Fluorescence microscopy
An optical method for studying tuberculosis pathogens, which are stained with fluorochromes and, as a result, begin to glow under ultraviolet light.
For this examination, special devices are used, which consist of an ultraviolet-producing element and a filter system. Many microbes do not have their own luminescence, so there are various methods for staining them to study using a special device. One of the methods is fluorochrome plating, i.e. staining with intensely diluted fluorochromes. This technique is used for bacterioscopic examination of tuberculosis pathogens.
How is this analysis carried out?
PCR testing for tuberculosis is carried out in several stages. Let's look at each in detail.
- First, DNA molecules are divided into complementary strands by heating to high temperatures.
- Then primers are introduced into the resulting material. One of their types is complementary to the DNA of the 1st chain (its beginning), the second is complementary to the DNA of the 2nd (its end). A composition of four types of DDNTP is immediately added. Next, all components are connected.
- The composition is heated and a thermostable DNA polymerase is introduced into it. Afterwards, the samples under study are cooled. All this happens in thermostats (thermal cyclers).
- At the end, the specialist evaluates the results obtained. This is done using a special gel under ultraviolet rays. The electropherogram that is obtained is analyzed and the result is recorded.
The equipment with which the analysis is carried out is expensive and not available everywhere.
Mantoux test
Tuberculosis is usually detected in children using the Mantoux test. Its essence lies in the fact that pathogen antigens are introduced under the skin. Thus, the Mantoux test causes a reaction if a tuberculosis infection is present in the body. In this case, the injection site swells, turns red and becomes inflamed.
They are the causative agent of tuberculosis. The Mantoux test is usually done in the forearm. The body recognizes tuberculin as an infection. When the immune system is familiar with it, a focus of inflammation appears at the injection site.
Another option is the Pirquet test. Its essence is the skin application of tuberculin. This substance itself is safe and therefore cannot cause harm to humans. But tuberculin is highly allergenic, due to which it can cause corresponding reactions.
Before the Mantoux test result is assessed, it is forbidden to influence the injection site in any way. Thus, it cannot be wetted, scratched, or lubricated with brilliant green, iodine and other antiseptic drugs. It is not recommended to apply adhesive tape and bandages, which is practiced by some parents, so that the child does not touch the injection site. All this can negatively affect the results and lead to an inaccurate diagnosis.
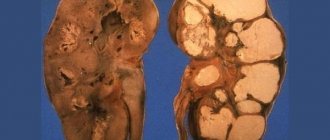
Kidney tuberculosis
Characteristic of the initial stage of development of infection in the body. Cortical structures are affected, but if the immune system eliminates the bacterium, they are restored on their own. Otherwise, kidney tuberculosis develops. In medical language, an infected person is called BK+ (Koch's bacillus, open form), BK- (Koch's bacillus, closed form) or CD? (periodic elimination of bacilli).
It is less common in children. The population aged 20-40 years is more susceptible to infection. It is difficult to diagnose; at first it may not manifest itself or may resemble other diseases (“a cold”, “a cold”, “a chronic disease has worsened”). Meanwhile, the bladder is gradually affected.
What ends up happening:
- impurities of pus in the urine (excess leukocytes);
- inflammation of the renal pelvis;
- which, in turn, causes pain when going to the toilet, aching pain in the lower back, and fever.
Externally, such urine looks abnormal, which is visible to the naked eye. It is dark in color and when it settles, a yellow sediment (pus) forms. With such a picture, we can say with 90% confidence about kidney tuberculosis.
Microscopic analysis of leukocytes will help confirm your guesses. When infected they are nail-shaped. If such cells are found, then the probability of tuberculosis infection approaches 100%.
Kidney tuberculosis can easily be confused with prostatitis, pyelonephritis and other diseases of the genitourinary system. Therefore, it is important to diagnose rather than start self-treatment based on symptoms or ignore the disease altogether.
The causative agent of tuberculosis belongs to the fungal family, is immobile and does not reproduce by spores. There are several varieties of rods, on average they are all no more than 10 micrometers. They differ in characteristics and resistance to external conditions.
Kidney tuberculosis is more difficult to diagnose than other forms. However, it can be detected, including in the early stages (through complex extensive diagnostics according to a well-designed plan). The main principle remains the same: the earlier tuberculosis is detected, the easier it is to treat.
What is a PCR urine test?
The polymerase chain reaction is guided by the principle of molecular biology. To examine urine (or other biomaterial), special enzymes are used. They can copy the DNA of microorganisms. Experts compare the material with the existing database and determine whether there is contamination. If the answer is positive, the degree of infection and the type of pathogen are determined.
Accuracy is important here, so laboratory workers must have the appropriate knowledge and skills.
In addition to tuberculosis, other infectious diseases (hepatitis, STIs, HIV, candidiasis, borreliosis, etc.) are also diagnosed using PCR.
Some parents are sure that this method can be used instead of Mantoux, but this is not the case. Even its high efficiency cannot replace the test, which is approved and mandatory in all preschool and school institutions. Providing a PCR result to a kindergarten or school may not be enough to admit a child to the children's group.
Flaws
This includes:
- high price (but it fluctuates depending on the dollar exchange rate and other factors);
- There are false results (about 10%).
False answers appear for various reasons.
- If urine collection was carried out incorrectly, the recommendations were violated.
- When a laboratory worker does not have the necessary knowledge to carry out the analysis or the technique for studying the material was violated.
- If the collected urine sample does not contain mycobacteria.
- There are many foreign impurities in urine that distort the result (usually in children).
All of the above is a reason to use additional diagnostic measures.
Urine and saliva analysis
To determine the tuberculosis bacillus in children and adults, bacteriological urine culture or PCR testing is performed. However, its absence in urine does not mean that a person is healthy. In subcompensated and decompensated tuberculosis, mycobacteria are often not detected.
Also, if tuberculosis is suspected, a general urine test is required. You can only donate the morning portion. During the night, the bladder fills with urine and the data obtained from its examination will be the most accurate. To take a urine test, you must first perform thorough hygiene of your intimate areas. Urine is collected in a special container, which should be stored in a cool place until submitted to the laboratory. The day before collection, in order to avoid distorting the results, it is not recommended to eat brightly colored foods and spicy foods.
Various changes can be detected in the TAM in pulmonary tuberculosis. One of these disorders is leukocyturia - the presence of a large number of leukocytes in the urine. In addition, erythrocyturia, the release of red blood cells in the urine, and proteinuria, the presence of protein in the urine, may be observed.
Also, to determine tuberculosis, a saliva test is performed. It is done in children and adults if any pulmonary disease is suspected. Saliva is collected in a special vessel. This can be done at home or at the medical facility where the study will be conducted.
Saliva analysis involves dripping a special reagent onto a smear, under the influence of which the saliva can change color. If the color has changed, this indicates the presence of mycobacteria in the body; if not, the person is not infected with Koch’s bacillus.
Tuberculosis is a very serious disease that, without timely and proper treatment, can be fatal. Laboratory tests for tuberculosis help determine the presence of mycobacteria in the body. To establish an accurate diagnosis, they are carried out simultaneously with other examination methods.
- Blood test - determines the level of leukocytosis and ESR. The latter indicator for tuberculosis significantly exceeds the norm (more than 40 mm/h).
- Detection of antibodies using enzyme immunoassays.
- Detection of class G immunoglobulins in serum – these are type-specific antibodies to mycobacillus. The method does not serve as a basis for a final diagnosis. In large cities with high population density, the serological method is not an indicator of human infection.
- The World Organization of Phthisiatricians believes that a mandatory criterion for verification is the determination of mycobacteria in sputum. 5 or more mycobacteria in the sample taken are considered positive.
- It is mandatory to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, which allows you to choose the right treatment regimen and combination of antibacterial drugs. This method is not fast, because it is based on sowing the culture in nutrient media. It takes more than two weeks. Until this point, the patient is treated according to the standard regimen. After receiving the analysis data, the tactics can be adjusted and a different antibiotic is selected.
- The Mantoux reaction is a universal method for mass detection of mycobacterial infection, which is used in schools. The method is based on the intradermal injection of weakened bacilli. An increase in papule to 5 mm or more is considered positive. A skin hyperreaction to the Mantoux test is a reason for further testing for tuberculosis.
Since the invention of X-rays, the main method for diagnosing pulmonary diseases has been the method of preliminary fluorography. Fluoroscopy is the most important way to determine the location of the pathological focus. If the infiltrate is located in places that are difficult to diagnose with x-rays, a tomographic examination is necessary, which allows you to determine clear boundaries of the affected tissue.
More detailed research
What blood tests are needed for tuberculosis?
A general blood test will suggest that there may be a problem. He will warn, give a clue, make you wary. It may not be taken if the goal is prevention.
Perhaps it is worth choosing more informative tests instead of OAC?
Diagnosing this disease only by deviation from the norm in the concentration of red blood cells in children and adults is a major task.
If tuberculosis is in the body, blood tests should provide information about ESR. This is the sedimentation rate of red blood cells. If the ESR is elevated, it means that not only inflammation is present in the body, but also the process of removing toxins is disrupted.
In the case of tuberculosis, ESR increases due to tissue inflammation and due to the accumulation of toxins produced by these microorganisms. ESR can also be used to determine pathological changes in tissues such as necrosis and more.
These blood parameters are often not studied in the general analysis. A general blood test determines professional suitability, for example, functional deviations. In many laboratories you can undergo more detailed diagnostics for a fee, on your own initiative, without a doctor’s referral. Before symptoms appear, it will become clear that the situation is dangerous and help and medication are needed.
If you can’t decipher the analysis, you should consult a therapist. However, they are easy to decipher. Decrypting it yourself will not take much time. It happens that only one indicator arouses suspicion.
The disease is determined by a combination of symptoms.
Types of blood tests for antibodies to tuberculosis
There are more accurate, more in-depth methods of blood testing than CBC that can detect tuberculosis. How to determine whether you have the disease using such blood tests will be discussed below.
An objective diagnosis is possible using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) approaches.
Does the ELISA method show the presence of tuberculosis?
Using ELISA, the presence of pathogenic antibodies in a patient is detected. The method is convenient because it allows you to simultaneously examine a large number of samples. However, it has low sensitivity and is recommended for use in areas with low incidence rates.
What changes does the PCR method detect?
The PCR method is one of the most effective. It is used to detect disease, determine severity and remission of treatment by finding the DNA of microbacteria.
PCR is used for:
- detection of progressive Koch's bacillus;
- test for the detection of extrapulmonary tuberculosis;
- rapid identification of foci of infection;
- diagnosis of disease relapses;
- monitoring the progress of treatment.
Both blood tests for antibodies to tuberculosis are considered quite reliable. But there are others.
Alternative blood test methods
Less common than PCR and ELISA for identifying pathogenic microbacteria is the Interferon Gamma Release Assays method. It can be performed instead of a tuberculin test. The reaction shows the formation of interferon gamma in response to the introduction of microbacteria. Based on the results, the presence of infection can be accurately determined.
Another alternative research method is QuantiFERON-TB Gold. This method is most often used to test children who have severe allergic reactions to a tuberculin test.
Important! Both methods do not allow determining the degree of infection - active or latent. The attending physician determines which type of blood tests will be used
Most often, the research is carried out comprehensively. A blood test for latent tuberculosis may not give any results at all
Your doctor will determine which type of blood tests will be used. Most often, the research is carried out comprehensively. A blood test for a latent form of tuberculosis may not give results at all.
Low red blood cell levels
Few people like to take a blood test. However, you can’t do without it. A general blood test will show in time that the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells is significantly reduced. These changes do not constitute a basis for diagnosis. But this is a reason for more detailed research.
A decrease in these indicators indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
If the time has not yet come for fluorography, whether there are symptoms of a pulmonary infection or not, but you want to make sure that Koch’s bacillus has not entered the body, it is rational to take a routine test.
Inflammation in the body of any etiology is always a cause for concern. Perhaps we will find out that he is not there?
Definition of tubercle bacilli
Mycobacterium tuberculosis are rods whose length does not exceed 10 micrometers, that is, one hundredth of a millimeter. They are immobile and do not form capsules or endospores. There are many types of them. The characteristics of each species depend on the nutrient medium and, over time, resistance to certain drugs. The causative agent belongs to lower fungi and is non-spore-bearing.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis under a microscope
A blood test does not always provide a complete picture of the disease. Tuberculosis bacteria in children or adults can be detected by examining urine. In this case, the presence of the disease can be determined in three different ways:
- Bacterioscopic;
- Bacteriological;
- Biological sample.
The levels of blood cells in the urine of children differ from the usual ones. During pregnancy, research results may be distorted, since the woman’s body has a double load. However, mycobacteria found in urine is a cause for concern and will require examination.
Bacterioscopic - urine analysis according to Ziehl-Neelsen
In this study, they do not take urine, but sediment. Then stained using the Ziehl-Neelsen method. But a negative result does not provide a 100% guarantee that there is no tuberculosis. Often the presence of the disease can be judged by lesions in the lungs and the presence of ailments associated with tuberculosis.
Procedure for analysis in children and adults:
- Carbol fuchsin enters the cell through the membrane.
- Afterwards, non-acid-resistant structures become discolored due to the ingress of H2SO4 and stained with methylene blue.
- As a result, all cells except mycobacteria change their color. They turn blue, and mycobacteria turn red.
Bacteriological research
If the bacteriscopic method does not reveal tuberculosis of the kidneys and other organs of the genitourinary system, then this type of study is performed.
- To do this, culture the urinary fluid taken in the morning three times. To test a patient’s urine for tuberculosis, sediment is taken from the bottom of the cup. On a nutrient medium, if mycobacteria are present, the result will appear in two to six weeks.
- When cultured on blood medium, an answer can be obtained within seven days.
- In the case of using potato medium, the result is in 30-45 days.
- Based on the results of the analysis, the doctor can prescribe antibiotics to the patient that can neutralize mycobacteria.
Analysis according to Nechiporenko
In addition to mycobacteria, a sign of tuberculosis can be an excess of leukocytes and erythrocytes. Now you can check the content of blood cells without taking a blood test in a hospital. The Nechiporenko study allows you to determine the number of blood cells that the urinary fluid contains. It gives more accurate results than general analysis in children or adults.
A more effective way to diagnose tuberculosis instead of mantoux is a biological test. Guinea pigs are used for research. The biological material donated by the patient is injected intraperitoneally or subcutaneously into the pigs. After a few months, the mumps can be used for accurate diagnosis. We just need to find out if she is infected. You can make a diagnosis earlier by taking a blood sample with tuberculin from the animal. The guinea pig is also given a puncture in the lymph nodes. Lymphodenitis is detected already after five days after infection.
Efficiency of methods
A biological test allows you to determine the presence of Koch bacilli in urine in 100% of cases.
A general urine test for tuberculosis is not considered an informative technique, since changes are observed only in 60% of patients. Most often, renal tuberculosis can be detected in this way. Nechiporenko’s analysis is also not very informative: it does not reveal what bacteria are present in urine, it only indicates the presence of inflammation, which is not always caused by tuberculosis.
A bacterioscopic examination is more informative and allows one to determine the presence of pathogens in a child or adult body with a probability of up to 80%.
Urine culture for tuberculosis is more informative. Due to too long a wait, it is often replaced with urine PCR: this technique allows you to determine the presence of mycobacteria even in the absence of renal changes, in case of lung lesions.
One of the effective diagnostic methods is a urine test for tuberculosis. To identify the disease, several modern research methods have been proposed that make it possible to detect specific signs of the disease. Timely diagnosis of tuberculosis is very important, since in the early stages it is much easier to eliminate the disease than in a long-term course.
A test for renal tuberculosis is necessary to detect signs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch bacillus) in the urine. This microorganism is the causative agent of the disease. With active tuberculosis, mycobacteria are present in the patient's biological fluids (blood, sputum, urine). Their detection makes it possible to establish a diagnosis and begin treatment in a timely manner.
A urine test for tuberculosis is prescribed if the patient has diseases of the excretory and reproductive systems that are not controlled by conventional treatment. Such pathologies include:
Long-term, chronic forms of the disease that are difficult to treat are a reason to suspect a mycobacterial etiology of the inflammatory process (renal tuberculosis). It is important to understand that pathogens do not necessarily damage only the lungs. It is possible to develop atypical forms, including those with damage to the urinary system. Through the bloodstream, pathogens can spread from other organs and affect the kidneys. To identify such forms of the disease, a urine test for tuberculosis is necessary.
To obtain a reliable research result, it is necessary to carefully prepare for the analysis. A few days before the procedure you need to:
1. Carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene;
2. If possible, stop using medications that affect kidney function (urine stimulants, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics);
3. Control the water regime - drink enough water (on average 2 liters per day), but do not allow excess fluid consumption, as this can provoke changes in the tests;
4. Do not eat foods that can color urine in an unusual color (carrots, berries, beets).
Women are not recommended to undergo testing during menstruation, since the detection of menstrual blood in the urine can be regarded as a sign of kidney pathology.
Immediately before collecting the material, in the morning, you need to thoroughly wash the external genitalia. This is necessary so that the analysis does not include the flora that is on the patient’s skin. When processing, it is not recommended to use strong antiseptics, as their residues will remain on the skin even after thorough rinsing. Exposure to an antiseptic may destroy some bacteria, which will blur the test result.
Urine in tuberculosis is collected in the morning. It is advisable to use special pharmaceutical containers that definitely do not contain third-party microflora. Jars adapted for analysis cannot be processed effectively enough at home, so when using such containers there is always a risk of getting a false positive result.
After collecting urine for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it is necessary to urgently deliver it to the laboratory. Before this, the analysis must be kept in a cool place so that bacteria do not multiply in the sample.
To test urine for mycobacteria, three methods for diagnosing the disease are used:
- Bacterioscopic technique;
- Bacteriological technique;
- Biological technique.
Each method for diagnosing a disease has its own advantages and disadvantages. In most cases, a combination of several methods is used to accurately confirm the diagnosis of tuberculosis.
A bacterioscopic urine test for Koch bacilli involves examining a sample under a microscope to detect mycobacteria. Biological material is placed on a glass slide, after which several reagents are applied to it, which stain mycobacteria in a certain color, which allows the pathogen to distinguish them from other microflora.
The most common method is Ziehl-Neelsen staining of microspecimens, since this technique clearly visualizes Koch bacilli, the causative agents of tuberculosis. It involves the latter use of sulfuric acid and methylene blue. After staining, the cytoplasm of the bacterium will have a crimson color. The rest of the flora is colored crimson or red. Mycobacteria must be especially carefully distinguished from smegma rods. These microbes are sometimes found in the urine of a healthy person. They are not pathogenic bacteria, their presence does not lead to the development of an inflammatory process. If a laboratory technician mistakes smegma rods for mycobacterium tuberculosis, an unreliable false-positive test result will be obtained.
The advantages of using the bacterioscopic method for diagnosing the disease include:
- Simplicity of research (does not require the use of specialized equipment and culture media);
- Cheapness of the technique;
- The ability to quickly get results.
The disadvantage of bacterioscopic diagnostics is the lack of information content. Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the urine may be present in small quantities that will not be detected during the study. In addition, urine analysis contains many unnecessary impurities that complicate microscopic examination. Foreign objects in the field of view may cause incorrect analysis results.
Due to its disadvantages, bacterioscopy is considered a preliminary screening method that allows for an initial examination of the patient. The research result will then be supplemented with more informative ways to detect the disease.
The absence of mycobacteria on microscopy does not confirm that the patient does not have tuberculosis.
In this case, it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological analysis, which is the gold standard for diagnosing the disease. The bacteriological technique involves cultivating bacteria from biological material on a nutrient medium. Urine is sown on blood or potato medium and placed in a special apparatus - a thermostat. There, the sample is cultivated for several days, after which a laboratory assistant evaluates the growth of microorganisms in it. If there are colonies on the medium that are characteristic of the tuberculosis bacterium, then a sample is taken from them and re-subcultured onto another clean medium. Manipulation is necessary to obtain a clean colony without collateral microorganisms of other species.
The sample is re-cultured in a thermostat. Grown colonies are assessed according to the following criteria:
• Morphological criteria (appearance of Koch's bacillus under a microscope);
• Cultural properties (characteristic color of colonies, assessment of shapes, sizes, etc.);
• Biochemical properties (the reaction of a microorganism to certain nutrients);
• Serological properties (interaction with samples of antibodies specific to the causative agent of tuberculosis).
Based on the listed indicators, the type of microorganism that is the causative agent of the disease is determined.
Bacteriological analysis has a number of important advantages:
• High information content of the technique;
• Absence of side microorganisms in the final sample;
• Less chance of research error.
An additional advantage of the method is the ability to test for sensitivity to antibiotics. To do this, samples of several antibacterial agents are placed on the sown colonies. Those drugs to which the microorganism is sensitive will inhibit the growth of colonies. The technique is very important in practical medicine, as it allows the patient to be prescribed treatment for a disease of the genitourinary system that will be effective.
The disadvantage of using bacteriological diagnostics is the long period of research.
During diagnosis, it is necessary to cultivate microorganisms twice in a thermostat, so the diagnostic result can be obtained in at least 3-4 days. In most cases, the waiting period increases to a week.
Thus, bacterioscopy and bacteriological examination complement each other well. Bacteroscopic diagnostics allows you to quickly examine the composition of the microflora of urine; it is used for urgent examination of the patient. At this stage, the patient is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics that affect not only mycobacteria, but also other possible pathogens. Urine culture for tuberculosis takes longer, but is more informative. Its result confirms or refutes the bacterioscopic data. Based on the antibiotic sensitivity test, the treatment used is adjusted; if necessary, more highly specialized agents are prescribed that actively destroy Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Biological diagnostics is an additional research method that is used in severe diagnostic cases. If it is not possible to identify the pathogen using bacteriological examination, then the laboratory animal is infected with the patient’s biological material. Guinea pigs are most sensitive to Mycobacterium tuberculosis; rats or mice are less commonly used.
Some time after infection, the animal is opened, preparations are prepared from its blood and tissues and they are examined for the content of tuberculosis pathogens. To get results in the early stages, you can use the Mantoux or Diaskintest test. Biological methods are the most accurate research. The probability of detecting mycobacteria during this procedure is 100%. The disadvantage of the study is the long cultivation period and the complexity of the technique (the need to use laboratory animals). Biological diagnostics are used when the disease lasts for a long time and there is no effect of treatment.
Thus, urine examination can detect tuberculosis of the kidneys and other organs of the genitourinary system. Detection of mycobacteria allows us to confirm the presence of the disease and promptly prescribe treatment.
Tuberculosis is a dangerous pathology that everyone should know about. Have you had a urine test for tuberculosis? Leave your opinion on the analysis and share your personal experience in the comments.
Tuberculosis is a serious disease. To date, no 100% effective method of prevention has been invented. Microbacteria that provoke it are not uncommon in the environment.
Immunization is successful in approximately 70% of cases. In 30% of cases it is not effective, according to statistics.
Timely diagnosis increases the chances of a speedy recovery without consequences. Children undergo mantu, and adults undergo fluorography. The study is conducted on average once every one to two years. It is not recommended to carry them out frequently. And yet, it is natural for everyone to want to control the situation and not let everything take its course.
Is it possible to detect (diagnose) tuberculosis using blood tests?
Tests for tuberculosis are done in different ways, including blood tests.
Preparation for analysis
Requirements that must be met before taking the OAM (general urinalysis):
- use the average portion of urine obtained immediately after waking up;
- the material is collected in a clean container in an amount of 50-100 ml;
- before donation, wash the external genitalia without using detergents;
- the resulting material is delivered to the laboratory no later than 10-11 a.m. (less than 2 hours after the analysis).
Urine collection for bacterioscopy and culture is carried out according to the same rules, but more stringent requirements are imposed on urine containers. They must be strictly sterile, so it is not recommended to touch their inner surface and edges, and immediately close the lid after filling. Before delivery to the laboratory, the collected material is stored in the refrigerator.
The following can change urine levels and its color: anti-tuberculosis drugs (rifampicin), diuretics, antiviral drugs, acetylsalicylic acid, vitamin-mineral complexes, etc.
Women need to take the test during the absence of menstrual bleeding.
What is a test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Studying urine allows us to identify the very presence of bacteria, determine their type, and assess the general condition of the genitourinary system. The test is based on the acid resistance of bacteria. During chemical manipulations, they become different in color.
A urine test is prescribed for:
- lack of positive dynamics in the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system (cystitis, pyelitis, epididymitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis);
- signs of kidney tuberculosis (difficulty, frequent or painful urination, abnormal color and smell of urine, lower back pain, in men - asymmetrical enlargement of the scrotum);
- tuberculosis of other organs;
- positive or questionable Mantoux result (fluorography, diaskintest).
Evaluation of the results occurs in conjunction with an examination, study of the patient’s chart, collection of anamnesis, and the results of other procedures. However, the identified tuberculosis bacteria clearly indicate kidney tuberculosis. In men, prostate tuberculosis is possible.
With pulmonary tuberculosis, general urine parameters remain virtually unchanged, but the bacteria themselves may also be present. Urinalysis is effective in detecting latent tuberculosis (compensated), but less effective in identifying subcompensated and decompensated types.
Before the analysis, it is important to follow a number of recommendations and take into account contraindications.
Ignoring the following nuances may distort the result:
- You cannot take the test during menstruation and within two days after its end. Before taking the material, you need to wash yourself with clean warm water (do not use chemicals). The first morning urine sample (before breakfast) is taken for analysis.
- Only fresh urine is collected. Can be stored for several hours in the refrigerator with the lid closed. The presence of other bacteria (an initially dirty glass or microbes entering an open container) can provoke a false negative result.
- The liquid must be collected in a clean jar or medicine glass. If a child needs to be tested, then the parents’ task is to control and explain the nuances of preparation.
You can donate urine, blood, saliva and sputum for analysis in the largest laboratories such as Hemotest, Invitro, Helix. Prices range from 275 rubles (Nechiporenko analysis) to 8,200 (innovative immunoassay of plasma).
The presented cost is relative (the final value depends on the geographical location and a number of individual indicators). You can find out more about the price list on the laboratory websites.
Essence and methodology
Mycobacterium tuberculosis belongs to the lower fungi and are rods no more than one hundredth of a millimeter long. In urine analysis, they can be detected in three ways: bacterioscopic, bacteriological, or using a biological sample.
- Bacterioscopic (Ziehl-Neelsen). The essence of the method is that mycobacteria are not able to live in an acidic environment, therefore, to identify them, special reagents are used that stain all unstable structures. First, they are decolorized with sulfuric acid, after which a solution of methylene blue is introduced. Due to this, all structures and cells acquire a bright blue color, with the exception of mycobacteria, which becomes crimson-red.
The disadvantage of this method is that it is quite difficult to clear urine of foreign impurities, which reduces the accuracy of the study (to increase the diagnostic value of the study, urine is taken using a catheter).
- Bacteriological. Another way to identify tuberculosis pathogens in a urine test is bacteriological. To perform this, urine sediment is taken, after which it is cultured in a nutrient medium.
The downside of the method is the rather long wait for the result. The exact timing varies depending on the type of medium used for cultivating the biomaterial. When using blood medium, the result will have to wait about 7 days, potato medium - 30-45 days.
Photo 2. Result of the bacteriological test: bacteria that were in the patient’s urine sediment were grown in a Petri dish.
- Biological sample. The most sensitive method for detecting mycobacteria, which is often used instead of the Mantoux test.
To conduct the study, a urine sample is injected into the guinea pig; after a few months, the animal can be used for accurate diagnosis. To make a diagnosis earlier, you can take a tuberculin test from the mumps.
The accuracy of bacterioscopic and bacteriological analysis is about 80%, the accuracy of a biological sample is 100%.
To detect tuberculosis of the genitourinary system, not only bacteriological, but also general urine analysis is used. Indicators of the disease are not only mycobacteria, but also characteristic nail-shaped leukocytes, protein (proteinuria), nonspecific bacteria, and an increase in the concentration of red blood cells. An acidic reaction of a biomaterial sample is observed in approximately 60% of cases, and therefore cannot be considered an accurate diagnostic criterion.
Reference. The most informative indicator of tuberculosis, according to most experts, is the classic triad: pyuria (the presence of pus in the sample), albuminuria (or traces of protein), and an acid reaction.
Decoding the results
Normally, Mycobacterium tuberculosis is not detected in urine, so the reference values of the analysis will look like this:
- tuberculosis microbacteria were not detected - negative result;
- MBT was detected in the urine - a positive result.
A positive result almost always indicates damage to the kidneys or urinary tract, and a negative result can indicate either the absence of the disease or a false negative result. If the patient has had contact with a carrier of the disease or has specific symptoms of tuberculosis, he needs a set of additional studies.
Blood and urine tests for tuberculosis
V.A. Koshechkin, Z.A. Ivanova
The elements of red blood, as a rule, change little during tuberculosis. Only after acute loss of blood from the lungs or intestines can anemia occur. A slight decrease in hemoglobin levels can be seen in chronic forms of fibrous-cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis.
One of the indicators of the activity of the tuberculosis process is ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). Accelerated ESR correlates not only with the activity and extent of the current fresh process, but also with the exacerbation of chronic, especially fibrocavernous, processes.
Elements of the leukocyte fraction of blood react more actively to the tuberculosis process. Conventionally, there are three phases of changes in the leukocyte fraction of blood associated with the nature of the lesions in pulmonary tuberculosis. 1. Neutrophil phase of the fight. In the blood, the proportion of neutrophils is increased, resulting in a shift of the formula to the left. Eosinophils are absent, the number of lymphocytes and monocytes is reduced. 2. Monocyte phase - overcoming the infection. In the blood, the number of lymphocytes is increased, the blood count is shifted to the left, the number of neutrophils is reduced, and single eosinophils are detected. 3. Recovery phase. The proportion of lymphocytes and eosinophils is increased. Blood counts are gradually returning to normal. This division into phases reflects only the general reaction of the blood.
Nuclear shift of neutrophils in tuberculosis In addition to the quantitative, the group of neutrophils has a qualitative characteristic, which is much more subtle and earlier indicates various pathological processes.
Adult tuberculosis is usually a secondary process; most often it causes only an increase in band neutrophils in the blood. With pronounced infiltrative-pneumonic forms and phenomena of decay of lung tissue, a shift of neutrophils to the left is detected quite clearly and can reach up to 20-30% of stabs.
The pulmonary infiltrate does not decay, and focal forms of tuberculosis during the period of their first detection or exacerbation with low-grade fever and mild functional disorders give a less pronounced shift. At the same time, the remaining elements of the hemogram may not reveal any deviations from the norm. Therefore, careful determination of the nuclear shift is of particular importance in tuberculosis.
The doctrine of nuclear shift of neutrophils was put forward by Arnet (1905) based on the study of blood in various infections, including tuberculosis.
Carrying out complex calculations with numerous sketches, Arnet noticed a certain pattern in the configuration of neutrophil nuclei.
The blood of a healthy person contains:
- 5% of neutrophils with undiluted constrictions, unsegmented nucleus (class I);
- 35% of neutrophils with two segments connected by a filamentous constriction (class II);
- 41% neutrophils with three segments (class III);
- 17% neutrophils with four segments (class IV);
- 2% neutrophils with five segments (class V).
In addition to segmenting the nucleus, Arnet also took into account its shape. Thus, for the first class, he identified several subclasses according to the degree of depression of the unsegmented nucleus. The remaining classes are divided into subclasses depending on the shape of the segments.
During infections, in proportion to their severity, the number of multi-segmented forms decreases, the number of low-segmented (2-3 segments) and non-segmented (which are relatively young cells) increases.
Urinalysis Urine excretion in patients with tuberculosis is almost normal. Pathological changes in urine can occur if tuberculosis affects the kidneys or urinary tract. In patients with chronic forms of pulmonary or bone tuberculosis, signs of amyloidosis may be detected.
The indication for a urine test for tuberculosis is the suspicion of the presence of pathology. Often such diagnostics are required for people who cannot have a Mantoux test or tuberculin test due to contraindications. In order for the polymerase chain reaction study to give correct results, it is important to prepare for the donation of biological fluid.
What to do next
If the size exceeds 20 mm, it is necessary to undergo a series of tests at a tuberculosis dispensary. If a child has a positive Diaskintest, then it is necessary to be examined by a phthisiatrician. Tests such as bacteriological urine culture, blood test, and CT scan are prescribed. For adults, an X-ray or film of the lungs is taken.
If there is a cough, sputum is examined. If, upon examination of the body, enlarged lymph nodes are found, they are sent for an ultrasound. As a result, there may be no deviations from the norm.
If treatment is refused, the patient is registered and the test is repeated 1-2 times in six months. If Diaskintest is negative, then the immune system has coped with mycobacteria. According to patient reviews, this is the best subcutaneous test that is well tolerated by the body. Unlike tomography and other types of research, this test does not expose the body to radiation. Infection with tuberculosis infection after the procedure is excluded.
In rare cases, general health may deteriorate. Sometimes the temperature rises or intermittent headaches occur. The Mantoux reaction can be large even in the absence of tuberculosis pathogens in the body. This value occurs after the BCG vaccination has been given. If the Diaskintest results are positive, and the tests and x-rays are good, then you need to be tested again. This happens in patients after treatment for tuberculosis infection. It is necessary to be examined further.
Decoding and evaluation of analysis results
Once the analysis is ready, the laboratory provides a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the result. A qualitative assessment reflects the presence of pathogenic bacteria, and a quantitative assessment reflects their concentration in 1 ml of urine.
The name of the detected microorganisms is usually indicated in Latin, for example Klebsiella pneumonia.
The concentration of bacteria is calculated in units of CFU/ml (stands for colony-forming unit, that is, a cell that gives rise to the development of a new colony of microorganisms).
There are several stages of bacterial growth. Grades 1, 2 and 3 (up to 1000 CFU/ml) are considered clinically insignificant. This is due to the fact that urine is not a sterile liquid and normally contains a small amount of opportunistic microbes.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: X-ray examination of the lungs
Grade 4 (indicated as 1*104 or 10,000 CFU/ml) and above indicates abundant growth of pathogenic microflora and requires treatment. In this case, the conclusion of the study indicates the sensitivity of the pathogen to antimicrobial drugs.
But it should be remembered that only a doctor always evaluates the test result and prescribes treatment.
What methods are used instead of urine analysis: Mantoux test, Pirquet test, PCR, ELISA
Today there are many ways to diagnose tuberculosis, but none of them is able to detect the disease with 100% accuracy. For this reason, a set of techniques is used to make a diagnosis, which includes blood tests, sputum tests, tuberculin tests and instrumental research methods (fluorography, radiography).
The cheapest and most common method for detecting tuberculosis is the Mantoux and Pirquet tuberculin tests. Their main disadvantage is the high probability of obtaining false positive and false negative results.
Blood tests (PCR, ELISA) are accurate and specific, but at the same time they are quite expensive and are not carried out in all laboratories.
Fluorography, x-ray examination and sputum analysis are used to diagnose the pulmonary form of the disease and are practically uninformative in identifying extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
Reference. The most accurate and effective method for diagnosing all forms of tuberculosis today is the PCR, or polymerase chain reaction, method; to identify the extrapulmonary form - a biological test.
Specific tests
Even if deviations from the norm are found in the general, most significant indicators, you will need to submit sputum or saliva to the laboratory and undergo fluorography. In first place in importance among people at risk is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent test, which determines the presence of specific antibodies.
Polymerase chain reaction testing is the most effective and accurate diagnostic method. It allows you to detect Koch's bacillus DNA in biological material. Unfortunately, this requires special equipment. Not every laboratory has it.
What tests are best to take for prevention?
To determine the problem and interpret poor health, it is sometimes important to know what a general analysis will show. In another situation, it is important to know what specific studies have shown.
Preparation for the procedure
Before taking the test, the patient needs to carry out preparatory measures. They depend on what material will be taken:
If it is necessary to donate blood, a sterile tube must be prepared. An anticoagulant is added to it - a special solution that prevents blood clotting
The collected material is placed in it and mixed carefully. Blood is collected from a vein with a disposable syringe. The procedure is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach.
Blood can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than five hours. If you neglect this rule, the analysis results may be inaccurate. A week before donating the biomaterial, you should stop taking any medications. You cannot donate blood after drinking alcoholic beverages. In the presence of chronic infectious or inflammatory diseases, the procedure is postponed until the person has fully recovered.
It is imperative to maintain maximum sterility during the procedure.
Therefore, it is important to get tested only in trusted clinics under the guidance of an experienced specialist. It should be remembered that minimal ingress of foreign microorganisms can give an incorrect result.
To avoid this, the doctor may order a repeat test.
Preparing for analysis
How to donate urine? To prevent urine from becoming the reason for an incorrect answer, you need to collect it correctly. Preparation is important.
If the test is planned for an adult, then 1-2 days before the test you need to forget about sexual intercourse. It is important to tell your doctor about antibiotic therapy (if any in recent weeks). You need to wait at least a month and only then start the examination
Any medications will affect the test result. The best time to collect is morning. No food or drinks are allowed beforehand. The genitals are not washed first. It is important to purchase a special vacuum set in which urine will be collected. Putting it in a regular jar and then pouring it won’t work. As a result, bacteria or viruses from the external environment will enter the urine, which will interfere with obtaining a reliable result. Contact with the external environment should be avoided. A special set consists of a sterile jar with a lid, a test tube and a tube. A person empties his bladder into a jar. It is important to collect the first portion of urine. Afterwards the container is closed and the test tube is inserted. It will fill with content on its own. Negative pressure will affect this. Once the tube is filled, the container and tube are discarded. The resulting biomaterial is taken to the laboratory, where the analysis itself will be carried out. Only a test tube containing urine is delivered.
If for some reason the subject is unable to collect urine himself, a specialist from the clinic will come to his aid. Specially trained people will arrive with everything necessary and will do everything without mistakes.
Urine collection rules
Urine for tuberculosis will show the presence of Koch bacilli only if the sample is taken correctly. Preparation is required and includes:
- Avoiding consumption of products that color urine 1-2 days before collecting biological fluid. These are beets, carrots, blueberries;
- To the exclusion of the use of a number of medications for the treatment of concomitant diseases - diuretics, antipyretics, B vitamins.
If the treatment of a previously diagnosed disease does not require a break in taking medications, you should inform your doctor about this. You should also not drink alcohol the day before, and it is advisable to refrain from smoking. To detect mycobacteria, a clean urine sample is required, so women during menstruation should not be tested.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: What is a PCR test for tuberculosis
To accurately establish a disease with kidney damage, a morning urine sample is needed. They collect it by following several rules:
- You need to prepare a container with a lid in advance - special sample jars are sold in pharmacies;
- Wash the genital area thoroughly and it is better to do this without soap;
- Collect a medium portion of urine. That is, start urinating into the toilet, then direct the stream into a jar and then back into the toilet. For research, 50 ml of urine is enough;
- Immediately close the container with a screw cap and place in a cool place.
In most cases, a urine sample for Mycobacterium tuberculosis is collected at home. But he needs to be taken to the laboratory as soon as possible. In “fresh” urine, Koch bacilli are more easily determined and therefore the result of such tests is rarely false negative.
What are the disadvantages
This diagnostic method is more exceptional than natural, there are reasons for this
First of all, the high cost of the method is taken into account. The equipment is expensive, state clinics do not have the opportunity to purchase it due to the high price, but most paid laboratories have the equipment, and analysis is done there. Existing disadvantages:
Existing disadvantages:
- The method detects killed bacteria that died after treatment, while PCR shows a positive result. There is no point in conducting research immediately after chemotherapy, since the result will be unreliable;
- Tuberculosis mycobacteria are susceptible to mutation, which leads to the ineffectiveness of the method, while the DNA strand cannot be consistently synthesized.
The test medium must be carefully selected; blood or urine is collected only if contamination is suspected. Sputum should not be taken for examination if bone tuberculosis is suspected
. In this situation, the diagnosis will be incorrect.
The blood and urine of a tuberculosis patient is rarely taken for PCR testing; identifying the disease in this way is doubtful. In these biological environments, the pathogen is determined only in case of sepsis, or in the case of. Local forms are most common; in them, blood and urine may remain unchanged. Most often, sputum is taken for examination.
In what cases is analysis prescribed?
Urine examination for the presence of tubercle bacilli can be carried out in the following cases:
- if there is a suspicion of tuberculosis, the appearance of accompanying symptoms;
- if such a diagnosis was made to relatives and friends with whom the patient spent a lot of time;
- with long-term unsuccessful treatment of a person for cystitis, inflammation of the bladder, prostate gland, ovaries, kidney pathologies, urolithiasis and other diseases;
- to determine the type of mycobacteria, select and adjust treatment methods;
- if necessary, assess the condition of the body and the urinary system in particular;
- if testing for tuberculosis gives a positive or questionable result;
- in a set of measures to prevent tuberculosis.
Infection with tuberculosis occurs through airborne droplets, contact, and hematogenous routes. The symptoms include the following body reactions:
- severe cough, expectoration of bloody sputum;
- fever up to 38°C, excessive sweating;
- chest pain and shortness of breath during exercise;
- loss of appetite and rapid decrease in body weight;
- decreased activity, loss of strength, frequent colds.
The risk zone includes people who take steroid hormones for a long time, avoid vaccinations, have bad habits and do not adhere to sanitary and hygienic standards, and whose immunity is lowered due to constant overwork and stress. If the first signs of the disease and suspicion of tuberculosis appear, you should contact a specialist and undergo the appropriate tests.
Definition of symptoms
At the first stage, when the patient has just sought medical help, the doctor must detect signs of the disease. Clinical manifestations of tuberculosis include a prolonged cough, hemoptysis, increased body temperature, sweating, increased fatigue and decreased performance.
It is important to pay attention to these symptoms, as they indicate the possible development of the disease. In addition, at this stage, the characteristics of the evolution of the disease should be clarified. The doctor asks the patient whether he has had contact with people diagnosed with tuberculosis.
The doctor asks the patient whether he has had contact with people diagnosed with tuberculosis.
Conclusion
Urine analysis for PCR is a technique that can be used by everyone without exception. It is not recommended for children, as the result may be false
It is important to properly prepare for the analysis and collect material. Collection is carried out at home independently, assistance from a specialist and collection in a clinic are allowed (if necessary)
Do not place urine in containers not intended for analysis. A special set can be purchased here. The diagnostics themselves are carried out by qualified laboratory workers, adhering to all the rules. Without expensive equipment, it will be impossible to test urine using PCR.
The technique is effective and can detect tuberculosis even when the number of mycobacteria in the body is minimal. But, despite this, the Mantoux test cannot be replaced with it. In this way, it is advisable to confirm the diagnosis or monitor whether there is a relapse.
Urine culture tank: essence of the method and research algorithm
A urine culture tank is a microbiological analysis carried out in special laboratory conditions that determines the presence of pathogenic bacteria, their quantity and susceptibility to treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Urine analysis is carried out under conditions of absolute sterility according to the following algorithm:
- centrifugation of urine to isolate microscopic sediment;
- cultivating bacteria in a nutrient medium and growing them at a temperature similar to human (36-37 degrees);
- transferring the obtained strains onto a glass slide and staining them;
- study of the morphology of the obtained cultures and their identification;
- determination of sensitivity to antibiotics (antibioticogram).
The result is ready in 7-10 days.