Causes of the anomaly
According to medical statistics, most often the humpback kidney anomaly occurs as a result of intrauterine development, that is, it has a congenital form. It is characterized by a humpbacked kidney, the bulging outline of the organ itself on the monitor during an ultrasound. Almost half of the cases of abnormal organ structure occur in the urinary system. The nature of the appearance of such changes is not clear and appears to be a genetic failure of unknown origin.
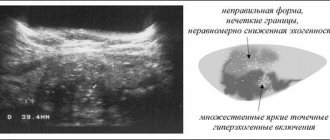
When conducting diagnostics, such a kidney pathology is often mistaken by a specialist for a neoplasm, but upon closer examination, ultrasound shows an undamaged body of the kidney itself, which is not typical for cancerous tumors of various origins. A humpbacked kidney is usually diagnosed by chance during an examination for another disease or simply a routine medical examination if the patient is at risk for a certain pathology of the urinary system.
Doctors most often use a collective image of the causes of this kidney formation.
5 main reasons:
- Genetic incompatibility of parents.
- Poor state of the environment and its impact on the body of the mother and fetus.
- Complications during pregnancy.
- Exposure to various types of radiation and radiation (especially in areas of radiation contamination).
- Excessive use of medical drugs.
Studies have found that the humpback kidney appears in the first trimester of pregnancy, during the period when the urinary system is established at the cellular level. In the developing body of the fetus, a certain genetic malfunction occurs, leading to the proliferation of kidney tissue and the appearance of a spherical, crescent-shaped, oval protrusion.
There are a certain number of cases when the development of kidney formation is not associated with congenital defects in the structure of the urinary system. Protrusion appears against the background of other diseases and processes:
- Neoplasms in neighboring areas, leading to compression of the organ and its deformation.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes occurring in the kidney.
- The formation of tumors of the kidney itself.
- Tuberculosis of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms
The pathology is accompanied by a change in the outer surface of the kidneys, which will be clearly noticeable during a diagnostic study.
However, patients very rarely seek medical help due to the fact that in the initial stages of development of kidney nephrosclerosis no symptoms appear.
Signs begin to clearly appear when pathological changes have completely affected the entire kidney.
At this moment, compactions and a lumpy surface are already observed on the outer surface of the kidneys.
Moreover, if the cause of nephrosclerosis is glomerulonephritis or hypertension, the surface layer of tissue becomes fine-grained, and if the kidneys are damaged by atherosclerosis, large nodules are observed on the surface.
It should be noted that nephrosclerosis is still easier to identify based on the results of the tests.
Although, along with this, there are signs that can be noticed by the patient himself.
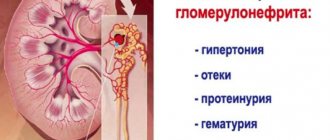
The main symptoms include nocturia and polyuria, the formation of protein in the urine, and a decrease in the density of the urinary fluid.
Increased blood pressure
The patient experiences increased swelling, which is visible initially only on the facial part, and subsequently throughout the entire body.
The patient also begins to experience quite frequent increases in blood pressure, which can provoke not only overload of the cardiovascular system, but also cause a stroke.
Unfortunately, against such a background, retinal detachment or swelling of the optic nerve papilla may occur, as a result of which the person may simply go blind.
Patients may complain of frequent headaches.
Symptoms
In the case of a congenital form of kidney anomaly, there are no symptoms. The patient does not feel any discomfort and continues his life activities, sometimes even unaware of the presence of such a defect in his urinary system. And this can continue for the rest of his life.
Symptoms begin to appear in the presence of other pathological processes associated with the physiology of the kidney. The risk group includes people who have:
- Anatomical location unusual for the kidney (prolapse, wandering kidney).
- If there are adhesions, the organ is fixed in a certain place.
- Fusion of the upper poles (horseshoe kidney).
- Impaired blood flow in the kidney.
- Receiving various types of injuries in the kidney area.
When the abdominal organs are compressed for various reasons, pain and an infectious-inflammatory process may occur. Then various symptoms appear, such as thickening of blood vessels and arteries, girdle pain, and complicated bowel movements. Complications may occur in the form of metabolic disorders.
Diet and foods for polycystic kidney disease
Congenital renal diseases require constant monitoring, diagnosis and clinical judgment. Polycystic kidney disease is a congenital pathology characterized by the formation of a large number of cysts in the kidneys. The form of polycystic disease is bilateral and is hereditary. In this article we will talk about the disease, its symptoms, and also look at nutrition for polycystic kidney disease.
Pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease is a congenital pathology characterized by the formation of a large number of cysts in the kidneys
The main reason for the formation and progression of polycystic kidney disease is ontophylogenesis with incorrect and incomplete formation and fusion of convoluted and straight canals. Deformed channels of the organ make it difficult for the normal passage of urine due to the appearance of cystic formations. In addition to malformed nephrons or abnormal niphrons, there are also correctly formed nephrons. Polycystic kidney disease coexists well with other pathologies of the renal system, kidneys and other organs. In appearance, the organs affected by polycystic disease resemble a bunch of grapes; morphologically, the existing cysts are of completely different sizes (diameter 6-8 cm), as a result of which the entire organ is completely filled with them.
The renal pelvis and calyx are deformed, their shape is elongated, and the organ itself is increased in size, sometimes the organ can reach up to 2 kg in weight. The formation of large cysts in the area of the renal hilum causes a process of hemodynamic disorder, i.e. disruption of proper blood flow.
Symptoms of the disease
Local symptoms include severe pain in the lumbar region
Most often, polycystic kidney disease is completely asymptomatic, and the disease is detected at autopsy. However, experts divide the symptoms of polycystic disease into local and general. Local symptoms include:
- severe pain in the lumbar region;
- the appearance of a urinary disorder;
- periodic and sharp pain radiating to the genitals.
Common symptoms of polycystic pathology include:
- fatigue, malaise, weakness;
- thirst, dry mouth;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- increase in body temperature.
During palpation of the abdominal cavity, enlarged and lumpy kidneys are felt, proteins, red blood cells, and white blood cells are detected in the urine; the functionality and performance of the kidneys is significantly reduced. The further morphological state of the pathology is reduced to the formation of chronic renal failure, thirst, anemia and azotemia. Arterial hypertension increases due to renal ischemia, organ performance decreases, acute chronic pyelonephritis is formed, and as a result, organ suppuration and calculi are formed.
Diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease
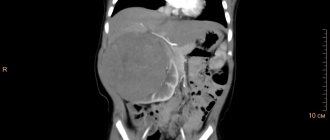
In modern medicine, ultrasound examination is prescribed to diagnose and detect polycystic kidney disease.
A popular way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
In modern medicine, for the diagnosis and detection of polycystic kidney disease, the following is prescribed:
complete hereditary examination for the presence of renal pathologies;
- ultrasound examination during pregnancy in any trimester, however, the 30th week of fetal development is considered an important examination;
- Conducting ultrasound examinations for children aged one year;
- conducting radiopaque secretory urography, computed tomography, PET and MRI.
If it is impossible to detect pathology, retrograde pyelography is performed. In case of renal failure with chronic nephritis, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Treatment of polycystic pathology
A diet for polycystic kidney disease prevents tissue depletion and the formation of kidney failure. Therefore, doctors often recommend that their patients follow a diet and monitor their diet. Namely, limiting the consumption of unwanted foods helps to inhibit the development of other pathologies of the renal system.
Prohibited products:
The main prohibited product for this disease is table salt.
- salt;
- fatty and fried foods;
- horseradish, garlic and onion;
- canning products;
- seasonings and spices;
- pickles and pickled foods.
Watch the amount of carbohydrates and fats you consume. Doctors recommend consuming carbohydrates in the form of corn, oatmeal and barley porridge.
How is an anomaly diagnosed?
As a rule, due to the lack of symptoms, the diagnosis of humpback kidney is not carried out specifically. The anomaly is discovered completely by accident on an ultrasound. The main task of the specialist is to accurately distinguish a physiological feature from a neoplasm. The main difference between cancer and anomaly will be the intact structure of the body of the kidney itself. But when diagnosing an anomaly, additional studies are carried out to exclude the possibility of a kidney tumor.
During the study, a computed tomography scan is performed using a contrast agent to study in detail the shape and structure of the kidney. If disturbances in the blood supply to the kidney are detected, examinations of the vessels of the urinary system are prescribed. During diagnosis, X-rays, radioisotope scanning, urography and arteriography are used. It happens that complex instrumental diagnostics cannot give an accurate result, then, as a last resort, specialists resort to radial diagnostics and prescribe a kidney biopsy.
Diagnostics
Basic methods for diagnosing the disease:
- blood test - cannot reliably guarantee cancer, but it shows the real condition of the body and indicates whether there are problems with the functioning of the main organs, as well as whether anemia is present;
- urine analysis - thanks to a chemical test, the doctor has information about the level of red blood cells, determines the qualitative state of the urine for the presence of uncharacteristic impurities in it;
- MRI with contrast - provides a complete image of a cross-section of the human body in the right places. In this case, a contrast agent is injected through a catheter so that the size and location of the tumor can be diagnosed as accurately as possible;
- cavography - diagnoses not only cancer, but also reveals the possible presence of metastases through the use of isotropes;
- aortography is a type of x-ray that allows you to examine the kidney from the inside, the state of the circulatory system that fills it, as well as look into the inner layers of the pathology;
- selective renal arteriography - done with a contrast component, assesses the degree of mobility of the organ and the condition of its blood arteries;
- puncture biopsy is justified in controversial situations when there is disagreement about the final “verdict” about the nature of the origin of the anomaly.
How to detect bone cancer: symptoms and manifestations of the disease. This article examines the causes of acute leukemia.
In the comments https://stoprak.info/vidy/molochnoj-zhelezy/kak-provoditsya-krasnaya-ximioterapiya-brudy.html reviews about chemotherapy for breast cancer.
Treatment
The tumor is amputated by nephrectomy. Type of operation – open – using a laparoscope. A good result if the compaction is not too large (up to 4 - 5 cm). In this case, we can talk about complete recovery.
Oncologists argue that the only solution to this problem that can guarantee at least some confidence that further metastasis will not occur is surgical intervention.
How the operation is done is shown in this video:
Unfortunately, radiation and chemotherapy rehabilitation regimens have not proven to be an effective treatment option. They are sometimes used in combination - before surgery, or in the last stages of the disease, when the patient is no longer operable, and the main task of doctors is to somewhat alleviate his physical condition and improve the quality of life.
Their low effectiveness is explained by the too aggressive nature of tumor development and its rapid transition from stage to stage.
Kidney cancer, how long do patients live and what is the prognosis of the disease?
The prognosis for kidney cancer, as with any cancer, depends on the stage of the malignant process and the effectiveness of treatment. The criterion for the effectiveness of therapy for kidney cancer is five-year survival.
Kidney cancer, five-year survival prognosis is:
- at stage 1 about 90%;
- at stage 2 – 65-70%;
- at stage 3 – about 50%;
- The five-year survival rate for stage 4 kidney cancer is 10%.
Wilms tumor has a good prognosis; in the absence of metastasis, cure is possible in 70-90% of all cases.
If papillary kidney cancer is present and it is diagnosed at stage 1 of the disease, with the correct selection of treatment, the prognosis is quite optimistic.
In all cases, the following matters: age, lifestyle, bad habits of patients, nutrition, methods of treatment, including alternative methods of treatment. The prognosis also depends on how the patient’s body has withstood and accepted the treatment. If you undergo rehabilitation and clinical studies, then in case of relapses it is possible to undergo new, more effective types of treatment. Five-year survival rate can be 65-75%.
Conclusions! Using modern diagnostic methods, international WHO, TNM and clinical classifications, dividing tumors into groups and types, it is possible to accurately determine the type of cancer, reduce diagnostic and tactical errors and prescribe the correct treatment. Consequently, the prognosis improves and the life expectancy and complete recovery of patients from the disease increases.