Kidney stone disease is one of the urological pathologies characterized by the formation of stones in the calyces and pelvis of the kidney.
It is a form of urolithiasis. The basis of the disease is impaired metabolism and difficulty urinating as a result of malfunction of the paired organ.
Where do kidney stones come from?
There is no exact answer to the question: “Where do kidney stones come from?” We can only name the contributing factors that cause this disease. These include:
- metabolic disorder;
- urological infections;
- dysfunction of urine flow;
- increased acidity of urine (with urate stone);
- excessive intake and formation of oxalates;
- increased function of the parathyroid gland;
- hypervitaminosis A and D;
- diseases of the liver, stomach and intestines (gastritis, colitis, hepatitis);
- para- and hemiparesis;
- diseases of the joints and musculoskeletal system;
- numerous bone fractures;
- heat, which increases the concentration of urine;
- water too rich in minerals;
- heredity.
Kidney stone disease
With kidney stones, the metabolism in the body is disrupted.
May be characterized by infectious processes, including those associated with urinary tract infections. Nervous and endocrine regulation is disrupted. Often there is a disorder of emptying or an abnormality of the urinary system. Stones in the ureter are formed from urinary salts, mainly in the renal pelvis. Salts precipitate and promote inflammatory processes in the pelvis.
Relapses often occur with kidney stones. Relapses are due to the fact that the pathological process is extensive, affecting not only the kidneys, but also the bladder. The disease is widespread.
Kidney stone disease is the formation of stones in the kidney system. The disease is common due to the presence of unfavorable environmental factors. Although the etiology of the disease is not fully understood.
It should also be noted that the stones have different origins. Including a certain classification of stones. In first place, inorganic compounds. In second place are magnesium compounds.
The third place is occupied by uric acid derivatives. Sometimes patients are diagnosed with polymineral stones. Relapses are usually caused by a urinary infection. This is due to the vital activity of infectious agents; their waste products are excreted in urine, which means its composition and characteristics are disrupted.
go to top
The main causes of kidney stones include external and internal factors. Chronic pathologies also play a role in the etiology of the disease. As a result, the causes of the disease are divided into the following groups:
- Lifestyle;
- nutrition;
- vitamin deficiency;
- harmful working conditions;
- medications
The lifestyle is most often passive, that is, without the necessary physical activity. A person leads a sedentary lifestyle, including poor nutrition. Nutrition must be complete and must include vitamins and microelements.
Harmful working conditions also play an important role. Kidney stones are often a consequence of unfavorable working conditions. Some medications affect pathological changes in the kidneys and stones form. Mainly ascorbic acid and antibiotics.
The causes of kidney stones can be an abnormal development of the urinary system. The following diseases also play a role:
- poisoning;
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- infectious diseases.
go to top
The clinical picture of kidney stones is determined by the course of the pathological process. The pathological process may have a protracted course. There is also a chronic course, which is accompanied by periods of exacerbation and remission.
Stones can be localized in the right or left kidney. In some cases, a bilateral process is observed, that is, stones are located in both the right and left kidneys. The main symptoms of the disease are:
- sharp and dull pain;
- hematuria;
- purulent phenomena.
Sometimes kidney stones are asymptomatic. Renal colic is the main symptom of the disease. The symptoms of the disease also include the following signs:
- severe pain in the lower back;
- lower abdominal pain;
- patient's anxiety
Sometimes kidney stones are characterized by frequent urination. This includes vomiting and nausea. There is also an intestinal cut. Positive Pasternatsky syndrome occurs.
A complication of the disease is acute renal failure. In the presence of large stones, severe symptoms occur. However, in the initial period there are no symptoms. Then the patient complains of fatigue and weakness.
Read more on the website: bolit.info
This site is for informational purposes only!
go to top
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of kidney stones is based on medical history. Taking an anamnesis involves finding out the necessary information. Including possible causes and a history of underlying disease.
Clinical studies can determine inflammatory responses. Urine tests also show hematuria and pus in the urine. A clear diagnostic method is the presence of stones in the urine.
X-ray examination methods are widely used. A clear picture of the disease is revealed by survey urography. However, not all stones are detected by radiography.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine the condition of the organs of the renal system. Ultrasound diagnostics of the bladder is also very relevant. An additional method for diagnosing kidney stones is excretory urography.
Excretory urography allows you to assess the functional characteristics of the kidneys. And also determine the location of the stones. In the photographs, the stones appear as a filling defect.
Diagnosis is also based on consultation with specialists. In this case, it is a nephrologist and urologist. These specialists can not only determine the diagnosis, but also prescribe appropriate treatment.
go to top
Prevention
How can you prevent kidney stones? Prevention should be aimed at a healthy lifestyle and active physical exercise. Also for good nutrition. Prevention of this disease includes:
- elimination of infections;
- treatment of gastrointestinal tract pathologies;
- prevention of poisoning.
Eliminating the infectious agent not only reduces the risk of developing this disease, but also prevents complications. Infection most often leads to relapses. Relapses tend to recur. Which is kidney stone disease.
Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract must be treated in a timely manner. This is due to the fact that this pathology progresses quite quickly. Banal gastritis leads to stomach ulcers. Poisoning causes intoxication of the body.
Due to the resulting intoxication, metabolism is disrupted. As a result of metabolic disorders, irreversible processes occur. Stones and excrement form in the urine.
It is also necessary to work in favorable conditions. Hard work in hazardous work contributes to the development of various diseases. Including the development of kidney stones.
It is also important to consume the required amount of vitamins. This includes avoiding the use of medications if there are kidney pathologies. If there are abnormalities of the urinary system, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
It is necessary to treat underlying diseases only under medical supervision. Self-medication is excluded! At the initial stage of the disease, clinical examination is important.
go to top
Treatment
In the treatment of kidney stones, conservative and surgical methods are used. It should be remembered that treatment is prescribed directly by a urologist. Usually the stones are removed surgically. However, in the presence of uric acid derivatives, conservative treatment methods are used.
The conservative technique uses citrates. They allow you to dissolve stones. And thereby improve the patient’s condition.
Patients with kidney stones are advised to follow certain measures. These measures include measuring water balance. Also, the methodology that must be followed includes:
- diet;
- herbal treatment;
- drug therapy;
- physical training.
It is also often necessary to resort to physiotherapeutic procedures. The method of sanatorium-resort treatment is also widely used. Typically, surgical intervention is gentle, but in the presence of a severe process, kidney surgery is used to remove stones.
The diet should be selected individually. However, there are principles of diet therapy for patients. They include the following provisions:
- varied food;
- taking a certain amount of fluid;
- exclusion of some products.
There is another treatment method. But it applies to people who develop small crystals instead of stones. In this case, the following actions are taken:
- one liter of liquid on an empty stomach;
- usually seven to ten times a day.
A liter of liquid includes mineral water, tea with milk, and a decoction of dried fruits. This liquid is the most effective. Promotes the removal and dissolution of crystals.
go to top
In adults
Kidney stone disease in adults is observed in different age categories. Mostly in people between twenty and forty years old. Most often, stones form in the kidneys of middle-aged and young people.
It should also be noted that men get sick more often than women. But if women get sick, the disease is quite severe. Stones in women usually occupy the entire kidney cavity.
Large stones in women cause relapses. But at the initial stage the disease occurs without symptoms. However, nonspecific complaints are significant. Women make the main complaints about certain conditions:
- fatigue;
- weakness;
- lower back pain.
These conditions lead to the development of pyelonephritis. The risk of developing kidney failure begins to increase. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly begin treatment for symptoms that predispose to complications.
In adults, kidney stones develop quite severely. Performance decreases and general condition worsens. What are the main symptoms of this disease? The main symptoms of the disease include:
- pain;
- increased urination;
- vomit;
- nausea.
If the patient is elderly, stones usually affect the bladder. The bladder produces excrement of various origins. However, the elderly age of the patient in the presence of an infectious agent aggravates the disease process.
go to top
In children
Kidney stones in children are usually a recurrent disease. This is due not only to the localization of the pathological process, but also to the condition of the child. Girls and boys are equally susceptible to the disease.
Stones in children are also localized in the bladder. The disease is quite common in children. This is due to metabolic disorders. Especially at the age of hormonal changes. Then, over time, the disease worsens.
The etiology of the disease in children is associated with various diseases. Hereditary pathology and developmental anomalies also play a role. There is also a high probability of an infectious process. Infection in combination with kidney stones is a more dangerous symptom.
What are the main symptoms of the development of the disease in children? The main symptoms of the development of the disease in children include:
- urinary disturbance;
- lower back pain;
- fever;
- dyspepsia.
It should also be noted that excrement in children is quite frequent than in adults. However, renal colic is practically not observed in children. Unlike adults.
Very young children also have no symptoms of renal colic. But the following clinical signs are observed:
- anxiety;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- fever;
- intoxication.
Immediate diagnosis is required for these conditions. Laboratory research is very relevant. After diagnosis, it is necessary to apply a treatment method.
go to top
Forecast
In case of kidney stones, the prognosis depends on many circumstances. Including the age of the patient. And also from possible causes of the disease.
The prognosis is worst if the disease is complicated by infections. Often a more severe complication may occur. There is a high probability of a recurrent course of the disease.
If a relapse occurs, the disease may develop into a chronic stage. Accordingly, the prognosis is unfavorable. Relapses should be prevented!
go to top
Exodus
The outcome of the disease may be kidney failure. But in order to prevent its development, it is necessary to adhere to therapeutic therapy. This helps promote favorable outcomes.
In addition to the conservative technique, it is necessary to apply surgical intervention. It depends on the type of stones. Larger stones lead to poorer outcomes.
Surgery helps to improve the healing process. However, treatment must be comprehensive. This contributes to the development of favorable outcomes.
go to top
Lifespan
The earlier treatment is started, the more options there are to exclude the chronic stage of the disease. This also helps to increase life expectancy. In addition, its quality improves.
If the disease develops in women, the size of the stone will affect life expectancy. If the size is large, it is necessary to urgently resort to surgical techniques. This improves the picture of the disease.
But the operation should be prescribed according to indications. Otherwise, adverse consequences may occur. Be treated under medical supervision!
Source: https://bolit.info/pochechnokamennaya-bolezn.html
How are stones formed?
Kidney stones arise as a result of certain physical and chemical processes. There is a huge amount of salts in the urine, which one day stop dissolving and begin to linger in the kidneys. At first these are tiny grains of sand, but gradually, grouping together, they form larger formations - stones.
The basis of a renal calculus can be: blood, bacteria, fibrin, or a foreign body. The further process of salt sedimentation will depend on their concentration.
What it is?
Kidney stone disease is the formation of stones in the kidney system. The disease is common due to the presence of unfavorable environmental factors. Although the etiology of the disease is not fully understood.
It should also be noted that the stones have different origins. Including a certain classification of stones. In first place, inorganic compounds. In second place are magnesium compounds.
The third place is occupied by uric acid derivatives. Sometimes patients are diagnosed with polymineral stones. Relapses are usually caused by a urinary infection. This is due to the vital activity of infectious agents; their waste products are excreted in urine, which means its composition and characteristics are disrupted.
go to top
Signs of the disease
Kidney stone disease has the following symptoms:
- periodic pain (renal colic) in the lumbar or abdominal area;
- increased pain with physical activity;
- with severe pain - nausea and vomiting;
- spontaneous passage of stones;
- urination with pain;
- bloating.
The disease begins to manifest itself quite clearly. The patient experiences attacks of renal colic. Sometimes the pain is so severe that the person is prescribed a strong pain reliever. On average, an attack lasts no more than a day.
Renal colic is explained by strangulation of the formed calculus in the ureter. This leads to the fact that urine stops passing and intrarenal pressure increases. Anuria often occurs, which is reflexive in nature. The illness may be accompanied by fever.
When examining a patient, a doctor may identify the following symptoms:
- feeling of pain when palpating in the kidney area;
- on palpation, pain due to movement of the ureter;
- lower back pain.
Urinalysis during an attack indicates fresh white and red blood cells, and protein levels are also elevated. Possible increase in ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate). The passage of kidney stones usually begins immediately after an attack of colic.
The disease is dangerous because as a result of damage to the mucous membrane of the urinary tract, hematuria occurs (the presence of blood in the urine). This is due to stones with sharp edges.
Only in 13% of cases the process of passing kidney stones is asymptomatic. Moreover, without an obvious process of inflammation and pyelonephritis.
Causes
Kidney deposits can form at different ages.
Kidney deposits can form at different ages. 70-75% of cases of the disease occur in patients aged 20-40 years. Moreover, men get sick more often. Stones are usually deposited in the right kidney, less often in the left, and only in 10% of cases do they appear in two kidneys at once.
Half of the cases are single stones. But sometimes there are a hundred or more of them. The size of the calculus can be from a grain of sand and reach up to 12 cm and a weight of 2 kg. The largest are coral-shaped formations.
Kidney stones can occur for reasons that can be divided into two groups:
- Climate, the patient's lifestyle, food and water belong to the group of external factors.
- Internal factors include the structure of the urinary tract, various injuries, metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance, lack of vitamins, and a long-term sedentary lifestyle.
The causes of urolithiasis are as follows:
- It turns out that even the place of residence is of considerable importance for the development of ICD. Thus, people living in the Arctic and in the south are more susceptible to this disease. It's all about the concentration of vitamin D, which is involved in phosphorus-potassium metabolism. There is a lot of it in yolk, butter and liver. It is produced by the body under the influence of sunlight. Too much or too little sun can lead to too little or too much sun, which can cause illness.
- Climate. In a constantly hot climate, the body loses a lot of fluid, which is why the urine is oversaturated with salts, which can be deposited in the kidneys.
- Regular consumption of hard drinking water can also provoke the deposition of calcium salts in this organ.
- Diet. Dry food, irregular meals, and monotonous food increase the concentration of salts in the body. Excess meat and fatty foods increase the amount of uric acid, which contributes to the deposition of urate. Dairy and plant foods contribute to the formation of phosphates, since they cause the accumulation of phosphate alkaline salts in the body. Spicy dishes, marinades, spices, and pickles lead to the formation of oxalates.
- CNS disorders cause metabolic disorders, which leads to changes in water-salt balance.
- Endocrine disorders, especially in the functioning of the parathyroid glands, contribute to the ingress of calcium phosphate salts into the urine. Malfunctions of the adrenal glands cause the accumulation of nitrogenous substances. Dysfunction of the sweat glands is also significant.
- A lack of colloids in the urine leads to the precipitation of salts.
- Sometimes the formation of stones is facilitated by diseases of the stomach, liver and intestines.
- A sedentary lifestyle, for example, staying in bed for a long time due to a serious injury.
- The acid-base level of urine is also important.
Course and prognosis
Kidney stone disease has a favorable prognosis. After the stone passes, in most cases the disease no longer reminds of itself.
Complications of nephrolithiasis (a synonym for the disease) are dangerous, which worsen the disease process, followed by transition to the chronic stage. Complications include: pyelonephritis, symptomatic hypertension, chronic kidney failure, hydropyelonephrosis.
The most dangerous condition is the formation of stones on both sides with the subsequent development of renal failure, which arose due to a parathyroid adenoma with signs of hyperparathyroidism.
Complications
Complications of kidney stones most often manifest themselves in the form of pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys.
Complications of kidney stones most often manifest in the form of pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys. Purulent pyelonephritis is especially dangerous. Sometimes there is a blockage of the urinary tract. As a rule, this situation requires urgent surgical intervention and, at a minimum, the installation of a catheter for the outflow of urine from the pelvis, ureter or bladder.
The following complications of this disease may also occur:
- Calculous pyonephrosis. In this case, purulent cavities appear in the kidney tissue.
- Acute renal failure.
- Calculous paranephritis. With this complication, pus accumulates in the tissue near the kidney.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on clinical data. In this case, there are the following signs of the disease:
- renal colic;
- deterioration of urine composition;
- pain radiating to neighboring organs and tissues;
- passing stones in urine;
- relevant X-ray and instrumental examination data.
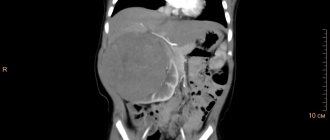
Computed tomography of the kidneys
If renal colic bothers the right side, the disease may resemble the symptoms of an attack of appendicitis or cholecystitis in the acute stage. The disease can also be confused with kidney infarction, which often occurs as a result of heart and vascular diseases. Renal colic, compared to renal infarction, is characterized by more intense pain. Therefore, it is important to correctly differentiate kidney stone disease and its symptoms.
Reliable information about existing kidney stones will be provided by the following diagnostic methods: radiography, tomography, pneumo-urography, pyelography, excretory urography. Sometimes isotope radiography and retrograde pyelography are used. Using diagnostic methods, you can obtain information about the location of the stone, the degree of dysfunction of the kidney and urinary tract. This is necessary to determine the correct method of treating kidney stones.
Surgical removal of stones
The operating method is lithotripsy. Involves removing stones using a shock wave. Various types of waves are used. This method is considered the most effective. A distinctive feature of wave lithotripsy is the absence of negative effects on the body. This method of surgery is performed remotely, with a mediocre effect on the affected area, through a catheter. The process of treatment and rehabilitation after surgery lasts three months. During this time, the stones should collapse and the pain should go away.
Complications after surgery are possible, but rare. This surgical method is considered safe. Possible negative consequences:
- Violation of heart contractions;
- increased blood pressure;
- stimulation of the nervous system;
- attacks of colic.
The pathology is treated with physiotherapy. It is effective with a healthy lifestyle; you need to perform simple physical exercises and follow a diet. This will lead to natural removal of stones.
How is the disease treated?
When renal stone colic is a concern and in case of severe pain, a 1 ml injection of Morphine solution with 1 ml of 0.1% Atropine solution is administered. A warm bath or heating pad is recommended for the lumbar region (if there is no inflammation or swelling). If the procedures do not give positive results and the colic is pronounced, novocaine anesthesia of the spermatic cord is used. The patient may need to have a catheter placed in the ureter.
Depending on what caused the stones, treatment of kidney stones is carried out as follows:
- if kidney stones are caused by a urinary infection, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs, sulfonamides, nitrofurans.
- if the cause is uric acid diathesis, reduce the intake of purine bases. You cannot eat fried meat, offal, or broths on meat.
- for urate stones, the patient is prescribed a diet of dairy and plant products.
- mineral water such as Truskavetskaya, Kislovodskaya and Zheleznovodskaya is prescribed for phosphate stones.
- in case of oxaluria, the diet includes foods that remove oxalic acid salts and increase the alkaline composition of urine. The prescribed water to drink is Essentuki, Pyatigorsk and Zheleznovodsk.
- for uraturia, alkaline waters of Essentuki, Borjomi, Truskavets are recommended.
Kidney stone disease also requires spa treatment, but only after removal of the stone. Also, therapeutic rest is recommended if the anatomical features of the urinary tract predispose the spontaneous passage of stones.
Surgery to remove kidney stones is performed if:
- attacks of colic are repeated too often;
- if the disease is accompanied by pyelonephritis of any stage;
- when the likelihood of the stone passing out on its own is low;
- for large stones;
- in case of a dangerous stone structure;
- with kidney blockage;
- when stones do not move through the ureter for three months;
- if there is only one kidney;
- if the disease is complicated by hematuria that threatens the patient’s life.
Pathogenesis
Stone formation requires the following reasons:
- high salt content;
- the presence of large particles - colloids;
- acidity must correspond to the crystallization point;
- the outflow of urine is obstructed (urostasis).
Depending on the medium in which the initial change occurs (salt or colloid), the center of the future stone will be either a salt crystal or a compound (conglomerate) of organic substances.
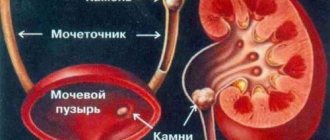
The growth of stones occurs as an alternation of processes of organic sedimentation and salt concentration. Stones can move from their original location. So, having originated in the kidneys, they are then found in the ureter. Often stones form in the kidney tubules in the form of plaques.
Stones in the kidneys and ureter
In addition, stone formation is also observed in the renal papillae. This occurs as a result of the movement of nodules (special microparticles) in the body of the kidney as a result of impaired lymphatic drainage (with pyelonephritis or excess calcium salts). The particles migrate towards the papillae, linger in them and become the center of stone formation.
Stones disrupt the organic matter of the kidneys, constantly irritating the tissues of the calyces and pelvis and facilitating infection to penetrate the parenchyma.
Prevention
The disease involves the main preventive measure - the impact on eliminating metabolic disorders. As part of preventive measures, infections or inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract that predispose to the formation of stones should also be promptly identified and treated.
Physical activity plays a big role. You should move as much as possible to reduce the risk of developing the disease. It is also recommended to avoid sleep deprivation and oversleeping.
The amount of fluid consumed should not be less than one and a half liters per day. Adequate and balanced nutrition and diet play an important role. You should not abuse alcohol and meat products. It is advisable to avoid drinking coffee and chocolate.
Treatment of the disease using traditional methods
Treatment is to get rid of stones and prevent recurrence in the kidneys. Therapy consists of a complex of effects on the body. Treatment with conservative methods helps:
- Eliminate the main symptom – acute pain syndrome;
- get rid of stones;
- cure infection;
- prevent the re-development of pathology.
Drug treatment and a diet that involves eliminating foods containing purine can help get rid of stones. You need to eat plant foods. Sanatorium treatment is prescribed.
Kidney stone disease: Causes of development, Symptoms, how to Treat?
Kidney stones are hard crystalline structures that form in the kidneys. Kidney stones are accompanied by severe pain in the lower back or side. It usually moves gradually towards the abdomen, scrotum and genitals as the stone moves through the urinary tract.
Why are kidneys needed?
Healthy kidneys remove waste from the blood, which leaves the body along with the urine produced by the kidneys. They are located approximately in the middle of the back under the ribs.
What is a kidney stone?
Kidney stones are hard crystalline structures that form in the kidneys. In size they can range from very tiny to much more massive. Stones are made up of waste products found in urine.
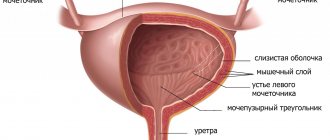
However, they can either remain inside the kidneys or leave the body through the urinary tract (consisting of the ureter, bladder and urethra).
If the size of the stone is too large, it can become lodged in the kidney or urinary tract, causing very severe pain.
How do I understand that I have kidney stones?
Kidney stones are accompanied by severe pain in the lower back or side. It usually moves gradually towards the abdomen, scrotum and genitals as the stone moves through the urinary tract. Other symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Fever
- Increased urge to urinate
What are the causes of the development of kidney stones?
There are four types of kidney stones:
- Calcium stones:
These are the most common type of kidney stones. Calcium, not required by bones and muscles, settles in the kidneys. They usually manage to get rid of the excess calcium in their urine, but sometimes small pieces of calcium still remain in the kidneys and accumulate over time. - Struvite stones:
Struvite stones are more common in women. They usually form as a result of chronic urinary tract infection. Typically, struvite stones are composed of ammonia. - Urate stones:
Urate stones form due to excess uric acid in the urine. You are at risk if you regularly eat high-protein foods or if you have had chemotherapy. - Cystine stones:
Cystine stones are quite rare. The disease that causes the deposition of this type of kidney stones is transmitted genetically and is called cystinuria.
Risk factors
- Not drinking enough fluids, especially water
- Cases of kidney stones among close relatives
- A diet rich in protein and sodium but low in fiber
- Being male
- Age from 20 to 70 years
- Prolonged immobility or bedriddenness
- Taking certain medications.
What needs to be done to prevent the recurrence of kidney stones?
Most people who have had kidney stones have a 50% chance of experiencing a recurrence within the next 10 years. However, there are certain measures to reduce this risk:
- Drink at least 2 liters of fluid (clean water is best) per day. Your doctor may measure your diuresis (the process of making and releasing urine) to make sure you are drinking enough fluids.
- Don't eat more than 1,500 mg (about 1 teaspoon) of salt per day. This amount includes the salt contained in semi-finished products. Check nutrition labels on foods and keep track of how much salt (sodium) is in the food you eat.
- Try not to eat more than 2 servings of meat per day. Each serving should not exceed 170-220 mg.
If you have repeatedly had kidney stones, your doctor may refer you to see a specialist to determine the exact cause of its development. Some people need to take medications to prevent kidney stones from recurring.
How is kidney stone disease treated?
When the stones are small, they can often be removed naturally through urine. To relieve the pain that accompanies this process, your doctor may prescribe medications.
If the stone is too large or has caused an infection, the doctor will use a special shock wave device to split it into smaller fragments. This procedure is called extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy.
A urologist (urinary tract specialist) may also insert a thin instrument through the urethra and into the bladder to look for a stone. Once discovered, there are 2 options: pull it out or break it into small pieces. With any choice, you will first be given a local anesthetic drug.
Finally, another treatment method is surgery. Moreover, in some cases it is the only way to cure kidney stones.
Questions to ask your doctor
- Which treatment option is optimal in my case?
- What pain medications should I take?
- Will I need surgery?
- Will the stones come out on their own?
- Do I need to change my diet?
- Do I need to make any lifestyle changes?
- What is the likelihood that I will encounter kidney stones again in the future?
- Are my children at risk?
- In what cases should you seek help?
- Should I call an ambulance if the pain is very severe?
Loading…
Source: https://mojdoktor.pro/pochechnokamennaja-bolezn/