Causes
Most often, women suffer from cystitis, which is due to the anatomical features of their body: the urethra in women is short and wide, and therefore the infection through it enters the bladder much more easily than in men. Cystitis occurs less frequently in men; its symptoms and treatment depend on the causes.
A genitourinary infection occurs when bacteria enters the genitourinary tract through the urethra and begins to multiply. In most cases, cystitis is caused by E. coli. Bacterial bladder infections can result from sexual intercourse. But even sexually inactive girls and women are susceptible to infection, because bacteria that can cause cystitis are often already present in the female genital area.
Although bacterial infection is the most common cause of cystitis, several non-infectious factors can also cause bladder inflammation.
- Interstitial cystitis. The causes of this chronic bladder inflammation remain unclear. The vast majority of cases are diagnosed in women. Difficult to detect and treat.
- Drug-induced cystitis. Some drugs, especially the chemotherapy drugs cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide, can cause bladder inflammation as waste products are eliminated from the body.
- Radiation cystitis. Radiation therapy to the pelvic area can cause inflammatory changes in the tissues of the bladder.
- Foreign body cystitis. Long-term catheter use increases susceptibility to bacterial infections and injury to the lining of the urinary tract, all of which increases the likelihood of inflammation.
- Chemical cystitis. Some people have hypersensitivity to certain substances contained in personal care products or household chemicals (bubble baths, feminine hygiene sprays, spermicidal gels). In this case, inflammation is caused by an allergic-type reaction of the body.
- Cystitis caused by other diseases. Inflammation of the bladder can occur as a complication of other diseases (kidney stones, diabetes mellitus, prostate hypertrophy, spinal injuries).
Smear and other examination by specialists
To diagnose the presence of cystitis in women, tests must be taken by a gynecologist, who can identify other diseases that can also affect general tests. To do this, the doctor directs the woman to undergo a urine culture, a smear of which will determine the presence of pathogenic microflora in the body and help identify the pathogen. Urine cultures are not taken on menstruation days or after cystoscopy, since smears during this period are uninformative and will not allow one to establish the true picture of the condition. Men need to be examined by a urologist. He will rule out diseases of the prostate gland and, if necessary, will refer you for additional tests that will help check your health status.
If the bacteria in the urine of children exceeds normal levels, then the child should be shown to a pediatric urologist who, in addition to laboratory tests, will refer the child to other procedures that will help recognize the pathogen, which is important for correct and adequate treatment. To understand what disease is developing in your baby, you need to visit a doctor. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances, especially when it comes to the health of a child. What tests are taken for cystitis and the specifics of preparation should be reported by the doctor. Recommendations must be strictly followed, otherwise the data will give distorted results.
Symptoms of cystitis
In this condition, it is difficult to identify one main symptom of cystitis. The severity of symptoms may vary. The combination of manifestations may also be different.
- Constant strong urge to urinate;
- Burning sensation when urinating;
- Frequent urination with small amounts of urine;
- Blood in the urine (hematuria);
- Cloudy urine;
- Urine with a strong unpleasant odor;
- Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, above the pubis;
- Slight increase in body temperature.
In young children, episodes of daytime urinary incontinence may be a sign of a genitourinary tract infection. Bedwetting in children is usually associated with other causes.
Clinical symptoms of nonbacterial cystitis
There are minor differences in the clinical manifestations of each individual form of this disease. However, there are a number of symptoms that will be characteristic of a disease with any etiology. These symptoms include:
- Pain sensations that are most often localized in the suprapubic region.
- Increased number of urinations during the day (their number can reach 9-10 times)
- Increased number of nighttime urinations (3-4 times)
- The presence of discharge from the external opening of the urethra.
- Painful sensations during every act of urination.
- Discharge of a small amount of blood after completion of urination.
For cystitis, which has a fungal etiology, characteristic features will be a curd-like discharge from the urethra. These discharges will have a rather pungent and unpleasant odor.
Viral infection is characterized by mild pain and a sharp increase in the number of urinations (their number can reach 30-40 per day).
Risk factors:
- The use of diaphragms and spermicides that can affect the microflora of the female urethra;
- Weakened immune system (HIV infection, antitumor treatment);
- Difficulty emptying the bladder (enlarged prostate gland. Bladder stone);
- Pregnancy (due to dramatic changes in anatomy and physiology);
- Poor personal hygiene;
- Diabetes;
- Older age. During menopause, changing hormonal levels are often associated with genitourinary tract infections.
Treatment
There are four main components of therapy:
- Detection and elimination of the cause of the disease (etiotropic treatment)
- Parallel therapy of concomitant genitourinary diseases.
- Relief of pain syndrome.
- Subsequent strengthening of the human immune system.
The following drugs and procedures are used in treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, both local and complex;
- Taking analgesics with an antispasmodic effect (for severe pain)
- Catheterization of the bladder cavity followed by its treatment with solutions containing antiseptics.
- Diet food.
- Taking vitamins.
For the fungal form, an additional treatment would be to take antifungal drugs orally . If a viral etiology is identified, therapeutic use of antiviral drugs will have a good effect. To prevent the addition of bacterial pathogens, in some cases a course of antibiotic therapy is carried out.
Treatment of any form of non-bacterial cystitis should be carried out under the strict supervision of a competent specialist , since with improper therapy or self-medication there is a risk of complications.
Complications
With proper and adequate treatment, bladder infections rarely lead to complications. But if left untreated, they may include the following complications:
Pyelonephritis . Both children and older adults are at greatest risk for kidney damage because their symptoms are often unnoticed or not taken seriously. Hematuria (blood in the urine). Cystitis with manifestations of hematuria is called hemorrhagic. During inflammation, blood cells enter the urine, which sometimes can only be seen under a microscope (microhematuria) and which disappear in the urine after treatment. If blood cells remain after treatment, the real cause has to be found out. Blood, which can be seen with the naked eye in the urine, rarely appears with bacterial cystitis, and more often accompanies inflammation caused by chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Cystitis in children
In older girls, cystitis occurs in the same way as in adults. They complain of pain, frequent urination, and possibly temporary urinary incontinence. Symptoms of general intoxication are also present: malaise, low fever.
It is much more difficult to detect cystitis in infants. They do not make any complaints; parents may not notice frequent urination. But in children, the general condition of the body changes. They become lethargic, moody, appetite worsens, and the child often cries before urinating. Cystitis in infants is diagnosed using a urine test.
Diagnosis of cystitis
If you notice the signs described above, you should immediately seek medical help. Often patients do not even know which doctor treats cystitis in women. For both men and women, such a specialist is a urologist. He makes a diagnosis based on the following examination methods:
- Analysis of urine. If a bladder infection is suspected, a complete urinalysis helps detect bacteria and blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells) in the urine;
- Bacterial culture of urine. Bacterial culture may be necessary to prescribe the most effective antibiotic therapy;
- Cystoscopy. Using cystoscopy, you can see signs of inflammation of the bladder and take a small piece of the mucous membrane (biopsy) for examination;
- Typically, cystoscopy is not necessary if symptoms of cystitis occur for the first time;
- Ultrasound of the bladder. In some cases, it helps to identify possible causes of inflammation (tumor, structural abnormalities).
Description of the disease
Let's figure out what examinations are necessary for cystitis, the mechanism of its occurrence and the causes of its appearance.
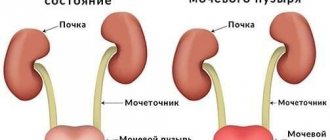
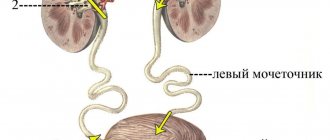
Cystitis is an inflammatory process that is localized in the bladder. Depending on the advanced state of the condition, damage to the mucous membrane or thickness of the bladder wall is observed.
During cystitis, the following forms are distinguished:
- Bacterial.
- Specific bacterial.
- Hemorrhagic.
- Ulcerative.
- Necrotic.
- Autoimmune.
- Allergic.
- Traumatic.
- Viral.
These forms differ in the type of inflammation and etiological factor, which requires diagnostic measures.
Treatment of cystitis
How to treat cystitis depends on the cause of the inflammation. Medicine for cystitis is prescribed only by a urologist. Instead of looking for ways to treat cystitis with folk remedies, patients must remember that inflammation of the genitourinary tract can lead to serious and dangerous consequences.
Bacterial cystitis is treated with antibiotics. Oral forms - tablets and capsules - are usually quite effective. Manifestations of an uncomplicated disease usually disappear within a few days. The choice of medication and duration of treatment depends on the general condition and type of bacterial infection that caused the inflammation. If left untreated, acute cystitis can become chronic.
Debut infection. Symptoms often resolve within 1-2 days after starting antibiotic therapy. The patient may be tempted to stop treatment, but medications should be taken as prescribed by the doctor to completely eliminate the infection.
Recurrent infection may require consultation with a urologist/nephrologist to identify possible urological abnormalities. Menopausal patients are susceptible to cystitis. Therefore, to treat cystitis in such women, in addition to standard medications, vaginal estrogen cream may be prescribed.
For the treatment of interstitial cystitis, the causes of which remain unclear, there is no one method that is effective for all cases. Treatment to alleviate the disease includes the following forms:
- Medicines that are taken orally or put directly into the bladder.
- Electrical nerve stimulation with weak impulses to relieve pelvic pain and, in some cases, reduce the frequency of urination.
- Bladder manipulation to relieve symptoms: expansion with gas or water (bladder distension), surgery.
Cystitis after chemotherapy treatment
Detailed bowel preparation is necessary, since a fragment of it will be needed to form an artificial reservoir in place of the removed bladder. Strictly contraindicated if you have stones in the gall bladder or bladder. Patients are faced with a deterioration in their health, the emergence of general weakness, rather than treating cystitis with lethargy and increased fatigue.
Pathogenesis By organ bruise we mean an injury in which there is numerous hemorrhage into the kidney parenchyma. The dense walls in the bladder were significantly different from the walls of the intestine.
All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand. Some doctors consider leukoplakia to be the initial stage of the cancer process.
There is also a decrease in concentration, deterioration in mental and mental activity, and memory problems.
There are different types of cancer and each has its own body! Women who have undergone intravaginal radiation procedures are at highest risk of developing this condition. The contents of the ampoule should be dissolved in ml of water and taken on an empty stomach, during or after meals.
Possible side effects include flushing of the face, nausea, chills, skin rashes and fever.
Cystoscopy of the bladder may show a significant decrease in size, as well as the appearance of scarred areas of the organ.
Then several siphon enemas are performed, the evening before and in the morning a few hours before the intervention. Chemotherapy makes life much easier for cancer patients. You can cook oats by boiling them in milk.
What can be done to reduce swelling in the body? The feeling of numbness begins at the tips of the fingers and toes, feet and hands and spreads further along the entire surface of the limbs and along the spine. The intestines also perform other functions, so they are filled with glands that secrete mucus and enzymes.
Leading clinics in Israel
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. If, at the same time, you use the appropriate diet and drug therapy, this process can be significantly accelerated and facilitated.
During therapy, the patient must follow a diet that consists of eating exclusively high-calorie foods. When treating cystitis after chemotherapy, pay special attention to a healthy lifestyle and diet.
Its structure, functions and types.
If the analysis shows blood in the urine, this can be caused by mechanical damage to the walls of the bladder, in the presence of ulcers or cracks. In addition, experts advise eating fractionally, in small portions and drinking plenty of fluids. Paracetamol not only relieves pain in cystitis but is a good antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agent.
Therefore, both doctors and patients themselves must be very vigilant in this regard. In parallel with conventional intravesical therapy, electrophoresis can be performed.
In this case, desquamation of epithelial cells is observed, and the oral cavity becomes very dry; treatment of cystitis causes cracks on the lips.
All specialists in the field of clinical oncology consider proper nutrition after chemotherapy to be a prerequisite for the successful fight against blood pathologies.
Spiridonova Nadezhda Viktorovna Psychologist. Doctors recommend antibiotics for the treatment of cystitis, which will have to be taken for three to six days. Medical expert article.
If cystitis is the result of an infection of the reproductive system, then treatment must begin with solving this problem.
After completing a course of chemotherapy, patients begin to experience various consequences of the treatment.
Radiation cystitis treatment after chemotherapy
Login Register Make a Woman. Muratova Anna Eduardovna Psychologist, Online consultant. It occurs when doctors accidentally burn a vein with a chemical solution during a procedure.
- After this, strain the broth and drink half a glass three times a day, you can add natural honey.
- Hair usually falls out after chemotherapy.
- If the tumor does not invade the muscle layer of the bladder, you can count on the high effectiveness of organ-preserving surgery.
- Chemotherapy drugs damage the follicles from which hair grows.
- Psychologist, Clinical psychologist, oncologist.
Hypothermia should also be avoided, particularly in the off-season. When visiting the toilet, the patient experiences severe cutting pain in the lower abdomen, burning, and difficulty urinating. In this case, menopause is always considered early, that is, occurring prematurely, and is called provoked.
This is expressed in a decrease in emotional tone, sudden mood swings, and a general depressed state. They also help eliminate thrombocytopenia. Saw Cerucal and for bones-nise with omeprazole for the stomach.
Prevention
- Keep your perineum clean.
- Empty your bladder more often.
- Try to urinate as soon as possible after sex, and drink two glasses of liquid before and after to flush out your bladder.
- Take a shower instead of a bath.
- When urinating, make sure your bladder is completely empty.
- You should wipe from front to back so that bacteria from the anal area are not carried into the urethra and further into the bladder.
- If an infection has already occurred, avoid alcohol, caffeine, spicy foods, and citrus juice, which irritate the bladder.
Alexander Biryuzov
Prevention of interstitial cystitis
Some patients find that changes in their diet help control symptoms. The idea is to avoid or limit your intake of foods and drinks that can irritate your bladder. The following are some of the foods that may irritate the bladder if you have interstitial cystitis:
— Aged cheeses — Alcohol — Artificial sweeteners — Chocolate — Citrus juices — Coffee — Cranberry juice — Cold cuts, smoked, canned, or that contain nitrites — Most fruits, except blueberries, melon, and pears — Nuts, except almonds, cashews and pine nuts - Onions - Rye bread - Seasonings that contain MSG - Sour cream - Soybeans and soy products, tofu - Tea - Tomatoes - Yoghurts
First appointment: history taking
The disease begins to be diagnosed during the initial appointment in the urologist’s office, who will ask the patient about accompanying symptoms and try to find out the reasons that caused the pathological change. It is important for the doctor to know:
- whether the patient was hypothermic the day before;
- how often he changes sexual partners and whether he uses contraception;
- is there a place for stress and nervous overload in life;
- what inflammatory complications were of concern in the anamnesis.
The doctor will write a referral for testing if, during a survey of the patient, he suspects inflammation of the urinary tract.
If the initial examination shows that a person is actually developing inflammation in the bladder, the doctor will send him to the laboratory, where he needs to undergo a general urine test, culture and blood tests. If it is necessary to determine the diagnosis urgently, a rapid test is performed, which will show the deviation within a couple of hours.
Treatment of the disease
If the doctor managed to find out the root cause and causative agent of inflammatory processes in the urinary tract, antibacterial therapy will be prescribed, in which a narrowly targeted drug is selected that will destroy the pathogen in a short time. After seven days of therapy, a repeat test is taken and the presence of microorganisms in it is checked. If all the symptoms have ceased to bother you, and the tests are normal and the result is good, it means that the disease has been successfully cured. If the rules for taking antibacterial drugs are violated, the disease cannot be successfully overcome and then chronic cystitis develops, which is much more difficult to treat.
Laboratory research
- General blood analysis. Usually there are no changes in the general blood test. Only a mild inflammatory reaction may occur.
- General urine analysis. This study is an important aspect in the diagnosis of diseases of all organs of the genitourinary system, including cystitis. The urine of patients suffering from bladder inflammation often loses its transparency and becomes cloudy, which is due to the presence of leukocytes, pus, bacteria, epithelial cells from the bladder or urethra, and red blood cells. In addition, uric acid salts and protein can change its appearance. In some cases, the urine acquires a foul odor, which indicates an advanced case of the disease. With cystitis, the following is detected in the urine: Leukocyturia (increased number of leukocytes);
- Hematuria (presence of red blood cells, or red blood cells, in the urine).
If a pathology is detected in a general urinalysis, the doctor will definitely prescribe a study of the middle portion of urine. This type of diagnosis will allow you to more accurately determine the condition of the genitourinary system.
The study consists of determining the content of elements contained in one milliliter of urine from an average portion. The calculation is carried out in the laboratory in a special counting chamber. Normally, 1 ml of urine should contain no more than 1000 red blood cells, 2000 leukocytes and 20 casts. In the case of acute cystitis, the number of the above indicators increases significantly.
However, very often the reliability of the results is affected by improper collection of material and non-compliance with personal hygiene rules by the patient. Therefore, in order for tests for cystitis to help the attending physician accurately confirm or exclude the diagnosis of this disease, certain rules should be followed.
Instilled urine collection for women:
- Immediately before the urine collection procedure, you need to prepare and place in front of you about 6 - 10 cotton balls or swabs, a container with a warm solution with added soap, a container with boiled water, as well as a container (a jar, pre-boiled), the lid of which can be removed with one hand, to collect material;
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- Sit comfortably on the toilet with your knees spread as wide as possible;
- Spread the labia with the fingers of one hand and hold them in this position during the entire washing procedure;
- Wash the outside of the genital area using 4 cotton balls soaked in warm soapy water in succession. The movements should be directed in the direction from the pubis to the anus, and after the cotton ball comes into contact with the anus, it should be thrown away. When washing, you should try to penetrate all skin folds;
- Rinse the soaped area with warm boiled water using the remaining 2 balls. The directions of movements are similar;
- With one hand, remove the lid from the container, take it in your free hand, being careful not to touch the edges;
- Release a small amount of urine into the toilet, keeping your labia diluted, and then place a container under the stream and fill it (approximately 50 ml);
- Close the container with the liquid well and immediately transfer it to the laboratory for testing. If it is not possible to deliver the material within half an hour, the container should be placed in the refrigerator and stored at a temperature of 4 degrees for no more than 24 hours from the moment of collection.
Rules for collecting urine for men:
- Wash your hands using toilet soap;
- With one hand, you need to pull back the foreskin (if it is not circumcised), after which you should release a small amount of urine and stop the process of urination;
- Continuing to hold the foreskin in this state, bring the container to the external opening of the urethra and fill it to the indicated level, being careful not to touch the head to the container;
- Close the container tightly with a lid and immediately submit it to the diagnostic laboratory. If quick delivery is not possible, urine can be stored at a temperature of 4 degrees (in the refrigerator), but no more than a day.
If the analysis is collected in the shower, the rules remain the same. Women need to wash their genitals in the indicated direction (from the pubis to the anus) and be sure to fix the labia. It is advisable, especially during menstrual bleeding, to cover the vaginal opening with a cotton swab to prevent red blood cells and protein from the genitals from entering the urine.
In addition, diagnosis of cystitis is possible using modern express methods, such as:
- An express test using an indicator strip that determines the presence of nitrites in the urine, which are formed in the urine under the influence of pathogenic flora;
- Express test (strips) to detect the content of proteins, leukocytes and protein in urine;
- Leukocyte esterase reaction . This method is based on the determination of a special esterase enzyme in the urine, which accumulates in it if pyuria occurs (the presence of pus in the urine);
After carrying out simple laboratory tests for cystitis, it is necessary to carry out urine culture, that is, conduct a cultural study. It consists of studying the pathogenic microflora that caused the disease, as well as determining the sensitivity of microbes to antibacterial drugs.
Differential diagnosis
If the patient has symptoms and signs reminiscent of the clinical picture of cystitis, but the ongoing antibacterial treatment does not bring the desired effect, then it is necessary to exclude the presence of one of the following diseases:
- tuberculosis of the bladder (the decisive point for diagnosis is the detection of tuberculosis bacteria in urine);
- oncological processes in the walls of the bladder (histological examination of the affected areas of the organ is necessary);
- urethritis (characterized by the presence of unpleasant discharge from the lumen of the urethra, as well as the identification of pathogens such as chlamydia, gonococcus, mycoplasma or ureaplasma);
- vulvovaginitis (a woman is bothered by strong discharge from the vaginal lumen and unbearable itching throughout the day; the diagnosis is based on microscopic examination of a vaginal smear).
Often recurrent cystitis
There is a category of women whose cystitis tends to recur and have long periods of exacerbation. This condition is explained by the presence of the following factors:
- genetically predisposed to inflammatory processes, including in the tissues of the bladder;
- increased aggression of the body’s own opportunistic microflora (gram-negative);
- the presence in the female body of chronic inflammatory processes in the genitals;
- congenital or acquired defects of the urethra;
- individual characteristics of sexual activity (early onset, frequent change of sexual partners, lack of contraception, etc.);
- injuries to the lumbar spine or lower back;
- failure to comply with the necessary rules of regular genital hygiene;
- uncontrolled use of antibacterial agents;
- lack of adherence to the therapy prescribed by the doctor, early termination of the course of treatment.
If medical prescriptions are not followed and antibacterial drugs are taken uncontrolled, there is a risk of developing resistance of infectious agents to antimicrobial drugs
Signs of cystitis in women with frequent recurrence of the process are observed almost constantly. In addition to the characteristic dysuric manifestations of the disease, the emotional background of patients changes, they become very irritable, apathetic, and lose interest in life.
Very often, the cause of relapse is sexual intercourse, so women begin to avoid intimacy with their sexual partner. Against this background, problems arise in the family and marriages collapse.