The term “oliguria” in medicine refers to low urine output. It does not necessarily accompany or occur with pathology. Adapting to external and internal conditions, the body is forced to change urine production and reduce fluid loss. However, finding out what such a symptom means, an adequate response or impaired renal function is very important, especially in pediatric practice.
Among the factors causing oliguria, a special place is occupied by nephritis with damage to the ability to filter, acute and chronic kidney infection, the negative effect of medications, the response of the adrenal glands to a stressful stimulus, disturbed water balance in the body, and electrolyte shifts.
What amount of urine is considered normal and what does it depend on?
During the day, healthy kidneys of an adult produce about 1.5 liters of urine. Typically this volume is ¾ of the total liquid drunk. In addition, ¼ of it is excreted through the skin with sweat, with breathing, and is part of the feces.
For men, the total volume is slightly higher (up to 2 liters) than for women (1.6 liters), provided that one to two liters of fluid are ingested. The minimum is 500 ml of urine when drinking 800 ml of liquid.
In a newborn baby, with proper nutrition, the amount of urine excreted monthly increases from 200–600 ml to 800 ml per year. The first 3 days after birth, a small volume of urine is called transient oliguria. This is considered a normal phenomenon and is associated with the gradual adaptation of the kidneys to independent work.
At 5 years old, a child already secretes up to 900 ml, by 10 years old - 1200 ml
Older people are treated as adults.
The mechanism of urine formation involves 2 processes:
- filtration in the renal glomeruli;
- reverse absorption (reabsorption) in the tubules.
They maintain the necessary fluid balance for the human body. The state of dehydration (loss of fluid) is caused by:
- increased sweating in hot weather and during fever;
- profuse vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- blood loss;
- massive burn surface on the skin;
- accumulation of fluid in cavities (pleural, abdominal).
At the same time, filtration is reduced, and maximum fluid is retained in the body. This mechanism of oliguria is accompanied by an increased concentration of dissolved substances in the urine and a high specific gravity.
In the case of overhydration (flooding) caused by heavy drinking, intravenous fluid administration to a patient in a hospital, diuresis with healthy kidneys should increase, and the specific gravity of urine should significantly decrease.
The occurrence of oliguria without connection with loss or intake of fluid serves as a signal of pathological conditions, impaired filtration or reabsorption.
Why does oliguria occur?
The most common causes of oliguria are hidden in:
- kidney damage;
- general circulatory disorders;
- damage to urinary structures;
- impaired nervous and hormonal regulation.
They are conventionally divided into:
- renal (renal) - associated with pathological changes and kidney diseases, characteristic of acute glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, chronic nephritis, polycystic disease, nephrosclerosis;
- extrarenal - caused by other disorders (circulatory system, significant dehydration, liver damage, neuroendocrine diseases);
- postrenal - arise due to obstructed outflow caused by an enlarged prostate gland, a stone in the pelvis or ureter, a tumor, accumulated blood (hematoma).
At high temperatures, the doctor recommends drinking more, this reduces dehydration and intoxication
Oliguria is an important sign of acute and chronic renal failure. Let's look at the most common reasons.
Common infectious diseases that occur with high intoxication, fever, are accompanied by loss of fluid with profuse sweat, vomiting, and diarrhea. Children are very sensitive to diarrhea. Therefore, any enterocolitis threatens the baby’s body with dehydration.
The most significant infectious disease is cholera. The patient loses fluid with incessant diarrhea and frequent vomiting. If the water-electrolyte composition is not compensated with treatment, then oliguria will be followed within a few hours by complete anuria with kidney block.
In acute glomerulonephritis, inflammation affects small capillaries in the glomeruli. Autoimmune formations block the filtration of primary urine, and swelling of the medulla compresses the tubules. Therefore, both main mechanisms ensuring water balance are disrupted.
Acute pyelonephritis is caused by infection of the pelvis and calyces. In severe cases, it spreads to the tubules and glomeruli, causing inflammation and swelling. Compression of the kidney parenchyma can cause significant stagnation of urine in the pelvis. The process is caused by a mechanical obstruction along the outflow tract (stone, tumor, congenital narrowing of the ureters).
The affected kidney increases in size to the point of hydronephrosis. Urine excretion is compensated for some time by a second healthy organ. But in the absence of surgical intervention, oliguria occurs first, then anuria.
Heart failure in decompensated myocardial diseases (acute infarction, malformations, myocardial dystrophy, cardiomyopathy, hypertension and others) helps to reduce renal filtration, since it reduces cardiac output, the amount of blood passing through the renal membrane.
Heart failure is one of the causes of oliguria
Thromboembolism in the renal artery or compression of a similar vein sharply disrupts local blood flow, causing ischemia of the kidney tissue up to necrosis of individual structures. Oliguria is an obligatory component of the disease manifestation.
In the practice of doctors, oliguria is observed after surgical treatment, large blood loss, or the administration of a high dose of diuretics, as a reaction to the drug Methotrexate.
Consequences and complications
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, oliguria can lead to a complete cessation of urine output (anuria), which poses an immediate threat to life.
Uncontrolled use of diuretics by patients with oliguria can contribute to the development of acute renal failure, which is also highly likely to cause death.
Oliguria in nephrotic syndrome indicates the severity of the patient's condition - the less urine produced during the day, the more severe the kidney condition. Severe oliguria is dangerous because damaged kidney tissue may not recover even after correction of the condition, and the patient will require hemodialysis or a kidney transplant.
Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 “First Kiev Medical College”, specialty “Laboratory diagnostics”.
The information is generalized and is provided for informational purposes. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous to health!
Do you know that:
In the UK there is a law according to which a surgeon can refuse to perform an operation on a patient if he smokes or is overweight. A person must give up bad habits, and then, perhaps, he will not need surgical intervention.
According to many scientists, vitamin complexes are practically useless for humans.
When lovers kiss, each of them loses 6.4 calories per minute, but at the same time they exchange almost 300 types of different bacteria.
Even if a person's heart does not beat, he can still live for a long period of time, as the Norwegian fisherman Jan Revsdal demonstrated to us. His “engine” stopped for 4 hours after a fisherman got lost and fell asleep in the snow.
The rarest disease is Kuru disease. Only members of the For tribe in New Guinea suffer from it.
.
The patient dies of laughter
. The disease is believed to be caused by eating human brains.
A job that a person doesn’t like is much more harmful to his psyche than no job at all.
In an effort to get the patient out, doctors often go too far. For example, a certain Charles Jensen in the period from 2020 to 2019
. survived more than 900 operations to remove tumors.
Over the course of a lifetime, the average person produces no less than two large pools of saliva.
There are very interesting medical syndromes, for example, compulsive swallowing of objects. One patient suffering from this mania had 2,020 foreign objects in her stomach.
According to WHO research, talking on a mobile phone for half an hour every day increases the likelihood of developing a brain tumor by 40%.
In 5% of patients, the antidepressant Clomipramine causes orgasm.
Our kidneys are capable of purifying three liters of blood in one minute.
Most women are able to derive more pleasure from contemplating their beautiful body in the mirror than from sex. So, women, strive to be slim.
Human bones are four times stronger than concrete.
The human brain weighs about 2% of the total body weight, but it consumes about 20% of the oxygen entering the blood. This fact makes the human brain extremely susceptible to damage caused by a lack of oxygen.
Oral hygiene – a necessity or a marketing conspiracy?
Each of us has heard stories about people who never brushed their teeth and had no problems doing so. So, most likely, these people either did not know about the presence of...
Oliguria is a disorder that manifests itself in a decrease in the amount of urine.
To find out the reason for the decrease in urine output, you should consult a doctor. He will study the symptoms and refer you for examination.
What forms of quantitative urinary disorders are observed in pathology?
In addition to oliguria, the symptoms of diseases of the urinary system are usually distinguished:
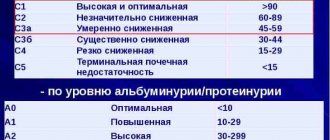
- anuria - daily diuresis is reduced to 50 ml or less, urine does not flow from the kidneys into the bladder, even with the insertion of a catheter, the absence of residual urine is detected (in contrast to acute retention with difficult exit);
- polyuria - much more urine is produced than fluid consumed (more than 2 liters per day), a symptom indicating kidney disease and hormonal disorders.
Pathological conditions are often accompanied by alternating signs of polyuria, oliguria and anuria. They may indicate the stage of damage to the renal mechanisms.
How much urine should be excreted per day?
Prerenal anuria can be observed:
- in a severe state of shock;
- with hypotension of cardiac origin;
- with renal artery thrombosis;
- acute massive blood loss.
Renal anuria is most often a dangerous symptom of poisoning (ethylene glycol, heavy metal salts, low-quality alcohol, acetic acid). Other reasons may be:
- tubular necrosis during renal ischemia;
- disruption of tubular patency by uric acid salts and drugs of the sulfonamide group;
- acute and chronic nephritis.
The postrenal type is always associated with obstructed outflow through the urinary tract, its blockage, and compression.
Necrosis of the renal tubular epithelium
Polyuria is characterized not only by increased urine output, but also by its highly diluted composition with low specific gravity. Often accompanied by an abnormal feeling of thirst and heavy drinking (polydipsia). With polyuria, the regulation of reabsorption of water in the tubules (reabsorption) is disrupted.
The symptom may be of renal origin - with damage to the tubular apparatus (tubulopathies), and is the initial stage of chronic renal failure caused by kidney pathology. It is also observed during the recovery period in acute renal failure.
Extrarenal causes of polyuria are neuroendocrine disturbances in the regulation of water and electrolyte balance. It can develop with Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, acromegaly.
As a compensatory reaction, polyuria accompanies:
- consequences of hypertensive crisis;
- attacks of paroxysmal tachycardia;
- therapy of heart failure when removing fluid from edematous tissue.
How does oliguria manifest?
Oliguria is not a disease, but one of the signs of urinary dysfunction. Listing “symptoms of oliguria” is the wrong option; it itself is a symptom. One can only point out the connection with other signs that help to correctly identify the disease.
Oliguria is a condition for which a nephrologist will help determine the cause.
The clinical picture for various reasons is accompanied by persistent symptoms used in cases of differential diagnosis.
With infections that cause general dehydration, patients develop:
- diarrhea;
- frequent vomiting;
- profuse sweating;
- heat;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- retraction of the eyeballs;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- muscle flaccidity;
- tachycardia or bradycardia, arrhythmia;
- decreased blood pressure;
- convulsions;
- confused consciousness.
With postrenal oliguria with mechanical compression of the urinary structures, the following are observed:
- intense pain in the lower back, abdomen, above the pubis, radiating to the groin and external genitalia;
- nausea and vomiting;
- flatulence (bloated stomach);
- abdominal muscle tension;
- fever with chills;
- painful tapping on the lower back.
In the case of acute glomerulonephritis, oliguria is accompanied by:
- headache;
- high blood pressure;
- pain in the lower back, stomach;
- severe weakness;
- moderate increase in temperature;
- loss of appetite, nausea;
- shortness of breath and signs of pulmonary congestion.
One of the common complaints with increasing myocardial failure is cardiac arrhythmia.
Heart failure manifests itself:
- swelling on the feet and legs;
- pronounced tachycardia during movements;
- shortness of breath;
- persistent cough;
- complaints of fatigue, pain in the heart;
- blueness of lips and fingertips;
- swelling of the neck veins;
- enlarged abdomen (ascites);
- the appearance of a venous ring around the navel.
Thromboembolism of the renal artery causes renal infarction followed by necrosis, accompanied by:
- acute pain in the lower back, unlike renal colic, they do not radiate to the groin, perineum, and are not accompanied by dysuric symptoms;
- drop in blood pressure;
- vomiting;
- bloating;
- stool retention.
As you can see, oliguria is a sign that requires urgent intervention and clarification of the circumstances of its occurrence. A long-term reduction in urination can lead to irreversible changes in the kidney parenchyma.
Treatment
Treatment of oliguria is aimed at:
- eliminating the cause;
- treatment of the disease;
- restoration of blood circulation;
- adjusting body balances;
- eliminating possible complications.
The choice of medications depends on the causes or processes of the disease identified during the diagnosis process. Oliguria is a process that can be stopped. The excretion of urine from the body in a normal volume returns to normal almost immediately after the cause or symptoms of its progression are eliminated.
Separately, and more carefully, it is worth considering the treatment of oliguria in pregnant women and children. Untimely contact with specialists can lead to the complication of oliguria - a complete absence of urine. Treatment with folk remedies in this case is unacceptable.
Some people who have identified symptoms of the disease try to get rid of them on their own using diuretics. But this should not be done, because such drugs can change the test results and the structure of urine. First you need to determine the causes of the pathology (only when consulting a doctor), and only then begin treatment. The only thing a person can do on his own during the treatment process is to adhere to the diet prescribed by a specialist.
Diagnostics
Every adult can determine diuresis per day by comparing the liquid drunk and the volume of excreted urine collected in a container. You can suspect a symptom by infrequent urination against the background of thirst and drinking a significant amount of water.
The above symptoms should prompt increased attention to determine the specific cause.
Urinalysis, blood analysis, tests for the content of nitrogenous substances, and electrolytes are checked. Kidney damage is indicated by the presence of protein, red blood cells in urine sediment, and renal epithelial cells. Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky allows you to identify the impaired ability of the kidneys to concentrate excreted substances. Nechiporenko's test confirms the connection with inflammation and the role of bacteriuria.
Cystoscopy with examination of the bladder and urethra helps to identify cystitis, tumor, blockage of one of the ureters
Excretory urography provides information about the excretory function of both kidneys, destruction of the collecting structures, kidney enlargement, and tumor growth. Computed tomography is used in the differential diagnosis of unclear lesions.
Consequences and complications
If oliguria is not treated in a timely manner, there is a risk of developing a disorder such as anuria. Complete cessation of urination entails poisoning of the body with waste products, which can cause internal organ failure, leading to death.
If oliguria develops against the background of acute renal failure, it must be treated promptly. Oliguria sometimes becomes chronic, in which case there is a possibility that the kidneys may fail.
How to treat oliguria?
It is not oliguria that requires treatment, but the cause that caused it. After the examination, the doctor includes in the treatment regimen:
- urgent hemodialysis, hemosorption to eliminate the filtration block and signs of renal failure;
- an attempt to remove retained urine by catheterizing the bladder and ureter;
- cardiac medications to support myocardial strength and restore normal contractions.
During therapy, depending on the cause, the following are used:
- diuretics - to relieve edema;
- antibiotics – for the purpose of anti-inflammatory treatment;
- special antidotes for poisoning;
- solutions of Hemodez, Reopoliglyukin - to combat shock and intoxication;
- anticoagulants – in cases of renal artery thrombosis;
- means for correcting blood pressure;
- cytostatics for glomerulonephritis.
To relieve mechanical retention of urine flow, it may be necessary to operate on the patient for emergency reasons. The stone and tumor are removed.