The appearance of a strong burning sensation in the groin area, which occurs mainly after urination, occurs in every person at different periods of life. The danger is the development of a persistent inflammatory process in the bladder and the appearance of chronic painful cystitis, which significantly worsens a person’s quality of life.
What is chronic cystitis
After the appearance of frequent pain in the groin area, patients begin to look for information about what chronic cystitis is and why it occurs. The algorithm for the appearance of pathology associated with inflammation of the bladder includes the obligatory experience of the patient having an acute form of cystitis, which was poorly treated and caused complications. Elimination of severe pain in this case does not indicate self-healing, but indicates the transition of the disease to the chronic stage, to get rid of which special anti-inflammatory drugs are already needed.
Reasons for development
Chronic cystitis is often provoked by gram-negative pathogenic microorganisms, which are:
Various viruses and bacteria contribute to the development of chronic cystitis.
- enterobacteria;
- viruses;
- fungal microorganisms;
- pathogens of the protozoan class.
The development and exacerbation of chronic cystitis occurs under the following circumstances:
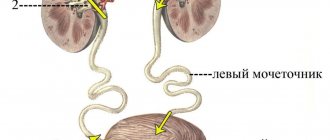
- When negative factors confluence on the mucous membranes of the external genitalia, the pathogen actively multiplies, after which it penetrates into the genitourinary organs through the urethra and affects the urinary tract, causing the organ to become inflamed. This distribution pattern is typical for the female body. In men, the urethra is longer, so microbes often do not reach their target and die on the outer tissues of the mucous membrane.
- The pathogen progresses in the kidneys, from where it enters the bladder along with urine, remains there and begins its active life.
- Pathological processes can occur in the urea itself, for example, various types of inclusions can form. The latter irritate the walls of the bladder, causing inflammation of the mucous membrane and the addition of a bacterial infection.
However, the presence of a pathological pathogen in the body does not always cause permanent cystitis. If a person has strong protective functions, they will constantly suppress viruses and bacteria, so the disease has no chance of progressing.
Other factors
However, there are other, external factors due to which the disease will begin to progress. Among the most common are:
HIV and AIDS provoke the appearance of cystitis in a chronic form.
- insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia;
- frequent hypothermia;
- promiscuous sex life and ignoring contraception;
- systemic pathologies - HIV, AIDS, diabetes mellitus;
- neoplasms of various etiologies;
- hormonal and endocrine disorders;
- diseased kidneys;
- untimely emptying of the bladder;
- abuse of bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- regular stress and nervous tension.
Causes of chronic cystitis
Chronic cystitis occurs in women much more often due to the structural features of the urethral tube - it is shorter and thicker than the male one. The close proximity of the vaginal and anal areas increases the risk of penetration of opportunistic microorganisms. During pregnancy, expectant mothers often develop chronic severe cystitis, provoked by toxicosis, compression of the urethra and adjacent organs of the urinary system.
Common initiating factors for the development of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- untimely urination;
- urethral injuries;
- diseases of the pelvic organs.
Sometimes certain drugs - sulfalimide and cytostatics - lead to allergic inflammation of the bladder and urethra due to the influence of chemically created substances. In this case, chronic allergic cystitis is diagnosed.
Doctors rarely observe chronic cystitis in men at a young age, however, against the background of the development of prostatitis, urethritis and cystitis can occur during exacerbation of the disease. The benign changes that prostate hyperplasia provokes invade adjacent tissues in the male population and also provoke catarrhal lesions.
Fact. According to medical statistics, less than 1% of men suffer from bladder inflammation.
Causes and risk factors
The main reason for the development of the disease is the lack of adequate treatment for the acute form of the disease. In this case, irreversible changes occur in the tissues of the genitourinary system, which cannot be completely eliminated. Other possible causes of the development of pathology include infection of the genitourinary system (viruses, fungal and bacterial infections transmitted during sexual intercourse), trauma and toxic damage to the bladder.
There are also secondary risk factors that can lead to relapse:
- Surgical operations on the pelvic organs, for example, the use of catheters, cystoscopes and other medical instruments).
- Long-term bowel dysfunction (chronic constipation).
- Promiscuous sex life, frequent changes of partners, unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Pathologies of the urinary system, for example, inflammation of the urethra.
- Uncontrolled use of medications, most often hormonal.
- Lack of personal hygiene.
- Errors in nutrition, in particular, consumption of fatty, fried, salty foods, large amounts of spices and herbs.
- Sedentary lifestyle, lack of proper physical activity.
- The presence of foci of infection in the body, for example, untreated caries, inflammation of the tonsils, purulent abscesses.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Prolonged exposure to negative temperatures on the female body (general or local hypothermia).
Symptoms of the disease
In men and women, chronic cystitis has symptoms similar to those of the disease in its acute form, but the intensity of the discomfort in this case is less pronounced. Having studied the characteristic symptoms and treatment, it is easier to choose.
Clinical picture:
- “excruciating” and painful urine output;
- constant desire to urinate (dysuria);
- strong urge to go to the toilet (nocturia);
- blood clots in the urine.
The clinical symptoms of chronic cystitis in women rarely differ from the manifestations of the disease in the stronger half of humanity. The risk of developing cystitis is higher if a person has: overwork, immune failure, chronic constipation and dehydration.
Symptoms of pathology
The symptoms of chronic cystitis, in contrast to acute ones, are characterized by a blurred pattern of progression. If the disease is in remission, symptoms may not appear at all. In the acute stage, advanced cystitis manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- increased desire to visit the restroom, but when urinating the amount of urine is negligible;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor of urine, a change in its color to a darker one;
- pathological discharge from the vagina, itching and burning of the external genitalia;
- pain when urinating.
Pain during cystitis in the relapse stage is pronounced and constantly bothers you, even when the person has already gone to the toilet. If characteristic symptoms develop, the patient is contraindicated from doing anything on his own and trying to take medications at his own discretion. The fact is that chronic cystitis itself is a pathological complication, so in order to get rid of it forever, you will need a well-chosen, comprehensive treatment that can only be prescribed by a doctor. If the treatment regimen is inadequate, there is a high probability of developing severe complications, one of which is pyelonephritis.
Treatment of chronic cystitis in adults
Most doctors prescribe drugs with antiseptic or antibiotic effects to effectively suppress inflammation of the mucous membrane. Let's learn how to treat chronic inflammation with medications.
- Ciprofloxacin. An effective eliminater of microorganisms, which is used for inflammation of the bladder. The maximum therapeutic effect is observed when the drug is combined with Pefloxacin and Levofloxacin. Uncomplicated cystitis includes treatment with antibiotics for no longer than 5 days.
- Furosemide. The presence of inflammation of the pancreas requires correction of the treatment regimen for chronic cystitis when taking Furosemide. Some tablets for this disease react negatively with a drug that has a diuretic effect, and the doctor decides how to take and combine them.
- Monural. In uroseptics, the main active ingredient is fosfomycin trometamol (an antibiotic). Thanks to it, monural destroys microbes and bacteria, including chlamydia, so it is prescribed for sexually transmitted infections. Contraindications: Monural should not be used by pregnant women and children under 5 years of age. Monural can cause nausea and diarrhea.
- Drotaverine. Like monural, Drotaverine reduces burning, but the main focus of the remedy is to eliminate spasm and pain. It is used for 4-5 days until the unpleasant symptoms disappear, but it is better to use it after the causes of chronic cystitis have been clarified in the laboratory.
- Urolesan. A herbal medicine for those who are interested in how to cure a chronic illness with environmentally friendly drugs. The composition contains only herbal components, the course of administration is 1–2 weeks, in case of complications with pyelonephritis - 4 weeks (1–2 tablets each).
- Canephron. Another herbal remedy that helps relieve bladder inflammation is the use of rosemary and centaury leaves. There are no adverse reactions, and the pain usually goes away within a few hours after taking the pill.
Before treating chronic cystitis, it is necessary to undergo the appropriate tests: a general analysis of urine and blood, a smear from the urethra, and sometimes a Nechiporenko test.
Hardware treatment of chronic cystitis in women and men may include a course of treatment using electrophoresis, iontophonoresis, ultrasound and laser equipment. With this combination, the cure rate for chronic cystitis is very high.
Reference. Auxiliary treatment of cystitis with folk remedies and at the same time with medications gives excellent results.
Diagnosis of the disease
During the period of remission, it is possible to determine inflammation only by analysis. In this case, women must be examined by a gynecologist, men – by a proctologist. Ongoing research:
- blood tests - general, biochemistry;
- urine - general, antibiotic sensitivity test, Nechiporenko test;
- examination of smears from the urethra;
- Ultrasound, cystoscopy and cystography.
Hardware studies help to determine the degree of change in the membrane, the localization of lesions, pathologies of the urinary organs, and the presence of stones. Therefore, how to treat chronic cystitis becomes clear only after a complete examination.
Therapy with folk remedies
As a preventive measure or if there is a high probability of a relapse, you can also use herbal medicinal components - after consuming an aqueous solution, everyone who takes it feels significant relief.
- Rowan and lingonberry. The healers of ancient times knew how to cure chronic urological disease. The two components are mixed in a 3:1 ratio and infused for 4 hours. You need to drink 100 ml of this decoction four times a day.
- Chicory. 3 tbsp. l. infused in boiling water (a glass), and then the resulting infusion is consumed one spoonful three times a day.
- Nettle. The antibacterial properties of nettle help remove bacteria from inside the urethra and bladder. Stinging nettle (1 tbsp) is poured with boiling water and given to the patient after 10 minutes of infusion. Take with the same frequency as chicory. After 3 days, the manifestation of cystitis disappears. It is also available in tablet and capsule form.
- Ginger Antiseptic, diuretic and antiviral effects improve the condition of the mucous membranes. Pickled ginger root can be used as an additive to dishes, and fresh ginger root can be used in tea or lemon drink. The antimicrobial effect also leads to the restoration of the inflamed prostate gland in men, or the uterus in women.
Natural antibiotics include sage, calendula, plantain and tansy. Local application of tea leaves of these herbs to the bladder area also has a beneficial effect. Elimination of chronic cystitis by treatment with known folk remedies is best combined with medications in order to achieve the maximum positive effect.
Traditional recipes for the treatment of cystitis
At home, time-tested natural remedies are often used. The most popular folk methods of treatment are the use of chamomile, cranberry, and millet decoctions. Treatment with the use of such drugs can only be done after consultation with a doctor.
Cranberry
Cranberry leaves and berries are an effective remedy to cure cystitis or reduce the number and duration of periods of exacerbation. Berries are best consumed fresh on an empty stomach (if there are no contraindications, for example, diseases of the digestive system).
A healing decoction is prepared from cranberry leaves. To do this, they are crushed, 1 tbsp. l. pour the resulting raw material with a glass of hot water and leave for 20 minutes. Drink 50 ml three times a day for 7-10 days.
Millet
To prepare a millet decoction, take 2 tbsp. l. cereals, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over them, after which the millet is boiled over low heat for 5 minutes. The resulting liquid is poured into a deep container through gauze or a sieve and cooled.
You should adhere to the recommended treatment regimen:
- on the first day of therapy, you need to take 20 ml of the drug with an interval of 1 hour;
- on the second day the dosage is increased: the patient takes 60 ml of decoction;
- On the third and subsequent days, the recommended amount is 100 ml every hour.
The duration of therapy is about 1 week.
Chamomile
To prepare the decoction, you need to take 10 g of raw materials (you can purchase it at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself), pour 1 glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, then cool and strain. The resulting product is taken orally 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
The duration of treatment is not limited; you can use the product until the symptoms of the pathology disappear.
Chronic cystitis in children
In children and adolescents, signs of chronic inflammation of the urethra most often appear in girls (mainly between the ages of 4 and 12 years). An infant can also get this disease if he is exposed to hypothermia. Another option: the disease can appear as a result of receiving poor-quality medical services - catheterization or cystoscopy.
Chronic cystitis in children is eliminated using the same methods as in adults, using drugs without contraindications for use in childhood. A pediatrician determines how to get rid of a disease in a child.
Advice. A spoonful of honey taken at night, which gently relieves mild inflammation, has a positive effect on the child’s genitourinary system.
Diet for chronic cystitis
After treatment, remission occurs, but if the diet is improper, signs of the disease may return. By eliminating certain foods, the patient can forget about the exacerbation of chronic cystitis due to the food factor. The first step is to exclude fried, spicy and overly salty foods, which irritate the bladder mucosa.
Prohibited products:
- citrus;
- fermented milk;
- spices;
- caffeinated products;
- alcoholic drinks;
- sweets.
A gentle diet for chronic cystitis does not allow you to completely get rid of chronic cystitis, but it minimizes the occurrence of pain.
Symptoms, signs
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage and the woman’s immunity.
Exacerbations can occur 1-2 times a year, but sometimes the pathology is asymptomatic - then the disease can only be detected through endoscopic examination.
During an exacerbation of cystitis, there may be symptoms of acute or subacute inflammation.
The most important sign that is always there is aching
Blood in the urine may indicate an ulcerative lesion, but this is rarely observed in chronic cystitis.
During periods of exacerbation, a woman experiences frequent urination and pain.
In severe forms there is severe pain syndrome. The pain increases as the bladder fills.
In acute cystitis, there is a significant increase in body temperature, nausea, and vomiting. Chronic forms during an exacerbation proceed more mildly - and there are no such symptoms.
Urine has a cloudy color and an unpleasant odor. Rarely does pain occur in the lumbar region.
During periods of exacerbation of inflammation, caused by infections or viruses, severe symptoms of the underlying disease may be observed. This is especially evident in the case of sexually transmitted infections.
Nonspecific discharge from the genitals, itching, and burning occur. Additional symptoms occur individually.
Complications of chronic cystitis
There is a dangerous risk of the chronic disease turning into bullous cystitis, which is characterized by the rapid development of lymphoid tissue in the submucosal layer of the bladder. The follicles pose a serious risk to humans and are usually removed surgically.
Common secondary diseases:
- the occurrence of bacteriologically provoked inflammation of the kidneys - pyelonephritis;
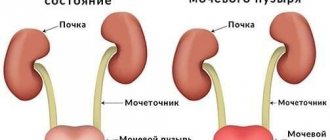
- the appearance of backflow of urine into the ureter - vesicoureteral reflux;
- the formation of thickening of the walls and a decrease in the volume of the bladder (interstitial cystitis).
Long-term chronic inflammation of the bladder can lead to the development of cancer of the urinary system. Although chronic cystitis during pregnancy is considered normal, if signs of the disease remain after childbirth, then prompt treatment of the inflammation should be started. Most often, complications arise if there is an exacerbation of chronic cystitis, leading to increased inflammation in the urethra.
Diagnosis of cystitis
Chronic cystitis is difficult to diagnose and treat.
The difference between chronic cystitis:
- relapses after viral diseases, hypothermia, nervous stress and decreased immunity;
- the structure of the walls and muscle tissue of the bladder deteriorates;
- occurs with any disease of the urinary system and diseases in the genital area;
- Symptoms in this form of the disease are very often less pronounced than at the beginning of the disease.
To avoid the transition of acute cystitis to a chronic state, you must follow some rules:
- take medications until cystitis is completely cured;
- follow a diet that contributes to the positive dynamics of treatment;
- for the duration of treatment, refrain from playing sports and active recreation;
- drink enough fluids to help flush out the infection from the body;
- empty the bladder in a timely manner, stagnation of urine in it promotes the proliferation of microorganisms;
- do not wear synthetic or tight underwear;
- Carry out hygiene procedures in the morning and before bed;
- be systematically observed by a urologist.
Prevention of chronic cystitis
To prevent inflammation in the urethra, it is necessary to adhere to a certain lifestyle and protect the groin area from adverse traumatic influences - temperature, chemical and mechanical.
Another available “cure” is an increase in physical activity, which leads to the prevention of congestion in the pelvic organs. Drinking clean water is of great importance, helping to quickly remove harmful substances and wash away germs from the walls of the bladder. The optimal daily amount of water is 2–2.5 liters.
Is it possible to cure chronic cystitis? With due persistence, this is possible, but it is better to prevent the appearance of such an insidious disease and adhere to preventive measures.
How to diagnose?
You cannot determine your problem on your own. For example, pain during urination may indicate an inflammatory process in the genitals.
Diagnostics consists of prescribing the following studies:
- full gynecological examination;
- bacteriological urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and upper urinary tract;
- tests for sexually transmitted infections;
- endoscopy.
To determine why the process became chronic, cystoscopy may also be recommended. If the mucous membrane of the bladder is deformed, it is advisable to prescribe a biopsy simultaneously with this study. It will confirm or rule out the presence of precancerous lesions.
To correctly assess the condition of the mucous and submucous membranes of the organ, tomography is prescribed.