catheter helps remove urine from the bladder and rinse the cavity. Also, using a tube, you can introduce various medicinal substances into the bladder cavity.
In men, catheterization is performed to remove urine and rinse the bladder. A catheter can be made from a variety of materials, but it is a hollow tube with one or two holes at the end. The catheter cavity is slightly expanded.
The urethral tube was first used in medicine back in 1929.
In men, it is more difficult to carry out the described procedure than in women due to the longer urethra (22-25 cm). Also, a man’s urinary canal has two physiological narrowings, which makes inserting the tube quite difficult.
Initially, soft tubes are used for catheterization (less pain). If the doctor is unable to insert a soft catheter, then a hard catheter is used (can only be inserted by a doctor).
Important! In general, the use of a metal catheter in modern medicine is quite infrequent, since it is a painful method that can severely injure the canal.
But in rare cases, it is necessary to insert just such a tube. The situation should be discussed with your doctor and find out who will perform the procedure.
To properly insert a metal catheter, a man needs a doctor with extensive experience in this field.
Indications for procedures (regardless of gender):
- Urinary retention in acute or chronic form. The delay may be associated with various pathologies:
- urethral tumor,
- BPH,
- bladder paralysis,
- damage to the spinal cord, structures of the urethra and others;
- For the purpose of rinsing for inflammatory diseases of the bladder;
- When do you need to get vesicular urine for analysis?
In this list, each doctor notes infectious urethritis, spasm of the urinary sphincter. Also, catheterization is not performed in the absence of urine (anuria).
If you have certain diseases of the genital area, the described procedure may also not be carried out, so you need to warn your doctor about everything in advance.
For what reasons do complications arise:
- Incomplete examination;
- Ignoring the rules of asepsis;
- Incorrect insertion of the catheter. This is especially true when introducing a metal tube;
- Use of force during the procedure.
If catheterization is done incorrectly, this leads to infection of the urinary system and the development of certain diseases.
The walls of the urethra can also be damaged (most often observed in men).
Complications of the first group can also occur in women and usually occur in an equal distribution between the sexes.
- two soft sterile catheters, different in diameter,
- two gauze pads and cotton balls,
- glycerol,
- tray,
- tweezers,
- syringe Janet,
- diaper,
- latex gloves,
- containers for urine.
Rubber catheters are an elastic tube up to 30 cm long (for men, for women 12-15 cm long).
The outer end of the tube is cut off or has a funnel-shaped extension. The metal tube is curved and has a rounded inner end.
It is very important to follow the correct algorithm for bladder catheterization in men.
The external opening of the urethra is washed with a cotton ball. The ball must be moistened.
With his left hand, the doctor takes the penis just below the head. Using the index finger and thumb of the left hand, the doctor spreads the lips of the external opening of the urethra.
The catheter is smoothly inserted into the urethra. In this case, you need to place it between the fourth and fifth fingers of your right hand, and carefully hold the second end with tweezers.
When removing the tube from the bladder, you must clamp its free end. This prevents the urethra from being irrigated with bladder contents.
With the correct technique of catheterization of the bladder in men, pain is weak or completely absent.
The patient is placed on his back and his legs are spread apart. The doctor stands to the left of the lying patient.
The outer end of the urethra is treated with antiseptics, then the doctor takes the penis with his left hand and releases the passage inside. The doctor inserts the catheter with his right hand, his beak should be facing down.
When inserting, you must carefully pull the penis onto the instrument.
Under the influence of its own gravity, the catheter will penetrate freely deep into the external sphincter. Here will be the first obstacle.
To pass this bend, the doctor moves the penis and the tube to the midline and gradually lowers it down towards the scrotum. It will be necessary to overcome the resistance of the sphincter, but you should not exert any force.
If everything is done correctly, the doctor can easily move further in the right direction. Correctly inserted, the catheter can be easily rotated in the bladder cavity to the sides (but only along the longitudinal axis).
As for the insertion of a metal instrument, this is a serious manipulation and can only be performed by a doctor with extensive experience and extreme caution. Rough insertion leads to damage to the canal walls, hemorrhage and dangerous complications.
The catheterization procedure should only be performed by professionals in clinics and hospitals.
In men, catheterization is more difficult than in women. This is due to the structural features of the urinary system. It is important to properly prepare for the procedure and carefully discuss all your concerns with the doctor.
With the correct approach, the bladder catheterization procedure in men has no complications.
A fairly common nursing inpatient procedure is urinary tract catheterization. Sexual differentiation plays a paramount role when carrying out such manipulation. The procedure with a soft catheter is used much more often in men than in women. This is caused by differences in the male and female genitourinary systems.
In women, the urinary tract is quite passable and wide, this allows the procedure to be carried out quickly and efficiently. In men, the urinary system contains a long narrow urethral passage, about 30 cm long, as a result, the technique of catheterization of the bladder is more complicated in them, due to the risk of injury to the mucous membrane.
Particularly difficult for the catheter to pass is the area of localization of the cavernous bodies at the border with the spongy bodies in men.
Catheterization of the bladder in men is performed if it is necessary to forcefully empty the urinary reservoir, as well as to perform treatment and diagnosis of certain diseases. You can also distinguish a procedure such as cystoscopy, which is one of the options for catheterization of the urinary tract.
Referral to such a study involves inserting a cystoscope into the cavity for diagnostic purposes. Cystoscopy is performed under general anesthesia.
Inserting a catheter into the bladder carries a risk of injury to the urethral canal, so the use of soft probes is preferable.
| Name | Properties | Functional |
| Foley with two channels | An expandable container inflated with air for securing the catheter; through the first stroke, the balloon is inflated, and through the other, urine flows out. | Permanent catheterization. |
| Three-channel foley | There is one more passage for administering medications. | Drainage, cleaning, administration of medications. |
| Timmana | There is a curved tip. | For prostate adenoma. |
| Pezzer catheter | The probe is secured by a plate-shaped thickening. | Long-term. |
| Nelaton probe | Rounded end, small size. | Little used, previously long-term catheterization, now single-use. |
Carrying out manipulation in men is almost always associated with painful sensations, which means it is advisable to use local anesthetics to place a catheter.
To carry out the manipulation you need to prepare:
- antiseptic;
- sterilized set of materials (tampons, napkins, diaper);
- container filled with liquid;
- tweezers or clamps;
- the probes themselves.
When carrying out the manipulation in question in men, it is necessary to take into account that the urinary tract is covered with mucous membrane and is susceptible to injury and infection, therefore the procedure is not applicable if damage is present, as this can cause complications.
In this case, it is advisable to use an epicystostomy. Access for installing an epicystostomy opens through the abdomen, in an operating room using anesthesia.
The catheter is fixed to the anterior abdominal wall with sutures and adhesive tape. The advantages of epicystostomy also include:
- absence of irritation of the urethral canal and its injury;
- maintaining patient mobility;
- the ability to monitor the resumption of normal urination.
It is also possible to catheterize the bladder using rigid catheters. These procedures are within the competence of the physician and are used when it is impossible to install a soft catheter.
Technique
The manipulation is performed with the patient lying on his back, legs apart and bent. Immediately before inserting a catheter into the urethra, genital hygiene is carried out from front to back.
Before catheterization, the outlet is treated with an antiseptic. For men, it is advisable to inject a small amount of a lubricant (for example, glycerin) and an anesthetic into the urethra (2% lidocaine can be used).
Catheterization in a man is most often performed with a rubber Foley catheter. To carry out the manipulation, it is advisable to use the following execution algorithm:
- clean hands of dirt, disinfect with an antiseptic, wash the patient from front to back in order to prevent infection;
- prepare a disinfected kit (swabs, syringe, clamp);
- put on gloves, open access to the urethra using sterile material, carefully move the foreskin, treat the penis with an antiseptic;
- then a solution of glycerin and an anesthetic are injected into the urinary tract to facilitate insertion of the probe and relieve pain;
- then, insert the probe using a clamp or tweezers into the urinary tract to a depth of about 7 centimeters. By advancing the probe in stages at each pass to a depth of about 5 centimeters, they achieve outflow of the contents, this indicates the insertion of a catheter into the bladder;
- after the outflow of contents has stopped, the urinary tract is washed with an appropriate antiseptic until clear liquid is removed;
- At the end of the procedure, carefully remove the probe from the urinary tract and re-disinfect the genitals with an antiseptic.
Indications
Recommendations
Sometimes, even if proper care of the urinary indwelling catheter has taken place, the algorithm prescribed by the doctor has been followed exactly, problems still arise. In this situation, it is very important not to engage in amateur activities.
An unscheduled visit to a urologist may be required if:
- urine leakage;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of blood in urine;
- stagnation of urine;
- a significant increase in the volume of urine excreted;
- bleeding from the area in which the catheter is installed;
- changes in the smell of the biological fluid, its shade, and physical characteristics.
In addition, consultation with a specialist is required if discomfort occurs during urination or if body temperature rises.