The areas of the kidney through which urine enters the renal cups are usually called pyramids because of their shape. They, slightly rising above the calyxes, are always surrounded by urine. During the study, the reflected ultrasound wave is transformed using a special program into a black and white image, which is then displayed on the screen. Different media reflect the signal differently. Dense structures reflect the wave better. If the kidney is healthy, the monitor will display a dark image created by voids and cavities filled with urine. The pyramids and other dense parts of the organ in the image will have different shades.
With pathologies, the papillae of the pyramids become denser and may become covered with salt crystals or become deformed. The echogenicity of the kidney increases. Light spots will appear on the screen and the contrast will increase. This phenomenon is called protruding pyramid syndrome.
Main causes of hyperechogenicity
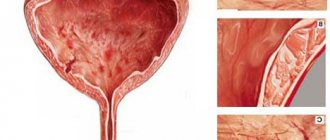
Hyperechogenicity of the kidneys occurs when these paired organs, under the influence of any reason, change their shape, structure or size. This usually occurs when metabolic processes are disrupted, injuries or uncontrolled tissue growth in certain areas. Formations that cause super-strong reflection most often occur in the parenchyma and renal pyramids and can appear on the screen as white dots and spots of various sizes (see photo).
There are many reasons for hyperechogenicity. But most often it is caused by the following pathologies:
- salt crystals (sand) and stones;
- multiple cysts;
- inflammatory purulent processes;
- carbuncles and hematomas after bruises;
- fatty degeneration of pyramids;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
Sharp outlines and white spots on an ultrasound may indicate more than just kidney disease. Sometimes the cause may be underweight.
What is perimedullary kidney ring?
Many different environmental factors in which humanity lives provoke the occurrence of metabolic changes in the body. As a result of such disorders, new compounds are formed, which accumulate over time in certain organs and lead to the development of various diseases.
Nephrocalcinosis of the kidneys - what is it?
Nephrocalcinosis is a pathological inflammatory process that is characterized by diffuse precipitation of calcium phosphate salts on the walls of the renal tubules or in their parenchyma itself.
This disease often develops as a result of a disturbance in calcium metabolism in the human body for some reason. Calcium salts crystallize and are deposited in organ tissues, mainly in kidney tissue, and sclerosis (scarring) develops. Nephrocalcinosis in almost all variants of development leads to renal failure (chronic).
Types of pathogenetic aspects of disease development
There are two types of nephrocalcinosis, which are distinguished according to etiological factors:
- With the development of sclerosis and deposition of calcium elements on previously unchanged renal parenchyma, we can speak of a primary form of nephrocalcinosis;
- In the secondary form of the disease, the sediment is fixed on the scarred tissues of the kidney. This type of nephrocalcinosis begins simultaneously both from the cortical part and from the tubular epithelium.
The disease is classified according to the location of calcifications in the kidney:
- Cortical nephrocalcinosis (calcium deposits are formed mainly in the cortical layer of the kidney);
- Medullary (calcium precipitates in areas of the renal pyramids).
The formation of calcium phosphate and its fixation in the kidneys is caused by hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria (increased calcium concentration in the blood and urine). Due to the increased load, the kidneys cannot cope with their basic functions; sediment is fixed inside the epithelial cells of the renal tubules.
Then dystrophic changes in the epithelium occur, calcium salts pass into the interstitial part of the renal tissue or into the lumen of the tubules, clogging them (cylinders). In the parenchyma, metastatic foci of calcium fixation provoke activation of the immune system, which leads to the replacement of normal kidney tissue with connective tissue.
Inflammatory changes occur due to blockage of the kidney tubules and disruption of the normal passage of urine. Pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis of the kidney often occur as a complication.
Deposition of calcium salts in the kidney Signs and symptoms
Nephrosclerosis and deposition of calcium salts in the renal parenchyma can have many different clinical manifestations.
First of all, signs of calcium intoxication appear in the body:
- Nausea, bouts of vomiting;
- Weakness and malaise, feeling of thirst;
- Headaches and pain in the heart area;
- Heart rhythm disturbances, changes in the ECG (shortening of the period of heart contraction);
- Itching of the skin, dryness and signs of peeling;
- The joints are subject to deformation, painful sensations appear in them when moving;
- The motility of the intestines and stomach is disrupted, resulting in painful abdominal cramps and constipation.
- Emotional lability;
- Signs of hypertension may appear;
If the kidney tubules and their epithelial cells are affected, then pain occurs in the lumbar region, and pyelonephritis or hydronephrosis may develop.
In case of blockage of the urinary tract, clinical signs of urolithiasis appear.
Due to pathological calcification of the renal tubules, their sensitivity to the influence of antidiuretic hormone decreases, resulting in the following symptoms:
- Persistent decrease in urine osmotic pressure;
- Increased daily diuresis;
- Polydipsia (as a result of extreme thirst).
Treatment
The treating doctor, having fully studied all the results of the patient’s research, prescribes drug treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the root cause of the disease:
- In case of severe dehydration of the body and disturbance of the acid-base balance, it is necessary to carry out intravenous drip infusion of solutions (sodium or potassium citrate, potassium aspartate, sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium chloride).
- If hypercalcemia is not significant, treatment with folk remedies, which necessarily include diet, is acceptable.
- B vitamins are prescribed orally or in injection form.
- With the progression of renal failure or the development of a coma, hemodialysis is performed.
- For hypercalcemia, a solution of magnesium sulfate or sodium phosphate is administered intravenously.
- It is possible to prescribe hormonal medications (prednisolone or thyrocalcitonin).
- If signs of pyelonephritis appear, treatment appropriate to this disease.
Source: https://mybabic.com/info/perimedulljarnoe-kolco-pochki-chto-jeto/
Signs of protruding pyramid syndrome
The clinical manifestations of hyperechoic pyramid syndrome are similar to those of other kidney diseases:
- fatigue, weakness;
- change in urine color to dark brown;
- pain in the lumbar region of the back;
- heat;
- high blood pressure, which is very difficult to bring down (not always);
- nausea and vomiting;
- spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen and groin.
To achieve a complete picture of the condition of the kidneys, an ultrasound scan is required. A specialist can easily determine the presence of hyperechoic inclusions and examine the condition of the parenchyma against the background of prominent pyramids.
One of the types of pathologies of the renal pyramids is perimedullary ring syndrome. White ring-shaped spots are visible on the monitor screen during ultrasound examination. The disease occurs due to fibrous formations and calcification of the papillae of the pyramids and is a consequence of endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus and malfunction of the parathyroid glands), pyelonephritis and some other diseases. There are experts who consider the condition in question not to be a separate disease, but a stage in the development of protruding pyramid syndrome.
Nephrocalcinosis
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P R S T U V X C CH W E Y Z Nephrocalcinosis
is a disease that belongs to the group of calcifications. Calcinosis, also known as calcareous degeneration, is a form of pathology of calcium metabolism in the body: calcium salts precipitate from liquids (they were dissolved in liquids), depositing in the interstitial tissue and cells.
Nephrocalcinosis is a variant of metastatic calcification, in which calcium salts are diffusely deposited in the kidney tissue, which causes inflammatory-sclerotic changes and renal failure.
Types of nephrocalcinosis according to clinical manifestations:
With primary, no changes in the kidneys are observed, but with secondary, kidney pathology occurs along with the processes of precipitation of calcium salts. Nephrocalcinosis can occur, for example, with alkaline milk syndrome or Burnett's syndrome. It is likely to occur in children who are transferred from natural feeding to cow's milk with herbal supplements. Read more about the reasons below.
Among the causes of primary nephrocalcinosis are:
- conditions in which too much calcium enters the body (familial and idiopathic hypercalcemia of newborns, hypervitaminosis D, Burnett's syndrome, Lightwood-Fanconi syndrome, Addison's disease, sarcoidosis, excessive intravenous administration of calcium salts)
- conditions in which mobilization of calcium from bones occurs (tumors of bones and some organs, hyperparathyroidism, myeloma, metastases of tumors in the bones, post-castration and corticosteroid osteoporosis, postmenopausal osteoporosis, osteomyelitis, multiple bone fractures, Paget's disease, neuroplegia, immobilization, thyrotoxicosis)
- hypophosphatasia (impaired calcium binding in bones)
- oxalosis, cystinosis, calciphylaxis, in which normally unnecessary calcium is deposited in tissues
- tubulopathies and various diseases that occur with acidosis (chronic tubular acidosis of Buttler-Albright, transient tubular acidosis of Lightwood, oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe, glucose-phosphate aminoaciduria de Toni-Debreu-Fanconi, hyperchloremic acidosis, respiratory acidosis)
Secondary nephrocalcinosis: causes
Among the most likely reasons are:
- radiation nephrosclerosis
- ischemic cortical necrosis of the kidneys
- abuse of sulfonamides, thiazide diuretics, phenacetin, ethacrine diuretics, anthranil diuretics
- uncontrolled use of amphotericin
- mercury salt poisoning
Nephrocalcinosis can be caused by renal and extrarenal acid-base balance disorders. This is mainly metabolic and respiratory acidosis, in rare cases it is metabolic alkalosis. With these diseases, the level of calcium in the blood increases and its excretion in the urine increases. The degree of calciuria can be a maximum of 400-600 milligrams in 24 hours.
Pathogenesis of calcinosis
The matrix for calcium salts inside cells is lysosomes and mitochondria. Outside the cells, these are collagen and elastic fibers plus glycosaminoglycans of the main substance of the interstitial tissue. Calcium salts can be deposited in the form of grains, pockets of lime, which are distributed more or less in different cases. In areas with lime, bone tissue may form, and around it there will be inflammation and a fibrous capsule.
Local and general factors play a role in the pathogenesis of calcinosis. Therefore, forms of calcification, in addition to the criterion of the location of calcifications, are distinguished according to pathogenetic factors. Calcification can be metastatic, metabolic and dystrophic, which is also known as (petrification).
Pathogenesis of nephrocalcinosis
There is an abnormally large influx of calcium into the kidneys; it accumulates in the epithelial cells of the human kidneys. When too much intracellular calcium accumulates, cell degeneration occurs. The deposited calcium enters the interstitial space or the lumen of the tubules. During this process, cylinders are formed that block the tubules, causing their dilation and atrophy. Salt deposits in the interstitium cause a lymphoproliferative reaction, followed by nephrosclerosis.
With nephrocalcinosis, infection and stone formation occur, so this disease becomes the source of pyelonephritis and/or hydronephrosis. The pathogenesis of primary nephrocalcinosis in children and adults is characterized by the fact that the proximal part of the nephron is affected first, and the glomerulus and distal part are affected later. If nephrocalcinosis is secondary, then calcium is deposited simultaneously in the distal nephron.
With nephrocalcinosis there is usually an underlying disease. Therefore, two groups of symptoms appear at once, as well as concomitant hypercalcemia. Calcium toxicity causes the following symptoms:
- fatigue
- general weakness
- vomit
- nausea
- dry skin
- thirst
- constipation
- itching
- joint deformity
- joint pain
- mental instability
- keratoconjunctivitis
- seizures
- ataxia
- shortening of systole duration on the electrocardiogram
With kidney damage, when the transport of substances in the tubules is disrupted and their sensitivity to antidiuretic hormone is lost, the following occur:
- isosthenuria
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- attacks of renal colic are likely (during the passage of stones)
- pain in the lumbar region
Persistent changes in the urinary sediment are often observed; it contains a large number of bacteria, leukocytes, salt casts and red blood cells. Later, edema, proteinuria, and arterial hypertension are recorded. During this period, as a rule, symptomatic and laboratory signs of kidney failure appear.
Complications:
- Chronic renal failure
- Acute renal failure
- Obstructive uropathy
- Stones in the kidneys
Diagnosis of nephrocalcinosis at the stage of its appearance is based on information obtained using a puncture biopsy of the kidney. A method such as plain radiography is relevant only in severe cases, when the calcification of the renal pyramids is significantly pronounced.
To approximately determine the degree of calciuria, diagnosticians sometimes use the Sulkovich test. To clarify the cause of the disease, the patient’s urine and blood are examined for calcium and phosphorus content, and the activity of parathyroid hormone in the blood and alkaline phosphatase are determined. It is necessary to identify urinary excretion of hydroxyproline, acid-base balance, creatinine and phosphate clearance.
When diagnosing, nephrocalcinosis is distinguished from a spongy kidney, in which the cystic spaces are filled with condensate of calcium salts.
It is necessary to eliminate the cause of calcium metabolism disorders in the body as early as possible. For severe dehydration, infusions are made of a solution of sodium bicarbonate or sodium citrate, potassium citrate and aspartate for acidosis, and for alkalosis, infusions of sodium and ammonium chloride are given.
If hypercalcemia is moderate, the patient is advised to adhere to a diet with foods that contain little or no calcium. Vitamin B6 and infusion of magnesium sulfate solution are attributed. Treatment of acute hypercalcemia consists of infusion of a solution of magnesium sulfate, sodium phosphate, sodium EDTA. Doctors may prescribe the administration of thyrocalcitonin or prednisolone.
Treatment of progressive renal failure is mandatory with hemodialysis. It is important to adequately treat pyelonephritis, which causes progression of kidney failure. With secondary nephrocalcinosis, it is important to identify and treat the underlying disease, which is the etiological factor.
The prognosis with effective treatment at the onset of the disease is good. Patients with progressive nephrocalcinosis have an unfavorable prognosis, because in advanced cases uremia occurs, threatening the health and life of the patient.
- You should get the optimal amount of calcium (no more and no less) in your daily diet.
- You should not take calcium supplements without a doctor's prescription.
- It is important to treat kidney diseases in a timely manner.
- If suspicious symptoms or any health problems appear, you should immediately consult a general practitioner, family doctor or highly specialized doctor.
Is something bothering you? Do you want to know more detailed information about Nephrocalcinosis, its causes, symptoms, methods of treatment and prevention, the course of the disease and diet after it? Or do you need an inspection? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Eurolab clinic is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, study external signs and help you identify the disease by symptoms, advise you and provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home. The Eurolab clinic is open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic: Phone number of our clinic in Kyiv: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multi-channel). The clinic secretary will select a convenient day and time for you to visit the doctor. Our location and directions are listed here. Look in more detail about all the clinic’s services on its personal page.
If you have previously performed any tests, be sure to take their results to a consultation with your doctor. If the studies have not been performed, we will do everything necessary in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
You ? It is necessary to take a very careful approach to your overall health. People do not pay enough attention to the symptoms of diseases and do not realize that these diseases can be life-threatening. There are many diseases that at first do not manifest themselves in our body, but in the end it turns out that, unfortunately, it is too late to treat them. Each disease has its own specific signs, characteristic external manifestations - the so-called symptoms of the disease. Identifying symptoms is the first step in diagnosing diseases in general. To do this, you simply need to undergo examination by a doctor several times a year in order not only to prevent a terrible disease, but also to maintain a healthy spirit in the body and the organism as a whole.
If you want to see a doctor, use the online consultation section, perhaps you will find answers to your questions there and read tips on caring for yourself. If you are interested in reviews about clinics and doctors, try to find the information you need in the All Medicine section. Also register on the Eurolab medical portal to be constantly aware of the latest news and information updates on the site, which will be automatically sent to you by email.
If you are interested in any other types of diseases and groups of human diseases, or you have any other questions or suggestions, write to us, we will definitely try to help you.
www.eurolab.ua
Diagnostics
If the doctor suspects a patient has kidney disease, it is necessary to undergo not only an instrumental examination, but also a laboratory examination, including:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- stool examination.
Next, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound to clarify. This is usually enough to make a diagnosis. But in special cases, X-ray with contrast agent or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be suggested.
According to statistics, approximately 5% of newborns have kidney defects. The safety and information content of a method such as ultrasound make it indispensable when examining children.
All these procedures make it possible to assess the condition of the kidneys and pyramids in particular, and to identify the causes of the pathological process.
Calcifications in the kidneys: causes, symptoms and treatment of kidney calcification
The kidneys are a vulnerable organ that is susceptible to various infections, injuries and colds.
Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor their health and immediately engage in treatment if any problems arise.
The kidneys remove all excess substances from the body with urine, cleansing it of unfavorable compounds, so the stability of their work is important.
Experts recommend periodically undergoing routine tests and ultrasound examinations of the kidneys.
When metabolic processes are disturbed, calcium salts - calcifications - are deposited in the renal parenchyma.
These are the most common stone-like formations, which are areas of dead kidney tissue covered with a dense sediment of calcium salts.
They are formed in the zone of infiltration inflammation.
Often the development of calcifications is observed with concomitant diseases.
Kidney stones can be detected in adults and newborns (regardless of age and gender).
Salts are removed from the body along with urine. When metabolic processes are disturbed, unwanted substances accumulate in the kidneys.
components that turn into stones without proper treatment.
They can occur in the form of calcifications - deposits of calcium salts that are deposited on the walls of the kidneys, disrupting their functions.
There are a large number of factors that can provoke kidney calcification. This manifests itself when the urinary system is dysfunctional or inflamed.
Often formations are detected in women during pregnancy, in the placenta. The cause of their appearance may be intrauterine infections. Also, the presence of deposits may indicate impaired blood circulation in the placenta.
That is, stones signal unfavorable processes or poor-quality treatment of diseases.
If there is a massive accumulation of calcifications, you should undergo a high-quality diagnosis and consult a doctor to prescribe therapeutic measures.
Basically, calcifications develop due to inflammation of the kidneys - glomerulonephritis. Also, such a pathology can manifest itself after
untreated or recently suffered renal tuberculosis.
These types of deposits are formed due to tabulopathy, Graves' disease, cystinosis, vitamin D deficiency, renal failure, and pyelonephritis.
Kidney calcification is typical for athletes who consume large amounts of protein.
To treat kidney diseases, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method .
In this case, there are no symptoms of kidney damage, and the pathology can be identified as a result of a medical examination and ultrasound examination.
The condition characterizing the appearance of calcifications in the urine is called nephrocalcinosis, which can be primary or secondary:
- With impaired development and congenital diseases of the urinary organs, when the tubules are affected (tubulopathy), calcium loss occurs in the area of the papillae and the filtration processes deteriorate. This phenomenon is called primary nephrocalcinosis, it is characterized by calcium deposits in the proximal region of the nephron.
- Secondary nephrocalcinosis is formed during sclerosis, ischemic necrosis of renal tissue as a result of a tumor process or vascular pathology. Sometimes it occurs due to mercury poisoning or excess drugs (ethacrine diuretics and amphotericin B). In this case, calcium accumulates in all parts of the nephron.
The disease can be asymptomatic (if calcification does not reduce the filtration capacity of the kidneys and there is no obstruction of the ureter).
In other situations, symptoms of kidney calcification are:
- general malaise;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- constipation;
- itching;
- pain in the joints;
- rapid fatigue;
- dizziness;
- decreased appetite and sleep.
These symptoms are associated with blockage of the urinary tract by stones.
Also, small urates and mucus may be detected in the urine. A large formation can block the lumen in the ureter, causing severe pain and blood in the urine.
With a large number of calcifications and with an increase in their size, the following symptoms appear:
- copious and frequent urination;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- more yellow skin tone;
- swelling of the limbs;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth (due to the accumulation of urinary toxins in the blood);
- dehydration of the body, strong and unquenchable thirst;
- increased blood pressure;
- an increase in the amount of protein in the urine.
The doctor can determine the deposition of certain deposits in the kidneys using an x-ray examination.
Due to the fact that the consistency of the stone is similar to bone, a dense stone-like formation is clearly visible on the x-ray.
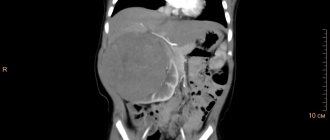
A more detailed study can be carried out using magnetic resonance or computed tomography. In this case, the exact parameters and location of the calcification are determined.
In the early stages, a puncture biopsy is considered an effective research method, since pathological changes cannot be seen using X-rays and ultrasound.
Kidney ultrasound is required mostly to identify concomitant kidney diseases.
The doctor also prescribes blood and urine tests to determine the concentration of this component. An examination of parathyroid hormone and vitamin D levels is required.
A biochemical study of blood and urine is carried out, which reveals the presence of phosphorus and calcium, acid-base balance, alkaline phosphatase activity and the excretion of hydroxyproline in urine.
MRI shows calcifications in the parenchyma of the right kidney
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the factors that provoke kidney calcification.
To normalize calcium volume, the following methods are used:
- sodium citrate and bicarbonate are introduced;
- for alkalosis, sodium chloride (ammonium) is prescribed (to change the balance to an alkaline environment); for acidosis, potassium aspartate (citrate) is administered (to change the balance to an acidic environment);
- B vitamins;
- diet with limited intake of calcium ions into the body.
Diet for kidney calcifications is of paramount importance.
To reduce the intake of calcium in the body, the consumption of sunflower seeds, mustard, and sesame is limited.
You should also not eat:
- hard and processed cheeses;
- halva;
- feta cheese;
- almond;
- condensed milk;
- yeast;
- wheat flour and bran;
- walnuts and nutmegs;
- dill;
- parsley;
- poppy;
- legumes;
- milk;
- garlic;
- oatmeal;
- sour cream;
- cottage cheese;
- black bread and cabbage.
The main nutrition corresponds to treatment table No. 7 (to reduce extractive components and accelerate the removal of toxins).
Salt is excluded, cilantro, cinnamon, citric acid, and cumin are added to the diet.
The following measures are also used to remove salts:
- the use of diuretics and herbs (but the volume of fluid does not increase);
- the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, since excreted salts cause pain, irritating the mucous membrane.
There are no basic principles for the prevention of calcinosis, since there are many reasons for the appearance of the pathological process.
But doctors advise timely and comprehensive treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases.
You need to monitor your diet by consuming high-quality foods and monitoring the composition of drinking water. You also need to lead an active lifestyle.
The recovery period depends on the stage of the pathological process.
Basically, in the initial stages, therapy becomes effective, but as renal failure develops and progresses, severe complications can develop with the appearance of uremia, which without surgery can lead to death.
Recommendations for the treatment of the syndrome
White pyramid syndrome in the kidneys is treated comprehensively. The main objectives are to relieve the patient of pain and eliminate the causes of the pathological condition.
Treatment includes medication, diet, physical therapy and homeopathic remedies. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
Note! Drug therapy should be carried out only as prescribed by a doctor (urologist or nephrologist) and under his strict supervision.
The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and antibacterial agents, analgesics, and herbal medicines.
Changes in nutrition play a big role - changing the regime and diet. Eliminate the following factors forever:
- fatty, smoked, fried foods;
- strong alcohol, coffee and black, steeply brewed tea;
- tomato juice and tomatoes;
- carbonated colored drinks;
- hot and spicy dishes.
More attention is paid to fresh fruits and vegetables, low-fat fish, and dairy products.
Considerable importance is given to the drinking regime. A person with kidney pathologies should drink a lot of clean, non-carbonated water per day. This amount is easy to calculate yourself: 30 ml for every kg of body weight. The volume of water you drink should be increased gradually, without creating a stressful situation for the body and preventing the appearance of edema.
Failure to comply with the doctor’s instructions threatens the patient with the disease becoming chronic and complications leading to death.
Therapy and prescriptions
To reduce the level of calcium in the blood, it is very important to exclude the following foods: sunflower oil, mustard, sesame seeds, various types of cheeses. You should not eat wheat flour, bran, almonds, dairy products, or oatmeal.
You should adhere to diet No. 7, which causes the removal of toxins from the body.
Among the folk methods for treating kidney diseases, strawberries and strawberry leaves in the form of a decoction can be noted. The decoction is taken orally for about 10 days daily.
Gooseberries, viburnum and sea buckthorn have a good effect (anti-inflammatory and diuretic effect).
A decoction prepared for warm sitz baths from birch and sage leaves improves blood circulation in the vascular bed of the kidneys and relieves inflammation.
Prohibited foods for kidney nephrocalcinosis Prognosis
With the progression of renal nephrocalcinosis, the prognosis for the future is unfavorable, since the development of renal failure and uremia is inevitable. With timely diagnosis of the disease and proper treatment, the prognosis for the development of the disease is more favorable. It is impossible to cure nephrocalcinosis with folk remedies, so it is very important to consult a doctor in time.
Treatment of hyperechoic pyramid syndrome is complex and is aimed at relieving pain syndromes and eliminating pathological preconditions.
Timely detection of illness involves drug therapy, during which a urologist or nephrologist prescribes antibiotics, analgesics, antispasmodics, as well as drugs that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects to the patient. A change in routine and diet is required, including proper rest, drinking plenty of fluids, eating low-fat foods, fresh vegetables and fruits.
When the disease passes into the chronic stage, physiotherapeutic procedures and homeopathic medicines are recommended.
A fruit and vegetable diet is required
Prevention of hyperechoic syndrome
The best prevention of the syndrome is considered to be timely detection of diseases of the genitourinary system with subsequent treatment under the guidance of a qualified specialist. And for this, each person must take care of himself and not skip preventive examinations.
It is important to remember that hypothermia of the legs and lower back, sexually transmitted infections, bad habits, improper and irregular nutrition, poor water quality can become a trigger for the occurrence of serious diseases of various organs, but primarily the kidneys.
( 1 ratings, average: 3.00 out of 5)
SEO analysis of the site pochkipro.ru
Oct 16, 2020 — Hyperechoic inclusions are formations or compactions that appear on organs.
Hyperechoic formation is detected using ultrasound diagnostics, and, most often, by accident. Jan 29, 2020 - Dilation of the renal pelvis in medical terminology is called pyeloectasia. This is a consequence of a pathology that causes obstructed urine flow.
E. coli in urine in normal quantities is useful and necessary for the human body. But exceeding the norm indicates an inflammatory process.
Problematic urination is a fairly common phenomenon that almost every person has experienced at least once in their life. Anyone who has experienced this will forever remember the torment that can be experienced. Most often, problematic urination is explained.
Enlargement of the renal pelvis in medical terminology is called pyeloectasia. This is a consequence of a pathology that causes obstructed urine flow.
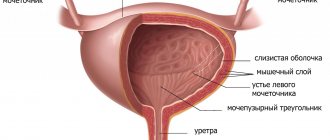
Nov 1, 2020 - Under normal conditions, the bladder can store and hold urine for two to five hours. In children, bladder capacity changes with age.
Constant headaches and dizziness are among the most common symptoms with which patients consult a doctor. Dizziness can be very severe, in which a person moves objects or himself. This is certainly an illusion, but it is what it is.
Hyperechoic inclusions are formations
Source
En: Questions for beginners (1
These are different syndromes. As with a complete examination of any other organ, it is necessary to examine the kidney in a second projection to study its cross section. It should be remembered that the lower parts of the kidney are located closer to the sensor, the upper parts are further away from it, i.e. the longitudinal axis goes from top to bottom and from the central axis of the body in the lateral direction.
The kidneys are a paired organ and perform several functions in the human body simultaneously. Therefore, during a diagnostic ultrasound examination, a mandatory examination of both kidneys is carried out. Dysfunction may begin on one side and affect the other.
Hyperechoic inclusions in the kidneys can be observed in either one or two. The location of inclusions is very diverse and depends on predisposing unfavorable factors. When this pathology is detected, treatment is carried out, and patients regularly undergo preventive examinations.