Severe swelling of the bladder mucosa characterizes a disease known as bullous cystitis. People suffer from such cystitis mainly in the autumn-winter season. Women experience discomfort and pain when urinating.
At the initial signs of the disease, it is important to see a doctor for emergency treatment so that complications do not develop. The bullous form develops in the last stages of cystitis without timely treatment. The mucous membrane of the bladder permanently loses its shape, and the inflammation worsens. At risk are patients with existing inflammation in the body, with a weakened immune system.
Forms of the disease
According to the nature of the course, cystitis occurs:
- Spicy. It occurs spontaneously under the influence of a provoking factor. It is characterized by the appearance of pronounced unpleasant sensations that worsen the patient’s quality of life.
- Chronic. Develops due to improper treatment of the previous form of the disease. It is characterized by a wave-like course, in which periods of exacerbation are replaced by remission. The disease has less pronounced symptoms and therefore often remains undetected.
Based on its origin, cystitis is divided into the following types:
- Bacterial. Caused by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms (Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, chlamydia).
- Viral. It is considered a complication of infections caused by herpes virus, influenza, adenoviruses, and cytomegalovirus.
- Non-infectious. It develops against the background of irritation of the mucous membranes of the bladder with chemicals, medications, and foreign objects.
Bacterial cystitis is caused by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms (Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, chlamydia).
How does it manifest?
It is quite difficult to recognize the signs of bullous cystitis. Its symptoms are not much different from other forms of cystitis. Usually, before an acute attack of pain, a person becomes hypothermic. Women who do not know how to dress for the weather may face the following problems:
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Pain when urinating.
- Constant urge to go to the toilet.
- Cloudiness and darkening of urine.
- Body temperature rises to 38.5 degrees.
- General weakness.
Peculiarities
It occurs depending on the age and gender of the patient.
In children
Bullous cystitis in children occurs at 1-2 years of age, which is explained by the immaturity of the immune system, due to which the body cannot resist bacterial and viral infections. In children over 3 years of age, the disease is rarely diagnosed. The bullous form develops 4-6 weeks after the penetration of pathogenic flora into the mucous membranes of the baby’s bladder. Provoking factors include:
- increased permeability of vascular walls, facilitating the spread of bacteria and viruses in the body;
- low functional activity of the spleen, which is responsible for the functioning of the hematopoietic system;
- accelerated metabolism;
- structural features of the genitourinary organs in girls (wide and short urethra, close location of the anus).
Factors that provoke cystitis include the structural features of the genitourinary organs in girls.
During pregnancy
Bullous cystitis in pregnant women occurs when the catarrhal form of the disease is not treated correctly. This is facilitated by the inability to use powerful antibacterial agents, a physiological decrease in immunity and impaired blood supply to the pelvic organs. Compression of the bladder by the growing uterus prevents its normal emptying; stagnation of urine provokes the development of inflammatory processes. Cystitis in a pregnant woman has a protracted course, the disease is dangerous due to the possibility of intrauterine infection of the fetus.
What is bullous cystitis?
This form of inflammatory lesion of the bladder is not considered an independent disease. It manifests itself as a complication of the chronic form of cystitis, as a consequence of untimely examination and late start of treatment.
Long-term exposure to the inflammatory reaction on the bladder tissue causes the development of pathological processes, manifested by congestive hyperemia (areas overflowing with blood) and bullous edema - the formation of many cavities filled with blood serum leaking from the capillaries (serous fluid).
Swelling manifests itself in a progressive manner, which leads to a violation of the integrity of the mucous epithelium and deprives the bladder walls of their protective properties, which creates the risk of deep damage to the structural tissues of the bladder.
Bullous lesions of the bladder tissue with the formation of many spherical cavities protruding onto the surface of the mucous lining of the bladder are diagnosed in adult patients and children. Clinical features of the pathological lesion are determined by the gender, age and general condition of the patient.
Causes
The main cause of bullous cystitis is improper treatment of infections caused by:
- bacteria (staphylococcus, E. coli, streptococcus, Trichomonas, chlamydia);
- viruses (enterovirus, adenovirus, herpes, influenza virus);
- mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- parasites (cercariae, schistosomes).
Schistosomes can cause disease.
Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the tissues of the organs of the excretory system in the following ways:
- Ascending. The spread of infection is facilitated by non-compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene and unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Hematogenous. Bacteria enter the urinary organ through the bloodstream from distant foci of infection.
- Lymphogenic. Pathogenic microorganisms circulate in the lymphatic system, spreading throughout the body.
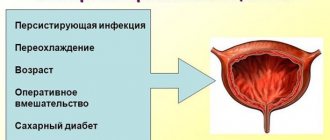
Factors contributing to the development of infection include:
- hypothermia of the body (this explains the fact that the disease often worsens in the cold season);
- injury to the bladder (during medical procedures, traumatic types of sex, surgical interventions);
- a sedentary lifestyle, which contributes to impaired blood supply to the pelvic organs (bullous cystitis often occurs in bedridden patients);
- complications of chemotherapy for cancer (drugs have an irritating effect on the mucous membranes of the excretory system, contributing to the occurrence of swelling and inflammation);
- radiation exposure (disrupts cell division processes, causing pathological changes in tissues);
- allergic reactions to foods, medications, intimate hygiene products;
- neurogenic dysfunctions of the bladder (typical for children and the elderly);
- changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy, menstruation and menopause.
Additional techniques
Prolonged treatment of bullous cystitis in children and adults requires the use of immunological drugs. Medicines with effective immunomodulation function are:
- Reaferon;
- Viferon.
Often, specialists use a treatment regimen for bullous cystitis in children, such as CAP + alpha-2-interferon. A complex immunoglobulin remedy will help you quickly get rid of this pathology.
The drug Tomicide has an antibacterial effect on the infection. With the help of this therapy, immunoglobulin A increases in the bladder and its mucosa. The drug has no contraindications. It is non-toxic and harmless. The medication is used 10-12 times. The dosage is selected for each child individually (taking into account his age). The installation can be combined with an enema. The last procedure is carried out using warm solutions of eucalyptus and chamomile. This treatment regimen is aimed at improving blood circulation in the pelvis.
Therapy for bullous cystitis includes physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Experts advise using electrophoresis with a 2% solution of calcium chloride, Terrylitin or Lidase. Physiotherapeutic techniques strengthen the walls of the inflamed organ. Such procedures must be carried out 3-4 times a month.
- You can get rid of the bullous form of the disease in question using electrophoresis with zinc or with 1% Furagin or Furadonin.
- It is possible to treat the pathology in question comprehensively, using instillations and electrophoresis with supratonal frequency currents.
- If bullous cystitis is detected in a teenager, then application wraps are used. To do this, you can use panties made of paraffin or ozokerite. It is recommended to undergo 8-10 such procedures. To quickly eliminate the symptoms of the disease, experts advise alternating the wrap with instillation.
- Often, instillations of medicinal products are combined with galvanic current and ultrasound. Such complex therapy increases the therapeutic effect.
If the child is experiencing severe pain, then he is given antispasmodics and painkillers.
Herbal medicine for bullous cystitis includes the use of lingonberry, juniper, and cranberry juice leaves. Traditional and traditional medicine is given to children only after consultation with a pediatrician. If necessary, you will need to consult a pediatric urologist or gynecologist.
Bullous cystitis is often diagnosed in patients who can be classified as adherents of self-medication. When nagging pain in the lower abdomen or difficulty urinating occurs, these people go for advice to a neighbor or to the nearest pharmacy for an antimicrobial drug.
Incorrectly selected antibiotic therapy provokes enlargement of infectious foci inside the bladder, replacement of epithelial cells with coarse fibrous tissue.
Symptoms of the disease
The pathology is characterized by increased intensity of symptoms, which include:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by urination, radiating to the perineum, lower back and anus.
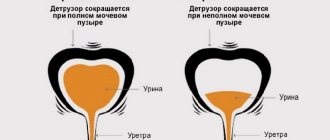
- Frequent urge to urinate. The patient is forced to visit the toilet every 10 minutes, urine is released in small portions or is absent altogether. Pain during urination is explained by increased excitability of the nerve endings, causing contractions of the bladder neck. In addition, swelling of the mucous membranes helps to reduce the volume of the organ.
- Itching and burning in the external genital area.
- Changes in urine characteristics. Urine becomes cloudy and dark brown or red in color, which is associated with damage to the blood vessels. In severe cases of the disease, the urine has a brown color and a sharp putrid odor.
- Urinary retention. It occurs due to spasm of the external urethral sphincter and reflex contraction of the pelvic muscles. Accompanied by severe cramping pain.
- Urinary incontinence. Urine leaks after emptying the bladder, when coughing, sneezing, and lifting heavy objects.
- Signs of body intoxication. In acute cystitis, the patient complains of fever, chills, aching muscles and joints, general weakness, and loss of appetite.
Therapy methods
Bullous cystitis occurs with pain in the lower abdomen and when urinating. A child may have an inflamed bladder due to hypothermia or other factors. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician. Therapy is prescribed after a complete examination of the child. Particular attention is paid to the results of laboratory tests. Bullous cystitis in children differs from other forms of this disease by severe swelling of the bladder mucosa, which contains serum fluid.
Without therapy, inflammatory changes increase, causing deformation of the mucosa. Treatment of bullous cystitis lasts 5-8 days. Experts do not recommend treating the disease with cauterizing medications. Otherwise, a burn may occur.
Treatment of bullous cystitis includes following a light diet. The child is advised to drink plenty of fluids. It is necessary to complete a full course of therapy so as not to provoke a chronic form. At the initial stage of therapy, antibiotics are taken.
Treatment of the disease includes taking silver nitrate. The dosage is increased gradually. The course of therapy consists of 15-20 sessions. To improve the circulation of the bladder and mucous membranes, silver nitrate and collargol are used. This treatment regimen has a cauterizing effect.
Treatment of bullous cystitis includes instillations using 10% dibunol liniment. This agent stabilizes the membrane, having an antiseptic effect on the inflamed organ. Instillation is carried out using novocaine. Before giving the injection, you must empty your bladder. Instillations are contraindicated for vesicopelvic reflux.
Prevention
To avoid the development of bullous cystitis or its exacerbation, it is recommended to adhere to several rules:
- avoid drafts;
- do not sit in the cold;
- dress according to the season, wear long jackets and coats;
- treat chronic diseases, do not ignore doctor’s advice;
- eliminate bad habits;
- women visit a gynecologist once every six months, men – a urologist;
- if you have a history of cystitis, stick to a diet.
Compliance with the above points prevents the exacerbation of cystitis and its transition to a bullous form.
Bullous cystitis is one of the types of inflammation of the bladder, which occurs with severe swelling of the mucous membrane.
It should be regarded not as an independent disease, but as a complication of an acute form of pathology.
Content
Treatment
To treat cystitis, medications, physiotherapy, and folk recipes are used. During therapy, adherence to a special diet and drinking regimen is indicated.
Medicines
The treatment regimen for bullous cystitis includes the following medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin). The active substance accumulates in the affected area, contributing to the disappearance of unpleasant symptoms. Medicines are used in the form of tablets, rectal suppositories and injections.
- Diuretics (Furosemide). Eliminate swelling of the mucous membrane, normalize the process of emptying the bladder. The duration of therapy depends on the intensity of the disease manifestations.
- Antibiotics (Monural, Nolitsin). They eliminate the causative agent of infection and prevent the development of dangerous complications. To get rid of unpleasant symptoms, a single dose of Monural is enough.
- Uroseptics (Canephron, Fitolysin). Herbal preparations can be used in the treatment of cystitis in pregnant women and infants. They are used in combination with antibiotics for long courses.
Physiotherapy
The following physiotherapeutic procedures are used to treat cystitis:
- Electrophoresis. Provides delivery of drugs to inflamed areas of the mucous membranes through electric current. The procedure helps reduce the intensity of swelling, the disappearance of pain and spasms.
- Magnetotherapy. The magnetic field destroys bacteria and viruses, removes toxic substances from the body.
- Inductothermy. The method is based on relieving inflammation with electric current. During the procedure, blood circulation is normalized and the functions of nerve endings are restored.
- Magnetophoresis. The action is similar to electrophoresis, but the active substances are moved through a magnetic field.
- EHF. High-frequency therapy is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field that eliminates inflammation, pain and spasms.
Homeopathy
For bullous cystitis, the following homeopathic remedies are prescribed:
- Borax (Borax). Normalizes urination, eliminates false urges.
- Dulcamara (Dulcamara). Used in the presence of bloody impurities in the urine. The drug relieves severe pain and accelerates tissue healing.
- Digitalis (Digitalis). Helps get rid of severe pain in the lower abdomen.
The drill normalizes urination and eliminates false urges.
These drugs are used as prescribed by a doctor, in combination with traditional therapy drugs. They have minimal side effects, so they can be used during pregnancy.
Traditional methods
Taking medications is combined with the use of the following folk remedies:
- Chamomile infusion. 1 tbsp. l. the herbs are poured into 200 ml of boiling water, left for half an hour, then filtered. Take 100 ml 3 times a day.
- Millet infusion. 100 g of millet are thoroughly washed, poured with 1 glass of boiling water, and left for 20 minutes. After this time, the grains are ground to obtain a cloudy liquid, which is used as medicine. The drug is taken 3-4 times a day for a week.
- Dill seed decoction. 1 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with 200 ml of boiling water, heated in a water bath for 10-15 minutes. The finished broth is passed through gauze and taken 100 ml 4-5 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
ethnoscience
Along with medications, doctors usually recommend a decoction of natural ingredients:
- Lingonberry. Take fresh leaves and chop. Then 2 tbsp. The mixture is poured with cold water and brought to a boil. The broth should boil for 20 minutes. Then cover the product with a lid, leave for 2 hours, and filter. Drink all day. The course of treatment is 10-12 days.
- Take crushed parts of horsetail and chamomile in equal parts and mix. The mixture is poured with boiling water and left for 3-5 hours. Drink all day. The course of treatment is 14 days.
- The cut cherry branch is cut into sticks and poured with boiling water. The product should infuse for 12 hours. Pour hot water into the bath, diluting with infusion. Sit in the bath with your feet. The procedure lasts 20 minutes. Course – 7 days.
You should not self-medicate. It is better to consult a doctor at a medical facility. It will help you quickly make a diagnosis, prescribe the necessary medications, and eliminate the manifestations of pathology.
Diet
Following a diet for cystitis prevents irritation of the mucous membranes of the bladder and promotes the removal of mucus and pathogenic microorganisms. Sour vegetables and fruits, spicy foods, smoked meats and sausages, alcohol, and sweet carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet. Milk porridges, lean meat and fish, fruits and vegetables with a neutral taste are healthy. The amount of fluid consumed is adjusted to 2-2.5 liters per day. Berry fruit drinks, still mineral water, and green tea are useful.
Treatment of cystitis in children - drugs
Cystitis is characterized by inflammation of the bladder and, unfortunately, often occurs in children. Many mothers cannot understand the cause of the unpleasant symptoms and begin to attribute the child’s crying to other diseases, but you need to know everything about the treatment of cystitis in children in order to cope with this disease and know what to do.
Signs of illness in a child
The disease can appear in children of both sexes, as a rule, it is rare in infants, and affects children 2-5 and 12-16 years old. Babies often cry when the first symptoms of the disease appear, and older children can talk in more detail about the unpleasant sensations and the places where the inflammation is most concentrated.
If you do not pay attention to the first manifestations of the disease in time, it can become chronic, and then treatment will become much more difficult.
Have you been fighting CYSTITIS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure cystitis by taking it every day...
Read more "
Children at an early age cannot tell their parents about pain, but adults can easily understand what is bothering the baby based on the following signs:
- frequent urination;
- temperature rise to 38, and sometimes 39 degrees;
- dark urine (a sign not always present);
- crying while urinating. Many children hold their stomachs during acute pain.
Read about the types of cystitis in our article.
For older children who are able to describe their symptoms, the following signs appear:
- frequent urge to urinate (frequency reaches three or four times per hour);
- cloudy urine (a characteristic but not always common sign);
- increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees;
- pain when going to the toilet;
- possible urinary incontinence.
The danger of this disease is that if timely diagnosis and treatment are not carried out, the infectious process can spread to the kidneys. Such a transition threatens the development of pyelonephritis.
There are many blood vessels and nerve endings around the bladder, so the appearance of inflammation cannot go unnoticed by adults. In any case, they will notice the baby’s changed condition.
Causes
Experts say that the main reason for the development of this disease in children is the entry into the body of bacteria that cause inflammation. The most common are Escherichia coli and various types of staphylococci, chlamydia and streptococci. The infection most often enters the child's body through the ascending route. Bacteria rise through the urethra to the urinary tract, and from there pass to the bladder. As a result, an inflammatory process occurs.
The immune system in children is still weak, and the walls of the bladder are thinner than in adults, so the infection often settles in the child’s urinary tract.
Risk factors that may lead to the development of cystitis include:
- Rare and incomplete urination.
- Diseases of urolithiasis.
- The presence of foreign bodies in the bladder and damage to its walls and mucosa.
- A process that occurs with purulent inflammation. Diseases that can worsen cystitis include sore throat and pneumonia.
- Gynecological diseases in girls. Such diseases must be taken seriously and treated promptly.
- Various infections that appear in the intestinal area.
- Changes occurring with the acid-base balance in the composition of urine.
- Violation of the rules of genital hygiene.
- The presence of helminths in the child’s body. They usually emerge from the anus at night and cause infection by crawling towards the urethra.
- Appendicitis can also trigger the disease if the appendix is located in the pelvic floor area.
In addition to the main reasons listed above, there are factors that can provoke cystitis. These often include constipation that occurs due to poor nutrition, excessive fatigue due to the imposition of sports and physical activity on the child. This may include a practice of visiting saunas with parents where adults are present.
Tests for inflammation in children
The results of the tests directly depend on the preparation for taking the tests. If the preparatory work procedure is carried out incorrectly, a false positive result is possible.
Before donating urine, you need to wash your baby with water without using soap.
It is important to know that urine must be collected in a special container. Such a container can be purchased at any pharmacy. You should not collect urine in a baby food jar because experts may find sugar or protein particles in such containers. However, the presence of leukocytes cannot in any way be caused by the condition of such a jar.
To properly collect urine from infants, it is recommended to use a urine collector. It is easily installed on the child's genitals because it has a special Velcro.
You should not squeeze a cotton swab soaked in urine into a container, because cotton wool can retain some of the particles that make up the urine.
Pressing on the diaper in order to drain a few drops into the container is also not recommended, because modern diapers contain a special gel that locks in moisture. After such a spin, the analysis results may be inaccurate.
Tests can show the amount of blood and light flakes in urine. If an increased amount of such substances is detected in the urine, this indicates an inflammatory process and damage to the soft tissues of the bladder.
If mucous discharge is present in the urine, this indicates the presence of harmful organisms in the urinary tract cavity.
Normally, protein should not be in the urine, but if it is detected, then its amount should not exceed 0.036 grams per liter. If the figure approaches one, it is worth re-testing, and if the protein content reaches 3 grams per liter, then there is a serious cause for concern.
How to determine cystitis in a child - symptoms
Newborns who develop cystitis are characterized by an asymptomatic form, and in this case it is difficult to recognize the disease. Even if your baby develops minor symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Symptoms indicating the presence of inflammation include:
- frequent crying of the baby and his restlessness, especially at night;
- urination occurs intermittently;
- the child goes to the toilet in small quantities;
- urine acquires a specific smell and color;
- white flakes, blood and cloudy sediment are observed in the urine;
- crying intensifies during urination;
- Sometimes there is a delay in urination.
All these symptoms indicate changes in the baby’s condition and prompt adults to seek urgent treatment.
To treat cystitis, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method
This cheap odorous remedy will get rid of cystitis forever! Sold in every pharmacy, called...
Identifying symptoms in a six-month and 2-year-old child
In children under one year of age, it is difficult to recognize symptoms, but they are observed with careful attention to the health of your baby. Usually parents notice even the slightest changes in their baby’s well-being. Typical symptoms in a six-month-old child include:
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- pain and crying when urinating;
- darkening of urine;
- the appearance of odor in urine;
- increased body temperature;
- loss of appetite.
A two-year-old child, especially girls, is more likely than at an early age to experience bladder inflammation. At this age, the baby is already able to tell his parents about the unpleasant sensations experienced while going to the toilet. The composition of his urine changes, and pain appears in the lower abdomen.
In general, all the same symptoms are observed as in young children.
At the first complaints from a small child, you need to seek qualified help.
Cystitis in boys
Experts say that according to statistics, 1% of boys under eleven years of age have been exposed to cystitis. This inflammation most often occurs in children under four years of age.
Recovery and positive dynamics depend on the correct and timely identification of symptoms of the disease. If you recognize and defeat the disease in time, you can insure yourself against raging complications.
The genitourinary system in boys is represented by the ureter, kidneys, bladder and urethra, which includes two sphincters. The greatest likelihood of transmission of microbes occurs in the area of \u200b\u200bthe urethra and foreskin. Unlike the genitourinary system in girls, whose urethra is wider, boys are less susceptible to cystitis due to the anatomical features of the structure of the body.
The peak period for infection occurs between newborn and two years of age. Bacteria travel from the urethra up the urinary tract to the bladder.
If parents noticed a change in the behavior of a newborn boy for the first time and consulted a doctor in time, the likelihood of the disease occurring in the future is reduced to a minimum, but it is still better to avoid provoking factors.
In young boys, inflammation of the urethra often occurs, which is one of the main causes of this disease.
It is important for parents to monitor the cleanliness of their child’s genitals and carry out hygiene procedures as often as possible. It is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of the foreskin, because it is in it that pathogenic microbes can accumulate.
In newborn boys, the foreskin is narrowed, but hygiene procedures must be carried out without fail.
This disease is less common in adolescents, and this is explained by the appearance of prostate secretion, which reliably protects it from inflammation.
The symptoms in boys and girls are similar and have almost no differences. The pain that occurs during the process of urination intensifies at the end and after it is completed.
How and with what to treat?
The treatment of childhood cystitis in the initial stages of inflammation is carried out by a pediatrician. If the disease is confirmed and is accompanied by severe symptoms, the child is referred to a pediatric urologist. Tests are carried out in the same order and according to the same scheme as for adults.
To properly prescribe medication, parents need to consult a doctor. There is no need to carry out independent treatment, because only a specialist can provide qualified assistance and prescribe effective medications. The doctor prescribes medications based on tests and general symptoms.
Diagnosis of the disease takes place in several stages:
- Taking a urine test.
- Ultrasonography.
- Visit to a pediatric gynecologist (for girls).
- If the disease is acute, cystoscopic and x-ray examinations are prescribed.
Based on the examination results provided, the doctor may prescribe:
- antibacterial drugs: Monural, Amoxiclav, Cefuroxime. You cannot carry out treatment yourself, because only the doctor knows what type of bacteria to prescribe medicine for;
- drugs for immunostimulation;
- cystone: tablets based on mumiyo;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- vitamin complexes;
- prescription of Biseptol for effective control of staphylococci and E. coli;
- Sometimes the doctor prescribes treatment with Sumamed. It is prescribed when the baby is allergic to penicillins.
Diet for illness
When prescribing a course of treatment for a child, the doctor will ask the parents to follow a special feeding order for their baby. The following menu will be assigned to the child:
- Fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir and fermented baked milk).
- Porridges from various grains.
- Drink in increased volumes. Fruit drinks, cranberry infusions, sugar-free compote and still mineral water are often prescribed.
- Decoctions made from medicinal herbs. These include: birch leaves, string and valerian.
The urologist will ask parents to exclude fried and smoked foods, salty and fatty foods, and sweets from the baby’s diet. If a child really wants to try sweets, it is allowed to eat honey, marmalade or marshmallows.
Homeopathic treatment
The use of homeopathic remedies is used to relieve symptoms of inflammation and support the body's immune system. Homeopathic remedies are prescribed for the general normalization of all systems and organs in the human body.
When taking medications, the child is limited in eating sweets and smoked foods. The advantages of homeopathic medicines when used in children are that they eliminate the presence of unpleasant smell and taste, which children dislike so much.
Homeopathy, often used for inflammation, is barberry, as well as marshmallow and rosehip. Rosehip gives the body strength and fills it with vitamin C, while barberry eliminates lethargy and normalizes the body's strength to fight disease.
Treatment of a child at home
At the age of five, the onset of the disease takes place in just a few days, so it is important to pay attention to the symptoms in time: burning, pain when urinating, frequent urge to go to the toilet and other signs characteristic of this disease.
Treatment is carried out in a complex of measures, including: adherence to bed rest and a certain diet prescribed by the doctor. Medication and folk treatment are combined with regular hygiene procedures.
When a disease occurs, the doctor often prescribes immunostimulating drugs and antibiotics.
The use of baths with chamomile or other antimeptic extracts can relieve inflammation and alleviate the general condition of the patient. The use of baths for children should be agreed with the attending physician.
Add five tablespoons of herbs to one liter of water: chamomile, sage and calendula. You need to wait for the broth to cool completely and add water to it so that the total temperature does not exceed 37 degrees. This solution is dissolved in the bath or washed off the child with it.
It is advisable to wash your child with this decoction after each trip to the toilet.
To most effectively combat the disease, it is recommended to use infusions and decoctions of herbs such as:
- sage;
- Linden;
- cowberry;
- calendula;
- celery;
- plantain.
These plants are prepared according to a special recipe and consumed orally; if necessary, baths with herbs can be performed.
Before choosing an infusion or decoction as a treatment, you should definitely consult your doctor, because not all herbs are equally beneficial for the child’s body.
Many pediatricians recommend giving flaxseed: its preparation consists of adding three tablespoons of seeds to boiling water. A liter of boiling water is infused and given to children depending on age (from one teaspoon to two).
Another effective way against inflammation is lingonberry leaves. Preparation proceeds like normal tea brewing. Consumption is carried out at ten or fifteen milliliters per day.
Bullous and catarrhal cystitis
If you do not provide timely assistance to a sick child and do not take appropriate measures, the disease can develop into a more complicated form - bullous cystitis. With this type of cystitis, inflammation occurs not only in the mucous membrane of the bladder, but also in additional swelling of the serum fluid.
Catarrhal cystitis differs from other types in that inflammation is concentrated only in the bladder mucosa. The main symptoms are associated with severe pain when urinating and the acute course of the disease.
These types of cystitis are treated with medication, with the addition of traditional recipes, if such measures are allowed by the doctor.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures are aimed at strengthening the immune system of the child’s body, as well as protecting the child from excessive cooling.
Proper nutrition and prevention are the key to health and the absence of relapses.
It is important for parents to know that regularly changing their child’s underwear and hygiene procedures associated with washing can provide protection against the occurrence of an inflammatory process.
It is recommended to drink more fluid, especially for those babies who have problems with salt in their urine. Fruit drinks, compotes without sugar and mineral water are used as liquids.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you in the video how to properly collect urine for analysis:
Complications and consequences
Bullous cystitis is complicated by:
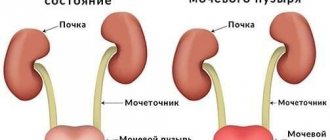
- Paracystitis. Occurs when pathogenic microflora spreads to the tissue surrounding the bladder. Requires urgent surgical intervention.
- Pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the kidneys is characterized by a severe course, accompanied by a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, intoxication of the body, and swelling of the soft tissues.
- Transition to the interstitial form. The inflammatory process covers the muscle layer, which makes standard therapy ineffective. Sometimes the only way to get rid of severe pain is to remove the bladder.
The main point
The main cause of bullous cystitis is a chronic inflammatory process in the bladder or other pelvic organs. Constant irritation causes structural changes in the cells of the mucous layer: swelling with serous contents is added to bacterial inflammation.
Effective diagnostic methods: ultrasound of the bladder and cystoscopy, which is possible only in the non-acute stage of the disease. The treatment regimen is based on instillations of various antibiotics. Additional therapy: the use of immunostimulants, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy.