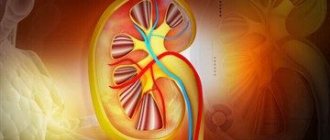
Anuria is a clinical symptom inherent in many diseases and pathological conditions. It consists in the absence of urine entering the bladder while maintaining adequate water load. Daily diuresis with anuria does not exceed 50 ml, i.e., less than 2 ml of urine enters the bladder per hour.
With anuria, daily diuresis does not exceed 50 ml
Anuria should be distinguished from acute urinary retention. In the latter case, the bladder becomes full of urine, and the lack of urination is due to an obstruction in its outflow. With anuria, the bladder is empty, since urine is either not excreted by the kidneys or does not enter it due to blockage of the ureters.
Anuria is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt and adequate treatment.
Urine standards
Anuria can be calculated by diuresis. This is a certain volume of urine excreted by the kidneys per day. Norms range from 800 to 1500 ml. Any deviations beyond the lower limit indicate violations. A healthy person goes to the toilet 4-8 times a day (1 time at night). Rare cases of urination (2-3 times and a complete absence of urge) indicate problems with the kidneys.
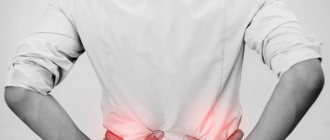
Typically, anuria causes pain, and passing urine does not relieve the condition. It should not be confused with oliguria, when the amount of fluid excreted does not exceed 400 ml per day. The danger of anuria is the rapid development of complications that can lead to death.
Folk remedies
When the doctor prescribes treatment, alternative medicine recipes can be used as a supplement to it:
- Nettle infusion - brew the herb in a thermos, leave for a couple of hours, cool, strain and consume internally.
- A decoction of birch branches and buds - the raw materials are poured with boiling water, infused and filtered. A glass of the prepared product must be drunk immediately.
- Hop cones - pour boiling water over them and leave for three hours. Take three times a day.
- Tincture of rose hips - pour alcohol or vodka over the component, leave for several days, strain. Take the medicine five drops, first dilute with water.
- Vegetable juice mixture – mix carrot, beet and cucumber juice. Drink a glass in the morning and evening.
- Oat straw - pour boiling water, boil over low heat for ten minutes, then strain and take throughout the day.
Kinds
There are several types of anuria. According to the nature of the manifestations and the cause of occurrence:
- False or excretory . An obstacle to the separation of urine is compression and disruption of the lumen due to a tumor or stones.
- True or secretory . It is characterized by a violation of the urinary process against the background of the development of acute renal failure (glomerulonephritis, tissue necrosis).
There are many more types of anuria due to their occurrence. This is the difficulty of diagnosing primary pathology:
- Arenal . In an adult, the pathology manifests itself after surgery on the kidney (resection or complete removal). In newborns, intrauterine pathologies are observed (absence of a kidney, fusion of the lumen of the canals).
- Prerenal . The progression of the disease begins after the blood flow in the organs is disrupted. Often the form develops along with heart failure if the patient exhibits pathological edema.
- Renal . The consequence of such anuria is impaired kidney function after infections, poisoning with external toxins or incorrect dosage of medications. The renal form is observed with large-scale loss of skin (burns).
- Postrenal . Appears from blockage of the urinary tract with kidney stones or against the background of tumor growth. This form of anuria has a more positive prognosis compared to all others if the formation is in the initial stage and there are no metastases.
What diseases can it be associated with?
Acute heart failure, thrombosis and embolism, tumors and neoplasms in the retroperitoneal space, shock conditions cause prerenal anuria.
The last stages of chronic glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis, nephroangiosclerosis, acute glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, polycystic disease and nephrotuberculosis, systemic collagenosis, vasculitis, sepsis, massive trauma and extensive burns underlie renal anuria.
Congenital pathologies, traumatic conditions and the consequences of surgical interventions cause arenal anuria.
Renal colic and developed iatrogenic conditions in some cases provoke reflex anuria.
Ureteral stones, tumors, scars and inflammatory processes in the retroperitoneal space, damage due to improperly performed operations are the root cause of excretory anuria.
Stages
In anuria, not only forms of development are observed, but also levels of progression. Between these stages, a short time may pass in just a few days or even hours; the patient is at risk of developing coma and further complications:
- Stage 1. The sensation of urination stops, and after 3 hours the patient may experience discomfort and specific symptoms depending on the cause.
- Stage 2. The development of this form can range from 15 to 72 hours. The patient develops signs of poisoning from breakdown products of protein origin - nausea, the smell of ammonia from the mouth or vomiting.
- Stage 3. Persistent changes occur in the central nervous system. Weakness, chronic fatigue, and a state of delirium appear. Movements become uncontrollable.
- Stage 4. The development of uremia begins with complete poisoning of the body. Renal and heart failure are clearly evident. The patient swells, experiences constant thirst, and has no appetite.
What is autism
Autism is a mental disorder characterized by disturbances in the emotional and communication spheres. It appears already in early childhood and remains with a person for life. People suffering from this disorder have difficulty with social interaction and demonstrate poor development of emotional intelligence.
Autistic people are withdrawn and immersed in their inner world. Communication with other people is difficult for them, since they are completely devoid of empathy. Such people are not able to understand the social meaning of what is happening. They do not perceive facial expressions, gestures, intonations of people, and cannot determine the emotions hidden behind external manifestations.
What do autistic people look like from the outside? You can recognize them by their distant gaze, as if directed inwards. Such people seem emotionless, like robots or dolls. When talking, autistic people avoid making eye contact with people.
The behavior of autistic people is often stereotypical, patterned, and mechanical. Their imagination and abstract thinking are limited. They can repeat the same phrases many times, ask the same type of questions and answer them themselves. Their life is subject to a routine, deviation from which is very painful. Any change is a big stress for autistic people.
The wonderful film “Rain Man” starring Dustin Hoffman and Tom Cruise is dedicated to this disease. If you want to see with your own eyes what autism looks like from the outside, I recommend watching this movie.
An individual with a mild form of autism is not much different from ordinary people.
Because of his autistic traits, he may come across as strange, aloof, and “out of this world.” Sometimes neither he himself nor those around him are aware of the diagnosis. Many famous people suffer from this disease, but this does not prevent them from living a full life.
Among them are singers Courtney Love and Susan Boyle, actress Daryl Hannah, director Stanley Kubrick.
Causes
The development of anuria is always associated with problems of the urinary system. Previously, the factor of anuria before diagnosis was considered to be blockage of the ureter by a stone, but for this they must be blocked on both sides. The main causes of anuria are:
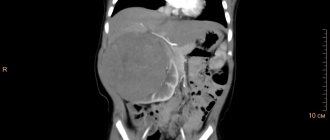
- Cancerous and benign tumors
The main reason for the lack of urine in the bladder is the development of a tumor. When the foreign tissue reaches a large size, it compresses both ureters, so the channels through which urine exits are blocked.
Bladder cancer is a malignant tumor. Pathology occurs to a greater extent in men. You can learn the causes, how cancer is diagnosed and what treatments are available at different stages.
- Heart failure
As blood pressure drops, the kidneys begin to filter urine less well. If in the renal vessel this indicator is below 80 mm, urine filtration stops.
- Intoxication
Anuria is often caused by withdrawal syndrome after alcohol poisoning; heavy metals (lead, mercury, cadmium) have a strong effect on the kidneys. If work involves constant contact with these elements, the accumulation of toxins will make itself known through the kidneys.
- Infections and inflammation
Anuria develops against the background of long-term chronic kidney diseases. The main pathologies are considered to be inflammation of the renal pelvis and glomeruli. The kidney tissue gradually becomes thinner, and the filtration function is impaired.
Features of the pathology
What is anuria, and is the absence of urine always a manifestation of this pathology? It is characterized by the absence of diuresis or its decrease to 30-50 milliliters per day. It differs from other disorders, such as acute urine retention, by the lack of fluid in the bladder.
Urine does not enter the bladder either because the ureters are blocked by formations (for example, stones, tumors), or because urine for some reason has ceased to be produced at all. The patient does not experience the urge to urinate.
With the mentioned urinary retention, the bladder, on the contrary, is filled with urine, and the patient suffers from urges, but urine is not excreted due to the presence of certain obstacles. It is often accompanied by severe pain in the urinary organs and pubic area.
Symptoms
Anuria has several manifestations, but patients report the same complaints. The final diagnosis is established only after laboratory and instrumental studies.
Signs:
- no urge to go to the toilet to urinate;
- severe renal failure;
- swelling throughout the body, often in the limbs;
- with kidney infections there is pain;
- thirst, lethargy, headaches, apathy;
- Deviations from the digestive, respiratory and nervous systems begin (convulsions, muscle spasms, cracked tongue, hiccups).
The final manifestation is renal coma and poisoning of the body. A critical state of anuria occurs on days 7-9.
Features in men and women
Anuria affects both male and female genders equally. The manifestations are no different, but in men the pain syndrome is more pronounced. When examining and palpating the groin, the patient may grimace or pull back his hand.
A large percentage of the development of pathology occurs in older people. And in the age group from 18 to 45 years, such cases are much less common.
How is it different for men and women?
Anyone can experience the disease, regardless of age and gender. It has been recorded that anuria occurs more often in men than in women. The symptoms are the same for both sexes, but men may experience the most severe pain syndrome.
Anuria in women can occur during pregnancy. During this period, the expectant mother's kidneys are subject to additional stress. At the same time, certain hormones (progesterones) negatively affect the biotone of the bladder.
This raises the risk of kidney infection. Pressure from the uterus becomes stronger, and this creates conditions for delaying the outflow of urine. The possibility of developing hypertension and pyelonephritis sharply increases (after the third trimester). In the absence of adequate therapy, causes of renal anuria arise.
Diagnostics
If a patient does not produce urine within 12 hours, this condition does not always indicate anuria. But delaying urine for more than 24 hours already indicates abnormalities. The doctor must rule out acute fluid retention at the level of the prostate and urethra. Only an empty bladder indicates pathology. During the diagnosis, the patient is asked how long he has not drunk water or other liquids.
Symptoms and complaints cannot be an objective assessment of the patient's condition. To confirm the diagnosis, special urological studies using excretory urography are necessary.
During diagnosis, urine is not visible after administration of contrast or is visible only in the renal cavity:
- Additionally, an ultrasound of the kidneys is performed to detect or exclude urolithiasis, oncological processes and other pathologies of the pelvis.
- For complete clarification, laboratory tests are performed; they are the final point of diagnosis. The standard includes a general and biochemical blood test. Typically, with anuria, the number of leukocytes increases if an infection is associated with the pathology.
- An in-depth study is done to determine oncology and abnormal kidney function. Thanks to tomography, it is possible to judge the condition of the parenchyma (kidney tissue), whether there are purulent lesions.
Using this method, the doctor establishes a differentiated diagnosis. If anuria is excluded, and the absence of urine is caused by its acute retention, a cystoscope will help identify it. It is inserted into the cavity of the bladder. If it is complete, anuria is refuted. With this pathology, the organ looks fallen, and urine is not released from the ureters.
Which doctor should I contact for anuria?
What anuria is and how dangerous it is is already clear. Of course, consultation with a urologist is extremely important for such pathologies, but there are cases when it will simply be a waste of time for both – the patient and the doctor.
If a patient produces small amounts of urine during the day, and he did not drink a lot of water during the heat, then this is normal and there is no point in worrying. But the next day you need to do a simple study - during the day, record the entire amount of water you drink and the fluid you secrete. To the one that is released, you need to add 300 ml; they are consumed through breathing and sweating.
If the numbers are approximately the same, then there is no need to worry, kidney function is normal. If the amount of fluid you drink is much higher than that excreted in the urine, and signs of edema are noticeable on the body, in this case you should not waste a minute, but urgently go to see a urologist.
Treatment
Elimination of anuria should be carried out in a short time. The complicated condition threatens the patient's life. Therapy is selected individually, depending on the reasons that provoked anuria.
Prerenal and renal forms provide emergency medical care with the administration of drugs for the heart and maintaining the activity of the organ:
- 1 ml of caffeine in solution is injected subcutaneously, and glucose is administered intravenously.
- If there is a threat of shock, blood pressure is restored.
- If complications develop, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit (resuscitation) to connect the patient to an artificial kidney machine.
- Correction of water-salt metabolism is carried out.
- If you lose a lot of blood, it is necessary to stabilize the pressure in the veins. To do this, Dextran or Polyglucin is administered.
Treatment of other forms of anuria is carried out only with the use of surgery. For this purpose, the patient is hospitalized in surgery, additional studies are performed and emergency care is provided. The operation will not be planned, but urgent. To prevent anuria and uremia, hemodialysis and percutaneous nephrectomy are performed. It involves percutaneous removal of the organ.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - a
| Treatment of lung abscess |
| Treatment of brain abscess |
| Treatment of liver abscess |
| Treatment of splenic abscess |
| Treatment of overuse headaches |
| Treatment of pituitary adenoma |
| Treatment of adnexitis |
| Treatment of acromegaly |
| Treatment of alcoholism |
| Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis |
| Treatment of alcoholic liver disease |
| Treatment of allergic dermatitis |
| Treatment of alopecia |
| Treatment of alveolitis |
| Treatment of amoebiasis |
| Treatment of liver amyloidosis |
| Treatment of renal amyloidosis |
| Treatment of sore throat |
| Treatment of aneurysm |
| Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis |
| Treatment of kidney aplasia |
| Treatment of aplastic anemia |
| Treatment of ovarian apoplexy |
| Treatment of appendicitis |
| Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) |
| Treatment of ascariasis |
| Treatment of ascites |
| Treatment of pulmonary atelectasis |
| Treatment of atherosclerosis |
| Treatment of atypical pneumonia |
| Treatment of autoimmune hepatitis |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.
Complications
Anuria is always combined with impaired renal function. Complete blockage of urine provokes the accumulation of breakdown products, which gradually poison the body. This leads to a complex condition - uremia. The pathology is characterized by intoxication of the body, which can cause death.
Sometimes a severe clinical condition does not improve with treatment, which leads to disruption of brain structures and functions. A number of neurological symptoms develop, leading to a coma. Uremic coma has a poor prognosis. If the patient is rescued from this condition, he will have severe neurological deficits for the rest of his life.
You can also watch this video, where they talk about the causes of anuria, what severe kidney diseases are associated with anuria, what folk method you can use if you are overtaken by this unpleasant symptom.
Why is anuria dangerous?
Once the diagnosis of anuria is established, emergency care for this disease is simply necessary, for the reason that it threatens not only deterioration of health, but can also lead to the death of the patient. You need to be very vigilant and at the first signs of this disease, immediately consult a doctor. A urologist solves such problems.
In a person with anuria, protein gradually accumulates in the body, which can lead to general intoxication. Another complication caused by anuria is neurological disorders. If there is no treatment for a long time, this can lead to the person falling into a coma.
Uremic coma is very dangerous for humans. Even with timely treatment, although in most cases it is possible to save the patient, he may remain disabled. It carries with it irreversible consequences of neurological deficits, and it will be impossible to get rid of them.
Autism in children: symptoms, signs and treatment
Autism is a disease associated with a violation of a person’s social adaptation, speech function, and mental development. When autism is diagnosed early in children, treatment can have noticeable results, and the main focus of therapy is the education and socialization of the child. The situation with the recognition and treatment of autism in Russia is not simple; timely diagnosis and correction of autism becomes primarily the task of parents.
Back in the middle of the last century, autism was a fairly rare disease. But over time, more and more children are identified as suffering from it. The statistics provided in the United States, where this disease is being closely studied, are indicative. In the 1970s there was a ratio of one autistic person per 10 thousand children, 15 years ago - one per 250 children, now - one per 88 children or one autistic person per 52 boys and 250 girls.
In Russia, there are no official data on the number of autistic children: such a count is not carried out. By rough standards, there are tens of thousands of “rain children” in our country and we differ little from America.
The rise in cases of autism in children is a matter of serious concern, but has not yet been motivated. Scientists only agree that autism is provoked by a complex of factors, and not by one single cause.
Possible triggers for autism include:
- genetic modifications;
- organic lesions of the central nervous system (encephalitis, abnormal development of parts of the brain);
- hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders;
- exposure to viral and bacterial infections;
- mercury poisoning (including when a child is vaccinated);
- excessive use of antibiotics;
- chemical effects on the mother's body during pregnancy.
Whether these factors can actually cause autism in children has not been fully identified. But it is clear that with a hereditary predisposition to this disease, any serious impact on the child can lead to autism, including severe fright or infection.
Signs and symptoms of autism in children
In order to recognize autism in a child in time, you need to carefully observe his behavior and record manifestations that are atypical for children of the same age. Of course, this task faces primarily parents.
In a broad sense, autism is a group of diseases that share some common symptoms (autism spectrum disorders). They are especially obvious when the child reaches the age of one and a half to two years. Here they are:
- Speech impairment . Some autistic children do not speak at all, others are far behind their peers in speech development. Children under the age of 12 months do not walk, can make the same sounds, at 2 years they have an extremely poor vocabulary (about 15 words), by 3 years they are almost unable to combine words. But autistic children can repeat words and phrases heard somewhere like an echo, invent their own words (neologisms), while many do not use speech to communicate. Autistic people talk about themselves in the third person and do not use addresses or personal pronouns.
- Lack of emotional contact with people , primarily with parents. Children with autism do not look people in the eye, do not reach out to their parents, or smile. Autistic people often resist their parents' attempts to pick them up and caress them. In their behavior, such children are similar to those who are deaf or blind: they do not distinguish their parents from other people, and do not notice that someone is addressing them.
- Problems in socialization . Being among others, a child with autism experiences severe discomfort and, over the years, anxiety. "Children of the rain" can run and hide if someone actively contacts them. They do not know how to play with peers, they cannot build friendly relationships, because they do not understand the emotions of other people, the rules of games. Autistic people prefer solitude, which protects them from strong feelings about their inability to communicate.
- Attacks of aggression . Any frustration or failure can cause a child to have an outburst of anger, provoke hysteria, or a physical attack. Aggression in autistic children can be directed at others and at themselves, the latter was recorded in 30% of patients.
- Weak interest in toys . A child with autism does not know how to play with different objects, cars, dolls. Such children are usually not capable of symbolic actions, that is, they cannot depict some objects with the help of others due to poorly developed abstract thinking. For example, if a mother asks her to make tea in a toy bowl, the child will not stir an empty cup with a spoon or will not be able to replace the spoon with a chopstick; he can only repeat someone else’s actions, seen and heard. A manifestation of autism in children is also the non-standard use of toys: for example, a child does not roll a car, but spins its wheel for hours. Another option is a commitment to only one toy or part of it, to the same small objects.
- Stereotypical behavior, fear of change . Autistic children tend to do the same things over and over again: repeating the same word, running in circles, swaying from side to side, looking at rotating objects, twirling something, etc. They are characterized by compulsive behavior, that is, adherence to certain rules and routines. If this routine is violated, they become very worried, resist, and become aggressive. This reaction can happen either when moving to another apartment, or if someone rearranges the toys on the shelf.
Each case of the disease is individual: childhood autism may have all of the listed symptoms, or may manifest itself only in some features of behavior and speech. There are milder forms of the disease, in which the autistic person finishes school, works, and starts a family. Such cases are common in the United States and the West, where autism is promptly recognized by doctors.
There are not only behavioral, but also physical and physiological signs of autism in children. It cannot be said that all of them are found in every patient with autism, but there is some tendency towards these characteristics of the body.
- Too acute or, conversely, dull sensory perception.
- Cramps.
- Weakened immunity.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Growth of bacteria and yeast in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Pancreatic dysfunction.
Diagnosis of autism in children
In order to suspect an autism spectrum disorder, a child must have three symptoms at the same time:
- difficulties in social interaction;
- communication disorders;
- repetitive, stereotypical behavior.
It is important to note that with childhood autism (classic), all these signs appear in the first three years of the child’s life.
For a more accurate diagnosis, a specialist in these types of diseases or a neuropsychologist conducts a study according to the criteria of two international classifications of mental disorders and diseases: ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, developed by WHO in 1992) and DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders , or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, updated by the American Psychological Association in 2013.) Medical diagnosis requires a child to have at least six symptoms from these classifications.
The decision is made by observing the child in his usual environment and interviewing parents. Standardized documents are also used for these purposes. Parents are asked questions from the Autism Diagnostic Interview Revised (ADI-R), anamnesis data is collected using the Autism Diagnostic Observation Scale (ADOS), which also prescribes certain actions on the part of parents. In the hospital setting, the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) is used. These are only basic methods of diagnosis, but they are used mainly in the USA and Europe.
In Russia, diagnosing childhood autism is difficult due to the lack of standards and appropriate training for medical personnel. A pediatrician is usually unable to suspect autism due to a child's atypical behavior, and parents rarely report such facts. Normally, if childhood autism is suspected, it is necessary to undergo a medical commission, which, in addition to the attending physician, should include a neurologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, preferably the presence of a specialist in autism spectrum diseases, as well as parents and educators (if the child attends kindergarten).
When diagnosing autism, it can be very difficult to differentiate it from diseases with similar symptoms, especially in early childhood. Confusion in diagnoses is another problem in Russian medicine. The problem is serious because autism in children is treated very differently from mental retardation or schizophrenia, and improper treatment forever deprives an autistic person of hope for a normal life.
Differential diagnosis of autism with other diseases
Childhood autism (or Kanner syndrome) differs from other types of autism spectrum disorders (ASD), most notably Asperger syndrome. This is a milder form of the disease, in which the child’s intellectual and speech development does not lag behind the age norm, but he still experiences difficulties communicating and understanding other people. Another form of ASD is high-functioning autism, which differs from classic autism by the normal IQ level of patients.
Childhood disintegrative disorder, or a regressive form of autism in children. This is the most dangerous type of autism, but it is this form of ASD that is experiencing the greatest increase in incidence. Disintegrative disorder is detected after 4 years. Before this, there are no serious deviations in the child’s development, but then symptoms of autism suddenly appear, followed by developmental regression. With enhanced therapy, the child can be helped in this case as well.
Hearing and vision impairment. If the baby does not look people in the eyes, behaves distantly, and does not answer questions, you should first check whether everything is in order with the senses, especially if there is no ritual behavior.
Mental retardation. In this case, children interact with the world more easily, make emotional contact, play with toys, in early childhood they often do not have a tendency to make monotonous movements, and do not have speech disorders specific to autism.
Schizophrenia. It is quite difficult to differentiate from autism, since their symptoms are very similar. Yet childhood schizophrenia is a much rarer disease, occurring after the age of three. With schizophrenia, children experience hallucinations, delusions, and their intelligence and speech suffer to a lesser extent than with autism.
Hospitalism (deprivation syndrome). In hospitalism, mental and physical retardation is a consequence of the child’s isolation from the mother, which occurs in children who have been placed in orphanages since birth or who suffer from the indifference and coldness of their parents.
The earlier autism is detected in a child, the greater the effect of therapy for the disease, allowing the person to become a part of society.
Treatment and correction of autism in children
There are many professional techniques and rehabilitation programs that describe how to treat autism in children. Among the most popular are “Applied Behavior Analysis”, “Floor Time”, TEACH and others developed in the USA. And in all cases, therapy is based on teaching children certain behavior scenarios and active communication with them. In this context, the extent to which it will be possible to reduce the manifestations of autism in a child directly depends on the efforts of his parents.
There are still few specialists in our country who would closely work with autistic people using existing behavioral methods. Still, finding a knowledgeable psychiatrist is necessary. In correctional educational institutions, such children are not given enough attention, but work with autists should be carried out comprehensively: in the psychiatrist’s office, in schools, and in kindergartens. And in any case, individual therapy is primarily the concern of parents, no matter what country they live in.
There are a number of basic recommendations for parents on correcting autism in children:
- Instilling in a child the necessary life skills should be based on very frequent repetition of the same actions. Even if a child, for example, has learned to brush his teeth, later you need to “go through” this lesson with him again and again.
- An autistic person must have a strict daily routine that parents should not disturb.
- Abrupt changes in the child’s environment and habits are prohibited.
- You need to communicate with your child as often as possible and spend a lot of time with him.
- You can learn to establish contact with a child through the same persistent repetitions and frequent contact with him, but you should not raise your voice, scold or punish the child.
- With early childhood autism, frequent emotional contact with the baby will help: pick him up, caress him, rock him, play with him, speak kind words.
- Communication is possible through the exchange of cards and pictures in cases where verbal interaction is difficult.
- You should not allow your child to become overtired; you need to take breaks between classes and games, allowing him to be alone.
- Regularly doing physical exercises with your child will help relieve stress and strengthen his physical development.
- Do not suppress the child’s initiative and do not rush him in performing actions.
Parents must show remarkable patience and consistency in teaching and raising an autistic person , creating the most calm environment for him at home. To do this, you should also take care of your mental well-being, taking rest breaks and visiting a psychologist for consultations on raising a child. Parents' help is required in the adaptation of an autistic person not only at home, but also on the street, in kindergarten, and at school. By stubbornly but gently overcoming his resistance and reluctance to communicate, parents ultimately make it clear to the child that it is possible for him to communicate with words, play with peers, and so on.
Drug treatment for autism
There is no drug therapy for autism. Drug treatment is used if necessary to eliminate individual symptoms.
Medicines are prescribed mainly to eliminate inappropriate behavioral reactions: self-aggression and aggression directed at other people, depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders (irresistible desires), increased physical activity. In such cases, antipsychotics and psychostimulants are prescribed.
But you cannot overdo it with the use of psychotropic drugs for autism. By suppressing the signs of autism in children, making their lives outwardly safer, such treatment leads to further regression of intellectual and speech abilities.
Dysbacteriosis, which arises from improper functioning of the intestines in autistic children, involves treatment with probiotics, which create beneficial microflora in the intestines.
The lack of vitamins, minerals and some amino acids, detected through tests, is compensated by the use of medicinal complexes containing vitamins: C, E, B6, B12; minerals: zinc, calcium, magnesium, selenium, molybdenum, chromium, manganese; acids: folic and lipoic.
Therapy with polyunsaturated fatty acids omega-3, contained in flaxseed and fish oil, reduces irritation in the intestines and has a calming effect on the psyche.
Administration of the hormone secretin, which is not sufficiently secreted by the patient's pancreas, can improve his general condition and concentration.
Digestive enzymes help normalize stools and better assimilate food.
The abundance of yeast fungi and pathogenic bacteria, low body resistance and dysbacteriosis make it necessary to treat with anti-candidiasis, antibacterial and antiparasitic agents.
Immunostimulating therapy will be useful in almost every case of autism. Children suffering from autoimmune diseases require special treatment with the administration of steroids and immunoglobulin.
When there is an increased content of heavy metals in the body, chelation is sometimes used, that is, the removal of these metals from the body using special drugs (for example, dimercaptosuccinic acid, or DMSA).
Manifestations of autism can be alleviated by a special diet. To do this you need:
- Avoid foods containing casein (milk) and gluten (wheat, rye, oats, barley),
- do not consume products containing preservatives and dyes,
- stick to a yeast-free diet
- reduce sugar consumption,
- eat more foods containing fiber
- to drink a lot of water,
- give priority to protein foods over carbohydrate foods.
Regardless of diet, children with autism may have serious imbalances in many substances:
- Deficiency of vitamins A, E, C, B6, B12, B3, folic acid, magnesium, taurine, microelements: zinc, selenium, manganese, molybdenum, chromium, vanadium.
- Deviations in the level of adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine, increased concentration of opiate-like hormones (endorphins).
- Increased levels of mercury, tin, aluminum, arsenic, and antimony in the body.
Treatment for childhood autism, both behavioral and medicinal, is very individual in all cases. Before using any medications, you need to conduct tests to determine the problems associated with autism. Only a doctor can professionally decide how to treat autism; With diets and drug therapy, you need to monitor their effectiveness - such drugs do not help all children.