Urinalysis for urolithiasis
When diagnosing urolithiasis, a urine test, along with other diagnostic measures, can answer the question about the causes of the pathology and comprehensive treatment methods.
Urolithiasis is a very common disease, and in recent years there has been an upward trend among the population around the world.
Most often, urolithiasis is found in people of working age (20-50 years), less often in children and the elderly. This disease occurs three times more often in men than in women.
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the disease, even if symptoms have not manifested themselves, and to find appropriate solutions to prevent serious complications.
What signs may indicate the presence of stones?
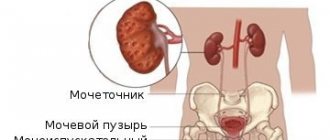
Urolithiasis is a disease of the kidneys and urinary tract, a characteristic feature of which is the formation of stones of various structures, sizes and shapes. Stones can be located in the renal pyramids, calyces, pelvis, ureters, urethra and bladder.
In the initial stages, the disease is most often asymptomatic, but when the stone reaches a certain size, it begins to show its presence.
There are a number of characteristic signs that may indicate that a stone is moving through the urinary tract:
- Depending on the location of the formation, pain occurs in the lumbar region, groin, and lower abdomen.
- Nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting.
- Frequent urination accompanied by pain.
- An increase in body temperature is often observed.
- Dysuria is a disturbance in the process of urine excretion (interruption, incomplete emptying of the bladder, scanty urine output).
- Visible blood appears in the urine - hematuria.
- The presence of turbidity, flakes and sediment in the urine.
- Anuria is the absence of urination due to complete blockage of the urinary tract by stones.
These symptoms should prompt an immediate visit to a nephrologist or urologist for a thorough medical examination and timely treatment.
Delay in treatment can cause serious complications such as:
- renal colic is a severe acute condition caused by sudden obstruction of the urinary tract by a calculus and an obstruction to the outflow of urine;
- hydronephrosis – enlargement of the renal collecting area as a result of urine pressure, the outflow of which is blocked by a stone;
- kidney shrinkage – nephrosclerosis;
- development of chronic renal failure as a result of obstruction of the urinary tract.
The diagnostic process includes laboratory tests of urine and blood, as well as hardware tests to clarify the location of the stone and its size.
What can urine analysis tell you?
Urine contains various metabolic products, and its physical state, microbiological and chemical composition can indicate the presence of malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs.
The main tests performed for urolithiasis include:
- clinical;
- biochemical.
During a clinical urine test, various indicators are examined, but the most important are the following:
- Color and transparency. With urolithiasis, the urine becomes cloudy (due to the presence of protein, mucus, bacteria), contains flakes and sometimes blood.
- Density of urine. With ICD this indicator is increased.
- Presence of sediment and insoluble particles. In urine with urolithiasis there is sediment in the form of sand and salts (phosphates, oxalates, urates). In this case, a chemical analysis of the urinary stone is performed.
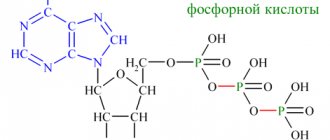
- Acidity pH, which allows you to predict the chemical composition of possible stones (acidic environment - urates, slightly acidic - oxalates, alkaline - phosphate stones). The alkaline environment of the biomaterial may indicate a bacterial infection.
- A urine test for urolithiasis reveals the presence of red blood cells - erythrocytes, which indicates injury to the genitourinary tract from the stone.
- Leukocytes. An increased content of white blood cells in urine (leukocyturia) indicates the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system.
- Protein in the urine (proteinuria). It is an indicator of the development of inflammation and the presence of infection in the urinary organs, as well as pathological changes in the kidneys.
- in urine sediment of cylinders and their composition. An increased number of these components may indicate urolithiasis.
Biochemical urine analysis allows you to determine the following parameters:
- Daily amount of urine. Low values of this parameter indicate urolithiasis.
- Amino acids. An increased content of some of them may also indicate urolithiasis.
To obtain more accurate results, identify the inflammatory process and determine the content of individual components of the biomaterial composition (erythrocytes, leukocytes), the Nechiporenko analysis can be carried out.
An hourly collection and examination of daily urine (Kakovsky-Addis test) allows us to identify urolithiasis and other pathologies of the urinary system.
Bacteriological culture of urine is carried out to determine the quantitative and qualitative composition of the microflora in urine and its sensitivity to antibiotics in the treatment of pyelonephritis, which is one of the main causes of relapses of urolithiasis.
How to properly prepare material for analysis
In order to obtain the most reliable results, certain conditions must be met.
General clinical analysis:
- For research, biomaterial accumulated in the bladder overnight is collected, so morning urine is taken to obtain objective data;
- before collection it is necessary to carry out hygiene procedures;
- collection is carried out in clean, dry containers;
- You should not take certain medications before the test;
- Urine should be transported only at above-zero ambient temperatures;
- The study of the material is usually carried out an hour and a half after it is collected.
Urinalysis for biochemistry:
- the container for biomaterial must be sterile; it is better to use containers for collecting urine, which can be purchased at the pharmacy;
- carrying out hygienic procedures is a prerequisite to ensure the reliability of the results;
- analysis collection begins in the morning (from 6-7 o’clock) and ends at the same time a day later;
- the very first portion of urine (nighttime) is poured out (it is not used for analysis);
- within 24 hours, the material is collected in a special container;
- to obtain a reliable result, all daily urine must be collected, so it is not recommended to leave the apartment;
- After collecting the last portion (the next morning), the urine should be mixed and poured into a container for analysis (100 g), on which the volume of all collected liquid per day and your body weight should be recorded.
During the collection of biomaterial, you should follow the usual eating and drinking regime. The analysis results are prepared from several hours to several days, depending on the types of studies performed.
Based on the test results, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis, finds the cause of the disease and prescribes treatment. In the diagnostic process, tests for urolithiasis include a study of the biochemical composition of the blood.
If necessary, hardware methods are used (ultrasound, x-ray methods, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging).
These studies help to visually assess the location of the stone, its size and shape, as well as the degree of obstruction of the urinary tract.
Source: https://pochki2.ru/bolezni/mochekamennaya/analiz-mochi.html
Additional Information
Since it is not always possible to obtain stones for analysis in case of urolithiasis, you should be aware of diagnostic methods that allow you to assess the composition of stones using indirect methods with a high degree of reliability.
These methods include:
- Radiological description of the stone: calcium stones are clearly visible on the radiograph; struvite and cystine stones have low contrast; xanthine and urate stones are not detected on an x-ray (non-contrasting stones).
- Microscopy of urine sediment to identify microlites (small crystals that serve as the basis for the growth of stones).
- Study of urine pH (acidity). Mostly urate stones grow in acidic urine.
- Bacteriological examination of urine - the presence of bacteria in the urine is one of the risk factors for urolithiasis and the appearance of protein and mixed stones.
- Cystine test - allows you to identify cystine stones.
How to determine urolithiasis using a blood test
Urolithiasis is one of the most common and complex diseases. The deviation involves the formation of stones in different parts of the genitourinary tract. Most often, stones are found in the patient's bladder or kidneys. Sometimes relapses can occur, so it is very important to conduct a quality diagnosis of urolithiasis as early as possible.
Usually there are no problems with determining the pathology, but this does not mean that you can get tested for urolithiasis at the first clinic you come across. This should only be done by highly qualified specialists. The effectiveness of further treatment of urolithiasis will depend on the correct diagnosis of the deviation.
How to correctly diagnose urolithiasis?
When making a diagnosis, it is very important to pay attention to the collection of anamnesis. The doctor should ask the patient about the nature and duration of pain.
This also includes their location and intensity.
The specialist is obliged to find out whether the patient suffers from nausea, vomiting, chills, whether there are signs of hematuria in the urine, whether this pathology has been observed in the patient before and whether surgical interventions have been performed.
As for the external inspection, it includes the following:
- Visual inspection of the lumbar area.
- If the disease affects a woman, a two-handed examination of the vagina.
- Examination of the external genitalia.
- Palpation of the affected organs from the abdomen.
- Rectal examination of the prostate gland.
Before laboratory diagnosis of urolithiasis is carried out, the patient is placed on his side and the affected kidney is determined using deep palpation. Further, it is important to carry out instrumental diagnostic methods.
What tests are taken for diagnosis?
The first thing you need to do after arriving at the hospital is a urine and blood test. Urine is necessary for microscopic examination of sediment. This will help determine the cellular composition and detect harmful bacteria. Almost all patients have blood in their urine, but if it is absent, this does not mean that there are no stones.
When statistical studies were carried out, experts found that more than 65% of patients had 5 red blood cells in the urine sediment in the field of view. This has nothing to do with the size of the stones, but almost always indicates their movement along the ureters.
A urine test can also determine the following data:
- leukocyte count;
- acidity of urine;
- presence and abundance of crystals and bacteria.
Blood analysis
To understand how to determine urolithiasis using a blood test, you need to understand the normal level of leukocytes. If their quantity is exceeded, it is very likely that the kidneys will hurt. Also in this case, most patients have an infectious lesion of the urinary system.
By conducting a study of the level of urine acidity, electrolytes and creatine, specialists can determine the functionality of the kidneys at the moment, as well as the metabolic risks of stone formation in the near future. At the same time, doctors do not ignore the level of thyroid hormones.
If the level of uric acid in the blood exceeds the norm, this will indicate the patient’s predisposition to gout or an increased concentration of the same uric acid in urine. If the same situation is observed with calcium, the patient will be subject to secondary or primary hyperparathyroidism.
Daily urine analysis
This study helps the doctor understand the question of what were the causes of metabolic problems, which, in turn, provoked the formation of stones. Daily analysis is one of the types of diagnostics that allows you to select effective ways to prevent pathology and identify other pronounced deviations in the patient’s physical condition.
After examining this analysis, the specialist will be able to confirm or deny the presence of the following ailments:
- Kidney failure.
- The presence of a large number of stones.
- Stones in both ureters.
- Transplanted or one kidney.
- Remaining stones after surgery.
- ICD at an early stage.
Radiation diagnostics of urolithiasis
Radiation diagnostics of urolithiasis includes x-ray examination and computed tomography. Ultrasound remains one of the main methods for detecting kidney stones. With its help, the urologist can determine the number of stones, their size, shape and location. This method is used as an alternative if computed tomography (CT) is not possible.
Note! The only drawback of ultrasound is that with a certain localization of stones in the ureters, they are almost impossible to see. Therefore, it is more effective to perform intravenous pyelography or CT here.
Intravenous pyelography
Before specialists began to use the most effective method for diagnosing urolithiasis, that is, computed tomography, intravenous pyelography or urography was often used. Over time, it faded into the background, as it does not show sufficient sensitivity for the most detailed diagnosis.
The essence of the examination is that the patient is injected with contrast into a vein and several x-rays are taken. Intravenous pyelography is useful because it allows you to examine not only the kidneys, but also the entire genitourinary system of the patient. But if a person has an allergic reaction to a contrast agent, other types of diagnostics will have to be selected.
Conclusion
Doctors prefer to use CT scans only if the patient is facing surgery. This will allow you to determine the size of the stone, its position and location in as much detail as possible. If the stones are small, an x-ray or ultrasound will be sufficient.
Source: https://procistit.ru/zabolevaniya-mochepolovoj-sistemy/diagnostika-mochekamennoj-bolezn.html
How are kidney stones classified?
We mentioned above that the types of stones can be different. According to their composition, kidney stones are divided into urates, oxalates, and phosphates. But much more often the type of kidney stones is mixed, although one of the minerals still predominates.
The composition of the stone is not the only thing that is taken into account when classifying renal formations. Among the criteria to take into account:
- Number of stones. In approximately 50% of cases, victims have single stones, but the presence of two or three elements in the kidneys is often diagnosed. In rare cases, multiple stones may be observed.
- Location. It can be either one- or two-sided. In this case, stones are located not only in the kidney, but also in the bladder and ureter.
- Form. Stones vary in shape and can be round or flat, with spikes or edges. There are also coral-shaped formations.
- Dimensions. The size of a urate calculus can resemble the eye of a needle or occupy the volume of the entire organ. Let's consider kidney stones - what types of stones can be depending on the size. They speak of microliths if the formation reaches up to 10 mm. If they exceed 1 cm, we are talking about macrolite. Coral stone can exceed 15 cm.
- Density. This indicator is of no small importance, since in the case when the density of stones formed in the kidneys exceeds 1000 Hounsfield units, it is not possible to crush them accurately. You have to either repeat lithotripsy or select other treatment methods.
We will talk about what exactly is included in this or that type of kidney stones later. As for the composition of stones, it should be noted that almost all of them include calcium. Its percentage in the total mass can reach 75-80%, that is, we are talking about calcium salts of numerous acids.
Those stones that contain calcium are clearly visible on x-rays and are called x-ray positive. If we are talking about pure urates, these stones are not displayed on x-rays. Accordingly, any of the elements of this type is called X-ray negative. Mention should also be made of stones of organic origin, which include protein, cystine, cholesterol, and xanthine formations.
Urine analysis for kidney stones explanation
Urolithiasis (synonym: urolithiasis) is the deposition of crystals of various types in the organs of the urinary system. Most stones are composed of calcium salts, phosphates or uric acids.
They are often no larger than a grain of rice; in rare cases they are more than 4-5 centimeters long. Average age of incidence: from 20 to 50 years. Men suffer more often from urolithiasis than women.
Urinalysis for urolithiasis is an important part of the examination of patients with side pain (colic).
Laboratory examination of urine for urolithiasis
Laboratory testing is ordered to check the quantity, odor, color, specific gravity, composition and quality of urine. It helps diagnose diseases of the bladder, kidneys and systemic metabolism.
Chemical analysis of urinary stones provides information about the presence, severity or course of urinolithiasis. In clinical practice, the Nechiporenko analysis, the Zimnitsky test and a general study of urinary components are performed.
Preparing for the study
You need to donate biological fluid on an empty stomach and in the morning. Before any laboratory examination, the genitals should be washed to prevent pathogens from entering the material.
If a 24-hour fluid collection is required, the patient will be advised to maintain genitourinary hygiene until the end of the examination. The local therapist or nephrologist will give specific recommendations for preparation.
Self-diagnosis is strictly prohibited.
When analyzing according to Nechiporenko, a distinction is made between average and initial urine. Before receiving a medium stream of urine, the outer genital area is cleansed. 3-5 seconds after the start of urination, approximately 10-25 ml of liquid is collected in a sterile container (cup). Once an average urine sample is obtained, contaminants should be prevented from entering as they may interfere with test results.
The second morning urine is less concentrated than the first and is suitable for glucose test strips, protein diagnostics and the detection of metabolically active substances - pyridinoline and deoxypyridinoline.
Spontaneous urine can be collected at any time of the day and is the simplest method of obtaining samples. However, it is not suitable for microbiological studies and analysis of urinary sediments, but is a necessary method for detecting chlamydia.
With the Zimnitsky test, urine is collected for 24 hours. The collection procedure ends with the reception of the first morning urine of the next day. This must be done at the same time as on the initial day. On average, about 500-2000 ml of urine is obtained from a healthy person. It is needed to analyze and detect a certain amount of substances in the urine (for example, protein).
Microscopic analysis of urine may be necessary to more accurately evaluate test strip results. First, the laboratory technician centrifuges the sample to separate the liquid from the solid components, called the “pellet.” Then he looks at it under a microscope.
Types of required tests
Laboratory tests are used, among other things, to determine the presence, severity, and course of disease. They play an important role in monitoring the health of pregnant women. If it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the kidneys, bladder, urinary tract or metabolic disease, a complete urinalysis is required.
In case of urolithiasis, urine sediment is analyzed. It detects casts, epithelial cells, leukocytes, red blood cells, bacteria and crystals. Microscopic hematuria can also be identified and further evaluated by a qualified specialist.
Test strips help detect infections and bleeding in the genitourinary area. To detect and differentiate proteinuria, quantitative measurement of total protein is performed.
On microscopic examination, “hematuria” is defined as “blood in the urine.” The 2012 American Urological Association (AUA) guidelines recommend initiating urologic evaluation in patients with recurrent and asymptomatic microscopic hematuria of unknown cause.
Urine cytology examines urine for the presence of abnormal cells. Urincytology has high specificity (accuracy), especially in the diagnosis of aggressive tumors and bacterial invasions (90-100%). In some cases, it helps to identify a specific infectious disease that contributes to stone formation.
As part of the health screening according to screening test guidelines, urine testing for protein, glucose, red blood cells, white blood cells and nitrites should be performed every two years.
According to birth control and abortion guidelines, urine testing for chlamydia should be performed once a year in sexually mature women under 25 years of age.
False result
The test strip can actually show the presence of certain substances in the urine. However, she says little about the number of these elements and the anatomical changes of the urinary tract.
Various factors can lead to incorrect results. If a patient collects a urine sample at home, this increases the likelihood of pathogens being introduced. False readings also occur if a woman is in the luteal phase of her menstrual cycle or is taking certain medications.
Source: https://za-dolgoletie.ru/info/analiz-mochi-pri-kamnjah-v-pochkah-rasshifrovka/
Interpretation of results
There are several types of kidney stones:
- Calcium or oxalate stones. The basis of these stones are calcium salts - oxalates (oxalic acid salts) and/or phosphates (phosphoric acid salts). The frequency of occurrence is about 80%.
- Struvite stones - consist of ammonium phosphate - up to 15%.
- Urate stones - consist of uric acid salts - 5-10%.
- Cystine stones – 1-2%.
- Protein, xanthine and mixed – less than 1%.
Studying the chemical structure of urinary stones will allow the attending physician to better understand the reasons for their formation, decide on further examination, choose the optimal treatment tactics and, most importantly, choose the most effective ways to prevent the formation of kidney stones.
What is a urine test for kidney stones?
The kidneys themselves contain salts, their amount has certain norms. But as soon as salt deposition exceeds the norm, kidney failure occurs and leads to the formation of stones. What should a person do in such cases, how to get rid of the disease.
Wine dissolves kidney stones
How can you identify kidney stones without going to the clinic?
Kidneys are an important organ in our body. They are able to filter and remove toxins from the human body. Any disease can cause kidney dysfunction. Therefore, it is worth taking care and taking tests in a timely manner to check the functionality of the kidney.
People who have a hereditary predisposition to urolithiasis should be especially attentive to their health. Signs of kidney disease are characterized by certain symptoms. And the person will immediately understand that this organ requires immediate medical intervention. All kidney diseases are usually characterized by the following symptoms:
- Severe pain in the lumbar region.
- Increased body temperature.
- Swelling of the limbs.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet.
- Change in urine color.
Pain in the lumbar region is very painful, and most often, the patient takes painkillers. If it is a kidney stone, then the effect of painkillers is very low. The pain becomes dull, but does not go away. And to relieve the pain, you have to take stronger drugs.
All these symptoms indicate that the sick person urgently needs to go to a medical facility. Even with minor, mild pain, it is worth getting diagnosed, since the initial stage of the disease may not be expressed in acute pain.
What tests are done to detect kidney stones?
If a person suspects kidney stones, he should urgently contact a urologist and have his kidneys checked. He will conduct an examination and prescribe tests that will confirm or refute the suspicion.
During the examination, the doctor will not be able to confirm for certain whether there is a stone or not. But he will be able to feel the enlarged organ. If the patient is of a slender build, then the possibility of detecting renal pathology is high.
So, to confirm the preliminary analysis, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- General urine analysis.
- Ultrasound.
- Tomography.
- X-ray.
- General blood analysis.
The main material for studying kidney pathology is urine. It is she who is able to show the presence of inflammation through chemical processes.
Kidney stones can change the color of the urine, making it dark and even containing blood.
If there is a high salt content in the urine, then there is a high probability that the stone is still present in the kidney tissue. It is the salts in urine that make it possible to determine the composition of the formed stone.
In acute renal colic, phosphorus, calcium, acid and creatinine increase in urine. By performing blood biochemistry, you can see an increase in leukocytes and a decrease in hemoglobin. If you do all the tests together, you can identify the disease and determine the cause of the kidney pathology.