Urinary tract infections in children are the second most common after diseases of the respiratory system, although they suffer from cystitis less often than adults. Inflammation of the bladder is considered to be a girl's disease, but in infants (children under 1 year old) the sex ratio among those affected is 50:50.
With increasing age, girls begin to predominate over boys, and by 3 years this ratio becomes similar to adults, more than 75% of patients are girls. The signs of cystitis in children are the same as in adults, but chronic inflammation of the bladder in this category of patients is much less common.
Causes of cystitis in children and routes of infection
In the vast majority of cases, cystitis is of infectious origin. The ways in which microbes enter the bladder can be divided into 3 groups shown in the table.
| Path | Where | Causes |
| Descending | From the ureters | Obstructed outflow of urine from the kidneys, congestion in the ureters |
| Rising | From the urethra, vagina, anus | Proximity of organs, non-compliance with hygiene standards |
| Hemato- and lymphogenous | From foci of inflammation in the body | Weakened immunity, generalized infection |
Important! Primary infection of the bladder by microbes is usually not enough to cause cystitis - nature provides for the self-cleaning of the organ from pathological elements.
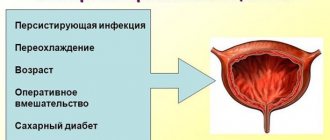
Concomitant factors that contribute to the establishment of infection in the bladder are:
- Temporary decrease in immunity - hypothermia, stress, recent illness;
- Anomalies of the urinary tract or tumors of the pelvic organs;
- Injuries to the bladder or nearby organs;
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder (most often of a neurogenic nature), which promotes the accumulation of bacteria that are normally excreted freely and do not cause any harm - the organ’s reaction to pain during urination;
- Systemic diseases - diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies, lupus erythematosus, etc.;
- Chemo- and radiotherapy.
A noticeable provoking factor for the development of cystitis in children 1–3 years old was the introduction of such care products as a diaper into everyday life. Industrial absorbents keep urine and feces in close proximity to the urethra, in conditions ideal for microbial growth: warm and humid. With the slightest error in caring for a child, these seemingly useful hygiene items become a breeding ground for bacteria, most often pathogenic.
Diagnosis of the disease
Timely seeking medical help is the key to successful treatment. The doctor finds out when the first complaints appeared and examines the little patient. The basis of diagnosis is laboratory tests. A specialist can use the following techniques:
- General urine analysis. A large amount of protein in urine indicates the presence of pathological microflora in the bladder. In addition, the doctor pays attention to the presence of mucus, blood, and epithelium in the urine being studied.
- Bacteriological culture of urine. Tests carried out in a laboratory make it possible to determine which microorganisms cause the disease.
- General blood analysis. The study is mandatory during hospitalization. With its help, it is possible to identify the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. The study allows you to determine how correctly the child’s urinary system functions.
- Ultrasound of the bladder. The examination helps determine the presence of serious morphological changes in the mucosa and the presence of foreign bodies.
- Cystoscopy. Such a study is indicated for chronic otitis in a child and is carried out exclusively during remissions. Using a special instrument (endoscope), the doctor examines the inner surface of the bladder.
A specialist makes a diagnosis after a thorough examination
Acute cystitis, due to the similarity of symptoms, must be differentiated from gynecological pathologies in girls, acute appendicitis, bladder tumors, pyelonephritis in children of both sexes. The examination plan may include consultation with a pediatric surgeon or gynecologist.
Cystitis in a child: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Most often the disease occurs acutely. Cystitis in a child manifests itself:
- Frequent urination – every 15 – 30 minutes;
- Pain and pain when urinating, these factors provoke fear of urination in the child;
- Turbidity and darkening of urine, and in some cases the appearance of blood, and with hemorrhagic cystitis - the appearance of meat-colored urine;
- Pain in the lower abdomen on palpation or at rest;
- A general deterioration in well-being—in children under 2–3 years of age, a rise in temperature is possible, sometimes significant, which significantly worsens their condition.
Establishing a diagnosis is difficult only for very young children - temperature readings can accompany many other diseases, but these children are not yet able to talk about their feelings. Sometimes in children 3 to 5 years of age, differentiation is made from appendicitis.
But in general, an experienced doctor does not have any difficulties in determining the disease.
Forms of manifestation of cystitis
In children, two main forms of the disease can be identified: acute and chronic. Acute manifestations of the inflammatory process in children can develop even within a few hours. It is accompanied by superficial inflammation on the mucous membrane of the surface of the bladder. With adequate treatment, acute manifestations of the disease can be cured in 7–11 days.
Chronic cystitis develops due to frequent manifestations of acute cystitis. This type of disease most often occurs in children suffering from other pathogenic diseases that contribute to the development of the disease. The chronic form of cystitis lasts a long time and is less treatable than the acute form of cystitis. In the acute course of the disease in a child, all layers of the walls of the bladder are affected (the mucous membrane itself, the outer and muscular layers).
A pathogenic inflammatory process in the bladder cavity can have a focal localization, and also completely affect its walls (diffuse cystitis). In cases where the pathological process of inflammation affects the neck of the bladder, this type of disease is called cervical. If the area of Lieto's triangle is affected, the disease is called trigonitis.
Cystitis in a child: treatment
The goal of treatment is to normalize the process of urination - eliminating urinary retention, relieving pain and eliminating infection.
In the first two cases, antispasmodics (No-spa, papaverine) and analgesics are used.
Treatment of infection is carried out with antibacterial drugs.
In previous years, biseptol (Bactrim) was most often prescribed in the age norm. This medicine suppresses many of the most common microbes, including those that cause cystitis in children. But in recent years, the majority of bacteria (more than 50%) have developed resistance to this drug, which means its effectiveness has decreased.
Important! The increase in the resistance of microorganisms is partly due to non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations, in particular, with the early withdrawal of prescribed medications: when the person feels better, he stops taking the medication and spreads into the environment bacilli that have multiplied after exposure to the drug and have increased resistance to its components.
In this regard, penicillin antibiotics of the latest generations (Augmentin, Amoxiclav) are now more often prescribed. Furagin, as well as Monural, are also widely used for the treatment of cystitis in children. These drugs also belong to antibiotics and have a very rapid positive effect on the course of the disease.
Of the immunomodulators prescribed for chronic cystitis in children, as well as to prevent relapse of acute cystitis, the drug Uro-Vaxom, which stimulates the restoration of cellular immunity, should be noted.
When making a diagnosis and choosing treatment methods, a number of laboratory tests are carried out in parallel. In particular, a culture test for drug sensitivity is required - the results are ready in 2 days.
If the drugs prescribed before receiving test results are ineffective, the main medication is changed.
As a result of properly selected therapy, the following occurs:
- Reduction and elimination of pain;
- Urination is streamlined, its frequency is reduced, and the bladder is completely emptied;
- Test results return to normal;
- The general condition of the child is normalized.
What do you need to know to prevent acute cystitis from becoming chronic?
In approximately half of the cases, chronicity of the process and resumption of inflammation are associated with premature cancellation of the prescribed treatment.
The fact is that when treating cystitis, the effect of therapy occurs very quickly. Literally 1-2 days of taking medication - and there was no trace left of the former pain and frequent debilitating urge to urinate.
This is due to the fact that medications are excreted through the urinary system. Thus, when taking drugs, their concentrations in urine are always high. This gives a quick therapeutic effect and relieves the symptoms of acute inflammation.
Therefore, when there is an obvious improvement in the baby’s condition, parents often independently decide to stop taking the medication. Thus, they create resistance of bacteria to the action of these drugs. They didn’t kill the bacteria, but they “fed” them and temporarily calmed them down.
The process goes into “sleep mode” and can resume at any time. In the future, under any unfavorable conditions (illness, hypothermia, decreased immunity), cystitis will recur. And choosing a treatment for such antibiotic-resistant flora will be very difficult.
Aids and care for a sick child
Proper organization of a regimen at home is of great importance for restoring health.
Necessary:
- Ensure rest, and at the first stage - bed rest;
- Avoid cooling the pelvic area and the body as a whole;
- Carry out physiotherapy - warm baths on the perineum with solutions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, etc.), dry heat on the lower abdomen;
- Provide plenty of warm drinks - non-carbonated mineral water, tea, cranberry and lingonberry juice (which have the ability to remove germs);
- Diet: exclusion of fried, smoked, salty foods, chocolate and other sweets. Eating steamed foods;
- Observe sanitary and hygienic conditions and follow doctor's instructions.
Important: if urination is very painful, it is recommended to put the child in the bath before urinating and run warm water on the perineal area. Turn off the water after finishing urination. In this way, pain is significantly reduced, and the child does not develop fear of urination due to possible pain. Such procedures are carried out during each urination until the pain goes away.
General information about the disease
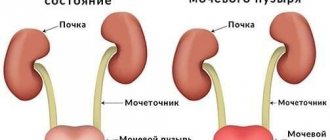
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder wall. This disease can develop in a child at any age.
Among infants, the prevalence of cystitis is approximately the same in both boys and girls. By preschool age the situation changes - girls get sick much more often (3-5 times) than boys.
There are reasons for this.
- Anatomical features of the external genitalia of girls. Girls have a shorter and wider urethra than boys. And the close location of natural reservoirs of microflora (anus, vagina) can contribute to urinary tract infection.
- Immunological and hormonal changes in the body of teenage girls reduce the protective functions of the genitourinary tract mucosa. Therefore, girls may experience colpitis and vulvovaginitis.
It is worth mentioning certain clothes that teenage girls prefer to wear (thongs, tight jeans with an open waist in the autumn-winter period). This is always a step towards infection of the genitourinary system, up to infection of the kidneys (pyelonephritis).
How to prevent the disease from recurring
After an illness, prevention is important to prevent relapse. For this we recommend:
- avoid hypothermia;
- drink large amounts of liquid: mineral water, juices, weak tea, limit spicy, smoked foods, coffee, fast food in the menu;
- active physical activity, sports, outdoor games to prevent stagnation in the pelvis;
- visiting a doctor for six months at least once a month, in the absence of further exacerbations - once a month.
If new symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor for help, and under no circumstances should you let the disease progress!
ethnoscience
There are several ways to heal with herbs. In most cases, sitz baths are used. The fact is that during the inflammatory process it is worth carefully monitoring the child’s personal hygiene. Baths will help relieve inflammation faster and make the patient’s life easier at home.
The following herbs should be used as medicine:
- horsetail;
- juniper;
- birch leaves;
- lingonberry;
- plantain;
- chamomile and calendula.
Birch leaves have excellent anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and diuretic effects. In addition, birch leaves contain large quantities of vitamin C. You can prepare a decoction of birch leaves in advance or add them to the bath and let it brew for a while. The duration of the bath is about 25 minutes.
Horsetail has anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. The plant is rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements. It is widely used as a treatment for cystitis and urethritis.
Juniper has a powerful antiseptic effect. It is used as a medicine during therapeutic procedures for diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract. The fruits of this plant are of particular value.
Lingonberry helps with kidney pathologies; it perfectly relieves inflammation. It is recommended to prepare a decoction of lingonberries and mix it with a decoction of chamomile and calendula. Chamomile is an excellent antiseptic; it will help relieve inflammation and relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Treating yourself with herbs at home is an excellent solution, but do not forget about drug therapy and doctor’s recommendations.
In the first days, the patient must remain in bed. With timely treatment, the unpleasant signs of cystitis will become less noticeable by the end of the first or second from the start of treatment.
Symptoms
Due to the fact that the child cannot always accurately describe the clinical picture, and in some cases may be completely silent about the signs that bother him, diagnosis is often carried out untimely.
In general, cystitis in a child manifests itself as follows:
- urine becomes dark yellow;
- the child becomes restless, often wakes up at night, cries;
- increased temperature (however, it should be noted that the temperature does not always increase with cystitis);
- too frequent or, on the contrary, too infrequent urination;
- the child may involuntarily urinate on himself;
- there may be blood in the urine;
- pain in the groin area;
- each process of urination may be accompanied by sharp pain and burning, while there remains a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- urine may have a strong, unpleasant odor.
It should be noted that if the clinical picture includes an increase in temperature and attacks of fever, then it is quite possible that the pathological process has affected the kidneys and pyelonephritis develops. However, only tests can show this for sure.
Children's medications for cystitis
The disease cystitis is widespread among children. This is especially true for young representatives of the fair half of humanity - due to the anatomical structure of the urinary system. And, of course, the first assistants in the fight against the disease are medications. They help get rid of inflammation in a short time, preventing the disease from developing and becoming more complex. What exactly and how to take children's medications for cystitis correctly - you will find out in the article.
Treatment with drugs
As we have already found out, the main reason for the development of cystitis is inflammation caused by bacteria. Therefore, the most effective way to eliminate the disease is to prescribe antibiotics.
Under no circumstances should you try to independently determine the type of drug - this is, in principle, impossible, since the causative agent may be a microorganism that is not afraid of the chosen medication, which means that the effect of it will be zero. The selection of the product is based on the results of a urine culture test.
In addition, cystitis is often caused by a fungus or a virus - antibiotics will not help here.
Most often prescribed:
To reduce the severity of pain, use a heating pad. Reviews indicate that this measure is very effective. It is placed in the perineum (squeezed between the legs). You can't keep her on her stomach - this promotes the spread of germs and infection of the kidneys.
Rosehip decoction has also proven itself well. It is prepared like this:
- Take 8 tablespoons of raw materials per liter of water;
- boil;
- leave for several hours in a thermos;
- cool;
- filter.
A little honey is added to the finished drink to improve the taste. This tool provides:
- strengthening the immune system;
- elimination of vitamin deficiency;
- activation of urination.
In addition, it is recommended to give your baby infusions of the following herbs:
All of them are prepared according to this recipe:
- Take a tablespoon of herb per glass of boiling water;
- stand until cool;
- filter.
Divide the resulting volume into three portions. Give the child one at a time before meals.
Recommendations for parents
It is important not only to quickly start giving antibacterial drugs, but also to completely cure this disease. It is an unforgivable mistake of many parents when they give antibacterial agents until the child feels better. But relief comes immediately, because antibacterial agents act quickly. And this is where the problems begin. Pathogenic microorganisms that still remain in the body feel great and continue to spread further. As a result, the child is soon diagnosed with chronic cystitis.
To put an end to the problem with urinary tract forever and prevent chronic cystitis, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment. The functional product DoroMarine can help with this. It has a pronounced therapeutic effect, has a 100% natural composition, which includes: Angustata kelp, sea cucumber extract, sea calcium. providing the children's body with all useful vitamins and microelements. The polysaccharides included in the complex complement the action of the other components:
- beckons - promotes rapid and unhindered elimination of fluid (the child goes to the toilet painlessly and completely empties the bladder);
- alginate – strengthens the body’s immune defense;
- fucoidan – prevents infection in the urethra;
- laminaran – cleanses the body of toxins, restores the functioning of the urinary system.
Doromarin is recommended for the complex treatment of inflammatory diseases of the bladder, since this product has a wide spectrum of action:
- is the basis of a healthy diet, which is very important for a growing body. During illness, many children refuse to eat, but they should still receive vitamins in order to recover faster. Doromarin, which contains iron, magnesium, iodine, zinc, etc., will help them with this;
- increases the body's defenses, stimulates the production of immune cells. It helps destroy dangerous bacteria and viruses, so many children taking DoroMarine do not need antibiotic therapy;
- is an excellent sorbent. Doromarin quickly relieves all symptoms of intoxication.
Due to the stimulation of the production of immune cells, the rapid absorption of macro- and microelements, and the ability to quickly remove pathogenic bacteria naturally, Doromarin vitamins are recommended by many pediatricians and nephrologists in the country. This complex helps both in the initial stages of the development of inflammation and in the rapid development of the inflammatory process. Vitamins Doromarin are recommended for the treatment of young patients not only with acute form, but also with chronic cystitis.
Why is bladder inflammation dangerous?
Abnormal structure, dysfunction and the entry of microbes into the bladder are the key causes of cystitis in children.
If there are no malfunctions in the urinary system, the bladder itself is cleared of pathogenic microflora during urination. Its mucous membrane is highly resistant to infections. Cystitis in 90% of cases is caused by bacteria:
- klebsiella;
- coli;
- staphylococcus;
- a combination of several microbes.
Many parents are interested in whether their child can develop viral cystitis. Yes maybe. Pathogens of adenoviral, herpetic and influenza infections provoke a violation of the outflow of urine from the bladder. This creates favorable conditions for the growth of bacteria.
An unbalanced diet is one of the key reasons for changes in urine pH and the formation of sand in the kidneys. When it gets into the bladder, it injures the mucous membrane, which increases the risk of infectious inflammation by 4 times.
In 9 out of 10 cases, cystitis in a small child occurs due to a decrease in immune status and impaired urine flow. Urologists identify several provoking factors:
- vesicoureteral reflux (backflow of urine from the bladder);
- hypothermia of the body;
- functional urinary disorders;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- vitamin and mineral deficiency;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- urinary tract infections;
- phimosis (narrowing of the foreskin) in boys;
- kidney stone disease;
- bacterial tonsillitis;
- diabetes;
- vulvovaginitis in girls;
- unbalanced diet;
- chronic pneumonia;
- helminthic infestations;
- insertion of a catheter or cystoscope into the bladder;
- treatment with antibiotics, cytostatics.
Cystitis in a one-year-old child with weak immunity and hypovitaminosis is often caused by fungi, usually from the genus Candida. Trichomonas inflammation of the ureter occurs mainly in teenage girls who are sexually active.
Childhood cystitis often develops into a sluggish form, which is difficult to treat. Chronic inflammation provokes structural changes in the bladder, as a result of which its functions are impaired. Possible complications of the disease include:
- sclerosis of the cervix;
- vesicoureteral reflux;
- bladder diverticula;
- peritonitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- paracystitis;
- prostatitis (in teenage boys).
In a child under 8 years of age, the disease is complicated by spasms of the external urethral sphincter. As a result, a reflex delay in the outflow of urine occurs. This condition is dangerous due to stone formation in the bladder, expansion of the calyces and pelvis of the kidneys.
Inflammation of the bladder is classified depending on its origin, course and characteristic changes:
- Infectious (involving microorganisms) and non-infectious origin of cystitis (as a result of the action of chemical, toxic and medicinal agents).
- The course of the disease is acute or chronic. The latter occurs latently (without showing clinical signs) or with periods of exacerbations and remissions (recurrent).
- Changes in the organ can be catarrhal, hemorrhagic, ulcerative, polyposis and cystic in nature.
For proper treatment, it is necessary to take into account all the features of cystitis.
Infectious inflammation occurs in the following cases:
- migration of pathogens into the bladder from the external genitalia (ascending path);
- the presence of pyelonephritis (infectious inflammation of the renal pyelocaliceal system), in this case there is a descending path;
- the presence of foci of infection anatomically distant from the bladder (transfer of microorganisms through the flow of lymph and blood);
- inflammation of neighboring organs (intestines, uterus, appendages).
If the disease occurs without the participation of infectious agents, then it is called non-infectious.
Provoking factors are:
- impaired outflow of urine;
- hypothermia;
- immunodeficiency.
Acute cystitis is characterized by changes affecting the mucous membrane of the bladder, while chronic cystitis causes pathological processes in the underlying tissues.
Acute inflammation involves rapid development of clinical manifestations. As a result of improperly selected treatment or its absence, the disease sometimes becomes chronic.
Chronic inflammation of the bladder can occur either without pronounced symptoms or with pronounced signs. In the first case, there is a latent form of chronic cystitis, in the second - a recurrent form.
What causes the chronic course of the disease?
Chronization occurs due to the absence or incorrectly selected treatment, in the presence of immunodeficiency, as well as the structural and functional characteristics of the bladder.
Pathologies that may contribute to the development of chronic inflammation include:
In some cases, diagnosing the disease can be difficult. This is due to the fact that children cannot always explain what causes them discomfort. Especially in infancy.
However, even in children under one year of age, the disease can be suspected. Parents should monitor their baby's behavior during urination. If this process bothers the baby, he begins to be capricious. There is also an increase in urges. At the same time, the amount of urine is small.
Older children may complain of:
- pain when urinating;
- frequent urge with a small amount of urine excreted;
- the urge to urinate, which is false (occurs when the nerve endings are excessively irritated);
- loss of urinary control;
- the appearance of blood at the end of urination (usually a few drops).
After the child has gone to the potty, you can notice a change in the color of the urine, the appearance of mucous flakes in it, due to which it becomes cloudy. In some cases, signs of general intoxication syndrome develop (fever, changes in behavior).
The above symptoms of cystitis in children are characteristic of acute and exacerbation of chronic inflammation. During the period of remission, there are no clinical manifestations. However, with the slightest exposure to a provoking factor (hypothermia, vulvovaginitis, etc.), an exacerbation occurs.
In uncomplicated cases of cystitis, treatment of the disease in children is usually carried out on an outpatient basis.
Drinking regime
To detoxify the body and sanitize the bladder, the baby should drink as much fluid as possible. The following daily amounts are recommended for each age:
- half a liter for children under one year of age;
- for young children (1-3 years old) one liter;
- for preschoolers and schoolchildren more than one and a half liters of liquid.
Preference should be given to liquids that have uroseptic and detoxification properties. These include weakly concentrated fruit drinks (lingonberry, cranberry), dried fruit compote, and weak lemon tea.
If the baby refuses the offered liquid, allow him to drink whatever he likes. However, you should avoid drinking carbonated drinks!
It is necessary to exclude smoked, pickled, spicy foods, and chocolate from the children's diet. Meat dishes should be given with caution.
Infants should remain breastfed. A new type of complementary food cannot be introduced for acute cystitis.
Acute cystitis that occurs in children responds well to treatment with uroseptic drugs (Furamag). Antibacterial therapy is prescribed in the presence of strict indications determined by the doctor (severe and prolonged intoxication syndrome, massive bacteriuria, etc.).
Taking antispasmodics (No-spa) will help relieve pain.
In children, chronic cystitis is treated according to the principles of acute inflammation of the bladder (drinking plenty of fluids, following a diet and taking medications).
However, it is worth noting that of all the pharmacological drugs used for cystitis, antibacterial therapy is almost always prescribed. Taking uroseptic is also recommended during the remission phase for the purpose of prevention.
During the period of remission, physiotherapy (thermal procedures, iontophoresis of drugs) is indicated.
In case of chronic inflammation, special attention is paid to eliminating the source of infection (treatment of vulvovaginitis, strengthening the body's defenses, eliminating neurocirculatory disorders of the bladder).
With long-term use of antibiotics, the normal intestinal microflora is inhibited (the drugs act not only on pathogenic microorganisms). In this regard, indigestion, allergies, and decreased immunity occur. To restore normal microflora, experts recommend taking pre- and probiotics.
Prebiotics are food components that help stimulate the growth and activity of intestinal microflora. Probiotics are live bacteria that are beneficial to humans.
Treatment of cystitis in children can be done at home.
Dried lingonberry leaves can be used for children over twelve years of age.
It is prepared as follows: one tablespoon of raw material is poured with one glass of boiling water and covered with a lid. After twenty minutes you need to strain. Give children one glass twice a day.
For young children (over one year old), dried and chopped parsley root can be used. To prepare, take half a teaspoon of greens and one glass of boiling water. Leave for twenty minutes. Take half a glass 1-2 times a day.
Incorrectly treated acute inflammation becomes chronic.
Cystitis can become a source of pyelonephritis. For a girl, persistently recurring inflammation of the bladder can leave an imprint on her reproductive function.
To prevent cystitis, you need:
- maintain hygiene and promptly treat diseases of the external genitalia;
- avoid hypothermia;
- strengthen the immune system;
- use underwear for babies only from natural materials.
Prevention
To avoid cystitis, you should follow these recommendations:
- protect the baby from hypothermia;
- monitor his hygiene;
- change underwear daily;
- ensure a normal diet and proper vitamin supplementation.
Cystitis is an easily curable disease. If you follow the doctor's instructions, the pain will disappear within 2 days. However, improvement in well-being often leads to parents stopping giving medications. This, in turn, provokes the overflow of the untreated acute form into the chronic one. To prevent this problem from happening, all medications are taken in full course.